The Impact of Information Consumption Pilot Policy on Urban Land Green Use Efficiency: An Empirical Study from China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Research on Information Consumption and the ICPP
2.2. Research on ULGUE
2.3. Literature Review Summary
3. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypothesis
3.1. Direct Impact of the ICPP on ULGUE
3.2. Analysis of the Influencing Mechanism of the ICPP on ULGUE
3.2.1. Expand the Scale of Digital Transactions
3.2.2. Nurture Future Industrial Developments
3.2.3. Promote Green Consumption Behaviors
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Model Setting
4.1.1. Benchmark Regression Model
4.1.2. Causal Mediating Effect Model
4.2. Variable Selection and Data Source
4.2.1. Dependent Variable
4.2.2. Independent Variable
4.2.3. Mediator Variables
4.2.4. Control Variables
4.3. Data Sources
5. Empirical Analysis
5.1. The Baseline Regression Results
5.2. Endogeneity Test
5.3. Robustness Test
5.4. Robustness Test of Transformation Model
5.5. Mediating Effect Test
5.6. Analysis of Heterogeneity
5.6.1. Resource Endowment Heterogeneity
5.6.2. Transport Infrastructure Heterogeneity
5.6.3. Geographical Location Heterogeneity
6. Discussion and Conclusions
6.1. Discussion
6.2. Conclusions
6.3. Recommendations
6.4. Limitation and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- Parallel trend test
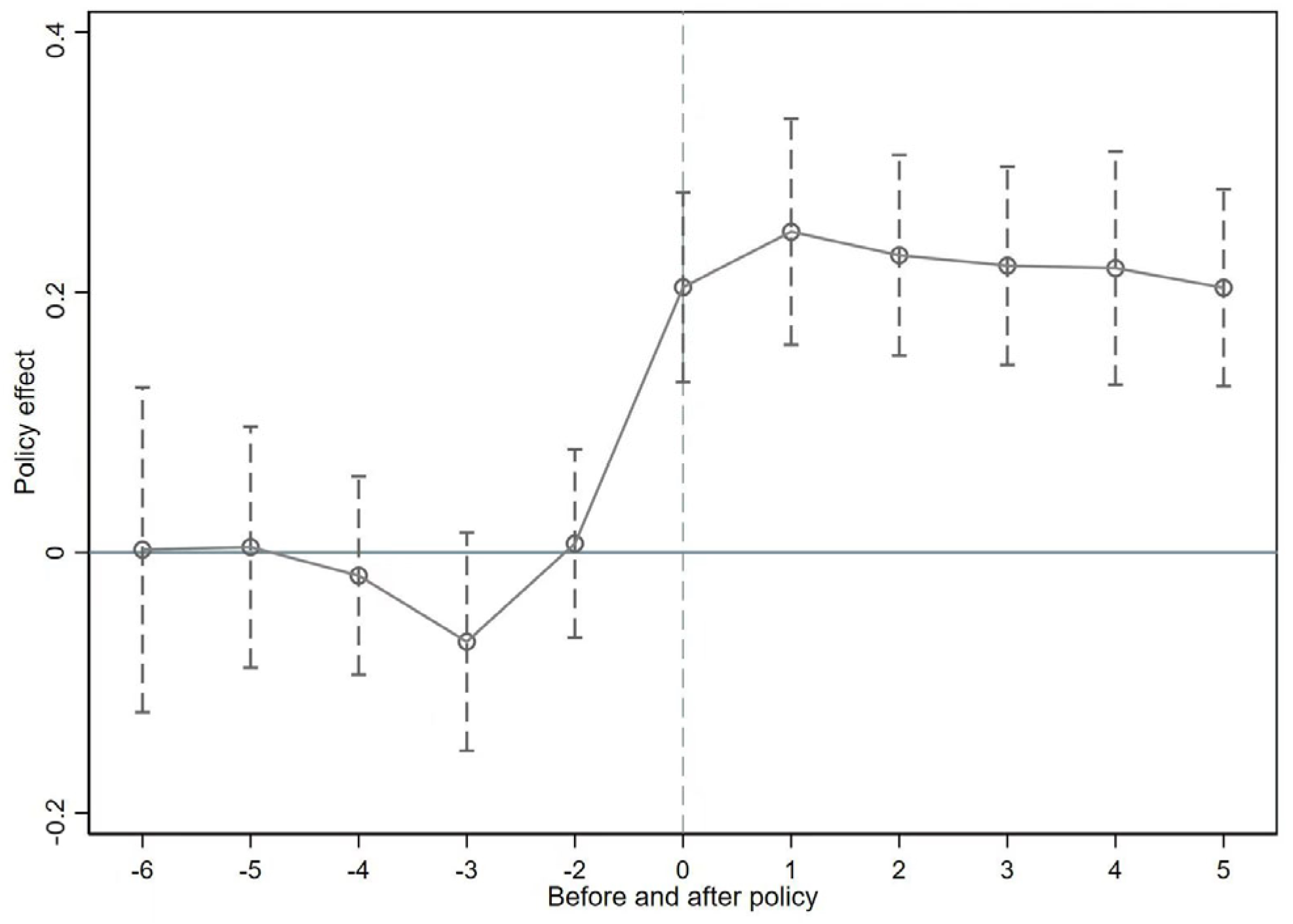
- 2.
- Placebo test
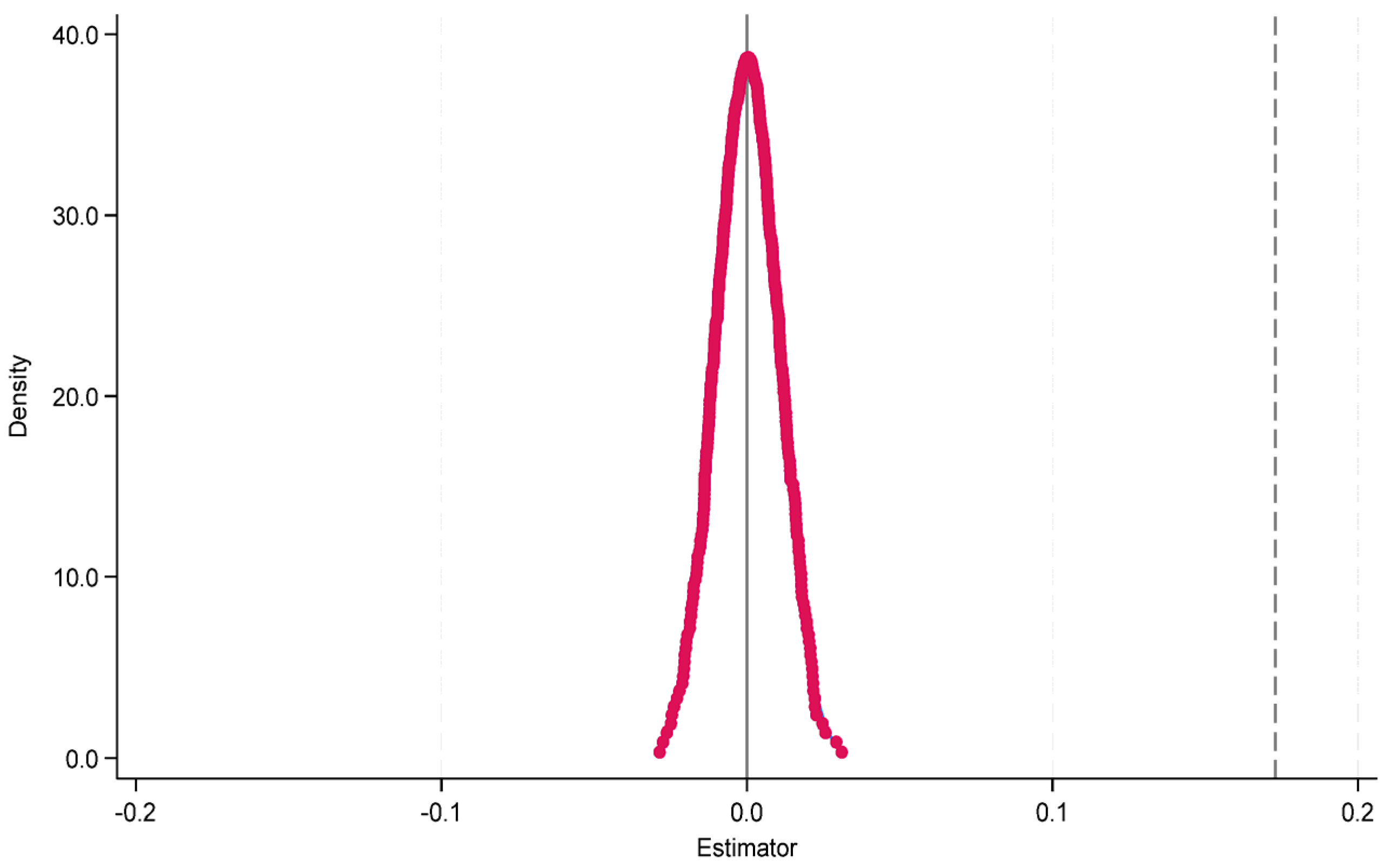
- 3.
- Two-step test of mediating effect
| Variable | lnExp (1) | lnNewI (2) | GC (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICPP | 0.222 *** (4.037) | 0.241 *** (4.246) | 0.047 *** (5.860) |
| Constant | 0.006 (0.732) | 0.010 (1.222) | −0.003 ** (−2.235) |
| Control | YES | YES | YES |
| Control_Squ | YES | YES | YES |
| City FE | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 3653 | 3653 | 3653 |
References
- Birthal, P.S.; Hazrana, J.; Negi, D.S.; Bhan, S.C. Climate change and land-use in Indian agriculture. Land Use Policy 2021, 109, 105652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magazzino, C.; Cerulli, G.; Shahzad, U.; Khan, S. The nexus between agricultural land use, urbanization, and greenhouse gas emissions: Novel implications from different stages of income levels. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canesi, R.; D’Alpaos, C. The Evaluation of Sustainable Development Projects in Marginal Areas: An A’WOT Approach. Land 2024, 13, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudapakati, C.P.; Bandauko, E.; Chaeruka, J.; Arku, G. Peri-urbanisation and land conficts in Domboshava, Zimbabwe. Land Use Policy 2024, 144, 107222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schewenius, M.; McPhearson, T.; Elmqvist, T. Opportunities for increasing resilience and sustainability of urban social–ecological systems: Insights from the URBES and the cities and biodiversity outlook projects. Ambio 2014, 43, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, R.; Aziz, G.; Khan, M.S. The Nexus Between Intensive Land Utilization, Energy Efficiency, and Economic Growth: Application of Advanced Econometric Approaches. Land Degrad. Dev. 2025, 36, 2217–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhan, L.; Jiang, G.; Si, H. Understanding the nonpoint source pollution loads’ spatiotemporal dynamic response to intensive land use in rural China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yang, F.; Liu, K.; Liang, T.; Wang, L. The effects of low-carbon city pilot policy on urban land green use efficiency: Evidence from 284 cities in China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Daaku, K.N. Engaging students in planning for superfund site remediation and redevelopment. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 278, 111567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienow, A.; Stenger, D.; Menz, G. Sprawling cities and shrinking regions–forecasting urban growth in the Ruhr for 2025 by coupling cells and agents. Erdkunde 2014, 68, 85–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Xue, S.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, Q.; Ali, M.; Xu, R.; Xu, J.; Ding, T.; Wang, J.; Huang, Z.; et al. Framework of land use planning for an energy producing city of Northwest China based on water-energy-food nexus. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 451, 142126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.T.; Yong, Y.J.; Yuan, C.G. Measurement of Urban Land Green Use Efficiency and Its Spatial Differentiation Characteristics: An Empirical Study based on 284 Cities. China Land Sci. 2019, 33, 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wei, Y.; Zheng, X.; Xie, L. Temporal–spatial characteristics of urban land use efficiency of China’s 35mega cities based on DEA: Decomposing technology and scale efficiency. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z. Impact of China’s Energy-Consuming Right Trading on Urban Land Green Utilization Efficiency. Land 2024, 13, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; Zhou, C. Impact of Industrial Intelligence on China’s Urban Land Green Utilization Efficiency. Land 2024, 13, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrardi, L.; Cambini, C.; Rondi, L. Artificial intelligence, firms and consumer behavior: A survey. J. Econ. Surv. 2022, 36, 969–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.M.; Gray, T.J.; Gainous, J. Digital information consumption and external political efficacy in Latin America: Does institutional context matter? J. Inf. Technol. Politics 2017, 14, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, B. How does the Chinese pilot policy on information consumption affect carbon emissions? Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2023, 41, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Luo, Y.; Guo, S.; Yang, X.; Chen, S. Information consumption city and carbon emission efficiency: Evidence from China’s quasi-natural experiment. Environ. Res. 2024, 255, 119182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhu, P.H.; Qian, X.Y. National information consumption demonstration city construction and urban green development: A quasi-experiment from Chinese cities. Energy Econ. 2024, 130, 107313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetina, K.K. The epistemics of information: A consumption model. J. Consum. Cult. 2010, 10, 171–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Han, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, G. The product demand model driven by consumer’s information perception and quality perception. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 535, 122352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeck, L.; Graves, S.C.; Lanza, G. Development and analysis of digital twins of production systems. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 62, 3544–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, F.; Wang, B.; Wei, Z. The rise of the internet city in China: Production and consumption of internet information. Urban Stud. 2015, 52, 2313–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucks, W.M.; Mosler, H.J. Information preferences and corresponding consumption behavior in common pool resource management. Soc. Psychol. 2011, 42, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinn, M.D.; Fairlie, R.W. ICT use in the developing world: An analysis of differences in computer and internet penetration. Rev. Int. Econ. 2010, 18, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zherebin, V.M.; Kova, N.A.; Makhrova, O.N. Consumption in the Information Society. Russ. Educ. Soc. 2010, 52, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higón, D.A.; Gholami, R.; Shirazi, F. ICT and environmental sustainability: A global perspective. Telemat. Inform. 2017, 34, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadok, M.; Chatta, R.; Bednar, P. ICT for development in Tunisia: “Going the last mile”. Technol. Soc. 2016, 46, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Cai, X.; Dai, Q. Research on the Influence of National Information Consumption Pilot on Urban Innovation Level. Reform Econ. Syst. 2024, 1, 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.; Cai, X.; Zhang, Z.H. How does National Information Consumption Pilot Policy Affect IndustrialStructure Optimization?Dual Perspective of Supply Side and Demand Side. Res. Econ. Manag. 2023, 44, 40–58. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Hu, S.C.; Wu, L.F. Does Information Consumption Promote High-quality Economic Development?Evidence from National Information Consumption City Pilot Policies. Res. Econ. Manag. 2023, 44, 77–96. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, M.Y.; Lin, J.N.; Nie, H.H. Does Digital Transformation Promote Common Prosperity withinFirms? Evidence from Chinese A share Listed Firms. Quant. Econ. Tech. Econ. Res. 2022, 39, 50–70. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Shu, B.; Wu, Q. Urban land use efficiency in china: Spatial and temporal characteristics, regional difference and influence factors. Econ. Geogr. 2014, 34, 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Masini, E.; Tomao, A.; Barbati, A.; Corona, P.; Serra, P.; Salvati, L. Urban growth, land-use efficiency and local socioeconomic context: A comparative analysis of 417 metropolitan regions in Europe. Environ. Manag. 2019, 63, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroso, N.H.; Zevenbergen, J.A.; Lengoiboni, M. Urban land use efficiency in Ethiopia: An assessment of urban land use sustainability in Addis Ababa. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilov, S.M.; Chen, Y.; Quang, N.H.; Nguyen, M.N.; Leighton, B.; Paget, M.; Lazarow, N. Estimation of urban land-use efficiency for sustainable development by integrating over 30-year landsat imagery with population data: A case study of Ha Long, Vietnam. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, K.; Yang, S. Land use efficiency and influencing factors of urban agglomerations in China. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, D.; Li, J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, D.; Chen, W. Cultivated land use efficiency and its driving factors in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Hu, B.; Kuang, B.; Zhou, M. Regional differences and dynamic evolution of urban land green use efficiency within the Yangtze River Delta, China. Land Use Policy 2021, 106, 105449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Xiao, Y.; Tan, H.; Guo, Z.; An, B. What were the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and the influencing factors of urban land green use efficiency? A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Hu, C.; Liu, C. Study on the spatial–temporal evolution and driving mechanism of urban land green use efficiency in the Yellow River Basin cities. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wen, L.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, A.; Gil, J.M. Synergistic impacts of carbon emission trading policy and innovative city pilot policy on urban land green use efficiency in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 118, 105955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Xiao, D. Can Open Government Data Improve City Green Land-Use Efficiency? Evidence from China. Land 2024, 13, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Xu, H.; Jiang, C.; Deng, S.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z. Has the Digital Economy Improved the Urban Land Green Use Efficiency? Evidence from the National Big Data Comprehensive Pilot Zone Policy. Land 2024, 13, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Guo, L.; Liu, Y. The Impact of Innovative City Pilot Policy on Urban Land Green Use Efficiency: A Quasi-Natural Experiment from China. Land 2025, 14, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.; Li, H. Impact of digital economy on urban land green use efficiency: Evidence from Chinese cities. Environ. Res. Commun. 2024, 6, 055008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Xiao, F.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F. Spillover Effects of Urban Expansion on Land Green Use Efficiency: An Empirical Study Based on Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data in China. Land 2024, 13, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Li, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhu, Z.; Peng, X.; Liu, Y.; Liao, D.; Zhao, K. Unlocking the potential of collaborative innovation to narrow the inter-city urban land green use efficiency gap: Empirical study on 19 urban agglomerations in China. Environ. Impact Assess Rev. 2024, 104, 107341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, G. On exports and economic growth. J. Dev. Econ. 1983, 12, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.L.; Hu, W.J.; Chen, T.Q. Research on the Influence Mechanism and Spatial Spillover Effect of Information Consumption Pilot Policy on Improving Urban Carbon Productivity of Cities. Mod. Financ. Econ. J. Tianjin Univ. Financ. Econ. 2024, 44, 39–55. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Y. Energy Consumption, CO2 Emission and Sustainable Development in Chinese Industry. Econ. Res. 2009, 44, 41–55. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.H.; Zhang, L.F. Research on the Regional Variation of Carbon Productivity in China. China Ind. Econ. 2011, 5, 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L. Analysis of the change of artificial intelligence to online consumption patterns and consumption concepts. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 7559–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, M.; Jia, F.; Yu, J. Developing urban infrastructure constructions for increasing e-commerce sales: The moderating roles of aging population. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2024, 124, 1971–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoglu, E.; Batista e Silva, F.; Lavalle, C. Quantifying and modelling industrial and commercial land-use demand in France. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 519–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Yang, L.; Dong, J. Management of urban land expansion in China through intensity assessment: A big data perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 153, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ma, L.; Guo, F.; Chen, Y. Internet of things technology in ecological security assessment system of intelligent land. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 99772–99782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, K.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Yan, X.W. Digital Economy and Green and Low-Carbon Transformation of Land Use: Spatial Effects and Moderating Mechanisms. Land 2024, 13, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jiang, P. Does e-commerce infrastructure increase enterprise productivity? Evidence from China’s e-commerce demonstration city. Int. J. Financ. Econ. 2024, 30, 1758–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X.W.; Xu, N. Can Information Consumption Promote the Digital Transformation of Enterprises? Empirical Evidence from China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 11026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Lin, K.; Liu, B.; Wang, H. Does robotization improve the skill structure? The role of job displacement and structural transformation. Appl. Econ. 2024, 56, 3415–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghelea, C.; Aceleanu, M.I. Education–Determinant of Consumer’s Conditions in an Era of Technological Change. Amfiteatru Econ. J. 2014, 16, 535–549. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.; Wang, F.; Song, G.; Liu, L. Digital transformation on enterprise green innovation: Effect and transmission mechanism. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cezarino, L.O.; Liboni, L.B.; Oliveira Stefanelli, N.; Oliveira, B.G.; Stocco, L.C. Diving into emerging economies bottleneck: Industry 4.0 and implications for circular economy. Manag. Decis. 2021, 59, 1841–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Dou, H.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, J.; Lei, X.; Huang, X. A strategy of building a beautiful and harmonious countryside: Reuse of idle rural residential land based on symbiosis theory. Habitat Int. 2025, 155, 103238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.M.; Pu, J.F.; Xia, F.Z. Innovative Allocation of Land Element to Ensure the Development of New Quality Productivity: Theoretical Logic, Basic Pattern and Pathway Mechanisms. China Land Sci. 2024, 38, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Niu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, L. A Model to Analyze Industrial Clusters to Measure Land Use Efficiency in China. Land 2024, 13, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhai, J. Development of a cross-scale landscape infrastructure network guided by the new Jiangnan watertown urbanism: A case study of the ecological green integration demonstration zone in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Li, W.; Zhang, D.; Yan, Y.; Xu, T. How do You want to restore?—Assessing the public preferences and social benefits of ecological restoration for natural rubber plantation in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 823778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, M.S.; Biswas, M.I.; Azad, N. The role of online information sources in enhancing circular consumption behaviour: Fostering sustainable consumption patterns in the digital age. Bus Strategy Environ. 2025, 34, 1419–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oncioiu, I.; Priescu, I.; Banu, G.S.; Chirca, N. Green Consumers’ Responses to Integrated Digital Communication in the Context of Multichannel Retail. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Zhao, J. The Implementation Effect of Information Embedded Regulatory Tools on Promoting Online Green Consumption Behavior in Digital Era: Green Purchase Scenario Simulation and Regulatory Tools Design Experiments. Manag. World 2022, 38, 142–162. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, J.M. From Accuracy to Agility: The Dynamic lmpact of Digital Information Intervention on the Decision-Making Process of Green Agricultural Product Consumption. Collect. Essays Financ. Econ. 2024, 6, 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, C.; Liu, H.; Xu, A.; Zhang, J. Green logistics of fossil fuels and E-commerce: Implications for sustainable economic development. Resour. Policy 2023, 85, 103991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, M.J. Simulating Seoul’s greenbelt policy with a machine learning-based land-use change model. Cities 2023, 143, 104580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busato, F.; Chiarini, B.; Cisco, G.; Ferrara, M. Green preferences. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 3211–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Tian, Y. Impact of Land-Use–Land Cover Changes on the Service Value of Urban Ecosystems: Evidence from Chengdu, China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2024, 150, 05024028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.W.; Yang, Y. Research on multifunctional transformation of rural land use under the background of urban-rural integration. J. Zhengzhou Univ. 2020, 53, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.H. Overcoming barriers to ecologically sensitive land management: Conservation subdivisions, green developments, and the development of a land ethic. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2004, 24, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernozhukov, V.; Chetverikov, D.; Demirer, M.; Duflo, E.; Hansen, C.; Newey, W.; Robins, J. Double/debiased machine learning for treatment and structural parameters. Econ. J. 2018, 21, 1–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farbmacher, H.; Huber, M.; Lafférs, L.; Langen, H.; Spindler, M. Causal mediation analysis with double machine learning. Econ. J. 2022, 25, 277–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.Q.; Xing, W. The U-shaped Relationship Between Household Consumptionand E-commerce Market Scale. Financ. Trade Econ. 2015, 11, 131–147. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.H.; Zhang, P.K.; Du, Y.H. How Robots Reshape the Urban Labor Market: From a Perspective of Migrants Job Tasks. Trends Econ. 2020, 10, 92–109. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.F.; Ren, Y. The Construction and Strategic Outlook of Green Consumption Measuring Indicator System in the 14th Five-Year Plan of China. Environ. Manag. China 2020, 12, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Golin, M.; Romarri, A. Broadband internet and attitudes toward migrants: Evidence from Spain. Eur. J. Political Econ. 2024, 85, 102579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.; Angelstam, P.; Elbakidze, M.; Axelsson, R.; Degerman, E. Green infrastructures and intensive forestry: Need and opportunity for spatial planning in a Swedish rural–urban gradient. Scand. J. For. Res. 2013, 28, 143–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T. Mediating Effects and Moderating Effects in Causal Inferenc. Chin. Ind. Econ. 2022, 5, 100–120. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Fernandez, C.; Wu, C.T.; Schatz, L.K.; Taira, N.; Vargas-Hernández, J.G. The shrinking mining city: Urban dynamics and contested territory. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2012, 36, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Q.; Luo, S. The dilemma of land green use efficiency in resource-based cities: A perspective based on digital transformation. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1339928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ye, X.; Ma, X. Does the clusters of high-speed railway network match the urban agglomerations? A case study in China. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2024, 95, 101968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, J.C. Network infrastructure, inclusive green growth, and regional inequality: From causal inference based on double machine Learning. Quant. Econ. Tech. Econ. Res. 2023, 40, 113–135. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Li, Y.; Nie, C. The effect of place-based policy on urban land green use efficiency: Evidence from the Pilot Free-Trade Zone establishment in China. Land 2023, 12, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Z.Y.; Ye, J.S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Liang, B. Smart Cities, Smarter land Use? Unveiling the efficiency gains from China’s digital urban transformation. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 171, 113151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Indicator Type | Indicator Name | Indicator Connotation | Units | N | Mean | sd | Min | Max | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Land | Area of land used for urban construction | Km2 | 3653 | 147.666 | 173.098 | 15 | 895 | [41] |
| Captial | Total investment in fixed assets | CNY 100 million | 3653 | 1870 | 1850 | 48.919 | 9440 | [43,44,45] | |
| Labor | Employees in secondary and tertiary industries | 10,000 person | 3653 | 53.527 | 60.992 | 4.750 | 326.737 | [43,44,45] | |
| Expected output | Economic benefits | Value added of secondary and tertiary industries | CNY 100 million | 3653 | 2528.25 | 3352.536 | 97.300 | 18,790.2 | [43] |
| Social benefits | Per capita disposable income of urban residents | CNY | 3653 | 31,622.61 | 10,750.74 | 11,691.1 | 66,068 | [45] | |
| Ecological benefits | Green covered area as of completed area | % | 3653 | 40.327 | 6.095 | 14.33 | 61.58 | [43,44,45] | |
| Unexpected output | Pollutant emissions | Based on entropy method, industrial sulfur dioxide emission, industrial comprehensive calculation of industrial wastewater discharge and industrial smoke and dust discharge | — | 3653 | 0.074 | 0.071 | 0.002 | 0.424 | [40,43] |
| Carbon emissions | Total CO2 emissions | 10,000 t | 3653 | 3380 | 3050 | 196.855 | 15,700 | [45] |
| Variable | Symbol | Obs | Mean | Std.Dev | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable | ULGUE | 3653 | 0.552 | 0.275 | 0.015 | 1.235 |
| Independent variable | ICPP | 3653 | 0.235 | 0.424 | 0 | 1 |
| Control Variables | lnRgdp | 3653 | 10.819 | 0.561 | 9.507 | 12.101 |
| Fin | 3653 | 2.628 | 1.182 | 1.037 | 6.898 | |
| UI | 3653 | 18.893 | 7.782 | 4.863 | 44.401 | |
| Inter | 3653 | 2.750 | 1.850 | 0.308 | 9.559 | |
| lnTec | 3653 | 5.533 | 1.773 | 1.792 | 10.032 | |
| lnPop | 3653 | 5.900 | 0.678 | 3.850 | 7.255 | |
| FDI | 3653 | 0.016 | 0.021 | −0.029 | 0.112 | |
| Mediator variables | lnExp | 3653 | 14.177 | 1.688 | 10.712 | 18.549 |
| lnNewl | 3653 | 5.327 | 1.850 | 1.792 | 10.271 | |
| GC | 3653 | 0.533 | 0.166 | 0.121 | 0.887 |
| Variable | Random Forest (1) | Random Forest (2) | Lasso (3) | Xgboost (4) | Enet (5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICPP | 0.223 *** (8.952) | 0.227 *** (9.378) | 0.232 *** (10.934) | 0.209 *** (15.741) | 0.148 *** (6.437) |
| Constant | −0.001 (−0.348) | −0.002 (−0.372) | −0.001 (−0.154) | −0.001 (−0.220) | 0.003 (0.655) |
| Control | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Control_Squ | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| City FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 3653 | 3653 | 3653 | 3653 | 3653 |
| Variable | Endogeneity Test (1) | Refine Urban Areas (2) | Interactive Fixed Effect (3) | Exclusion Concurrent Policies (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICPP | 1.173 *** (2.741) | 0.228 *** (10.163) | 0.230 *** (10.716) | 0.205 *** (8.536) |
| Constant | — | −0.003 (−0.685) | 0.025 *** (5.920) | −0.002 (−0.470) |
| Control | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Control_Squ | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| City FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 3653 | 3601 | 3653 | 3653 |
| Variable | Change the Sample Segmentation Ratio | Replacement Model | Interactive Model (5) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kfolds = 3 (1) | Kfolds = 8 (2) | SVM (3) | Neural Network (4) | ||
| ICPP | 0.217 *** (10.038) | 0.218 *** (8.836) | 0.187 *** (18.254) | 0.231 *** (10.829) | 0.219 *** (39.795) |
| Constant | −0.002 (−0.385) | −0.002 (−0.435) | 0.023 *** (4.967) | −0.001 (−0.155) | — |
| Control | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Control_Squ | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| City FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 3653 | 3653 | 3653 | 3653 | 3653 |
| Variable | Total Effect (1) | Treatment Group Direct Effect (2) | Control Group Direct Effect (3) | Treatment Group Indirect Effect (4) | Control Group Indirect Effect (5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnExp | 0.228 *** | 0.223 *** | 0.210 *** | 0.018 *** | 0.004 *** |
| lnNewI | 0.220 *** | 0.220 *** | 0.202 *** | 0.018 *** | −0.001 |
| GC | 0.219 *** | 0.220 *** | 0.202 *** | 0.019 *** | −0.000 |
| Variable | Resource-Based Cities | Non-Resource–Based Cities | HSR Cities | Non-HSR Cities | Inland Cities | Coastal Cities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | ||||
| ICPP | 0.249 *** (8.673) | 0.154 *** (3.842) | 0.235 *** (8.004) | 0.138 *** (6.591) | 0.246 *** (5.592) | 0.185 *** (6.306) |
| Constant | −0.004 (−0.811) | −0.004 (−0.582) | −0.001 (−0.255) | −0.002 (−0.184) | −0.003 (−0.396) | −0.002 (−0.454) |
| Control | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Control_Squ | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| City FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 1456 | 2197 | 2349 | 1304 | 1105 | 2548 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, W. The Impact of Information Consumption Pilot Policy on Urban Land Green Use Efficiency: An Empirical Study from China. Land 2025, 14, 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14050945
Fu Y, Wang Z, Zhao W. The Impact of Information Consumption Pilot Policy on Urban Land Green Use Efficiency: An Empirical Study from China. Land. 2025; 14(5):945. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14050945
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yunpeng, Zixuan Wang, and Wenjia Zhao. 2025. "The Impact of Information Consumption Pilot Policy on Urban Land Green Use Efficiency: An Empirical Study from China" Land 14, no. 5: 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14050945
APA StyleFu, Y., Wang, Z., & Zhao, W. (2025). The Impact of Information Consumption Pilot Policy on Urban Land Green Use Efficiency: An Empirical Study from China. Land, 14(5), 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14050945





