The Impact of Opening a High-Speed Railway on Urban Innovation: A Comparative Perspective of Traditional Innovation and Green Innovation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Mechanism Analysis
2.1. Literature Review
2.2. Mechanism Analysis
3. Research Design
3.1. Model Building
3.2. Variable Setting
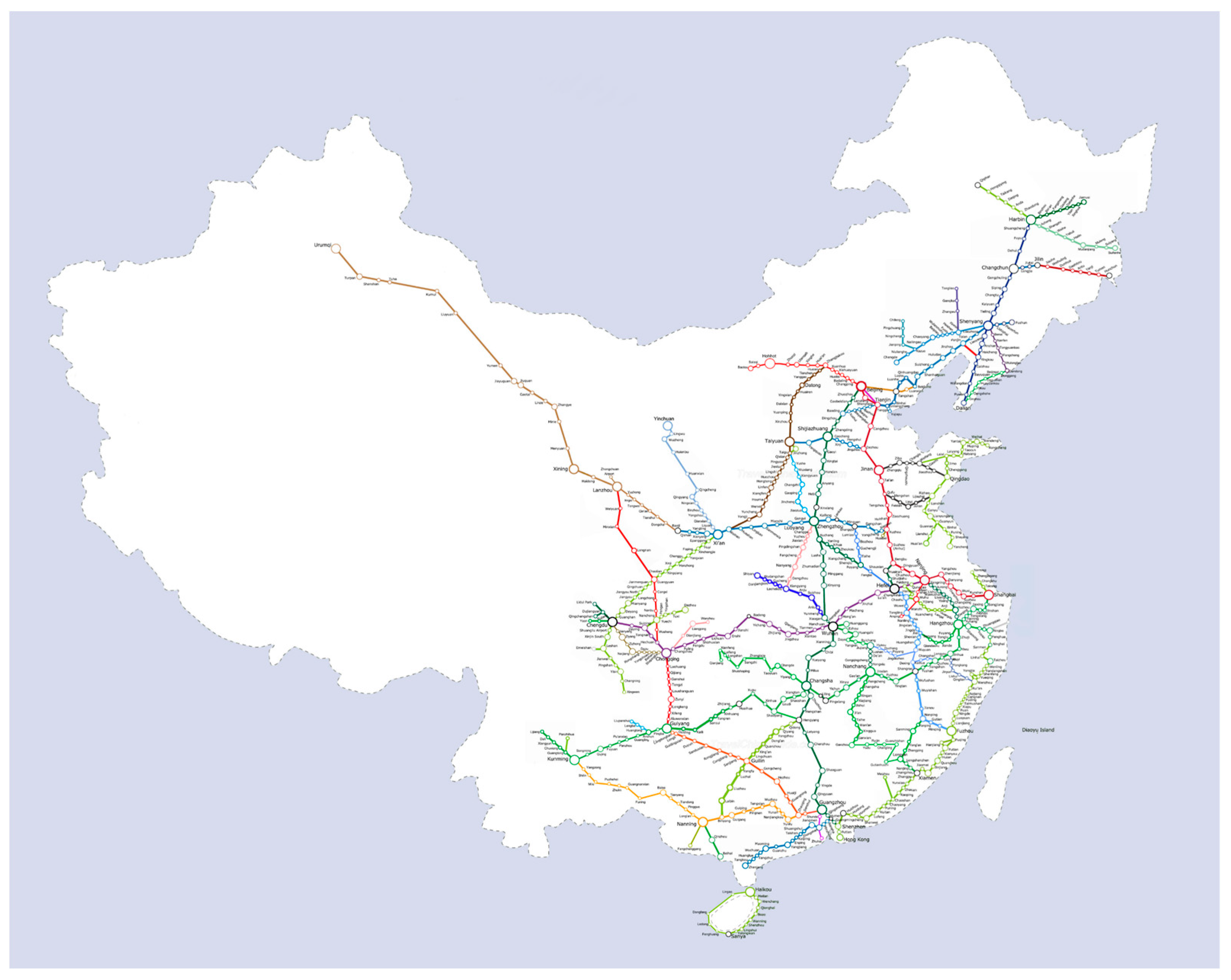
3.2.1. Core Explanatory Variable: Opening of the HSR
3.2.2. Dependent Variable: Urban Innovation
3.2.3. Control Variable
3.2.4. Subsubsection
3.3. Data
4. Empirical Results
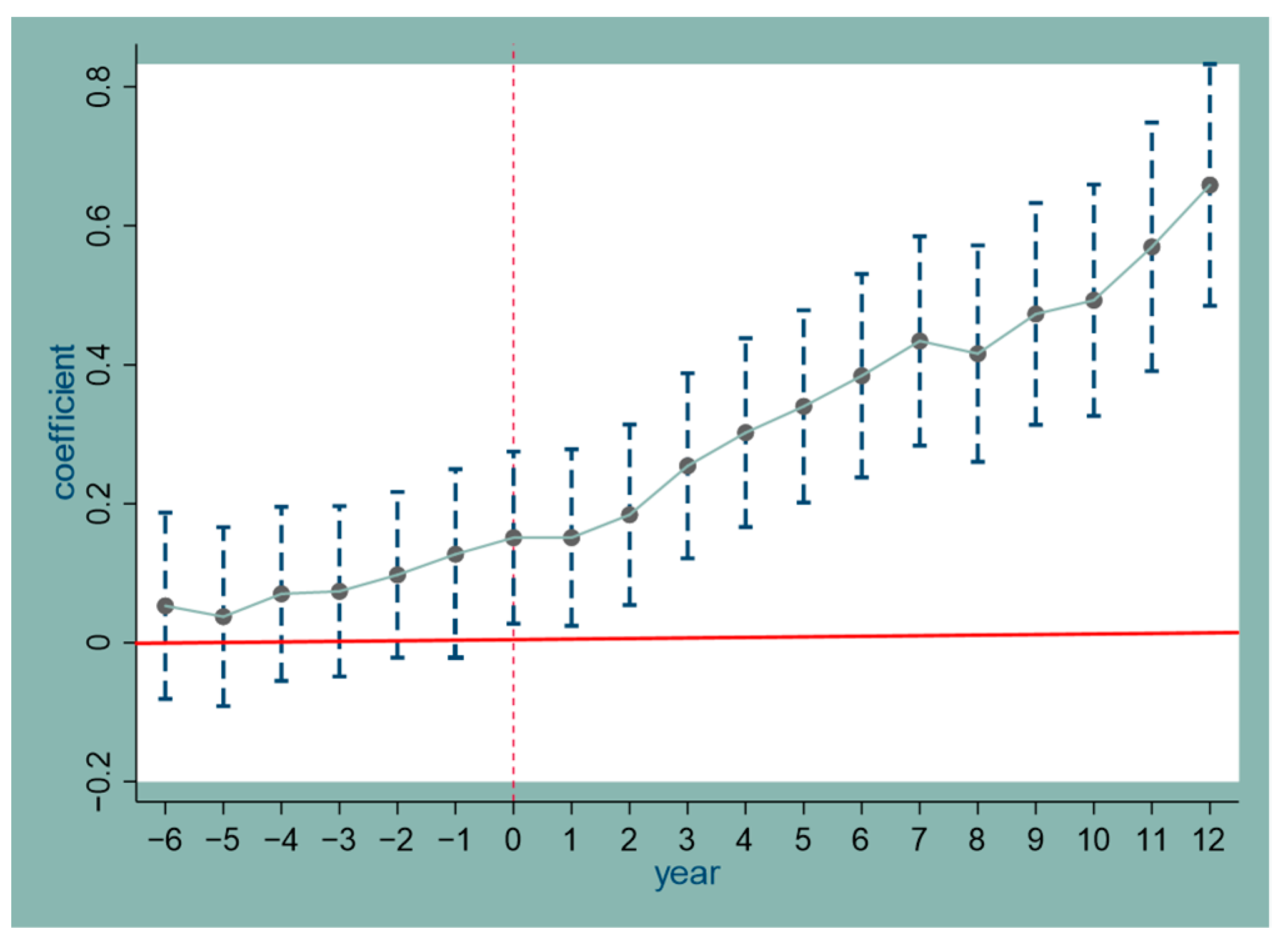
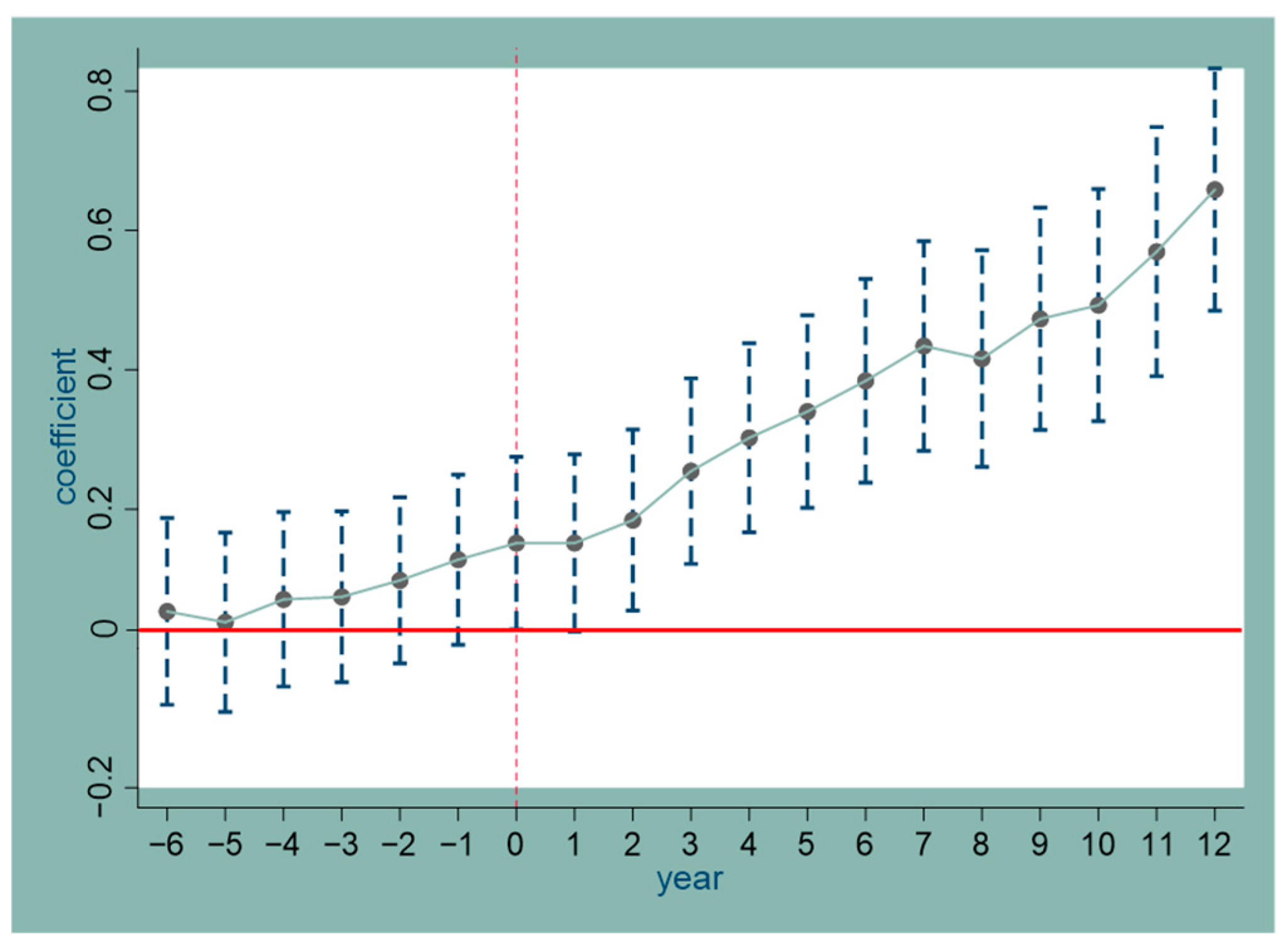
4.1. Parallel Trend Test
4.2. Basic Analysis
4.3. Robustness Test
4.3.1. Regression Analysis Based on the PSM-DID Method
4.3.2. Replace the Dependent Variable
4.3.3. Instrumental Variable Method
4.3.4. Tailed Regression
4.4. Mechanism Analysis
4.4.1. Mediating Effect Test Based on Talent Factors
4.4.2. Inspection of Regulation Mechanisms Based on Communication Infrastructure
4.5. Heterogeneity Analysis
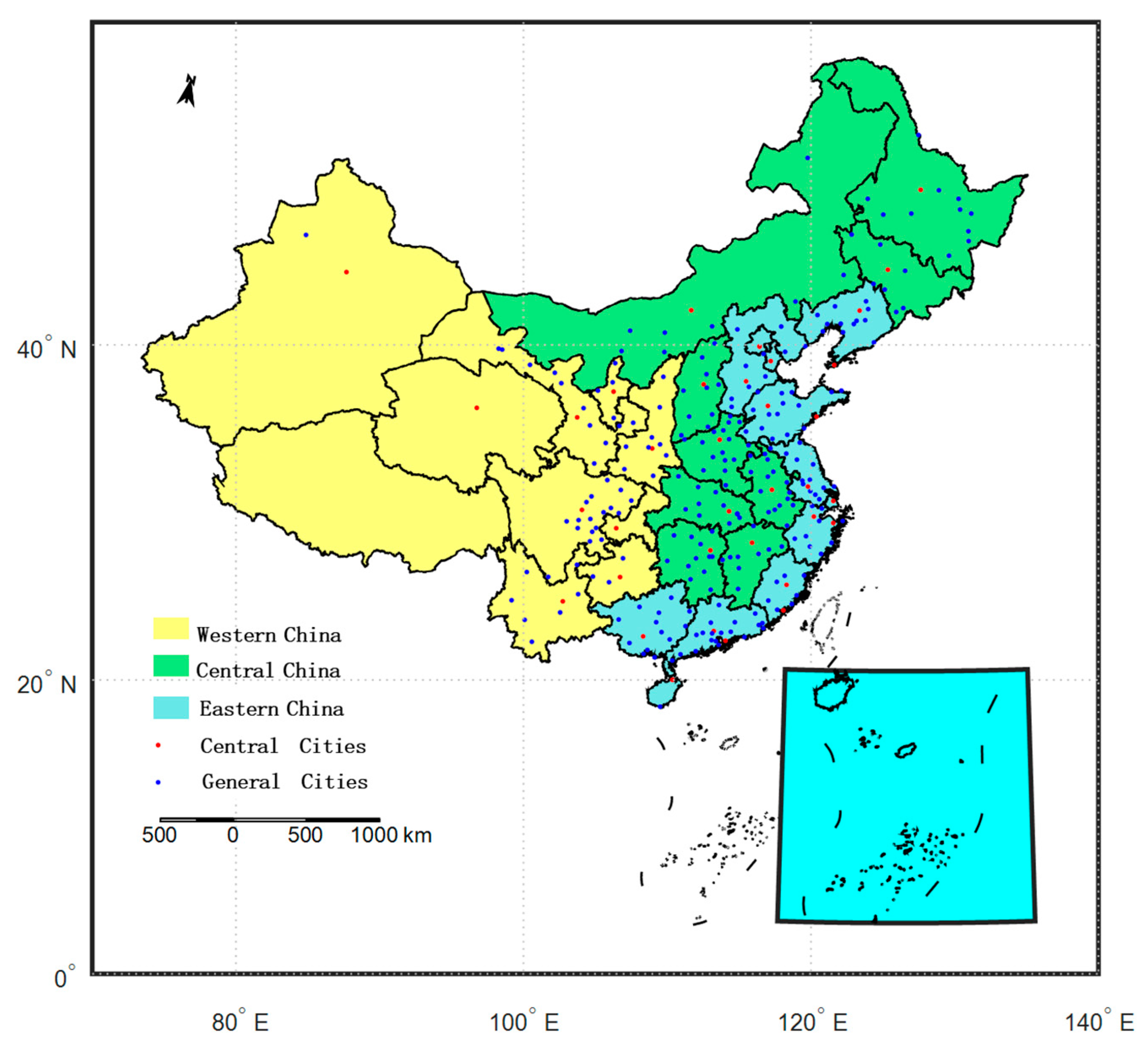
4.5.1. Location Heterogeneity
4.5.2. City-Level Heterogeneity
5. Conclusions and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaw, S.; Fang, Z.; Lu, S.; Tao, R. Impacts of high-speed rail on railroad network accessibility in China. J. Transp. Geogr. 2014, 40, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Lin, S.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, J. Does high-speed railway promote regional innovation growth or innovation convergence? Technol. Soc. 2021, 64, 101472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, J. Operation of high-speed rail and reduction of corporate pollution: Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2023, 30, 3562–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meersman, H.; Nazemzadeh, M. The contribution of transport infrastructure to economic activity: The case of Belgium. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2017, 5, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.T.; Liu, T.Y. Does the high-speed rail network improve economic growth? Pap. Reg. Sci. 2022, 101, 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, R.E., Jr. On the mechanics of economic development. J. Monet. Econ. 1988, 22, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, X. High-speed rail and urban innovation: Based on the perspective of labor mobility. J. Asia Pac. Econ. 2022, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lu, H.; Lv, Y. High-speed railway Facilities, Intercity Accessibility and Urban Innovation Level—Evidence from Cities in Three Chinese Megacity Regions. Land 2022, 11, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, D.; Li, J.; Wu, M. High-speed railways and collaborative innovation. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2022, 93, 103717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fan, Q.; Tao, C. The Impact of High-Speed Rail on Regional Green Innovation Performance-Based on the Dual Perspective of High-Speed Rail Opening and High-Speed Rail Network. Policy J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 32, 106795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y. How does high-speed railway affect green innovation efficiency? A perspective of innovation factor mobility. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 265, 121623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, X.; Tao, L. The impact mechanism of high-speed railway on regional green innovation spillover under multi-dimensional paths. Environ. Impact Asses. 2022, 95, 106795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cai, S. The construction of high-speed rail and urban innovation capacity: Based on the perspective of knowledge Spillover. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 63, 101539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, T.; Wang, Z. High-speed rail and Collaborative Innovation: Evidence from University Patents in China. SSRN Electron. J. 2020. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/338660579_High-Speed_Railway_and_Collaborative_Innovation_Evidence_from_University_Patents_in_China (accessed on 7 July 2023).
- Zhenkai, S.; Jun, S.; Zhengning, P. Transportation infrastructure and productivity growth: Effects of railway speed-up on firm’s TFP in China. China Econ. 2018, 13, 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Hassink, R. How to unlock regional economies from path dependency? From learning region to learning cluster. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2005, 13, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassink, R. Regional innovation support systems: Recent trends in Germany and East Asia. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2002, 10, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simandan, D. Options for moving beyond the canonical model of regional path dependence. Int. J. Urban Reg. 2012, 36, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantos, P.; Gumbau Albert, M.; Maudos, J. Transport infrastructures, spillover effects and regional growth: Evidence of the Spanish case. Transp. Rev. 2005, 25, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaringella, L.; Chanaron, J. Grenoble–GIANT Territorial Innovation Models: Are investments in research infrastructures worthwhile? Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2016, 112, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsekouras, K.; Chatzistamoulou, N.; Kounetas, K.; Broadstock, D.C. Spillovers, path dependence and the productive performance of European transportation sectors in the presence of technology heterogeneity. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2016, 102, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, M.; Slavtchev, V. Determinants of the efficiency of regional innovation systems. Reg. Stud. 2011, 45, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.R.; Dingel, J.I. A spatial knowledge economy. Am. Econ. Rev. 2019, 109, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simandan, D. Roads to perdition in the knowledge economy. Environ. Plan. A 2010, 42, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beule, F.; Van Beveren, I. Does firm agglomeration drive product innovation and renewal? An application for Belgium. Tijdschr. Econ. Soc. Ge 2012, 103, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acemoglu, D.; Moscona, J.; Robinson, J.A. State capacity and American technology: Evidence from the nineteenth century. Am. Econ. Rev. 2016, 106, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, B. Trade integration, market size, and industrialization: Evidence from China’s National Trunk Highway System. Rev. Econ. Stud. 2014, 81, 1046–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum-Snow, N.; Brandt, L.; Henderson, J.V.; Turner, M.A.; Zhang, Q. Roads, railroads, and decentralization of Chinese cities. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2017, 99, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Razzaq, A.; Kizys, R.; Bao, Q. High-speed rail and urban green productivity: The mediating role of climatic conditions in China. Technol. Forecast Soc. 2022, 185, 122055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Lin, X.; Yang, H. Corrigendum to “Booming with Speed: High-speed rail and Regional Green Innovation”. J. Adv. Transp. 2022, 2022, 9859614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Zhai, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, W.; Lu, J. How to promote the development of a green economy: Talent or technology? —Evidence from China’s high-speed rail. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 953506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaap, T.; Oosterhaven, J. Measuring the welfare effects of infrastructure: A simple spatial equilibrium evaluation of Dutch railway proposals. Res. Transp. Econ. 2011, 31, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Mei, L. Policy-driven open strategy: Lessons from China’s high-speed rail industry. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2022, 63, 101671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zheng, J. The impact of high-speed rail on innovation: An empirical test of the companion innovation hypothesis of transportation improvement with China’s manufacturing firms. World Dev. 2020, 127, 104838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Xu, Y. Does high-speed rail promote urban innovation? Evidence from China. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2023, 86, 101464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wan, K. How does the selection of national development zones affect urban green innovation?—Evidence from China. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e268111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J. Can High-Speed Rail Help Achieve Urban Green Development? From a Spatial Perspective. Front. Env. Sci-Switz. 2022, 10, 894697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, X. Collaborative evolution of regional green innovation system under the influence of high-speed rail based on Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2022, 29, 69101–69116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnoz, P.; Lelarge, C.; Trevien, C. Communication costs and the internal organisation of multi-plant businesses: Evidence from the impact of the French high-speed rail. Econ. J. 2018, 128, 949–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. High-speed railway, factor flow and enterprise innovation efficiency: An empirical analysis on micro data. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2022, 82, 101305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yan, J.; Ran, Q.; Yang, X.; Su, X.; Shen, J. Does the opening of high-speed railways improve urban livability? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2022, 82, 101275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Lin, X.; Yang, H. Booming with speed: High-speed rail and regional green innovation. J. Adv. Transp. 2021, 2021, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Cai, M.; Wong, W. Impacts of high-speed rail on the industrial developments of non-central cities in China. Transp. Policy 2023, 134, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Su, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y. The impact of High-Speed Rail opening on city economics along the Silk Road Economic Belt. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Meng, W.; Hou, X. The impact of high-speed rails on urban economy: An investigation using night lighting data of Chinese cities. Res. Transp. Econ. 2020, 80, 100819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autor, D.H. Outsourcing at will: The contribution of unjust dismissal doctrine to the growth of employment outsourcing. J. Labor. Econ. 2003, 21, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, J. The influence of high-speed rails on urban innovation and the underlying mechanism. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e264779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, T.; Levine, R.; Levkov, A. Big bad banks? The winners and losers from bank deregulation in the United States. J. Financ. 2010, 65, 1637–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, P.R.; Rubin, D.B. The central role of the propensity score in observational studies for causal effects. Biometrika 1983, 70, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSR | 4845 | 0.286 | 0.452 | 0 | 1 |
| Ln(Innoit + 1) | 4845 | 3.957 | 1.964 | 0 | 10.876 |
| Ln(Ginnoit + 1) | 4845 | 2.068 | 1.75 | 0 | 8.872 |
| LnPgdp | 4845 | 10.085 | 0.988 | 6.924 | 14.461 |
| Ind | 4845 | 0.385 | 0.095 | 0.086 | 0.835 |
| LnFdi | 4845 | 11.387 | 2.144 | 0 | 16.835 |
| Fin | 4845 | 0.391 | 0.067 | 0.056 | 0.861 |
| Urb | 4845 | 0.354 | 0.241 | 0.034 | 1.036 |
| LnStu | 4845 | 4.003 | 0.282 | 1.841 | 5.96 |
| LnNet | 4845 | 4.493 | 1.123 | −2.807 | 8.206 |
| Sup | 4845 | 0.196 | 0.049 | 0.011 | 0.519 |
| LnInf | 4845 | 6.477 | 0.880 | 3.766 | 10.355 |
| Tal | 4845 | 0.018 | 0.024 | 0.000 | 0.143 |
| Slope | 4845 | 10.617 | 5.584 | 1.592 | 27.139 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ln(Innoit + 1) | Ln(Ginnoit + 1) | |||||
| HSR | 0.239 *** | 0.536 *** | 0.202 *** | 0.376 *** | 0.603 *** | 0.288 *** |
| (0.026) | (0.029) | (0.026) | (0.030) | (0.031) | (0.030) | |
| LnPgdp | 0.755 *** | 0.055 | 0.574 *** | 0.022 | ||
| (0.029) | (0.041) | (0.030) | (0.047) | |||
| Ind | 2.209 *** | −0.524 ** | 3.149 *** | 0.444 * | ||
| (0.191) | (0.209) | (0.199) | (0.234) | |||
| LnFdi | 0.055 *** | −0.003 | 0.059 *** | 0.004 | ||
| (0.009) | (0.008) | (0.009) | (0.009) | |||
| Fin | 1.916 *** | 1.382 *** | 1.841 *** | 1.073 *** | ||
| (0.197) | (0.182) | (0.207) | (0.204) | |||
| Urb | 0.355 ** | 0.177 | 0.834 *** | 0.748 *** | ||
| (0.144) | (0.166) | (0.143) | (0.187) | |||
| LnStu | −0.421 *** | 0.088 * | −0.436 *** | −0.015 | ||
| (0.055) | (0.050) | (0.058) | (0.056) | |||
| LnNet | 0.361 *** | 0.0273 | 0.221 *** | −0.094 *** | ||
| (0.020) | (0.019) | (0.021) | (0.021) | |||
| Sup | 3.384 *** | 3.462 *** | 3.971 *** | 4.369 *** | ||
| (0.301) | (0.282) | (0.315) | (0.317) | |||
| Constant | 7.668 *** | −6.816 *** | 5.709 *** | 6.144 *** | −6.817 *** | 4.105 *** |
| (0.128) | (0.379) | (0.539) | (0.145) | (0.393) | (0.606) | |
| Controls | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Year F.E. | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| City F.E. | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| R2 | 0.8316 | 0.7812 | 0.8398 | 0.7371 | 0.6978 | 0.7544 |
| Observations | 4845 | 4845 | 4845 | 4845 | 4845 | 4845 |
| Number of id | 285 | 285 | 285 | 285 | 285 | 285 |
| (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | (11) | (12) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | Ln(Innoit + 1) | Ln(Ginnoit + 1) | ||||
| Pre-Policy | Post-Policy | DID | Pre-Policy | Post-Policy | DID | |
| Difference | 0.204 | 0. 235 | 0.021 | 0.276 | 0. 308 | 0.032 |
| S.E. | 0.042 | 0.067 | 0.092 | 0.041 | 0.065 | 0.087 |
| T-stat | 4.8 | 0.96 | 2.85 | 2.26 | 0.083 | 1.87 |
| P | 0.000 *** | 0.239 | 0.007 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.206 | 0.003 *** |
| Variables | (13) | (14) | (15) | (16) | (17) | (18) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ln(Innoit + 1) | Ln(Ginnoit + 1) | |||||
| HSR | 0.107 *** | 0.469 *** | 0.129 *** | 0.234 *** | 0.546 *** | 0.216 *** |
| (0.028) | (0.033) | (0.028) | (0.029) | (0.031) | (0.029) | |
| LnPgdp | 0.781 *** | 0.062 | 0.769 *** | 0.117 ** | ||
| (0.032) | (0.044) | (0.031) | (0.045) | |||
| Ind | 1.125 *** | −1.381 *** | 3.051 *** | −0.845 *** | ||
| (0.212) | (0.224) | (0.203) | (0.229) | |||
| LnFdi | 0.079 *** | −0.014 | 0.057 *** | −0.003 | ||
| (0.010) | (0.008) | (0.009) | (0.009) | |||
| Fin | 1.174 *** | 1.170 *** | 1.491 *** | 1.218 *** | ||
| (0.220) | (0.195) | (0.210) | (0.199) | |||
| Urb | 0.039 | −0.135 | 0.278 * | 0.169 | ||
| (0.152) | (0.178) | (0.147) | (0.182) | |||
| LnStu | −0.544 *** | 0.112 ** | −0.428 *** | 0.054 | ||
| (0.062) | (0.053) | (0.059) | (0.055) | |||
| LnNet | 0.494 *** | 0.130 *** | 0.437 *** | 0.048 ** | ||
| (0.022) | (0.020) | (0.021) | (0.021) | |||
| Sup | 2.239 *** | 1.469 *** | 2.786 *** | 2.923 *** | ||
| (0.336) | (0.303) | (0.321) | (0.309) | |||
| Constant | 8.361 *** | −5.011 *** | 7.277 *** | 6.598 *** | −7.913 *** | 4.436 *** |
| (0.136) | (0.419) | (0.578) | (0.139) | (0.401) | (0.591) | |
| Controls | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Year F.E. | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| City F.E. | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| R2 | 0.8393 | 0.7678 | 0.8454 | 0.8339 | 0.7872 | 0.8393 |
| Observations | 4845 | 4845 | 4845 | 4845 | 4845 | 4845 |
| Variables | (19) | (20) |
|---|---|---|
| Ln(Innoit + 1) | Ln(Ginnoit + 1) | |
| HSR | 2.496 *** (0.826) | 2.357 *** (0.779) |
| Constant | −2.420 *** (0.798) | −3.297 *** (0.742) |
| Controls | Yes | Yes |
| Year F.E. | Yes | Yes |
| City F.E. | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.7107 | 0.6954 |
| First-stage regressions IV | −0.004 *** (0.001) | −0.004 *** (0.001) |
| Cragg–Donald Wald F statistics | 17.645 | 17.645 |
| Wu–Hausman | p = 0.012 | p = 0.011 |
| Observations | 4845 | 4845 |
| Variables | (21) | (22) | (23) | (24) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ln(Innoit + 1) | Ln(Ginnoit + 1) | |||
| 1% | 5% | 1% | 5% | |
| HSR | 0.200 *** | 0.198 *** | 0.285 *** | 0.265 *** |
| (0.026) | (0.027) | (0.030) | (0.030) | |
| LnPgdp | 0.009 | −0.014 | −0.015 | 0.022 |
| (0.041) | (0.039) | (0.046) | (0.044) | |
| Ind | −0.429 ** | 0.277 | 0.508 ** | 1.222 *** |
| (0.212) | (0.223) | (0.238) | (0.253) | |
| LnFdi | 0.010 | 0.028 *** | 0.017 * | 0.038 *** |
| (0.009) | (0.010) | (0.010) | (0.011) | |
| Fin | 1.656 *** | 1.594 *** | 1.308 *** | 1.380 *** |
| (0.198) | (0.218) | (0.222) | (0.247) | |
| Urb | 0.174 | −0.100 | 0.702 *** | 0.264 |
| (0.167) | (0.169) | (0.188) | (0.191) | |
| LnStu | 0.062 | −0.058 | −0.028 | −0.064 |
| (0.053) | (0.058) | (0.060) | (0.066) | |
| LnNet | 0.076 *** | 0.163 *** | −0.067 *** | 0.025 |
| (0.021) | (0.024) | (0.024) | (0.027) | |
| Sup | 3.792 *** | 3.240 *** | 4.718 *** | 3.996 *** |
| (0.299) | (0.326) | (0.336) | (0.370) | |
| Constant | 4.949 *** | 3.916 *** | 3.284 *** | 1.371** |
| (0.541) | (0.530) | (0.607) | (0.601) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year F.E. | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City F.E. | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.841 | 0.841 | 0.751 | 0.729 |
| Observations | 4845 | 4845 | 4845 | 4845 |
| Variables | (25) | (26) | (27) | (28) | (29) | (30) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ln(Innoit + 1) | Ln(Ginnoit + 1) | |||||
| Talantit | Ln(Innoit + 1) | Ln(Innoit + 1) | Talantit | Ln(Ginnoit + 1) | Ln(Ginnoit + 1) | |
| Talantit | 0.002 *** | 0.002 *** | ||||
| (0.000) | (0.000) | |||||
| HSR | 37.356 *** | 0.582 *** | 0.655 *** | 37.356 *** | 0.627 *** | 0.704 *** |
| (6.596) | (0.038 | (0.040) | (6.596) | (0.036) | (0.039) | |
| LnPgdp | 16.060 *** | −0.035 | −0.003 | 16.060 *** | −0.020 | 0.013 |
| (3.901) | (0.023) | (0.023) | (3.901) | (0.021) | (0.023) | |
| Ind | 786.585 *** | 1.404 *** | 2.932 *** | 786.585 *** | 1.534 *** | 3.146 *** |
| (30.521) | (0.188) | (0.186) | (30.521) | (0.178) | (0.178) | |
| LnFdi | 28.361 *** | 0.289 *** | 0.344 *** | 28.361 *** | 0.218 *** | 0.276 *** |
| (1.308) | (0.008) | (0.008) | (1.308) | (0.008) | (0.008) | |
| Fin | 303.185 *** | 1.352 *** | 1.941 *** | 303.185 *** | 1.347 *** | 1.968 *** |
| (37.474) | (0.218) | (0.228) | (37.474) | (0.207) | (0.219) | |
| Urb | 316.208 *** | −0.342 *** | 2.273 *** | 316.208 *** | −0.050 | 0.598 *** |
| (12.506) | (0.077) | (0.077) | (12.506) | (0.073) | (0.074) | |
| LnStu | 54.990 *** | −0.582 *** | −0.475 *** | 54.990 *** | −0.535 *** | −0.422 *** |
| (9.624) | (0.056) | (0.059) | (9.624) | (0.053) | (0.056) | |
| LnNet | −5.842 | 0.674 *** | 0.663 *** | −5.842 | 0.484 *** | 0.472 *** |
| (3.717) | (0.021) | (0.023) | (3.717) | (0.020) | (0.022) | |
| Sup | −345.319 *** | 4.485 *** | 3.814 *** | −345.319 *** | 3.834 *** | 3.126 *** |
| (53.008) | (0.307) | (0.323) | (53.008) | (0.291) | (0.310) | |
| Constant | −974.920 *** | −2.027 *** | −3.921 *** | −974.920 *** | −2.648 *** | 4.646 *** |
| (54.090) | (0.334) | (0.342) | (56.090) | (0.316) | (0.328) | |
| Sobel Goodman-1 | 0.073 ***(z = 5.505) 0.073 ***(z = 5.500) | 0.077 ***(z = 5.534) 0.077 ***(z = 5.553) | ||||
| Goodman-1 | 0.073 ***(z = 5.509) | 0.077 ***(z = 5.538) | ||||
| Indirect effect | 0.073 ***(z = 5.505) | 0.077 ***(z = 5.534) | ||||
| Direct effect | 0.582 ***(z = 15.238) | 0.627 ***(z = 17.312) | ||||
| Total effect | 0.655 ***(z = 16.298) | 0.704 ***(z = 18.258) | ||||
| Mediating effect ratio | 11.08% | 10.88% | ||||
| Controls R2 Observations | Yes 0.516 4845 | Yes 0.756 4845 | Yes 0.726 4845 | Yes 0.516 4845 | Yes 0.724 4845 | Yes 0.685 4845 |
| Variables | (31) | (32) | (33) | (34) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ln(Innoit + 1) | Ln(Ginnoit + 1) | |||
| HSR | 0.202 *** | 0.173 *** | 0.288 *** | 0.225 *** |
| (0.0263) | (0.0277) | (0.0295) | (0.0310) | |
| LnInf | 0.0342 | 0.00418 | 0.0189 | |
| (0.0209) | (0.0234) | (0.0234) | ||
| c.c_HSR#c.c_LnInf | 0.0873 *** | 0.178 *** | ||
| (0.0249) | (0.0279) | |||
| LnPgdp | 0.0551 | 0.0477 | 0.0211 | 0.0153 |
| (0.0414) | (0.0415) | (0.0467) | (0.0465) | |
| Ind | −0.524 ** | −0.581 *** | 0.444 * | 0.326 |
| (0.209) | (0.209) | (0.234) | (0.234) | |
| LnFdi | −0.00281 | −0.00107 | 0.00393 | 0.00873 |
| (0.00790) | (0.00793) | (0.00890) | (0.00889) | |
| Fin | 1.382 *** | 1.333 *** | 1.072 *** | 0.974 *** |
| (0.182) | (0.182) | (0.204) | (0.204) | |
| Urb | 0.177 | 0.166 | 0.748 *** | 0.722 *** |
| (0.166) | (0.166) | (0.187) | (0.186) | |
| LnStu | 0.0875 * | 0.0757 | −0.0146 | −0.0417 |
| (0.0498) | (0.0499) | (0.0560) | (0.0560) | |
| LnNet | 0.0273 | 0.0415 ** | −0.0945 *** | −0.0592 *** |
| (0.0190) | (0.0198) | (0.0215) | (0.0221) | |
| Sup | 3.462 *** | 3.267 *** | 4.371 *** | 3.942 *** |
| (0.282) | (0.288) | (0.318) | (0.323) | |
| Constant | 5.709 *** | 5.502 *** | 4.082 *** | 3.966 *** |
| (0.539) | (0.551) | (0.620) | (0.618) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year F.E. | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City F.E. | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.8398 | 0.8403 | 0.7544 | 0.7566 |
| Observations | 4845 | 4845 | 4845 | 4845 |
| (35) | (36) | (37) | (38) | (39) | (40) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Ln(Innoit + 1) | Ln(Ginnoit + 1) | ||||
| Eastern | Central | Western | Eastern | Central | Western | |
| HSR | 0.087 ** | 0.254 *** | 0.171 *** | 0.159 *** | 0.244 *** | 0.336 *** |
| (2.143) | (5.448) | (3.425) | (3.249) | (4.882) | (5.904) | |
| Constant | 2.358 ** | 3.463 *** | 1.200 | 0.540 | 1.464 * | −0.737 |
| (2.471) | (4.240) | (1.258) | (0.468) | (1.675) | (−0.680) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year F.E. | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City F.E. | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.885 | 0.814 | 0.845 | 0.813 | 0.742 | 0.720 |
| Observations | 1717 | 1700 | 1428 | 1717 | 1700 | 1428 |
| Variables | (41) | (42) | (43) | (44) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ln(Innoit + 1) | Ln(Ginnoit + 1) | |||
| Central City | General City | Central City | General City | |
| HSR | 0.106 ** | 0.221 *** | 0.084 | 0.285 *** |
| (2.258) | (7.632) | (1.411) | (8.815) | |
| Constant | 7.504 *** | 0.546 | 4.870 *** | 0.198 |
| (6.688) | (1.040) | (3.417) | (0.338) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year F.E. | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City F.E. | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.885 | 0.814 | 0.845 | 0.813 |
| Observations | 595 | 4250 | 595 | 4250 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, C.; Tan, K.; He, J. The Impact of Opening a High-Speed Railway on Urban Innovation: A Comparative Perspective of Traditional Innovation and Green Innovation. Land 2023, 12, 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091671
Ma C, Tan K, He J. The Impact of Opening a High-Speed Railway on Urban Innovation: A Comparative Perspective of Traditional Innovation and Green Innovation. Land. 2023; 12(9):1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091671
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Chang, Kehu Tan, and Jiangye He. 2023. "The Impact of Opening a High-Speed Railway on Urban Innovation: A Comparative Perspective of Traditional Innovation and Green Innovation" Land 12, no. 9: 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091671
APA StyleMa, C., Tan, K., & He, J. (2023). The Impact of Opening a High-Speed Railway on Urban Innovation: A Comparative Perspective of Traditional Innovation and Green Innovation. Land, 12(9), 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091671





