Linking Ecosystem Service and MSPA to Construct Landscape Ecological Network of the Huaiyang Section of the Grand Canal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
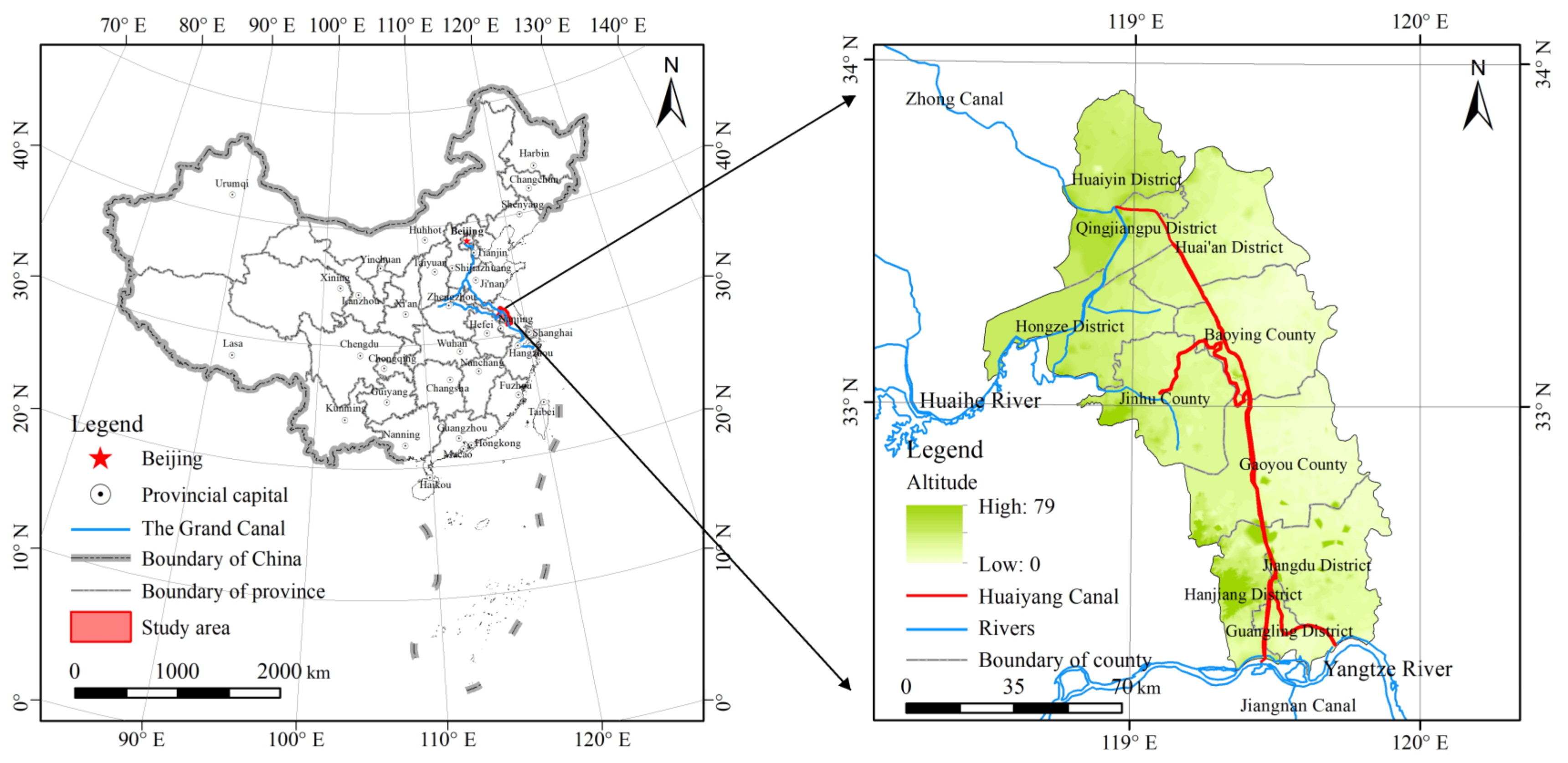
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.3. Research Framework
2.4. Research Methods
2.4.1. Ecosystem Service Evaluation
Water Conservation Service
- when the underlying surface is soil:
- when the underlying surface is water:where Vs(x) is the annual amount of water conservation per unit area of grid x when the underlying surface is soil (m3/m2), Pmean(x) is the monthly precipitation of grid x (mm), KW is the ratio of runoff rainfall to total rainfall, RW is the runoff reduction coefficient of surface vegetation, VWC(x) is the annual amount of water conservation per unit area of grid x when the underlying surface is water (m3/m2), and ETa(x) is the actual monthly evapotranspiration (mm).
Soil Conservation Service
Carbon Sequestration Service
Biodiversity Conservation Service
Integrated Ecosystem Services
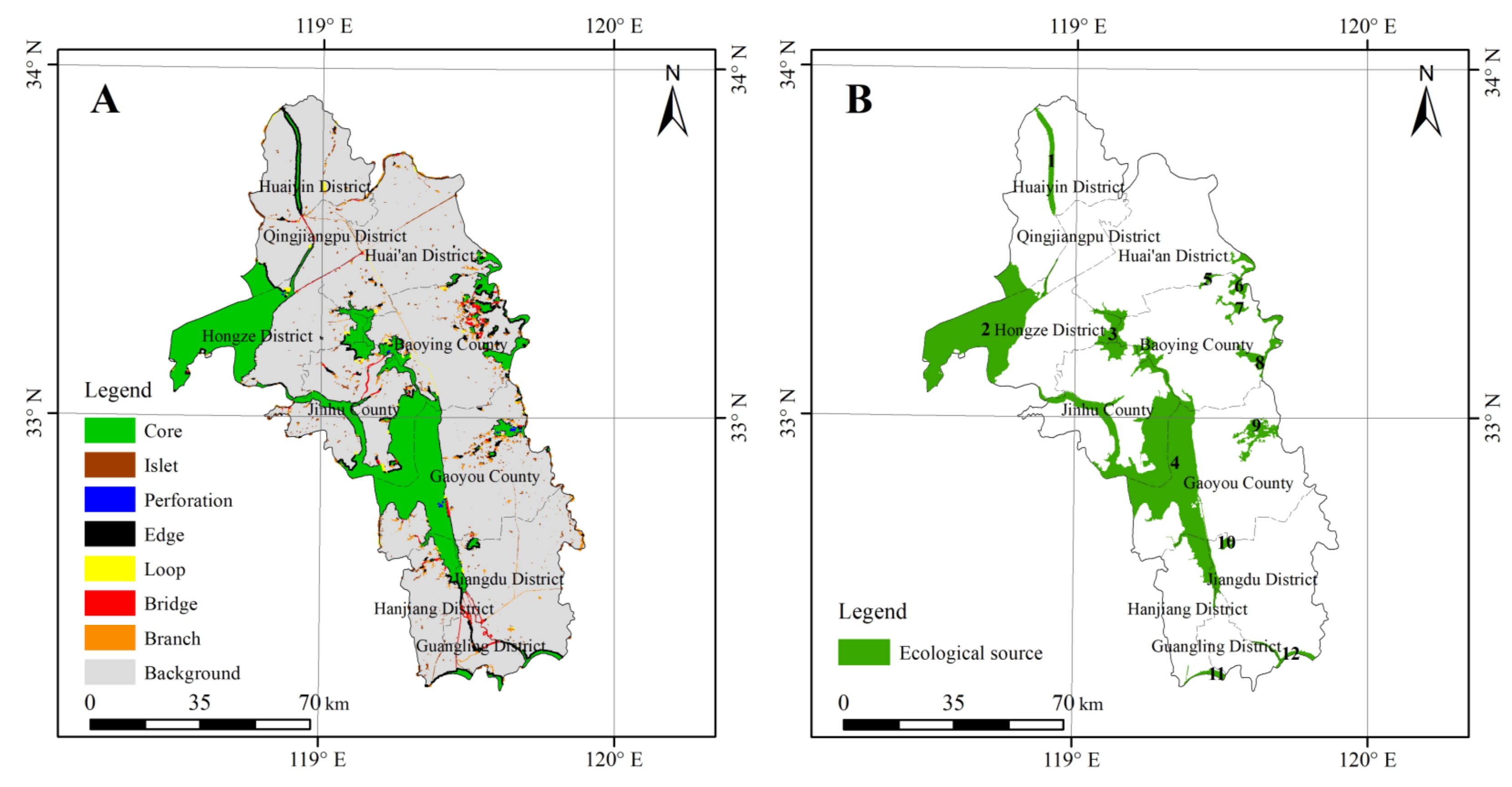
2.4.2. Identification of the Ecological Source
2.4.3. Construction of Ecological Resistance Surface
2.4.4. Extraction of Ecological Corridor
2.4.5. Identification of Ecological Nodes and Breakpoints
3. Results
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Evolution of Ecosystem Services
3.2. Ecological Source Analysis
3.3. Analysis of Ecological Corridor Path and Width
3.4. Analysis of Ecological Node and Breakpoint
4. Discussion
4.1. Ecological Network Optimization
4.2. Corroboration of the Scientific Conjecture
4.3. Policy Implication
4.4. Limitations and Outlook
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Wu, L.Y.; Han, Q.; Wang, X.; Zou, T.Q.; Fan, C. Estimation of remote sensing based ecological index along the Grand Canal based on PCA-AHP-TOPSIS methodology. Ecol. Indic. Toxicol. 2021, 122, 107214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Gan, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, C. Pollution level and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in riverside sediments of the Grand Canal (Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei section). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 105, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.L.; Han, J.Y.; Xu, L.G.; Zhang, Q. Spatial and seasonal variations of the contamination within water body of the Grand Canal, China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Zhang, H.F.; Sun, Z.F. Spatiotemporal variations of land urbanization and socioeconomic benefits in a typical sample zone: A case study of the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 117, 102187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.D.; Peng, J. Introduction of Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal and analysis of its heritage values. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2019, 26, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.K.; Lenzer, J.H. Mismatched canal conservation and the authorized heritage discourse in urban China: A case of the Hangzhou Section of the Grand Canal. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2020, 26, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Rollo, J.; Jones, D.S.; Esteban, Y.; Tong, H.; Mu, Q. Towards Sustainable Heritage Tourism: A Space Syntax-Based Analysis Method to Improve Tourists’ Spatial Cognition in Chinese Historic Districts. Buildings 2020, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, W.; Liu, Y.X.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, F.X. A new index for assessing heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal (Zaozhuang Segment): A case study. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, H.T.; Jiao, X.C.; Gai, N.; Chen, S.; Lu, G.H.; Yin, X.C.; Yamazaki, E.; Yamashita, N.; Tan, K.Y.; Yang, Y.L.; et al. Perfluoroalkyl substances in waters along the Grand Canal, China. Chemosphere 2017, 179, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.L.; Liu, X.J.; Liu, G.J.; Sun, Z.Q.; Xu, H.L. An approach to analyzing spatial patterns of protozoan communities for assessing water quality in the Hangzhou section of Jing-Hang Grand Canal in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Y.; Wei, M.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, S. Ecological network analysis and construction: A case study of the urban agglomeration of the Min River Delta, Chin. Resour. Sci. 2021, 43, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pili, S.; Serra, P.; Salvati, L. Landscape and the city: Agro-forest systems, land fragmentation and the ecological network in Rome, Italy. Urban For. Urban Green 2019, 41, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, N.S.; Magalhães, M.R. Methodology for mapping the national ecological network to mainland Portugal: A planning tool towards a green infrastructure. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 802–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge, C.B.; Fortin, M. Habitat network topology influences the importance of ecological traps in metapopulations. Ecosphere 2020, 11, e03146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.M.; Ma, Y.F.; Wang, J.L.; You, X.Y. Landscape pattern analysis and ecological network planning of Tianjin City. Urban For. Urban Green 2019, 46, 126479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Jin, X.B.; Han, B.; Sun, R.; Liang, X.Y.; Li, H.B.; Zhou, Y.K. Identification and optimization of ecological network in the plain area of the lower Yangtze River: A case study of Jintan District, Changzhou. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 3449–3461. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, P.T.; Fu, M.C. Construction of county-level ecological security pattern based on ecological protection red line and network in China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Hou, X.Y.; Yin, Y.J.; Cheng, F.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Dong, S.K. Research progress on landscape ecological networks. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 3947–3956. [Google Scholar]
- Gurrutxaga, M.; Lozano, P.J.; Barrio, G.D. GIS-based approach for incorporating the connectivity of ecological networks into regional planning. J. Nat. Conserv. 2010, 18, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, J. Planning for an extensive open space system: Linking landscape structure and function. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1991, 6, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linehan, J.; Gross, M.; Finn, J. Greenway planning: Developing a landscape ecological network approach. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1995, 33, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackovčin, P. A multi-level ecological network in the Czech Republic: Implementating the territorial system of ecological stability. GeoJournal 2000, 51, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongman, R.H.G.; Bouwma, I.M.; Griffioen, A.; Jones-Walters, L.; Doorn, A.M.V. The pan European ecological network: PEEN. Landsc. Ecol. 2011, 26, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobster, P.H.; Westphal, L.M. The human dimensions of urban greenways: Planning for recreation and related experiences. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 68, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascompte, J. Ecology structure and dynamics of ecological networks. Science 2010, 329, 765–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Säterberg, T.; Sellman, S.; Ebenman, B. High frequency of functional extinctions in ecological networks. Nature 2013, 499, 468–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, E.; Besson, M.; Brice, M.; Burkle, L.A.; Riva, G.V.D.; Fortin, M.; Gravel, D.; Guimarães, P.R., Jr.; Hembry, D.H.; Newman, E.A.; et al. Analysing ecological networks of species interactions. Biol. Rev. 2018, 94, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guimarães, P.R., Jr. The structure of ecological networks across levels of organization. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2020, 51, 433–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.X.; Hu, Z.Q.; Li, H.X.; Liu, J.L.; Zhang, X.; Lai, X.J. Construction of municipal ecological space network based on MCR model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongman, R.H.G.; Külvik, M.; Kristiansen, I. European ecological networks and greenways. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 68, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izakovièová, Z.; Swiader, M. Building ecological networks in Slovakia and Poland. Ekologia 2017, 36, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.Q.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.X.; Wu, J.S. Coupling ecosystem services supply and human ecological demand to identify landscape ecological security pattern: A case study in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Urban Ecosyst. 2017, 20, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Hu, Y.N.; Du, Y.Y.; Meersmans, J.; Qiu, S.J. Linking ecosystem services and circuit theory to identify ecological security patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, J.Q.; Peng, J.; Xu, Z.H.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, B. Integrating regional and interregional approaches to identify ecological security patterns. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2151–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, M.Q.; Hu, M.M.; Fan, C.; Wang, T.; Xia, B.C. Promoting landscape connectivity of highly urbanized area: An ecological network approach. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Xu, D.W.; Hu, S.S.; Shi, M.X. Ecological Network Optimization in Urban Central District Based on Complex Network Theory: A Case Study with the Urban Central District of Harbin. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orantes, M.J.C.; Kim, J.; Kim, J. Socio-Cultural Asset Integration for a Green Infrastructure Network Plan in Yesan County, Korea. Sustainability 2017, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, X.; Zhao, T.Y. Research on the Spatial Structure of County Greenway Network Based on Gravitation-Resistance Measurement-A Case Study of Ning’an in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Q.; Yue, D.P.; Wang, Y.H.; Kai, S.; Fang, M.Z.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Q.B.; Huang, Y. Optimization of ecological node layout and stability analysis of ecological network in desert oasis: A typical case study of ecological fragile zone located at Deng Kou County (Inner Mongolia). Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.J.; Shi, X.Y.; He, J.; Yuan, Y.; Qu, L.L. Identification and optimization strategy of county ecological security pattern: A case study in the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Song, W. Identifying ecological corridors and networks in mountainous areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, P.F.; Chen, K.X.; Qu, L.M.; Han, J.B.; Yang, Z.X. Determination of landscape ecological network of wetlands in the Yellow River Delta. Wetlands 2020, 40, 2729–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharrazi, A.; Akiyama, T.; Yu, Y.D.; Li, J. Evaluating the evolution of the Heihe River basin using the ecological network analysis: Efficiency, resilience, and implications for water resource management policy. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 572, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.N.; Liu, S.L.; Sun, Y.X.; An, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, M.Q. Ecological network construction of the heterogeneous agro-pastoral areas in the upper Yellow River basin. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 302, 107069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Lin, Z.L.; Ma, S.M.; Qi, J.L.; Yan, T.T. Assessing an ecological security network for a rapid urbanization region in Eastern China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 21, 2642–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Liu, Y.B.; Luo, X.Y. Integrating the MCR and DOI models to construct an ecological security network for the urban agglomeration around Poyang Lake, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 754, 141868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.X.; Wang, J.M.; Zhang, M.; Li, S.J. Construction of landscape ecological network based on landscape ecological risk assessment in a large-scale opencast coal mine area. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 125523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalkanen, J.; Toivonen, T.; Moilanen, A. Identification of ecological networks for land-use planning with spatial conservation prioritization. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 32, 353–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakiel, M.; Bernatek, A. Assessment of an ecological network at local scale in the context of landscape changes: A case study from NE Poland. In Landscape Analysis and Planning; Springer Geography, Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Q.C.; Zhang, Q.P.; Ji, Y.W.; Song, P.H.; Wang, Q.Q. An optimized evaluation method of an urban ecological network: The case of the Minhang District of Shanghai. Urban For. Urban Green 2021, 62, 127158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.N.; Liu, S.L.; An, Y.; Sun, Y.X. Biodiversity conservation of mountains-rivers-forests-farmlands-lakes-grasslands using an ecological network: A case study on the Zuoyoujiang River basin in Guangxi Province, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 8930–8938. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.Y.; Chen, C.D.; Tong, X.X.; Wu, S.J.; Zhou, W.Z. Developing and optimizing ecological networks for the towns along the Three Gorges Reservoir: A case of Kaizhou New Town, Chongqing. Chin. J. Ecol. 2017, 36, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Peng, J.; Dong, J.Q.; Zhang, Z.M.; Xu, Z.H.; Meersmans, J. Linking ecological background and demand to identify ecological security patterns across the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area in China. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2135–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.K.; Guo, X.L.; Wang, Y.C. Identifying and setting the natural spaces priority based on the multi-ecosystem services capacity index. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.C.; Wu, W.J.; Guo, J.; Ou, M.H.; Pueppke, S.G.; Ou, W.X.; Tao, Y. An evaluation framework for designing ecological security patterns and prioritizing ecological corridors: Application in Jiangsu Province, China. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 2517–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Shi, L.; Lu, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, S.F. The optimization of urban ecological network planning based on the minimum cumulative resistance model and granularity reverse method: A case study of Haikou, China. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 43592–43605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Zhang, P.T.; Zhang, G.J.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wei, M.H.; Jian, Q. Construction of ecological corridors in Changli County based on ecological sensitivity and ecosystem service values. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 2675–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Wang, C.G. The empirical formula of evaporation estimated by monthly mean temperature and precipitation. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 1980, S4, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Zhizhin, M.; Ghosh, T.; Hsu, F.C.; Taneja, J. Annual time series of global VIIRS nighttime lights derived from monthly averages: 2012 to 2019. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.L.; Gong, J.; Xu, C.X.; Cao, E.J.; Li, H.Y.; Gao, B.L.; Li, Y. Spatiotemporal variations and influencing factors of soil conservation service in Ziwuling Area. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 35, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, K.; Zhao, W.W. Soil conservation efficiency assessment based on land use scenarios in the Nile River Basin. Ecol. Indic. Toxicol. 2020, 119, 106864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoldus, H.M.J. An Approximation of the Rainfall Factor in the Universal Soil Loss Equation; John Wiley and Sons Ltd. Press: Chichester, UK, 1980; pp. 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.; Nearing, M.; Nicks, A.; Skidmore, E.; Valentin, C.; King, K.; Savabi, R. Using soil erosion models for global change studies. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 381–385. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H. Use and misuse of universal soil loss equation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1976, 31, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, K.L. Soil Erosion Prediction Model; China Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F. Research on Ecological Security Pattern in Qinglong County based on Ecological Protection Red Line and Ecological Network. Master’s Thesis, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, L.S.; Deng, G.H.; Gu, J.C. Dynamic changes of soil erosion in the Chaohu Watershed from 1992 to 2013. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 1708–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.B.; Zhang, J.J.; Cui, Y.P.; Zheng, H.; Zhu, L.Q. Assessment of territorial ecosystem carbon storage based on land use change scenario: A case study in Qihe River Basin. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.S.; Yang, Y.S.; Xie, J.S.; Du, Z.X.; Zhang, J. Total below ground carbon allocation in China’s forests. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2007, 27, 5148–5157. [Google Scholar]
- Giardina, C.P.; Ryan, M.G. Evidence that decomposition rates of organic carbon in mineral soil do not vary with temperature. Nature 2000, 404, 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, S.A.; Starr, M.; Clark, B.J.F. Tree biomass and soil organic carbon densities across the Sudanese woodland savannah: A regional carbon sequestration study. J. Arid. Environ. 2013, 89, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Fu, M.C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, P.T. Land-use change in Changli County, China: Predicting its spatio-temporal evolution in habitat quality. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Fu, M.C.; Wang, L.; Song, W.J.; Yu, J.F.; Wu, Y.B. Dynamic evolution and scenario simulation of habitat quality under the impact of land-use change in the Huaihe River Economic Belt, China. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrado, M.; Sabater, S.; Chaplin-Kramer, B.; Mandle, L.; Ziv, G.; Acuña, V. Model development for the assessment of terrestrial and aquatic habitat quality in conservation planning. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 540, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.Y.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhang, D.Z. Monitoring spatio-temporal dynamics of habitat quality in Nansihu Lake basin, eastern China, from 1980 to 2015. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.T.; Chen, S.S.; Xu, Y.; Li, G.Y.; Su, W.Z. Impacts of Land-Use Change on Habitat Quality during 1985–2015 in the Taihu Lake Basin. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogt, P.; Ferrari, J.R.; Lookingbill, T.R.; Gardner, R.H.; Riitters, K.H.; Ostapowicz, K. Mapping functional connectivity. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Vogt, P.; Velázquez, J.; Hernando, A.; Tejera, R. Key structural forest connectors can be identified by combining landscape spatial pattern and network analyses. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2011, 262, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Hortal, L.; Saura, S. Comparison and development of new graph-based landscape connectivity indices: Towards the priorization of habitat patches and corridors for conservation. Landsc. Ecol. 2006, 21, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.B.; Du, F.J.; Zuo, L.Y.; Jiang, Y. Integrating ecosystem services and rocky desertification into identification of karst ecological security pattern. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 36, 2113–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, Y. Identification and optimization of ecological security pattern in Xiong’an New Area. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaapen, J.P.; Scheffer, M.; Harms, B. Estimating habitat isolation in landscape planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1992, 23, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, X.L.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhang, Y. Ecological corridor construction based on important ecological nodes in Duliujian River Basin. Res. Environ. Sci. 2018, 31, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Yu, K.J.; Li, D.H. The width of ecological corridor in landscape planning. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2005, 25, 2406–2412. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.B.; Ren, J.H.; Zhang, P.; Jin, Y.; Liu, R.R.; Wang, X.C.; Lee, C.T.; Klemes, J.J. Entwining ecosystem services, Land Use Change and human well-being by nitrogen flows. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 308, 127442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunyawat, S.; Shrestha, R.P. Assessing Land Use Change and Its Impact on Ecosystem Services in Northern Thailand. Sustainability 2016, 8, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, I.; Kwon, H. Assessing the impacts of urban land use changes on regional ecosystem services according to urban green space policies via the patch-based cellular automata model. Environ. Manag. 2021, 61, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H.; Kleemann, J.; Furst, C. Impact assessment of land use changes using local knowledge for the provision of ecosystem services in northern Ghana, West Africa. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 103, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Ochuodho, T.O.; Yang, J. Impact of land use and climate change on water-related ecosystem services in Kentucky, USA. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.N.; Kang, S.Z.; Zhao, Y.H.; Zhou, Y.J.; Yan, J.; Lu, Y.R. Construction of ecological network in Qinling Mountains of Shaanxi, China based on MSPA and MCR model. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Land-Use Type | Ci-above | Ci-below | Ci-soil |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farmland | 45.56 | 8.61 | 130.75 |
| Woodland | 631.75 | 137.59 | 217.59 |
| Grassland | 4.42 | 27.88 | 120.49 |
| Water area | 0.45 | 0 | 79.63 |
| Construction land | 0.11 | 0 | 71.67 |
| Unused land | 0.11 | 0 | 73.23 |
| Threat Factor | Maximum Distance (km) | Weight | Spatial Decay Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paddy field | 6 | 0.6 | Exponential |
| Dry land | 6 | 0.6 | Exponential |
| Urban land | 10 | 0.9 | Exponential |
| Rural residential land | 8 | 0.7 | Exponential |
| Industrial and traffic land | 12 | 1 | Linear |
| Land-Use Type | Habitat Suitability | Paddy Field | Dry Land | Urban Land | Rural Residential Land | Industrial and Traffic Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paddy field | 0.3 | 0 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Dry land | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Forestland | 1 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| Shrubland | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| Sparse woodland | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.7 |
| Other woodland | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| High coverage grassland | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| River canal | 1 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| Lake | 1 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| Reservoir and pond | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Bottomland | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| Urban land | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Rural residential land | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Industrial and traffic land | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bare land | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Landscape Type | Area (km2) | Proportion of Forestland and Water Area (%) | Proportion of Total Area (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core | 1905.91 | 74.29 | 16.55 |
| Islet | 103.39 | 4.03 | 0.89 |
| Perforation | 4.36 | 0.17 | 0.04 |
| Edge | 317.35 | 12.37 | 2.76 |
| Loop | 38.23 | 1.49 | 0.33 |
| Bridge | 87.48 | 3.41 | 0.76 |
| Branch | 108.78 | 4.24 | 0.94 |
| Total | 2565.5 | 100 | 22.27 |
| Land-Use Type | Corridor Width (m) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 200 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1000 | 1200 | 1500 | |
| Farmland | 69.67 | 69.48 | 68.19 | 70.54 | 70.45 | 71.03 | 71.79 | 72.31 |
| Woodland | 3.05 | 3.62 | 3.15 | 1.83 | 1.61 | 1.31 | 1.26 | 1.07 |
| Grassland | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.28 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| Water area | 5.71 | 7.02 | 7.59 | 6.62 | 6.68 | 6.02 | 5.76 | 5.69 |
| Construction land | 21.31 | 19.65 | 20.79 | 20.86 | 21.13 | 21.51 | 21.05 | 20.78 |
| Unused land | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, F.; Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, M.; Zhang, P. Linking Ecosystem Service and MSPA to Construct Landscape Ecological Network of the Huaiyang Section of the Grand Canal. Land 2021, 10, 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10090919
Tang F, Zhou X, Wang L, Zhang Y, Fu M, Zhang P. Linking Ecosystem Service and MSPA to Construct Landscape Ecological Network of the Huaiyang Section of the Grand Canal. Land. 2021; 10(9):919. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10090919
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Feng, Xu Zhou, Li Wang, Yangjian Zhang, Meichen Fu, and Pengtao Zhang. 2021. "Linking Ecosystem Service and MSPA to Construct Landscape Ecological Network of the Huaiyang Section of the Grand Canal" Land 10, no. 9: 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10090919
APA StyleTang, F., Zhou, X., Wang, L., Zhang, Y., Fu, M., & Zhang, P. (2021). Linking Ecosystem Service and MSPA to Construct Landscape Ecological Network of the Huaiyang Section of the Grand Canal. Land, 10(9), 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10090919






