Optimization of Land Use Structure Based on the Coupling of GMOP and PLUS Models: A Case Study of Lvliang City, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
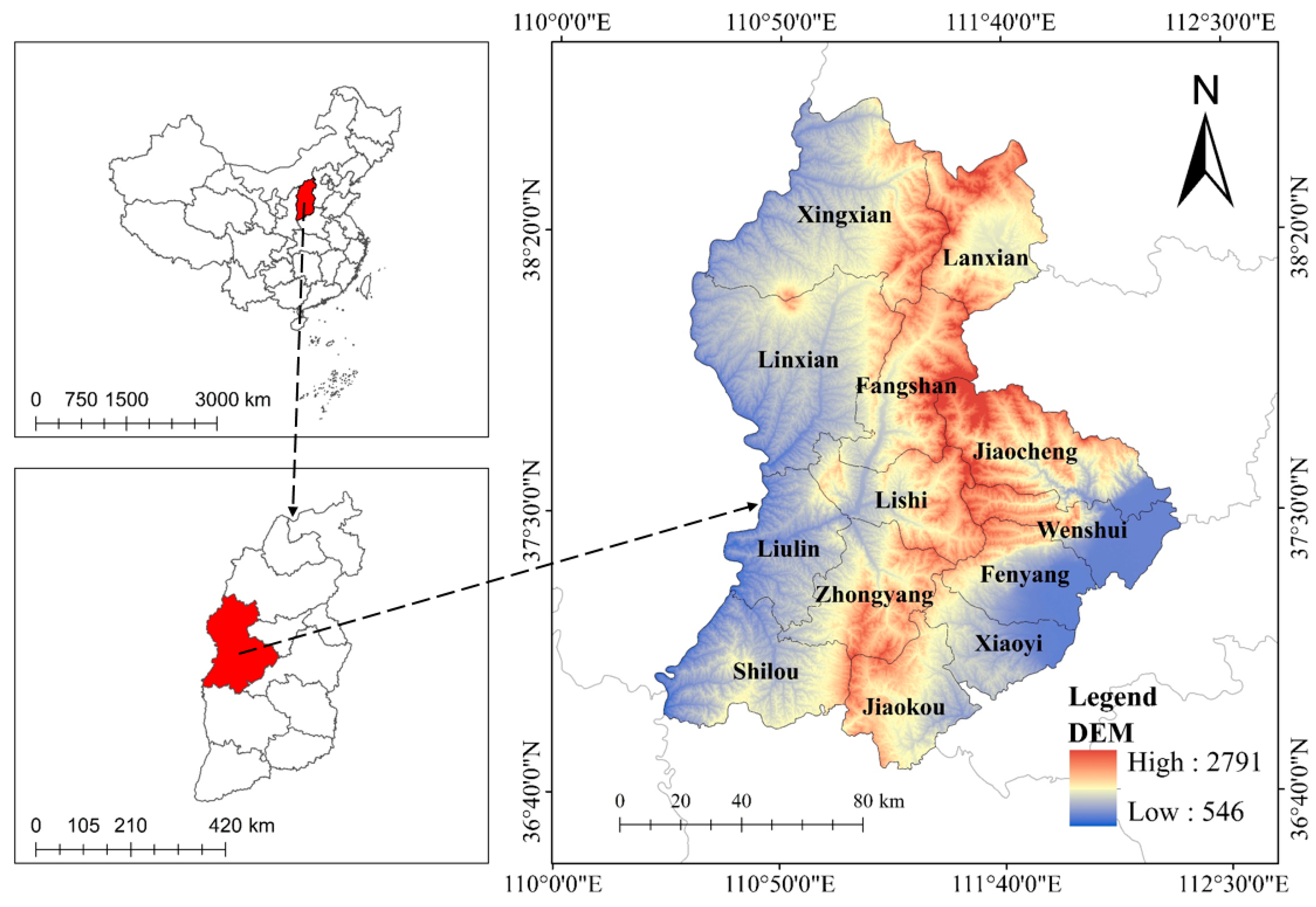
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
3. Design Framework and Methodology
3.1. Data Processing
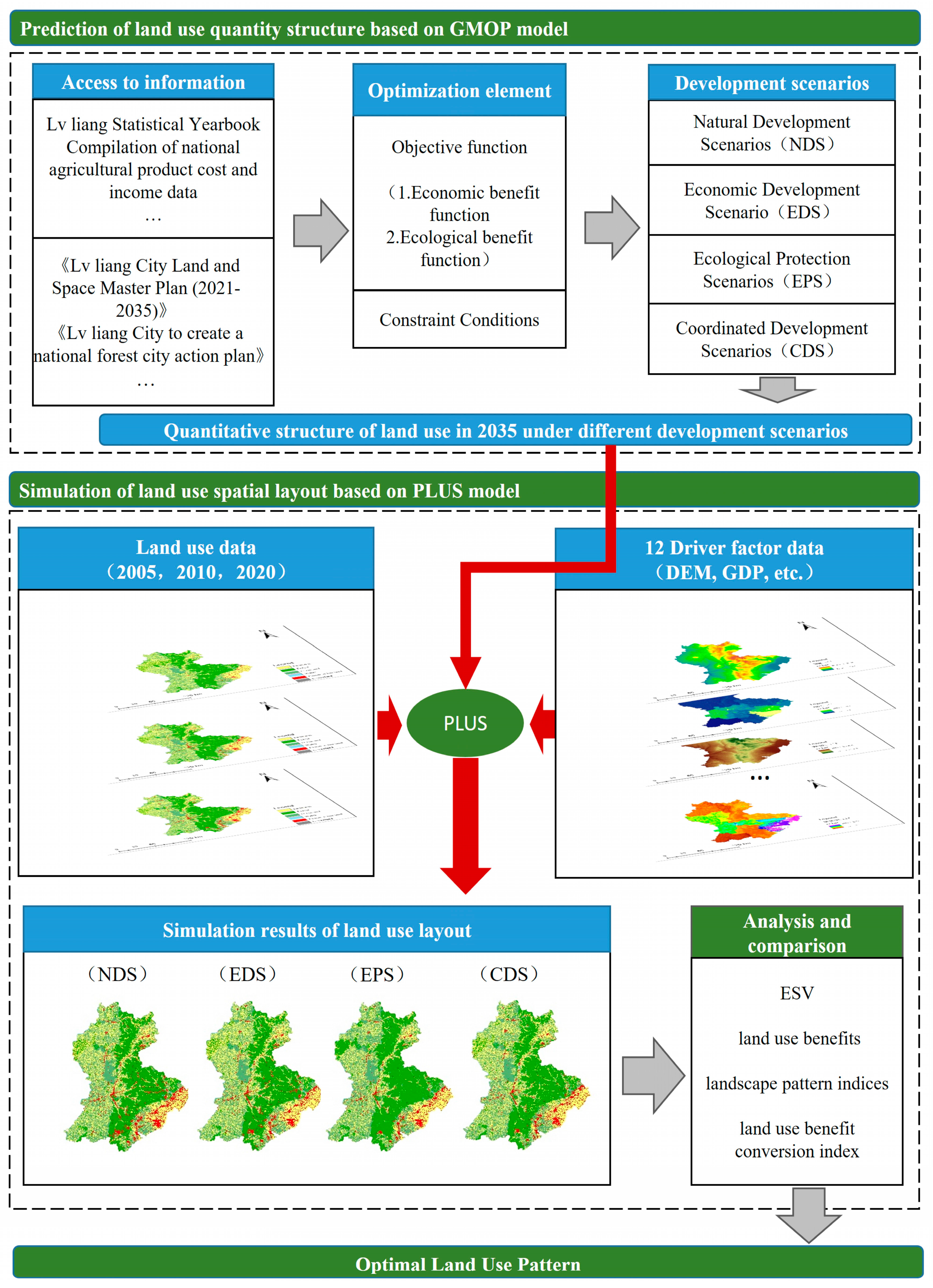
3.1.1. Research Framework
- (1)
- Prediction of Land Use Quantity Structure: The prediction of land quantity structure involves forecasting the proportions of different land types within a specific area in the future. Four different development scenarios are initially set, as follows: a natural development scenario (NDS), an economic development scenario (EDS), an ecological protection scenario (EPS), and a coordinated development scenario (CDS). The prediction of land use structure under the NDS is based on the land use data of Lvliang City from 2005 and 2020. Using the Markov Chain model, the land area for each type of land use in Lvliang City in 2035 is predicted. This process is implemented in the PLUS model. The EDS and EPS fall under single-objective planning problems, as each of these scenarios requires maximizing either economic or ecological benefits as the sole objective. By calculating and predicting the economic and ecological benefit coefficients for each land type in 2035 and setting constraints for each type of land use, the solution is achieved using LINGO20.0 software. LINGO, developed by Lindo System, Inc. (Chicago, IL, USA) in the United States, is an interactive solver for both linear and general optimization. It effectively addresses nonlinear programming challenges in addition to solving various linear and nonlinear equations, making it a highly versatile tool and an optimal choice for tackling complex optimization models. The CDS falls under multi-objective planning problems, solved using the NSGA-II.
- (2)
- Simulation of Land Use Structure Layout: Based on the predicted land use quantity structures under different scenarios, and using the 2020 land use data as the baseline, the spatial layout of land use in Lvliang City under various future development scenarios is simulated.
- (3)
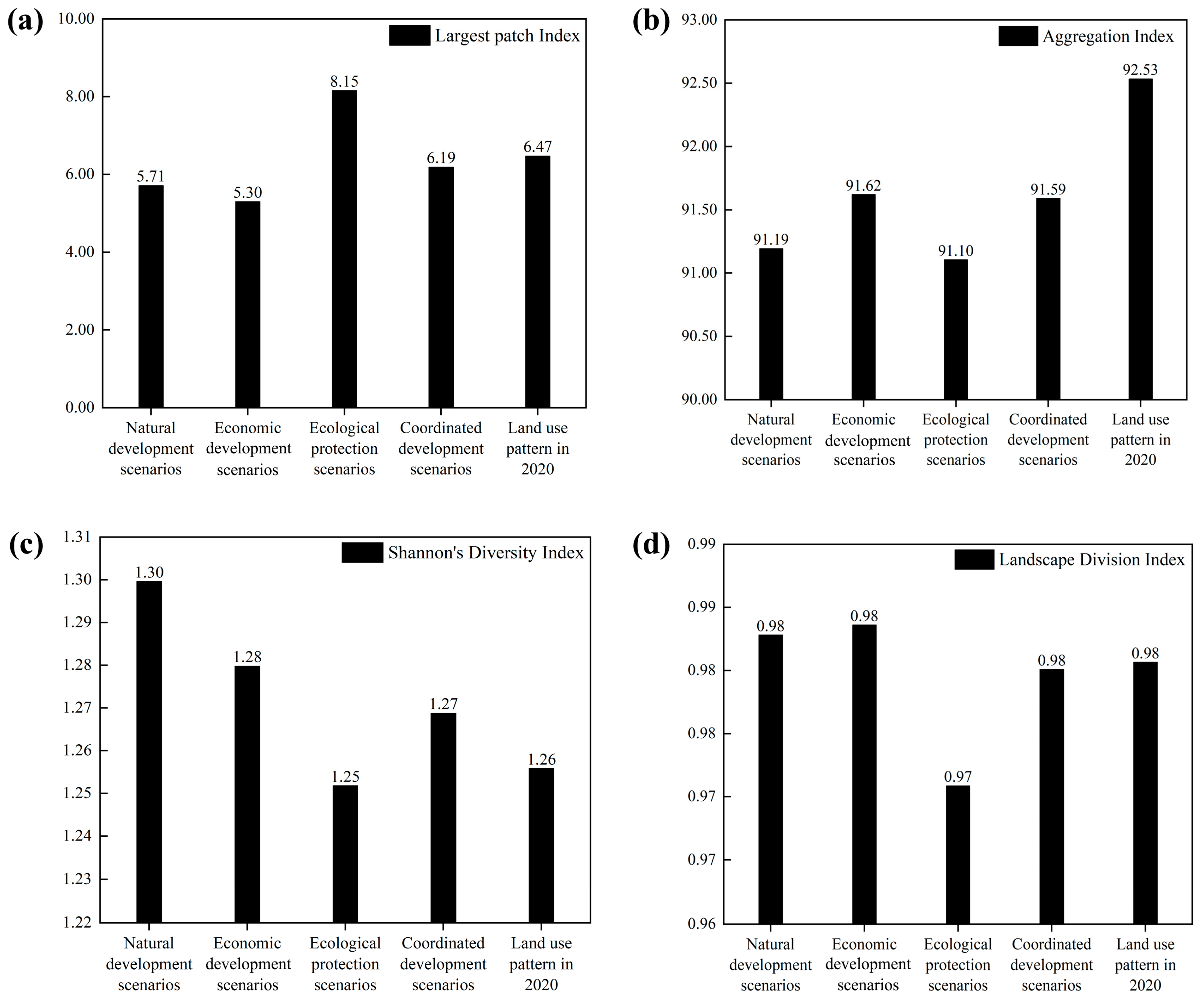
- Analysis of Land Use Layout: Based on the predicted areas of each land type under different scenarios, the benefits of land use are calculated using ecological and economic benefit coefficients. The ESV is calculated using the Xie Gaodi equivalent factor method. In this study, four landscape pattern indices are selected to analyze the land use layout under different scenarios. These indices include the aggregation index (AI), the largest patch index (LPI), the landscape division index (DIVISION), and the Shannon Diversity Index (SHDI), all calculated using Fragstats4.2 software. These landscape pattern indices reflect the aggregation and dispersion states of the landscape under different development scenarios. Additionally, a land use benefit conversion index is constructed to analyze the efficiency of conversion between ESV and land use benefits. Finally, a comprehensive analysis of land use benefits, ESV, landscape pattern indices, and land use benefit conversion indices under different scenarios is conducted to determine the optimal land use structure.
3.1.2. Verification of Simulation Accuracy
3.2. Methodology
3.2.1. The GMOP Model
3.2.2. The PLUS Model
- (1)
- Adaptation Probability. The LEAS module incorporates a stochastic sampling mechanism designed to reduce computational costs while simultaneously utilizing the random forest algorithm to assess the development probabilities associated with various land use types. The formula is presented as follows:where M denotes the total count of decision trees, X represents the vector that comprises the driving factors, hn(X) indicates the predicted land use type generated by the n-th decision tree, and d takes on a value of either 0 or 1.
- (2)
- Adaptive Inertia Coefficient. This coefficient is adaptively adjusted during repeated runs, based on the discrepancy between the expected land type data and the actual land type data. This mechanism effectively mitigates the uncertainties and complexities associated with natural processes and human activities involved in land use conversion. Consequently, it improves the accuracy of the simulation model and attains the intended outcomes regarding land use types [33]. The formula is as follows:where signifies the inertia coefficient for the k-th land use type at time t. Additionally, and represent the discrepancies between the actual land amount and the demand at times t − 1 and t − 2, respectively.
- (3)
- Optimization of Land Use Layout. Twelve factors, encompassing elevation, slope, population, soil type, GDP, road networks, rivers, and distance to the county government seat, are identified as driving forces for land use change. Concurrently, water bodies are designated as restricted areas during the optimization process. The precision of the model is assessed through two primary parameters: overall accuracy and the Kappa coefficient.
3.2.3. Constructing the Objective Function
- (1)
- Economic Benefit Function. The economic advantages of land are primarily defined by the economic output per unit area for each category of land. This study utilizes statistical yearbooks from Luliang City spanning the years 2017 to 2023. The output for cultivated and forest land is indicated by the values of agricultural and forestry production, respectively. The output for grassland is denoted by the value derived from animal husbandry, while the output for aquatic areas is represented by the fishery output value. Furthermore, the economic impact of construction land is demonstrated through the output values generated by the secondary and tertiary industries.
- (2)
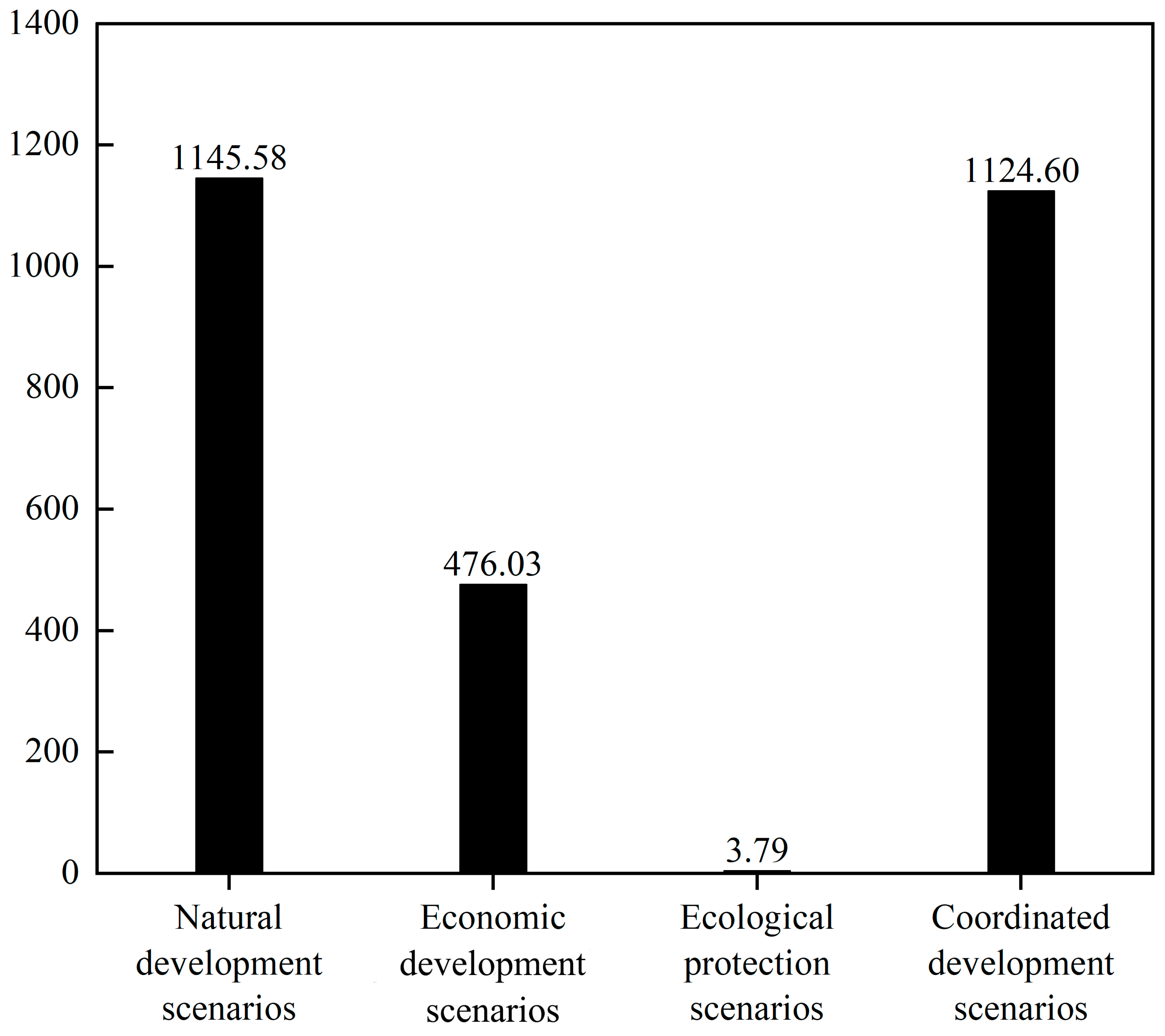
- Ecological Benefit Function. The ecological benefit coefficients of land are primarily assessed using the equivalent factor method, as suggested by researchers such as Xie Gaodi. This methodology primarily captures the ESV provided by land. Since the supply services of land ecosystems are already incorporated into the economic benefits, the ecological advantages encompass the regulatory, supporting, and cultural services of ecosystems. This study employs the terrestrial ESV equivalent factor method, as recommended by scholars, including Xie Gaodi [34], for the purpose of evaluation. Additionally, the equivalent factor table is adjusted based on the ratio of the NPP level in Lvliang City compared to the national average [35]. Data regarding the prices of local food crops and their yield per unit area are obtained by consulting the Lvliang Statistical Yearbook from 2016 to 2022. The ESV is quantified at one-seventh of the economic value linked to grain production per unit area of farmland. This value encompasses a range of ecosystem services, including supply, regulatory, supporting, and cultural services. Acknowledging that supply services are included within economic benefits, ecological benefits are delineated by regulatory, supporting, and cultural services. Annual coefficients for land ecological benefits are calculated, and these coefficients are projected for Lvliang City in 2035 using the GM (1: 1) model. To ensure the reliability of the revised eco-efficiency coefficients for land, a sensitivity index is employed to evaluate how variations in these coefficients affect the total ESV for each land type. The sensitivity of ESV to these coefficients is evaluated by modifying the eco-efficiency coefficients for each land type by ±50 percent. The formula is as follows:where CS denotes the sensitivity index that measures the response of a specific land type to the value of land ecosystem services. E1 and E2 represent the ESV in Lvliang City prior to and following the adjustment, respectively. V1i and V2i indicate the ecological benefit coefficients for the i-th land type before and after the adjustment, respectively. A CS value of less than 1 indicates that the ESV is inelastic regarding the ecological benefit coefficients of that land type. Lower CS values suggest a diminished responsiveness of the assessment of land ESV to the precision of the ecological benefit coefficients, thereby indicating a higher degree of rationality in the coefficients [36]. Relevant parameters are shown in Table 2 and Table 3.
3.2.4. Restrictive Condition
4. Results
4.1. Analysis of the Quantitative Structure of Land Use
4.2. Simulation Analysis of Spatial Layout of Land Use Structure
4.3. Land Use Benefits and ESV
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The GMOP and PLUS coupling models are used to determine land use structure and spatial distribution under various development objectives. By employing this coupled approach, land use patterns for Lvliang City are derived across four distinct development scenarios.
- (2)
- From the perspective of landscape patterns, the land use pattern under the CDS is characterized by minimal human disturbance, enhanced patch aggregation, greater species diversity, and improved ecological quality.
- (3)
- The land use benefits under the NDS, EDS, EPS, and CDS are 2392.902 billion yuan, 2025.413 billion yuan, 1577.543 billion yuan, and 1755.364 billion yuan, respectively. The ESV are 26.308 billion yuan, 26.087 billion yuan, 28.665 billion yuan, and 26.861 billion yuan, respectively. This shows that the CDS can meet economic development needs while also considering ecological environment protection.
- (4)
- Under the CDS, when the areas of cultivated land, grassland, forest land, water bodies, construction land, and unused land are 6724.29 km2, 6664.74 km2, 6581.84 km2, 126.94 km2, 1017.33 km2, and 0.42 km2, respectively, the land use benefit conversion index is at its highest.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, X.; Pu, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.E.; Gu, Z. Land-Use Spatio-Temporal Change and Its Driving Factors in an Artificial Forest Area in Southwest China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimal, B.; Zhang, L.; Keshtkar, H.; Wang, N.; Lin, Y. Monitoring and Modeling of Spatiotemporal Urban Expansion and Land-Use/Land-Cover Change Using Integrated Markov Chain Cellular Automata Model. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zscheischler, J.; Rogga, S.; Lange, A. The success of transdisciplinary research for sustainable land use: Individual perceptions and assessments. Sustain. Sci. 2018, 13, 1061–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.B.; Zhang, X.H. Land use structural optimization of Lilin based on GMOP-ESV. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2011, 21, S738–S742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuai, X.W.; Huang, X.J.; Wu, C.Y.; Li, J.B.; Lu, Q.L.; Qi, X.X.; Zhang, M.; Zuo, T.H.; Lu, J.Y. Land use and ecosystems services value changes and ecological land management in coastal Jiangsu, China. Habitat Int. 2016, 57, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MohanRajan, S.N.; Loganathan, A.; Manoharan, P. Survey on Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) change analysis in remote sensing and GIS environment: Techniques and Challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 29900–29926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, P.; Rodes-Blanco, M.; Viana-Soto, A.; Nieto, H.; García, M. The Role of Remote Sensing for the Assessment and Monitoring of Forest Health: A Systematic Evidence Synthesis. Forests 2021, 12, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Sang, L.L.; Zhao, C.S.; Hu, T.Y.; Liu, H.T.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.Y.; Miao, S.X.; Ju, Z.S. Evaluation of Spatiotemporal Changes in Cropland Quantity and Quality with Multi-Source Remote Sensing. Land 2023, 12, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.Q.; Chai, L.R.; Hou, F.J.; Chang, S.H.; Ma, Y.S.; Tsunekawa, A.; Cheng, Y.X. Quantifying Grazing Intensity Using Remote Sensing in Alpine Meadows on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability 2019, 11, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, A.Y.; Hu, C.M.; You, L. Evaluation and Prediction of Ecological Restoration Effect of Beijing Wangping Coal Mine Based on Modified Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Land 2023, 12, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.H.; Wen, Z.Z. Optimization of land use structure to balance economic benefits and ecosystem services under uncertainties: A case study in Wuhan, China. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 311, 127537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Lan, H.F.; Cao, Y.X.; Li, P.Y. Optimization of low-carbon land use in Chengdu based on multi-objective linear programming and the future land use simulation model. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 989747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, L.; Yang, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Qi, Y.; Ma, X.; Cao, L. Exploring the response of ecosystem service value to land use changes under multiple scenarios coupling a mixed-cell cellular automata model and system dynamics model in Xi’an, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 110009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Gu, C.-J.; Xiao, C. Multiple scenarios analysis on land use simulation by coupling socioeconomic and ecological sustainability in Shanghai, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 95, 104578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Nian, P.; Zhang, W. The prediction of interregional land use differences in Beijing: A Markov model. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 73, 4077–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, X.; He, X.; Li, X.; Yang, G.; Li, D.; Xu, W.; Qiao, X.; Li, C.; Sui, L. Multi-Scenario Simulation and Trade-Off Analysis of Ecological Service Value in the Manas River Basin Based on Land Use Optimization in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Han, F.; Gao, J.; Nguyen, T.; Chen, Y.; Huang, B.; Zhan, F.B.; Zhou, L.; Hong, S. Modeling urban growth by the use of a multiobjective optimization approach: Environmental and economic issues for the Yangtze watershed, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 13027–13042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Z.; Huang, Y.P. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Ecosystem Service Value in Wuhan Metropolitan Area Based on PLUS-GMOP Model. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, Y.M.; Gao, B.P.; Zheng, K.J.; Wu, Y.; Li, C. Multi-scenario simulation of ecosystem service value for optimization of land use in the Sichuan-Yunnan ecological barrier, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.X.; Sun, P.L.; Shen, D.D.; Li, N.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, K. Simulation Analysis of Land-Use Spatial Conflict in a Geopark Based on the GMOP-Markov-PLUS Model: A Case Study of Yimengshan Geopark, China. Land 2023, 12, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firozjaei, M.K.; Sedighi, A.; Argany, M.; Jelokhani-Niaraki, M.; Arsanjani, J.J. A geographical direction-based approach for capturing the local variation of urban expansion in the application of CA-Markov model. Cities 2019, 93, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; Soepboer, W.; Veldkamp, A.; Limpiada, R.; Espaldon, V.; Mastura, S.S.A. Modeling the spatial dynamics of regional land use: The CLUE-S model. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, P.H.; Tian, Y.S.; Chen, H.T.; Chen, Y.Y. Exploring the impact of integrated spatial function zones on land use dynamics and ecosystem services tradeoffs based on a future land use simulation (FLUS) model. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Guan, Q.F.; Clarke, K.C.; Liu, S.S.; Wang, B.Y.; Yao, Y. Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) model: A case study in Wuhan, China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 85, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Xue, M. Optimization and Simulation of Mountain City Land Use Based on MOP-PLUS Model: A Case Study of Caijia Cluster, Chongqing. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, R.; Wang, Z.; Guo, N.; Wei, M.; Zou, Y.; Hou, K. Multi-Scenario Land Use Optimization Simulation and Ecosystem Service Value Estimation Based on Fine-Scale Land Survey Data. Land 2024, 13, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, C.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Liu, J. Multi-objective land use optimization based on integrated NSGA-II-PLUS model: Comprehensive consideration of economic development and ecosystem services value enhancement. J. Clean Prod. 2024, 434, 140306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, P. Multi-Objective Optimization of Land Use in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region of China Based on the GMOP-PLUS Coupling Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Xin, C.L.; Tang, D.B.; Zhang, L.; Xin, S.J. Multi-scenario land use optimization and carbon stock assessment in Northwest China. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 4655–4665. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, P.F.; Wang, H.Y.; Qin, F.; Miao, C.H.; Zhang, F.F. Coupled MOP and PLUS-SA Model Research on Land Use Scenario Simulations in Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area, Central China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Guo, M.D.; Zhang, D.; Chen, R.Q.; Xi, C.F.; Yang, H.B. Coupling the Calibrated GlobalLand30 Data and Modified PLUS Model for Multi-Scenario Land Use Simulation and Landscape Ecological Risk Assessment. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.X.; Liu, X.P.; Zhang, D.C.; Zhang, J.B.; He, J.Y.; Xu, X.C. Simulating mixed land-use change under multi-label concept by integrating a convolutional neural network and cellular automata: A case study of Huizhou, China. GISci. Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 609–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.M.; Yuan, S.F.; Yang, L.X. Optimization and trade-off analysis of land use pattern in Hangzhou coupled with MOP and FLUS models. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 235–244. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Zhen, L.; Lu, C.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, C. An expert knowledge-based approach to ecosystem service valorisation. J. Nat. Resour. 2008, 5, 911–919. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Fu, J.Y.; Jiang, D.; Lin, G.; Cao, C.L. Land use optimization in Ningbo City with a coupled GA and PLUS model. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 375, 134004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Du, G.M.; Teng, H.; Wang, J.; Li, H.L. Multi-Scenario Land Use Change Simulation and Spatial Response of Ecosystem Service Value in Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Land 2023, 12, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.S.; Zhen, L.; Miah, M.G.; Ahamed, T.; Samie, A. Impact of land use change on ecosystem services: A review. Environ. Dev. 2020, 34, 100527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Guan, Q.; Lin, J.; Yang, L.; Luo, H.; Ma, Y.; Tian, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, N. The response and simulation of ecosystem services value to land use/land cover in an oasis, Northwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Wang, H.; Luo, K.; Yan, X.; Yi, S.; Huang, X. The Use of an Optimized Grey Multi-Objective Programming-PLUS Model for Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use in the Weigan-Kuche River Oasis, China. Land 2024, 13, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Halike, A.; Yao, K.; Wei, Q.; Yao, L.; Tuheti, B.; Luo, J.; Duan, Y. Ecosystem service valuation and multi-scenario simulation in the Ebinur Lake Basin using a coupled GMOP-PLUS model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Naerkezi, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B. Multi-Scenario Land Use/Cover Change and Its Impact on Carbon Storage Based on the Coupled GMOP-PLUS-InVEST Model in the Hexi Corridor, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Sha, J.; Zhou, J.; Jiao, Y. Quantification and Simulation of the Ecosystem Service Value of Karst Region in Southwest China. Land 2024, 13, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Data Type | Data Content | Data Description | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Land Use Type | Land use monitoring data for Lvliang City, 2005, 2010 and 2020 | The spatial resolution is 30 m × 30 m, and it was divided into six categories according to the purpose of the study | https://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 16 March 2024. |
| Topographic Data | Soil Type | Image element size is 1000 × 1000 | https://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 16 March 2024. |
| DEM | Initial resolution of 250 m × 250 m | https://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 16 March 2024. | |
| Slope | Initial resolution of 250 m × 250 m | Generated by DEM | |
| River Data | vector data | https://www.webmap.cn/, accessed on 16 March 2024. | |
| Meteorological Data | Rainfall Data | Image element size is 1000 × 1000 | https://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 16 March 2024. |
| Temperature Data | Image element size is 1000 × 1000 | https://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 16 March 2024. | |
| Social Data | GDP | Image element size is 1000 × 1000 | https://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 16 March 2024. |
| Population | Image element size is 1000 × 1000 | https://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 16 March 2024. | |
| County Government Locations | Image element size is 1000 × 1000 | https://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 16 March 2024. | |
| Primary roads Secondary roads Tertiary roads | Road vector data | https://www.webmap.cn/, accessed on 16 March 2024. |
| Efficiency | Farmland | Forest | Grassland | Waterbody | Construction Land | Unused Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| economic efficiency | 808.48 | 167.74 | 247.83 | 44.76 | 164,272.42 | 0.01 |
| eco-efficiency | 33.88 | 215.17 | 92.42 | 1316.57 | 0 | 2.47 |
| Year | Farmland | Forest | Grassland | Waterbody | Construction Land | Unused Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 0.0043 | 0.0268 | 0.0096 | 0.0036 | 0 | 0.0001 |
| 2020 | 0.0015 | 0.0093 | 0.0037 | 0.0011 | 0 | 0.0001 |
| Constraint | Prerequisite | Foundation |
|---|---|---|
| Total land area | X1 + X2 + X3 + X4 + X5 + X6 = 21,115.57 km2 | Total land area constraint. |
| Farmland | 4165.34 km2 ≤ X1 ≤ X1+, X1+ is the area of farmland in Lvliang City in 2020 | The Lvliang City Territorial Spatial Master Plan (2021–2035) calls for farmland holdings of 4165.342 km2. |
| Forest | 6334.67 km2 ≤ X2 ≤ 7528.98 km2 | Action Programme for the Creation of a National Forest City in Lvliang City: Lvliang citywide forest cover of more than 30 per cent, which is less than 1.1 times the current value in 2020. |
| Grassland | 6453.09 km2 ≤ X3 ≤ 6906.55 km2 | Greater than projected under natural development conditions and less than 1.1 times the current value in 2020. |
| Waterbody | 121.17 km2 ≤ X4 ≤ 129.76 km2 | Greater than the current value in 2020 and less than the projected value of natural development. |
| Construction land | 898.41 km2 ≤ X5 ≤ 1167.94 km2 | The State Council’s approval of the “Shanxi Province Land Space Planning (2021–2035)” requires that the expansion of the urban development boundary be controlled within 1.3 times the size of the urban construction land based on 2020, with 1.3 times the existing construction land in Lvliang City as the upper boundary, and the lower boundary as the status quo value in 2020. |
| Unused Land | 0.37 km2 ≤ X5 ≤ 0.52 km2 | Greater than the current value in 2020 and less than the projected value of natural development. |
| Land Type | 2020 | Development Scenarios | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Development | Economic Development | Ecological Protection | Coordinated Development | ||
| Farmland | 6972.40 | 6666.23 | 6972.40 | 5651.49 | 6724.29 |
| Forest | 6844.53 | 6473.01 | 6334.67 | 7528.98 | 6664.74 |
| Grassland | 6278.68 | 6453.08 | 6519.02 | 6906.55 | 6581.84 |
| Waterbody | 121.17 | 129.76 | 121.17 | 129.76 | 126.94 |
| Construction land | 898.41 | 1392.96 | 1167.94 | 898.41 | 1017.33 |
| Unused Land | 0.37 | 0.52 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.42 |
| Development Scenario | Land Use Benefits | Ecosystem Services Values |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Development Scenario | 23,929.02 | 263.08 |
| Economic Development Scenario | 20,254.13 | 260.87 |
| Ecological Protection Scenarios | 15,775.43 | 286.65 |
| Coordinated Development Scenario | 17,553.64 | 268.61 |
| 2020 Land Use Pattern | 15,837.95 | 270.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Zhong, A.; Li, Q. Optimization of Land Use Structure Based on the Coupling of GMOP and PLUS Models: A Case Study of Lvliang City, China. Land 2024, 13, 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081335
Wang Z, Zhong A, Li Q. Optimization of Land Use Structure Based on the Coupling of GMOP and PLUS Models: A Case Study of Lvliang City, China. Land. 2024; 13(8):1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081335
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhen, Anya Zhong, and Quanzhi Li. 2024. "Optimization of Land Use Structure Based on the Coupling of GMOP and PLUS Models: A Case Study of Lvliang City, China" Land 13, no. 8: 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081335
APA StyleWang, Z., Zhong, A., & Li, Q. (2024). Optimization of Land Use Structure Based on the Coupling of GMOP and PLUS Models: A Case Study of Lvliang City, China. Land, 13(8), 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081335






