Distribution of Pyrogenic Carbon in the Soil of a Cold Temperate Coniferous Forest 13 Years After a Severe Wildfire
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Soil Collection
2.3. Soil Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
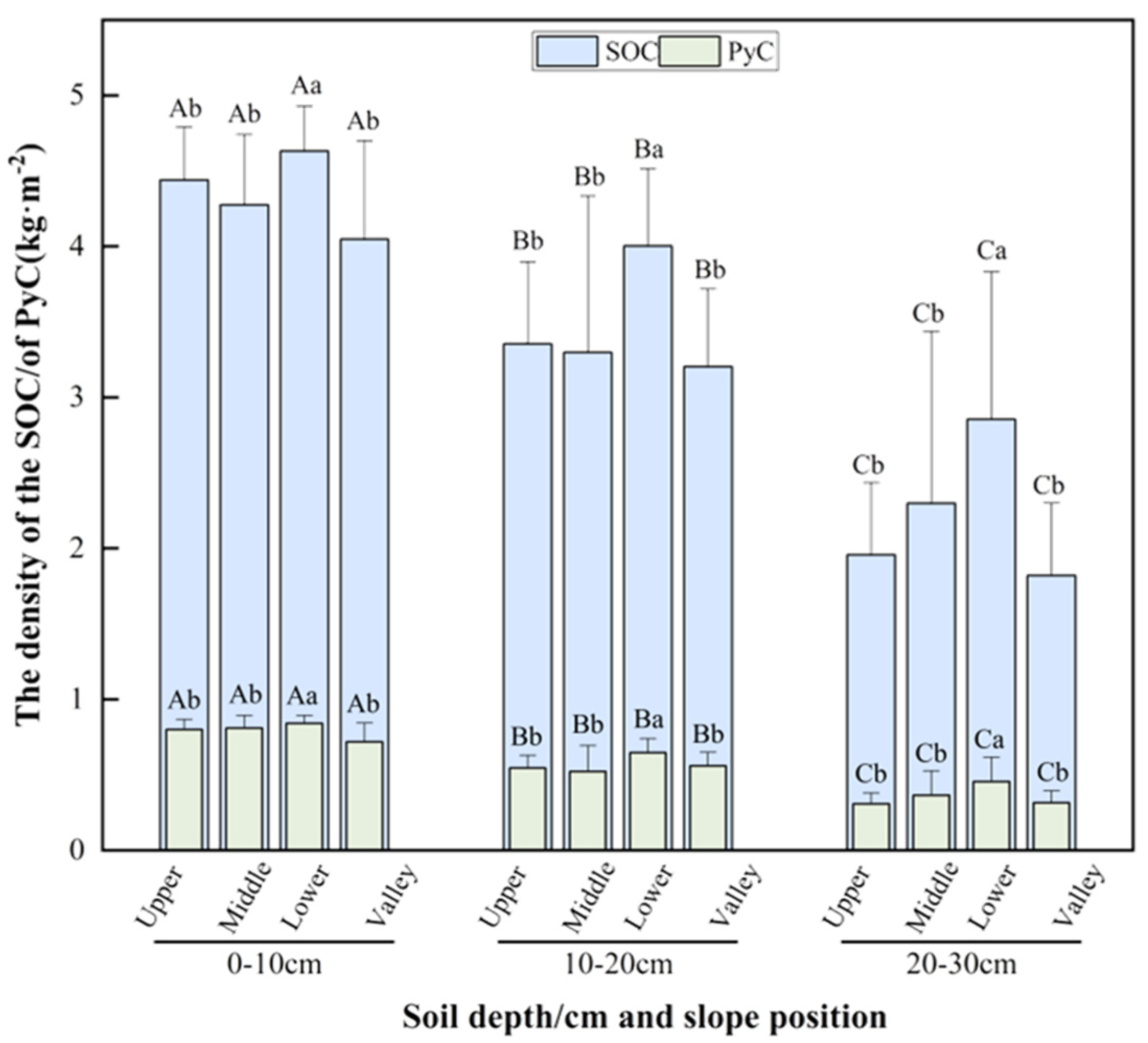
3.1. Slope Position Distribution of Pyrogenic Carbon in Soil
3.2. Soil Depth Distribution of Pyrogenic Carbon in Soil
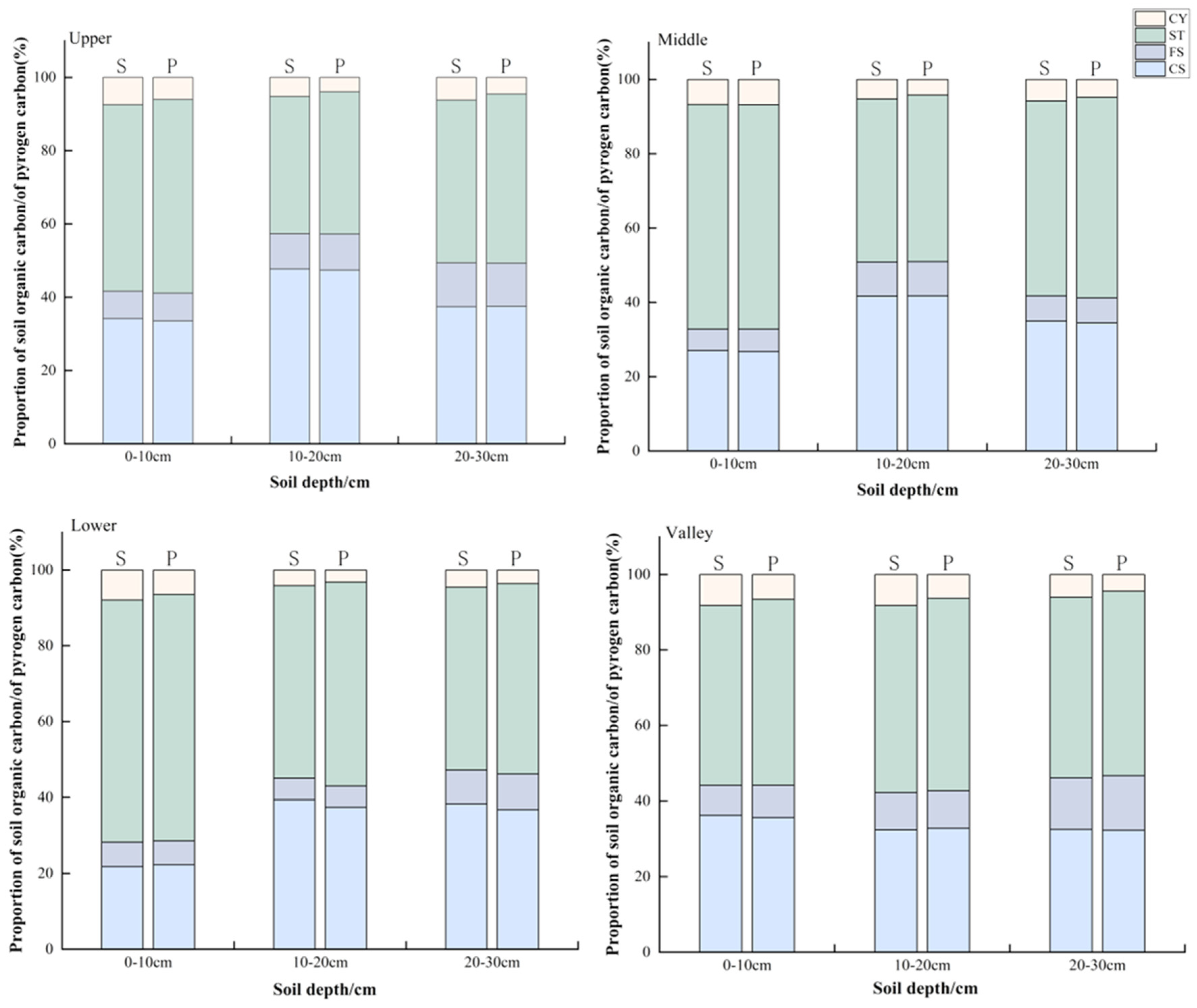
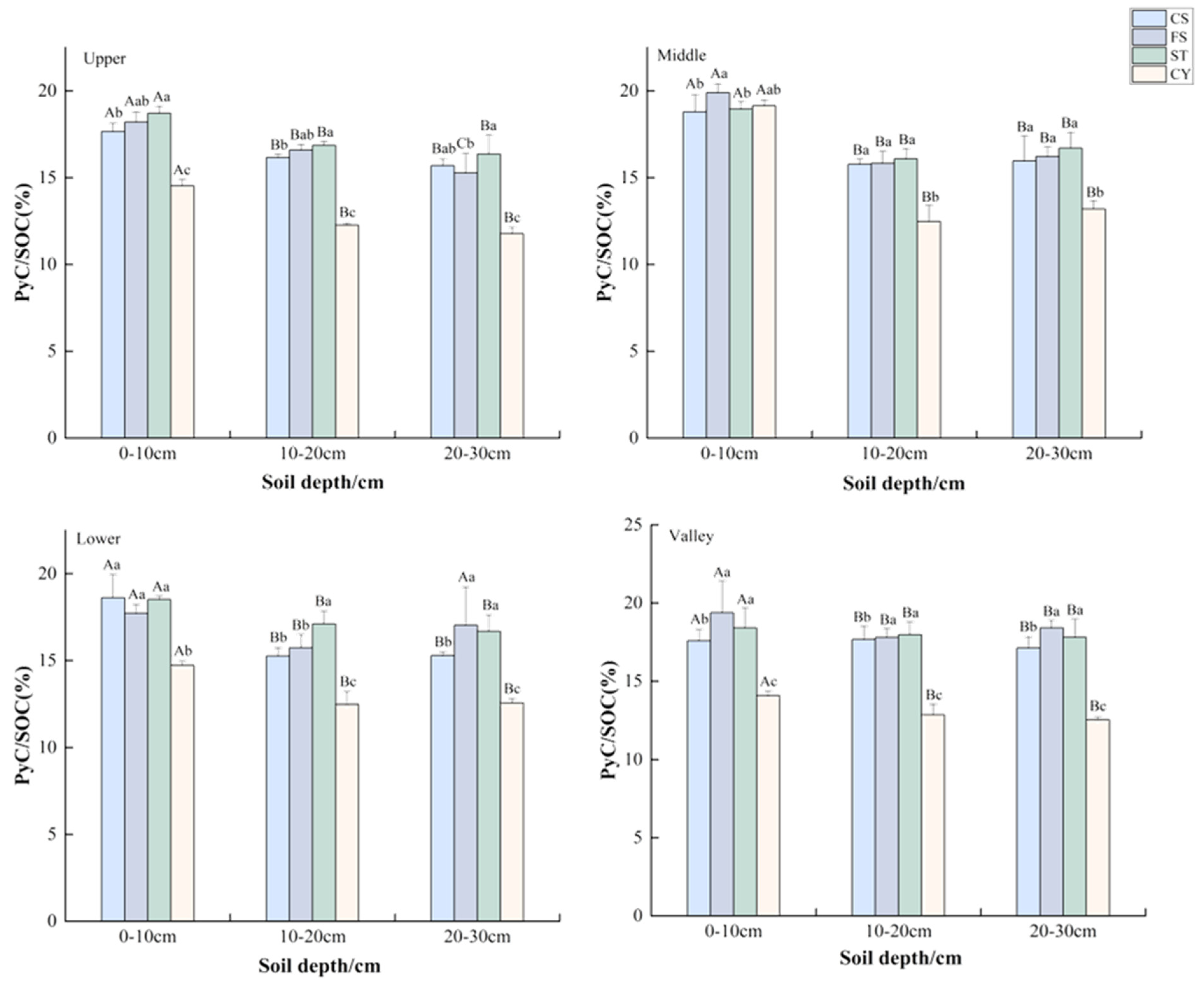
3.3. Size Fraction Distribution of PyC in Soil
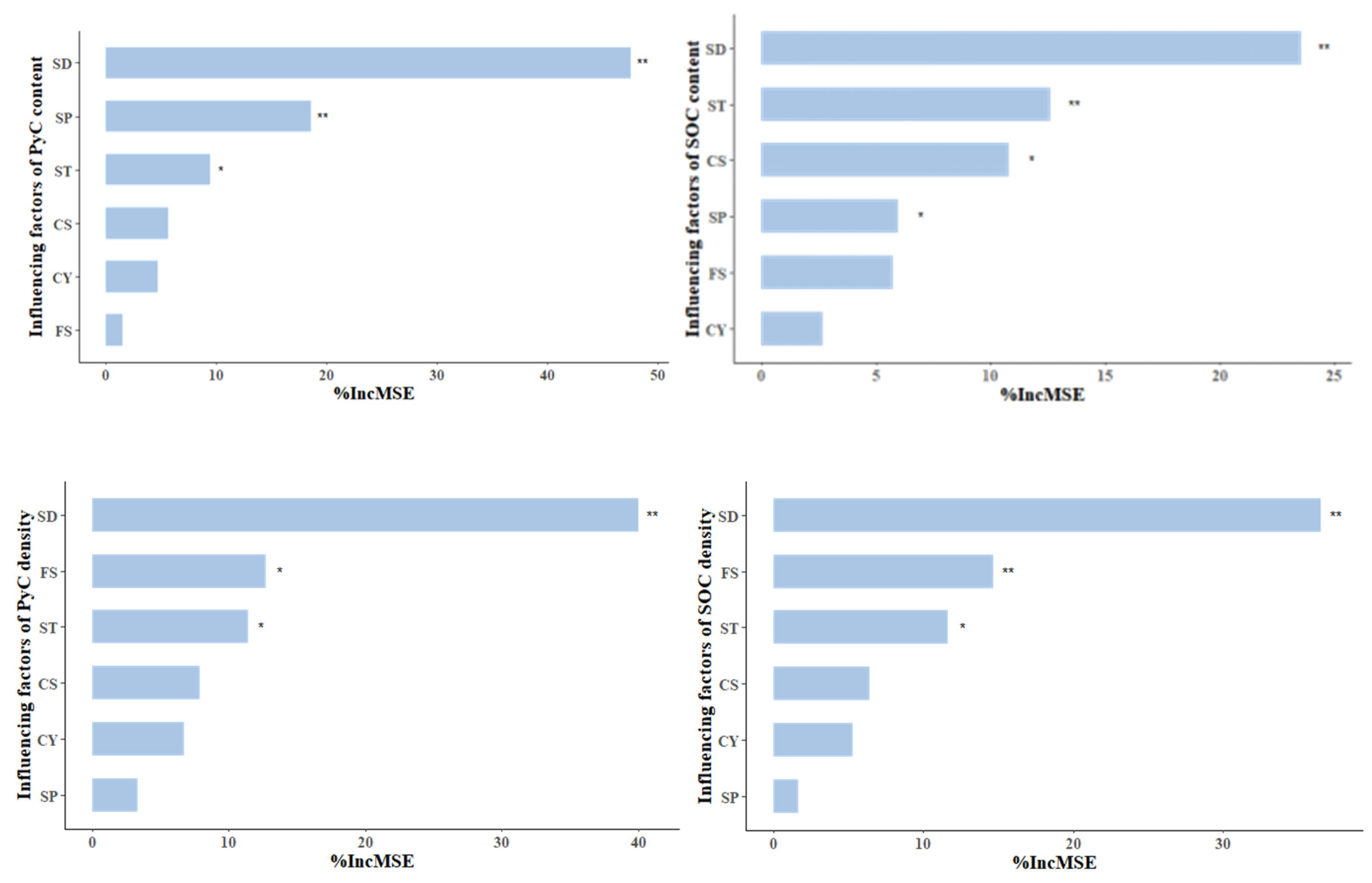
3.4. Random Forest-Based Factor Contribution Ranking
4. Discussion
4.1. Slope Position Distribution of Pyrogenic Carbon in Soil
4.2. Soil Depth Distribution of Pyrogenic Carbon in Soil
4.3. Size Fraction Distribution of PyC in Soil
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mukherjee, S.; Kumar, M. Cycling of Black Carbon and Black Nitrogen in the Hydro-geosphere: Insights on the Paradigm, Pathway, and Processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 144711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czimczik, C.I.; Schmidt, M.W.I.; Schulze, E.D. Effects of increasing fire frequency on black carbon and organic matter in Podzols of Siberian Scots pine forests. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2004, 56, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.W.I.; Skjemstad, J.O.; Gehrt, E.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Charred organic carbon in German chernozemic soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2001, 50, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, M.I.; Wynn, J.G.; Saiz, G.; Wurster, C.M.; McBeath, A. The Pyrogenic Carbon Cycle. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 43, 273–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, M.I.; Moyo, C.; Veenendaal, E.M.; Lloyd, J.; Frost, P. Stability of elemental carbon in a savanna soil. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1999, 13, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodowski, S.; John, B.; Flessa, H.; Amelung, W. Aggregate-occluded black carbon in soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 57, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiong, Z.; Kuzyakov, Y. Biochar stability in soil: Meta-analysis of decomposition and priming effects. GCB Bioenergy 2015, 8, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Abiven, S.; Torn, M.S.; Schmidt, M.W.I. Fire-derived organic carbon in soil turns over on a centennial scale. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 2847–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Bogomolova, I.; Glaser, B. Biochar stability in soil: Decomposition during eight years and transformation as assessed by compound-specific 14C analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlbusch, T.A.J.; Crutzen, P.J. Toward a global estimate of black carbon in residues of vegetation fires representing a sink of atmospheric CO2 and a source of O2. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1995, 9, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.W.I.; Noack, A.G. Black carbon in soils and sediments: Analysis, distribution, implications, and current challenges. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2000, 14, 777–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvluoma, J.; Miettinen, A.; Keskinen, R.; Rasa, K.; Lindberg, H. Structural and chemical changes in pyrogenic organic matter aged in a boreal forest soil. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soucémarianadin, L.N.; Quideau, S.A.; MacKenzie, M.D. Pyrogenic carbon stocks and storage mechanisms in podzolic soils of fire-affected Quebec black spruce forests. Geoderma 2014, 217–218, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soucémarianadin, L.N.; Quideau, S.A.; MacKenzie, M.D.; Munson, A.D.; Boiffin, J.; Bernard, G.M.; Wasylishen, R.E. Total and pyrogenic carbon stocks in black spruce forest floors from eastern Canada. Org. Geochem. 2015, 82, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggenberger, G.; Rodionov, A.; Shibistova, O.; Grabe, M.; Kasansky, O.A.; Fuchs, H.; Mikheyeva, N.; Zrazhevskaya, G.; Flessa, H. Storage and mobility of black carbon in permafrost soils of the forest tundra ecotone in Northern Siberia. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2008, 14, 1367–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, E.S.; Hockaday, W.C.; Turetsky, M.R.; Masiello, C.A.; Valentine, D.W.; Finney, B.P.; Baldock, J.A. Topographic controls on black carbon accumulation in Alaskan black spruce forest soils: Implications for organic matter dynamics. Biogeochemistry 2010, 100, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Hu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Ren, B.; Shi, S. Effects of Fire Severity and Topography on Soil Black Carbon Accumulation in Boreal Forest of Northeast China. Forests 2018, 9, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, C.M.; Schmidt, M.W.I. Black (pyrogenic) carbon: A synthesis of current knowledge and uncertainties with special consideration of boreal regions. Biogeosciences 2006, 3, 397–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Sun, L.; Wang, J.; Dou, X.; Ji, S.; Hu, T.; Gao, C. Effects of pyrogenic carbon addition after fire on soil carbon mineralization in the Great Khingan Mountains peatlands (Northeast China). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 864, 161102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauss, V.; Johnson, M.; Krull, E.; Daub, M.; Lehmann, J. Pyrogenic carbon controls across a soil catena in the Pacific Northwest. Catena 2015, 124, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, C.D.; Hatton, P.-J.; Bird, J.A.; Nadelhoffer, K.; Ward, C.P.; Stark, R.E.; Filley, T.R. Interacting Controls of Pyrolysis Temperature and Plant Taxa on the Degradability of PyOM in Fire-Prone Northern Temperate Forest Soil. Soil Syst. 2018, 2, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, E.A.; Feldpausch, T.R.; Marimon, B.S.; Morandi, P.S.; Phillips, O.L.; Bird, M.; Murakami, A.A.; Arroyo, L.; Quesada, C.A.; Marimon-Junior, B.H. Soil pyrogenic carbon in southern Amazonia: Interaction between soil, climate, and above-ground biomass. Front. For. Glob. Chang. 2022, 5, 880963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-González, M.A.; Rosa, J.M.D.L.; Aksoy, E.; Jeffery, S.; Verheijen, F.G.A. Spatial distribution of pyrogenic carbon in Iberian topsoils estimated by chemometric analysis of infrared spectra. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, E.S.; Kasischke, E.S.; Valentine, D.W.; Turetsky, M.R.; McGuire, A.D. Topographic influences on wildfire consumption of soil organic carbon in interior Alaska: Implications for black carbon accumulation. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2007, 112, G03017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksek, T.; Yüksek, F. Effects of altitude, aspect, and soil depth on carbon stocks and properties of soils in a tea plantation in the humid Black Sea region. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 4267–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, J.; He, H.; Chang, Y. Spatial point analysis of fire occurrence and its influence factor in Huzhong forest area of the Great Xing′an Mountains in Heilongjiang Province, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, B.; Amelung, W. Pyrogenic carbon in native grassland soils along a climosequence in North America. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.-k.; Long, J. Variation of soil organic carbon under different vegetation types in Karst Mountain areas of Guizhou Province, southwest China. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao = J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 22, 2253–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.; Cachier, H. Determination of black carbon by chemical oxidation and thermal treatment in recent marine and lake sediments and Cretaceous-Tertiary clays. Default J. 1996, 131, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.B.; Sang, Y.; Song, J.F.; Cui, X.Y. Content and Distribution of Black Carbon in Typical Forest Soils in Changbaishan Mountains. For. Res. 2016, 29, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Feng, Q.; Qin, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Deo, R.C.; Zhang, C.; Li, R.; Li, B. The role of topography in shaping the spatial patterns of soil organic carbon. Catena 2019, 176, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, L.; Pang, D.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, L.; Wu, M.; Li, X. Altitudinal distribution rule of Larix principis-rupprechtii forest’s soil organic carbon and its influencing factors in Liupan Mountain. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 6773–6785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cui, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, H. Effects of topographic factors on soil black carbon storage in coniferous forests at the north end of Greater Khingan Mountains. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2021, 45, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Gao, S.; Yao, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Gao, F. Characteristics of Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Accumulation under Different Vegetation Restoration in the Loess Hilly Region of Northwest Shanxi Province. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2021, 30, 1787–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangroo, S.A.; Najar, G.R.; Rasool, A. Effect of altitude and aspect on soil organic carbon and nitrogen stocks in the Himalayan Mawer Forest Range. Catena 2017, 158, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.A.; Kumar, M.; Bussmann, R.W. Altitudinal variation in soil organic carbon stock in coniferous subtropical and broadleaf temperate forests in Garhwal Himalaya. Carbon Balance Manag. 2009, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, J.A.; Shakesby, R.A.; Robichaud, P.R.; Cannon, S.H.; Martin, D.A. Current research issues related to post-wildfire runoff and erosion processes. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 122, 10–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplot, V.A.M.; Rumpel, C.; Valentin, C. Water erosion impact on soil and carbon redistributions within uplands of Mekong River. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19, GB4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming-kui, Z.; Zhao-yun, L.I.U. Soil Erosion-induced Selective Transfer of Various Forms of Organic Carbon in Red Soil Slope Field. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2009, 23, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xu, J.; Song, J.; Cui, X. Distribution characteristics and influence factors of soil black carbon of typical forest areas in northeast China. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2018, 38, 3313–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Xue, Y.; Lie, G.; Ye, L.; Huang, X. Soil Organic Carbon Storage on Different Slope Positions in Cunninghamia Lanceolata Stands. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 32, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, L.; Yao, Y.; Qin, F.; Guo, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, M. Spatial distribution of soil organic carbon and its influencing factors at different soil depths in a semiarid region of China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüneberg, E.; Schöning, I.; Kalko, E.K.V.; Weisser, W.W. Regional organic carbon stock variability: A comparison between depth increments and soil horizons. Geoderma 2010, 155, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcios, M.M.; Jaramillo, M.M.A.; do Vale, J.F.; Fearnside, P.M.; Barbosa, R.I. Soil charcoal as long-term pyrogenic carbon storage in Amazonian seasonal forests. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 22, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koele, N.; Bird, M.; Haig, J.; Marimon-Junior, B.H.; Marimon, B.S.; Phillips, O.L.; de Oliveira, E.A.; Quesada, C.A.; Feldpausch, T.R. Amazon Basin forest pyrogenic carbon stocks: First estimate of deep storage. Geoderma 2017, 306, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gao, L.; Sun, Y.; Cui, X. Distribution of Mineral-bonded Organic Carbon and Black Carbon in Forest Soils of Great Xing’an Mountains, China and Carbon Sequestration Potential of the Soils. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2018, 55, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.J.d.; Oliveira, D.; Nóbrega, G.N.; Barbosa, R.; Cordeiro, R.C. Pyrogenic carbon stocks and its spatial variability in soils from savanna-forest ecotone in amazon. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 340, 117980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, J.; Lehmann, J.; Rondon, M.; Goodale, C. Fate of soil-applied black carbon: Downward migration, leaching and soil respiration. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 1366–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, D.G. Forest soil disturbance intervals inferred from soil charcoal radiocarbon dates. Can. J. For. Res. 2003, 33, 2514–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.H.; Gao, L.; Cui, X.Y. Black carbon content and distribution in different particle size fractions of forest soils in the middle part of Great Xing’an Mountains, China. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao = J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 3111–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leifeld, J.; Fenner, S.; Müller, M. Mobility of black carbon in drained peatland soils. Biogeosciences 2007, 4, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodowski, S.; Amelung, W.; Haumaier, L.; Abetz, C.; Zech, W. Morphological and chemical properties of black carbon in physical soil fractions as revealed by scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Geoderma 2005, 128, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sampling Sites | Slope Position | Angle | Latitude and Longitude | Altitude (m) | Vegetation Type | Aboveground Biomass (t·ha−1) | Soil Texture | Soil Texture | Soil Bulk Density (g/cm³) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 cm | 10–20 cm | 20–30 cm | |||||||||
| 1 | Upper slope | 10°~22° | 123°15′43″ E–123°26′17″ E 51°27′17″ N–51°45′64″ N | 1030.6–1061.3 | Larix gmelinii, Betula platyphylla; Pinus pumila, Vaccinium uliginosum, Cyperaceae, Roseceae. | 38.0 | Brown coniferous forest soil | 44%CS, 13%FS, 38%ST, 4%CY | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.0 |
| 2 | 36.8 | 42%CS, 6%FS, 46%ST, 6%CY | 1.5 | 1.7 | 2.1 | ||||||
| 3 | 31.9 | 31%CS, 9%FS, 51%ST, 9%CY | 1.6 | 1.8 | 2.1 | ||||||
| 4 | Middle slope | 13°~17° | 123°25′20″ E–123°25′27″ E 51°27′20″ N–51°27′25″ N | 948.6–960.4 | Larix gmelinii, Pinus pumila, Betula platyphylla; Vaccinium uliginosum, Rhododendron dauricum. | 35.6 | 30%CS, 6%FS, 57%ST, 7%CY | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.7 | |
| 5 | 37.2 | 27%CS, 6%FS, 60%ST, 7%CY | 1.5 | 1.8 | 2.1 | ||||||
| 6 | 27.6 | 43%CS, 9%FS, 43%ST, 5%CY | 1.5 | 1.9 | 2.0 | ||||||
| 7 | Lower slope | 18°~19° | 123°15′30″ E–123°15′38″ E 51°27′31″ N–51°27′34″ N | 853.2–871.3 | Larix gmelinii, Pinus pumila, Betula platyphylla; Ledum palustre, Cyperaceae, Roseceae. | 19.3 | 33%CS, 7%FS, 54%ST, 6%CY | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.7 | |
| 8 | 35.8 | 35%CS, 8%FS, 53%ST, 5%CY | 1.0 | 1.4 | 1.6 | ||||||
| 9 | 27.0 | 29%CS, 6%FS, 59%ST, 6%CY | 1.2 | 1.6 | 1.7 | ||||||
| 10 | Valley | 14°~16° | 123°15′35″ E–123°15′43″ E 51°27′40″ N–51°27′45″ N | 727.2–731.5 | Larix gmelinii, Betula platyphylla; Vaccinium uliginosum, Ledum palustre. | 5.9 | 24%CS, 8%FS, 55%ST, 12%CY | 1.6 | 1.7 | 2.0 | |
| 11 | 7.1 | 40%CS, 11%FS, 43%ST, 6%CY | 1.5 | 1.8 | 2.0 | ||||||
| 12 | 7.5 | 34%CS, 11%FS, 49%ST, 5%CY | 1.5 | 1.7 | 2.0 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, L.; Peng, Y.; Hou, X.; Zhang, Y. Distribution of Pyrogenic Carbon in the Soil of a Cold Temperate Coniferous Forest 13 Years After a Severe Wildfire. Land 2025, 14, 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040851
Shi L, Peng Y, Hou X, Zhang Y. Distribution of Pyrogenic Carbon in the Soil of a Cold Temperate Coniferous Forest 13 Years After a Severe Wildfire. Land. 2025; 14(4):851. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040851
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Lina, Yuanchun Peng, Xingyu Hou, and Yun Zhang. 2025. "Distribution of Pyrogenic Carbon in the Soil of a Cold Temperate Coniferous Forest 13 Years After a Severe Wildfire" Land 14, no. 4: 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040851
APA StyleShi, L., Peng, Y., Hou, X., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Distribution of Pyrogenic Carbon in the Soil of a Cold Temperate Coniferous Forest 13 Years After a Severe Wildfire. Land, 14(4), 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040851






