The Oasisization Process Promotes the Transformation of Soil Organic Carbon into Soil Inorganic Carbon
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
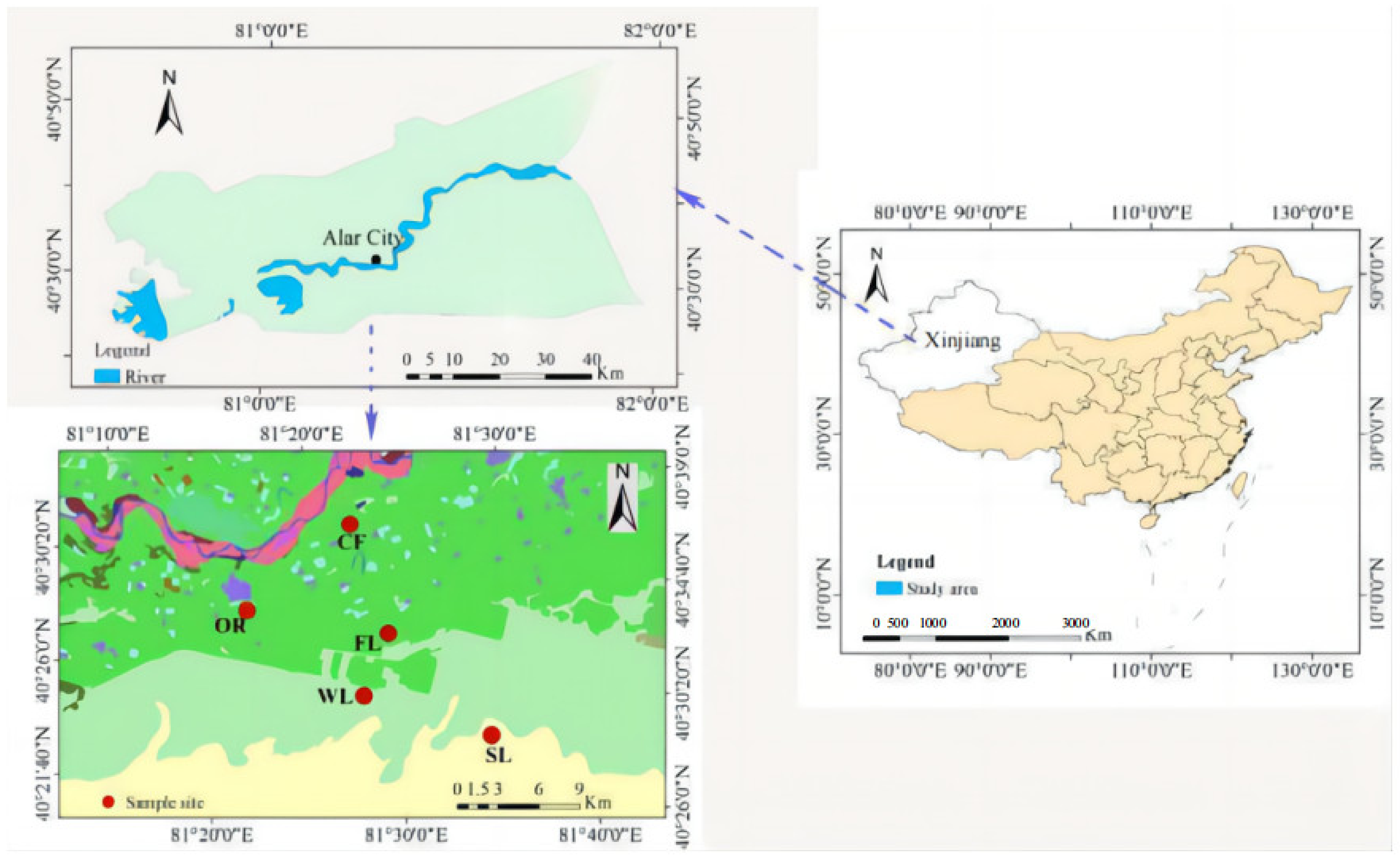
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Experimental Design and Soil Sampling
2.3. Soil Analysis
2.4. Calculation of Soil Carbon Sequestration Capacity for Different Land-Use Types
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
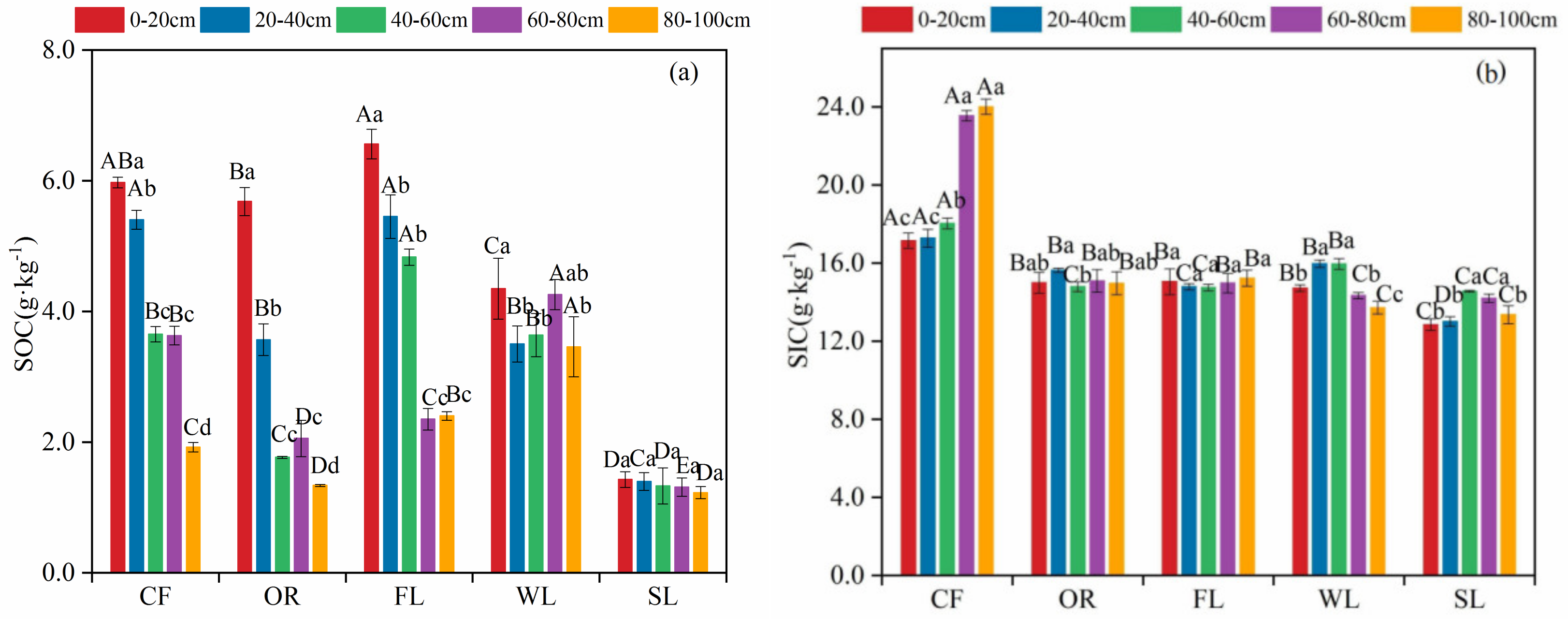
3.1. Vertical Distribution Features of SOC and SIC Content in Different Land-Use Types
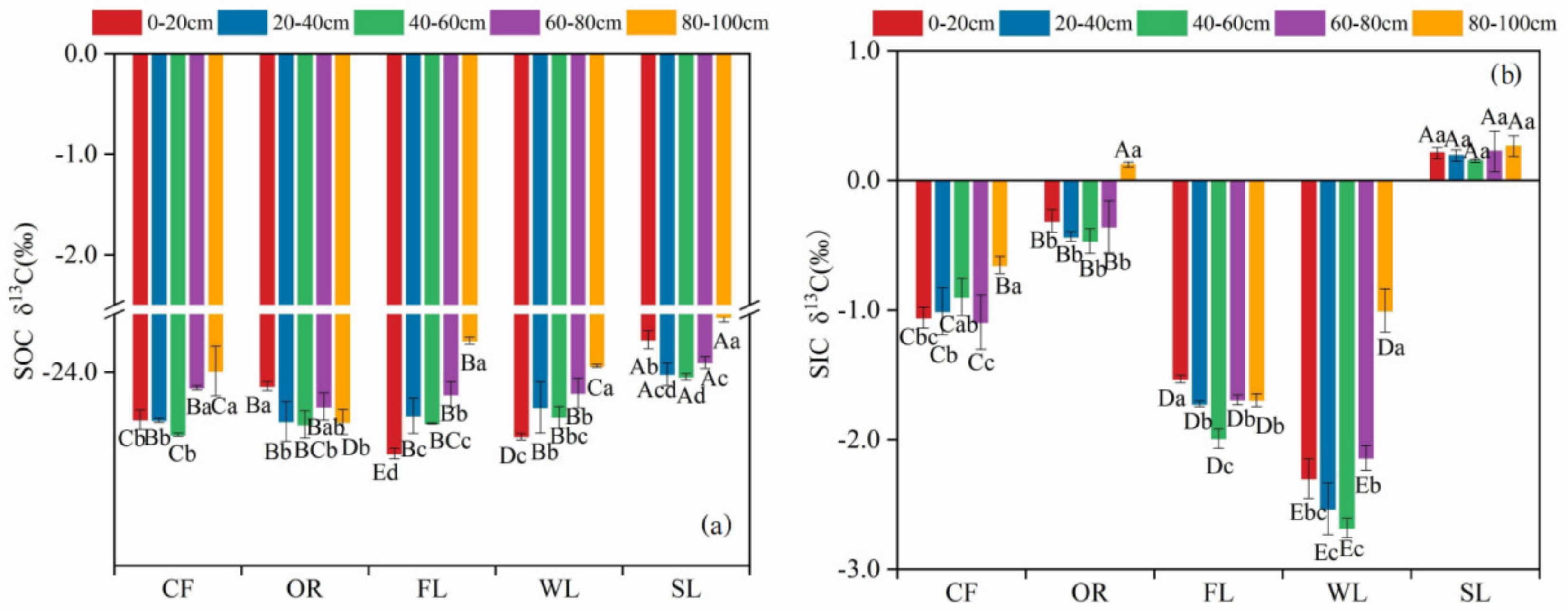
3.2. Vertical Distribution Characteristics of Stable Carbon Isotopes in Different Land-Use Types
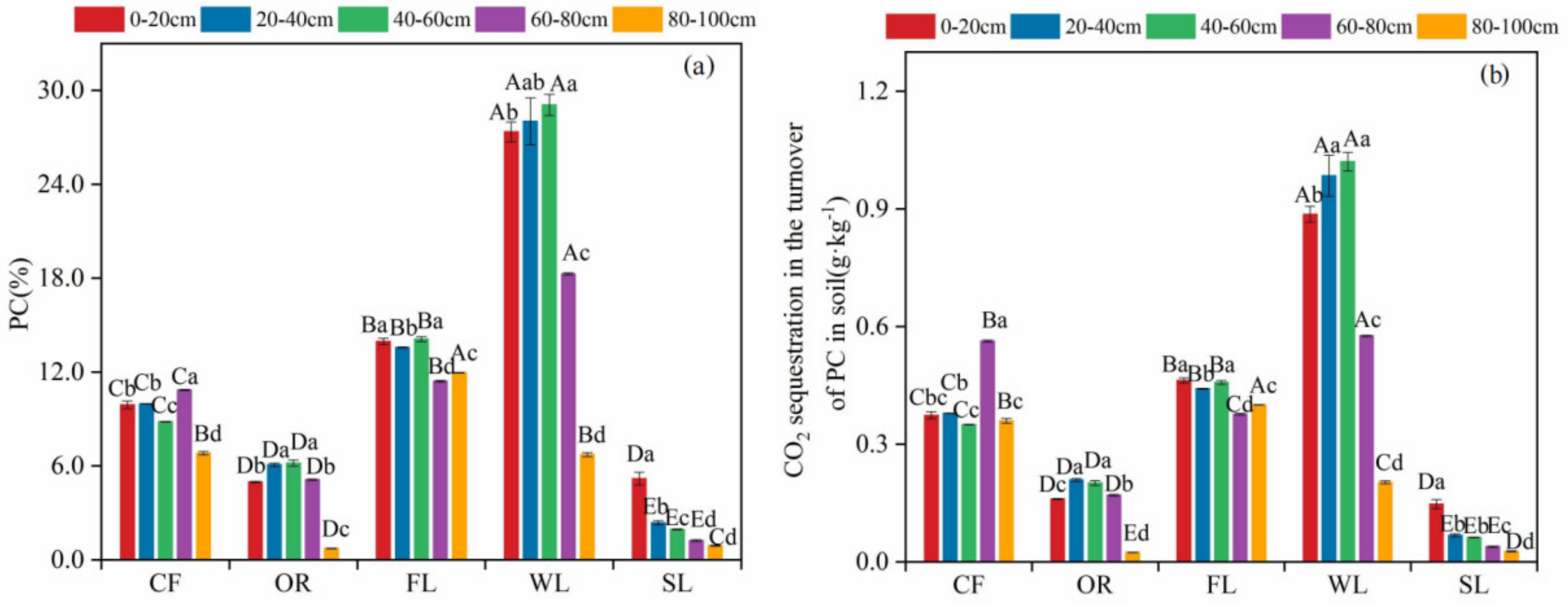
3.3. Proportion of PC to SIC in Soils of Different Land-Use Types and the Amount of CO2 Sequestered during Its Formation
3.4. Transfer Amount of SOC to SIC in Different Land-Use Types
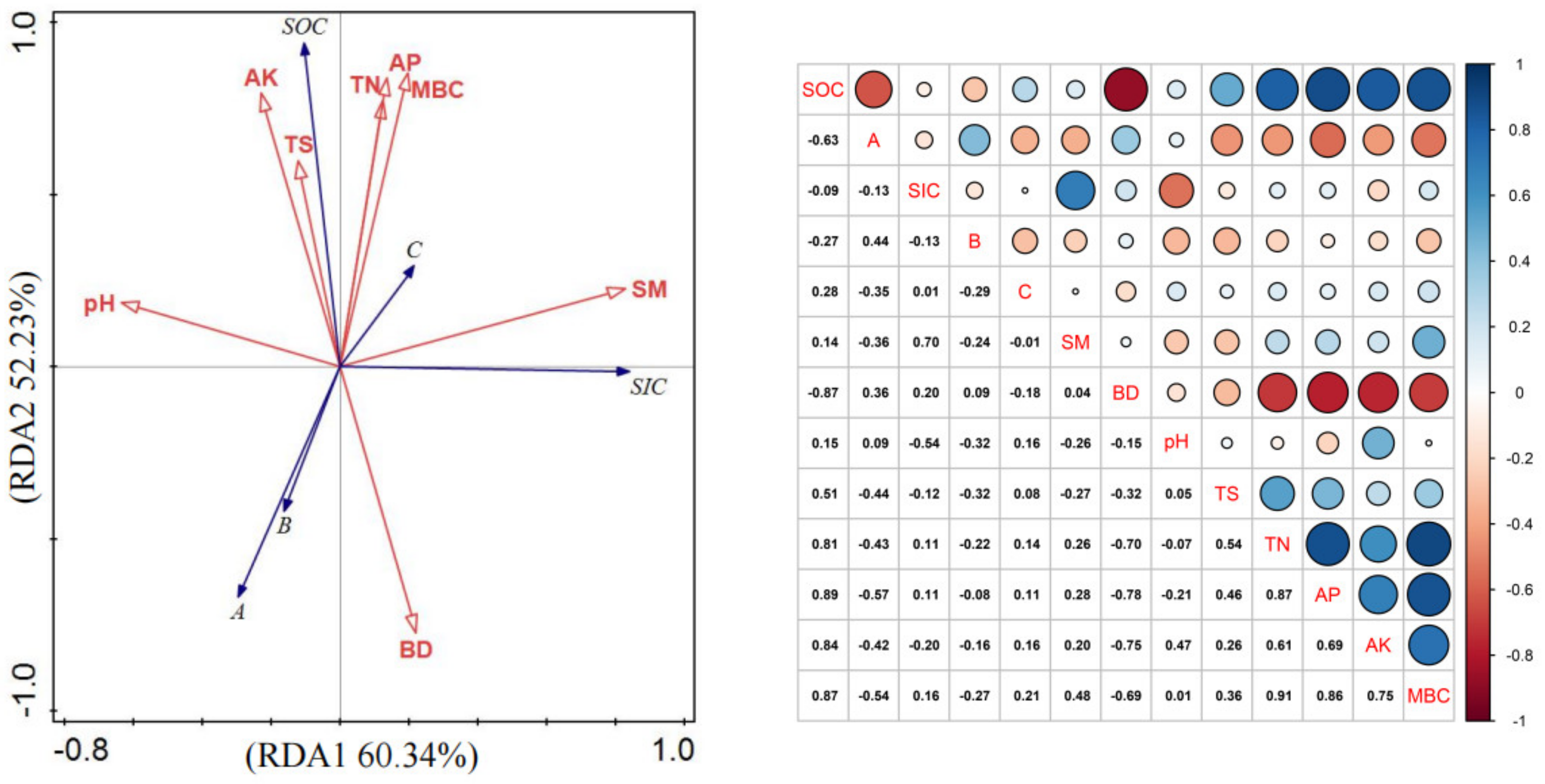
3.5. Driving Factors of Organic Carbon Transformation in the Oasis Creation Process
4. Discussion
4.1. Variations of Soil Carbon Stock in the Process of Oasis Creation
4.2. Carbon Sequestration Potential of Soils with Different Land-Use Types
4.3. Influence of Environmental Factors on the Transformation of Soil Organic Carbon Stock in an Oasis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, Y.; Wu, W.L.; Meng, F.Q.; Smith, P.; Lal, R. Increase in soil organic carbon by agricultural intensification in northern China. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Zhao, C.Y.; Ma, Q.L.; Li, Y.K.; Jing, H.J.; Sun, T.; Milned, E.; Easterd, M.; Paustiand, K.; Wen, A.Y.H.; et al. Carbon benefit sof wolf berry plantation on secondary saline land in Jingtai oasis, Gansu-a case study on application of the CBP model. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 157, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, J.; Hu, J.; Lu, Z.; Sun, H.; Yang, X. The impact of land use and cover change on soil organic carbon and total nitrogen storage in the Heihe River Basin: A meta-analysis. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 1578–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, F.; Lavallee, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Hansen, P.M.; Paustian, K.H.; Schipanski, M.; Wallenstein, M.D. In-N-Out: A hierarchical framework to understand and predict soil carbon storage and nitrogen recycling. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 4465–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Ding, J.L.; Zhang, Z.P.; Wang, J.J.; Chen, X.Y.; Han, L.J.; Shi, H.B.; Wang, J.Z. Soil salinity dynamics in arid oases during irrigated and non-irrigated seasons. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 13, 3823–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyachoti, S.; Jin, L.; Tweedie, C.E.; Ma, L. Insight into factors controlling formation rates of pedogenic carbonates: A combined geochemical and isotopic approach in dry land soils of the US Southwest. Chem. Geol. 2019, 527, 118503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, K.W.; Libohova, Z.; Adhikari, K.; Kome, C.; Maness, X.; Silman, M.R. Influence of Land Use and Topographic Factors on Soil Organic Carbon Stocks and Their Spatial and Vertical Distribution. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Shao, M.A.; Zhang, C.C.; Liu, Z.P.; Zou, J.L.; Xiao, J.F. Soil organic carbon in deep profiles under Chinese continental monsoon climate and its relations with land uses. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 82, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.; Mohapatra, M.; Latare, A. Impact of land use changes on soil quality and species diversity in the Vindhyan dry tropical region of India. J. Trop. Ecol. 2020, 36, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.P.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, C.Y. Soil organic and inorganic carbon and stable carbon isotopes in the Yanqi Basin of northwestern China. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, M.; Li, P.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Chang, Q. Variations in soil organic carbon decompositions of different land use patterns on the tableland of Loess Plateau. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 4337–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.Q.; Zhuang, Q.L. Leaf 13C data constrain the uncertainty of the carbon dynamics of temperate forest ecosystems. Ecosphere 2021, 12, e03741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.G.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, W.Z.; Gu, P.; Yang, J.; Liu, L.J. Review of progress in soil inorganic carbon research. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 100, 012129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, L.; Guilin, H. Stable nitrogen and carbon isotope compositions in plant-soil systems under different land-use types in a red soil region, Southeast China. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Wei, Z.; Wen, X. Evapotranspiration partitioning at the ecosystem scale using the stable isotope method—A review. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 263, 346–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Lan, W.; Sun, H.; Hu, Z. Annual study of hydraulic characteristics in surface flow constructed wetlands using hydrogen and oxygen stable isotope technology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 29502–29511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Mentler, A.; Mayer, H.; Blum, W.E. Soil aggregation, aggregate stability, organic carbon and nitrogen in different soil aggregate fractions under forest and shrub vegetation on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2010, 81, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, Z.; Yu, J.; Liang, J. Study on the Change in Vegetation Coverage in Desert Oasis and Its Driving Factors from 1990 to 2020 Based on Google Earth Engine. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Yuan, X.L.; Li, L.Y.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, R.Q.; Li, Z.G.; Liu, Y. Aggregational differentiation of soil-respired CO2 and its δ13C variation across land-use types. Geoderma 2023, 432, 116384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.X. Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.Z.; Li, B.G. Soil Science Experiment; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Breecker, D.O.; Bergel, S.; Nadel, M.; Tremblay, M.M.; Osuna-Orozco, R.; Larson, T.E.; Sharp, Z.D. Minor stablecarbon isotope fractionation between respired carbondioxide and bulk soil organic matter during laboratoryincubation of topsoil. Biogeochemistry 2015, 123, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bughio, M.A.; Wang, P.; Meng, F.; Qing, C.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Wang, X.; Junejo, S.A. Neoformation of pedogenic carbonates by irrigation and fertilizationand their contribution to carbon sequestration in soil. Geoderma 2016, 262, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, P.; Sarkar, B.; Bolan, N.; Chowdhury, S.; Desbiolles, J. Impact of carbonates on the mineralisation of surface soil organic carbon in response to shift in tillage practice. Geoderma 2019, 339, 94–105. Available online: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/142195/ (accessed on 18 May 2023). [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Gong, L.; Yang, Y.X.; Ding, Z.L.; Li, X.Z. Mineralization and Fixed Stable Carbon Isotopic Characteristics of Organic Carbon in Cotton Fields with Different Continuous Cropping Years. Agronomy 2023, 13, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.; Zhuang, Q. Microbial dormancy and its impacts on northern temperate and boreal terrestrial ecosystem carbon budget. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 4591–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Huang, Y.; Duan, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, J. Particulate and mineral-associated organic carbon fractions reveal the roles of soil aggregates under different land-use types in a karst faulted basin of China. Catena 2023, 220, 106721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.H.; Wang, Z.F.; Lu, C.; Huang, R.; Wang, F.H.; Gao, M. Effects of Land Use Type on the Content and Stability of Organic Carbon in Soil Aggregates. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2019, 40, 3816–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moharana, P.C.; Meena, R.L.; Nogiya, M.; Jena, R.K.; Sharma, G.K.; Sahoo, S.; Jha, P.K.; Aditi, K.; Vara-Prasad, P.V. Impacts of Land Use on Pools and Indices of Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen in the Ghaggar Flood Plains of Arid India. Land 2022, 11, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibet, E.; Musafiri, C.M.; Kiboi, M.N.; Macharia, J.; Ng’etich, O.K.; Kosgei, D.K.; Mulianga, B.; Okoti, M.; Zeila, A.; Ngetich, F.K. Soil Organic Carbon Stocks under Different Land Utilization Types in Western Kenya. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannatul, F.; Varun, P. A review on the possible factors influencing soil inorganic carbon under elevated CO2. Catena 2021, 204, 105434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, K.; Tian, C.; Mai, W. Progress of Euhalophyte Adaptation to Arid Areas to Remediate Salinized Soil. Agriculture 2023, 13, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, M. Linkages of C: N: P stoichiometry between soil and leaf and their response to climatic factors along altitudinal gradients. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1820–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somenahally, A.C.; McLawrence, J.; Chaganti, V.N.; Ganjegunte, G.K.; Obayomi, O.; Brady, J.A. Response of soil microbial Communities, inorganic and organic soil carbon pools in arid saline soils to alternative land use practices. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.F.; Zhang, R.; Cao, H.; Huang, C.Q.; Yang, Q.K.; Wang, M.K.; Koopal, L.K. Soil inorganic carbon stock under different soil types and land uses on the Loess Plateau region of China. Catena 2014, 121, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shao, W.; Ji, J. An invisible soil acidification: Critical role of soil carbonate and its impact on heavy metal bioavailability. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1273533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Xiao, J.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, P.; Meng, P.; Li, J. Carbon exchange of forest plantations: Global patterns and biophysical drivers. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 336, 109379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanian, K.; Pustovoytov, K.; Kuzyakov, Y. Pedogenic carbonates:Forms and formation processes. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 157, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, N.; Huang, L.; Shao, M. Vertical distribution of soil organic and inorganic carbon under different vegetation covers in two toposequences of the Liudaogou watershed on the Loess Plateau, China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 73, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.B.; Tao, Y.; Wu, L.; Li, Y.G.; Zhang, Y.M. Soil stoichiometry in different land-use categories in desert-oasis ecotones of the southern Taklimakan Desert. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, B.; Chen, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, H.; Chen, Y. “Fertile island” of Tamarix Chinensis accelerated the carbon decomposition in the coastal wetlands of the Yellow River Delta, China. Catena 2022, 211, 106034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.F.; Pu, C.; Liu, S.L.; Chen, Z.D.; Chen, F. Effects of tillage systems on soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in a double paddy cropping system in Southern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 153, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virk, A.L.; Liu, W.S.; Niu, J.R.; Xu, C.T.; Liu, Q.Y.; Kan, Z.R.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.L. Effects of Diversified Cropping Sequences and Tillage Practices on Soil Organic Carbon, Nitrogen, and Associated Fractions in the North China Plain. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Dong, Y.; Chang, X.; Nie, X.; Liu, L.; Xiao, H.B.; Lu, Y.M.; Zeng, G. Response of soil organic carbon and nitrogen stocks to soilerosion and land use types in the Loess hilly-gully region of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 166, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Hai, X.; Shangguan, Z.; Deng, L. Dynamics of soil microbial C:N:P stoichiometry and its driving mechanisms following natural vegetation restoration after farmland abandonment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gritsch, C.; Egger, F.; Zehetner, F.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S. The effect of temperature and moisture on trace gas emissions from deciduous and coniferous leaf liter. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 1339–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, L.; Yan, Y.; Cai, Y.; Xu, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.Q.; Xin, X.P. Effects of cultivation and agricultural abandonment on soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in a meadow steppe in eastern Inner Mongolia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 309, 107284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchi, L.; Walder, F.; Banerjee, S.; Colombi, T.; van der Heijden, M.G.; Keller, T.; Charles, R.; Six, J. Pedoclimatic factors and management determine soil organic carbon and aggregation in farmer fields at a regional scale. Geoderma 2022, 409, 115632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wei, J.; Cheng, J.; Li, W. Profile distribution of soil inorganic carbon along a chronosequence ofgrassland restoration on a 22-year scale in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Catena 2014, 121, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Li, Q.L.; Yan, X.; Wu, X.Z.; Liu, R.T.; Fang, Y. Desertification control on soil inorganic and organic carbon accumulation in the topsoil of desert grassland in Ningxia, northwest China. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 127, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, D.L.; Balesdent, J.; Pellerin, S. Reviews and syntheses:the mechanisms underlying carbon storage in soil. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 5223–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadamma, S.; Mayes, M.A.; Steinweg, J.M.; Schaeffer, S.M. Substrate quality alters microbial mineralization of added substrate and soil organic carbon. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2014, 11, 4451–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Physical and Chemical Factors | Importance of Ranking | Interpretation of Quantity/% | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SM | 1 | 36.5 | 13.2 | 0.002 |
| pH | 2 | 22.6 | 6.7 | 0.006 |
| MBC | 3 | 13.7 | 3.7 | 0.03 |
| AP | 4 | 12.9 | 3.4 | 0.062 |
| AK | 5 | 12.8 | 3.4 | 0.046 |
| BD | 6 | 12.5 | 3.3 | 0.04 |
| TN | 7 | 10.5 | 2.7 | 0.06 |
| TS | 8 | 6.5 | 1.6 | 0.142 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, J.; Gong, L.; Ma, X.; Zhu, H.; Ding, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, H. The Oasisization Process Promotes the Transformation of Soil Organic Carbon into Soil Inorganic Carbon. Land 2024, 13, 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13030336
Tang J, Gong L, Ma X, Zhu H, Ding Z, Luo Y, Zhang H. The Oasisization Process Promotes the Transformation of Soil Organic Carbon into Soil Inorganic Carbon. Land. 2024; 13(3):336. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13030336
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Junhu, Lu Gong, Xinyu Ma, Haiqiang Zhu, Zhaolong Ding, Yan Luo, and Han Zhang. 2024. "The Oasisization Process Promotes the Transformation of Soil Organic Carbon into Soil Inorganic Carbon" Land 13, no. 3: 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13030336
APA StyleTang, J., Gong, L., Ma, X., Zhu, H., Ding, Z., Luo, Y., & Zhang, H. (2024). The Oasisization Process Promotes the Transformation of Soil Organic Carbon into Soil Inorganic Carbon. Land, 13(3), 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13030336






