Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Response of Land Surface Temperature and Kernel Normalized Difference Vegetation Index in Yangtze River Economic Belt, China: Multi-Method Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Processing Methods
3. Research Methods
3.1. Trend Analysis
3.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3.3. K-Means Clustering
3.4. Generalized Additive Model
4. Results
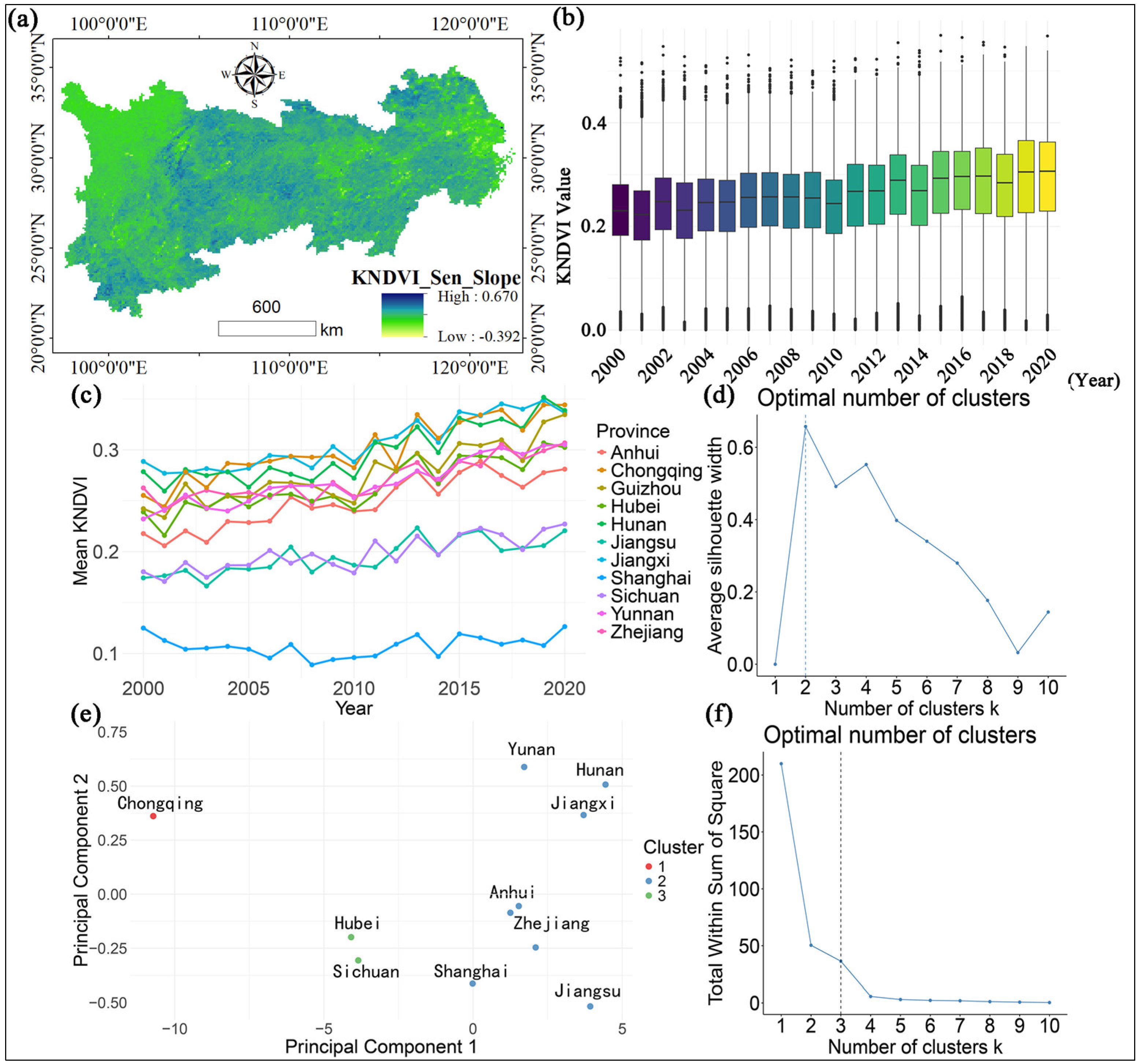
4.1. Analysis of KNDVI Trends over the Years
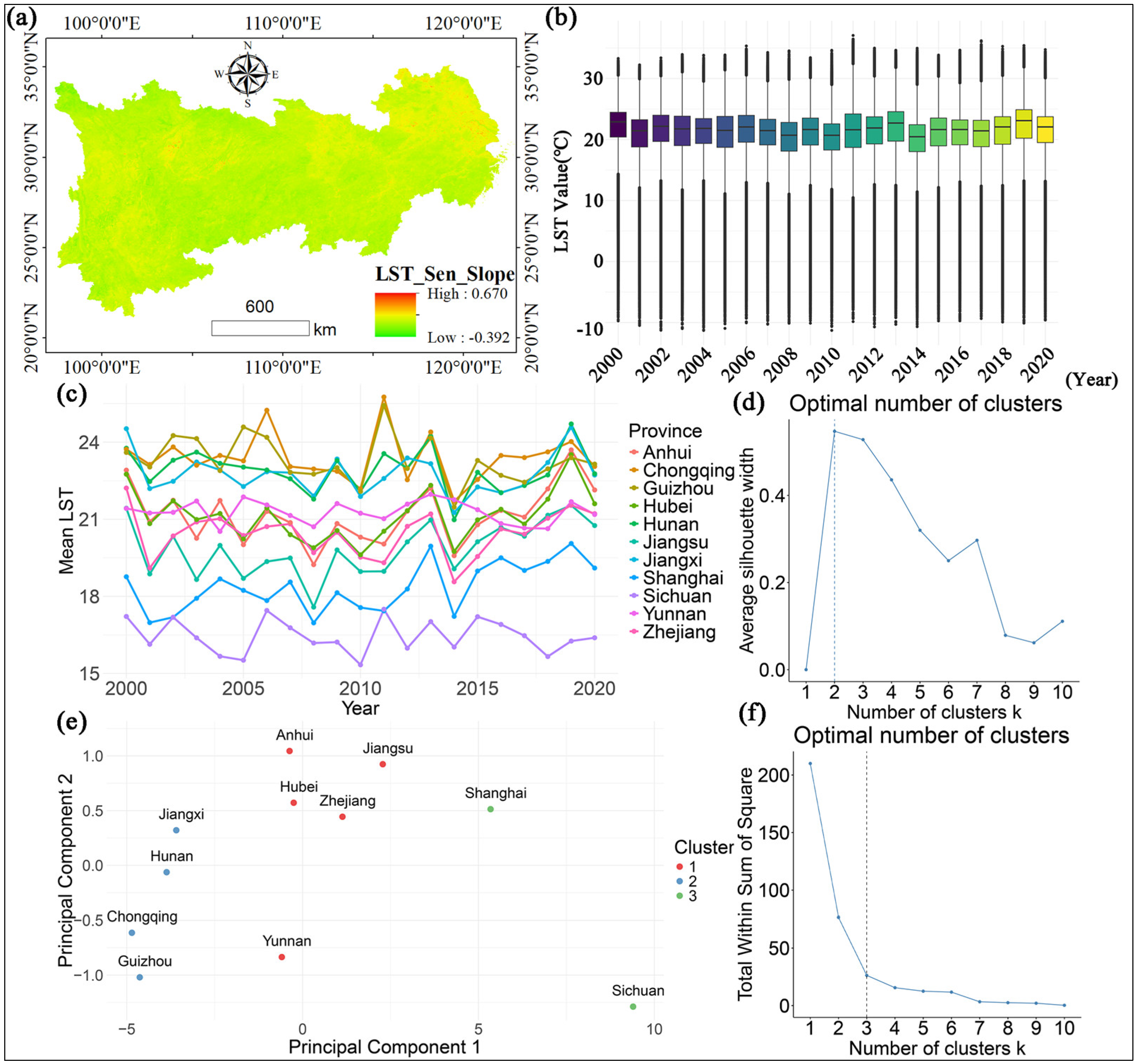
4.2. Analysis of LST Trends over the Years
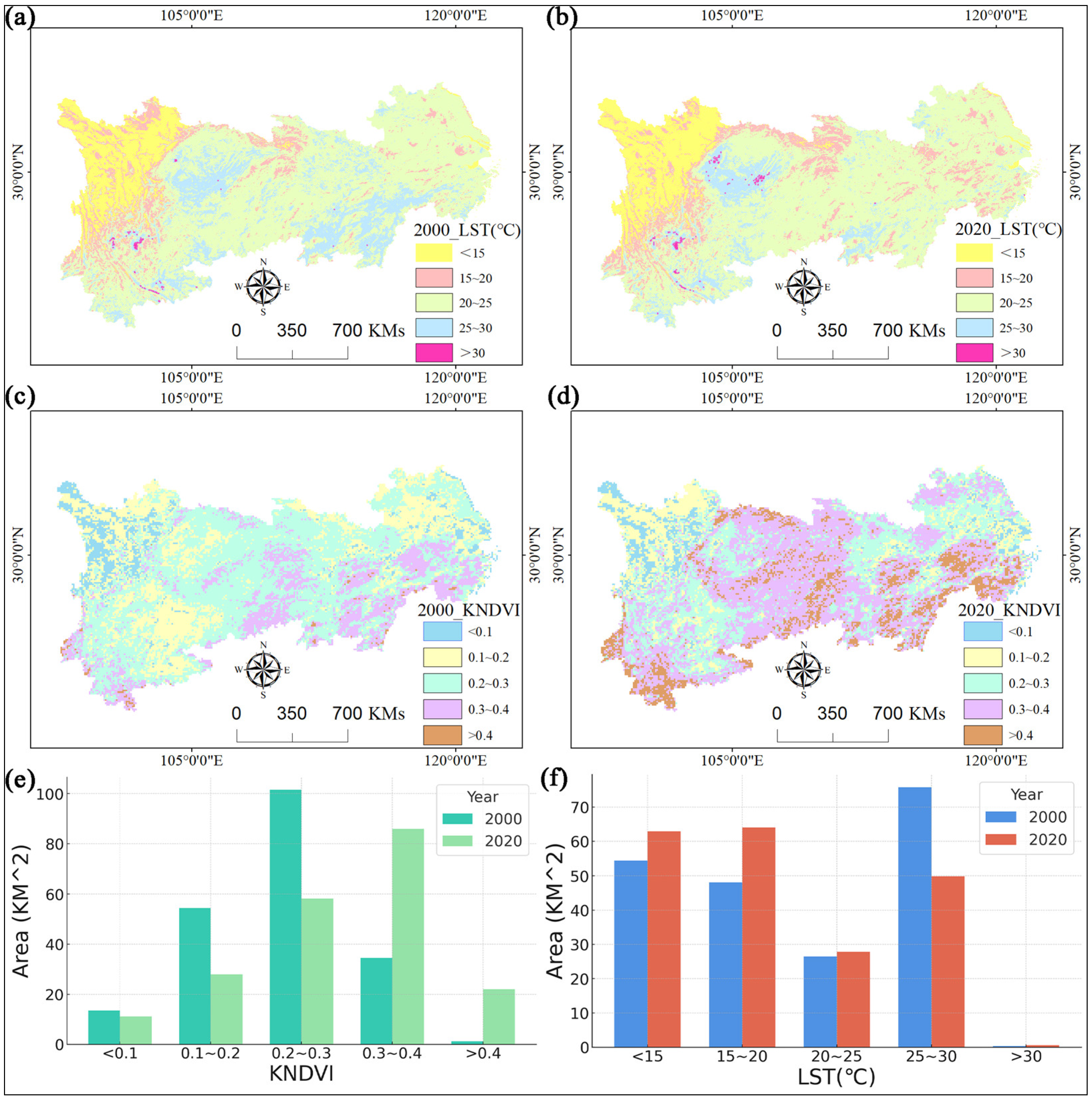
4.3. Analysis of LST Response to KNDVI in 2000 and 2020
4.4. Analysis of LST Response to KNDVI in Different Provinces
5. Discussion
5.1. Interaction Between Vegetation Cover and Land Surface Temperature
5.2. Impact of Urbanization on Ecosystems
5.3. Regional Differences and Ecological Responses to Climate Change
5.4. Response of LST and KNDVI to Climate Change
5.5. Limitations and Future Research Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, Y.; Tan, X.; Yao, Y.; Wang, L.; Shan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jing, Z. Uncovering Optimal Vegetation Indices for Estimating Wetland Plant Species Diversity. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhang, M.; Chen, E.; Zhang, C.; Han, Y. Impact of Seasonal Global Land Surface Temperature (LST) Change on Gross Primary Production (GPP) in the Early 21st Century. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 110, 105572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Jia, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, X.; Ren, K.; Mu, Q.; Kang, S.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Spatial Variations of the Relationships between Bacterial Diversity and Forest Ecosystem Multifunctionality in the Qinling Mountains, China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 203, 105638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Biederman, J.A.; Knowles, J.F.; Scott, R.L.; Turner, A.J.; Dannenberg, M.P.; Köhler, P.; Frankenberg, C.; Litvak, M.E.; Flerchinger, G.N.; et al. Satellite Solar-Induced Chlorophyll Fluorescence and near-Infrared Reflectance Capture Complementary Aspects of Dryland Vegetation Productivity Dynamics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 270, 112858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Schmid, B.; Zeng, Y.; Schuman, M.C.; Zhao, D.; Schaepman, M.E.; Morsdorf, F. Remotely Sensed Functional Diversity and Its Association with Productivity in a Subtropical Forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 290, 113530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Meng, L.; Chen, X. Analysis of Vegetation Dynamics from 2001 to 2020 in China’s Ganzhou Rare Earth Mining Area Using Time Series Remote Sensing and SHAP-Enhanced Machine Learning. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 84, 102887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, C.; Liu, P. Dynamic Evaluation of the Ecological Evolution and Quality of Arid and Semi-Arid Deserts in the Aibugai River Basin Based on an Improved Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 82, 102727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Moreno-Martínez, Á.; Muñoz-Marí, J.; Campos-Taberner, M.; Camps-Valls, G. Estimation of Vegetation Traits with Kernel NDVI. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 195, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Yew Gan, T.; Su, X.; Wu, H.; Shi, L.; Xu, P.; Fu, X. Evaluating Vegetation Vulnerability under Compound Dry and Hot Conditions Using Vine Copula across Global Lands. J. Hydrol. 2024, 631, 130775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Xu, D.; Luo, D.; Xiao, A.; Yuan, X. Study on the Impact of Land Use and Climate Change on the Spatiotemporal Evolution of Vegetation Cover in Chongqing, China. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, T.C.; Silveira, L.F.; Pironkova, Z.I.; Francisco, M.R. Greening and Browning Trends in a Tropical Forest Hotspot: Accounting for Fragment Size and Vegetation Indices. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 26, 100751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Duan, Z.; Tang, J. Capturing the Spatiotemporal Variations in the Gross Primary Productivity in Coastal Wetlands by Integrating Eddy Covariance, Landsat, and MODIS Satellite Data: A Case Study in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 149, 110154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Lin, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y. The Heterogeneous Effects of Microscale-Built Environments on Land Surface Temperature Based on Machine Learning and Street View Images. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Qiao, J.; Li, M.; Dun, Y.; Zhu, X.; Ji, X. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Ecological Environmental Quality and Its Dynamic Relationships with Landscape Pattern in the Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area: A Perspective Based on Nonlinear Effects and Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 480, 144102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Cao, S.; Gusev, A.; Guo, Y.; Ran, L.; Wei, X.; Mikalai, F. Nonlinear Effects of Agricultural Drought on Vegetation Productivity in the Yellow River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Jin, X.; Jin, Y.; Mao, X. Extraction of Grassland Irrigation Information in Arid Regions Based on Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 302, 109010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jia, W.; Lu, S.; He, J. Ecological Assessment and Driver Analysis of High Vegetation Cover Areas Based on New Remote Sensing Index. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 82, 102786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Indraganti, M.; Jawarneh, R.N. A Comprehensive Systematic Review: Impact of Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) on Land Surface Temperatures (LST) and Outdoor Thermal Comfort. Build. Environ. 2024, 249, 111130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, L.; Matzarakis, A. Influence of height/width proportions on the thermal comfort of courtyard typology for Italian climate zones. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 29, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Xv, D.; Tang, J.; Lu, J.; Wu, Y. Assessing the Effects of Urban Green Spaces Metrics and Spatial Structure on LST and Carbon Sinks in Harbin, a Cold Region City in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 113, 105659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanoori, G.; Soltani, A.; Modiri, A. Machine Learning for Urban Heat Island (UHI) Analysis: Predicting Land Surface Temperature (LST) in Urban Environments. Urban Clim. 2024, 55, 101962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tan, S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, E. Machine Learning in Modelling the Urban Thermal Field Variance Index and Assessing the Impacts of Urban Land Expansion on Seasonal Thermal Environment. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 106, 105345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Peng, C.; Teng, M.; Zhou, Z. Seasonal Variations for Combined Effects of Landscape Metrics on Land Surface Temperature (LST) and Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD). Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, T.; Yi, S.; Chen, J.; Han, X. Time-Series Simulation of Alpine Grassland Cover Using Transferable Stacking Deep Learning and Multisource Remote Sensing Data in the Google Earth Engine. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 131, 103964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, Y.; Hoyos, N.; Arellana, J. High Land Surface Temperatures (LSTs) Disproportionately Affect Vulnerable Socioeconomic Groups in Barranquilla, Colombia. Urban Clim. 2023, 52, 101757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.; Goswami, K.P. Evaluating the Influence of Biophysical Factors in Explaining Spatial Heterogeneity of LST: Insights from Brahmani-Dwarka Interfluve Leveraging Geodetector, GWR, and MGWR Models. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts ABC 2025, 138, 103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjin, K.; Alam, B.M. Assessing Changes in Land Cover, NDVI, and LST in the Sundarbans Mangrove Forest in Bangladesh and India: A GIS and Remote Sensing Approach. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2024, 36, 101289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zeng, X.; Zhu, Z.; Lan, Y.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yang, F. Exploring the Diurnal Variations of the Driving Factors Affecting Block-Based LST in a “Furnace City” Using ECOSTRESS Thermal Imaging. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 98, 104841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi Fard, M.; Thonet, T.; Gaussier, E. Deep k-Means: Jointly clustering with k-Means and learning representations. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 138, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, S. Fuzzy C-Means clustering algorithm for data with unequal cluster sizes and contaminated with noise and outliers: Review and development. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 165, 113856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, A.; Sudjianto, A. GAMI-Net: An explainable neural network based on generalized additive models with structured interactions. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 120, 108192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, D.N.; Rodrigues, W.; Bermejo, P.H. Temperature significantly changes COVID-19 transmission in (sub)tropical cities of Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Huang, G.; Zhang, M. Comparative Analysis of the Seasonal Driving Factors of the Urban Heat Environment Using Machine Learning: Evidence from the Wuhan Urban Agglomeration, China, 2020. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhang, M.; Kafy, A.-A.; Tong, B.; Hao, D.; Feng, Y. Predicting the impacts of urban land change on LST and carbon storage using InVEST, CA-ANN and WOA-LSTM models in Guangzhou, China. Earth Sci. Inform. 2023, 16, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhang, M.; Ren, B.; Zhang, Y.; Kafy, A.-A.; Li, J. Ventilation analysis of urban functional zoning based on circuit model in Guangzhou in winter, China. Urban Clim. 2023, 47, 101385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarian, N.; Krayenhoff, E.S.; Bechtel, B.; Hondula, D.M.; Paolini, R.; Vanos, J.; Cheung, T.; Chow, W.T.L.; de Dear, R.; Jay, O.; et al. Integrated Assessment of Urban Overheating Impacts on Human Life. Earths Future 2022, 10, e2022EF002682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; He, W. Influence of spatiotemporal changes of impervious surface on the urban thermal environment: A case of Huai’an central urban area. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 79, 103710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, C. Socioeconomic drivers of urban heat island effect: Empirical evidence from major Chinese cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Kong, Q.; Zhang, M.; Huang, H. New-type urbanization and ecological well-being performance: A coupling coordination analysis in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River urban agglomerations, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yiğit, İ.; Adigüzel, F.; Hu, C.; Chen, E.; Siyavuş, A.E.; Elmastaş, N.; Ustuner, M.; Kaya, A.Y. Impact of Urban Surfaces on Microclimatic Conditions and Thermal Comfort in Burdur, Türkiye. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaamala, A.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Nili, A.; Nyandega, D. Strategic tree placement for urban cooling: A novel optimisation approach for desired microclimate outcomes. Urban Clim. 2024, 56, 102084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingzhong, Y.; Lu, P. Differentiated childhoods: Impacts of rural labor migration on left-behind children in China. J. Peasant Stud. 2011, 38, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, E.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C.; Li, J. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use Change and Ecosystem Service Value Based on the Markov–FLUS Model in Ezhou City, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yuan, X.; Yuan, X.; Liu, S.; Guan, B.; Sun, J.; Chen, H. Evaluating the sustainability of rural complex ecosystems during the development of traditional farming villages into tourism destinations: A diachronic emergy approach. J. Rural Stud. 2021, 86, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shi, C.; Fang, C.; Feng, K. Examining the spatial variations of determinants of energy-related CO2 emissions in China at the city level using Geographically Weighted Regression Model. Appl. Energy 2019, 235, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiskopf, S.R.; Rubenstein, M.A.; Crozier, L.G.; Gaichas, S.; Griffis, R.; Halofsky, J.E.; Hyde, K.J.; Morelli, T.L.; Morisette, J.T.; Muñoz, R.C.; et al. Climate change effects on biodiversity, ecosystems, ecosystem services, and natural resource management in the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 137782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, L.S.; Segarra-Medina, C.; Gómez-Cadenas, A.; López-Climent, M.F.; Vives-Peris, V.; Zandalinas, S.I. Climate change-associated multifactorial stress combination: A present challenge for our ecosystems. J. Plant Physiol. 2022, 276, 153764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J. Urban expansion weakens the contribution of local land cover to urban warming. Urban Clim. 2022, 45, 101285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyprianou, I. Urban vulnerability in the EMME region and sustainable development goals: A new conceptual framework. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, R.; Jia, S.; Lv, A.; Zhu, W. A preliminary assessment of environmental flow in the three rivers’ source region, Qinghai Tibetan Plateau, China and suggestions. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 144, 105709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, C.; Kafy, A.-A.; Tan, S. Simulating the Relationship Between Land Use/Cover Change and Urban Thermal Environment Using Machine Learning Algorithms in Wuhan City, China. Land 2022, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Jin, W. The role of the Yangtze River Protection Law in the emergence of adaptive water governance in China. Ecol. Soc. 2023, 28, art32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yu, B.; Zhang, Y. Global concurrent climate extremes exacerbated by anthropogenic climate change. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eabo1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Bai, Z.; Shi, X.; Chen, X.; Chadwick, D.; Strokal, M.; Zhang, F.; Ma, L.; Chen, X. Challenges and strategies for agricultural green development in the Yangtze River Basin. J. Integr. Environ. Sci. 2021, 18, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiatante, G.; Pellitteri-Rosa, D.; Torretta, E.; Nonnis Marzano, F.; Meriggi, A. Indicators of biodiversity in an intensively cultivated and heavily human modified landscape. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, E.; Watermeyer, K.E.; Rowland, J.A.; Sato, C.F.; Stevenson, S.L.; Andrade, A.; Brooks, T.M.; Burgess, N.D.; Cheng, S.T.; Grantham, H.S.; et al. Scientific foundations for an ecosystem goal, milestones and indicators for the post-2020 global biodiversity framework. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 1338–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avtar, R.; Komolafe, A.A.; Kouser, A.; Singh, D.; Yunus, A.P.; Dou, J.; Kumar, P.; Gupta, R.D.; Johnson, B.A.; Minh, H.V.T.; et al. Assessing sustainable development prospects through remote sensing: A review. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 20, 100402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Qiu, S.; Ye, S. Remote sensing of land change: A multifaceted perspective. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 282, 113266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwakaire, C.M.; Onn, C.C.; Yap, S.P.; Yuen, C.W.; Onodagu, P.D. Urban Heat Island Studies with emphasis on urban pavements: A review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennewein, J.S.; Lamb, B.T.; Hively, W.D.; Thieme, A.; Thapa, R.; Goldsmith, A.; Mirsky, S.B. Integration of Satellite-Based Optical and Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery to Estimate Winter Cover Crop Performance in Cereal Grasses. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, J.; Fu, H.; Tang, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H.; Sun, Y.; Ning, X. Deep Learning for Multi-Source Data-Driven Crop Yield Prediction in Northeast China. Agriculture 2024, 14, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Kafy, A.-A.; Ren, B.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, S.; Li, J. Application of the Optimal Parameter Geographic Detector Model in the Identification of Influencing Factors of Ecological Quality in Guangzhou, China. Land 2022, 11, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, G.; Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Yang, S.; Wu, T.; Abakumov, E.; Zhao, J.; Cui, X.; et al. Spatiotemporal Variations in Compound Extreme Events and Their Cumulative and Lagged Effects on Vegetation in the Northern Permafrost Regions from 1982 to 2022. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Feng, H.; Wang, H.; Hao, C. The Spatiotemporal Evolution of Vegetation in the Henan Section of the Yellow River Basin and Mining Areas Based on the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, W.; Xing, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, D.; Niu, X.; Pu, W.; Liu, J.; et al. The Changes in Remoted Land Surface Temperature (LST) Triggered by Natural and Socioeconomic Factors in Typical Chinese Cities. Urban Clim. 2024, 58, 102151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Xu, X.; Guan, M.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, Y. Determining the contributions of climate change and human activities to vegetation dynamics in agro-pastural transitional zone of northern China from 2000 to 2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 134871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Chen, X.; Ruan, W.; Zheng, M.; Gen, K.; Li, X.; Deng, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M. Quantifying the direct and indirect effects of terrain, climate and human activity on the spatial pattern of kNDVI-based vegetation growth: A case study from the Minjiang River Basin, Southeast China. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrall, B.; Pickering, C.M. Alpine vegetation in the context of climate change: A global review of past research and future directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fu, B.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, S.; Wei, F.; Zhang, L. Vegetation resilience does not increase consistently with greening in China’s Loess Plateau. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Wang, N.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, Y. Spatiotemporal variations in eco-environmental quality and responses to drought and human activities in the middle reaches of the Yellow River basin, China from 1990 to 2022. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 81, 102641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, L.; Zhen, S.; Lin, Q.; Hu, X.; Li, J. Terrain or climate factor dominates vegetation resilience? Evidence from three national parks across different climatic zones in China. For. Ecosyst. 2024, 11, 100212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.; Dimitrova, A.; Muttarak, R.; Crespo Cuaresma, J.; Peisker, J. A meta-analysis of country-level studies on environmental change and migration. Nat. Clim. Change 2020, 10, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reba, M.; Seto, K.C. A systematic review and assessment of algorithms to detect, characterize, and monitor urban land change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 242, 111739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Georgescu, M.; Wu, J. Impacts of landscape changes on local and regional climate: A systematic review. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 1269–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Jiang, J.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, N. Research on quantitative assessment of climate change risk at an urban scale: Review of recent progress and outlook of future direction. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal Cilek, M.; Cilek, A. Analyses of land surface temperature (LST) variability among local climate zones (LCZs) comparing Landsat-8 and ENVI-met model data. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastour, H.; Hassan, Q.K. A Multidimensional Machine Learning Framework for LST Reconstruction and Climate Variable Analysis in Forest Fire Occurrence. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 83, 102849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; He, X.; Shangguan, D.; Li, D.; Dai, S.; He, B.; Yang, Q. Impacts of Climate Change and Anthropogenic Activities on Vegetation Dynamics Considering Time Lag and Accumulation Effects: A Case Study in the Three Rivers Source Region, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhou, W.; Qian, M.; Zha, E.; Cao, A.; Shi, X. Unveiling Differentiation Characteristics of Vegetation Restoration Potential for Browning Areas in China’s Hilly and Gully Region. Land 2025, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Yuan, Y.; He, Z.; Pang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, W.; Cen, Y.; Xiao, Y. Spatiotemporal Variations of Vegetation NPP Based on GF-SG and kNDVI and Its Response to Climate Change and Human Activities: A Case Study of the Zoigê Plateau. Forests 2025, 16, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Tian, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Ya, Q.; Li, Z. Spatio-Temporal Variation and Climatic Driving Factors of Vegetation Coverage in the Yellow River Basin from 2001 to 2020 Based on kNDVI. Forests 2023, 14, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Chen, M.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, F.; Huang, J.; Peng, D.; Wang, X. Prediction and Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Vegetation Index Based on Deep Learning and Environmental Factors in the Yangtze River Basin. Forests 2025, 16, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, H.; Wang, A.; Wang, P.; Hu, C.; Zhang, M. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Response of Land Surface Temperature and Kernel Normalized Difference Vegetation Index in Yangtze River Economic Belt, China: Multi-Method Analysis. Land 2025, 14, 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030598
Zhu H, Wang A, Wang P, Hu C, Zhang M. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Response of Land Surface Temperature and Kernel Normalized Difference Vegetation Index in Yangtze River Economic Belt, China: Multi-Method Analysis. Land. 2025; 14(3):598. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030598
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Hongjia, Ao Wang, Pengtao Wang, Chunguang Hu, and Maomao Zhang. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Response of Land Surface Temperature and Kernel Normalized Difference Vegetation Index in Yangtze River Economic Belt, China: Multi-Method Analysis" Land 14, no. 3: 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030598
APA StyleZhu, H., Wang, A., Wang, P., Hu, C., & Zhang, M. (2025). Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Response of Land Surface Temperature and Kernel Normalized Difference Vegetation Index in Yangtze River Economic Belt, China: Multi-Method Analysis. Land, 14(3), 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030598









