Abstract
Environmental impact assessment (EIA) is a key tool for both environmental and land management. It identifies potential adverse and unintended consequences of the projects on land use and the environment and derives possible mitigation measures to address these impacts. Calculating the volume and severity of impacts is complex and often relies on selections and simplifications. Moreover, calculating impacts associated with nomadic-pastoral (dynamic) land use is still an unresolved methodological problem. A full understanding of the patterns of dynamic land use in nomadic pastoralism is still lacking. Consequently, EIAs are currently able to predict the negative impacts associated with dynamic land use insufficiently. This article addresses this lacuna by modeling the spatial occupation of grazing land using a statistical modeling technique of structural equation modeling (SEM) and the R package lavaan for SEM, in order to explain the behavior of dynamic land use for EIA. Based on the concepts of the production of space and pastoral spatiality, we specified and tested a model of spatial occupation of grazing areas hypothesizing interrelationships between factors influencing the pastoral space using empirical data from two different ecological zones in Mongolia. The findings suggest that grazing areas, herd mobility, and herd size and composition have direct positive effects on each other. Compared to broad-scale pastoral movements, the herd size and composition significantly affect the size of grazing areas and the extent of fine-scale herding mobility. Herders occupy more pastoral space and increase their daily herding movements at their campsites when the population of livestock increases. By contrast, the herd size and composition do not considerably affect the herders’ decision to migrate for extensive grazing between their seasonal campsites. Likewise, the scale of grazing areas and fine-scale pastoral mobility do not affect significantly the broad-scale herding mobility between campsites. The broad-scale herding mobility is relatively independent of the fine-scale mobility; however, they covary. This is the first study to analyze and quantify the effects of grazing areas, herding mobility, and herd size and composition in the same study. EIA impact prediction should consider grazing areas as a dynamic space that is influenced by grazing orbits, fine and broad-scale herding movements including otor, livestock species, the number of animals as well as households at campsites.
1. Introduction
Land use is a complex process and operates at the interface of multiple socio-economic and environmental systems [1,2]. Land use in the context of nomadic pastoralism makes this interface more complex and non-linear due to the inherent dynamic equilibrium of pastoral systems [3]. Byambaa and de Vries [4,5] argue that current environmental impact assessments (EIAs) do not address this dynamic character in nomadic pastoralism and therefore, impacts associated with nomadic-pastoral (dynamic) land use are not sufficiently and appropriately predicted in EIA. EIA is a legally required tool for environmental management applied in more than 190 countries [6,7] and it is the key process that identifies potential adverse impacts of projects and initiatives at an early stage [8]. Moreover, EIA suggests possible mitigation measures to address negative impacts on the environment and people’s health and livelihood and informs decision-makers about those impacts. Thus, impact prediction about nomadic-pastoral land use in EIA needs to be improved in order to inform the decision-making properly.
In 2012, a complaint was filed to the Compliance Advisor Ombudsman (CAO) by the representatives of 89 herder households affected by the Oyu Tolgoi project in Mongolia, which is one of the largest known copper and gold deposits in the world. Herder households were concerned that the negative impacts of the project on their grazing areas were not appropriately quantified and the methodology used to identify impacts was not clear to the herders [9]. Indeed, impacts associated with grazing areas of each individual herder household were not identified sufficiently by the project [10]. Moreover, the impact prediction [10] failed to look at the interrelationship between grazing areas and pastoral mobility such as otor1 movements and did not consider the number of livestock and herd composition when conducting EIA. Environmental and social impact assessment of a new wind park project in Mongolia also failed to consider the characteristics of dynamic land use when identifying impacts on grazing areas [11]. These EIAs identified project impact areas as radial or linear zones around the project facilities and only impacts associated with grazing campsites located within these impact areas were addressed. Connections of the affected herders’ campsites with other seasonal grazing areas, which are used by the same herder, for instance, were not assessed sufficiently. Such links between seasonal grazing areas are dynamic as pastoral mobility is influenced by various climate, environmental and social factors. EIA’s objective is to identify these dynamic grazing areas affected by the project regardless of how they were generated. A framework by Slootweg, Vanclay et al. [12] suggests that interrelated impact pathways in nomadic pastoralism include impacts of projects such as mining on pasture land and impacts of pasture land use, such as overgrazing, on the environment [4] as well as on land use itself. Thus, impacts, as well as impact areas, of both project and pastoral land use need to be identified in EIA. Hence, so far there is a deficiency in addressing impacts associated with dynamic land use, as the current EIA methods primarily focus only on static land use such as mining interventions [4,5].
In recent years, the most commonly used method of land-use impact prediction has been the land-use impact assessment within life-cycle assessments. This method investigates the quantities of land-use changes [4]. It calculates land-use impacts as a function of (i) the area used for the land use process, (ii) the time required for the transformation and occupation process of land use, and (iii) the difference in land quality between the current and initial land use [13,14,15]. Thus, one of the key parameters of land-use impact is the area for a specific land-use type. This implies that in order to quantify nomadic-pastoral land use, an EIA needs to properly account for the dynamic aspects of this land-use type; there is a spatial variation in land use through the pastoral movements.
In the context of pastoralism, the complexities of spatiotemporal use of pasture land tend to be oversimplified in existing conceptual models [16] and have not been analyzed in a way that has led to an explanatory model of nomadic movement [17]. Explaining why, where, and how pastoral land use and movement occur requires considerable effort in terms of mobility modeling and evaluation [18]. The scientific understanding of land-use changes, which are both spatial and categorical, is still insufficient due to gaps in knowledge about the pattern and dynamics of land-use intensity [19]. Land-use intensity is a multidimensional process and can refer to different aspects including the land area used and the time required for land-use occupation processes [20]. To date, adequate approaches, conceptualizations, and datasets are often missing for measuring land-use intensity qualitatively and quantitatively to a sufficient extent [19,20,21].
A few land-use change models deal with both the location and the quantity of its change in an integrated way offering only case-specific solutions [21]. Jones, Antle et al. [22] note that the modeling of livestock systems is particularly complex as it requires a good understanding of the use of land by herds at various levels and the existing models of livestock systems mainly focus on predicting animal productivity, animal numbers, herd dynamics, and herd structure. From case studies, in various pastoral contexts, we know that it is possible to predict the probability of a livestock movement link between two locations [23,24]. There are also models that examine the dynamics of livestock in terms of sales, self-consumption, and stocking [25], and pasture land use with respect to the demands of domestic consumption and international trade [26]. Associations between herding practice and water availability as well as cattle productivity (intake rates, foraging behavior, milk yields, and body conditions) were also examined [27]. Moreover, it is possible to predict the resource selection patterns for cattle [28], and factors that can play a role in the generation of mobility patterns of grazing cattle are known [29].
Although extensive research exists on defining, categorizing, and explaining the variations in pastoral space and its mobility patterns, there is still a need for better insights, which would explain why, and how herders spatially occupy and alter their dynamic land use. Only with more detailed information on the significance of factors such as livestock species and size, location and size of grazing areas, and mobility patterns, is it possible to conduct an EIA in a more comprehensive way. Access to pastoral data is one of the challenges of rangeland science for better understanding the grazing interactions and processes comprehensively [18,30]. Liao [31], for instance, notes that significant shortcomings still exist in pastoral mobility quantification and only little empirical work has been conducted to quantify pastoral mobility extensively. Moreover, calculating the total impacts associated with a complex series of land occupations still remains unresolved and this is a methodological problem for impact assessment [32] as the current EIA methods are designed for static land use [4]. This study examined the following twofold questions to contribute to explanations and quantifications of the dynamic land use: How does dynamic land use produce pastoral space? How do factors influencing dynamic land use interrelate with each other? The article intends to address these questions by modeling and explaining the spatial occupation of grazing areas, using a structural equation modeling (SEM) technique based on empirical data collected from two different ecological zones in Mongolia. This is the first study, to our knowledge, to quantify the effects of grazing areas, herd mobility, and herd size on each other all together. Moreover, the empirical study presented in this study extends the previous works [33,34], which applied latent variable modeling in the evaluation and quantification of complex and dynamic interactions in nomadic pastoralism.
2. Model Specification
2.1. Measuring the Pastoral Space and Mobility
The methodological problem in impact assessment related to a series of land occupations requires us to improve our understanding of the spatial occupation of grazing land generated by pastoral mobility [4]. Two main types of herding mobility are used by pastoralists [35]. Broad-scale movements related to different seasons that occur between camps and fine-scale movements that include daily mobility within the pastoral unit. Various indicators have been suggested by scholars to measure the pastoral space and mobilities based on studies conducted on the sedentary to semi-sedentary or transhumance pastoral systems.
We characterize and quantify pastoral areas and mobility by applying the parameters of grazing orbit, length of daily herding movement, and distances between campsites which include the number of camps. Grazing orbit is a mobility area from the center of the household or a livestock enclosure where the path that animals circumnavigate from their enclosures to grazing and water resources and back to their enclosures in a grazing day [36]. Length of daily herding movement is an indicator of pastoral mobility and it measures the daily cumulative herd travel [31,36,37,38,39]. Pastoral mobility is also measured by the distance from camp, which considers a daily maximum distance from camp or the spatial stretch of daily herding movement [27,31,40]. Moreover, the number of camps is an indicator that measures the extent of grazing mobility [31]. This indicator refers to how many sites are used as camp locations during a seasonal cycle by pastoralists. Freedom in herd movements and the degree of constraints on herd mobility is measured by an angular distribution of footprint which refers to the mean angle in degrees from the livestock enclosure to the point of furthest travel, in a straight-line distance from the enclosure [31,36].
2.2. Modeling and Hypothesizing the Spatial Occupation of Grazing Land
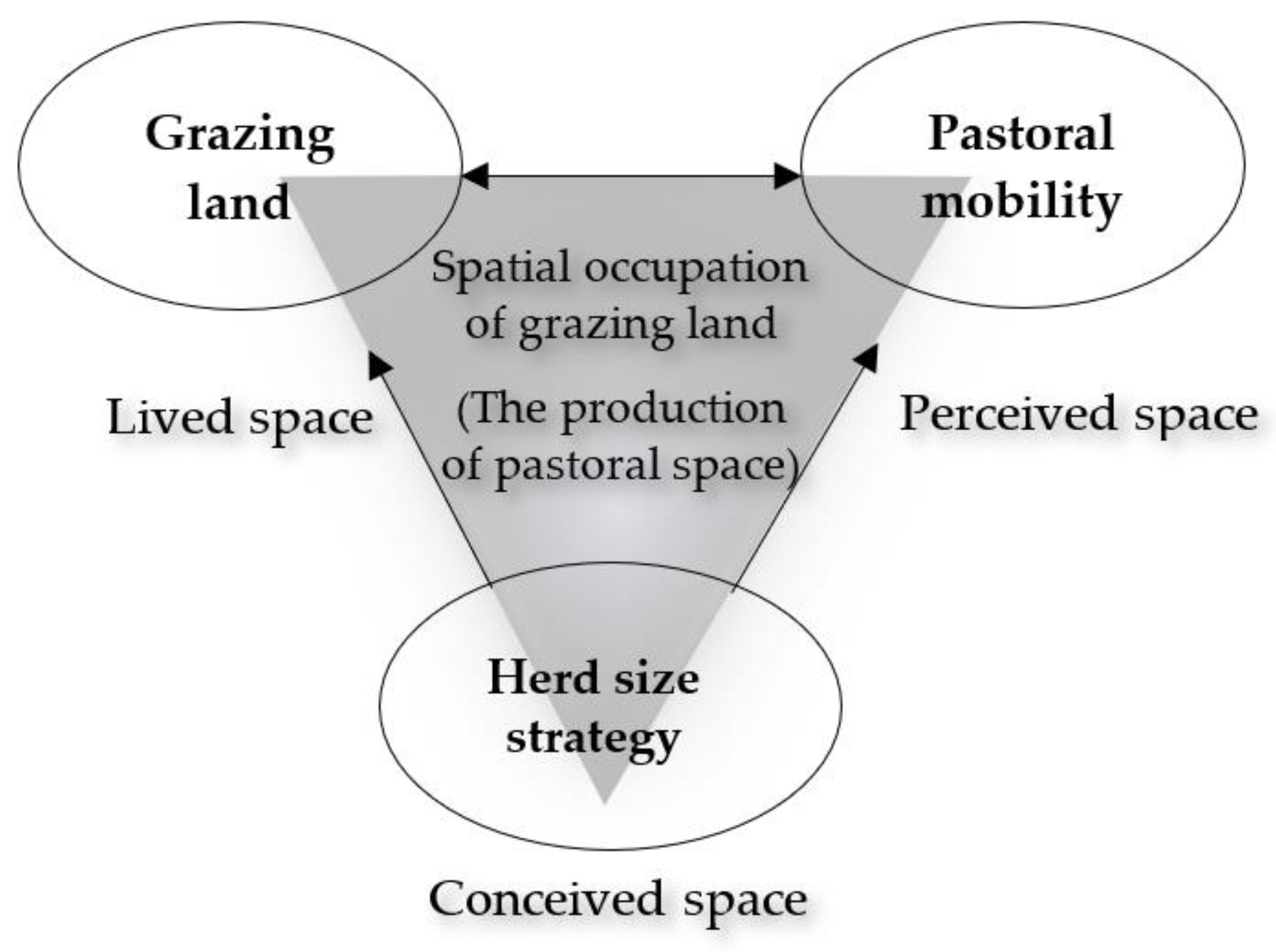
We specified a model formulating the relations between a set of parameters we discussed in the previous section. This model presents our assumptions about the spatial occupation of grazing areas and is based on Karplus and Meir’s [41] concept of pastoral spatiality developed under the Lefebvre [42] framework for the production of space. Lefebvre’s [42] spatial framework conceptualizes space as a triad consisting of perceived, conceived, and lived spaces interrelated to each other. These three elements produce a space linking physical and abstract aspects of any socially produced space. In his framework, a perceived space embraces the concrete physical space where we practice everyday activities. In contrast, a conceived space is a conceptualized space imagined by scientists, engineers, and planners through maps and plans creating a system where the spatial relations are imposed by order of signs and codes. A lived or representational space, in turn, is “the space of inhabitants, hence, space which is passively experienced and in which the imagination seeks to change appropriately. It overlays the physical space, making symbolic use of its objects” by which we imagine the space we live (see p.39 in [42]).
By drawing on the Lefebvre [42] framework, Karplus and Meir [41] defined the pastoral spatiality as an interrelated space produced through pastoral mobility (perceived space), social territoriality (conceived space), and pastoralists’ ideological attachment to space through symbols and cultural codes (lived space). Byambaa and de Vries’ [4] review concluded that the rationalist theory and linear cause-effect epistemologies are dominant underlying fundaments of EIA discourses. They argued that nomadic-pastoral land users need EIA theory to incorporate irrational logic and complex and unpredictable socio-ecological features of dynamic land use and they called for more adaptive or nomadic theories to be applied in EIA. Karplus and Meir’s [41] concept of pastoral spatiality incorporates the needs of dynamic land use as this framework was specifically conceptualized to understand pastoral space. They conceptualize that “pastoralists’ perceived space is produced as a series of temporary campsites linked by journey trails” (see p.39 in [41]). Thus, in our model, the perceived space is characterized by indicators related to pastoral mobility (Figure 1).
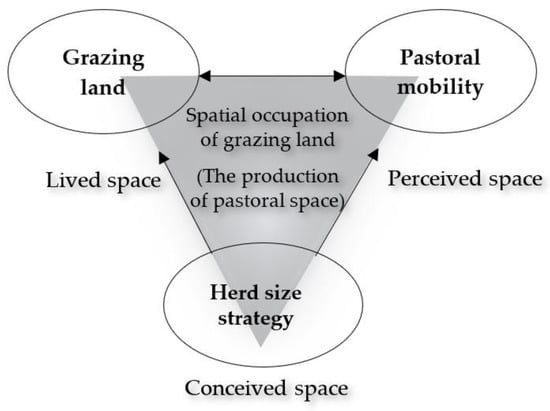
Figure 1.
The conceptual framework of spatial occupation of grazing land tested in this study.
Furthermore, according to Karplus and Meir [41], a pastoral conceived space is produced as social territoriality where spatial resources and social interaction are managed by means of a group of people. Our model uses the livestock population as a parameter characterizing the pastoral conceived space. Sayre, Davis et al. [43] note that land degradation in rangelands more often results from intensifying commercial livestock production. A recent study by Hilker, Natsagdorj et al. [44] also showed a clear connection between increases in animal population and overgrazing. Moreover, some countries successfully prevented grassland degradation by controlling the increase in livestock population [45,46]. Hence, the livestock population is the key indicator and rule of managing spatial resources of pasture land, and therefore, we link the herd size strategy to the pastoral conceived space in our model.
Lastly, according to Karplus and Meir [41], “continued production and reproduction of localities lead to lived space that gives precedence to ideologies of socio-spatial bonds”. Moreover, a herding pattern represented by a grazing orbit in different localities is the synergistic spatial product of social and ecological conditions in pastoralism [40]. In fact, an effective communal land-use system in pastoralism is driven by a complex mix of community dynamics, social relations, and the biophysical characteristics of the landscape [47], and traditional ecological knowledge [48]. Thus, in our model, the grazing land, which represents the grazing orbit, is linked to the lived space. We relate indicators of daily herding movements on campsites also to the lived space. This relation is necessary to understand the symbolic and cultural significance of the nomadic-pastoral lifestyle. We specify that, together, these factors relate to each other and contribute to the production of pastoral space (Figure 1).
Pastoral space in nomadic pastoralism is dynamic and varies in size and location due to herders’ decisions to migrate between grazing areas. Thus, it is improper to observe grazing areas, herding mobility, and herd size strategy from static observations. Instead, these factors are latent variables in our model. We hypothesize that the grazing land, pastoral mobility, and the herd size strategy are interrelated key factors of the pastoral space and quantified by grazing areas, both fine and broad scale herding mobilities, the number of households, and the number of animals (Figure 1). As so, the proposed model is defined by these three latent variables (factors): grazing land, pastoral mobility, and herd size strategy and in addition, seven observed variables (indicators): total grazing orbit, total length of daily herding movement, total number of households on campsites, total distance between campsites, total distance between campsites including otor, total number of animals, and total number of sheep and goats.
Based on the above conceptual model, we hypothesize (Figure 1) that the grazing land and pastoral mobility are interrelated (grazing land ~~ pastoral mobility) and measured by a factor related to herd size and composition, which we name herd size strategy (grazing land ~ herd size strategy; pastoral mobility ~ herd size strategy). Herd composition is related to the foraging and feeding of livestock species and depending on livestock diet selection, herders make decisions about the location and size of grazing areas. Thus, the number of sheep and goats which characterize herd composition is an indicator that measures herd size strategy in our model. We hypothesize that the herd size strategy has a direct effect on both the grazing land and pastoral mobility. The observed variables of daily grazing patterns and households on campsites measure the grazing land (grazing land =~ grazing orbit + length of daily herding movement + number of households on campsites). Moreover, pastoral mobility is quantified in our model by the total distances between all seasonal (spring, summer, autumn, winter) grazing camps including otor campsites (pastoral mobility =~ distance between campsites + distance between campsites including otor campsites + number of households on campsites). Otor is a traditional mobility strategy developed by Mongolian herders to cope with harsh winter [49] and it improves the effectiveness of grazing reserves [50]. Moreover, otor provides herders with the means to maintain livestock husbandry in highly variable and uncertain environments by accessing key resources through extensive movements [49]. Therefore, otor is an important indicator, which measures pastoral mobility. The number of households on each of those campsites is predicted by both the grazing land and pastoral mobility as the availability of pasture land and the needs for seasonal movements depend on access to grazing areas which influence the households’ decision to stay in or move out the campsites. The observed number of animals and the sheep/goat herd composition measure the herd size strategy.
3. Methodology and Data Collection
3.1. Study Areas
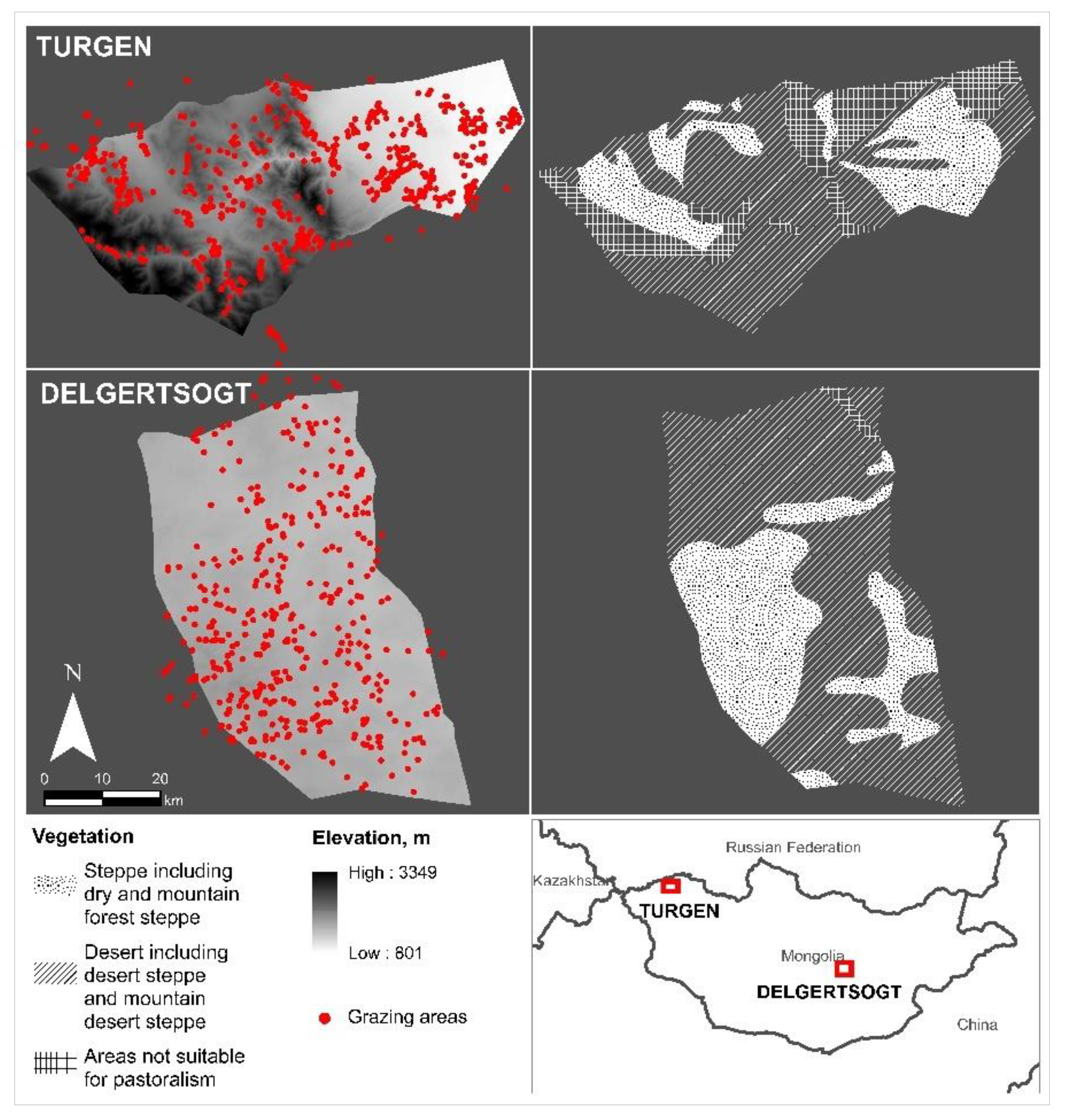
The study was conducted in two areas in Mongolia. The first area, Turgen soum2 of Uvs aimag3 is located in western Mongolia at an average altitude of 1763 m in a forest steppe region, approximately 1500 km from the capital city of Mongolia. The second, Delgertsogt soum of Dundgovi aimag is located at an average altitude of 1432 m in a semi-desert steppe region in southern Mongolia. However, both areas include dry and mountain forest steppe, desert and mountain desert steppe ecoregions in their entirety (Figure 2). Turgen had 340 herder households and 143,960 animals in 2018, whereas Delgertsogt had 380 herder households and 185,860 animals in total [51]. In both soums, households herd sheep, goats, cows (and yaks), horses, and camels and move between winter, spring, summer, autumn, and otor campsites. The herd composition and herding pattern differ in these two study areas due to their variations in altitude and climate conditions. Such different areas were chosen to include a representation of various movement patterns and herd composition which exist in Mongolian pastoralism.
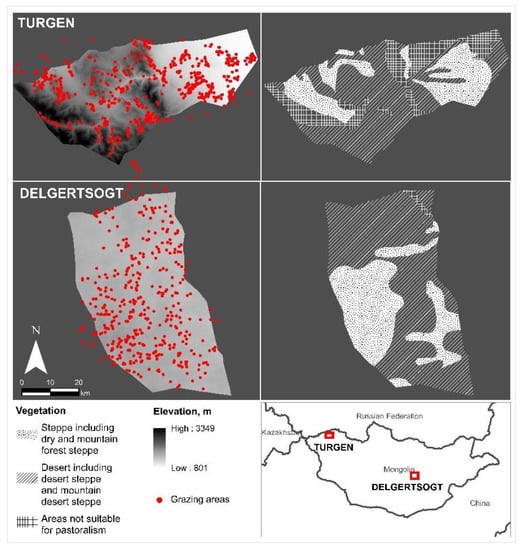
Figure 2.
Two study sites in Turgen and Delgertsogt soums of Mongolia.
Open grazing areas are owned by the state in both zones [52], however, they are de facto managed as common properties [53]. Formal possession rights are allocated to khot ail (groups of livestock keeping families [54]) in those soums to use grazing areas in winter and spring campsites [55]. Moreover, land rights on grazing lands in autumn, summer, and otor campsites are regulated through “manifestations and interpretations of herders’ customary rights and the reworked legacy of historical institutional arrangements” (see p.1401 in [56]).
3.2. Data Collection
Data were collected from the two study sites in Mongolia between July and September 2019. First, we used a survey questionnaire containing questions related to the movement pattern of animals. The design of the questionnaire used the indicators of pastoral land use and mobilities such as the grazing orbit, the length of daily herding movement, and the number of camps (Table 1). We administered the questionnaire through structured face-to-face interviews. To carry out the interviews, we visited the homes of herder households as well as various events such as community meetings and celebrations where many herders gathered. From each soum, we interviewed senior family members of 100 households in the Mongolian language and in total, received 200 responses from two soums to our questionnaire.

Table 1.
List of collected data on herd population, mobility, and grazing areas from two sites in Mongolia.
The face-to-face interviews we conducted with 200 herder households reveal that horses and camels graze freely in any pasture area. They graze within a much longer distance compared to sheep, goats, cattle, and yaks. Moreover, the herders who participated in the survey noted that horses and camels mostly graze outside their grazing orbit. Therefore, we considered the length of daily herding movement and the grazing orbit of only sheep, goats, and cattle (and yaks) in our model.
Mongolian herders used their ecological knowledge of plant-animal-environment relationships in their nomadic herding strategy [48]. Different knowledge systems such as the pastoralists’ own knowledge system were also used for understanding pastoral mobility [35]. Moreover, participatory mapping was used to obtain local spatial knowledge [57]. During the interviews, we also conducted participatory mapping with herders to identify the locations of their winter, summer, spring, autumn, and otor grazing areas using the local names printed on a map prepared in advance. Seasonal movements between winter, summer, spring, autumn pastures practiced by Mongolian herders have repeated patterns and the location of basic pasture types remains constant between years [48]. Therefore, herders who participated in the survey had good knowledge about their seasonal pastures and they provided us information about their grazing distances, locations, number of animals, grazing distances, and households, which share pasture in their campsites during the survey. Grazing locations were then further marked on a shapefile we obtained from the local authorities to measure distances between campsites using spatial analysis. The shapefiles included locations of grazing campsites of these soums allocated to herders for possession rights and were used as the second source of data for this study.
3.3. Structural Equation Modeling and Exploratory Factor Analysis
The methodological approach taken in this study is a structural equation modeling (SEM) technique. SEM is a methodology for explaining the patterns of relationships among variables and for estimating the magnitude of effects of one variable on the other. We use SEM to test and estimate complex relationships among both observed (indicators) and unobserved (factors) variables [58]. Factors representing nomadic-pastoral land use are not measured directly and therefore, they are latent variables. SEM fits into the purpose of this study in examining both latent and observed variables related to pastoral space in the same analysis. We tested Karplus and Meir’s [41] concept of pastoral spatiality by specifying a model of the spatial occupation of grazing land employing this concept. SEM is used for both confirmatory and exploratory purposes and it examines the extent of interrelationships among the variables [59]. Thus, SEM also suits our objective to quantify the pastoral areas and mobility by estimating the magnitude of effects of our variables on each other.
We followed the key steps of SEM [60]. First, we specified the model, while choosing indicators for observations and designing a questionnaire for data collection. We evaluated the model by applying exploratory factor analysis (EFA) using the Zhang, Jiang et al. [61] EFAutilities package in R. The EFA is conducted to test the assumptions between measured variables and to identify the common factors and covariation that explain the structure among our observed variables [62]. We tested the relationships among all our observed variables using the datasets derived from 200 survey responses including data on horses and camels by applying EFA. However, the factor loadings of variables of horses and camels were not significant. A factor loading for a variable is a measure of how much the variable contributes to the factor [63]. The face-to-face interviews with the herders also verified that the movement of horses and camels are substantially different from the daily grazing patterns that herders practice. Therefore, the EFA focused on data on sheep, goats, and cattle (and yaks).
Following the model evaluation, we estimated the model using the R package lavaan [64] which applies the maximum likelihood (ML) method to calculate the fit of the model and we evaluated model fit. We assessed the goodness of fit indices of the model with the Comparative Fit Index (CFI), Tucker–Lewis Index (TLI), Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA), and Standardized Root Mean Square Residual (SRMR). Some rules of acceptable criteria for goodness-of-fit indices exist although there are no well-established guidelines for adequate fit [65]. For the ML method, the cut-off values CFI > 0.95, TLI > 0.95, RMSEA < 0.06, and SRMR < 0.08 are suggested to assess whether the hypothesized model and the observed data fit sufficiently/significantly [66]. Moreover, SRMR < 0.10 and RMSEA ≤ 0.08 are suggested as acceptable fit [65,67].
A fitting model represents a tool that explains causal assumptions among variables and such results should support conclusions about matters to which the theory applies [68]. Thus, we interpreted the parameter estimates in connection with the concept of pastoral spatiality. Moreover, we interpreted the results following the Schreiber, Nora et al. [59] guidelines and recommendations for reporting results of SEM.
4. Results
4.1. Exploratory Factors
The results of the EFA show that the grazing orbit and the total length of daily herding movement load on the first factor (grazing land) ranged from 0.82 to 0.98 and this factor represents what we have called grazing land in our conceptual model (Table 2). The number of herder households on campsites also loads on the first factor with a value of 0.20 which is relatively significant compared to other variables.

Table 2.
Exploratory factor analysis of the observed variables of data used in the model testing and the factor loadings (Factor 1—Grazing land; Factor 2—Pastoral mobility; Factor 3—Herd size strategy; Estimation method—maximum likelihood; Rotation type—oblique).
Distance related two variables (the total distance between campsites and the total distance between campsites including otor campsite) as well as the number of households on campsites load on the second factor (pastoral mobility). The factor loadings ranged from 0.36 to 1.00. The total number of animals and the total number of sheep and goats load on the third factor (herd size strategy), which had factor loadings of 0.91 and 0.99 respectively. Our results of EFA validates the structure of the three factors we applied in our model considering the conceptual framework on pastoral spatiality. Following this analysis, the fit of the model was tested, and its parameters were estimated.
4.2. Estimation of the Model
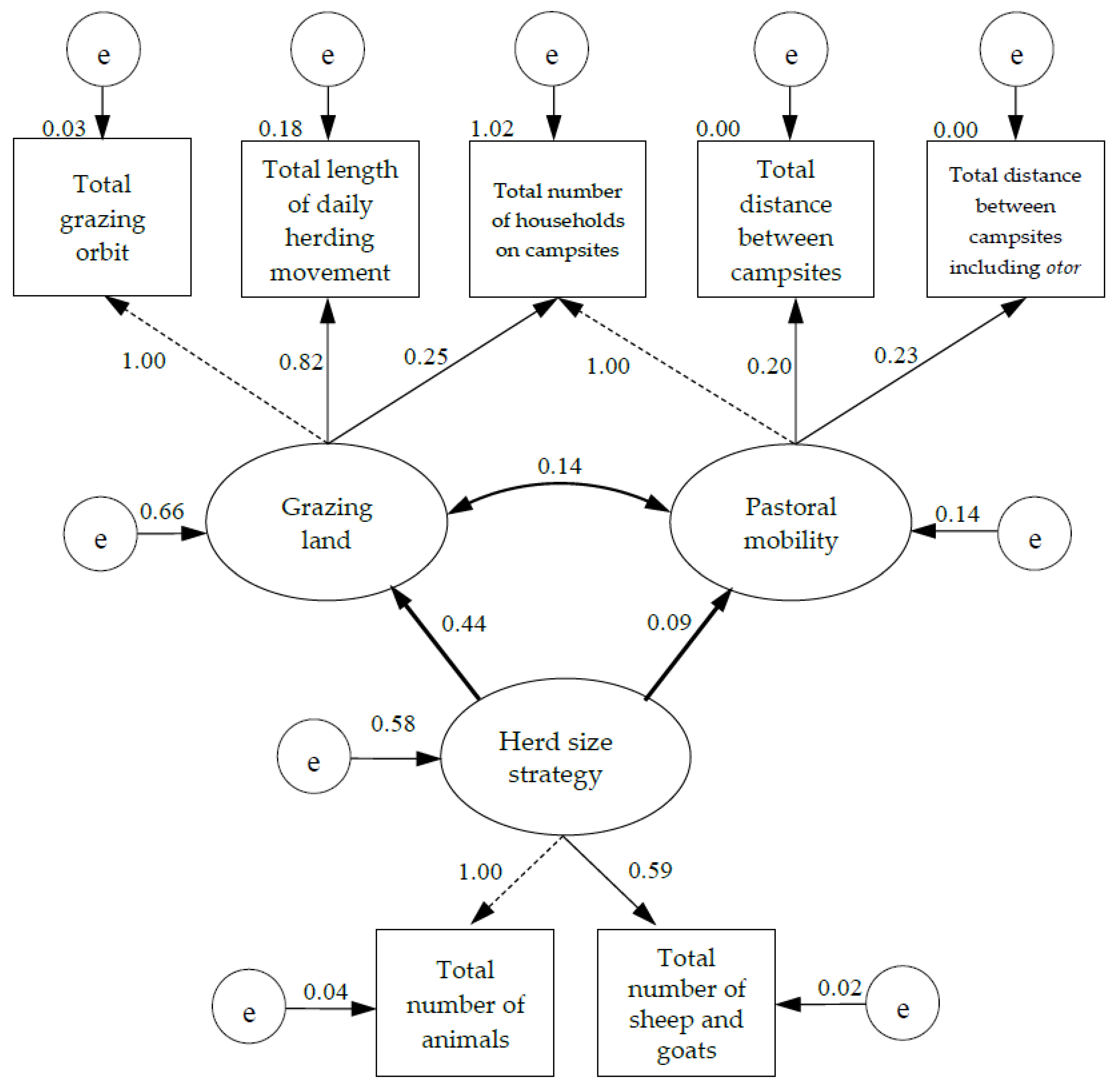
The estimation of the hypothesized structural equation model was carried out using the Rosseel [64] R package lavaan for SEM. We quantified the standardized factor loadings and parameter estimates of this model which we specified with R code4 using lavaan (Figure 3).
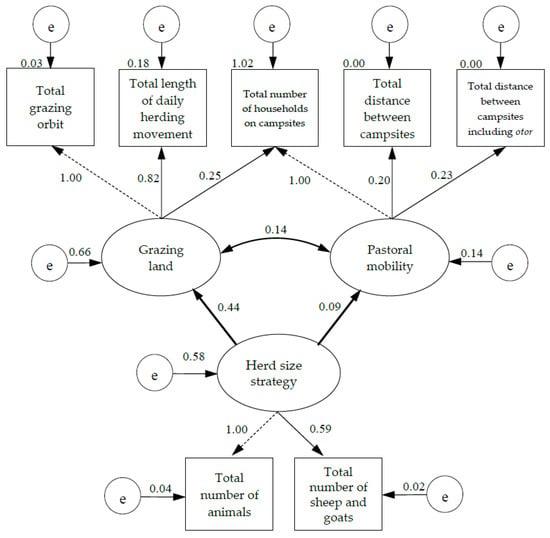
Figure 3.
Results for the structural equation model. Comparative Fit Index = 0.991, Tucker-Lewis Index = 0.981, Root Mean Square Error of Approximation = 0.068, Standardized Root Mean Square Residual = 0.027, e = error.
As presented in Table 3, the data we collected fitted with the model and resulted in reasonable fit indices. The relationships between the indicators of the model are shown in Table 4 and the correlation/covariance among the measurements are all positive in our model. Furthermore, Table 5 and Figure 3 illustrate the standardized factor loadings and parameter estimates for the structural model. Parameter estimates explain the effects of the factors and indicators on each other [69].

Table 3.
Model fitting test and fit statistics assessed with cut-off-values.

Table 4.
Correlation between the indicators of the structural equation model of spatial occupation of grazing land.

Table 5.
Standardized parameter estimates from the hypothesized structural equation model.
As presented in Figure 3, our structural equation model consists of measurement and structural components. The measurement component is shown using thin lines and the structural component is presented using bolded lines [59]. The latent variables are illustrated with ellipses, whereas rectangles represent our observed variables. The model shows the association between three latent and seven observed variables and predicts the changes in our measured variables with change in the latent variables. A minimum number of indicators per factor is two, and one indicator may measure more than one domain [60]. Thus, in our model, two indicators related to the number of livestock measured the factor of herd size strategy. The number of households on campsites also loads on two factors. One loading for each factor is fixed to one to assign a metric to each factor [60].
According to the model, both the total number of animals and the number of sheep and goats grew, with the increase of the herd size strategy factor. Herd size strategy increased by 0.59 of the standard deviation when the total number of sheep and goats increased by one standard deviation. An increase in the herd size strategy also led to an increase in the grazing land and a slight increase in the broad-scale pastoral movements. Moreover, 58% of the changes occurring in the herd size strategy influenced the grazing land and pastoral mobility. When the grazing land increased by one standard deviation, the herd size strategy increased by 0.44 of the standard deviation. Although, there is a positive association between the herd size strategy and pastoral mobility, the effect of the herd size strategy on pastoral mobility is small compared to its effect on the grazing land.
The indicators of grazing orbit, daily herding movement, and the number of households on campsites measure the grazing land. The number of households on campsites along with the distance-related indicators measure pastoral mobility. The grazing land and pastoral mobility co-vary positively. However, their effects on each other were found to be insignificant.
5. Discussion
Compared to other statistical methods, complex relationships including latent construct level hypotheses can be examined using SEM [70]. We modeled the spatial occupation of grazing land and analyzed the relationships between the grazing land, pastoral mobility, and the herd size strategy as unobserved latent constructs and we examined their associations with different measured variables. Structural parameters of SEM such as parameter estimates are interpreted as effects of one variable on the other [69]. In the following sections, we discuss the causal assumptions of our structural equation model.
5.1. Grazing Land
The grazing land is a latent variable, which represents the lived space in the concept we used in this study. This variable characterizes fine-scale movements and home range herding patterns in our model. According to the model specification, the number of households on campsites also quantifies the grazing land together with the grazing orbit and the daily herding movement. Households on campsites are the pastoral land users who define the land cover through how they decide to exploit the land area.
In our model, the grazing orbit represents the interconnected total home range grazing areas at herders’ winter, summer, spring, autumn, and otor campsites. However, the current methods used in EIA do not consider their connections as a series of land-use occupations. It is important that our model explains this link for EIA. Moreover, it is noteworthy that the model significantly links the pastoral land users with the pastoral areas and mobility and recognizes them as participants in the production of the pastoral space. As the scale of the grazing land and pastoral mobility is measured by how many pastoral land users share grassland resources on specific campsites, the land-use agreements and rights established between herders regulate the pastoral space in terms of how it is occupied. In fact, land users indicate their land tenure right boundaries based on their personal views on local dependency relations and social advocacy networks [71]. Thus, considering our conceptual underpinning (Karplus and Meir [41]) which gives precedence to ideologies of social and spatial connection, we can presume that our assumption about pastoral lived space is credible. In other words, the grazing land measured by the herding patterns and pastoral users is one of the key factors in the production of pastoral space.
Our model indicates that the grazing land has a strong positive effect on daily herding movements, this can be interpreted spatially. When the grazing orbit is larger, pastoral users practice long-distance herding, or reversely, the length of daily herding movement tends to be shorter when the grazing land is smaller. In contrast to the relationship between the grazing land and the daily herding movements, the grazing land has less effect on the number of households in the campsites. Over the last eight years, the number of herder households has increased by 17% in Mongolia [51]. With an increase in the number of households, there is no significant increase in the grazing land while the size of rangeland has stayed the same. This implies that the number of households on a specific campsite is not influenced by the size of the grazing land.
The effects of the latent variables of grazing land and pastoral mobility on each other were found to be positive, yet not significant. Herding on a smaller grazing area did not increase broad-scale pastoral mobility. Previous studies have reported that social, economic, and institutional factors limit the pastoral management decisions including choices between broad or fine-scale pastoral mobilities [72,73,74]. In our study areas, herders move a minimum of four times in different seasons between three to four distinct areas each year and they kept such a customary pattern of pastoral land use in post-socialist Mongolia [75]. In addition, seasonal movements are also related to climatic conditions. Thus, it is also possible that such norms of pasture use make broad-scale pastoral mobility more constant and independent of the fine-scale movements and size of grazing areas. On the other hand, it is alarming that herders are not practicing broad-scale movements even though when the number of animals increases in their grazing orbits as this might lead to overgrazing.
If we turn now to the relationship between the grazing land and the herd size strategy, the effect was found to be significant. The herd size strategy has a direct positive effect on the grazing land and indirect effects on the daily herding movements of animals and the number of households on seasonal campsites. The model suggests that with the increase in the number of animals, the size of the grazing land will increase too. Moreover, the changes in the number of animals on campsites would possibly affect the number of households and the length of daily herding movements of animals.
5.2. Herd Size Strategy
The herd size strategy in our model is a latent variable measured by the total number of animals and the total number of sheep and goats each herder household has at their campsites. This factor represents the conceived space in our model and the herd size and composition are influenced by this factor. In our study areas, pastoral land users herd five types of livestock: sheep, goats, cattle/yaks, horses, and camels. The EFA revealed that the grazing patterns of horses and camels are not correlated significantly with the factors of the model. The results suggest that particularly, the population of sheep and goats in the herd composition plays a considerable role in how the pastoral space is used by herders compared to other species. Sheep and goats have the ability to utilize a wide range of food sources as well as to cope with harsh climatic conditions [76]. Thus, it is likely that herding sheep and goats in home-range grazing areas is easier for herders due to their diet behavior. Moreover, these factors further indicate that the movement of sheep and goats better characterizes the spatial pattern of customary pastoral land use compared to the movement of cattle/yaks, horses, and camels. Saizen, Maekawa et al. [77] also noted that in contrast to other types of animals, goats have the greatest impact on grasslands in Mongolia where the data for this study have been collected.
Furthermore, the model suggests that the herd size strategy was found to have a direct effect on grazing land and pastoral mobility. In particular, the relationship between the herd size strategy and the grazing land increased while the herd size strategy was estimated to explain 44% of the variance that occurred in the grazing land. By contrast, only 9% of the changes occurring in pastoral mobility are explained by the herd size strategy. The herd size strategy has a direct positive effect on pastoral mobility; however, the effect was found to be minor. We hypothesized that the livestock population is the key indicator in managing the pastoral space and it influences the grazing pattern of animals as well as their movements. These parameter estimates support our hypothesis.
5.3. Pastoral Mobility
Pastoral mobility represents the perceived space in our model and is measured by the total distance between campsites located in different seasonal grazing areas and used for the purpose of extensive herding including areas for otor migration. These indicators consider the number of campsites used by herders for seasonal migration as we observed distances between campsites separately. It is interesting that pastoral mobility is measured with otor migration and the number of households as this emphasizes the importance of otor and herder households in nomadic pastoralism.
The herd size strategy was found to have a direct positive effect on pastoral mobility; however, the effect is not significant. Mobile pastoralism has many advantages such as resilience to droughts [78]. However, research by Kerven, Robinson et al. [74] in Kazakhstan has shown that the pastoralists are subjected to a number of limitations in using biophysical niches such as lack of access to water resources and financial constraints, thus most pastoralists’ choices of distributing their livestock are compromised despite the wide availability of pasture areas. Moreover, in their study conducted in the Mongolian Altai, Lkhagvadorj, Hauck et al. [73] revealed that herder families have reduced their seasonal migration due to high transportation costs and climate change resulted in a shortage of fodder. In the meantime, in this area, over the last 20 years, the livestock population has been increasing in response to market demand for products such as cashmere [77] and decreasing due to climatic factors such as dzud (severe winter) which killed millions of animals [51]. This tendency supports the weak relation between the herd size strategy and pastoral mobility. In other words, even though herders do not use all their seasonal migration campsites, the livestock number may still increase. Liao’s [18] model on herding decision making in southern Ethiopia also suggests that compared to community-level factors, households’ herd size plays a lesser role in the practice of extensive herding. Moreover, Karplus and Meir [41] noted spatial mobility as a central characteristic that distinguishes nomadic from sedentary societies and emphasized Lefebvre’s [42] view about social existence where he argued that every society produces its own space and those societies failing to produce their own space would disappear sooner or later. Thus, the nomadic pastoralists’ society should maintain both fine and broad-scale herding mobility to sustain its social existence and nomadic identity.
Lastly, the grazing land and pastoral mobility were shown to be dependent on each other, however, the magnitude of their relationship is not significant. A study carried out by Adriansen [35] in northern Senegal noted pastoralists’ preference for moving around within a small territory and their unwillingness to employ broad-scale movements themselves whilst their herds still being quite mobile. The model indicates that broad-scale movements between seasonal migration campsites do not decrease or substantially increase when the size of grazing orbit is large, or the degree of fine-scale movements is extensive. Thus, according to our hypothesized assumptions, the broad-scale movements are relatively independent of the fine-scale movements, but still associated with each other.
6. Conclusions
The dynamic pastoral space occupied by herders is one of the most important parameters which needs to be understood and predicted in any impact prediction in EIA in order to identify negative impacts associated with nomadic-pastoral land use. We used the SEM technique, which combines factor and multiple regression analyses, for explaining spatial occupation of grazing land for EIA. We specified a hypothesized structural equation model of dynamic pastoral space based on Karplus and Meir’s [41] concept of pastoral spatiality. We hypothesized that the grazing land, pastoral mobility, and the herd size strategy are interrelated factors and together they produce the pastoral space. Moreover, we hypothesized that these three factors are measured by grazing areas, both fine and broad scale herding mobilities, the number of households on campsites, and the number of animals. We estimated the structural relationships between land, mobility, and herd in the case of Mongolian pastoralism and quantified the direct effects of these factors on each other.
The assumptions tested in this study suggest that the herd size strategy has a direct effect on the pattern of grazing land and pastoral mobility and their effects on each other are all positive. Specifically, the findings indicate that the scale of the grazing land and pastoral mobility depends on the grazing orbit, fine and broad scale movements as well as the number of land users who are herding on particular seasonal campsites. Furthermore, the herd size strategy has a significant positive effect on the grazing land compared to pastoral mobility. This finding was unexpected and suggests that individual herder households’ decision-making regarding herd size and composition has more of an effect on fine-scale pastoral movements in their home range grazing areas than broad-scale extensive mobility between their seasonal campsites. The grazing land and pastoral mobility, in turn, covary but not considerably. Nevertheless, this study suggests that pastoral mobility is still one of the fundamental characteristics of the pastoral space associated with pastoral land use and herd size strategy in Mongolia.
We hope these results contribute to broadening the perspective of EIA methods with respect to predicting impacts associated with nomadic-pastoral land use. Particularly, our findings provide evidence with regard to identifying impact zones in EIA that impacts of the project on herd size strategy at a specific campsite significantly affect the size of grazing areas, pastoral mobility, and the number of herder households. Thus, this study extends EIA’s knowledge of the impact zones associated with nomadic-pastoral land use. Moreover, EIA impact prediction should consider grazing areas as a dynamic space which are shaped by herd size, composition, and mobility instead of looking at campsites as a static physical space. Therefore, EIA should distinguish impacts on pasture lands paying more attention to the details related to herding, specifically, to grazing orbits, fine and broad-scale herding movements including otor, livestock species, the number of animals as well as households at campsites.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.B. and W.T.d.V.; methodology, B.B. and W.T.d.V.; data collection, B.B.; formal analysis, B.B.; investigation, B.B.; writing—original draft preparation, B.B.; review, W.T.d.V.; visualization, B.B.; supervision, W.T.d.V.; funding acquisition, B.B. and W.T.d.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially supported by the Ministry of Education and Sciences of Mongolia, and the Chair of Land Management of the Technical University of Munich. The open access publication fee was covered by the Technical University of Munich.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all interviewees involved in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available in Bayarmaa Byambaa. (2020). Pastoral space and mobility datasets [Data set]. Zenodo. http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4379679 (accessed on 9 February 2020).
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to the herders from Uvs and Dundgovi aimags of Mongolia for taking the time to participate in our survey. We thank G. Sosorburam, Head of Tsahiurt bagh of Delgertsogt soum of Dundgovi aimag and G. Bayartogtokh from Turgen soum of Uvs aimag of Mongolia for their support in field data collection. The authors also gratefully thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive and valuable comments that helped us to improve the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Letourneau, A.; Verburg, P.H.; Stehfest, E. A land-use systems approach to represent land-use dynamics at continental and global scales. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 33, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.; Soepboer, W.; Veldkamp, A.; Limpiada, R.; Espaldon, A.V.O.; Mastura, S.S.A. Modeling the Spatial Dynamics of Regional Land Use: The CLUE-S Model. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinsstag, J.; Schelling, E.; Bonfoh, B.; Crump, L.; KrÄtli, S. The future of pastoralism: An introduction. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2016, 35, 335–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byambaa, B.; de Vries, W.T. The needs of nomadic-pastoral land users with respect to EIA theory, methods and effectiveness: What are they and does EIA address them? Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2019, 74, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byambaa, B.; de Vries, W.T. Evaluating the effectiveness of the environmental impact assessment process in Mongolia for nomadic-pastoral land users. Impact Assess. Proj. Apprais. 2020, 38, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.K. Environmental impact assessment: The state of the art. Impact Assess. Proj. Apprais. 2012, 30, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler, B. Environmental Assessment in a Changing World: Evaluating Practice to Improve Performance; Canadian Environmental Assessment Agency & International Association for Impact Assessment: Hull, QC, Canada, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, P.; Therivel, R. Methods of Environmental Impact Assessment, 3rd ed.; Morris, P., Therivel, R., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group, Taylor & Francis e-Library: Oxfordshire, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- CAO. Letter of Complaint Regarding the Oyu Tolgoi Project; Office of the Compliance Advisor Ombudsman, International Finance Corporation/Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency: Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- OyuTolgoi. Chapter C10: Land Use and Displacement. Environmental and Social Impact Assessment; Oyu Tolgoi LLC: Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tecol; SharedResources. Sainshand Wind Park Project Resettlement Action Plan; Sainshand Salkhin Park: Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Slootweg, R.; Vanclay, F.; van Schooten, M. Function evaluation as a framework for the integration of social and environmental impact assessment. Impact Assess. Proj. Apprais. 2001, 19, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koellner, T.; de Baan, L.; Beck, T.; Brandão, M.; Civit, B.; Margni, M.; Canals, L.M.; Saad, R.; de Souza, D.M.; Müller-Wenk, R. UNEP-SETAC guideline on global land use impact assessment on biodiversity and ecosystem services in LCA. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2013, 18, 1188–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeijer, E. Review of land use impact methodologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2000, 8, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milà i Canals, L.; Bauer, C.; Depestele, J.; Dubreuil, A.; Freiermuth Knuchel, R.; Gaillard, G.; Michelsen, O.; Müller-Wenk, R.; Rydgren, B. Key Elements in a Framework for Land Use Impact Assessment Within LCA (11 pp). Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2007, 12, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.; Dickman, C.; Wardle, G. Habitat use and behaviour of cattle in a heterogeneous desert environment in central Australia. Rangel. J. 2012, 34, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, M.J.; Istomin, K.V. Theories of Nomadic Movement: A New Theoretical Approach for Understanding the Movement Decisions of Nenets and Komi Reindeer Herders. Hum. Ecol. 2008, 36, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C. Modeling Herding Decision Making in the Extensive Grazing System in Southern Ethiopia. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2018, 108, 260–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erb, K.-H.; Haberl, H.; Jepsen, M.R.; Kuemmerle, T.; Lindner, M.; Müller, D.; Verburg, P.H.; Reenberg, A. A conceptual framework for analysing and measuring land-use intensity. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuemmerle, T.; Erb, K.; Meyfroidt, P.; Müller, D.; Verburg, P.H.; Estel, S.; Haberl, H.; Hostert, P.; Jepsen, M.R.; Kastner, T.; et al. Challenges and opportunities in mapping land use intensity globally. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldkamp, A.; Lambin, E.F. Predicting land-use change. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 85, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.W.; Antle, J.M.; Basso, B.; Boote, K.J.; Conant, R.T.; Foster, I.; Godfray, H.C.J.; Herrero, M.; Howitt, R.E.; Janssen, S.; et al. Toward a new generation of agricultural system data, models, and knowledge products: State of agricultural systems science. Agric. Syst. 2017, 155, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, G.; Apolloni, A.; Coste, C.; Wint, G.R.W.; Lancelot, R.; Gilbert, M. Predictive gravity models of livestock mobility in Mauritania: The effects of supply, demand and cultural factors. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Cai, S.; Moritz, M.; Garabed, R.; Pomeroy, L.W. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Pastoral Mobility in the Far North Region, Cameroon: Data Analysis and Modeling. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; John, R. Livestock dynamics under changing economy and climate in Mongolia. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Jiang, L.; Shen, G.Q.P. Embodied pasture land use change in China 2000–2015: From the perspective of globalization. Land Use Policy 2019, 82, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppolillo, P.B. The Landscape Ecology of Pastoral Herding: Spatial Analysis of Land Use and Livestock Production in East Africa. Hum. Ecol. 2000, 28, 527–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Clark, P.E.; Shibia, M.; DeGloria, S.D. Spatiotemporal dynamics of cattle behavior and resource selection patterns on East African rangelands: Evidence from GPS-tracking. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2018, 32, 1523–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Jurdak, R. Understanding the spatiotemporal pattern of grazing cattle movement. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayre, N.F.; de Buys, W.; Bestelmeyer, B.T.; Havstad, K.M. “The Range Problem” After a Century of Rangeland Science: New Research Themes for Altered Landscapes. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 65, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C. Quantifying multi-scale pastoral mobility: Developing a metrics system and using GPS-Tracking data for evaluation. J. Arid. Environ. 2018, 153, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koellner, T.; Scholz, R.W. Assessment of land use impacts on the natural environment. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2006, 13, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; John, R.; Shao, C.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Amartuvshin, A.; Brown, D.; Qi, J.; Han, J.; Lafortezza, R.; et al. Policy shifts influence the functional changes of the CNH systems on the Mongolian Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Gimenez, M.; Allington, G.; Angerer, J.; Reid, R.; Jamsranjav, C.; Ulambayar, T.; Hondula, K.; Batkhishig, B.; Batbuyan, B.; Tsevlee, A.; et al. Using an integrated social-ecological analysis to detect effects of household herding practices on indicators of rangeland resilience in Mongolia. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 075010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriansen, H.K. Understanding pastoral mobility: The case of Senegalese Fulani. Geogr. J. 2008, 174, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, B.; Shortridge, A.; WinklerPrins, A.M.G.A. Pastoral Herd Management, Drought Coping Strategies, and Cattle Mobility in Southern Kenya. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2009, 99, 309–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriansen, H.K.; Nielsen, T.T. Going Where the Grass Is Greener: On the Study of Pastoral Mobility in Ferlo, Senegal. Hum. Ecol. 2002, 30, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, M.; Hamilton, I.M.; Scholte, P.; Chen, Y.-J. Ideal Free Distributions of Mobile Pastoralists in Multiple Seasonal Grazing Areas. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 67, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wario, H.T.; Roba, H.G.; Kaufmann, B. Responding to mobility constraints: Recent shifts in resource use practices and herding strategies in the Borana pastoral system, southern Ethiopia. J. Arid. Environ. 2016, 127, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, B. Pastoral resource access and utilization: Quantifying the spatial and temporal relationships between livestock mobility, density and biomass availability in southern Kenya. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 21, 520–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karplus, Y.; Meir, A. The Production of Space: A Neglected Perspective in Pastoral Research. Environ. Plan. D Soc. Space 2013, 31, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, H. The Production of Space; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Sayre, N.F.; Davis, D.K.; Bestelmeyer, B.; Williamson, J.C. Rangelands: Where Anthromes Meet Their Limits. Land 2017, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, T.; Natsagdorj, E.; Waring, R.H.; Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y. Satellite observed widespread decline in Mongolian grasslands largely due to overgrazing. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batunacun; Wieland, R.; Lakes, T.; Yunfeng, H.; Nendel, C. Identifying drivers of land degradation in Xilingol, China, between 1975 and 2015. Land Use Policy 2019, 83, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Dries, L.; Huang, J.; Min, S.; Tang, J. The impacts of the eco-environmental policy on grassland degradation and livestock production in Inner Mongolia, China: An empirical analysis based on the simultaneous equation model. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senda, T.S.; Robinson, L.W.; Gachene, C.K.K.; Kironchi, G.; Doyo, J. An assessment of the implications of alternative scales of communal land tenure formalization in pastoral systems. Land Use Policy 2020, 94, 104535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Gimenez, M.E. The role of Mongolian nomadic pastoralists’ ecological knowledge in rangeland management. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Li, W. Why do herders insist on “Otor?” maintaining mobility in Inner Mongolia. Nomadic Peoples 2008, 12, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Giménez, M.E.; Batkhishig, B.; Batbuyan, B. Cross-boundary and cross-level dynamics increase vulnerability to severe winter disasters (dzud) in Mongolia. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2012, 22, 836–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSO. Mongolian Statistical Information Service. Available online: http://www.nso.mn/ (accessed on 9 February 2020).
- SGH. The Constitution of Mongolia; The State Great Hural (Parliament) of Mongolia: Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Upton, C. Living off the land: Nature and nomadism in Mongolia. Geoforum 2010, 41, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bold, B.-O. Socio-economic segmentation—“Khot-Ail” in nomadic livestock keeping of Mongolia. Nomadic Peoples 1996, 69–86. Available online: jstor.org/stable/43123494 (accessed on 9 February 2020).
- SGH. Law of Mongolia on Land; The State Great Hural (Parliament) of Mongolia: Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Upton, C. “Custom” and Contestation: Land Reform in Post-Socialist Mongolia. World Dev. 2009, 37, 1400–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrbach, B.; Anderson, S.; Laube, P. The effects of sample size on data quality in participatory mapping of past land use. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2016, 43, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D. Structural Equation Modeling: Foundations and Extensions, 2nd ed.; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, J.B.; Nora, A.; Stage, F.K.; Barlow, E.A.; King, J. Reporting Structural Equation Modeling and Confirmatory Factor Analysis Results: A Review. J. Educ. Res. 2006, 99, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 3rd ed; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Jiang, G.; Hattori, M.; Trichtinger, L. EFAutilities: Utility Functions for Exploratory Factor Analysis. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=EFAutilities (accessed on 9 February 2020).
- Watkins, M.W. Exploratory Factor Analysis: A Guide to Best Practice. J. Black Psychol. 2018, 44, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, A.; Pearce, S. A Beginner’s Guide to Factor Analysis: Focusing on Exploratory Factor Analysis. Tutorials Quant. Methods Psychol. 2013, 9, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosseel, Y. Lavaan: An R Package for Structural Equation Modeling. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 48, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schermelleh-Engel, K.; Moosbrugger, H.; Müller, H. Evaluating the Fit of Structural Equation Models: Tests of Significance and Descriptive Goodness-of-Fit Measures. Methods Psychol. Res. 2003, 8, 23–74. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.T.; Bentler, P.M. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. 1999, 6, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, R.J.; Lance, C.E. A Review and Synthesis of the Measurement Invariance Literature: Suggestions, Practices, and Recommendations for Organizational Research. Organ. Res. Methods 2000, 3, 4–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, K.A. Structural Equations and Causal Explanations: Some Challenges for Causal SEM. Struct. Equ. Model. A Multidiscip. J. 2010, 17, 654–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, J. The Foundations of Causal Inference. Sociol. Methodol. 2010, 40, 75–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullman, J.B.; Bentler, P.M. Structural Equation Modeling. In Handbook of Psychology, 2nd ed.; Weiner, I., Schinka, J.A., Velicer, W.F., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, W.T.; Bennett, R.M.; Zevenbergen, J.A. Neo-cadastres: Innovative solution for land users without state based land rights, or just reflections of institutional isomorphism? Surv. Rev. 2015, 47, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynor, E.J.; Coon, J.J.; Swartz, T.M.; Morton, L.W.; Schacht, W.H.; Miller, J.R. Shifting Cattle Producer Beliefs on Stocking and Invasive Forage: Implications for Grassland Conservation. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 72, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lkhagvadorj, D.; Hauck, M.; Dulamsuren, C.; Tsogtbaatar, J. Pastoral nomadism in the forest-steppe of the Mongolian Altai under a changing economy and a warming climate. J. Arid. Environ. 2013, 88, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerven, C.; Robinson, S.; Behnke, R.; Kushenov, K.; Milner-Gulland, E.J. Horseflies, wolves and wells: Biophysical and socio-economic factors influencing livestock distribution in Kazakhstan’s rangelands. Land Use Policy 2016, 52, 392–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Giménez, M.E. The effects of livestock privatization on pastoral land use and land tenure in post-socialist Mongolia. Nomadic Peoples 2001, 5, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, C. The behaviour of sheep and goats. In The Ethology of Domestic Animals: An Introductory Text; Jensen, P., Ed.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Saizen, I.; Maekawa, A.; Yamamura, N. Spatial analysis of time-series changes in livestock distribution by detection of local spatial associations in Mongolia. Appl. Geogr. 2010, 30, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freier, K.P.; Finckh, M.; Schneider, U.A. Adaptation to New Climate by an Old Strategy? Modeling Sedentary and Mobile Pastoralism in Semi-Arid Morocco. Land 2014, 3, 917–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | Migration of herders to fatten their animals or to escape drought or harsh winter to distant pastures other than their winter, summer, spring, and autumn campsites where grasses are available for grazing. |
| 2 | The second-level administrative subdivision of Mongolia. |
| 3 | The first-level administrative subdivision of Mongolia. |
| 4 | R code is included in Bayarmaa Byambaa. (2020). Pastoral space and mobility datasets [Data set]. Zenodo. http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4379679 (accessed on 9 February 2020). |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).