Assessing Land-Cover Change Trends, Patterns, and Transitions in Coalfield Counties of Eastern Kentucky, USA
Abstract
1. Introduction
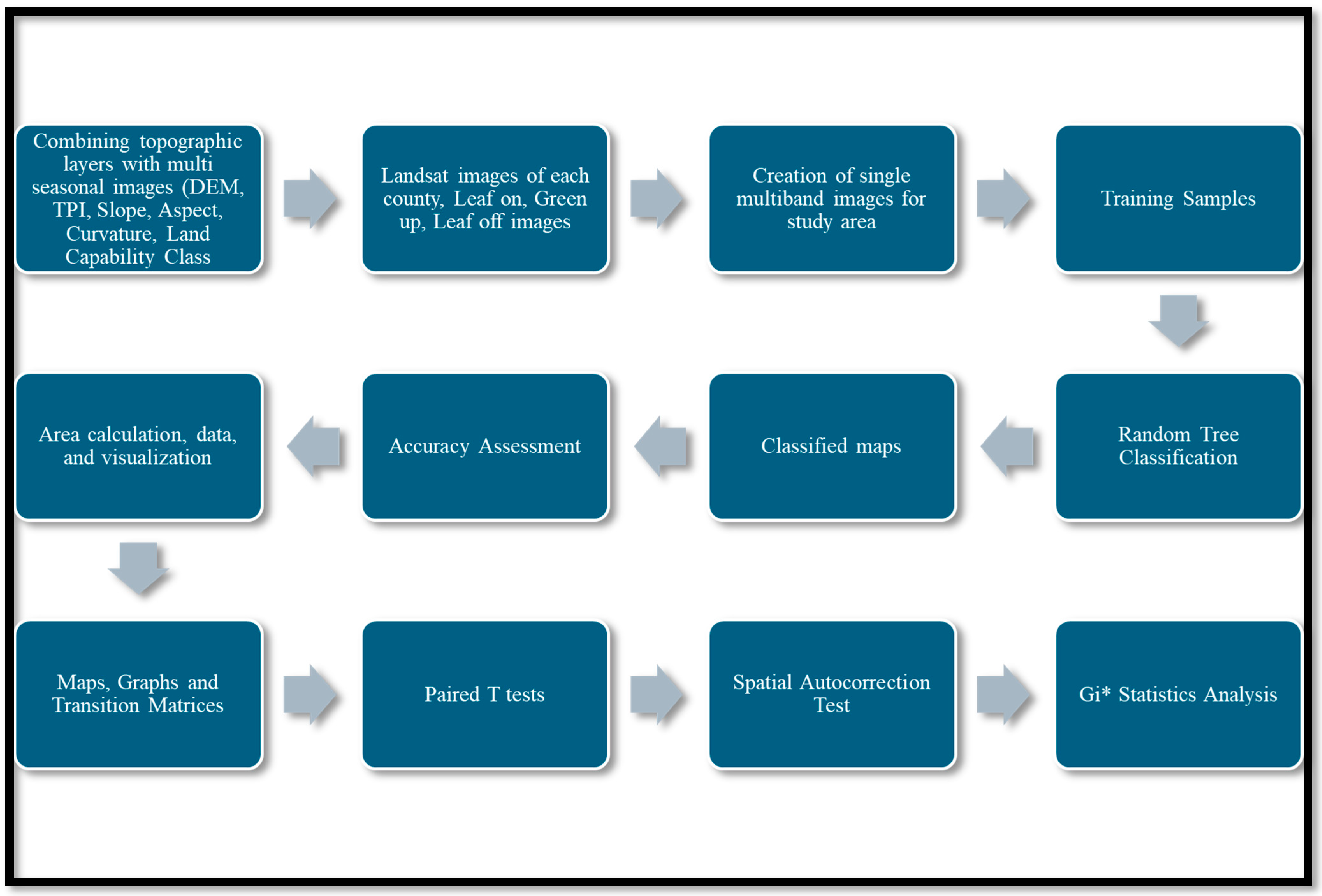
2. Methods
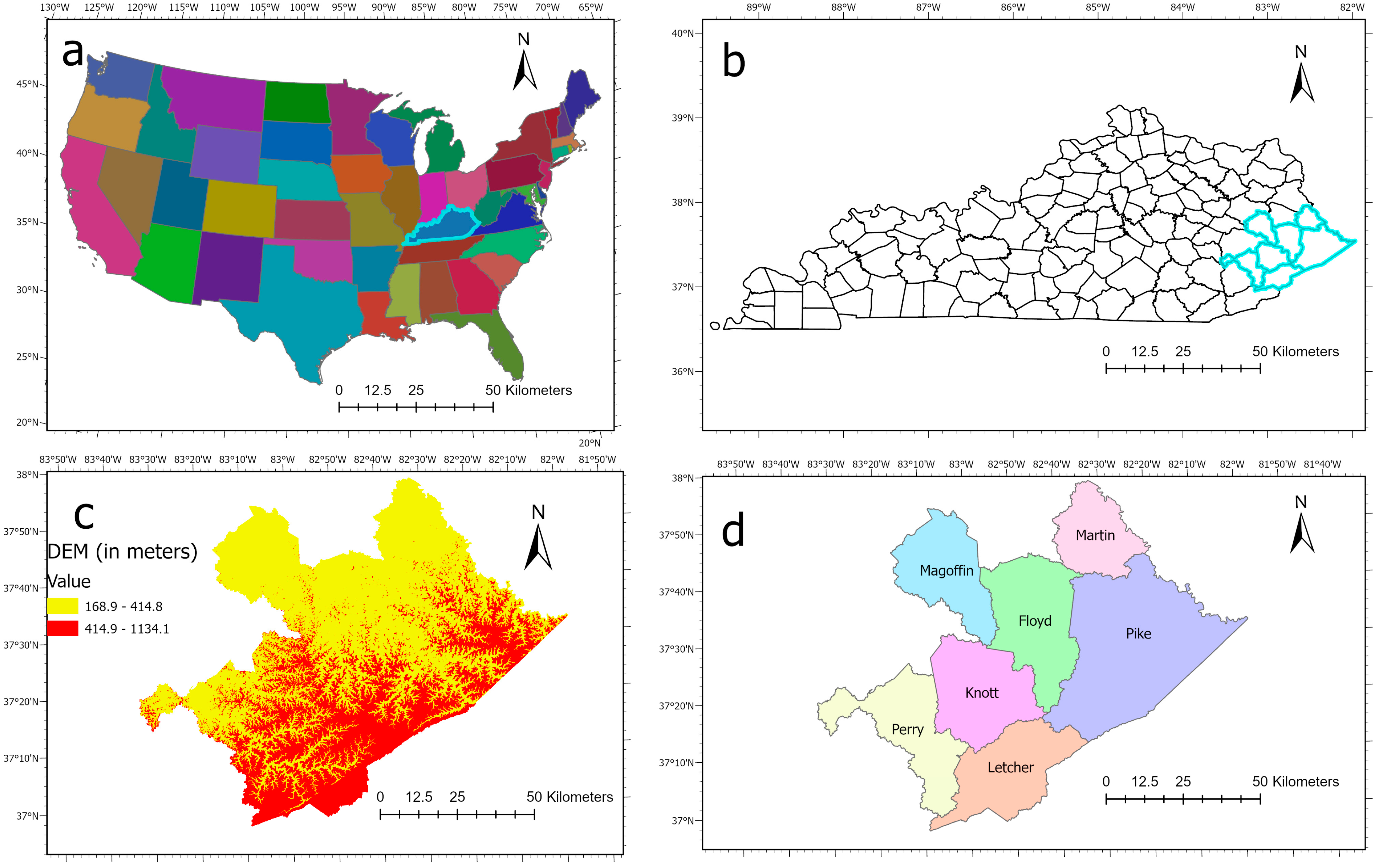
2.1. Study Area
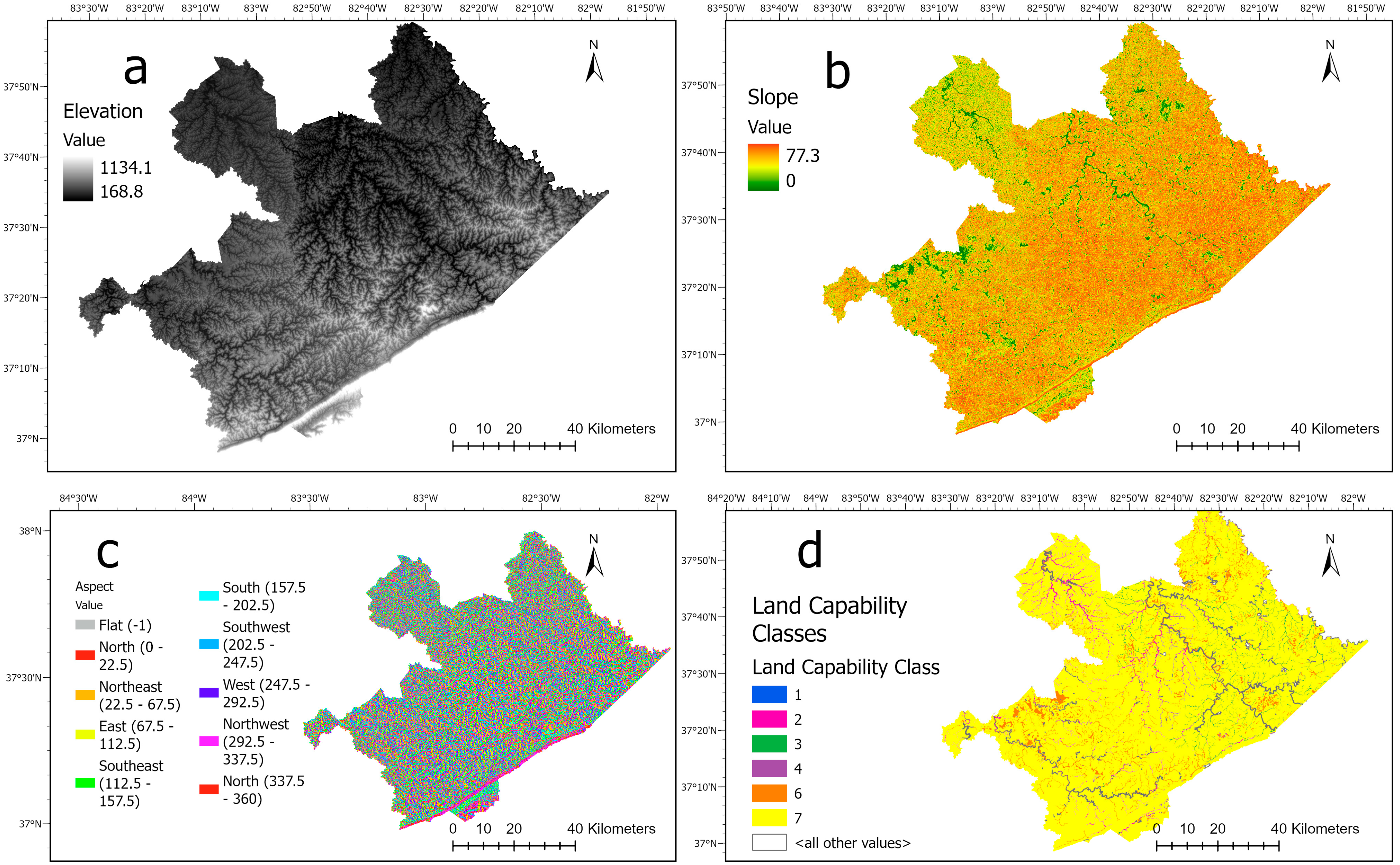
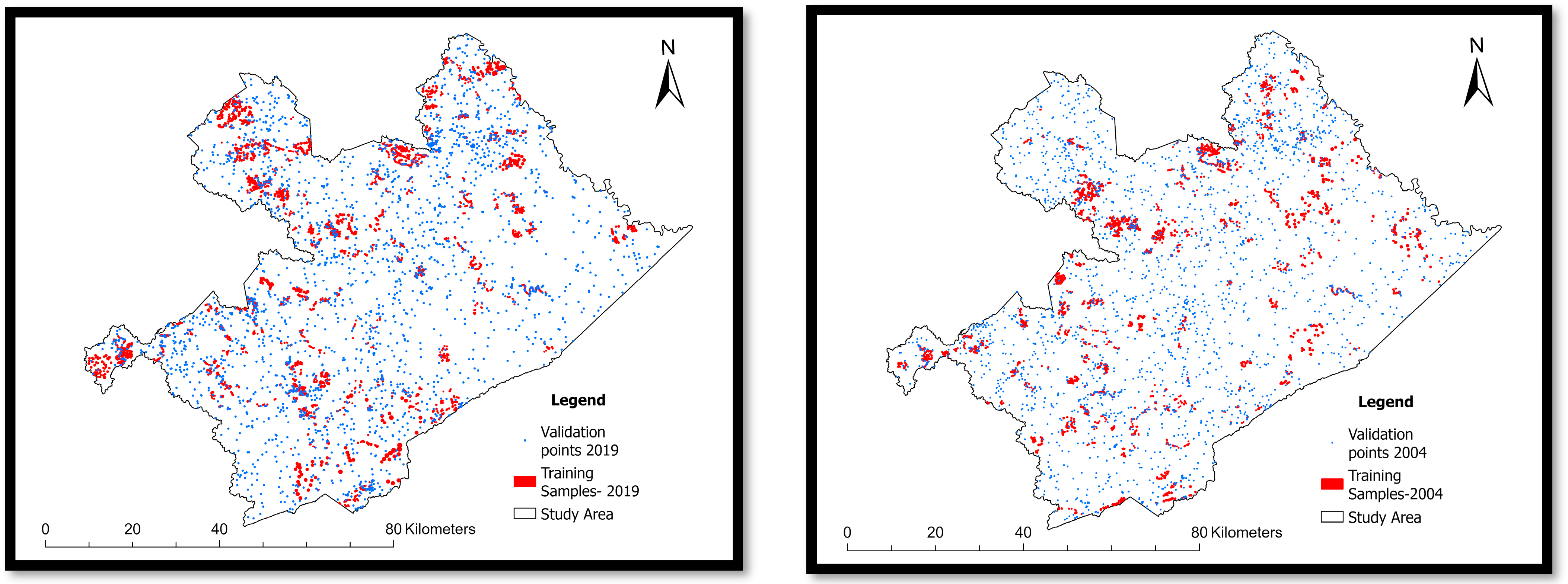
2.2. Data Preparation
2.3. Image Classification
| Serial Number | Land-Cover Class Value | Land-Cover Class Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | Developed | Areas with constructed materials, an impervious surface, a mixture of some vegetation, housing units, commercial and industrial buildings, roads, golf courses, etcetera. |
| 2 | 8 | Planted/Cultivated | Land used broadly for food and fiber; pastureland |
| 3 | 7 | Herbaceous | Land where the natural vegetation is grasses, grass-like plants and herbaceous vegetation |
| 4 | 4 | Forest land | Areas generally dominated by trees and a vegetation cover greater than 20% |
| 5 | 5 | Shrubland | Areas dominated by shrubs |
| 6 | 3 | Barren land | Areas where less than one-third of the area has vegetation, thin soil, sand or rocks and mine lands present |
| 7 | 1 | Water | Areas of open water generally with less than a 25% cover of vegetation or soil |
2.4. Transition Matrix Analysis
2.5. Spatial Autocorrelation
2.6. Accuracy Assessment
2.7. Hot Spot Analysis
2.8. Paired t-Tests
3. Results
3.1. Topographic Attributes
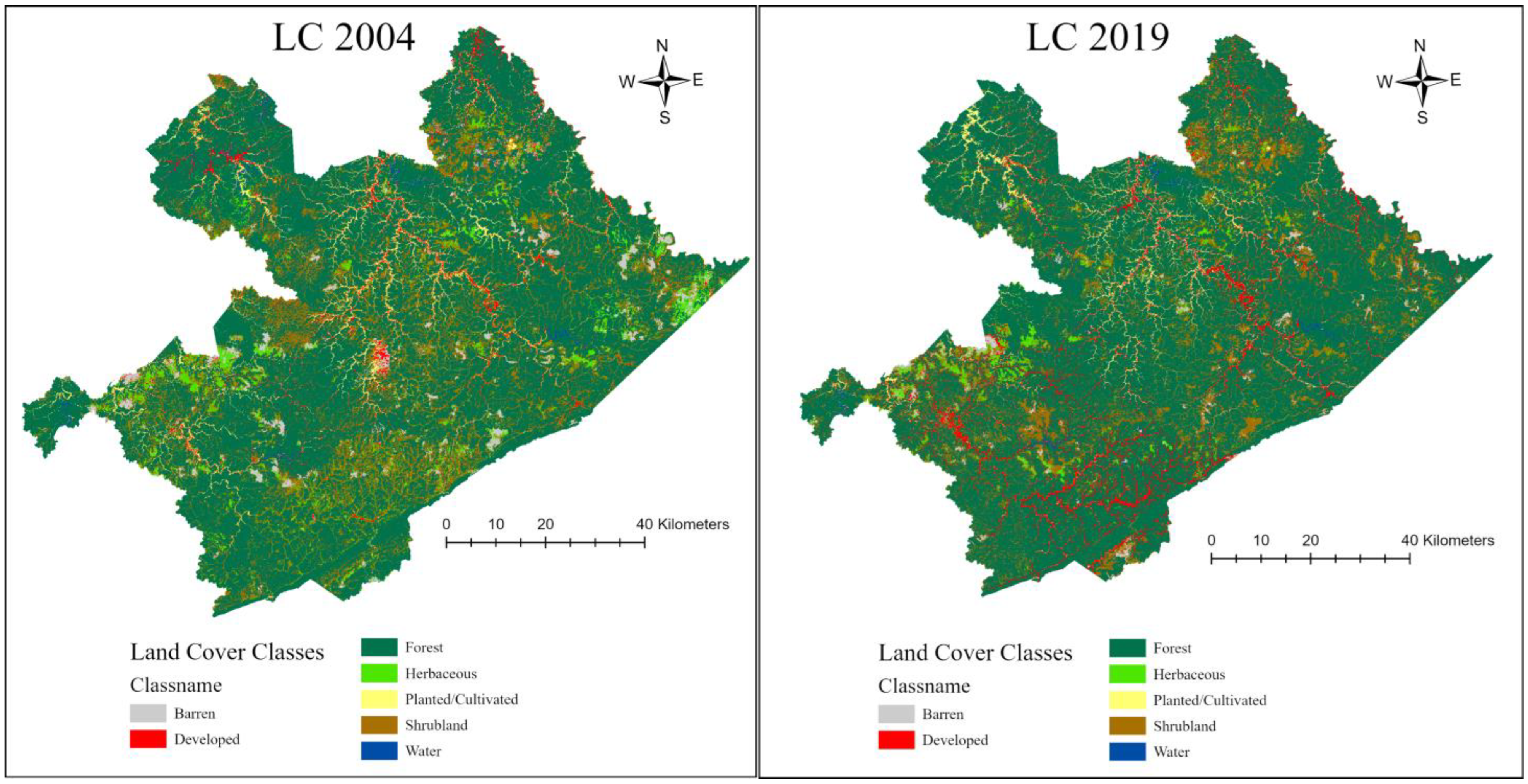
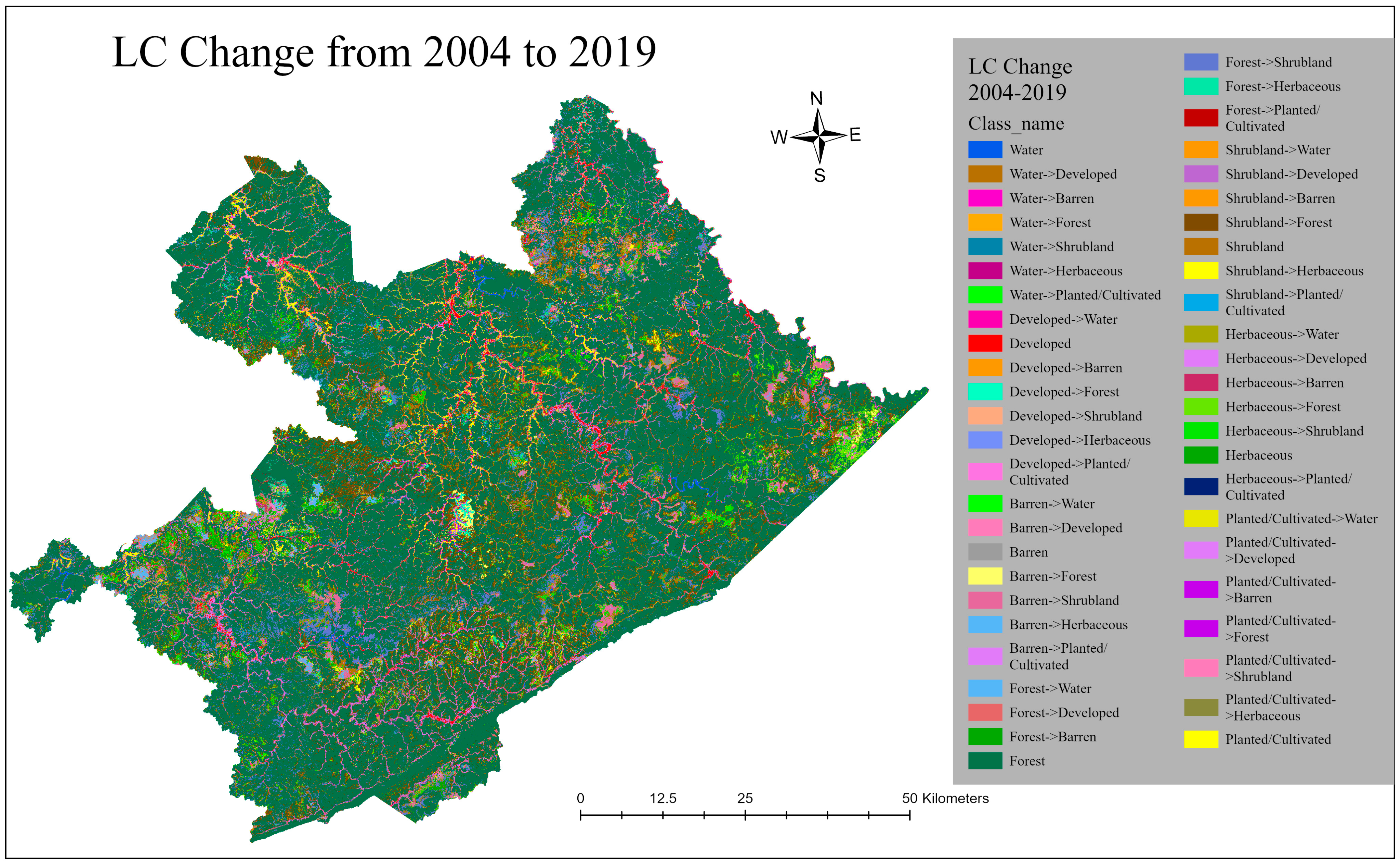
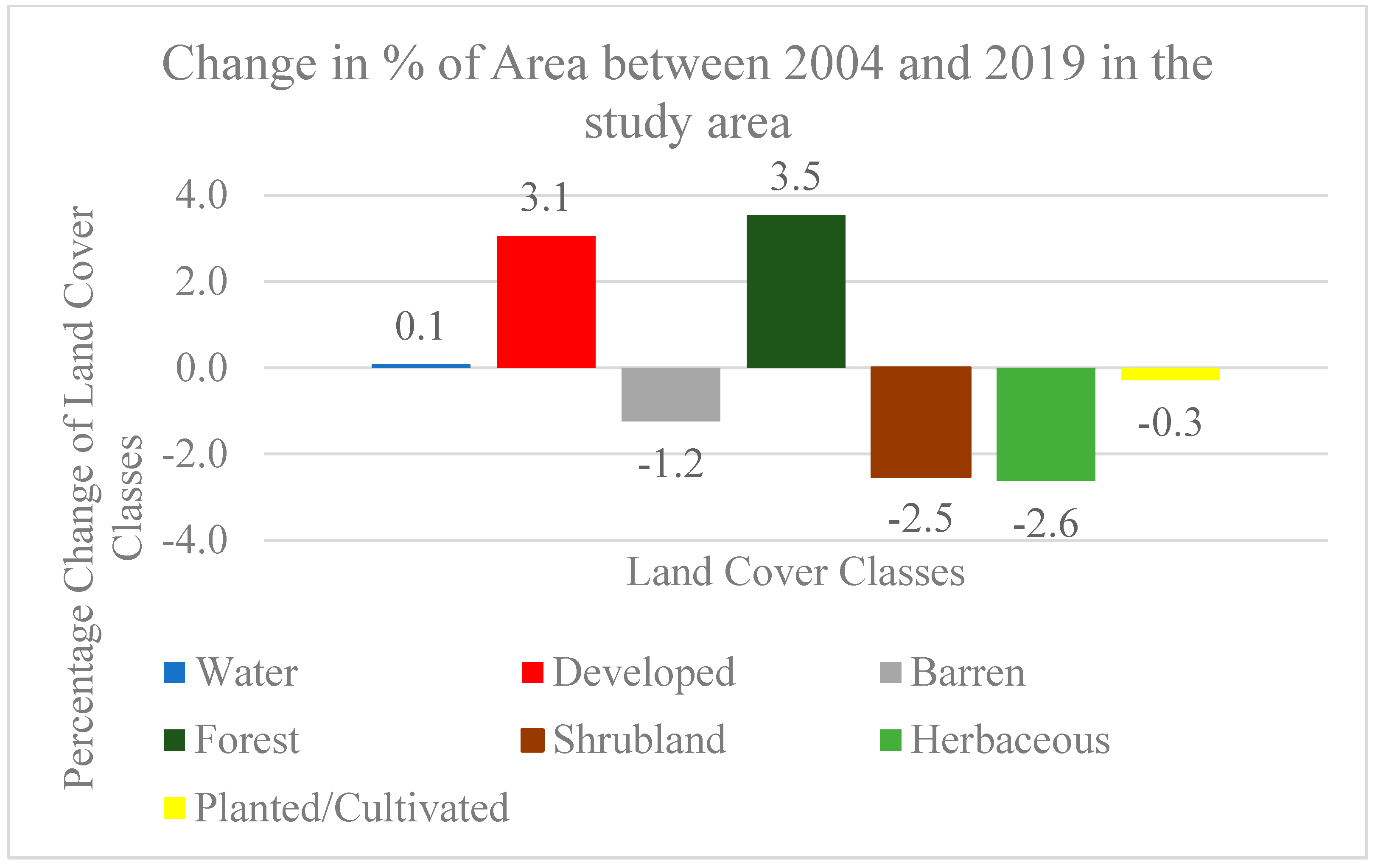
3.2. Land-Cover Change
3.3. Land-Cover Transition
3.4. Spatial Autocorrelation Results
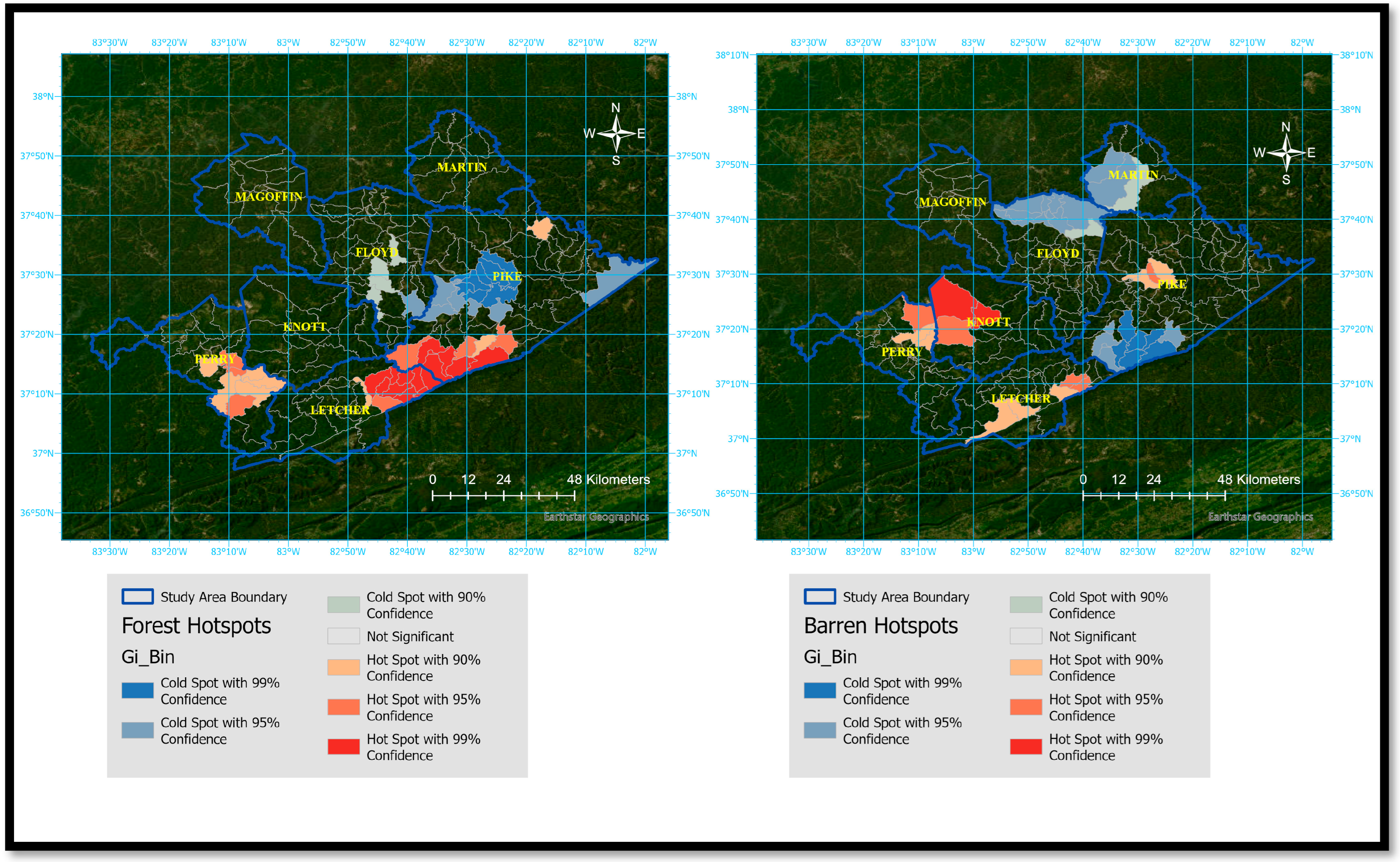
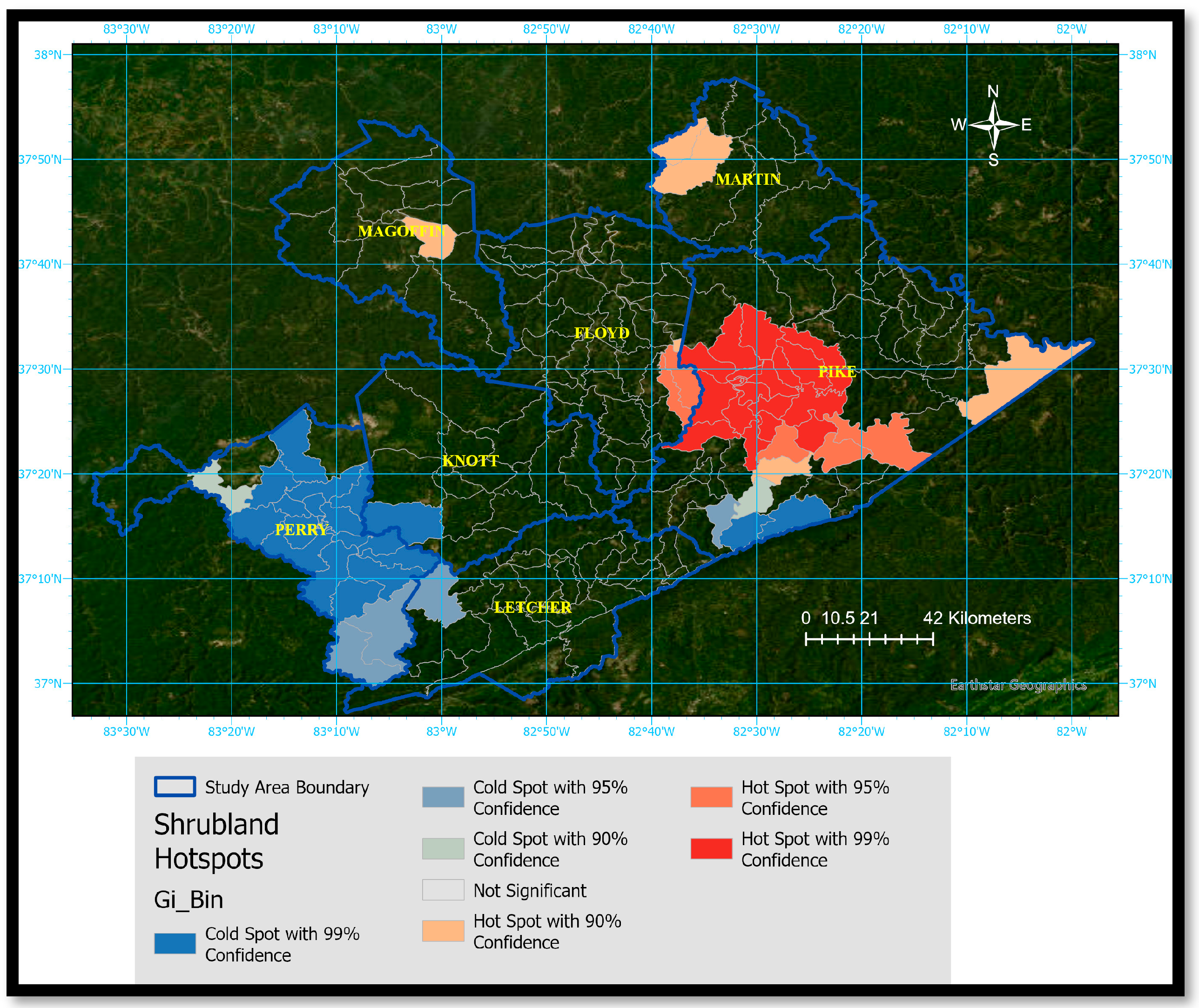
3.5. Hot Spot and Cold Spot Analysis
3.6. Accuracy Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banks, A. Coal Miners and Firebrick Workers: The Structure of Work Relations in Two Eastern Kentucky Communities. Appalach. J. 1983, 11, 85–102. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, E.V.; Zipper, C.E.; Soucek, D.J.; Daniels, W.L. Contaminants in Appalachian Water Resources Generated by Non-acid-forming Coal-Mining Materials. In Appalachia’s Coal-Mined Landscapes: Resources and Communities in a New Energy Era; Zipper, C.E., Skousen, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 217–243. ISBN 978-3-030-57780-3. [Google Scholar]
- Pond, G.J. Effects of Surface Mining and Residential Land Use on Headwater Stream Biotic Integrity in the Eastern Kentucky Coalfield Region; Kentucky Department for Environmental Protection, Division of Water: Frankfort, KY, USA, 2004.
- Davidson, W.H.; Hutnik, R.J.; Parr, D.E. Reforestation of Mined Land in the Northeastern and North-Central U.S. North. J. Appl. For. 1984, 1, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, I.P.; Welivitiya, W.D.D.P.; Nadeeka, P.M. Remote sensing based analysis of urban heat islands with vegetation cover in Colombo city, Sri Lanka using Landsat-7 ETM+ data. Urban Clim. 2013, 5, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeiser, J.M.; Baxley, D.L.; Robinson, B.A.; Morgan, J.J.; Stewart, J.N.; Barnard, J.O. A comparison of coal mine reclamation seed mixes in Kentucky: Implications for grassland establishment in Appalachia. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2016, 30, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, Z.; Reading, L. Effects of surface coal mining and land reclamation on soil properties: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 191, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swab, R.M.; Lorenz, N.; Byrd, S.; Dick, R. Native vegetation in reclamation: Improving habitat and ecosystem function through using prairie species in mine land reclamation. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 108, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, P.A.; Helmers, D.P.; Kingdon, C.C.; McNeil, B.E.; de Beurs, K.M.; Eshleman, K.N. Changes in the extent of surface mining and reclamation in the Central Appalachians detected using a 1976–2006 Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianciolo, T.R.; McLaughlin, D.L.; Zipper, C.E.; Timpano, A.J.; Soucek, D.J.; Schoenholtz, S.H. Impacts to water quality and biota persist in mining-influenced Appalachian streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipper, C.E.; Burger, J.A.; Skousen, J.G.; Angel, P.N.; Barton, C.D.; Davis, V.; Franklin, J.A. Restoring Forests and Associated Ecosystem Services on Appalachian Coal Surface Mines. Environ. Manag. 2011, 47, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.M.; Zipper, C.E.; Hester, E.T.; Schoenholtz, S.H. Hydrologic Effects of Surface Coal Mining in Appalachia (U.S.). J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2015, 51, 1436–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, K.; Yang, J.; Fang, L. Assessing Ecosystem Services from the Forestry-Based Reclamation of Surface Mined Areas in the North Fork of the Kentucky River Watershed. Forests 2018, 9, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, J.A.; Currie, W.S.; Eshleman, K.N.; Kuers, K.; Monteleone, S.; Negley, T.L.; Pohlad, B.R.; Thomas, C.L. Forest to Reclaimed Mine Land Use Change Leads to Altered Ecosystem Structure and Function. Ecol. Appl. 2008, 18, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zipper, C.; Angel, P.; Adams, M.B.; Sanderson, T.; Sena, K.; Barton, C.; Agouridis, C. The Forestry Reclamation Approach: An Essential Tool for Controlling Invasive Exotic Plants on Active Mine Sites. The Appalachian Regional Reforestation Initiative (ARRI). 2019. Available online: https://www.fs.usda.gov/treesearch/pubs/60463 (accessed on 14 September 2022).
- Gyawali, B.; Shrestha, S.; Bhatta, A.; Pokhrel, B.; Cristan, R.; Antonious, G.; Banerjee, S.; Paudel, K.P. Assessing the Effect of Land-Use and Land-Cover Changes on Discharge and Sediment Yield in a Rural Coal-Mine Dominated Watershed in Kentucky, USA. Water 2022, 14, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strager, M.P.; Strager, J.M.; Evans, J.S.; Dunscomb, J.K.; Kreps, B.J.; Maxwell, A.E. Combining a spatial model and demand forecasts to map future surface coal mining in Appalachia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, S.; Aronson, J.; Whaley, O.; Lamb, D. The relationship between ecological restoration and the ecosystem services concept. Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintas-Soriano, C.; Castro, A.J.; Castro, H.; García-Llorente, M. Impacts of land use change on ecosystem services and implications for human well-being in Spanish drylands. Land Use Policy 2016, 54, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wen, Z.; Chen, S.; Ding, S.; Zhang, M. Quantifying land use/land cover and landscape pattern changes and impacts on ecosystem services. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohannes, A.W.; Cotter, M.; Kelboro, G.; Dessalegn, W. Land use and land cover changes and their effects on the landscape of Abaya-Chamo basin, Southern Ethiopia. Land 2018, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.R. Remote Sensing of the Environment: An Earth Resource Perspective; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2000; 544p, ISBN 0134897331/9780134897332. [Google Scholar]
- Bielecka, E. GIS spatial analysis modeling for land use change. A bibliometric analysis of the intellectual base and trends. Geosciences 2020, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, G. Characterizing Spatiotemporal Pattern of Land Use Change and Its Driving Force Based on GIS and Landscape Analysis Techniques in Tianjin during 2000–2015. Sustainability 2017, 9, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.H.; He, X.; Porikli, F.; Bennamoun, M. Forest change detection in incomplete satellite images with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 5407–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelifi, L.; Mignotte, M. Deep learning for change detection in remote sensing images: Comprehensive review and meta-analysis. Ieee Access 2020, 8, 126385–126400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnadinger, Z. The Ecological Regions of Kentucky. Available online: https://www.kynativeplants.com/post/ecological-regions-of-kentucky (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Woods, A.J.; Omernik, J.M.; Martin, W.H.; Pond, G.J.; Andrews, W.M.; Call, S.M.; Comstock, J.A.; Taylor, D.D. Ecoregions of Kentucky (color poster with map, descriptive text, summary tables, and photographs): Reston, VA., U.S. Geological Survey (map scale 1:1,000,000). 2002. Available online: https://gaftp.epa.gov/EPADataCommons/ORD/Ecoregions/ky/ky_front.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Butler, P.R.; Iverson, L.R.; III, F.R.T.; Brandt, L.A.; Handler, S.D.; Janowiak, M.K.; Shannon, P.D.; Swanston, C.; Karriker, K.; Bartig, J.; et al. Central Appalachians Forest Ecosystem Vulnerability Assessment and Synthesis: A Report from the Central Appalachians Climate Change Response Framework Project; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Northern Research Station: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2015; p. 322.
- Duraisamy, V.; Bendapudi, R.; Jadhav, A. Identifying hotspots in land use land cover change and the drivers in a semi-arid region of India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- University of Kentucky, Martin-Gatton College of Agriculture, Food and Environment. Kentucky: By The Numbers Data Series. Available online: https://kybtn.ca.uky.edu/kentucky-numbers-data-series (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Roy, A.; Inamdar, A.B. Multi-temporal Land Use Land Cover (LULC) change analysis of a dry semi-arid river basin in western India following a robust multi-sensor satellite image calibration strategy. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendryx, M.; Zullig, K.J.; Luo, J. Impacts of coal use on health. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2020, 41, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriver, T.E.; Bodenhamer, A. The enduring legacy of black lung: Environmental health and contested illness in Appalachia. Sociol. Health Illn. 2018, 40, 1361–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yu, T.; Xu, J.; Pan, X.; Shao, W.; Zuo, J.; Yu, Y. Monitoring and Forecasting Green Tide in the Yellow Sea Using Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, J. Geometric Processing and Positioning Techniques. In Advanced Remote Sensing, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 59–105. ISBN 9780128158265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commonwealth of Kentucky, Kentucky’s Elevation Data & Aerial Photography Program. Available online: https://kyfromabove.ky.gov/ (accessed on 7 April 2022).
- United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service (USDA-NRCS). Soil Survey Geographic (SSURGO) Database for Kentucky. Available online: https://kygeoportal.ky.gov (accessed on 18 April 2022).
- Panuju, D.R.; Paull, D.J.; Griffin, A.L. Change Detection Techniques Based on Multispectral Images for Investigating Land Cover Dynamics. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondrade, N.; Dick, Ø.B.; Tveite, H. GIS based mapping of land cover changes utilizing multi-temporal remotely sensed image data in Lake Hawassa Watershed, Ethiopia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 1765–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basten, K. Classifying Landsat Terrain Images via Random Forests. Bachelor Thesis, Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Amini, S.; Saber, M.; Rabiei-Dastjerdi, H.; Homayouni, S. Urban Land Use and Land Cover Change Analysis Using Random Forest Classification of Landsat Time Series. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Galiano, V.F.; Ghimire, B.; Rogan, J.; Chica-Olmo, M.; Rigol-Sanchez, J.P. An assessment of the effectiveness of a random forest classifier for land-cover classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 67, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htitiou, A.; Boudhar, A.; Lebrini, Y.; Hadria, R.; Lionboui, H.; Elmansouri, L.; Tychon, B.; Benabdelouahab, T. The Performance of Random Forest Classification Based on Phenological Metrics Derived from Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 to Map Crop Cover in an Irrigated Semi-arid Region. Remote Sens. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 2, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esri. ArcGIS Pro; Version 3.0; Environmental Systems Research Institute: Redlands, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez Prentice, R.; Villoslada Peciña, M.; Ward, R.D.; Bergamo, T.F.; Joyce, C.B.; Sepp, K. Machine learning classification and accuracy assessment from high-resolution images of coastal wetlands. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballanti, L.; Blesius, L.; Hines, E.; Kruse, B. Tree species classification using hyperspectral imagery: A comparison of two classifiers. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, R.M. Field Methods in Remote Sensing; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; ISBN 1593850794. [Google Scholar]
- Bilucan, F.; Kavzoglu, T. The effect of auxiliary data (slope, aspect and elevation) on classification accuracy of Sentinel–2A image using random forest classifier. Intercont. Geoinf. Days 2021, 2, 143–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kindu, M.; Schneider, T.; Teketay, D.; Knoke, T. Land use/land cover change analysis using object-based classification approach in Munessa-Shashemene landscape of the Ethiopian highlands. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2411–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, K.; Yamashiki, Y.; Canales Torres, M.A.; Taipe, C.L.R. Crop classification of upland fields using Random forest of time-series Landsat 7 ETM+ data. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 115, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, J.M.; Knight, J.F.; Gallant, A.L. Influence of multi-source and multi-temporal remotely sensed and ancillary data on the accuracy of random forest classification of wetlands in northern Minnesota. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3212–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munthali, M.; Botai, O.J.; Munthali, M.G.; Botai, J.O.; Davis, N.; Adeola, A.M. Multi-temporal Analysis of Land Use and Land Cover Change Detection for Dedza District of Malawi using Geospatial Techniques Remotely Sensing Invasive Alien Plants View project Crop yields estimations: Applications of satellite indices View project Multi-. Artic. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2019, 14, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.R.; Hardy, E.E.; Roach, J.; Witmer, R.E. A Land Use and Land Cover Classification System for Use with Remote Sensor Data; United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1976.
- Dewitz, J. National Land Cover Database (NLCD) 2016 Products (ver. 3.0, November 2023); U.S. Geological Survey Data Release: Reston, VA, USA, 2019.
- Sokal, R.R.; Thomson, J.D. Applications of spatial autocorrelation in ecology. Dev. Numer. Ecol. 1987, 14, 431–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.R.; He, J. A Regression-Based Procedure for Markov Transition Probability Estimation in Land Change Modeling. Land 2020, 9, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, C.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, S. Understanding land use and land cover dynamics from 1976 to 2014 in Yellow River Delta. Land 2017, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-I. Correlation and Spatial Autocorrelation. In Encyclopedia of GIS; Shekhar, S., Xiong, H., Zhou, X., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 360–368. ISBN 978-3-319-17885-1. [Google Scholar]
- Posa, D.; De Iaco, S. Spatial Autocorrelation. In Encyclopedia of Mathematical Geosciences; Daya Sagar, B.S., Cheng, Q., McKinley, J., Agterberg, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–9. ISBN 978-3-030-26050-7. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Martín, J.M.; Rengifo-Gallego, J.I.; Blas-Morato, R. Hot Spot Analysis versus Cluster and Outlier Analysis: An enquiry into the grouping of rural accommodation in Extremadura (Spain). ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liping, C.; Yujun, S.; Saeed, S. Monitoring and predicting land use and land cover changes using remote sensing and GIS techniques—A case study of a hilly area, Jiangle, China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, J.; Wright, C.C. The Kappa Statistic in Reliability Studies: Use, Interpretation, and. Phys. Ther. 2005, 85, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Arya, S. Change Detection Techniques for Land Cover Change Analysis Using Spatial Datasets: A Review. Remote Sens. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 4, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, M.M.; Govers, G.; Kosmas, C.; Vanacker, V.; van Oost, K.; Rounsevell, M. Soil erosion as a driver of land-use change. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 105, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabio, E.S.; Arthur, M.A.; Rhoades, C.C. Influence of moisture regime and tree species composition on nitrogen cycling dynamics in hardwood forests of Mammoth Cave National Park, Kentucky, USA. Can. J. For. Res. 2009, 39, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Edwards, D.R. Long-term trend analysis of precipitation and air temperature for Kentucky, United States. Climate 2016, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, M.M.; Dortch, J.M.; Koch, H.J.; Zhu, Y.; Haneberg, W.C.; Wang, Z.; Bryson, L.S. Landslide Risk Assessment in Eastern Kentucky, USA: Developing a Regional Scale, Limited Resource Approach. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, Z.; Li, P.; Li, G.; Yuan, D.; Guo, J. Assessment and Effect of Mining Subsidence on Farmland in Coal–Crop Overlapped Areas: A Case of Shandong Province, China. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackworth, Z.J.; Lhotka, J.M.; Cox, J.J.; Barton, C.D.; Springer, M.T. First-year vitality of reforestation plantings in response to herbivore exclusion on reclaimed appalachian surface-mined land. Forests 2018, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.; Zipper, C. Restoring the Value of Forests on Reclaimed Mined Land. Virginia Cooperative Extension Publication Number 460-138. 2009. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10919/54950 (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- Mcgowan, E. Reclaiming Appalachia: A Push to Bring Back Native Forests to Coal Country, Yale School of the Environment. Available online: https://e360.yale.edu/features/reclaiming-appalachia-a-push-to-bring-back-native-forests-to-coal-country (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Rodgers, W.N. Land Cover Change and Its Impacts on a Flash Flood-Producing Rain Event in Eastern Kentucky. Masters Theses & Specialist Projects. 2014, p. 90. Available online: http://digitalcommons.wku.edu/theses/1363 (accessed on 5 February 2023).
- Commission for Environmental Cooperation. North American Land Change Monitoring System. 2020. Available online: https://storymaps.arcgis.com/stories/cb62207a38e1437f89165f5eac019f13 (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- Woodall, C.W.; Walters, B.F.; Russell, M.B.; Coulston, J.W.; Domke, G.M.; D’Amato, A.W.; Sowers, P.A. A Tale of Two Forest Carbon Assessments in the Eastern United States: Forest Use Versus Cover as a Metric of Change. Ecosystems 2016, 19, 1401–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, E.S.; Lutz, B.D.; King, R.S.; Fay, J.P.; Carter, C.E.; Helton, A.M.; Campagna, D.; Amos, J. How Many Mountains Can We Mine? Assessing the Regional Degradation of Central Appalachian Rivers by Surface Coal Mining. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8115–8122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pericak, A.A.; Thomas, C.J.; Kroodsma, D.A.; Wasson, M.F.; Ross, M.R.V.; Clinton, N.E.; Campagna, D.J.; Franklin, Y.; Bernhardt, E.S.; Amos, J.F. Mapping the yearly extent of surface coal mining in central appalachia using landsat and google earth engine. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackford, C.; Heung, B.; Baldwin, K.; Fleming, R.L.; Hazlett, P.W.; Morris, D.M.; Uhlig, P.W.C.; Webster, K.L. Digital soil mapping workflow for forest resource applications: A case study in the Hearst Forest, Ontario. Can. J. For. Res. 2021, 51, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kentucky Energy and Environment Cabinet. Mine Reclamation and Enforcement Natural Resource Mining. Available online: https://eec.ky.gov/Natural-Resources/Conservation/Pages/default.aspx (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Franklin, J.A.; Zipper, C.E.; Burger, J.A.; Skousen, J.G.; Jacobs, D.F. Influence of herbaceous ground cover on forest restoration of eastern US coal surface mines. New For. 2012, 43, 905–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, W.C.; Hannigan, K.P.; Kost, D.A. Coal mine reclamation with grasses and legumes in southern Illinois. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1989, 44, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, J.R.; Lookingbill, T.R.; McCormick, B.; Townsend, P.A.; Eshleman, K.N. Surface mining and reclamation effects on flood response of watersheds in the central Appalachian Plateau region. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilahun, A. Accuracy Assessment of Land Use Land Cover Classification using Google Earth. Am. J. Environ. Prot. 2015, 4, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Park, H.-D.; Sunwoo, C. Flood and gully erosion problems at the Pasir open pit coal mine, Indonesia: A case study of the hydrology using GIS. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2008, 67, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunsch, D.R. Ground-Water Geochemistry and Its Relationship to the Flow System at an Unmined Site in the Eastern Kentucky Coal Field. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, J.; Yu, P. Does coal mining have effects on land use changes in a coal resource-based city? Evidence from huaibei city on the North China plain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheis, M. Local economic impacts of coal mining in the United States 1870 to 1970. J. Econ. Hist. 2016, 76, 1152–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.; Richter, J.; Martin, B.; Peterson, C.; Le, T.-T.; Wiener, M.; Dockery, S. Evaluating Tree Growth and Soil Development on Restored Coal Mine Sites in Eastern Kentucky; UNC: Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pardieu, S. Biodiversity in Eastern Kentucky: Effects of Habitat Change, Surface Top Mining, and Current Reclamation Practices, Undergraduate Theses. 2023. Available online: https://scholarworks.bellarmine.edu/ugrad_theses/112/ (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Macdonald, S.E.; Landhäusser, S.M.; Skousen, J.; Franklin, J.; Frouz, J.; Hall, S.; Jacobs, D.F.; Quideau, S. Forest restoration following surface mining disturbance: Challenges and solutions. New For. 2015, 46, 703–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skousen, J.; Monteleone, A.; Tyree, M.; Swab, R.; Groninger, J.; Adams, M.; Buckley, D.; Wood, P.; Williams, R.; Eggerud, S.; et al. Establishing Small Tree and Shrub Species on Mined Lands Using the Forestry Reclamation Approach; Forest Reclamation Advisory No. 18; Appalachian Regional Reforestation Initiative: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2019; 9p.
- Li, M.; Yan, Q.; Li, G.; Yi, M.; Li, J. Spatio-Temporal Changes of Vegetation Cover and Its Influencing Factors in Northeast China from 2000 to 2021. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Forestry Reclamation Approach: Guide to Successful Reforestation of Mined Lands; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Northern Research Station: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, P.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Vegetation succession and soil infiltration characteristics under different aged refuse dumps at the Heidaigou opencast coal mine. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2015, 4, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Meng, Q. Using spatial syntax and GIS to identify spatial heterogeneity in the main urban area of Harbin, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 893414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-H.; Peng, F.-L.; Li, H.; Men, Y.-Q. Spatial autocorrelation and spatial heterogeneity of underground parking space development in Chinese megacities based on multisource open data. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 153, 102897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lei, L.; Li, Z.; Kuang, G. Similarity and dissimilarity relationships based graphs for multimodal change detection. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 208, 70–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Data Type Group | Spatial Resolution | Source of Data | Types of Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat data (2004, 2006, 2010, 2016, 2019) | 30 m | USGS/EROS | Raster |
| NAIP data (2004, 2006, 2010, 2016, 2020) | 1 m | KY Geoportal Image Service | Raster |
| NLCD data (2006, 2011, 2016, 2019) | 30 m | KY Geoportal Image Service | Raster |
| Surface-mined areas | KY Division of Mine Permits | Point and Polygons | |
| DEM data layer (2011) | 1.524 m (5 feet) | KY Geoportal Image Service | Raster |
| Land capability class (2012) | USDA NRCS Soil Survey Geographic Data base (SSURGO) | Vector data | |
| Kentucky roads (2015) | (30 m converted) | KY Geoportal | Vector data |
| National Hydrology Dataset (2023) | USGS | Vector data |
| Land-Cover Class | T-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 1.47 | 0.14 |
| Developed | 9.05 | 1.72 × 10−16 *** |
| Barren | −5.02 | 1.18 × 10−6 *** |
| Forest | 3.27 | 0.01 *** |
| Shrubland | −2.43 | 0.01 *** |
| Herbaceous | −6.52 | 6.02 × 10−10 *** |
| Planted/ Cultivated | −1.82 | 0.07 ** |
| 2019 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | Land-Cover Type | Water | Developed | Barren | Forest | Shrublands | Herbaceous | Planted/Cultivated | Total 2004 |
| Water | 18.56 | 3.79 | 1.12 | 15.27 | 2.79 | 0.58 | 2.25 | 44.36 | |
| Developed | 2.96 | 90.44 | 3.58 | 22.19 | 23.36 | 3.63 | 27.85 | 174.01 | |
| Barren | 0.93 | 10.34 | 21.58 | 24.54 | 90.12 | 30.16 | 1.51 | 179.18 | |
| Forest | 19.25 | 82.22 | 37.53 | 4471.14 | 383.44 | 29.4 | 27.15 | 5050.13 | |
| Shrublands | 4.79 | 95.95 | 15.58 | 650.14 | 305.98 | 39.71 | 24.46 | 1136.61 | |
| Herbaceous | 0.68 | 48.82 | 11.03 | 85.33 | 135.33 | 50.63 | 11.45 | 343.27 | |
| Planted/Cultivated | 2.43 | 60.51 | 0.32 | 34.42 | 15.93 | 1.51 | 95.77 | 210.89 | |
| Total 2019 | 49.6 | 392.07 | 90.74 | 5303.03 | 956.95 | 155.62 | 190.44 | 7138.45 | |
| Year | Land-Cover Classes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Developed | Barren | Forest | Herbaceous | Shrubland | Planted/ Cultivated | |
| 2004 | 0.468 | 0.267 | 0.153 | 0.338 | 0.358 | 0.542 | 0.499 |
| 2006 | 0.36 | 0.336 | 0.231 | 0.307 | 0.341 | 0.428 | 0.552 |
| 2010 | 0.542 | 0.345 | 0.26 | 0.396 | 0.236 | 0.671 | 0.638 |
| 2016 | 0.429 | 0.388 | 0.254 | 0.366 | 0.319 | 0.481 | 0.461 |
| 2019 | 0.367 | 0.432 | 0.194 | 0.41 | 0.271 | 0.408 | 0.613 |
| Years | Counties | Kappa’s Accuracy | Years | Counties | Kappa’s Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | Floyd | 0.84 | 2006 | Floyd | 0.84 |
| Knott | 0.75 | Knott | 0.79 | ||
| Letcher | 0.77 | Letcher | 0.83 | ||
| Martin | 0.86 | Martin | 0.85 | ||
| Magoffin | 0.77 | Magoffin | 0.78 | ||
| Perry | 0.84 | Perry | 0.81 | ||
| Pike | 0.77 | Pike | 0.8 | ||
| 2010 | Floyd | 0.85 | 2016 | Floyd | 0.89 |
| Knott | 0.85 | Knott | 0.81 | ||
| Letcher | 0.79 | Letcher | 0.89 | ||
| Martin | 0.83 | Martin | 0.85 | ||
| Magoffin | 0.8 | Magoffin | 0.79 | ||
| Perry | 0.83 | Perry | 0.82 | ||
| Pike | 0.84 | Pike | 0.79 | ||
| 2019 | Floyd | 0.85 | |||
| Knott | 0.84 | ||||
| Letcher | 0.78 | ||||
| Martin | 0.85 | ||||
| Magoffin | 0.8 | ||||
| Perry | 0.83 | ||||
| Pike | 0.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
K C, S.; Gyawali, B.R.; Lucas, S.; Antonious, G.F.; Chiluwal, A.; Zourarakis, D. Assessing Land-Cover Change Trends, Patterns, and Transitions in Coalfield Counties of Eastern Kentucky, USA. Land 2024, 13, 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13091541
K C S, Gyawali BR, Lucas S, Antonious GF, Chiluwal A, Zourarakis D. Assessing Land-Cover Change Trends, Patterns, and Transitions in Coalfield Counties of Eastern Kentucky, USA. Land. 2024; 13(9):1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13091541
Chicago/Turabian StyleK C, Suraj, Buddhi R. Gyawali, Shawn Lucas, George F. Antonious, Anuj Chiluwal, and Demetrio Zourarakis. 2024. "Assessing Land-Cover Change Trends, Patterns, and Transitions in Coalfield Counties of Eastern Kentucky, USA" Land 13, no. 9: 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13091541
APA StyleK C, S., Gyawali, B. R., Lucas, S., Antonious, G. F., Chiluwal, A., & Zourarakis, D. (2024). Assessing Land-Cover Change Trends, Patterns, and Transitions in Coalfield Counties of Eastern Kentucky, USA. Land, 13(9), 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13091541









