A Cooperative-Dominated Model of Conservation Tillage to Mitigate Soil Degradation on Cultivated Land and Its Effectiveness Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
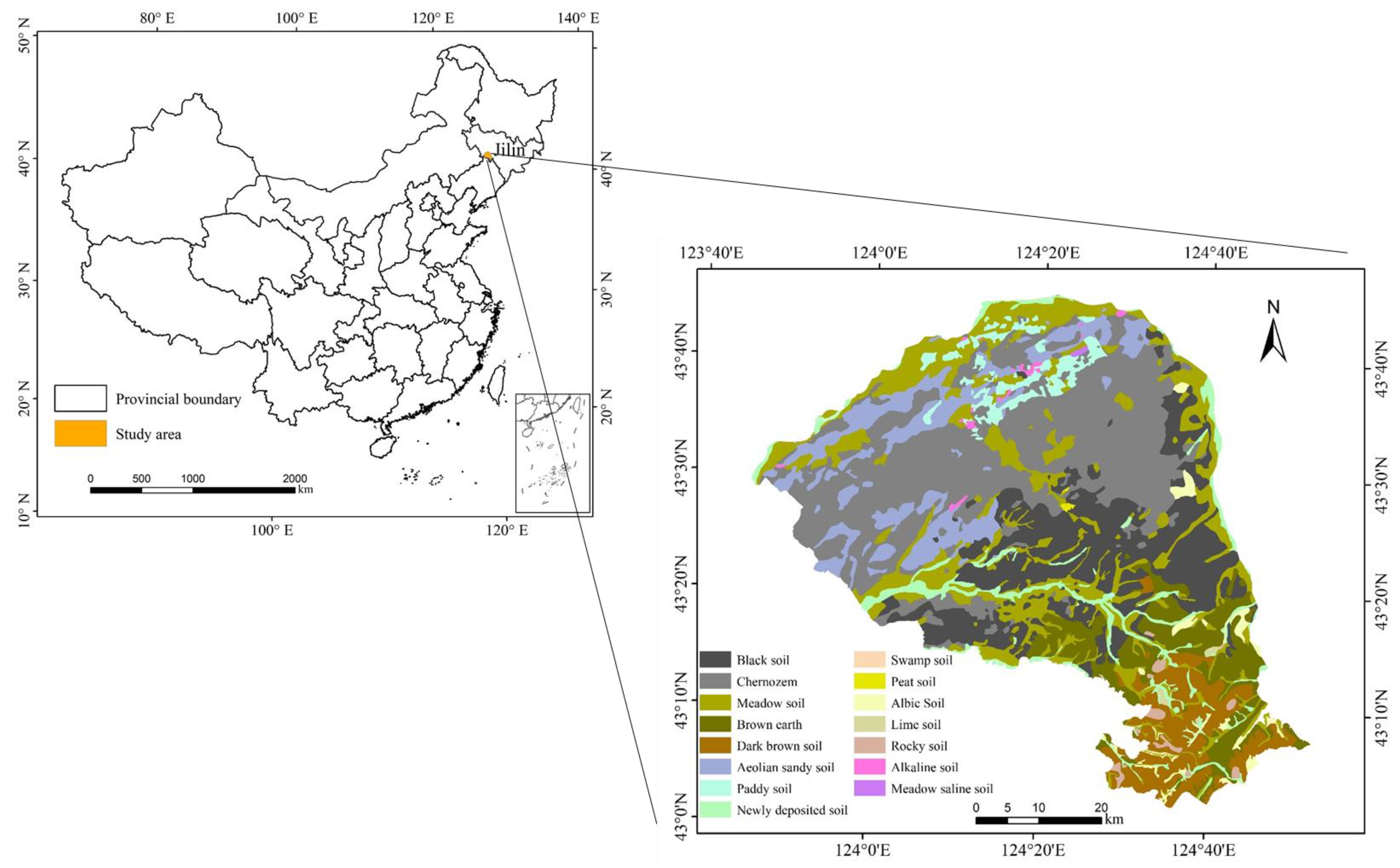
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Measurement of SOC and the Soil Structural Stability Index
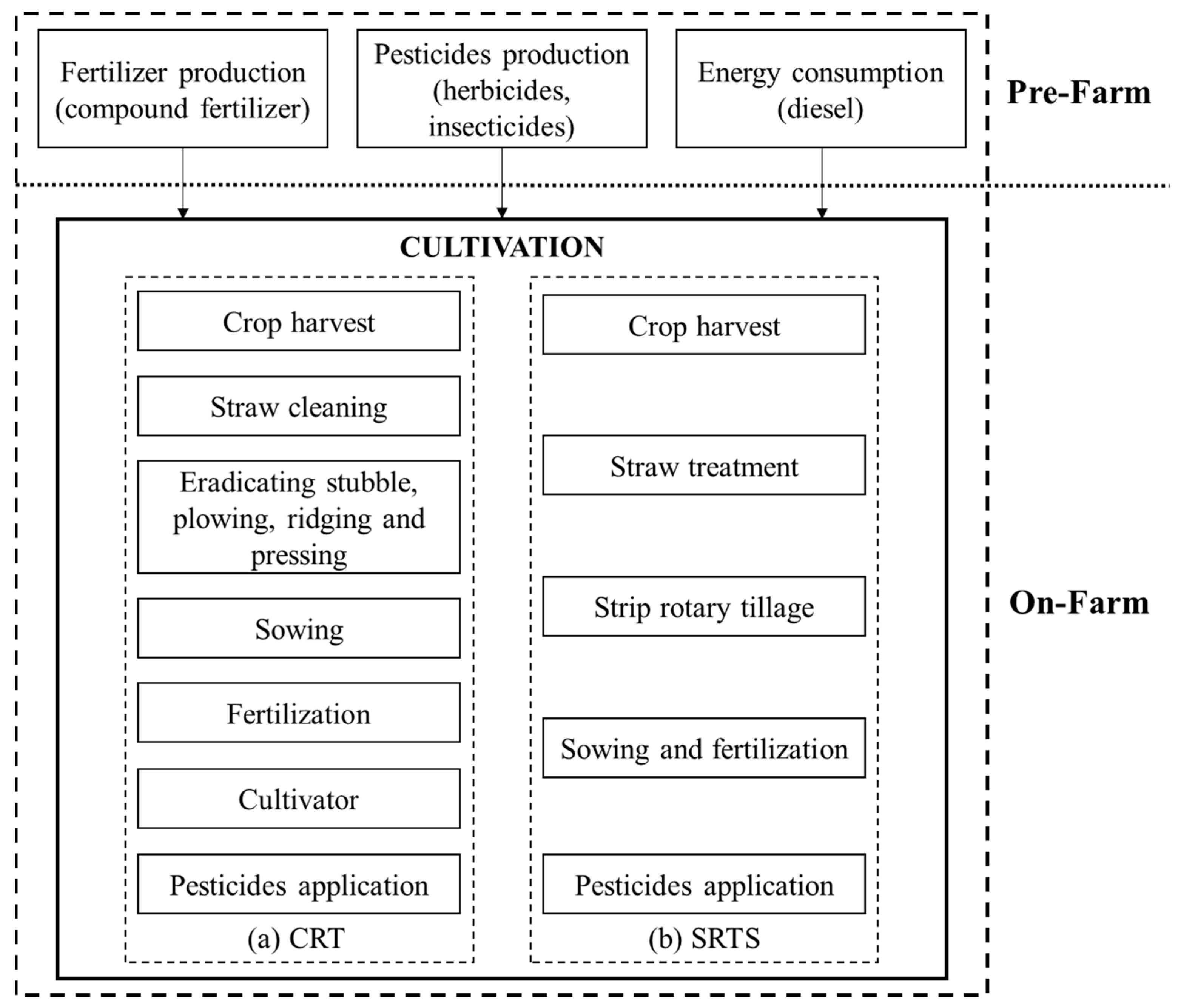
2.2.2. Measurement of Carbon Emissions
2.2.3. Measurement of Production Efficiency
2.2.4. Economic Benefits Assessment
2.3. Data Sources
3. Results
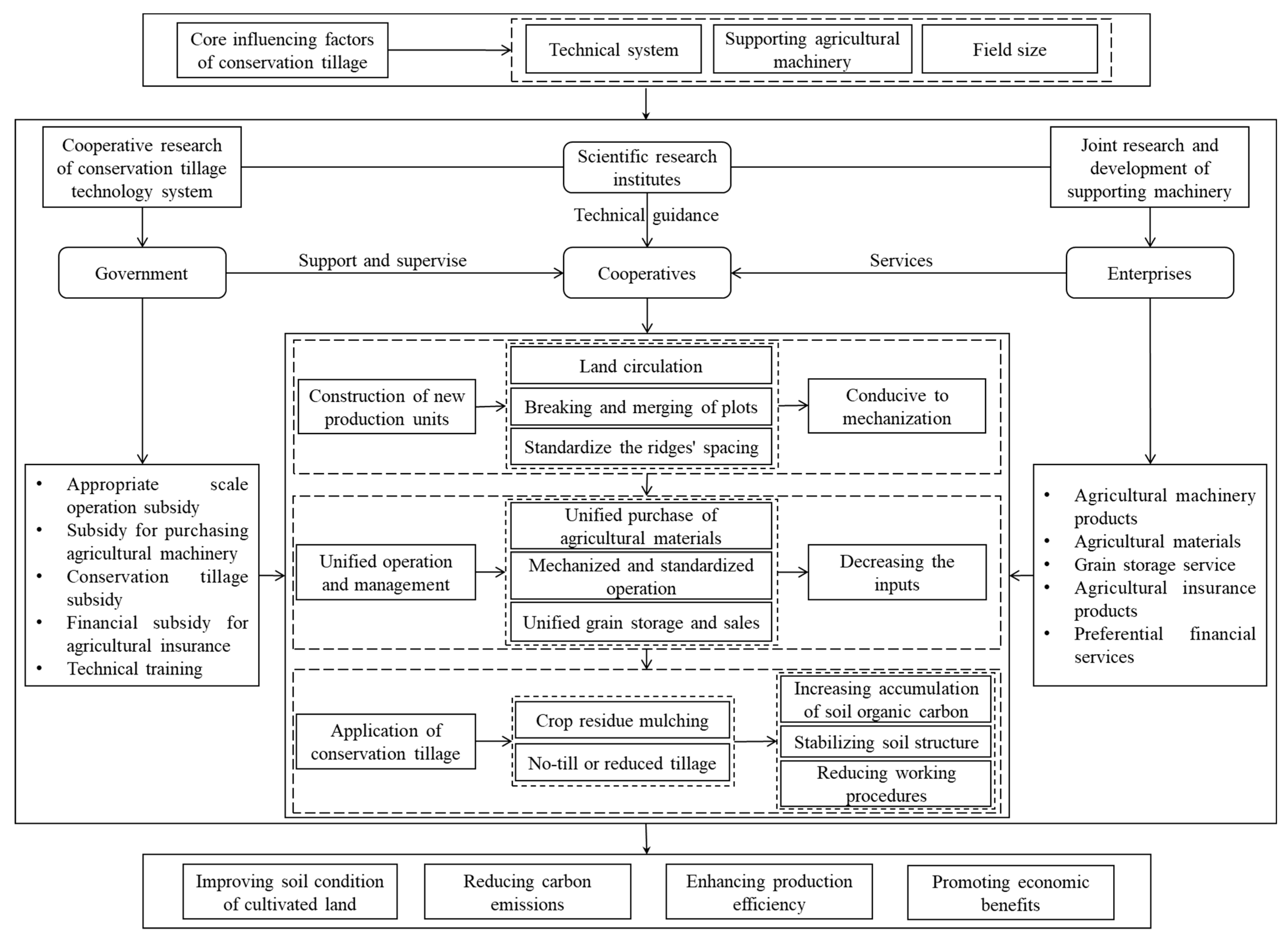
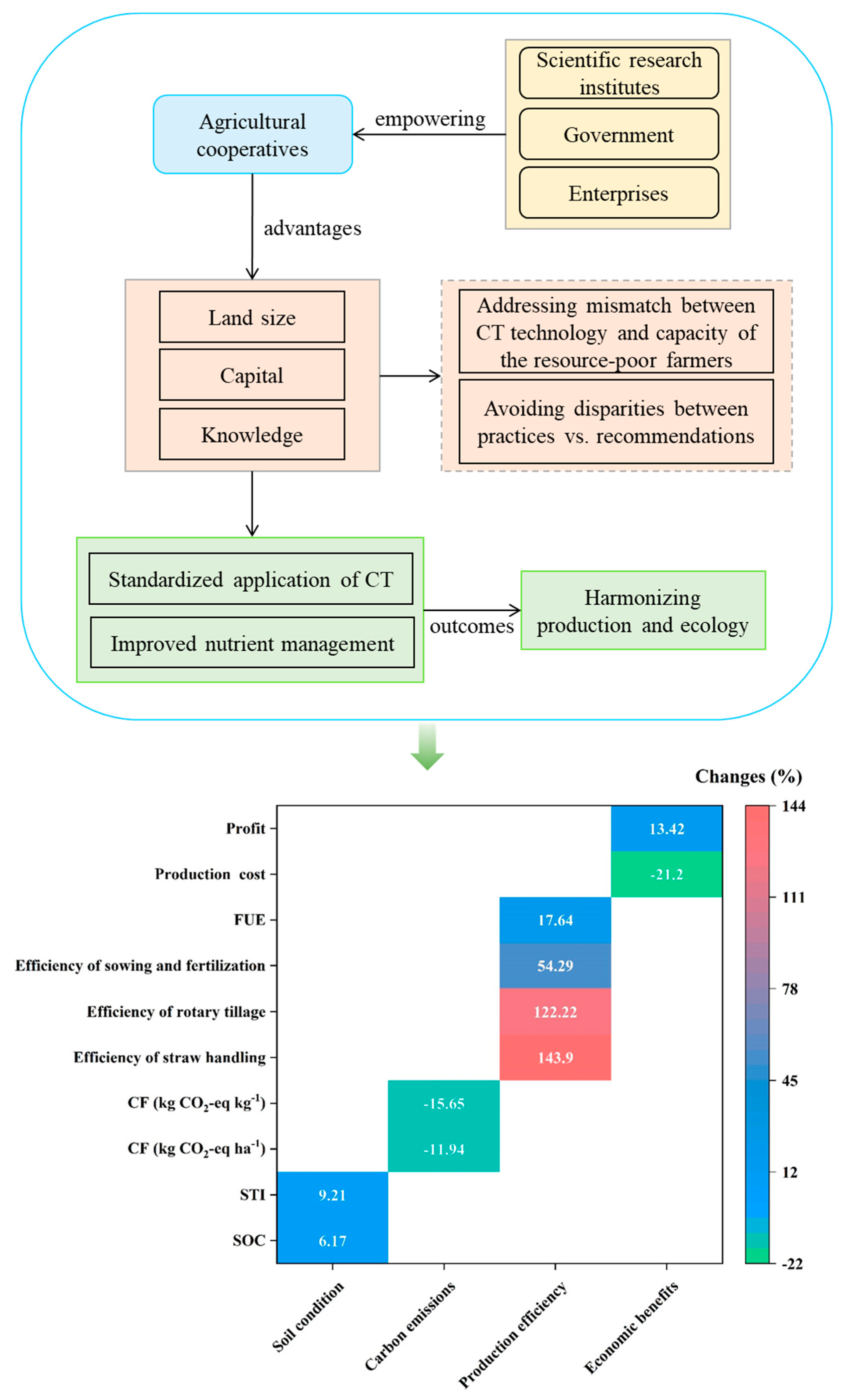
3.1. Cooperative-Dominated Conservation Tillage Model
3.1.1. Conceptual Framework of the Cooperative-Dominated Conservation Tillage Model
3.1.2. Role of Different Agents in the Cooperative-Dominated Conservation Tillage Model
3.2. Effectiveness Evaluation of the Cooperative-Dominated Conservation Tillage Model
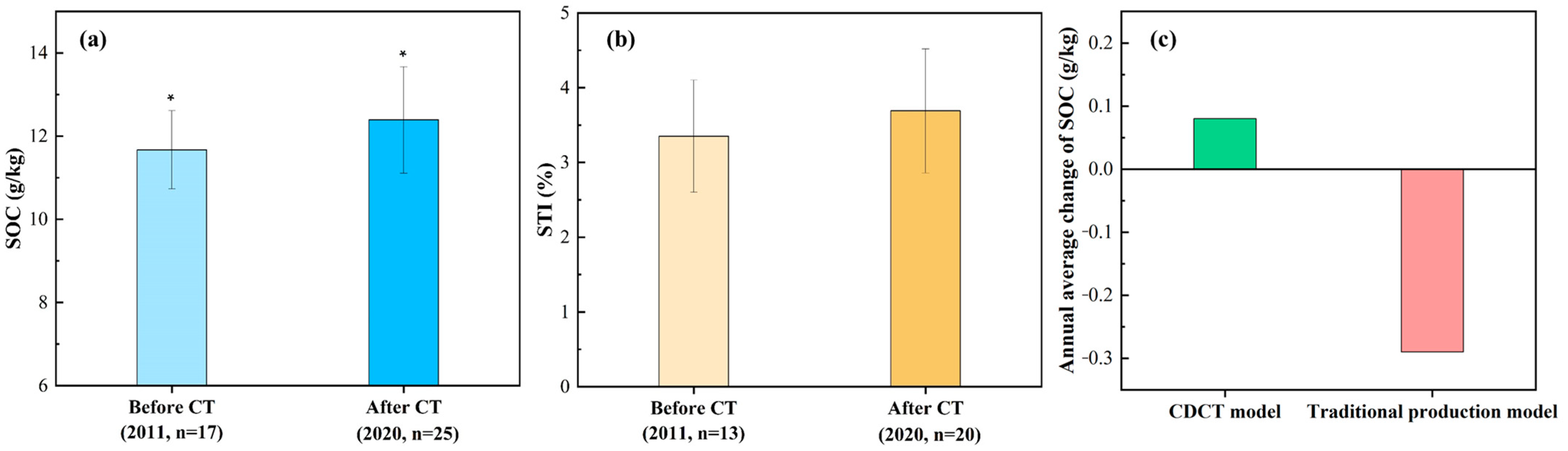
3.2.1. Changes in the Soil Condition of Cultivated Land under the CDCT Model
3.2.2. Characteristics of Carbon Emissions under the CDCT Model and the Traditional Production Model
3.2.3. Changes in Production Efficiency under the CDCT Model
3.2.4. Economic Benefits of the CDCT Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Strengths and Limitations of the CDCT Model
4.2. Policy Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Godfray, H.C.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food security: The challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duan, J.; Ren, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Reis, S.; Xu, J.; Gu, B. Consolidation of agricultural land can contribute to agricultural sustainability in China. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickson, R.J.; Deeks, L.K.; Graves, A.; Harris, J.A.H.; Kibblewhite, M.G.; Sakrabani, R. Input constraints to food production: The impact of soil degradation. Food Secur. 2015, 7, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; An, H.; Gao, X.; Jia, N.; Liu, S.; Zheng, H. Structural decomposition analysis of global carbon emissions: The contributions of domestic and international input changes. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 112942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, R. Restoring Soil Quality to Mitigate Soil Degradation. Sustainability 2015, 7, 5875–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arrieta, E.M.; Cuchietti, A.; Cabrol, D.; Gonzalez, A.D. Greenhouse gas emissions and energy efficiencies for soybeans and maize cultivated in different agronomic zones: A case study of Argentina. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wuepper, D.; Borrelli, P.; Finger, R. Countries and the global rate of soil erosion. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 3, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dong, H.; Jiang, T. Structural emission reduction in China’s industrial systems and energy systems: An input-output analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 6010–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, D.; Yu, Z. Land resource degradation in China: Analysis of status, trends and strategye. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2006, 13, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Ding, G.; Cruse, R.M. Soil erosion control practices in Northeast China: A mini-review. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 117, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Kasielke, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Zepp, H. May agricultural terraces induce gully erosion? A case study from the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Pei, J.; Li, S. Current Situations of Black Soil Quality and Facing Opportunities and Challenges in Northeast China. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 52, 695–701. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Lee Burras, C.; Kravchenko, Y.S.; Duran, A.; Huffman, T.; Morras, H.; Studdert, G.; Zhang, X.; Cruse, R.M.; Yuan, X. Overview of Mollisols in the world: Distribution, land use and management. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 92, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Cheng, S.; Fang, H.; Liu, G.; Yuan, W. Soil erosion affects variations of soil organic carbon and soil respiration along a slope in Northeast China. Ecol. Processes 2019, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Qiu, L.; Wei, X.; Liu, B.; Shao, M. Response of soil OC, N and P to land-use change and erosion in the black soil region of the Northeast China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 302, 107801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zheng, F.; Han, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yi, Y.; Feng, Z. Investigating Spatial Distribution of Soil Quality Index and Its Impacts on Corn Yield in a Cultivated Catchment of the Chinese Mollisol Region. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2016, 80, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xu, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, X. Characteristics of Material Migration During Soil Erosion in Sloped Farmland in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Trop. Conserv. Sci. 2019, 12, 1940082919856835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, J.; Wang, J.; Xue, Y. Evaluation of Cultivated Land Quality in Black Soil Area of Northeast China; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2017; p. 146. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.M.; Xu, X.; Jiao, X.G.; Sui, Y.Y.; Liu, X.B.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, J.M. Responses of Labile Organic Nitrogen Fractions and Enzyme Activities in eroded Mollisols After 8-year Manure Amendment. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ren, X.; Cheng, C.; Wang, S. Quantitative assessment of soil productivity and predicted impacts of water erosion in the black soil region of northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundson, R.; Berhe, A.A.; Hopmans, J.W.; Olson, C.; Sztein, A.E.; Sparks, D.L. Soil science. Soil and human security in the 21st century. Science 2015, 348, 1261071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Burras, C.L.; Lilli, E.; Zhang, X. Interrelationship among slope steepness, tillage practice and rainfall properties with surface runoff and soil loss on Mollisols in Northeast China. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 1860–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xie, Y.; Xia, D.; Ji, L.; Huang, G. A multi-sectoral decomposition and decoupling analysis of carbon emissions in Guangdong province, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.; Teclemariam, S.G.; Yan, C.; Yu, J.; Gu, R.; Liu, S.; He, W.; Liu, Q. Long-term effects of no-tillage management practice on soil organic carbon and its fractions in the northern China. Geoderma 2014, 213, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Dai, Z.; Veach, A.M.; Zheng, J.; Xu, J.; Schadt, C.W. Global meta-analyses show that conservation tillage practices promote soil fungal and bacterial biomass. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 293, 106841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kessel, C.; Venterea, R.; Six, J.; Adviento-Borbe, M.A.; Linquist, B.; van Groenigen, K.J. Climate, duration, and N placement determine N2O emissions in reduced tillage systems: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Tu, C.; Hoyt, G.D.; DeForest, J.L.; Hu, S. Long-term no-tillage and organic input management enhanced the diversity and stability of soil microbial community. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yuan, J.; Gao, S.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Vinay, N.; Mo, F.; Liao, Y.; Wen, X. Conservation tillage enhances crop productivity and decreases soil nitrogen losses in a rainfed agroecosystem of the Loess Plateau, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 122854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issaka, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Z.-Q.; Asenso, E.; Li, J.-H.; Li, Y.-T.; Wang, J.-J. Sustainable Conservation Tillage Improves Soil Nutrients and Reduces Nitrogen and Phosphorous Losses in Maize Farmland in Southern China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Man, M.; Wagner-Riddle, C.; Dunfield, K.E.; Deen, B.; Simpson, M.J. Long-term crop rotation and different tillage practices alter soil organic matter composition and degradation. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 209, 104960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Hussain, S.; Guo, R.; Sarwar, M.; Ren, X.; Krstic, D.; Aslam, Z.; Zulifqar, U.; Rauf, A.; Hano, C.; et al. Carbon Sequestration to Avoid Soil Degradation: A Review on the Role of Conservation Tillage. Plants 2021, 10, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Jia, G.; Zhang, X. The effects of eight years of conservation tillage on the soil physicochemical properties and bacterial communities in a rain-fed agroecosystem of the loess plateau, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 2475–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Li, J. Conservation tillage improves soil water storage, spring maize (Zea mays L.) yield and WUE in two types of seasonal rainfall distributions. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 215, 105237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xin, X.; Zhu, A.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Ding, S.; Mu, L.; Shao, L. Linking macroaggregation to soil microbial community and organic carbon accumulation under different tillage and residue managements. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 178, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panettieri, M.; de Sosa, L.L.; Domínguez, M.T.; Madejón, E. Long-term impacts of conservation tillage on Mediterranean agricultural soils: Shifts in microbial communities despite limited effects on chemical properties. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 304, 107144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Chethan, C.R.; Chander, S.; Kumar, B.; Dubey, R.P.; Bisen, H.S.; Parey, S.K.; Singh, P.K. Conservational Tillage and Weed Management Practices Enhance Farmers Income and System Productivity of Rice–Wheat Cropping System in Central India. Agric. Res. 2021, 10, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, K.A.; Al-Hashimi, A.; Meena, M.; Meena, V.S.; Langyan, S.; Shrivastava, M.; Sayyed, R.Z.; El-Enshasy, H.A.; Almunqedhi, B.M.A.; Singh, R. Conservation agricultural practices for minimizing ammonia volatilization and maximizing wheat productivity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 9792–9804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, V.L.; Schmer, M.R.; Stewart, C.E.; Sindelar, A.J.; Varvel, G.E.; Wienhold, B.J. Long-term no-till and stover retention each decrease the global warming potential of irrigated continuous corn. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 2848–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mei, K.; Wang, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhang, C.; Shang, X.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zhang, M.; Xia, F. Stimulation of N2O emission by conservation tillage management in agricultural lands: A meta-analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 182, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lal, R. A system approach to conservation agriculture. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 70, 82A–88A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daryanto, S.; Wang, L.; Jacinthe, P.A. Impacts of no-tillage management on nitrate loss from corn, soybean and wheat cultivation: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, M.; Li, G.; Rahim, N.; Tahir, M. Effect of conservation tillage on yield of spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and soil mineral nitrogen and carbon content. Int. Agrophysics 2021, 35, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Pan, C.; Guo, H. Factors Affecting the Promotion of Conservation Tillage in Black Soil—The Case of Northeast China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xue, C.; Yao, S.; Zhu, R. Conservation tillage, cropping systems and land productivity for households on the Loess Plateau. Resour. Sci. 2017, 39, 1259–1271. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Kuhn, N.J.; Zhao, R.; Cao, L. Net effects of conservation agriculture principles on sustainable land use: A synthesis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 6321–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; He, J.; Bharucha, Z.P.; Lal, R.; Pretty, J. Improving China’s food and environmental security with conservation agriculture. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2016, 14, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, W.; Renwick, A.; Yuan, P.; Ratna, N. Agricultural cooperative membership and technical efficiency of apple farmers in China: An analysis accounting for selectivity bias. Food Policy 2018, 81, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Wang, X.; Jin, S.; Yang, W.; Li, H. Impacts of cooperative membership on rice productivity: Evidence from China. World Dev. 2022, 150, 105669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.R.; Karlen, D.L.; Veum, K.S.; Moorman, T.B.; Cambardella, C.A. Biological soil health indicators respond to tillage intensity: A US meta-analysis. Geoderma 2020, 369, 114335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, C. Fertility of Soils. In A Future for Farming in the West African Savannah; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; p. 348. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Li, B.; Lu, Y. Micromorphological analysis of soil structure under no tillage management in the black soil zone of Northeast China. J. Mt. Sci. 2009, 6, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories; Prepared by the National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Programme—Volume 2, Energy. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Mobile Combustion; IGES: Kanagawa, Japan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.F.; Dou, Z.X.; He, P.; Ju, X.T.; Powlson, D.; Chadwick, D.; Norse, D.; Lu, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; et al. New technologies reduce greenhouse gas emissions from nitrogenous fertilizer in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8375–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Lu, F.; Wang, X. Estimation of greenhouse gases emission factors for China’s nitrogen, phosphate, and potash fertilizers. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 6371–6383. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- West, T.O.; Marland, G. A synthesis of carbon sequestration, carbon emissions, and net carbon flux in agriculture: Comparing tillage practices in the United States. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 91, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cao, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Shen, J.; Jiang, R.; et al. Closing yield gaps in China by empowering smallholder farmers. Nature 2016, 537, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, E. Beyond Markets and States: Polycentric Governance of Complex Economic Systems. Am. Econ. Rev. 2010, 100, 641–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kassam, A.; Friedrich, T.; Derpsch, R. Global spread of Conservation Agriculture. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 76, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Y. Application status and countermeasure analysis of conservation tillage. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2020, 41, 198–203. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ogle, S.M.; Swan, A.; Paustian, K. No-till management impacts on crop productivity, carbon input and soil carbon sequestration. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 149, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittelkow, C.M.; Liang, X.; Linquist, B.A.; van Groenigen, K.J.; Lee, J.; Lundy, M.E.; van Gestel, N.; Six, J.; Venterea, R.T.; van Kessel, C. Productivity limits and potentials of the principles of conservation agriculture. Nature 2015, 517, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hobbie, E.A.; Feng, P.; Niu, L.; Hu, K. Can conservation agriculture mitigate climate change and reduce environmental impacts for intensive cropping systems in North China Plain? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-L.; Lal, R.; Zhao, X.; Xue, J.-F.; Chen, F. Opportunities and Challenges of Soil Carbon Sequestration by Conservation Agriculture in China. Adv. Agron. 2014, 124, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Ying, H.; Chen, M.; Bai, J.; Xue, Y.; Yin, Y.; Batchelor, W.D.; Yang, Y.; Bai, Z.; Du, M.; et al. Optimization of China’s maize and soy production can ensure feed sufficiency at lower nitrogen and carbon footprints. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, S. Research on the model of mass autonomous land consolidation and its effect-a case study in San Chaping village, Ma Nasi county. Xinjiang. Econ. Geogr. 2013, 33, 131–136. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Ma, W.; Huang, C.; Zhang, W.; Mi, G.; Miao, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Pursuing sustainable productivity with millions of smallholder farmers. Nature 2018, 555, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Niu, W.; Ma, L.; Zuo, X.; Kong, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, M.; Xia, X. A company-dominated pattern of land consolidation to solve land fragmentation problem and its effectiveness evaluation: A case study in a hilly region of Guangxi Autonomous Region, Southwest China. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

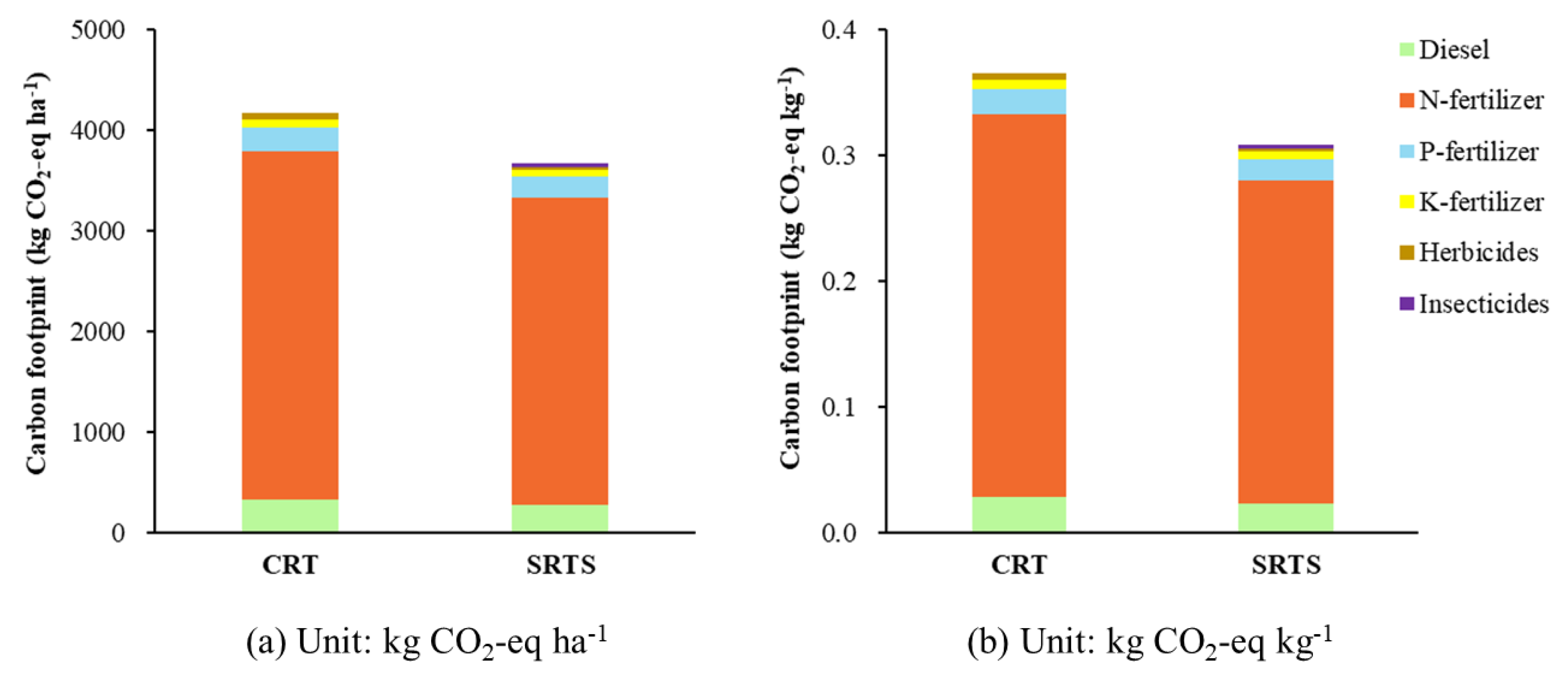
| Inputs | Unit | kg CO2-eq Unit−1 | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diesel | Liter | 2.56 | IPCC (2006) [52] |
| Fertilizer | |||
| N | kg | 13.5 | Zhang et al. (2013) [53] |
| P | kg | 2.332 | Chen et al. (2015) [54] |
| K | kg | 0.660 | Chen et al. (2015) [54] |
| Pesticides | |||
| Herbicides | kg | 17.242 | West and Marland (2002) [55] |
| Insecticides | kg | 18.084 | West and Marland (2002) [55] |
| Item | Unit | CRT | SRTS |
|---|---|---|---|
| N fertilizer input | kg/ha | 256.42 ± 10.49 | 226.31 ± 19.87 |
| P fertilizer input | kg/ha | 100.33 ± 1.87 | 89.22 ± 5.29 |
| K fertilizer input | kg/ha | 124.84 ± 8.88 | 112.73 ± 7.15 |
| Herbicide input | kg/ha | 3.55 ± 0.49 | 1.54 ± 0.23 |
| Insecticide input | kg/ha | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 1.75 ± 0.24 |
| Diesel consumption | L/ha | 126.67 ± 7.79 | 105.63 ± 5.30 |
| Maize yield | t/ha | 11.39 ± 0.74 | 11.89 ± 0.63 |
| Efficiency Indicators | CRT | SRTS |
|---|---|---|
| FUE (kg kg−1) | 23.65 ± 1.98 | 27.83 ± 2.25 |
| Operational efficiency (ha/d) | ||
| Straw handling | 4.1 ± 0.6 | 10.0 ± 1.8 |
| Rotary tillage | 4.5 ± 0.5 | 10.0 ± 1.4 |
| Sowing and fertilization | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 5.4 ± 1.6 |
| Item | SRTS | CRT |
|---|---|---|
| Cost component | ||
| (A) Mechanical operations | ||
| Harvesting | 917 ± 41 | 1100 ± 141 |
| Straw handling | 93 ± 16 | - |
| Eradication of stubble, plowing, ridging, and pressing | - | 680 ± 44 |
| Strip rotary tillage | 433 ± 52 | - |
| Sowing and fertilizing | 418 ± 49 | 460 ± 55 |
| Cultivator | - | 200 ± 14 |
| Spraying pesticides | 111 ± 46 | 200 ± 71 |
| (B) Agricultural materials | ||
| Seeds | 450 ± 54 | 552 ± 51 |
| Fertilizers | 2220 ± 161 | 2666 ± 185 |
| Pesticides | 367 ± 31 | 275 ± 54 |
| (C) Labor cost | 375 ± 67 | 700 ± 112 |
| Total cost | 5384 ± 165 | 6833 ± 131 |
| Maize income | 27,347 ± 1938 | 26,197 ± 1856 |
| Profit | 21,963 ± 2031 | 19,364 ± 1967 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Kong, X.; Wen, L.; Yao, D.; Dang, Y.; Chen, W. A Cooperative-Dominated Model of Conservation Tillage to Mitigate Soil Degradation on Cultivated Land and Its Effectiveness Evaluation. Land 2022, 11, 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081223
Liao Y, Zhang B, Kong X, Wen L, Yao D, Dang Y, Chen W. A Cooperative-Dominated Model of Conservation Tillage to Mitigate Soil Degradation on Cultivated Land and Its Effectiveness Evaluation. Land. 2022; 11(8):1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081223
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Yubo, Bangbang Zhang, Xiangbin Kong, Liangyou Wen, Dongheng Yao, Yuxuan Dang, and Wenguang Chen. 2022. "A Cooperative-Dominated Model of Conservation Tillage to Mitigate Soil Degradation on Cultivated Land and Its Effectiveness Evaluation" Land 11, no. 8: 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081223
APA StyleLiao, Y., Zhang, B., Kong, X., Wen, L., Yao, D., Dang, Y., & Chen, W. (2022). A Cooperative-Dominated Model of Conservation Tillage to Mitigate Soil Degradation on Cultivated Land and Its Effectiveness Evaluation. Land, 11(8), 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081223








