Determinants of Soil Bacterial Diversity in a Black Soil Region in a Large-Scale Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
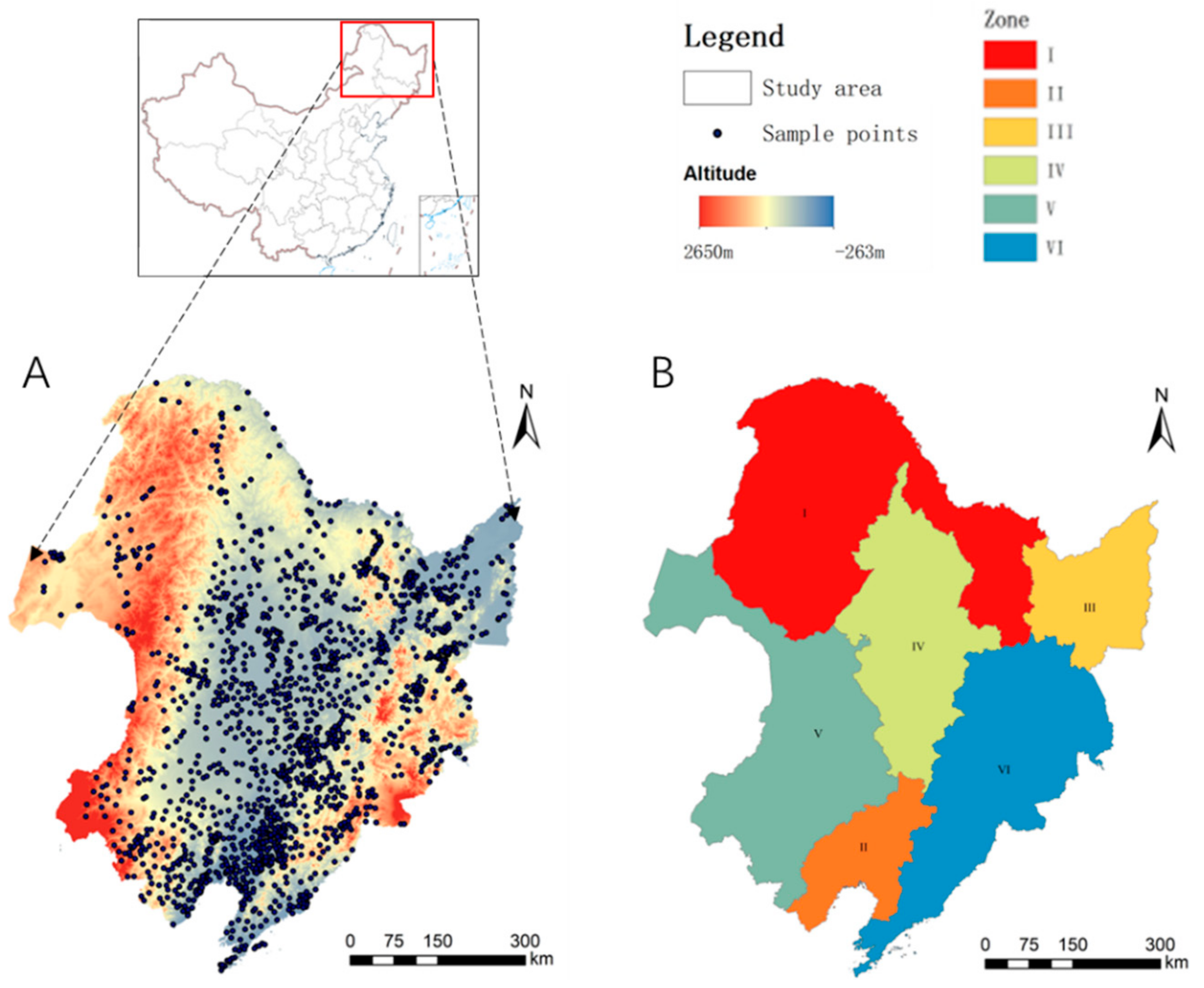
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. Soil Bacterial Abundance Data
2.2.2. Environmental Variables Data
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Research Method
2.4.1. Random Forest
2.4.2. Variation Partition
2.4.3. DbMEM
3. Results
3.1. Soil Bacterial Abundance Prediction Mapping
3.2. Soil Bacterial Abundance and Environmental Variables
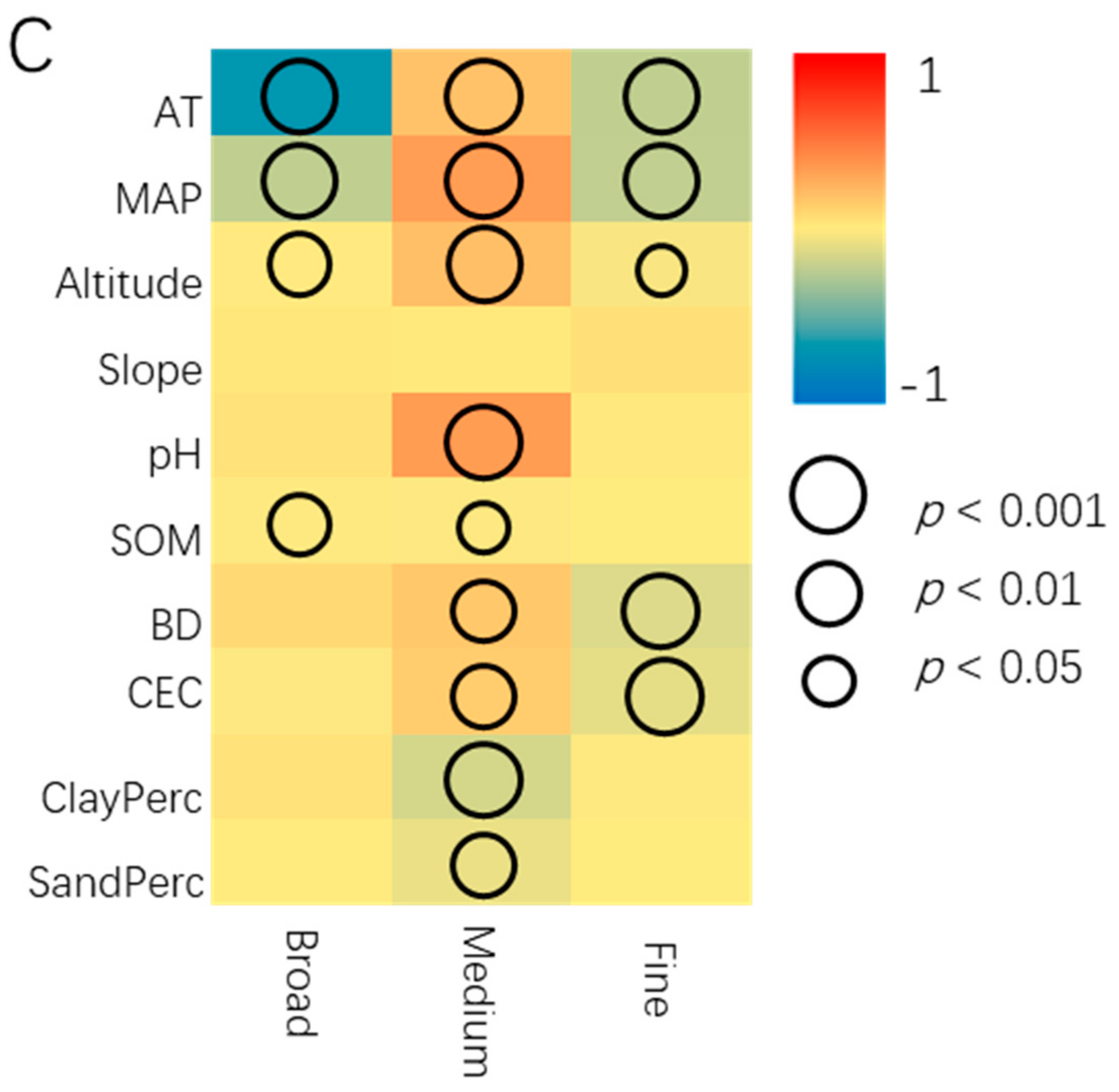
3.3. Soil Bacterial Abundance and Spatial Effect
3.4. Soil Bacterial Abundance under Different Zoning
4. Discussion
4.1. Particularity of Influencing Factors of Soil Bacterial Abundance in Black Soil Region
4.2. The Effect of Broad Scale on Soil Bacteria Is More Significant Than That of Medium and Fine Scale
4.3. Influencing Factors of Soil Bacterial Abundance in Different Partitions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Wang, D.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y. Soil quality assessment of croplands in the black soil zone of Jilin Province, China: Establishing a minimum data set model. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ren, X.; Cheng, C.; Wang, S. Quantitative assessment of soil productivity and predicted impacts of water erosion in the black soil region of northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, C.; Cai, Q.G.; Zhu, A.I.; Fan, H.M. Soil erosion along a long slope in the gentle hilly areas of black soil region in Northeast China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2007, 17, 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Liu, G. Erosion effect on the productivity of black soil in Northeast China. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2009, 52, 1005–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Reich, P.B.; Khachane, A.N.; Campbell, C.D.; Thomas, N.; Freitag, T.E.; Abu Al-Soud, W.; Sørensen, S.; Bardgett, R.D.; Singh, B.K. It is elemental: Soil nutrient stoichiometry drives bacterial diversity. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 19, 1176–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Sui, Y.; Yu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Chu, H.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. Soil carbon content drives the biogeographical distribution of fungal communities in the black soil zone of northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 83, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Anderson, I.C.; Singh, B.K. Response of Soil Properties and Microbial Communities to Agriculture: Implications for Primary Productivity and Soil Health Indicators. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schadt, C.W. Soil microbial community responses to multiple experimental climate change drivers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 999–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.P.; Marín-Spiotta, E.; Balser, T. Successional and seasonal variations in soil and litter microbial community structure and function during tropical postagricultural forest regeneration: A multiyear study. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 3532–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.L.; Pellizari, V.H.; Mueller, R.; Baek, K.; Jesus ED, C.; Paula, F.S.; Mirza, B.; Hamaoui, G.S., Jr.; Tsai, S.M.; Feigl, B.; et al. Conversion of the Amazon rainforest to agriculture results in biotic homogenization of soil bacterial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Fry, E.L.; Eldridge, D.J.; de Vries, F.T.; Manning, P.; Hamonts, K.; Kattge, J.; Boenisch, G.; Singh, B.K.; Bardgett, R.D. Plant attributes explain the distribution of soil microbial communities in two contrasting regions of the globe. New Phytol. 2018, 219, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, Y.; Joa, J.H.; Kang, S.S.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, M.; Song, J.; Weon, H.Y. Different types of agricultural land use drive distinct soil bacterial communities. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berner, D.; Marhan, S.; Keil, D.; Poll, C.; Schützenmeister, A.; Piepho, H.P.; Kandeler, E. Land-use intensity modifies spatial distribution and function of soil microorganisms in grasslands. Pedobiologia 2011, 54, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N. Embracing the unknown: Disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramae, E.E.; Yergeau, E.; Wong, L.C.; Pijl, A.S.; Van Veen, J.A.; Kowalchuk, G.A. Soil characteristics more strongly influence soil bacterial communities than land-use type. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 79, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rousk, J.; Bååth, E.; Brookes, P.C.; Lauber, C.L.; Lozupone, C.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Chavez, H.M.; Fierer, N.; Van Bodegom, P.M. Global drivers and patterns of microbial abundance in soil. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 1162–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Gao, Q.; Liu, S.; Ganjurjav, H.; Wang, X.; Su, X.; Wu, X. Soil bacterial and fungal diversity differently correlated with soil biochemistry in alpine grassland ecosystems in response to environmental changes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Eldridge, D.J. Cross-Biome Drivers of Soil Bacterial Alpha Diversity on a Worldwide Scale. Ecosystems 2019, 22, 1220–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffiths, R.I.; Thomson, B.C.; James, P.; Bell, T.; Bailey, M.; Whiteley, A.S. The bacterial biogeography of British soils. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1642–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constancias, F.; Terrat, S.; Saby, N.P.; Horrigue, W.; Villerd, J.; Guillemin, J.P.; Biju-Duval, L.; Nowak, V.; Dequiedt, S.; Ranjard, L.; et al. Mapping and determinism of soil microbial community distribution across an agricultural landscape. MicrobiologyOpen 2015, 4, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yu, Z.; Yao, Q.; Sui, Y.; Shi, Y.; Chu, H.; Tang, C.; Franks, A.E.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; et al. Biogeographic Distribution Patterns of the Archaeal Communities Across the Black Soil Zone of Northeast China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, P.P.; Carrillo, Y.; Pino, V.; Minasny, B.; McBratney, A. Soil Properties Drive Microbial Community Structure in a Large Scale Transect in South Eastern Australia. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, S.L.; Gibbons, S.M.; Owens, S.M.; Hampton-Marcell, J.; Johnston, E.R.; Jastrow, J.D.; Gilbert, J.A.; Meyer, F.; Antonopoulos, D.A. Spatial scale drives patterns in soil bacterial diversity. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 2039–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dray, S.; Legendre, P.; Peres-Neto, P.R. Spatial modelling: A comprehensive framework for principal coordinate analysis of neighbour matrices (PCNM). Ecol. Model. 2006, 196, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Natural Resources; National Bureau of Statistics. Main data bulletin of the third national land survey. Nat. Resour. Commun. 2021, 9, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, A. Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strobl, C.; Malley, J.; Tutz, G. An introduction to recursive partitioning: Rationale, application, and characteristics of classification and regression trees, bagging, and random forests. Psychol. Methods 2009, 14, 323–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, J.; de Baets, B.; Verhoest, N.E.; Samson, R.; Degroeve, S.; de Becker, P.; Huybrechts, W. Random forests as a tool for ecohydrological distribution modelling. Ecol. Model. 2007, 207, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Arshad, M.; Wang, J.; Triantafilis, J. Soil exchangeable cations estimation using Vis-NIR spectroscopy in different depths: Effects of multiple calibration models and spiking. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 182, 105990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R.L.; Wood, S.D.; Sheley, R.L. Mapping invasive plants using hyperspectral imagery and Breiman Cutler classifications (randomForest). Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P. Studying beta diversity: Ecological variation partitioning by multiple regression and canonical analysis. J. Plant Ecol. 2007, 31, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauman, D.; Drouet, T.; Fortin, M.J.; Dray, S. Optimizing the choice of a spatial weighting matrix in eigenvector-based methods. Ecology 2018, 99, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sui, Y.; Yu, Z.; Shi, Y.U.; Chu, H.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. High throughput sequencing analysis of biogeographical distribution of bacterial communities in the black soils of northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Zhou, X.; Guo, D.; Zhao, J.H.; Yan, L.; Feng, G.Z.; Gao, Q.; Yu, H.; Zhao, L. Soil pH is the primary factor driving the distribution and function of microorganisms in farmland soils in northeastern China. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terrat, S.; Karimi, B.; Horrigue, W.; Dequiedt, S.; Saby, N.; Lelièvre, M.; Nowak, V.; Tripied, J.; Régnier, T.; Jlivet, C.; et al. Mapping and predictive variations of soil microbial richness, bacterial and archaeal phyla across France. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Microbial Diversity 2017, Bari, Italy, 24–26 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fierer, N.; Jackson, R.B. The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dequiedt, S.; Saby NP, A.; Lelievre, M.; Jolivet, C.; Thioulouse, J.; Toutain, B.; Arrouays, D.; Bispo, A.; Lemanceau, P.; Ranjard, L. Biogeographical patterns of soil molecular microbial biomass as influenced by soil characteristics and management. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2011, 20, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z. Study on Regional System of Ecological Geography in China; The Commercial Press: Shanghai, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.F.; Shu, W.S.; Hao, Y.Q. Seasonal Climate Variations Promote Bacterial α-Diversity in Soil. Microb. Ecol. 2021, 83, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Zhu, Y.G.; Chu, H. Space Is More Important than Season when Shaping Soil Microbial Communities at a Large Spatial Scale. mSystems 2020, 5, e00783-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, C.A.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Horner-Devine, M.C.; Martiny, J.B. 2012. Beyond biogeographic patterns: Processes shaping the microbial landscape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borcard, D.; Legendre, P.; Drapeau, P. Partialling out the Spatial Component of Ecological Variation. Ecology 1992, 73, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranjard, L.; Dequiedt, S.; Chemidlin Prévost-Bouré, N.; Thioulouse, J.; Saby, N.P.A.; Lelievre, M.; Maron, P.A.; Morin, F.E.R.; Bispo, A.; Jolivet, C.; et al. Turnover of soil bacterial diversity driven by wide-scale environmental heterogeneity. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Provost, G.; Thiele, J.; Westphal, C.; Penone, C.; Allan, E.; Neyret, M.; van der Plas, F.; Ayasse, M.; Bardgett, R.D.; Birkhofer, K.; et al. Contrasting responses of above- and belowground diversity to multiple components of land-use intensity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiny, J.B.H.; Bohannan, B.J.; Brown, J.H.; Colwell, R.K.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Green, J.L.; Claire Horner-Devine, M.; Kane, M.; Krumins, J.A.; Kuske, C.R.; et al. Microbial biogeography: Putting microorganisms on the map. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looby, C.I.; Martin, P.H. Diversity and function of soil microbes on montane gradients: The state of knowledge in a changing world. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 9, fiaa122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunan, N.; Wu, K.; Young, I.M.; Crawford, J.W.; Ritz, K. Spatial distribution of bacterial communities and their relationships with the micro-architecture of soil. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2003, 44, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, S.; Song, C.; Shen, S.; Gao, P.; Cheng, C.; Cheng, F.; Wan, C.; Zhu, D. Spatial pattern of arable land-use intensity in China. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 104845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Ren, S.; Song, C.; Cheng, C.; Shen, S.; Yang, J.; Zhu, D. Spatial patterns of county-level arable land productive-capacity and its coordination with land-use intensity in mainland China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 326, 107757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Variables | I | II | III | IV | V | VI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT (°C) | 1955.82 | 3476.52 | 2380.96 | 2499.56 | 2805.46 | 2752.80 |
| MAP (10 mm) | 5225.00 | 4853.77 | 5575.94 | 5150.50 | 3772.33 | 5862.68 |
| Altitude (m) | 381.07 | 70.71 | 149.78 | 173.54 | 434.36 | 249.46 |
| Slope (°) | 1.20 | 0.65 | 1.23 | 0.47 | 1.06 | 1.83 |
| pH | 6.50 | 6.33 | 6.48 | 7.22 | 8.12 | 6.03 |
| SOM (g·Kg−1) | 57.05 | 26.47 | 50.59 | 30.45 | 26.10 | 32.89 |
| BD (kg/dm3) | 1.36 | 1.39 | 1.38 | 1.38 | 1.44 | 1.39 |
| CEC (cmol/kg) | 19.28 | 17.22 | 16.48 | 20.73 | 15.89 | 16.31 |
| ClayPerc (%) | 23.92 | 24.44 | 26.42 | 26.50 | 20.27 | 26.09 |
| SandPerc (%) | 46.90 | 44.99 | 41.53 | 46.43 | 54.24 | 26.09 |
| Chao1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pearson Coefficient | Explained Variance (%) | |
| Soil properties | ||
| pH | 0.487 ** | 4.184 |
| SOM | 0.123 ** | |
| BD | 0.149 ** | 0.723 |
| CEC | −0.011 | 0.000 |
| ClayPerc | −0.124 ** | 0.000 |
| SandPerc | 0.150 ** | |
| Climate | ||
| AT | −0.431 ** | 5.520 |
| MAP | −0.362 ** | |
| Terrain | ||
| Altitude | 0.601 ** | 3.169 |
| Slope | 0.002 | 0.000 |
| Spatial descriptors | ||
| Broad [148 km,222 km] | ||
| MEM1 | 0.673 ** | 8.336 |
| Medium [74 km,148 km] | ||
| MEM22 | 0.128 ** | 0.443 |
| Fine [30 km,74 km] | ||
| MEM38 | 0.059 | 0.368 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, J.; Tang, H.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, L.; Sang, L.; Huang, Y.; Shen, C.; Gao, B.; Niu, Z. Determinants of Soil Bacterial Diversity in a Black Soil Region in a Large-Scale Area. Land 2022, 11, 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11050731
Niu J, Tang H, Liu Q, Cheng F, Zhang L, Sang L, Huang Y, Shen C, Gao B, Niu Z. Determinants of Soil Bacterial Diversity in a Black Soil Region in a Large-Scale Area. Land. 2022; 11(5):731. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11050731
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Jiacheng, Huaizhi Tang, Qi Liu, Feng Cheng, Leina Zhang, Lingling Sang, Yuanfang Huang, Chongyang Shen, Bingbo Gao, and Zibing Niu. 2022. "Determinants of Soil Bacterial Diversity in a Black Soil Region in a Large-Scale Area" Land 11, no. 5: 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11050731
APA StyleNiu, J., Tang, H., Liu, Q., Cheng, F., Zhang, L., Sang, L., Huang, Y., Shen, C., Gao, B., & Niu, Z. (2022). Determinants of Soil Bacterial Diversity in a Black Soil Region in a Large-Scale Area. Land, 11(5), 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11050731








