The Multiscale Monitoring of Peatland Ecosystem Carbon Cycling in the Middle Taiga Zone of Western Siberia: The Mukhrino Bog Case Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
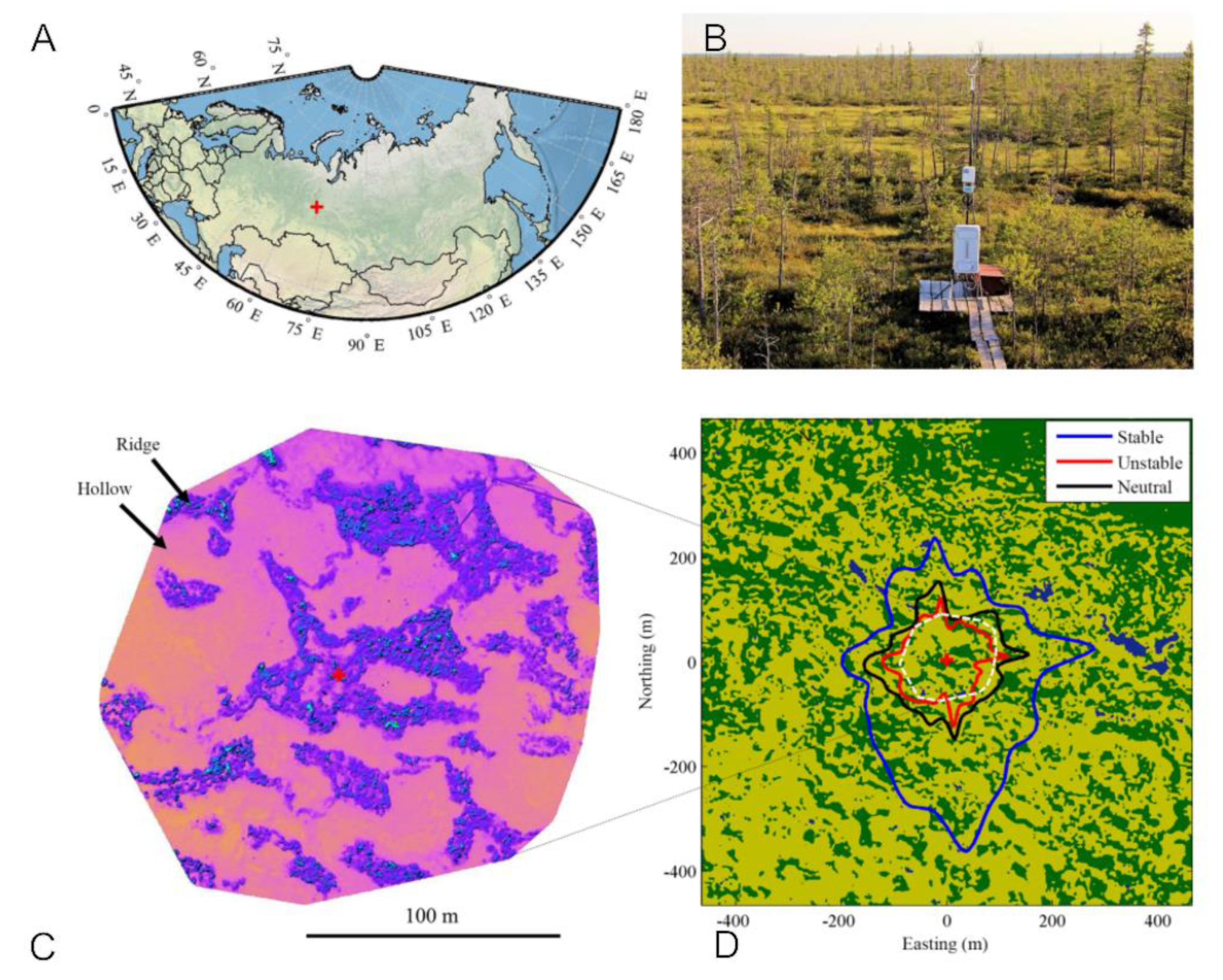
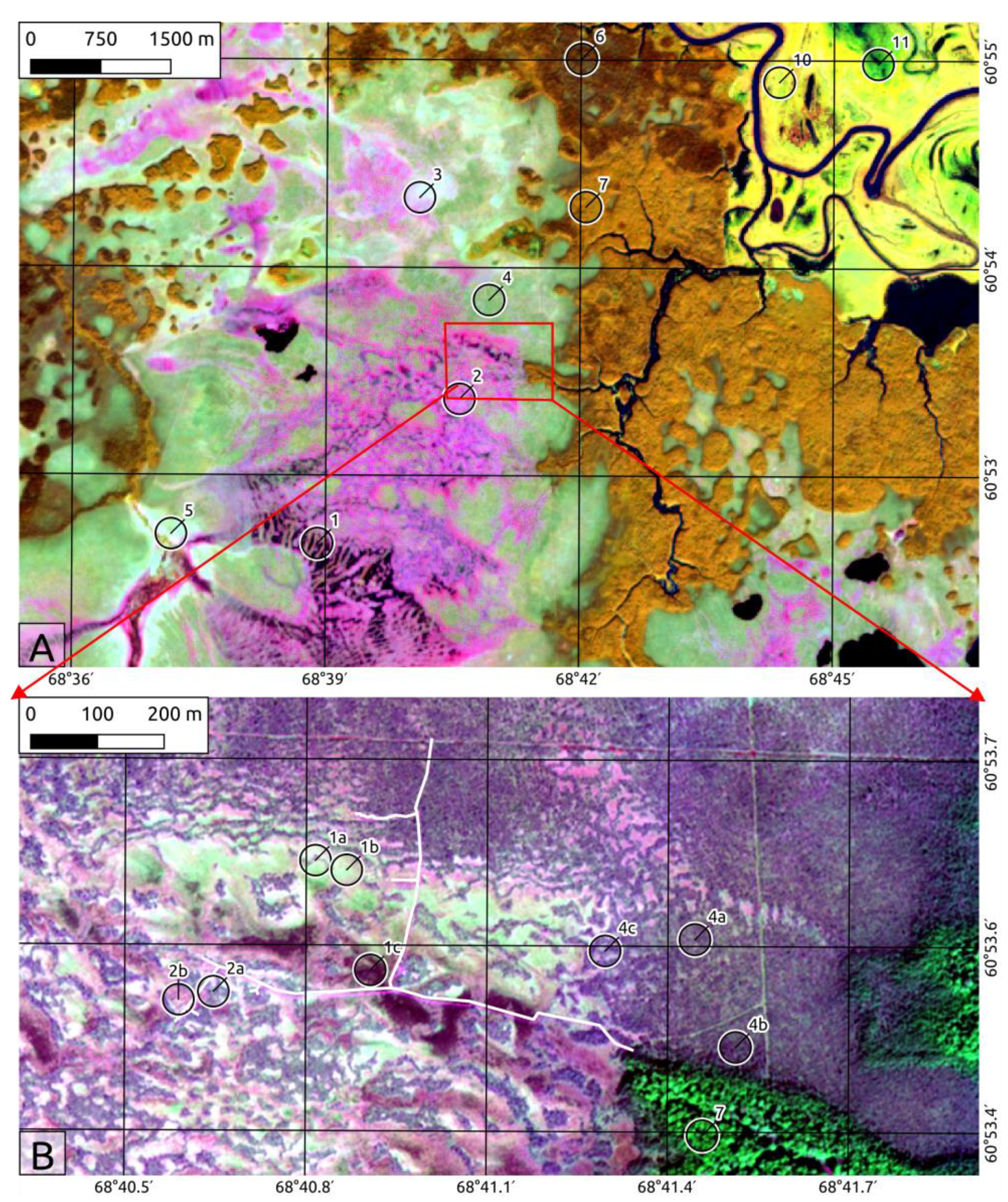
2.1. MFS Site Location
2.2. Landscape Position and Vegetation
- I.
- Ombrotrophic (Sphagnum dominated) raised bogs:
- 1.
- Ridge-hollow-pool patterned bogs and water tracks. This is the most waterlogged peatland complex consisting of three microtopes:
- 1a.
- Dwarf shrubs-Sphagnum ridges with Chamaedaphne calyculata, Andromeda polifolia, Sphagnum angustifolium, S. magellanicum, S. fuscum.
- 1b.
- Sphagnum lawns. Size of the lawns is 1000–10,000 m2 and occupied by Carex limosa, Eriophorum russeolum, Scheuchzeria palustris, Sphagnum balticum, S. papillosum.
- 1c.
- Water pools and waterlogged hollows with Sphagnum majus, S. jensenii, S. lindbergii, Carex limosa, Eriophorum russeolum. Water on the surface and sparse sphagnum cover or slightly higher in the beginning of summer and after long periods of rain.
- 2.
- Ridge-hollow patterned bogs. This mire type is the most widespread ombrotrophic patterned bog complex in West Siberia consisting of pine dwarf shrubs-Sphagnum (ryam) ridges and Sphagnum hollows more or less oriented across a rainwater flow. These complexes are situated usually on very slight sloping areas (gradient 0.003–0.008 m/km). The configuration and spacing of the ridges and hollows are related to the slope gradient of the peatland surface, but mostly they have an equal share in the complex. The ridge microtopes are dryer and 25–50 cm higher than hollows.
- 2a.
- Pine-dwarf shrubs: Sphagnum ridges with Pinus sylvestris, Ledum palustris, Chamaedaphne calyculata, Sphagnum fuscum. The pine height is usually 0.5–2.0 m and 3–10% cover.
- 2b.
- Sphagnum hollows. Vegetation is similar to 1a, but the size of hollows is smaller (10–100 m2).
- 3.
- Dwarf shrub: Sphagnum bog with sparse low pine trees (“Open bog”) with Pinus sylvestris, Chamaedaphne calyculata, Eriophorum vaginatum, Sphagnum angustifolium, S. divinum. The dwarf pine layer is very sparse or absent. These mire types occur on the border between oligotrophic raised bog and mineral uplands. This transition zone usually has a width of 100 to 200 m, rarely wider. They also may be developed in the transition (boundary) zone between raised bogs and minerotrophic fens.
- 4.
- Wooded pine-dwarf shrub-Sphagnum bog (ryam)
- 4a.
- Typical ryam with Pinus sylvestris, Ledum palustris, Chamaedaphne calyculata, Sphagnum fuscum. Ombrotrophic dwarf shrubs: Sphagnum hummock peatlands wooded by pine trees 0.5–4 m high. This type of bog is very common in West Siberia and covers large homogeneous areas or is presented as ridges in patterned bog complexes.
- 4b.
- Tall ryam with Pinus sylvestris, Ledum palustris, Chamaedaphne calyculata, Vaccinium myrtillus, Sphagnum angustifolium, S. divinum. Differs from the typical ryam by the height of the tree layer (6–10 m) and dominated by Sphagnum species in the ground layer.
- 4c.
- Ryam with small cotton grass: Sphagnum hollows with Pinus sylvestris, Ledum palustris, Chamaedaphne calyculata, Sphagnum fuscum on ryam hummocks and Eriophorum vaginatum, S. balticum in hollows. Differs from typical ryam with a presence of small hollows covered by cotton grass-Sphagnum balticum communities.
- II.
- Mesoologotrophic fens:
- 5.
- Sedge-Sphagnum fen (incl. sparse low birch fens) with Betula pubescens, Carex rostrata, Oxycoccus palustris, Sphagnum angustifolium, S. fallax, S. flexuosum). The tall sedge Sphagnum through-flow fens fed both by rain run-off and groundwater are often sparsely wooded by small birch trees.
- III.
- Upland forests
- 6.
- Dark coniferous and mixed forest with Pinus sibirica, Abies sibirica, Picea obovata, Populus tremula, Betula puescens and Vaccinium myrtillus, Maianthemum bifolium, Linnaea borealis, Gymnocarpium dryopteris, Hylocomium splendens, Pleurozium schreberi in the ground layer. There are typical climax forest communities on loamy soils in the West Siberian middle taiga.
- 7.
- Small-leaved forest with Betula pubescens, Populus tremula in the upper layer, young Pinus sibirica, Abies sibirica, Picea obovata trees, and Vaccinium myrtillus, Pleurozium schreberi on the ground. These are different stages of the post-fire succession.
- IV.
- Floodplains
- 8.
- Floodplain willow (Salix triandra, S. alba, S. viminalis, S. dasyclados). Highest floodplain level, flooding frequency 25–50%.
- 9.
- Meadows with Phalaroides arundinacea. Mid floodplain level flooded for 1–2 month, flooding frequency 50–75%.
- 10.
- Sedge wetlands with Carex aquatilis, Carex juncella. Low floodplain level flooded every year for 2–4 month.
2.3. Field Data Collection and Analysis
2.3.1. Meteorology
2.3.2. Hydrology
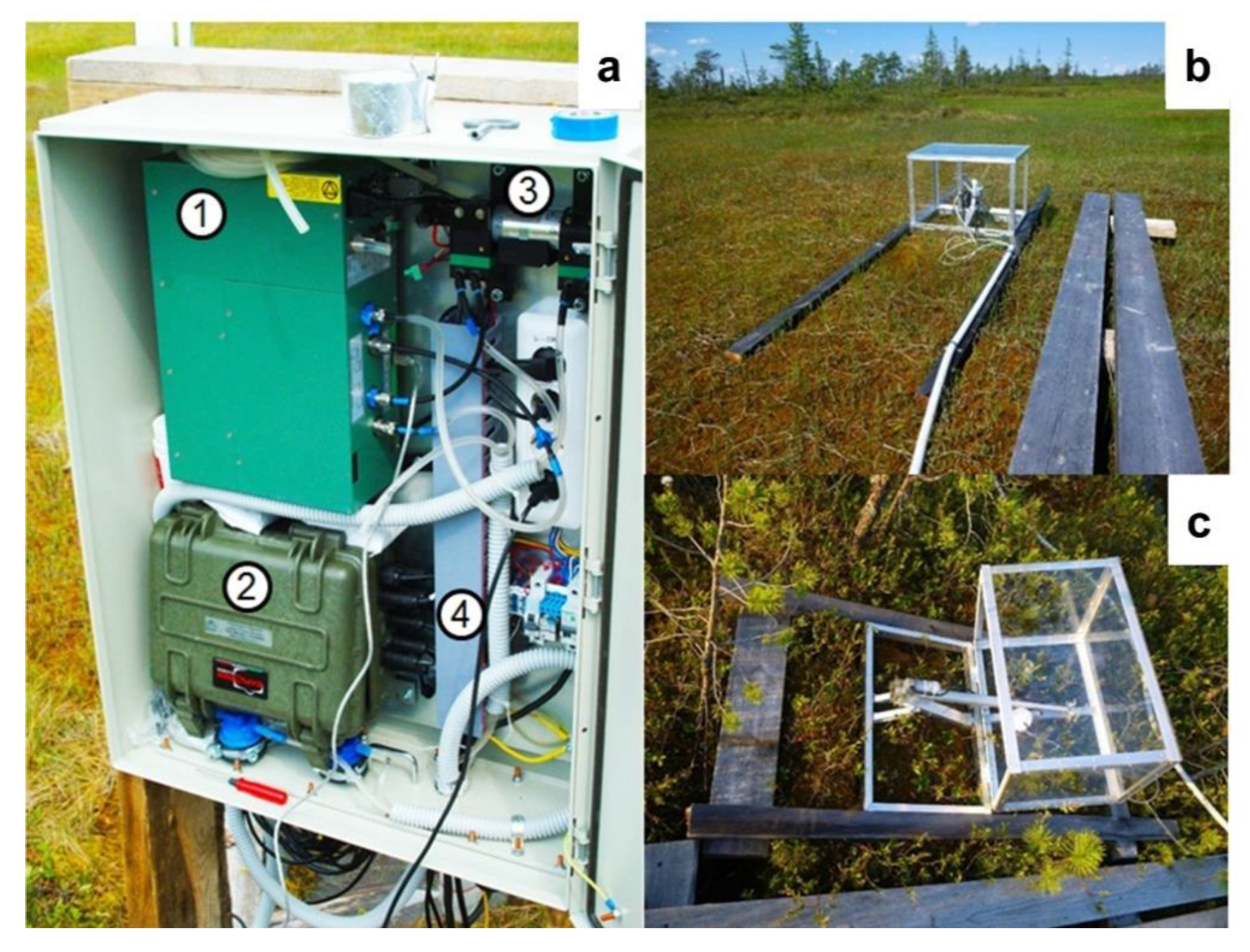
2.3.3. Chamber Measurements of Carbon Dioxide Fluxes
2.3.4. Eddy-Covariance Measurements
2.3.5. Sphagnum Annual Growth and Production
2.3.6. Decomposition Rate of Native and Standardized Substrates
2.3.7. Peat Sampling and Lab Work
2.3.8. Mapping
3. Results
3.1. Meteorology
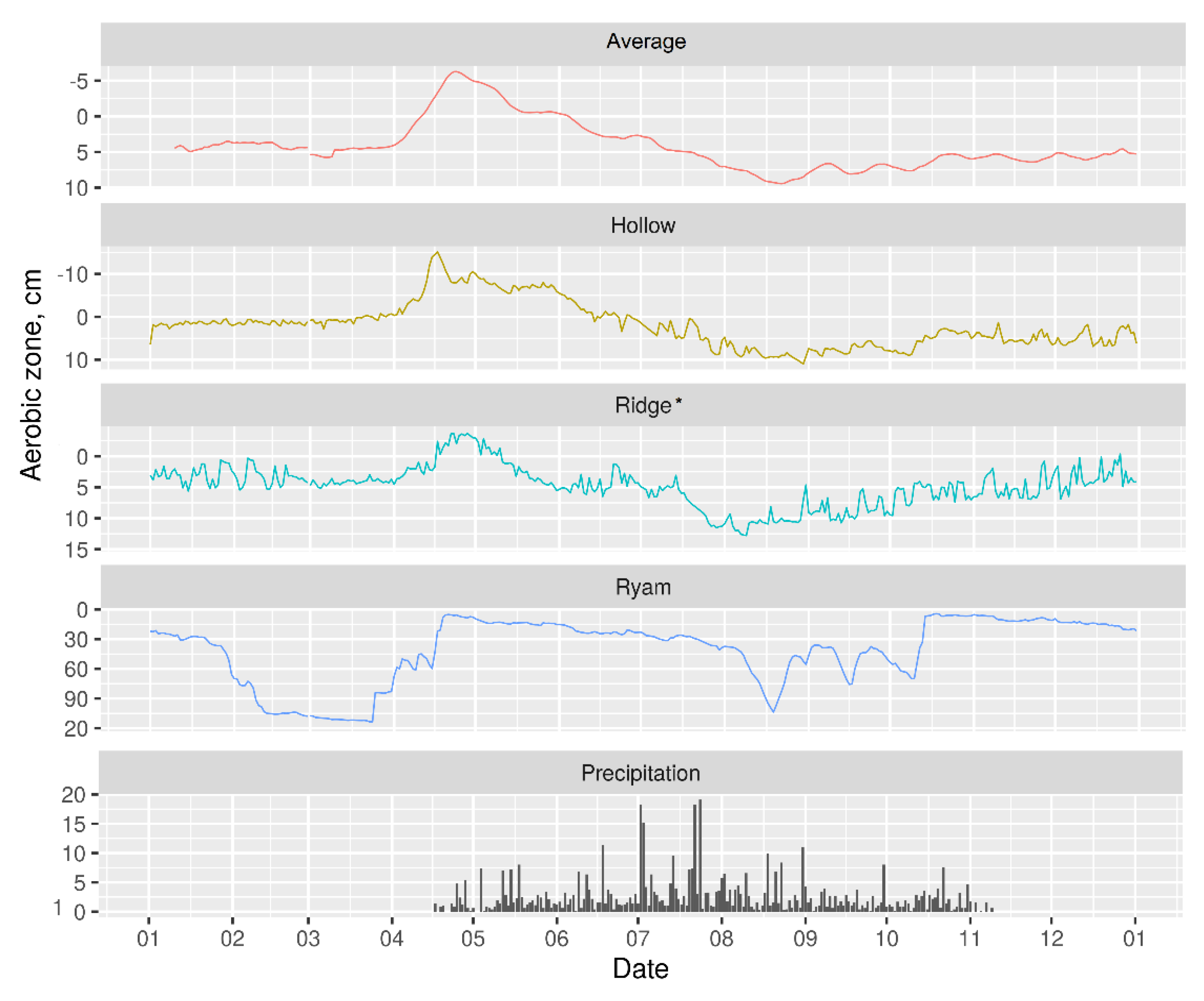
3.2. Hydrology
3.3. Carbon Dioxide Fluxes at a Local Scale
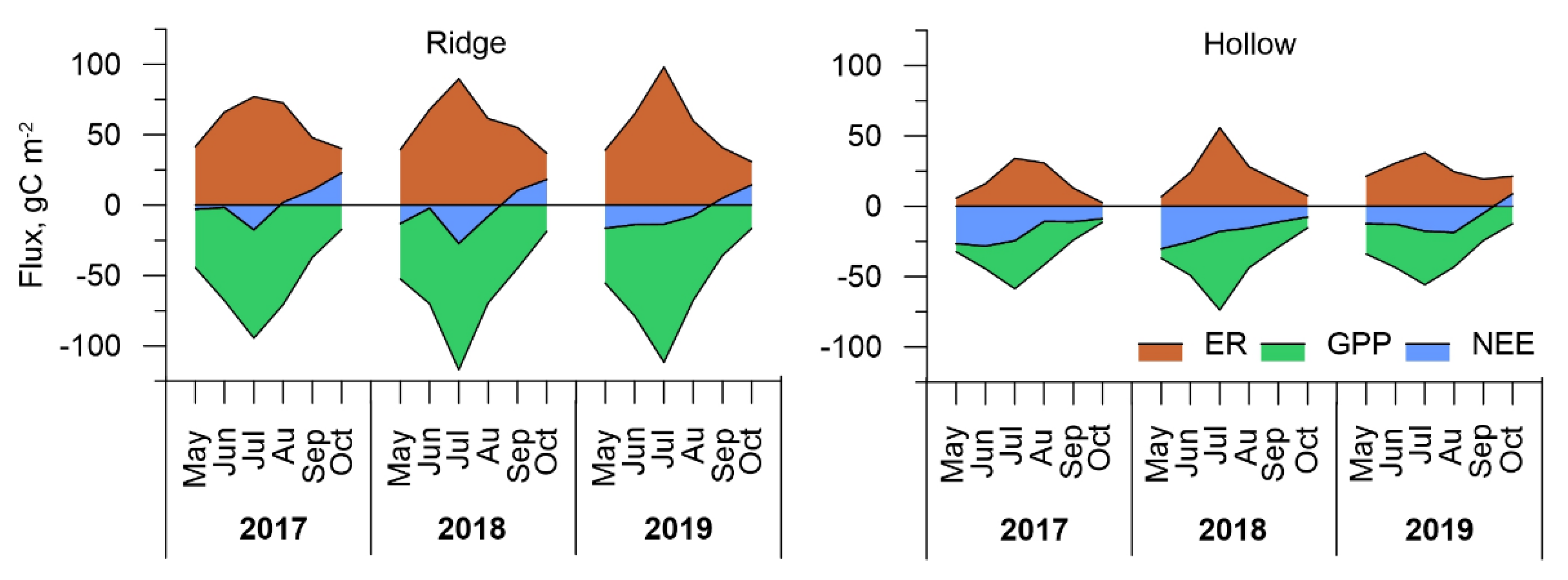
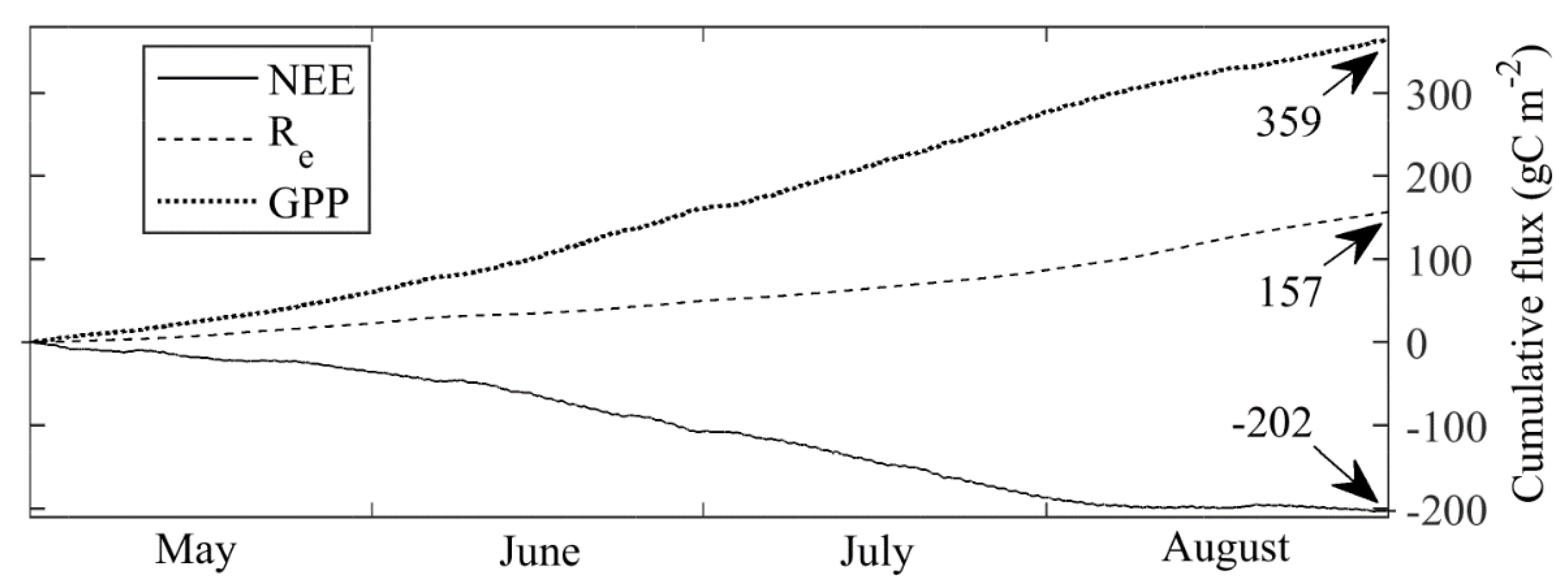
3.4. Carbon Dioxide Fluxes at Ecosystem Scale
3.5. Sphagnum Annual Growth and Production
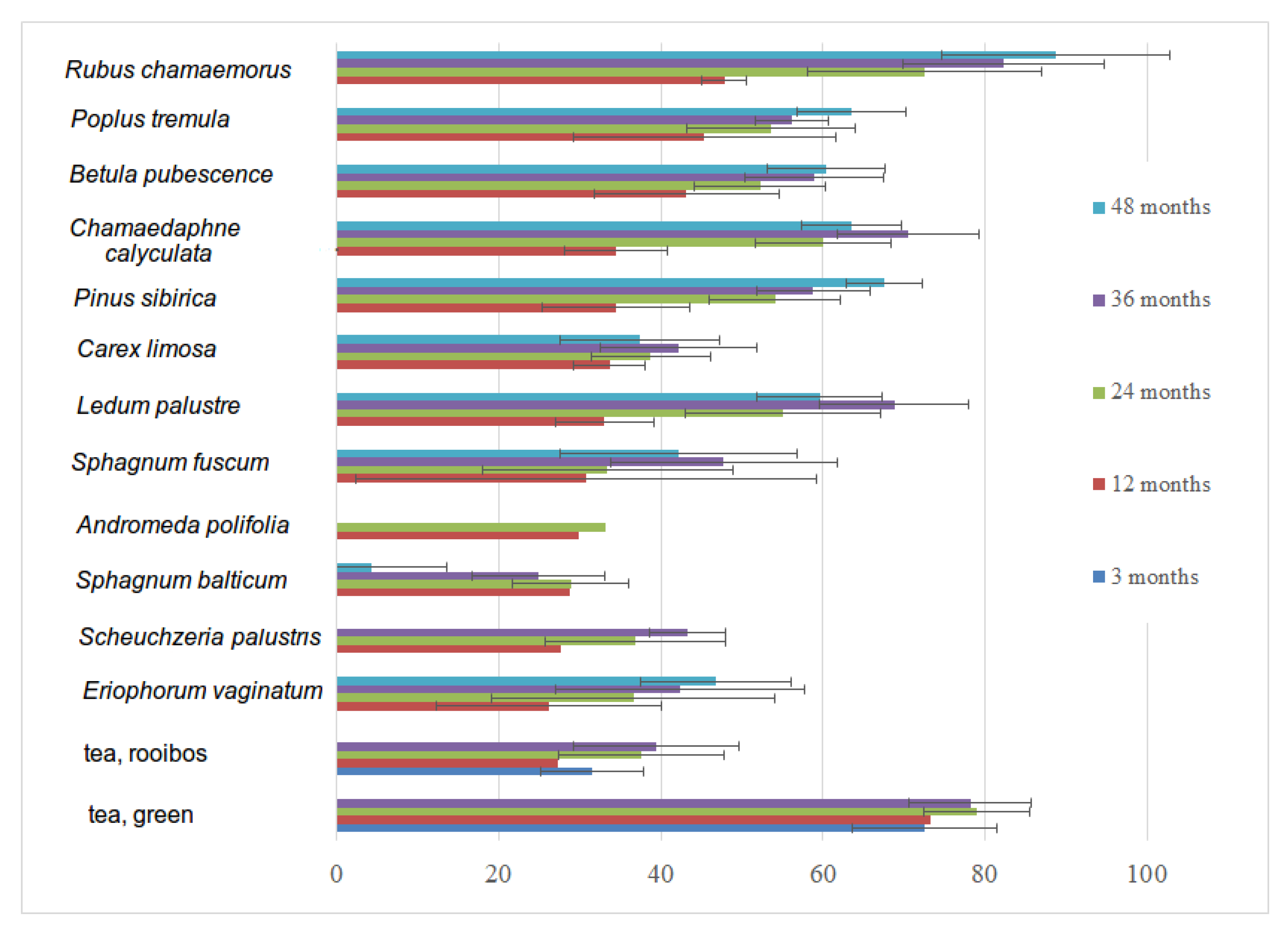
3.6. Decomposition Rate of Native and Standardized Substrates
3.7. Peat Stratigraphy and Rates of Peat and Carbon Accumulation
4. Discussion
5. Current Challenges and Future Development
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| n | Parameter | Equipment | Ridge | Hollow |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Air temperature and humidity at 2 m | Rotronic HC2A-S3 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | Atmospheric pressure | Campbell Scientific CS105 PTB101b | 1 | - |
| 3 | Wind speed and direction at 2 m | Young Wind Monitor 05103 | - | 1 |
| 4 | Wind speed and direction at 10 m | Young Wind Monitor 05103 | 1 | - |
| 5 | Incoming PAR | Li-Cor LI-190R | 1 | 1 |
| 6 | Reflected PAR | Li-Cor LI-190R | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | Net radiation balance | Kipp & Zonen NRLite | 1 | 1 |
| 8 | Ground heat flux | Hukseflux Heat Flux Sensor HFP01SC | 2 | 1 |
| 9 | Precipitation (summer) | HOBO Data Logging Rain Gauge RG3-M | - | 1 |
| 10 | Snow depth | Manual observations | - | 1 |
| 11 | Surface albedo | Calculated from Li-Cor LI-190R | 1 | 1 |
| № | Species | Number of Plots | 2019 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sphagnum angustifolium | 3 | 27 | 27 |
| 2 | Sphagnum balticum | 32 (30 in OTC) | 150 (130 in OTC) | 248 (238 in OTC) |
| 3 | Sphagnum capillifolium | 2 | 19 | 20 |
| 4 | Sphagnum fuscum | 4 | 34 | 36 |
| 5 | Sphagnum jensenii | 6 | 54 | 56 |
| 6 | Sphagnum divinum | 4 | 28 | 28 |
| 7 | Sphagnum majus | 2 | 19 | 17 |
| 8 | Sphagnum papillosum | 4 | 34 | 35 |
| Total number of measurements | 57 | 365 | 467 |
| Year of Installation | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decomposition Period, Months/Substrate | 3 | 12 | 24 | 36 | 48 | 3 | 12 | 24 | 36 | 12 | 24 | 3 | 12 | 3 |
| Andromeda polifolia | 8 | 6 | 8 | |||||||||||
| Betula pubescence | 8 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 8 | ||||
| Carex limosa | 8 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 7 | ||||
| Chamaedaphne calyculata | 8 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 6 | ||||
| Eriophorum vaginatum | 8 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 8 | ||||
| Ledum palustre | 8 | 8 | 8 | 5 | 8 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 8 | ||||
| Pinus sibirica | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 8 | ||||
| Populus tremula | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 8 | ||||
| Rubus chamaemorus | 8 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 7 | ||||
| Scheuchzeria palustris | 8 | 6 | 2 | 8 | 8 | 8 | ||||||||
| Sphagnum balticum | 8 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 8 | ||||
| Sphagnum fuscum | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 8 | ||||
| Tea, green | 24 | 24 | 24 | 23 | 64 | 60 | 54 | 8 | 78 | 24 | ||||
| Tea, rooibos | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 59 | 56 | 53 | 8 | 76 | 24 | ||||
| Vegetation Type/Substrate | A. polifolia Leaves | B. pubescence Leaves | C. limosa Leaves | Ch. calyculata Leaves | E. vaginatum Leaves | L. palustre | P. sibirica Leaves | P. tremula Leaves | R. chamaemorus Leaves | S. palustris | S. balticum Green Parts | S. fuscum Green Parts | Tea, Green | Tea, Rooibos |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coniferous forest | 79 | 78 | 79 | 67 | 74 | |||||||||
| Deciduous forest 10 years after cut | 39 | 37 | ||||||||||||
| Deciduous forest 40 years after cut | 32 | 31 | ||||||||||||
| Raised bog lawn | 66 | 71 | 40 | 69 | 40 | 40 | ||||||||
| Raised bog ryam | 22 | 1 | 73 | 70 | 74 | 79 | 44 | 52 | ||||||
| OTC dry, chamber | 32 | 31 | ||||||||||||
| OTC dry, control | 32 | 32 | ||||||||||||
| OTC wet, chamber | 31 | 32 | ||||||||||||
| OTC wet, control | 33 | 19 |
References
- Berglund, B.E. Human impact and climate changes—Synchronous events and a causal link? Quart. Int. 2003, 105, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosten, H. Peatlands, Climate Change Mitigation and Biodiversity Conservation: An Issue Brief on the Importance of Peatlands for Carbon and Biodiversity Conservation and the Role of Drained Peatlands as Greenhouse Gas Emission Hotspots; Nordic Council of Ministers: København, Denmark, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Callaghan, T.V.; Kulikova, O.; Rakhmanova, L.; Topp-Jorgensen, E.; Labba, N.; Kuhmanenm, L.-A.; Kirpotin, S.; Shaduyko, O.; Burgess, H.; Rautio, A.; et al. Improving dialogue among researchers, local and indigenous peoples and decision-makers to address issues of climate change in the North. Ambio 2020, 49, 1161–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsyganov, A.N.; Zarov, E.A.; Mazei, Y.A.; Kulkov, M.G.; Babeshko, K.V.; Yushkovets, S.Y.; Payne, R.J.; Ratcliffe, J.L.; Fatyunina, Y.A.; Zazovskaya, E.P.; et al. Key periods of peatland development and environmental changes in the middle taiga zone of Western Siberia during the Holocene. Ambio 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorham, E. Northern peatlands: Role in the carbon cycle and probable responses to climatic warming. Ecol. Appl. 1991, 1, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charman, D.J.; Beilman, D.W.; Blaauw, M.; Booth, R.K.; Brewer, S.; Chambers, F.M.; Christen, J.A.; Gallego-Sala, A.; Harrison, S.P.; Hughes, P.D.M.; et al. Climate-related changes in peatland carbon accumulation during the last millennium. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 929–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dise, N.B. Environmental science. Peatland response to global change. Science 2009, 326, 810–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Morris, P.J.; Liu, J.; Holden, J. PEATMAP: Refining estimates of global peatland distribution based on a meta-analysis. Catena 2018, 160, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, Y.; Smith, L.C.; MacDonald, G.M.; Kremenetski, K.V.; Frey, K.E.; Velichko, A.A.; Lee, M.; Beilmannr, D.W.; Dubinin, P.A. High-resolution GIS-based inventory of the west Siberian peat carbon pool. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycl. 2014, 18, GB3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubier, J.L.; Bhatia, G.; Moore, T.R.; Roulet, N.T.; Lafleur, P.M. Spatial and temporal variability in growing-season net ecosystem carbon dioxide exchange at a large peatland in Ontario, Canada. Ecosystems 2003, 6, 353–367. [Google Scholar]
- Olchev, A.; Novenko, E.; Desherevskaya, O.; Krasnorutskaya, K.; Kurbatova, J. Effects of climatic changes on carbon dioxide and water vapor fluxes in boreal forest ecosystems of European part of Russia. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 045007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovatskaya, E.A.; Dyukarev, E.A. The influence of environmental factors on the CO2 emission from the surface of oligotrophic peat soils in West Siberia. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2012, 45, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfter, C.; Campbell, C.; Dinsmore, K.J.; Drewer, J.; Coyle, M.; Anderson, M.; Skiba, U.; Nemitz, E.; Sutton, M.A. Drivers of long-term variability in CO2 net ecosystem exchange in a temperate peatland. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 1799–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saunois, M.; Bousquet, P.; Poulter, B.; Peregon, A.; Ciais, P.; Canadell, J.G.; Dlugokencky, E.J.; Etiope, G.; Bastviken, D.; Houweling, S.; et al. The global methane budget 2000–2012. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2016, 8, 697–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IPCC. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. In Climate Change: Synthesis Report; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- Naumov, A.V. Soil Respiration; Izd SO RAN: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2009; pp. 1–208. [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa, M.; Ito, A.; Machida, T.; Tsuda, N.; Niwa, Y.; Davydov, D.; Fofonov, A.; Arshinov, M. Annual variation of CH4 emissions from the middle taiga in West Siberian Lowland (2005–2009): A case of high CH4 flux and precipitation rate in the summer of 2007. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2012, 64, 17514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, A.G.; Olchev, A.V. Model of CO2 exchange in a sphagnum peat bog. Comput. Res. Model. 2016, 8, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, F.; Gogo, S.; Guimbaud, C.; Bernard-Jannin, L.; Hu, Z.; Laggoun-Défarge, F. Vegetation composition controls temperature sensitivity of CO2 and CH4 emissions and DOC concentration in peatlands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 107, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veretennikova, E.E.; Dyukarev, E.A. Diurnal variations in methane emissions from West Siberia peatlands in summer. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2017, 42, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veretennikova, E.E.; Dyukarev, E.A. Spatial and temporal dynamics of methane fluxes from the bog ecosystems of the southern taiga of Western Siberia. Boreal Environ. Res. 2021, 26, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirpotin, S.N.; Callaghan, T.V.; Peregon, A.M.; Babenko, A.S.; Berman, D.I.; Bulakhova, N.A.; Byzaakay, A.A.; Chernykh, T.M.; Chursin, V.; Interesova, E.A.; et al. Impacts of environmental change on biodiversity and vegetation dynamics in Siberia. Ambio 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Data Portal Serving the FLUXNET Community. Available online: https://fluxnet.org (accessed on 25 July 2021).
- Pallandt, M.; Kumar, J.; Mauritz, M.; Schuur, E.; Virkkala, A.-M.; Celis, G.; Hoffman, F.; Göckede, M. Representativeness assessment of the pan-Arctic eddy-covariance site network, and optimized future enhancements. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappalainen, H.K.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Petäjä, T.; Kurten, T.; Baklanov, A.; Shvidenko, A.; Bäck, J.; Vihma, T.; Alekseychik, P.; Arnold, S.; et al. Pan-Eurasian Experiment (PEEX): Towards holistic understanding of the feedbacks and interactions in the land–atmosphere–ocean–society continuum in the Northern Eurasian region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 14421–14461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.-B.; Knohl, A.; Lucas-Moffat, A.M.; Migliavacca, M.; Gerbig, C.; Gerbiga, C.; Vesala, T.; Peltola, O.; Mammarella, I.; Kolle, O.; et al. Strong radiative effect induced by clouds and smoke on forest net ecosystem productivity in central Siberia. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 250–251, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasakawa, M.; Machida, T.; Ishijima, K.; Arshinov, M.; Patra, P.K.; Ito, A.; Aoki, S.; Petrov, V. Temporal Characteristics of CH4 Vertical Profiles Observed in the West Siberian Lowland Over Surgut from 1993 to 2015 and Novosibirsk from 1997 to 2015. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 11261–11273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, D.K.; Dyachkova, A.V.; Fofonov, A.V.; Maksyutov, S.S.; Dyukarev, E.A.; Smirnov, S.V.; Glagolev, M.V. Measurements of methane and carbon dioxide fluxes from wetland ecosystems of the Southern Taiga of West Siberia. Proc. SPIE 2018, 10833, 1083389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovatskaya, E.A.; Dyukarev, E.A. Carbon budget of oligotrophic bog in southern taiga in Western Siberia. Plant Soil 2009, 315, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharanzhevskaya, Y.A.; Voistinova, E.S.; Sinyutkina, A.A. Spatial and temporal variations in mire surface water chemistry as a function of geology, atmospheric circulation and zonal features in the south-eastern part of Western Siberia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, J.; Serikova, S.; Vorobyev, S.N.; Rocher-Ros, G.; Denfeld, B.; Pokrovsky, O.S. Carbon emission from Western Siberian inland waters. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabrekov, A.F.; Runkle, B.R.K.; Glagolev, M.V.; Terentieva, I.E.; Stepanenko, V.M.; Kotsyurbenko, O.R.; Maksyutov, S.S.; Pokrovsky, O.S. Variability in methane emissions from West Siberia’s shallow boreal lakes on a regional scale and its environmental controls. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 3715–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terentieva, I.E.; Sabrekov, A.F.; Ilyasov, D.; Ebrahimi, A.; Glagolev, M.V.; Maksyutov, S. Highly dynamic methane emission from the west siberian boreal floodplains. Wetlands 2019, 39, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terent’eva, I.E.; Sabrekov, A.F.; Glagolev, M.V.; Lapshina, E.D.; Smolentsev, B.A.; Maksyutov, S.S. A new map of wetlands in the southern taiga of the West Siberia for assessing the emission of methane and carbon dioxide. Water Resour. 2017, 44, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, V.P.; Pokrovsky, O.S.; Vorobyev, S.N.; Krickov, I.V.; Manasypov, R.M.; Politova, N.V.; Kopysov, S.G.; Dara, O.M.; Auda, Y.; Shirokova, L.S.; et al. Impact of snow deposition on major and trace element concentrations and elementary fluxes in surface waters of the Western Siberian Lowland across a 1700 km latitudinal gradient. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 5725–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirpotin, S.N.; Antoshkina, O.A.; Berezin, A.E.; Elshehawi, S.; Feurdean, A.; Lapshina, E.D.; Pokrovsky, O.S.; Peregon, A.M.; Semenova, N.M.; Tanneberger, F.; et al. Great Vasyugan Mire: How the world’s largest peatland helps addressing the world’s largest problems. Ambio 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, K.E.; Novikov, S. Mires of Western Siberia, Their Structure and Hydrological Regime; Nauka: Moscow, Soviet Union, 1976; p. 447. [Google Scholar]
- Bleuten, W.; Zarov, E.; Schmitz, O. A high-resolution transient 3-dimensional hydrological model of an extensive undisturbed bog complex in West Siberia. Mires Peat 2020, 26, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Terentieva, I.E.; Glagolev, M.V.; Lapshina, E.D.; Sabrekov, A.F.; Maksyutov, S.S. Mapping of West Siberian taiga wetland complexes using Landsat imagery: Implications for methane emissions. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 4615–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Photos of the Peatland Landscape. Available online: https://www.flickr.com/photos/mukhrinostation/albums/72157632674684023 (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- Dyukarev, E.; Filippova, N.; Karpov, D.; Shnyrev, N.; Zarov, E.; Filippov, I.; Voropay, N.; Avilov, V.; Artamonov, A.; Lapshina, E. Hydrometeorological dataset of West Siberian boreal peatland: A 10-year records from the Mukhrino field station. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 2595–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhrino Field Station of Yugra State University—Russian Federation. Dynamic Ecological Information Management System—Site and Dataset Registry Web-Portal. Available online: https://deims.org/5eddca9f-d876-4e2b-b7c1-f7f13010a0ca (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Dyukarev, E.; Filippova, N.; Karpov, D.; Shnyrev, N.; Zarov, E.; Filippov, I.; Voropay, N.; Avilov, V.; Artamonov, A.; Lapshina, E. Hydrometeorological dataset of West Siberian boreal peatland: A 10-year records from the Mukhrino field station. (Version 2020/12) [Dataset]. Zenodo 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijp, J.J.; Metselaar, K.; Limpens, J.; Bartholomeus, H.M.; Nilsson, M.B.; Berendse, F.; Van der Zee, S.E. High-resolution peat volume change in a northern peatland: Spatial variability, main drivers, and impact on ecohydrology. Ecohydrology 2019, 12, e2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bleuten, W.; Filippov, I. Hydrology of mire ecosystems in central West Siberia: The Mukhrino field station. Dyn. Environ. Glob. Clim. Chang. 2008, 1, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dyukarev, E.A. Partitioning of net ecosystem exchange using chamber measurements data from bare soil and vegetated sites. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 239, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyukarev, E.; Godovnikov, E.; Karpov, D.; Kurakov, S.; Lapshina, E.; Filippov, I.; Filippova, N.; Zarov, E. Net ecosystem exchange, gross primary production and ecosystem respiration in ridge-hollow complex at Mukhrino bog. Geogr. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 12, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseychik, P.; Mammarella, I.; Karpov, D.; Dengel, S.; Terentieva, I.; Sabrekov, A.; Glagolev, M.; Lapshina, E. Net ecosystem exchange and energy fluxes measured with eddy covariance technique in a West Siberian bog. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9333–9345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mammarella, I.; Peltola, O.; Nordbo, A.; Järvi, L.; Rannik, Ü. Quantifying the uncertainty of eddy covariance fluxes due to the use of different software packages and combinations of processing steps in two contrasting ecosystems. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 4915–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabbatini, S.; Mammarella, I.; Arriga, N.; Fratini, G.; Graf, A.; Hörtnagl, L.; Ibrom, A.; Longdoz, B.; Mauder, M.; Merbold, L.; et al. Eddy covariance raw data processing for CO2 and energy flux calculation at ICOS ecosystem stations. Int. Agrophys. 2018, 32, 495–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosykh, N.P.; Vishnyakova, E.K.; Koronatova, N.G.; Sayb, E.A.; Filippova, N.V. Production and destruction processes in oligotrophic hollows in the middle taiga (OTC-experiment). In Carbon Balance of Western Siberia Peatlands in the Context of Climate Change, Proceedings of the International Conference, Khanty-Mansiysk, Russia, 19–29 June 2017; Lapshina, E.D., Mironycheva-Tokareva, N.P., Eds.; Publishing house of Tomsk State Univ.: Tomsk, Russia, 2017; pp. 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- Delarue, F.; Buttler, A.; Bragazza, L.; Grasset, L.; Jassey, V.E.; Gogo, S.; Laggoun-Défarge, F. Experimental warming differentially affects microbial structure and activity in two contrasted moisture sites in a Sphagnum-dominated peatland. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filippova, N.; Kosykh, N. Sphagnum Annual Growth in Mukhrino Field Station, West Siberia. Version 1.5. Yugra State University Biological Collection (YSU BC). Sampling Event Dataset. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/dataset/fae98fd0-c0a2-460f-a30c-53cb4c88006c (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Kosykh, N.P.; Koronatova, N.G.; Lapshina, E.D.; Filippova, N.V.; Vishnyakova, E.K.; Stepanova, V.A. Linear growth and production of Sphagnum mosses in the middle taiga zone of West Siberia. Environ. Dyn. Glob. Clim. Chang. 2017, 8, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keuskamp, J.A.; Dingemans, B.J.; Lehtinen, T.; Sarneel, J.M.; Hefting, M.M. Tea Bag Index: A novel approach to collect uniform decomposition data across ecosystems. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2013, 4, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djukic, I.; Kepfer-Rojas, S.; Schmidt, I.K.; Larsen, K.S.; Beier, C.; Berg, B.; Verheyen, K.; Caliman, A.; Paquette, A.; Gutiérrez-Girón, A. Early stage litter decomposition across biomes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628, 1369–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacDonald, E.; Brummell, M.E.; Bieniada, A.; Elliot, J.; Engering, A.; Gauthier, T.L.; Saraswati, S.; Touchette, S.; Tourmel-Coiechesne, L.; Strack, M. Using the Tea Bag Index to characterize decomposition rates in restored peatlands. Boreal Environ. Res. 2018, 23, 221–235. [Google Scholar]
- Filippova, N. Decomposition Dynamics of Native and Standard Substrates in Forests and Peatlands: Mukhrino Field Station, Western Siberia. Yugra State University Biological Collection (YSU BC). Occurrence Dataset. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/dataset/54641290-55dd-48d1-a1a7-25d6eee5d714 (accessed on 24 March 2021).
- Tolonen, K.; Turunen, J. Accumulation rates of carbon in mires in Finland and implications for climate change. Holocene 1996, 6, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QGIS Development Team. QGIS Geographic Information System. Open Source Geospatial Foundation. Available online: http://qgis.org (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- GRASS Development Team. GRASS 6.4 Users Manual. Open Source Geospatial Foundation, USA. Available online: http://grass.osgeo.org/grass64/manuals/ (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- McCauley, J.D.; Engel, B.A. Comparison of Scene Segmentations: SMAP, ECHO and Maximum Likelyhood. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Beilman, D.W.; Frolking, S.; MacDonald, G.M.; Roulet, N.T.; Camill, P.; Charman, D.J. Peatlands and their role in the global carbon cycle. Eos Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union 2011, 92, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafleur, P.M.; Moore, T.R.; Roulet, N.T.; Frolking, S. Ecosystem respiration in a cool temperate bog depends on peat temperature but not water table. Ecosystems 2005, 8, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebmann, C.; Aubinet, M.; Schmid, H.; Arriga, N.; Aurela, M.; Burba, G.; Clement, R.; De Ligne, A.; Fratini, G.; Gielen, B.; et al. ICOS eddy covariance flux-station site setup: A review. Int. Agrophys. 2018, 32, 471–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubinet, M.; Vesala, T.; Papale, D. (Eds.) Eddy Covariance: A Practical Guide to Measurement and Data Analysis; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Heidelberg, Germany; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta, M.; Pavelka, M.; Montagnani, L.; Kutsch, W.; Lindroth, A.; Juszczak, R.; Janouš, D. Soil surface CO2 efflux measurements in Norway spruce forests: Comparison between four different sites across Europe-from boreal to alpine forest. Geoderma 2013, 192, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelka, M.; Acosta, M.; Kiese, R.; Altimir, N.; Brümmer, C.; Crill, P.; Darenova, E.; Fuß, R.; Gielen, B.; Graf, A.; et al. Standardisation of chamber technique for CO2, N2O and CH4 fluxes measurements from terrestrial ecosystems. Int. Agrophys. 2018, 32, 569–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassey, V.E.J.; Signarbieux, C. Effects of climate warming on Sphagnum photosynthesis in peatlands depend on peat moisture and species-specific anatomical traits. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 3859–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juszczak, R.; Augustin, J. Exchange of the greenhouse gases methane and nitrous oxide at a temperate pristine fen mire in Central Europe. Wetlands 2013, 33, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikhailov, O.A.; Zagirova, S.V.; Miglovets, M.N.; Wille, C. Carbon dioxide fluxes in the ecosystem of meso-oligotrophic peatland during the transition period from autumn to winter. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2013, 6, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.C.; Ritson, J.P.; Verhoef, A.; Brazier, R.E.; Templeton, M.R.; Graham, N.J.D.; Freeman, C.; Clark, J.M. Sensitivity of peatland litter decomposition to changes in temperature and rainfall. Geoderma 2018, 331, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshydromet. Second Assessment Report of Roshydromet on Climate Change and Its Consequences on the Territory of the Russian Federation; Roshydromet: Russia, Moscow, 2014; pp. 18–235. [Google Scholar]
- The Ministry of Education and Science of Russia Will Launch a Program for the Development of Carbon Polygons. Available online: https://www.minobrnauki.gov.ru/press-center/news/?ELEMENT_ID=26691&sphrase_id=102783 (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Wu, Y.; Verseghy, D.L.; Melton, J.R. Integrating peatlands into the coupled Canadian Land Surface Scheme (CLASS) v3.6 and the Canadian Terrestrial Ecosystem Model (CTEM) v2.0. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 2639–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopatin, K.I.; Kashtanova, O.A.; Montile, A.I. An optimization model for the placement of oilfield facilities in the forest-bog zone of Western Siberia. Bull. Nizhnevartovsk State Univ. 2009, 1, 62–67. (In Russian). Available online: https://vestnik.nvsu.ru/2311-1402/article/view/49061 (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- Environmental Dynamics and Global Climate Change. About the Journal. Available online: https://edgccjournal.org/EDGCC/index (accessed on 25 July 2021).




| Microtope | Evapotranspiration, mm/day |
|---|---|
| Hollow | 7.8 ± 5.1 |
| Ridge | 7.6 ± 3.9 |
| Ryam * | 4.3 ± 3.9 |
| Open water | 7.0 ± 5.1 |
| Microtope/Year | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ridge | +13.4 | −22.0 | −32.1 |
| Hollow | −110.0 | −107.8 | −57.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dyukarev, E.; Zarov, E.; Alekseychik, P.; Nijp, J.; Filippova, N.; Mammarella, I.; Filippov, I.; Bleuten, W.; Khoroshavin, V.; Ganasevich, G.; et al. The Multiscale Monitoring of Peatland Ecosystem Carbon Cycling in the Middle Taiga Zone of Western Siberia: The Mukhrino Bog Case Study. Land 2021, 10, 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10080824
Dyukarev E, Zarov E, Alekseychik P, Nijp J, Filippova N, Mammarella I, Filippov I, Bleuten W, Khoroshavin V, Ganasevich G, et al. The Multiscale Monitoring of Peatland Ecosystem Carbon Cycling in the Middle Taiga Zone of Western Siberia: The Mukhrino Bog Case Study. Land. 2021; 10(8):824. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10080824
Chicago/Turabian StyleDyukarev, Egor, Evgeny Zarov, Pavel Alekseychik, Jelmer Nijp, Nina Filippova, Ivan Mammarella, Ilya Filippov, Wladimir Bleuten, Vitaly Khoroshavin, Galina Ganasevich, and et al. 2021. "The Multiscale Monitoring of Peatland Ecosystem Carbon Cycling in the Middle Taiga Zone of Western Siberia: The Mukhrino Bog Case Study" Land 10, no. 8: 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10080824
APA StyleDyukarev, E., Zarov, E., Alekseychik, P., Nijp, J., Filippova, N., Mammarella, I., Filippov, I., Bleuten, W., Khoroshavin, V., Ganasevich, G., Meshcheryakova, A., Vesala, T., & Lapshina, E. (2021). The Multiscale Monitoring of Peatland Ecosystem Carbon Cycling in the Middle Taiga Zone of Western Siberia: The Mukhrino Bog Case Study. Land, 10(8), 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10080824








