Assessment of Ecosystem Service Values of Urban Wetland: Taking East Lake Scenic Area in Wuhan as an Example
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
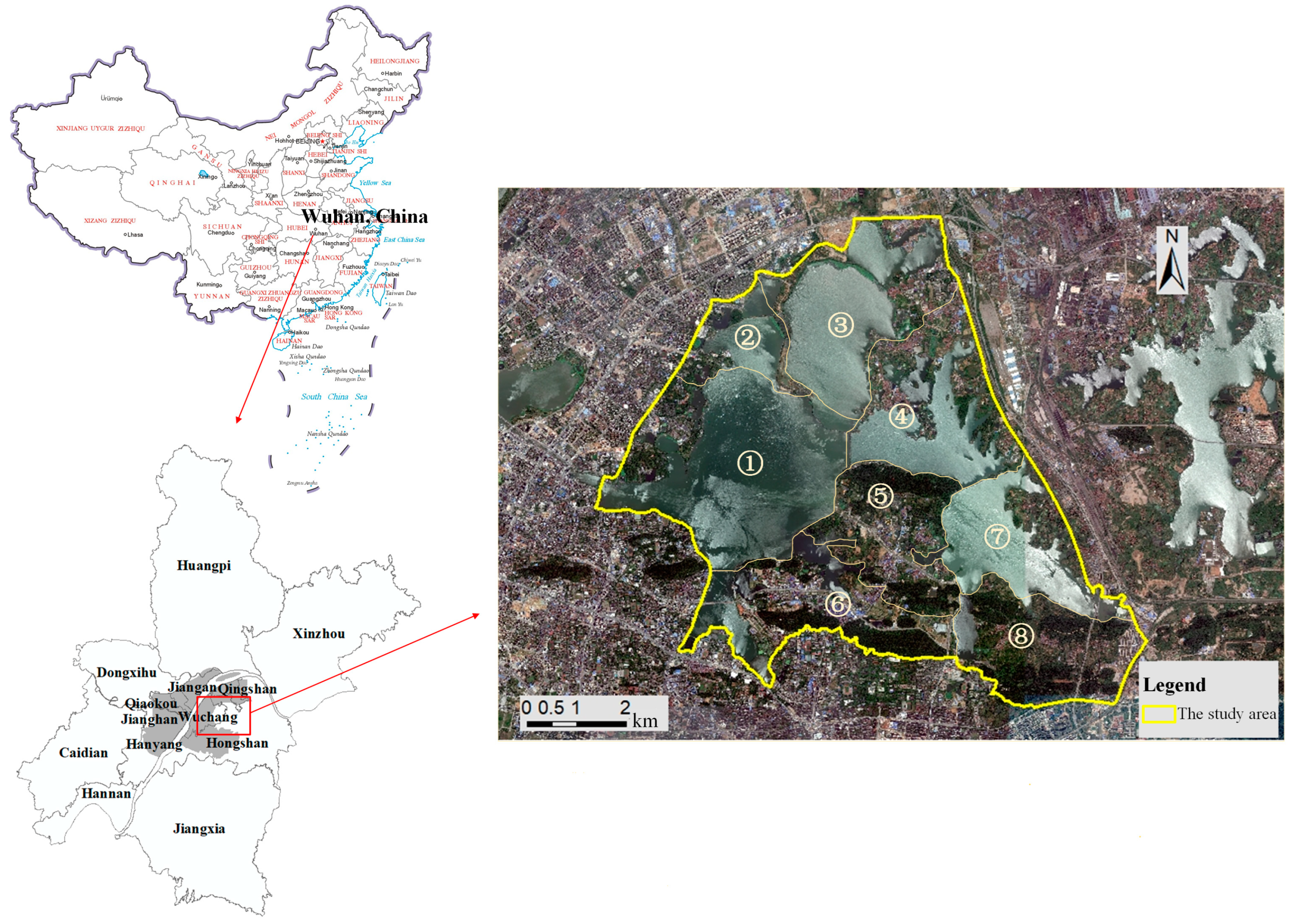
2.1. Study Area
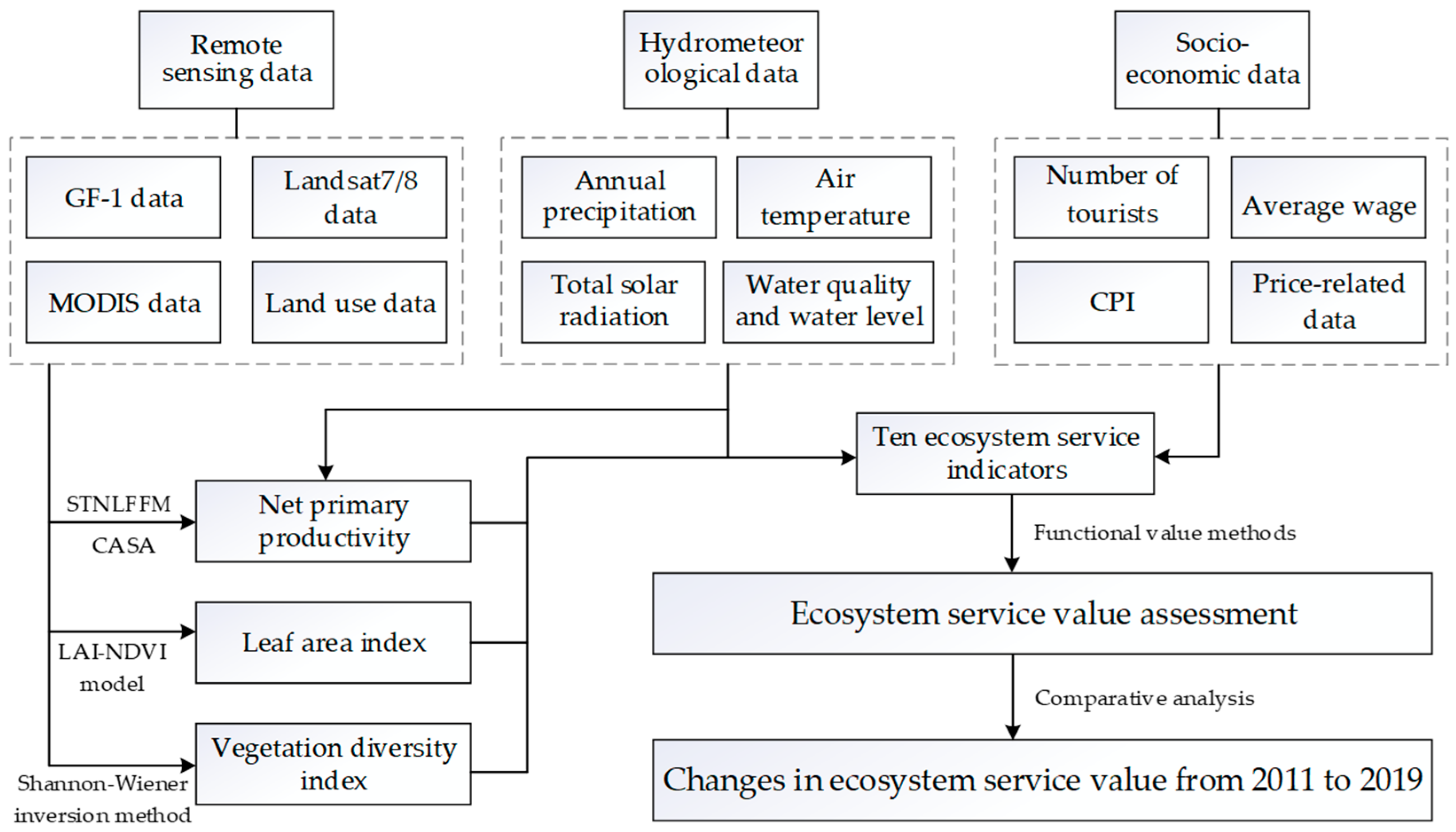
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Key Ecological Parameter Calculations
- Net primary productivity
- 2.
- Leaf area index
- 3.
- Vegetation diversity index
2.3.2. Ecosystem Service Value Assessment
3. Results
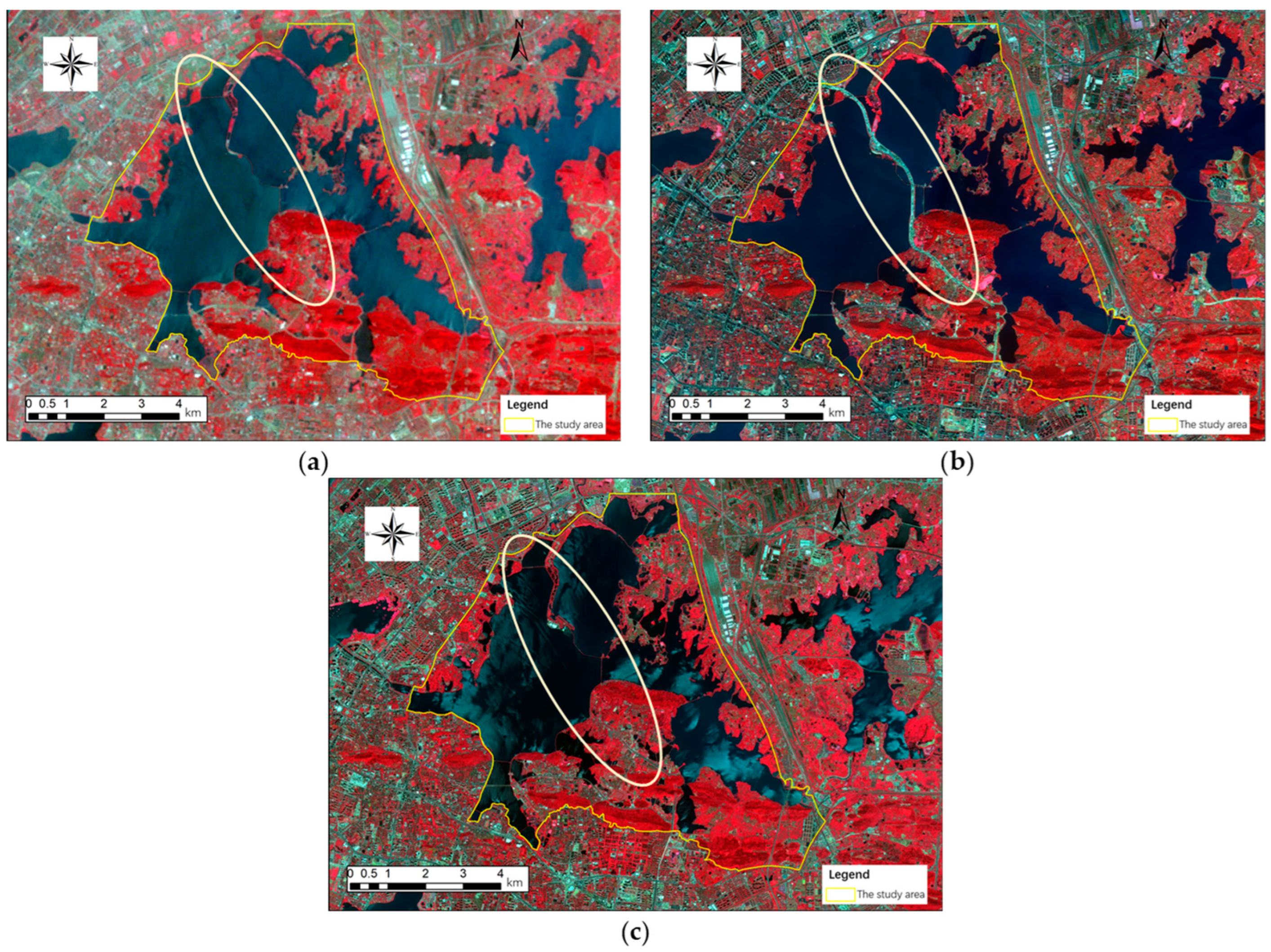
3.1. Changes in Land Cover in ELSA from 2010 to 2019
3.2. Key Ecological Parameters
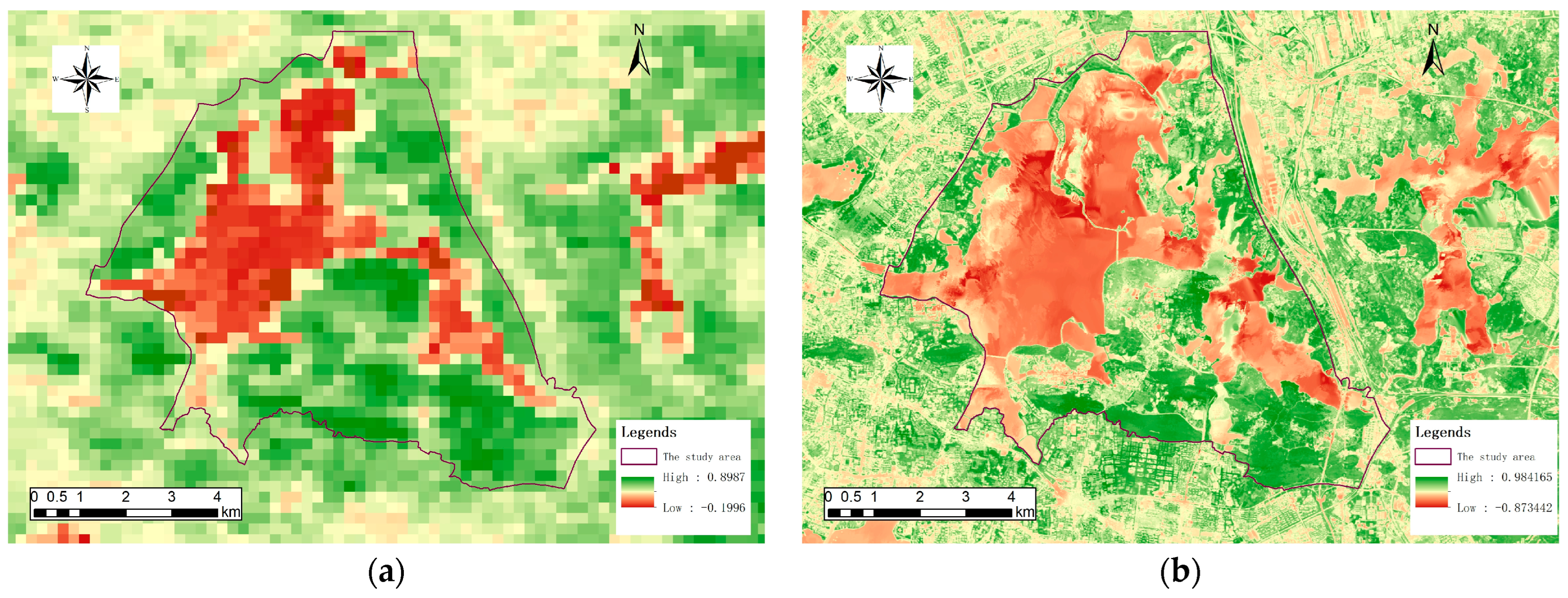
3.2.1. Net Primary Productivity
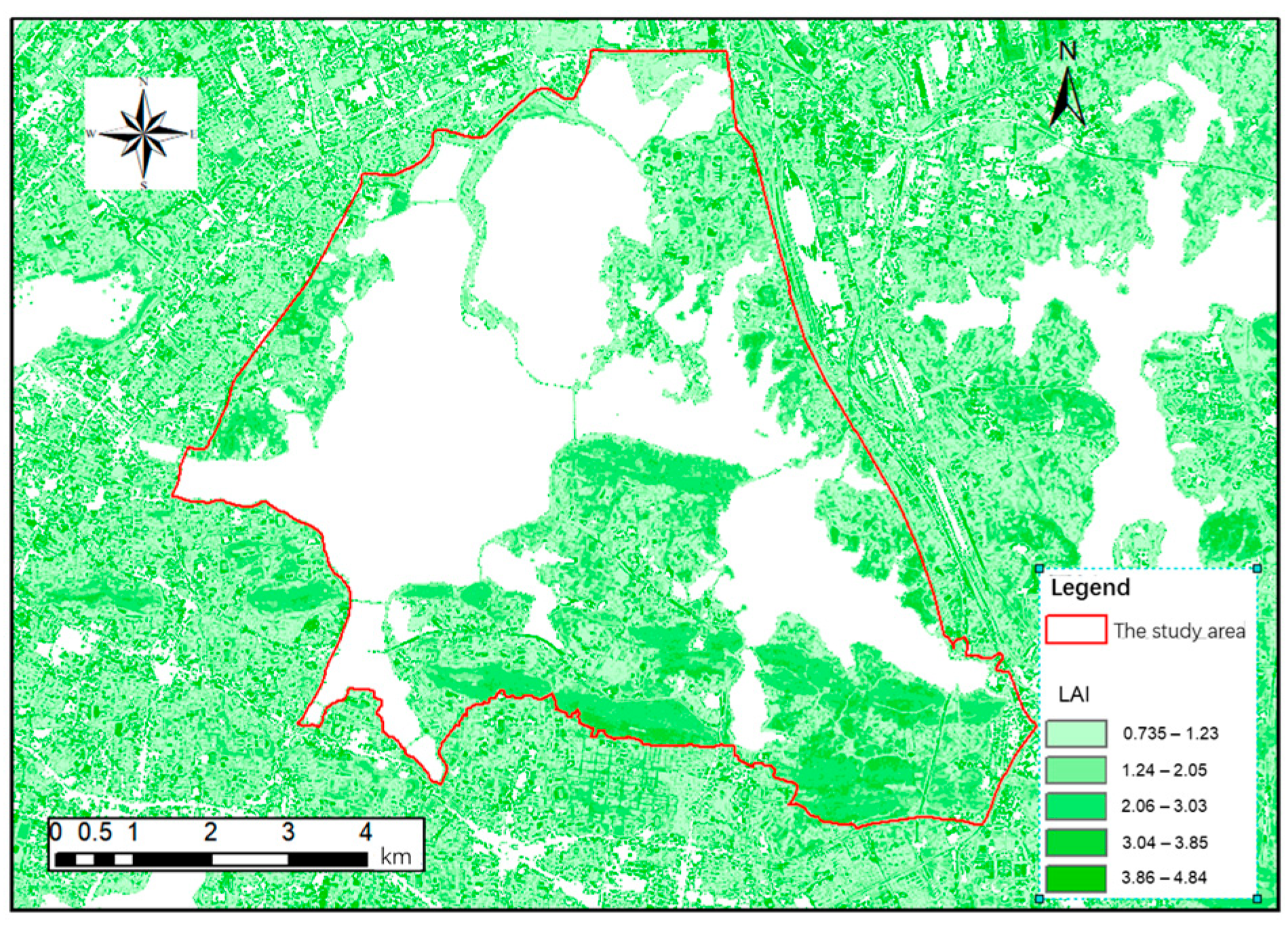
3.2.2. Leaf Area Index
3.2.3. Vegetation Diversity Index
3.3. Changes in ESVs in ELSA from 2010 to 2019
3.3.1. Dynamic Changes in the Total Value of Ecosystem Services
3.3.2. Dynamic Changes in the Value of Individual Ecosystem Services
3.3.3. Dynamic Changes in the Composition of the Value of Ecosystem Services
4. Discussion
4.1. The Differences in ESVs between Urban and Natural Wetlands
4.2. Changes in ESVs in the ELSA Region
4.3. The Culture Service Value in the ELSA Region
4.4. Limitations and Future Works
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, D.M.; Wainger, L.A.; Bartoldus, C.C.; Wakeley, J.S. Expanding Wetland Assessment Procedures: Linking Indices of Wetland Function with Services and Values; Defense Technical Information Center: Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; ISBN 1-56973-597-2. [Google Scholar]
- Maltby, E.; Acreman, M.C. Ecosystem Services of Wetlands: Pathfinder for a New Paradigm. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2011, 56, 1341–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekola, O.; Mitchell, G. The Niger Delta Wetlands: Threats to Ecosystem Services, Their Importance to Dependent Communities and Possible Management Measures. Int. J. Biodivers. Sci. Ecosyst. Serv. Manag. 2011, 7, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, N.C. How Much Wetland Has the World Lost? Long-Term and Recent Trends in Global Wetland Area. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2014, 65, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Niu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, H. Global Wetlands: Potential Distribution, Wetland Loss, and Status. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhao, X.; He, C.; Yin, D.; Meng, S. Impacts of Urban Expansion on Wetland Ecosystem Services in the Context of Hosting the Winter Olympics: A Scenario Simulation in the Guanting Reservoir Basin, China. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2019, 19, 2365–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Peng, J.; Qiu, S.; Liu, Y.; Dong, J.; Zhang, H. Responses of Spatial Relationships between Ecosystem Services and the Sustainable Development Goals to Urbanization. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 157868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Wu, B.; Zeng, Y.; Song, K.; Yi, K.; Luo, L. China’s Wetlands Loss to Urban Expansion. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2644–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, B.; Turner, R.K.; Morling, P. Defining and Classifying Ecosystem Services for Decision Making. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braat, L.C. The Value of the Ecosystem Services Concept in Economic and Biodiversity Policy. In Ecosystem Services; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 97–103. ISBN 978-0-12-419964-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Rao, E.; et al. Improvements in Ecosystem Services from Investments in Natural Capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; de Groot, R.; Braat, L.; Kubiszewski, I.; Fioramonti, L.; Sutton, P.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M. Twenty Years of Ecosystem Services: How Far Have We Come and How Far Do We Still Need to Go? Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Feagin, R.A.; Lu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, W.; He, W. Ecosystem Service Values and Restoration in the Urban Sanyang Wetland of Wenzhou, China. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 29, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Guan, D.; Huang, X.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, M. Evaluation of the Cultural Ecosystem Services of Wetland Park. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, K.G.; James, P. Changes in the Value of Ecosystem Services along a Rural–Urban Gradient: A Case Study of Greater Manchester, UK. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2013, 109, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datri, L.A.; Lopez, M.; Buchter, S.; Pazcel, E.M.; Gandini, M. Functional Urban Wetlands in Dysfunctional Cities. Curr. Landsc. Ecol. Rep. 2024, 9, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, L.M.; Epele, L.B.; Grech, M.G.; Kandus, P.; Miserendino, M.L. Wetland Genesis Rules Invertebrate Spatial Patterns at Patagonian Ponds (Santa Cruz, Argentina): A Multiscale Perspective. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 126, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Das, M.; Gupta, R. Comparison of Ecosystem Services Provided by an Urban and a Riverine Wetland: A Multi-Scale Evaluation from Lower Gangetic Plain, Eastern India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 79529–79544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Leng, W.; Liu, K.; Liu, L.; He, Z.; Zhu, Y. Object-Based Mangrove Species Classification Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Hyperspectral Images and Digital Surface Models. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Clinton, N.; Ji, L.; Li, W.; Bai, Y.; et al. Stable Classification with Limited Sample: Transferring a 30-m Resolution Sample Set Collected in 2015 to Mapping 10-m Resolution Global Land Cover in 2017. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Liang, J.; Huang, W.; Xu, W.; Li, B.; Wang, J. Extraction of Water Body Information from Remote Sensing Imagery While Considering Greenness and Wetness Based on Tasseled Cap Transformation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, J.; Shataee, S. Possibility Investigation of Tree Diversity Mapping Using Landsat ETM+ Data in the Hyrcanian Forests of Iran. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Qiu, G.; Lü, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, Y. Use of High-Resolution Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing and “Three-Temperature Model” for Transpiration Monitoring in Arid Inland River Catchment. J. Hydrol. 2014, 515, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, K.; Liu, L.; Myint, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; He, Z. Exploring the Potential of WorldView-2 Red-Edge Band-Based Vegetation Indices for Estimation of Mangrove Leaf Area Index with Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torresani, M.; Rocchini, D.; Sonnenschein, R.; Zebisch, M.; Marcantonio, M.; Ricotta, C.; Tonon, G. Estimating Tree Species Diversity from Space in an Alpine Conifer Forest: The Rao’s Q Diversity Index Meets the Spectral Variation Hypothesis. Ecol. Inform. 2019, 52, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, R.; Brander, L.; Van Der Ploeg, S.; Costanza, R.; Bernard, F.; Braat, L.; Christie, M.; Crossman, N.; Ghermandi, A.; Hein, L.; et al. Global Estimates of the Value of Ecosystems and Their Services in Monetary Units. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 1, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, P.; Chase, J.M. Global Patterns and Drivers of Tree Diversity Integrated across a Continuum of Spatial Grains. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Li, R.; Ding, Z.; O’Connor, P.; Kong, L.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, W.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, R.; et al. A New Remote-Sensing-Based Indicator for Integrating Quantity and Quality Attributes to Assess the Dynamics of Ecosystem Assets. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Jiang, W.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Y. Ecosystem Services Response to Rural-Urban Transitions in Coastal and Island Cities: A Comparison between Shenzhen and Hong Kong, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, Q.; Fan, P.; Shi, X. From Urban Greenspace to Health Behaviors: An Ecosystem Services-Mediated Perspective. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamel, P.; Hamann, M.; Kuiper, J.J.; Andersson, E.; Arkema, K.K.; Silver, J.M.; Daily, G.C.; Guerry, A.D. Blending Ecosystem Service and Resilience Perspectives in Planning of Natural Infrastructure: Lessons from the San Francisco Bay Area. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 601136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, S.; Kerachian, R.; Pourmoghim, P.; Behboudian, M.; Motlaghzadeh, K. Evaluating and Improving the Sustainability of Ecosystem Services in River Basins under Climate Change. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenfeld, J.G. Evaluating Wetlands within an Urban Context. Ecol. Eng. 2000, 15, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Huang, K.; Yu, Y.; Huang, B. A Comparative Analysis of Ecosystem Service Valuation Methods: Taking Beijing, China as a Case. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, Q. Water Ecosystem Service Quality Evaluation and Value Assessment of Taihu Lake in China. Water 2021, 13, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, B.; Dolui, G.; Pramanik, M.; Maity, S.; Biswas, S.S.; Pal, R. Urban Expansion and Wetland Shrinkage Estimation Using a GIS-Based Model in the East Kolkata Wetland, India. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 83, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Basu, T. Assessment of Peri-Urban Wetland Ecological Degradation through Importance-Performance Analysis (IPA): A Study on Chatra Wetland, India. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koko, I.A.; Misana, S.B.; Kessler, A.; Fleskens, L. Valuing Ecosystem Services: Stakeholders’ Perceptions and Monetary Values of Ecosystem Services in the Kilombero Wetland of Tanzania. Ecosyst. People 2020, 16, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallenberg, M.; de Winton, M.D.; Verburg, P.; Kelly, D.J.; Hamill, K.D.; Hamilton, D.P. Ecosystem Services of Lakes. In Ecosystem Services in New Zealand: Conditions and Trends; Manaaki Whenua Press: Lincoln, New Zealand, 2013; pp. 203–225. [Google Scholar]
- Mulatu, D.W.; Ahmed, J.; Semereab, E.; Arega, T.; Yohannes, T.; Akwany, L.O. Stakeholders, Institutional Challenges and the Valuation of Wetland Ecosystem Services in South Sudan: The Case of Machar Marshes and Sudd Wetlands. Environ. Manag. 2022, 69, 666–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Giannetti, B.F.; Almeida, C.M.V.B.; Sevegnani, F.; Li, R. Spatiotemporal Differentiation and Mechanism of Anthropogenic Factors Affecting Ecosystem Service Value in the Urban Agglomeration around Poyang Lake, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Xu, D.; Guo, P.; Wang, D.; Li, L.; Gao, J. Exploring Variations of Ecosystem Service Value in Hangzhou Bay Wetland, Eastern China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019, 37, 100944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Valck, J.; Beames, A.; Liekens, I.; Bettens, M.; Seuntjens, P.; Broekx, S. Valuing Urban Ecosystem Services in Sustainable Brownfield Redevelopment. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019, 35, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Shi, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Xie, G. Economic Values and Dominant Providers of Key Ecosystem Services of Wetlands in Beijing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 77, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Pinzón, L.; Sierra, L.; Trillas, F. The Economic Value of Wetlands in Urban Areas: The Benefits in a Developing Country. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, X. Changes of Aquatic Plants in Donghu Lake of Wuhan Based 1990-2020 Landsat Images. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2022, 46, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Ecosystem Research Network of China Chinese National Ecosystem Observation Research Network Science and Technology Resource Service System. Available online: http://www.cnern.org.cn. (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- Wuhan Municipal Statistics Bureau. Wuhan Statistical Yearbook—2011; Wuhan Municipal Statistics Bureau: Wuhan, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wuhan Municipal Statistics Bureau. Wuhan Statistical Yearbook—2015; Wuhan Municipal Statistics Bureau: Wuhan, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wuhan Municipal Statistics Bureau. Wuhan Statistical Yearbook—2019; Wuhan Municipal Statistics Bureau: Wuhan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T38582—2020; Forest Ecosystem Service Function Assessment Specification. State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Cheng, Q.; Liu, H.; Shen, H.; Wu, P.; Zhang, L. A Spatial and Temporal Nonlocal Filter-Based Data Fusion Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4476–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, J. Estimation of Net Primary Productivity of Chinese Terrestrial Vegetation Based on Remote Sensing. Chin Jour Plan Ecolo 2007, 31, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhou, G.; Yao, C. Study on the Green Volume of Different Types of Urban Green Spaces. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2015, 31, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yan, Q. Distribution Pattern of Tree Layer Species Diversity Based on RS and GIS: A Case Study of Water Conservation Forests in Montane Regions of Eastern Liaoning Province of China. Chin. J. Ecol. 2009, 28, 1749. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, E.; Weisner, S.E.B.; Johansson, M. Wetland Areas’ Direct Contributions to Residents’ Well-Being Entitle Them to High Cultural Ecosystem Values. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Sun, Z.; Cai, M.; Liu, L.; Wu, H.; Peng, Z. Impacts of Urban Blue-Green Space on Residents’ Health: A Bibliometric Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stigsdotter, U.K.; Ekholm, O.; Schipperijn, J.; Toftager, M.; Kamper-Jørgensen, F.; Randrup, T.B. Health Promoting Outdoor Environments—Associations between Green Space, and Health, Health-Related Quality of Life and Stress Based on a Danish National Representative Survey. Scand. J. Public Health 2010, 38, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.; Son, Y. Perceptions of Cultural Ecosystem Services in Urban Green Spaces: A Case Study in Gwacheon, Republic of Korea. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingua, F.; Coops, N.C.; Griess, V.C. Valuing Cultural Ecosystem Services Combining Deep Learning and Benefit Transfer Approach. Ecosyst. Serv. 2022, 58, 101487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jopke, C.; Kreyling, J.; Maes, J.; Koellner, T. Interactions among Ecosystem Services across Europe: Bagplots and Cumulative Correlation Coefficients Reveal Synergies, Trade-Offs, and Regional Patterns. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 49, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, B.; Zhu, Z. What Is the Spatiotemporal Relationship between Urbanization and Ecosystem Services? A Case from 110 Cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.X.; Li, J.; Guo, Z.Z.; Li, T. Trade-Offs between Carbon, Water, Soil and Food in Guanzhong-Tianshui Economic Region from Remotely Sensed Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 58, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Level | Shannon–Wiener Index | Value (CNY/hm2·a) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Index ≥ 6 | 50,000 |
| 2 | 5 ≤ Index < 6 | 40,000 |
| 3 | 4 ≤ Index < 5 | 30,000 |
| 4 | 3 ≤ Index < 4 | 20,000 |
| 5 | 2 ≤ Index < 3 | 10,000 |
| 6 | 1 ≤ Index < 2 | 5000 |
| 7 | Index < 1 | 3000 |
| Ecosystem Service | Indicator | Calculation Formula | Description | Evaluation Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provision | Water supply | : price of industrial water (CNY/m3). | Market value method | |
| Regulation | Climate regulation | : Difference between annual mean temperature and 100 °C (°C) | Alternative engineering method | |
| Flood regulation | : construction cost of artificial reservoirs per unit capacity (CNY/m3) | Shadow engineering method | ||
| Water purification | : treatment costs for total phosphorus and nitrogen pollutants (CNY/g). | Outcome reference method | ||
| Air purification | : charges for dust emissions (CNY/g). | Outcome reference method | ||
| Carbon sequestration and oxygen release | : industrial oxygen price (CNY/g). | Carbon tax method; shadow engineering method | ||
| Support | Biodiversity | : opportunity cost of species loss per unit area of vegetation (CNY/m2) | Outcome reference method | |
| Cultural | Tourism | : travel expenses; : consumer surplus; : time opportunity cost; : hourly payroll costs (CNY/h). | Travel cost method | |
| Scientific research | : average research cost per academic paper (CNY/paper) | Outcome reference method |
| Land Cover | Mean | Std |
|---|---|---|
| Forest | 2.20 | 0.83 |
| Grassland | 1.96 | 1.65 |
| Shrub | 1.48 | 0.87 |
| Ecosystem Service | Service Indicator | 2011–2015 | 2015–2019 | 2011–2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply service | Water supply | −4.95 | 6.71 | 1.43 |
| Regulation service | Carbon sequestration | 38.63 | 21.98 | 69.11 |
| Oxygen release | 38.63 | 21.98 | 69.11 | |
| Climate regulation | −34.90 | 48.32 | −3.45 | |
| Flood regulation | −3.25 | 5.09 | 1.67 | |
| Air purification | −26.41 | 59.10 | 17.08 | |
| Water purification | −20.04 | 9.81 | −12.19 | |
| Support service | Biodiversity | −5.04 | 23.37 | 17.15 |
| Culture service | Scientific research | −59.09 | 188.89 | 18.18 |
| Tourism | 42.43 | 198.51 | 325.17 | |
| Total | −1.13 | 102.76 | 100.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Xue, W.; Kang, D.; Peng, Z. Assessment of Ecosystem Service Values of Urban Wetland: Taking East Lake Scenic Area in Wuhan as an Example. Land 2024, 13, 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13071013
Sun Z, Xue W, Kang D, Peng Z. Assessment of Ecosystem Service Values of Urban Wetland: Taking East Lake Scenic Area in Wuhan as an Example. Land. 2024; 13(7):1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13071013
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zhihao, Wei Xue, Dezhi Kang, and Zhenghong Peng. 2024. "Assessment of Ecosystem Service Values of Urban Wetland: Taking East Lake Scenic Area in Wuhan as an Example" Land 13, no. 7: 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13071013
APA StyleSun, Z., Xue, W., Kang, D., & Peng, Z. (2024). Assessment of Ecosystem Service Values of Urban Wetland: Taking East Lake Scenic Area in Wuhan as an Example. Land, 13(7), 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13071013






