Spatial Properties of Soil Physical Quality Index S in Black Soil Croplands under Permanent Gully Erosion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
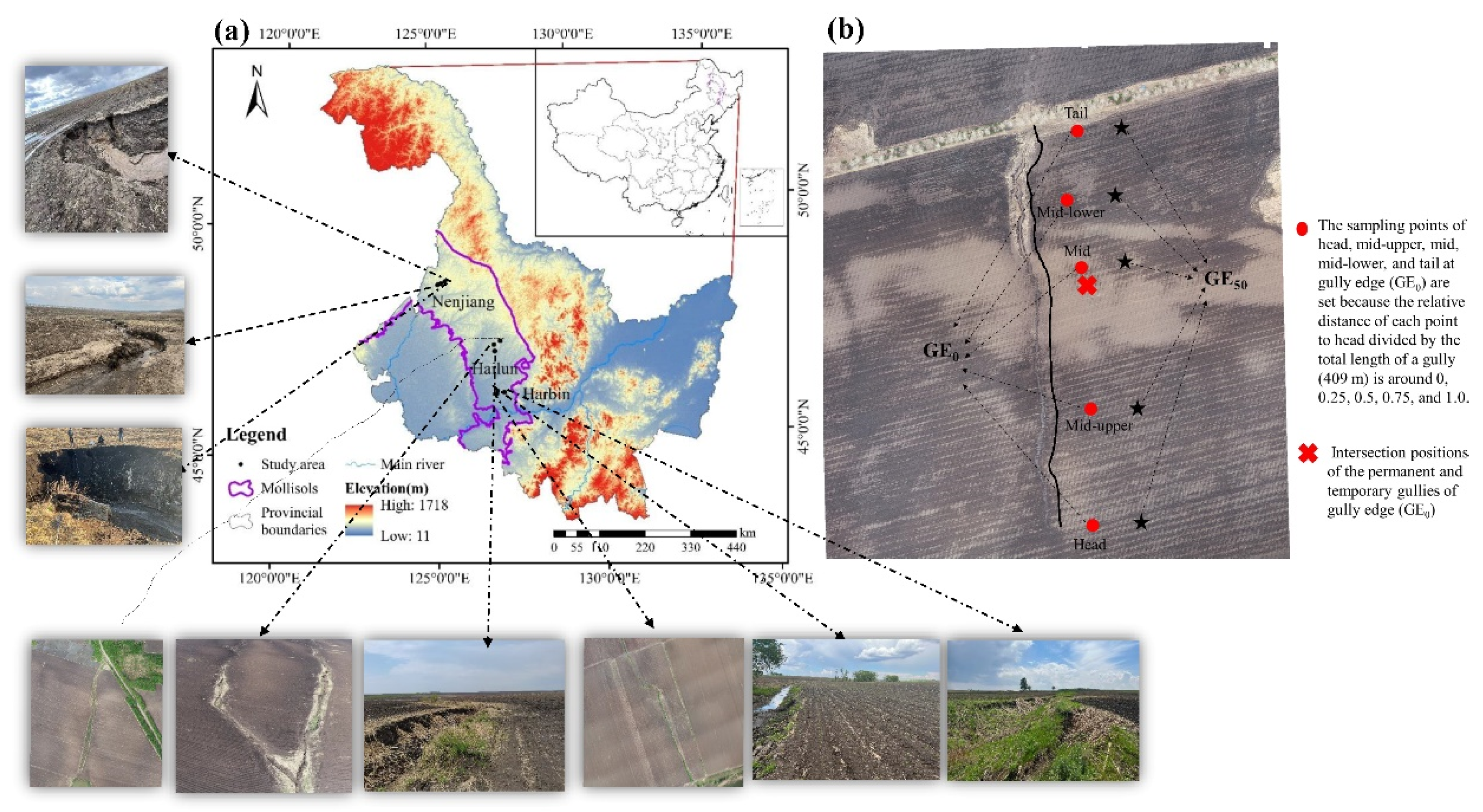
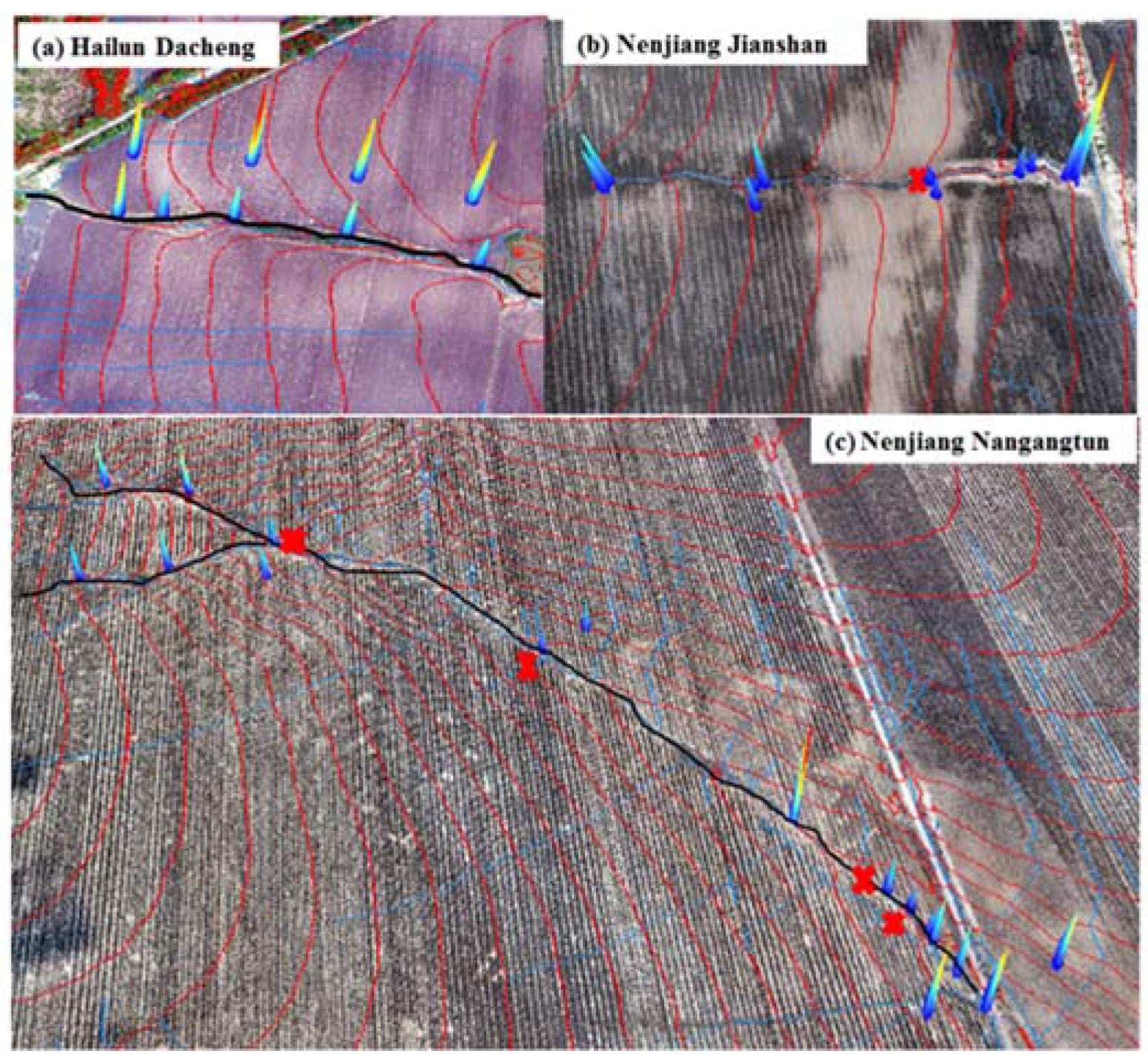
2.1. Research Site and Research Design
2.2. Soil Sampling and Measurement
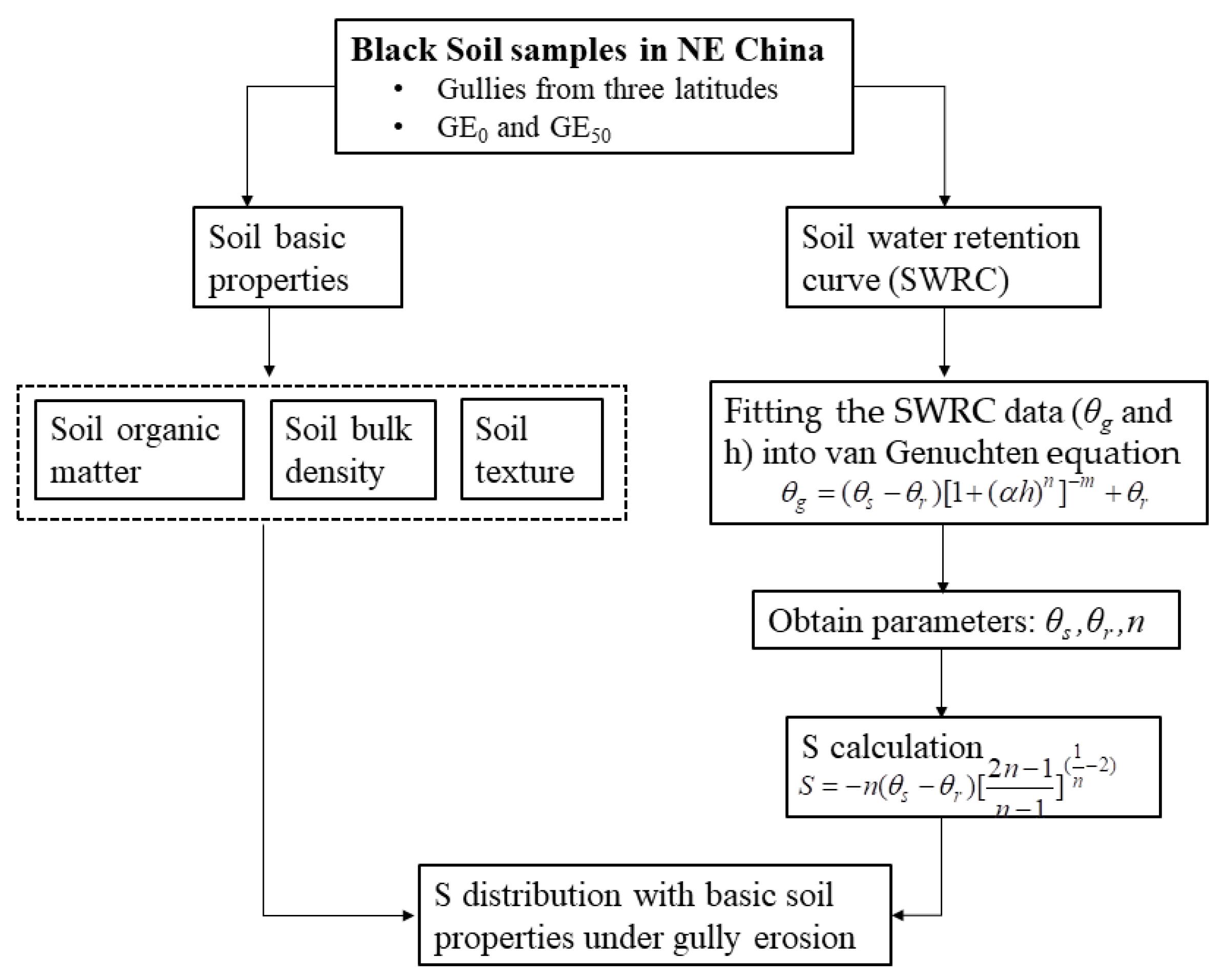
2.2.1. Soil Water Retention Curve and S Calculation
2.2.2. Soil Organic Matter and Particles
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Water Retention Curve Fitting Parameters
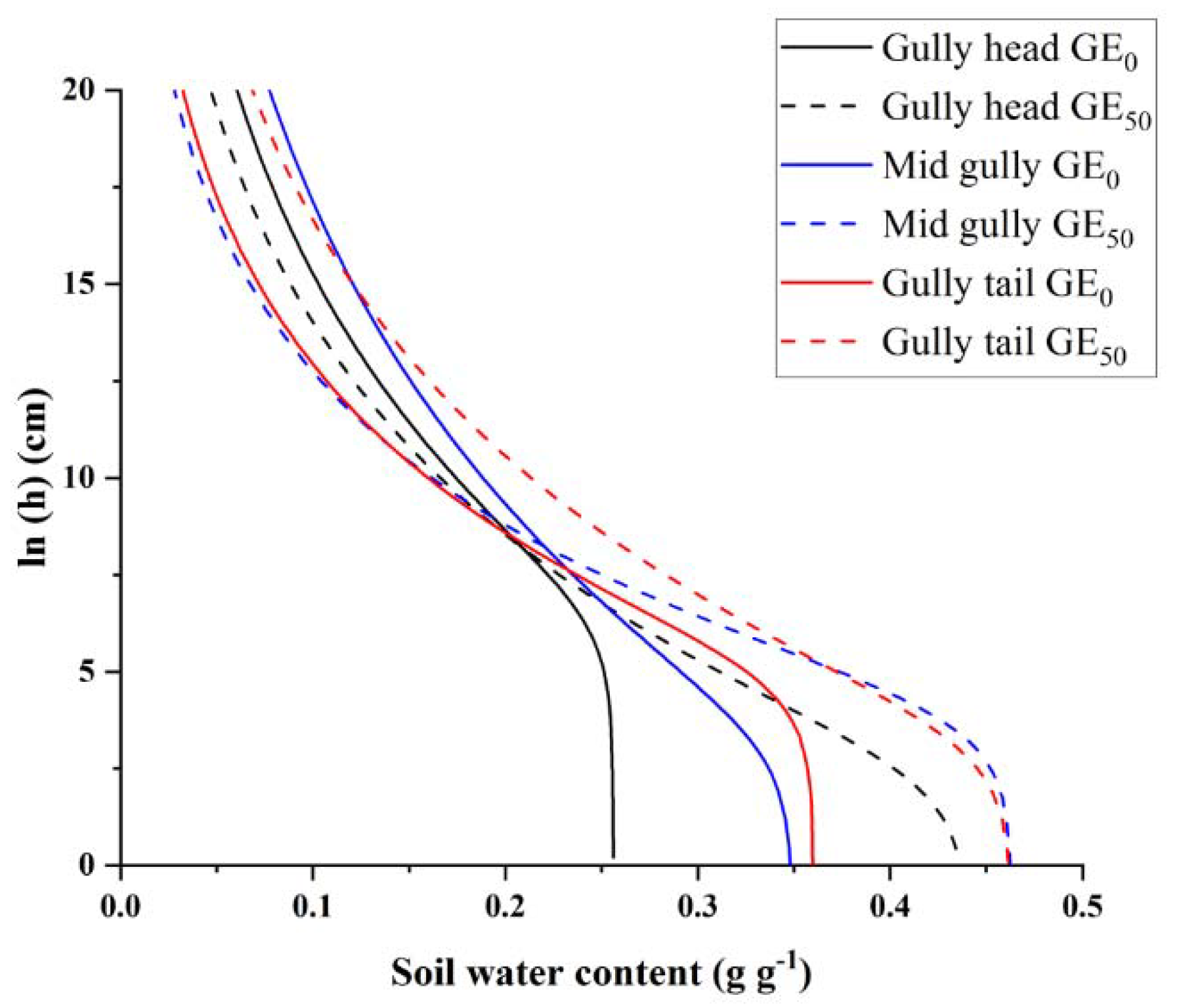
| Gully Erosion in Our Study and Other Types of Erosion in the Literature | θs | θr | α | n | S | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cm3 cm−3 | cm3 cm−3 | cm−1 | ||||
| 1 GE0 Gully head | 0.39 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.11 | 0.020 | This study (Hailun—Dacheng inclined at 1%) |
| GE0 Mid-upper gully | 0.43 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 1.10 | 0.024 | |
| GE0 Mid-gully | 0.45 | −2.54 | 0.07 | 1.01 | 0.022 | |
| GE0 Mid-lower gully | 0.49 | −0.47 | 2.83 | 1.02 | 0.018 | |
| GE0 Gully tail | 0.45 | −0.47 | 0.02 | 1.05 | 0.035 | |
| GE50 Gully head | 0.46 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 1.13 | 0.039 | |
| GE50 Mid-gully | 0.44 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 1.18 | 0.052 | |
| GE50 Gully tail | 0.52 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 1.11 | 0.038 | |
| No gully | 0.52 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 1.12 | 0.034 | |
| 2 Lightly eroded soil | 0.41 | 0.00 | 0.27 | 1.10 | 0.030 | Li et al. (2020) [28] |
| 2 Severely eroded soil | 0.30 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 1.12 | 0.025 | |
| 3 Non-erosion | 0.45 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 1.45 | 0.080 | Li et al. (2021) [22] |
| 3 Light erosion | 0.45 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 1.42 | 0.076 | |
| 3 Medium erosion | 0.44 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 1.40 | 0.071 | |
| 3 Heavy erosion | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 1.38 | 0.008 | |
| 4 Conventional tillage R | 0.045 | Tormena et al. (2008) [29] | ||||
| 4 Conventional tillage IR | 0.036 | |||||
| 5 Baseline | 0.57 | 0.73 | 1.15 | 0.058 | Wilson et al. (2019) [20] | |
| 5 Non-scraped | 0.48 | 0.15 | 1.19 | 0.056 | ||
| 5 Gully | 0.56 | 0.52 | 1.19 | 0.059 |
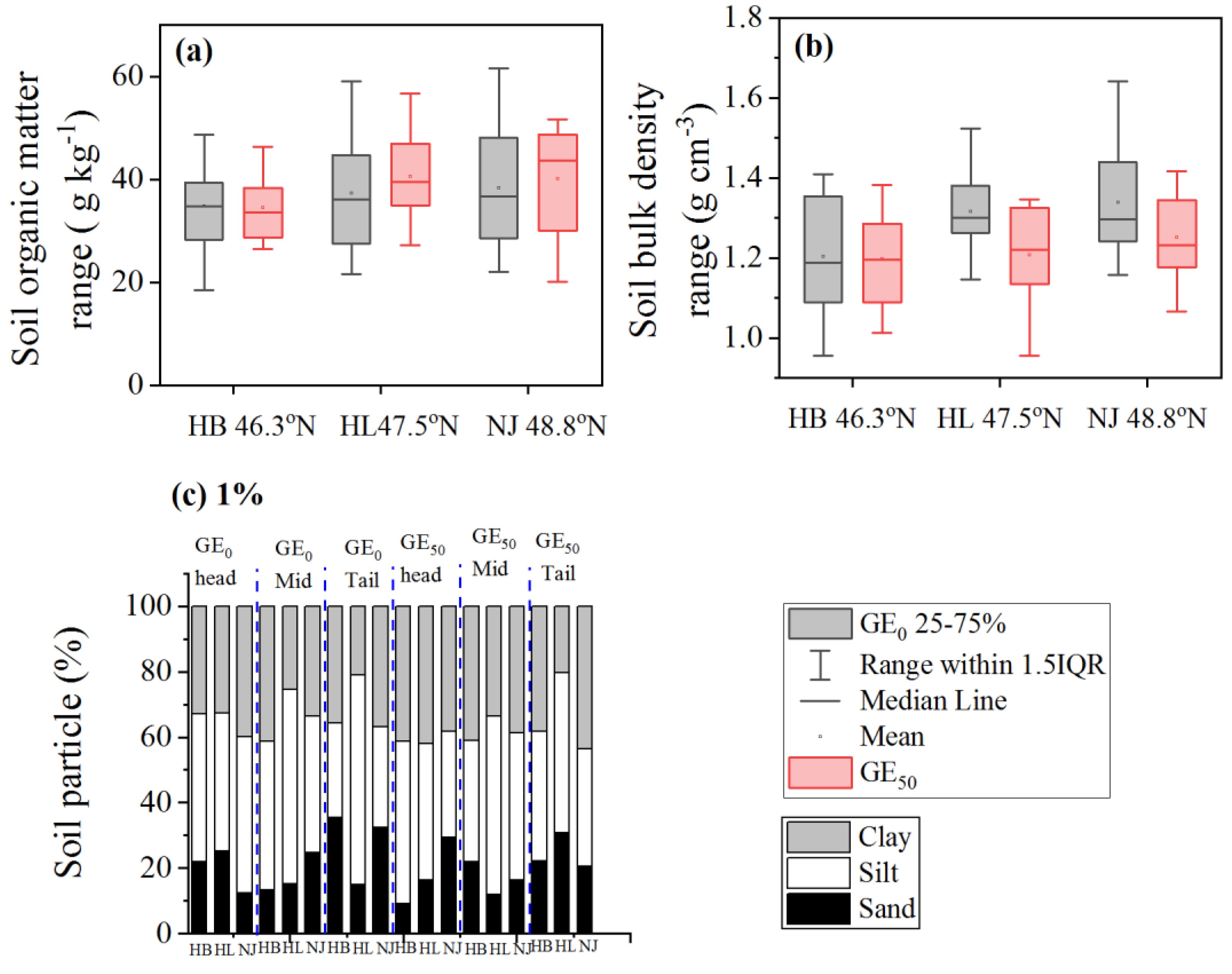
3.2. S-Index Value, SOM, and Bd Spatial Distribution
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Gully Erosion on Spatial Distribution of S
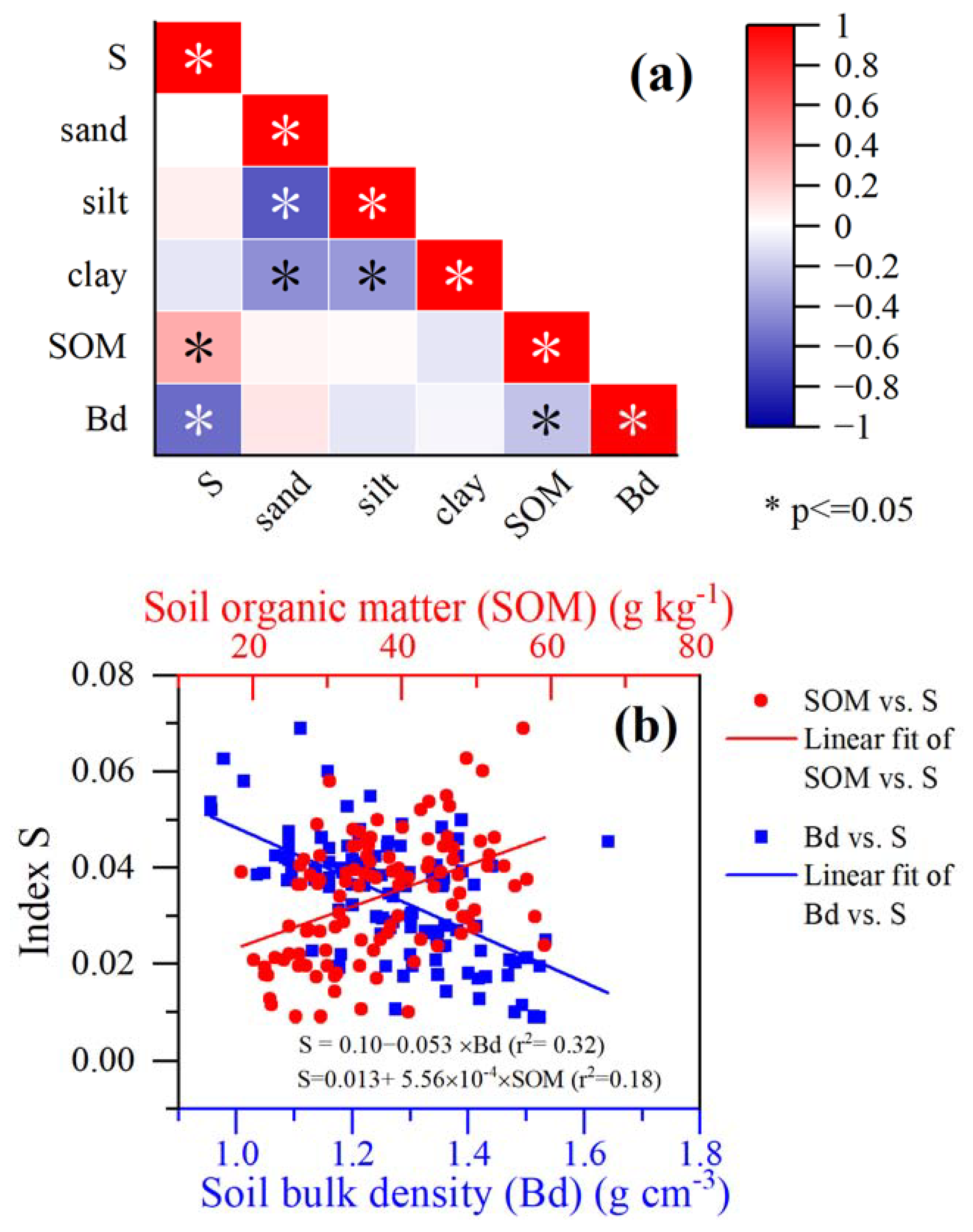
4.2. Influence of SOM, Clay Percentage, and Bd on Index S under Gully Erosion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tormena, C.A.; Karlen, D.L.; Logsdon, S.; Cherubin, M.R. Corn stover harvest and tillage impacts on near-surface soil physical quality. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 166, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, W.D.; Drury, C.F.; Tan, C.S.; Fox, C.A.; Yang, X.M. Use of indicators and pore volume-function characteristics to quantify soil physical quality. Geoderma 2009, 152, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, A.R. Soil physical quality—Part I. Theory, effects of soil texture, density, and organic matter, and effects on root growth. Geoderma 2004, 120, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Liang, A.; Jia, S.; Wei, S. Evaluation of physical quality in no-till and conventional till of a chinese Mollisol. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2015, 24, 954–958. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Xu, X.; Liu, M.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Developing pedotransfer functions to estimate the S-index for indicating soil quality. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 83, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.; Souza, E.; Netto, A.M.; de Almeida, A.Q.; Barros Junior, G.; Inacio Silva, J.R.; de Sousa Lima, J.R.; Dantas Antonino, A.C. Assessment of the physical quality of a Fluvisol in the Brazilian semiarid region. Geoderma Reg. 2017, 10, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, A.R. Soil physical quality: Part II. Friability, tillage, tilth and hard-setting. Geoderma 2004, 120, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, A.R. Soil physical quality—Part III: Unsaturated hydraulic conductivity and general conclusions about S-theory. Geoderma 2004, 120, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, N.K.; Chopra, U.K.; Singh, A.K.; Mohanty, M.; Somasundaram, J.; Chaudhary, R.S. Soil Physical Quality as Affected by Management Practices under Maize-Wheat System. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2014, 37, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlu, T.; Ersahin, S. Evaluation of soil physical quality in mollic ustifluvent, typic ustifluvent and typic ustorthent using Dexter’s S-theory. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2008, 6, 450–455. [Google Scholar]
- Naderi-Boldaji, M.; Keller, T. Degree of soil compactness is highly correlated with the soil physical quality index S. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 159, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, X. Current scenario of gully erosion and its control strategy in Mollisols areas of Northeast China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 320–326. [Google Scholar]
- Quinton, J.N.; Govers, G.; Van Oost, K.; Bardgett, R.D. The impact of agricultural soil erosion on biogeochemical cycling. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Cao, X.; Yuan, S.; Wang, W.; Feng, Y.; Qiao, B. Effects of Long-term Conservation Tillage on Soil Nutrients in Sloping Fields in Regions Characterized by Water and Wind Erosion. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T. Effects of vegetation spatial pattern on erosion and sediment particle sorting in the loess convex hillslope. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor-Mussery, A.; Laronne, J.B. The effects of gully erosion on the ecology of arid loessial agro-ecosystems, the northern Negev, Israel. Catena 2020, 194, 104712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahab, H.; Emami, H.; Haghnia, G.H. Effects of gully erosion on soil quality indices in northwestern Iran. J. Agric. Sci. Tech. 2018, 20, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Papanicolaou, A.N.; Wacha, K.M.; Abban, B.K.; Wilson, C.G.; Hatfield, J.L.; Stanier, C.O.; Filley, T.R. From soilscapes to landscapes: A landscape-oriented approach to simulate soil organic carbon dynamics in intensively managed landscapes. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2015, 120, 2375–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cruse, R.M.; Bingner, R.L.; Gesch, K.R.; Zhang, X. Evaluating ephemeral gully erosion impact on Zea mays L. yield and economics using AnnAGNPS. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.V.; Wells, R.R.; Dabney, S.M.; Zhang, T. Filling an ephemeral gully channel: Impacts on physical soil quality. Catena 2019, 174, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollobarren, P.; Capra, A.; Gelsomino, A.; La Spada, C. Effects of ephemeral gully erosion on soil degradation in a cultivated area in Sicily (Italy). Catena 2016, 145, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Wei, X.; Liu, B.; Shao, M. Soil erosion leads to degradation of hydraulic properties in the agricultural region of Northeast China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 314, 107388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J.; Nachtergaele, J.; Verstraeten, G.; Valentin, C. Gully erosion and environmental change: Importance and research needs. Catena 2003, 50, 91–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khalili, A.; Raclot, D.; Habaeib, H.; Lamachere, J.M. Factors and processes of permanent gully evolution in a Mediterranean marly environment (Cape Bon, Tunisia). Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 1519–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, G.; Xie, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Gao, Y.; Meng, L. Effect of topographic variations and tillage methods on gully erosion in the black soil region: A case-study from Northeast China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 3786–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reatto, A.; da Silva, E.M.; Bruand, A.; Martins, E.S.; Furquim Werneck Lima, J.E. Validity of the Centrifuge Method for Determining the Water Retention Properties of Tropical Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2008, 72, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, A.R.; Czyz, E.A. Applications of S-THEORY in the study of soil physical degradation and its consequences. Land Degrad. Dev. 2007, 18, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xie, Y.; Xin, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, W.; Gao, X.; Zhai, J.; Li, J. Validation and modification of the Van Genuchten model for eroded black soil in Northeastern China. Water 2020, 12, 2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tormena, C.A.; da Silva, A.P.; Del Carmen Imhoff, S.; Dexter, A.R. Quantification of the soil physical quality of a tropical Oxisol using the S index. Sci. Agric. 2008, 65, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, Q.; Wilson, G. Degradation of soil physicochemical quality by ephemeral gully erosion on sloping cropland of the hilly Loess Plateau, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavanti, R.F.R.; Montanari, R.; Panosso, A.R.; Freddi, O.S.; Paz-Gonzalez, A. Pedotransfer function to estimate the soil structural S index and spatial variability in an Oxisol within a livestock farming system. Eng. Agríc. 2020, 40, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garba, M.; Logah, V.; Wildemeersch, J.; Mahaman, S.; Yadji, G.; Quansah, C.; Bonsu, M.; Cornelis, W.; Abaidoo, R.C. Improvement in physical quality of a Sahelian Arenosol and implications on millet yield. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2016, 62, 947–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.B.; Gao, Y.H.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, J.X.; Yang, J.D.; Chen, J.Z.; Cai, C.F. Influence of gully erosion on hydraulic properties of black soil-based farmland. Catena 2023, 232, 107372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Filley, T.R.; Tong, Y.; Abban, B.; Singh, S.; Papanicolaou, A.N.T.; Wacha, K.M.; Wilson, C.G.; Chaubey, I. Tillage-induced surface soil roughness controls the chemistry and physics of eroded particles at early erosion stage. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 207, 104807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.H.; Chai, Y.F.; Chen, X.W. Effects of heavy machinery operation on the structural characters of cultivated soils in black soil region of Northeast China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 19, 351–356. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Han, S.; Zhao, P.; Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, E. Influence of soil physical and chemical properties on mechanical characteristics under different cultivation durations with Mollisols. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 224, 105520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Tullberg, J.N.; Freebairn, D.M. Wheel traffic and tillage effects on runoff and crop yield. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 97, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andruskaite, I.; Boguzas, V. Impact of tillage intensity with vertical arable layer stratification on water retention curves. Appl. Ecol. Env. Res. 2022, 20, 5277–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Nascimento, D.M.; Vieira Cavalieri-Polizeli, K.M.; da Silva, A.H.; Favaretto, N.; Parron, L.M. Soil physical quality under long-term integrated agricultural production systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 186, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igor, B.; Josip, T.L.; Paulo, P. Agriculture Management Impacts on Soil Properties and Hydrological Response in Istria (Croatia). Agronomy 2020, 10, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papiernik, S.K.; Lindstrom, M.J.; Schumacher, J.A.; Farenhorst, A.; Stephens, K.D.; Schumacher, T.E.; Lobb, D.A. Variation in soil properties and crop yield across an eroded prairie landscape. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2005, 60, 388–395. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. An Approach to the Changes of Black Soil Quality (I)—Changes of the Indices of Black Soil with the Year(s) of Reclamation. J. Shenyang Agrcultural Univ. 2002, 33, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, E.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y. Effect of Large-Scale Cultivated Land Expansion on the Balance of Soil Carbon and Nitrogen in the Tarim Basin. Agronomy 2019, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Z.; He, Y.B.; Gao, Y.H.; Chen, J.X.; Huang, Y.T.; Zhu, Y.F.; Song, F.H. Farmland damage speed and development stage of gully erosion in typical black soil region from 1970 to 2021. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 51–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Y.; Song, X.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Cai, C. Spatial Properties of Soil Physical Quality Index S in Black Soil Croplands under Permanent Gully Erosion. Land 2023, 12, 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091641
He Y, Song X, Li X, Gao Y, Yang J, Chen J, Chen J, Cai C. Spatial Properties of Soil Physical Quality Index S in Black Soil Croplands under Permanent Gully Erosion. Land. 2023; 12(9):1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091641
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Yangbo, Xingsheng Song, Xinyue Li, Yuhao Gao, Jingde Yang, Junxi Chen, Jiazhou Chen, and Chongfa Cai. 2023. "Spatial Properties of Soil Physical Quality Index S in Black Soil Croplands under Permanent Gully Erosion" Land 12, no. 9: 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091641
APA StyleHe, Y., Song, X., Li, X., Gao, Y., Yang, J., Chen, J., Chen, J., & Cai, C. (2023). Spatial Properties of Soil Physical Quality Index S in Black Soil Croplands under Permanent Gully Erosion. Land, 12(9), 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091641







