Combined Modification of Urbanization and Monsoon in Meiyu Precipitation Changes in the Megacity Shanghai, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
3. Urbanization Process in Shanghai and Precipitation Homogenization Test
3.1. Urbanization History in Shanghai
3.2. Homogenization Test of Precipitation Series
4. Long-Term Changes in PDM Associated with Urbanization
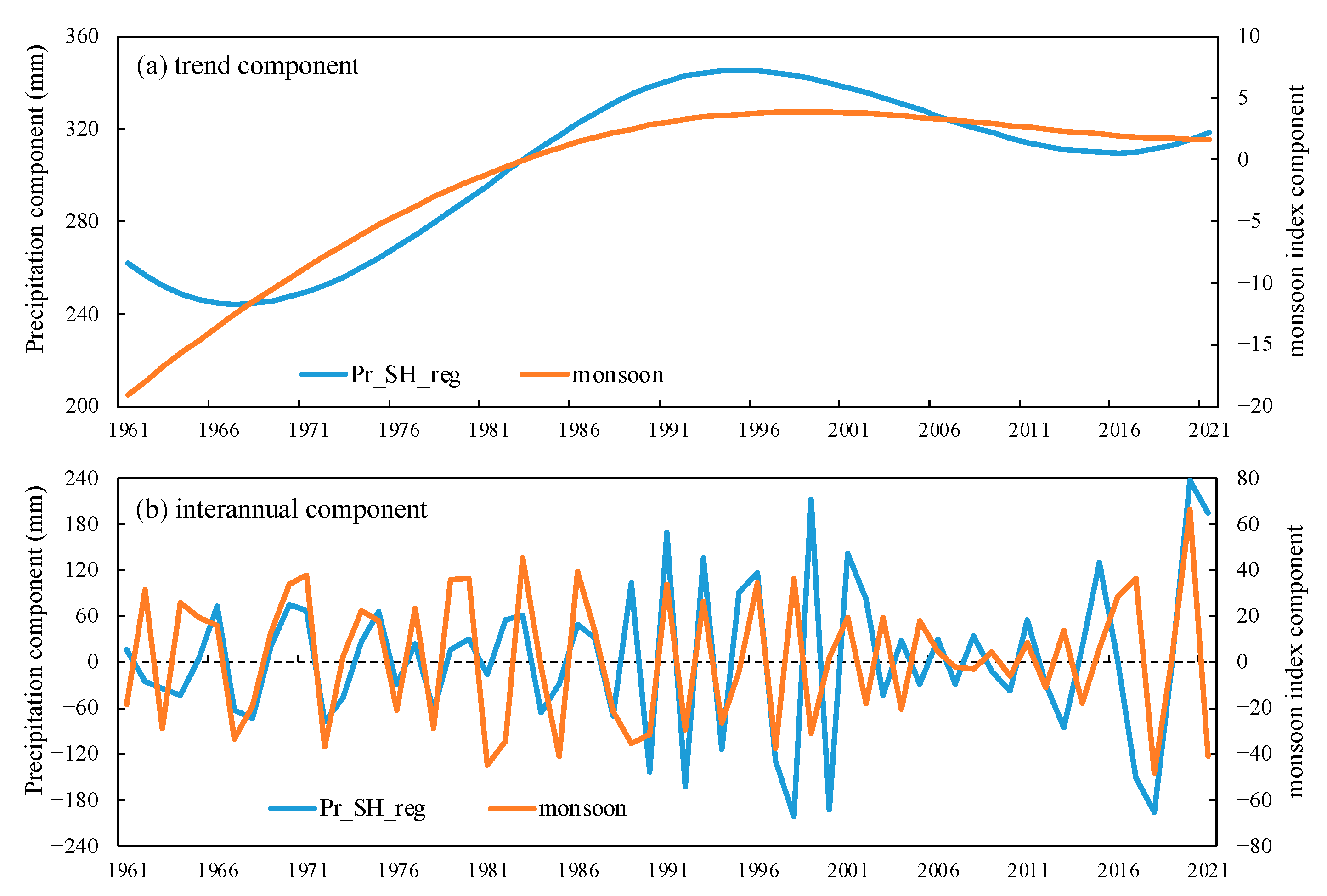
5. Influence of Monsoon on PDM during Two Different Urbanization Processes
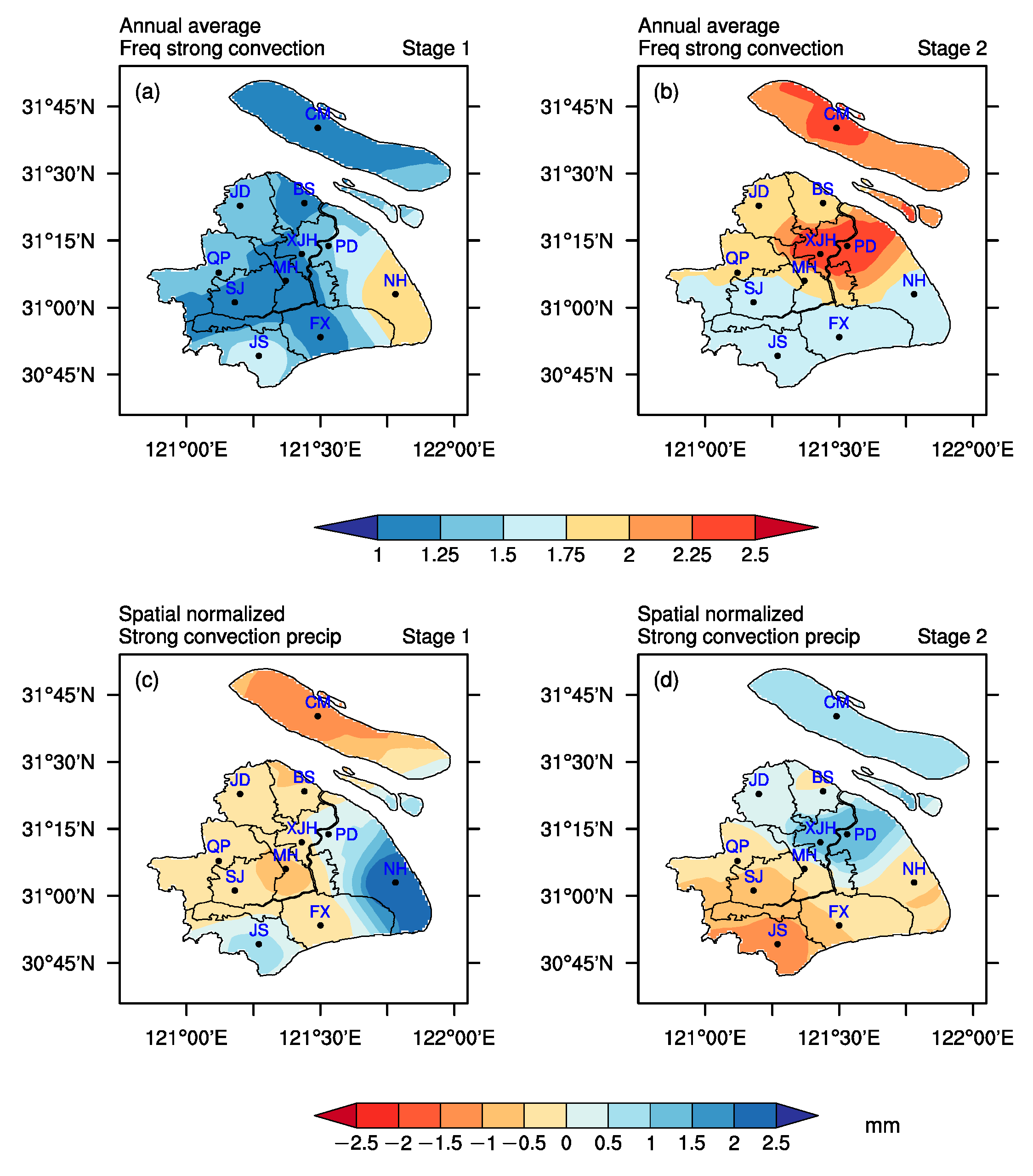
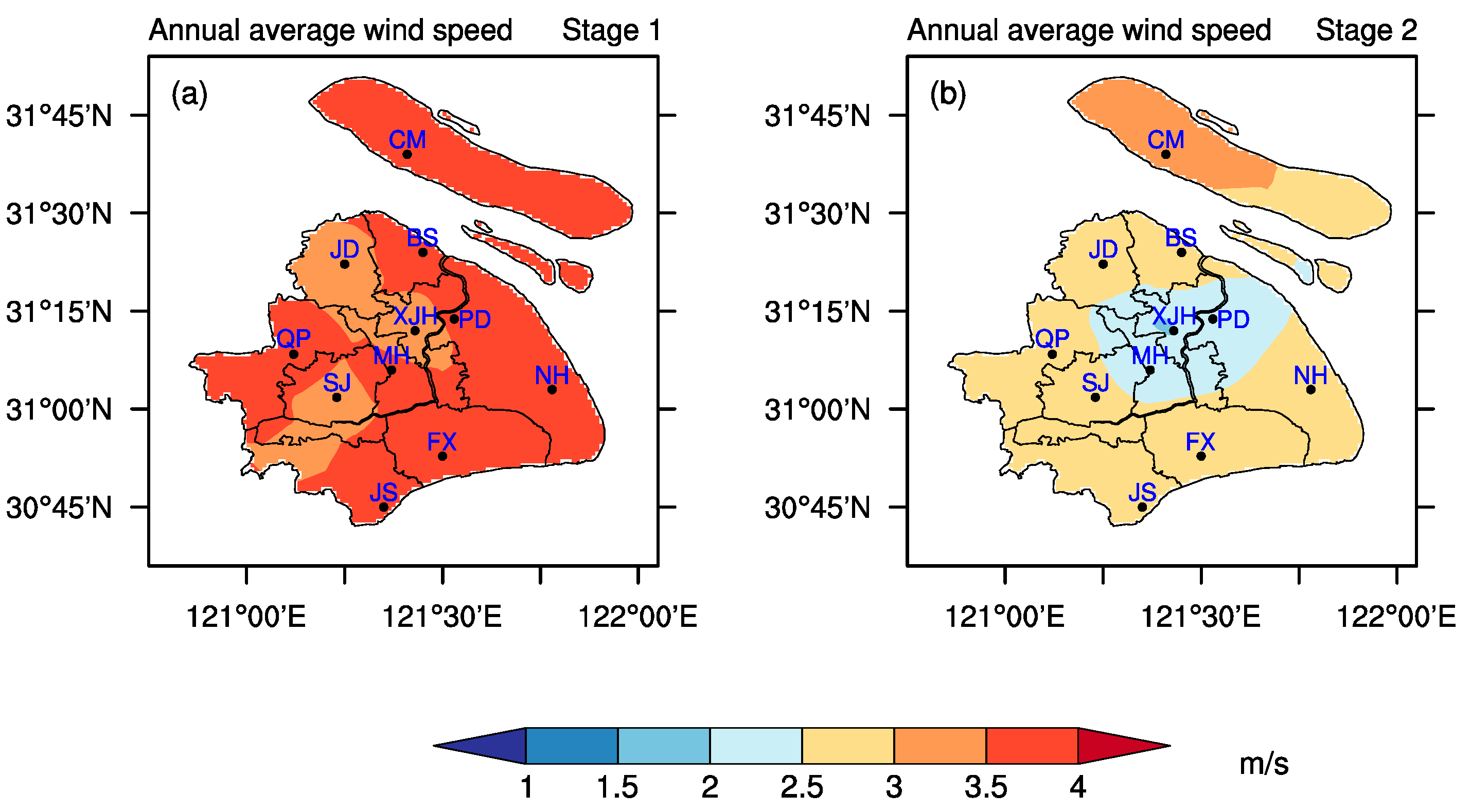
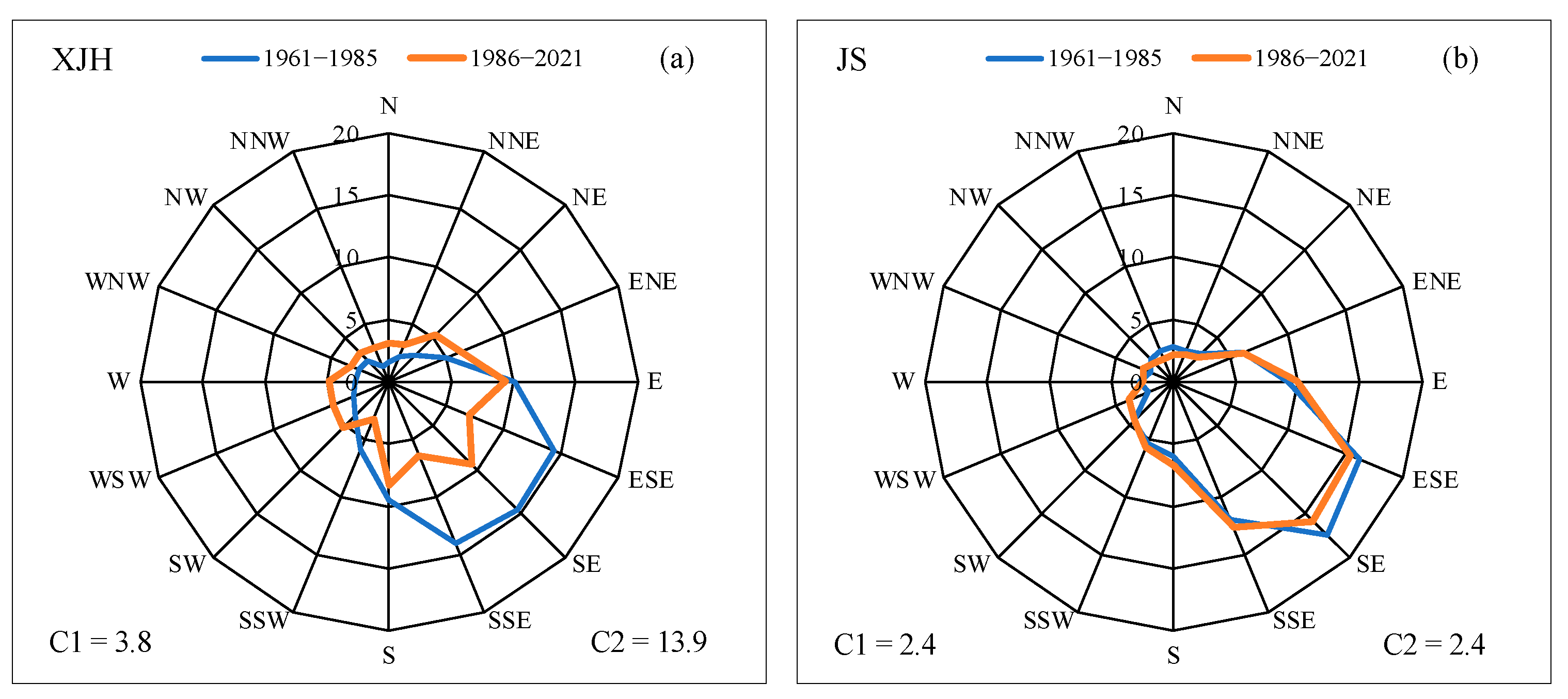
6. Effects of Urbanization on PDM in Two Different Urbanization Processes
7. Discussion and Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tao, S.-Y.; Chen, L.-X. A Review of Recent Research on the East Asian Summer Monsoon in China. In Monsoon Meteorology; Chang, C.P., Krishnamurti, T.N., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987; pp. 60–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y. Monsoons over China; Atmospheric and Oceanographic Sciences Library; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 16, ISBN 978-94-015-8302-2. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, P.; Hu, Z.-Z.; Ding, Y.; Qian, Q. The Extreme Mei-Yu Season in 2020: Role of the Madden-Julian Oscillation and the Cooperative Influence of the Pacific and Indian Oceans. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 2040–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Multiscale Variability of Meiyu and Its Prediction: A New Review. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninomiya, K.; Muraki, H. Large-Scale Circulations over East Asia during Baiu Period of 1979. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1986, 64, 409–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, J.-H.; Kwon, W.-T.; Ryoo, S.-B. Review of the Researches on Changma and Future Observational Study (Kormex). Adv. Atmos. Sci. 1997, 14, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y. Summer Monsoon Rainfalls in China. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1992, 70, 373–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y. Seasonal March of the East Asian Monsoon. In East Asian Monsoon; World Scientific Series on Asia-Pacific Weather and Climate; World Scientific: Singapore, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 3–53. ISBN 978-981-238-769-1. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, K.M.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.-T.; Johnson, R.; Keenan, T.; Cifelli, R.; Gerlach, J.; Thiele, O.; Rickenbach, T.; Tsay, S.-C.; et al. A Report of the Field Operations and Early Results of the South China Sea Monsoon Experiment (SCSMEX). Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2000, 81, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.-Z. The Record-Breaking Mei-Yu in 2020 and Associated Atmospheric Circulation and Tropical SST Anomalies. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 1980–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerknes, J. A Possible Response of the Atmospheric Hadley Circulation to Equatorial Anomalies of Ocean Temperature. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 1966, 18, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, P.; Hu, Z.Z.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Li, X.; Jiang, X. Challenges in predicting and simulating summer rainfall in the eastern China. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 2217–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enfield, D.B.; Mestas-Nuñez, A.M.; Trimble, P.J. The Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation and Its Relation to Rainfall and River Flows in the Continental U.S. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 2077–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mantua, N.J.; Hare, S.R.; Zhang, Y.; Wallace, J.M.; Francis, R.C. Pacific Interdecadal Climate Oscillation with Impacts on Salmon Production. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Lin, H. Sub-seasonal prediction over East Asia during boreal summer using the ECCC monthly forecasting system. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 52, 1007–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, W.; Fu, S.; Hsu, P. Influence of compound zonal displacements of the South Asia high and the western Pacific. subtropical high on Meiyu intraseasonal variation. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhu, C.; Lu, R.; Jiang, N.; Ma, S. Subseasonal forecast barrier of the North Atlantic oscillation in S2S models during the extreme mei-yu rainfall event in 2020. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 58, 2913–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-X.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Z. Characteristics of the Heat Island Effect in Shanghai and Its Possible Mechanism. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 20, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Qi, Y.; Guo, H. Effect of Urbanization on the Winter Precipitation Distribution in Beijing Area. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2009, 52, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Chen, F.; Miao, S.G.; Li, Q.C.; Xia, X.A.; Xuan, C.Y. Impacts of Urban Expansion and Future Green Planting on Summer Precipitation in the Beijing Metropolitan Area. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D02116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Ding, Y.; He, J.-H.; Tang, X. Study of Relationship between Urbanization Speed and. Change in Spatial Distribution of Rainfall over Shanghai. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2013, 19, 475–483. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Tian, F.; Smith, J.A.; Hu, H. Urban Signatures in the Spatial Clustering of Summer Heavy Rainfall Events over the Beijing Metropolitan Region: Urban Modification of Heavy Rainfall. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Yang, X.-Q. Ensemble Simulations of the Urban Effect on a Summer Rainfall Event in the Great Beijing Metropolitan Area. Atmos. Res. 2015, 153, 318–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Ding, Y. The Long-Term Variation of Extreme Heavy Precipitation and Its Link to Urbanization Effects in Shanghai during 1916–2014. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 34, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Niyogi, D. Meta-Analysis of Urbanization Impact on Rainfall Modification. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dou, J.; Wang, Y.; Bornstein, R.; Miao, S. Observed Spatial Characteristics of Beijing Urban Climate Impacts on Summer Thunderstorms. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2015, 54, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Ren, G.; Yan, P. Evidence for a Strong Association of Short-Duration Intense Rainfall with Urbanization in the Beijing Urban Area. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5851–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Mo, Y.; Xuan, Y.; Wang, Q.J.; Wu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zou, X. Impacts of Urbanization on Precipitation Patterns in the Greater Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Metropolitan Region in Northern China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 014042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Rainstorm-Induced Hazards Modified by Urbanization in Beijing. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2015, 54, 1496–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Yan, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y. Impact of Urbanization on Low-Temperature Precipitation in Beijing during 1960–2008. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 31, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Y. Simulation of Urban Climate with High-Resolution WRF Model: A Case Study in Nanjing, China. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 48, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Xia, B. An Analysis Study of the Impacts of Urbanization on Precipitation in Guangzhou. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2011, 31, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Zhong, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, X. Impact of City Belt in Yangtze River Delta in China on a Precipitation Process in Summer: A Case Study. Atmos. Res. 2013, 125–126, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, J.; Yan, Z.; Hu, Y.; Jia, G. Nested High-Resolution Modeling of the Impact of Urbanization on Regional Climate in Three Vast Urban Agglomerations in China: Climate impact of urbanization in China. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D21103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, J.; Wang, J.; Yan, Z. Impact of Anthropogenic Heat Release on Regional Climate in Three Vast Urban Agglomerations in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 31, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, D.-L.; Wu, M. Urbanization Enhanced Summertime Extreme Hourly Precipitation over the Yangtze River Delta. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 5809–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kishtawal, C.M.; Niyogi, D.; Tewari, M.; Pielke, R.A.; Shepherd, J.M. Urbanization Signature in the Observed Heavy Rainfall Climatology over India. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 1908–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chalakkal, J.B.; Mohan, M. Is the Monsoon Climatology Observed over the National Capital Region, Delhi Indicative of an Urban-Monsoon Linkage on Rainfall Modification? Urban Clim. 2022, 46, 101289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, Y. Numerical Study of the Impacts of Urban Expansion on Meiyu Precipitation over Eastern China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2015, 29, 237–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.; Xue, Y.; Duan, Q.; Liu, Z.; Oleson, K.W.; Liu, Y. Numerical Investigation and Uncertainty Analysis of Eastern China’s Large-Scale Urbanization Effect on Regional Climate. J. Meteorol. Res. 2021, 35, 1023–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Yang, Y.-W.; Yang, Q.-M. The Meiyu in Middle-Lower Reaches of Yangtze River during 116 Recent Years (I). Torrential Rain Disaster 2001, 1, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-Year Reanalysis Project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Cai, M. Impact of urbanization and landuse change on climate. Nature 2003, 423, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistler, R.; Kalnay, E.; Collins, W.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; Chelliah, M.; Ebisuzaki, W.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kousky, V.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 50-year reanalysis: Monthly means CD-ROM and documentation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 82, 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yan, Z.; Tu, K.; Wu, H. Changes of Precipitation and Extremes and the Possible Effect of Urbanization in the Beijing Metropolitan Region during 1960–2012 Based on Homogenized Observations. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 32, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L. Penalized Maximal F Test for Detecting Undocumented Mean Shift without Trend Change. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 368–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Pu, Q. New Techniques for the Detection and Adjustment of Shifts in Daily Precipitation Data Series. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 2416–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Wen, Q.H.; Wu, Y. Penalized Maximal t Test for Detecting Undocumented Mean Change in Climate Data Series. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2007, 46, 916–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Clinton, N.; Ji, L.; Li, W.; Bai, Y.; et al. Stable Classification with Limited Sample: Transferring a 30-m Resolution Sample Set Collected in 2015 to Mapping 10-m Resolution Global Land Cover in 2017. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, W. 40-Year (1978–2017) Human Settlement Changes in China Reflected by Impervious Surfaces from Satellite Remote Sensing. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Liang, P.; Grimmond, S.; Yang, X.; Lyu, J.; Ding, Y. Three-Dimensional Urban Thermal Effect across a Large City Cluster during an Extreme Heat Wave: Observational Analysis. J. Meteorol. Res. 2022, 36, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Tang, X.; He, J.-H.; Chen, L.-X. An East Asian Subtropical Summer Monsoon Index Defined by Moisture Transport. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2008, 14, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition: A Noise-Assisted Data Analysis Method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Wu, Z. A Review on Hilbert-Huang Transform: Method and Its Applications. Rev. Geophys. 2008, 46, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, P.; Yan, Z.-W.; Li, Z. Climatic Warming in Shanghai during 1873–2019 Based on Homogenised Temperature Records. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2022, 13, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, I.M.; Soden, B.J. Robust Responses of the Hydrological Cycle to Global Warming. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 5686–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.-S.; Panicker, A.S.; Lee, D.-I.; Park, S.-H. Estimates of Aerosol Indirect Effect from Terra MODIS over Republic of Korea. Adv. Meteorol. 2013, 2013, 976813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
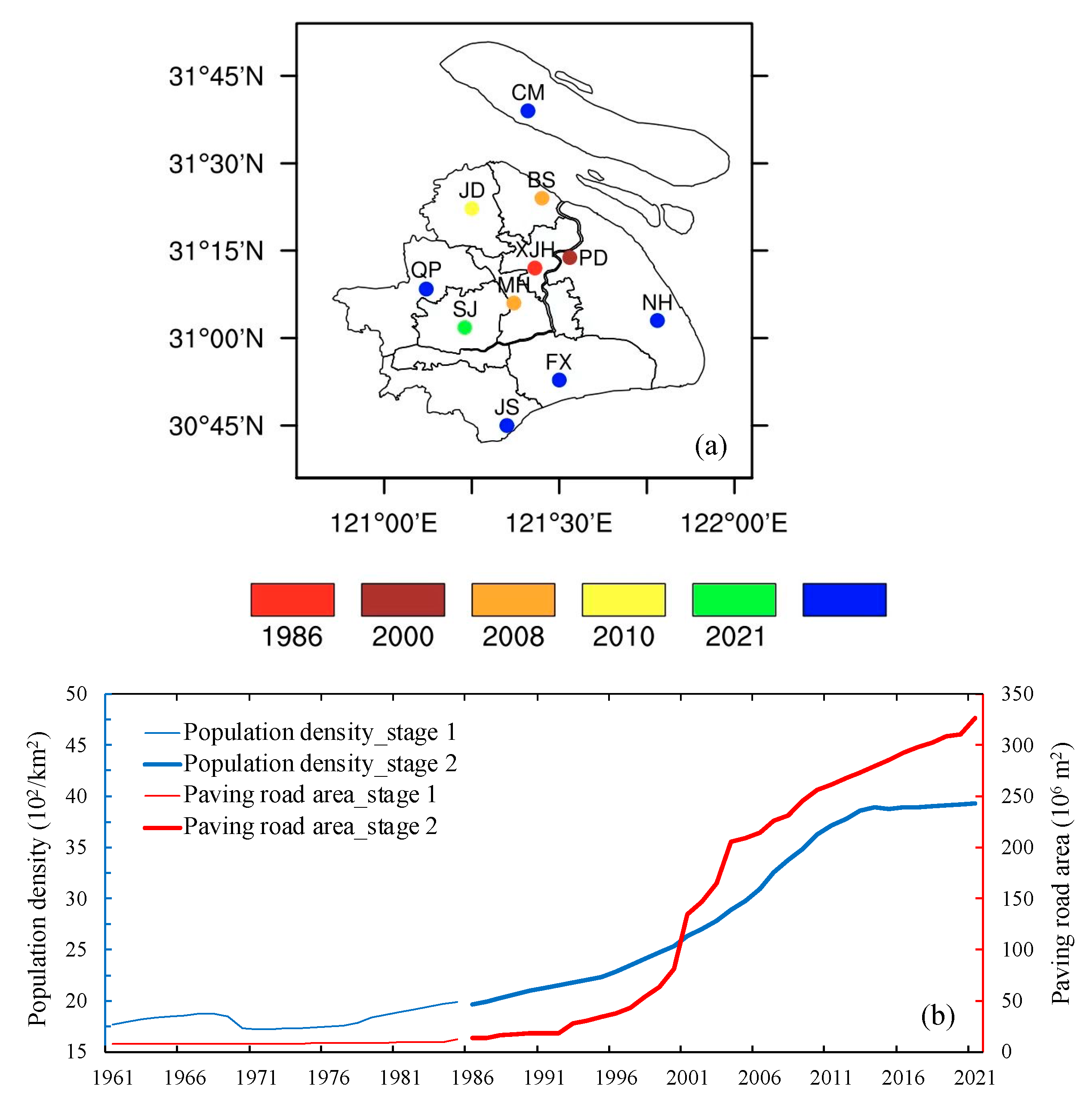
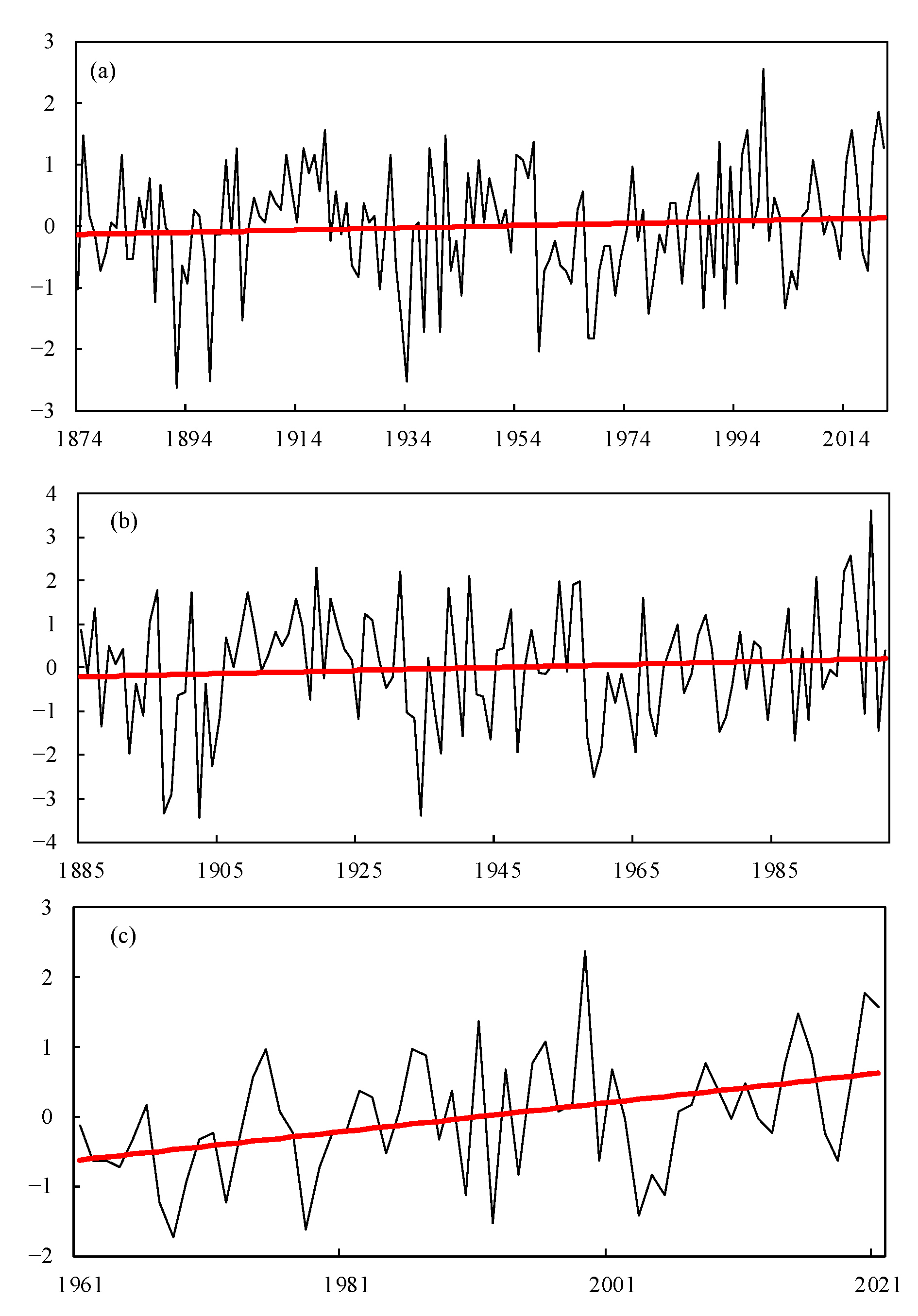
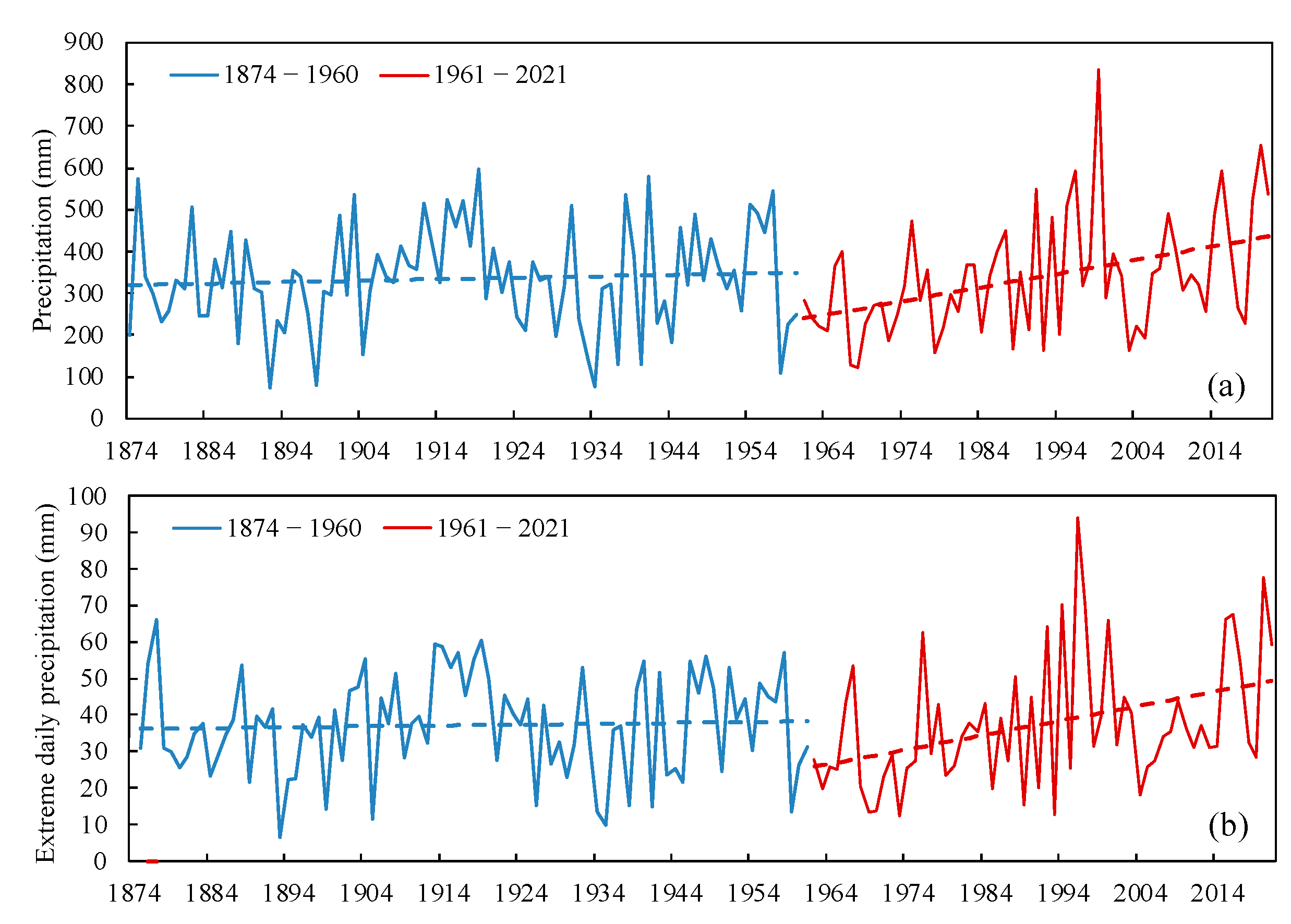
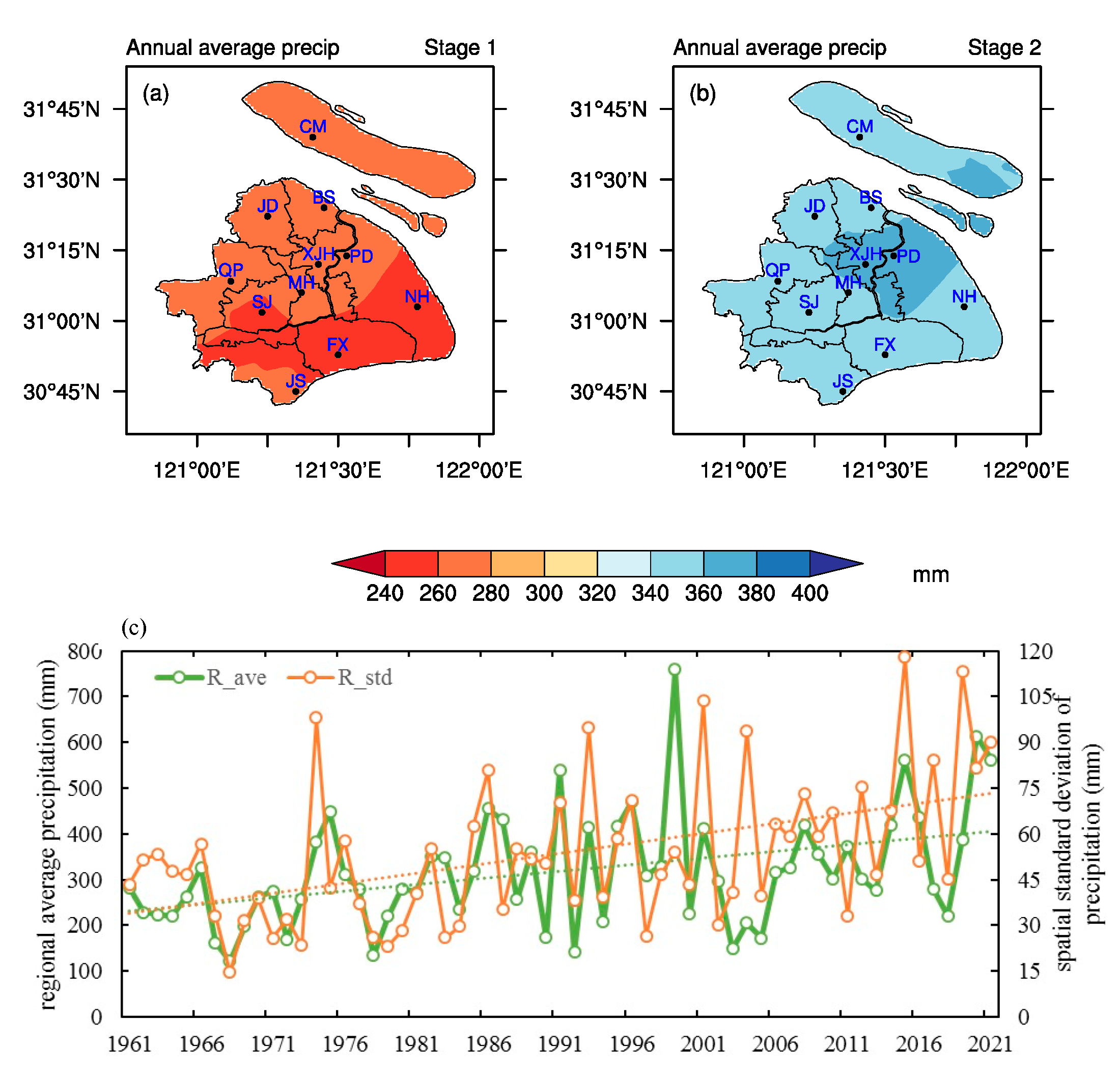


| Precipitation Component | Stage 1 (1961–1985) | Stage 2 (1986–2021) |
|---|---|---|
| Total precipitation | 0.38 | 0.07 |
| Large-scale precipitation | 0.49 | −0.08 |
| Convective precipitation | 0.07 | 0.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, W.; Zheng, Q.; Ma, Y. Combined Modification of Urbanization and Monsoon in Meiyu Precipitation Changes in the Megacity Shanghai, China. Land 2023, 12, 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12061216
Liang P, Zhang Z, Huang W, Zheng Q, Ma Y. Combined Modification of Urbanization and Monsoon in Meiyu Precipitation Changes in the Megacity Shanghai, China. Land. 2023; 12(6):1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12061216
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Ping, Zhiqi Zhang, Wenjuan Huang, Qingfeng Zheng, and Yue Ma. 2023. "Combined Modification of Urbanization and Monsoon in Meiyu Precipitation Changes in the Megacity Shanghai, China" Land 12, no. 6: 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12061216
APA StyleLiang, P., Zhang, Z., Huang, W., Zheng, Q., & Ma, Y. (2023). Combined Modification of Urbanization and Monsoon in Meiyu Precipitation Changes in the Megacity Shanghai, China. Land, 12(6), 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12061216







