Identification of Human SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibodies from Convalescent Patients Using EBV Immortalization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Donors, Cell Purification, and Infection with EBV
2.2. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Tests
2.3. IgG Characterization and Sequencing
2.4. Cell Expansion in Serum-Free Medium for Antibody Purification
2.5. SARS-Cov-2 Neutralization Test
3. Results
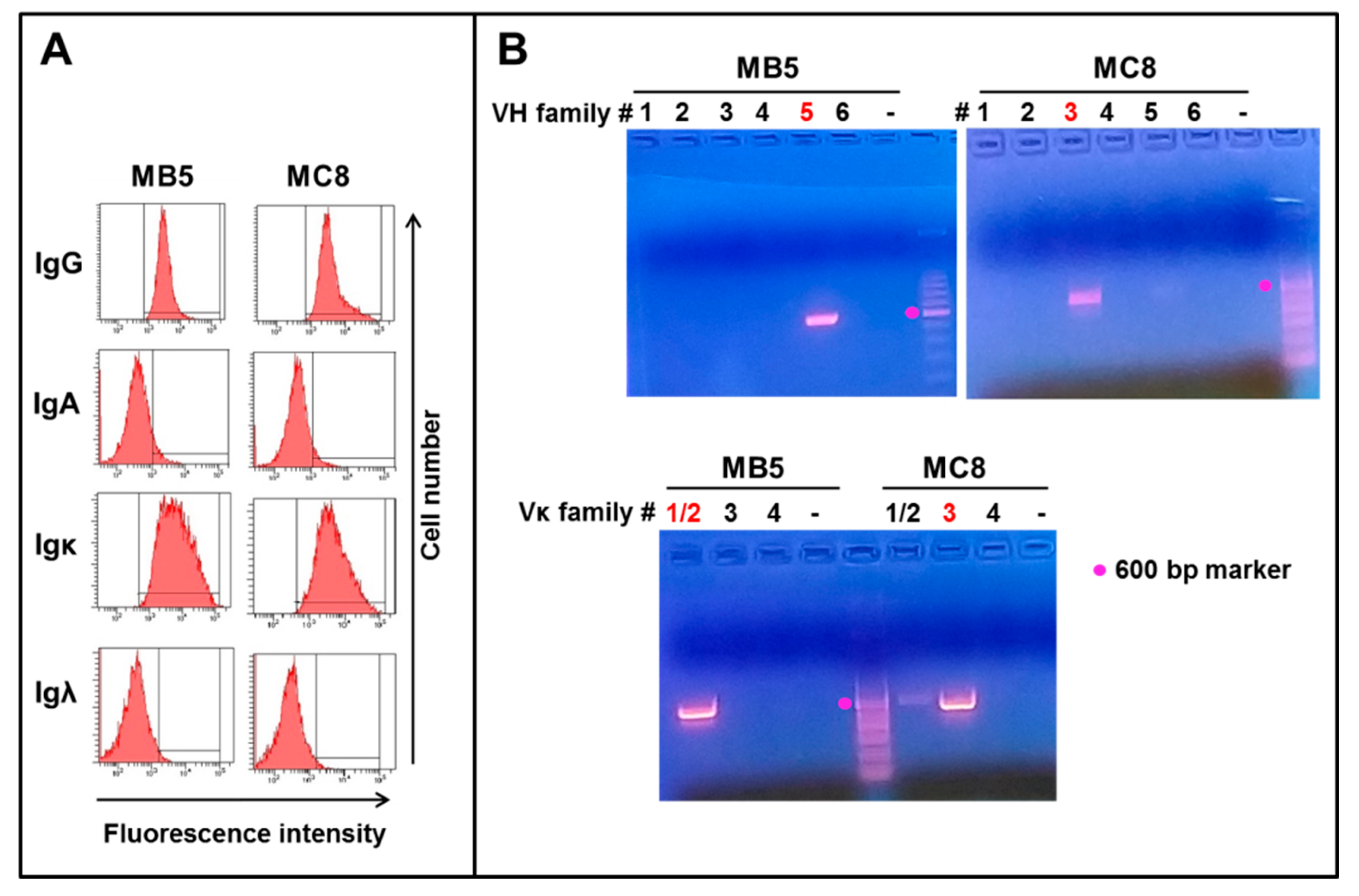
3.1. Isolation of Two EBV-Immortalized B Cell Clones Secreting Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG1 Monoclonal Antibodies
3.2. PCR Amplification and Sequencing of IgG1 Clones
3.3. Purification and Functional Assays
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corti, D.; Lanzavecchia, A. Efficient Methods To Isolate Human Monoclonal Antibodies from Memory B Cells and Plasma Cells. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saphire, E.O.; Schendel, S.L.; Gunn, B.M.; Milligan, J.C.; Alter, G. Antibody-mediated protection against Ebola virus. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, J.A.; Galvez, N.M.S.; Pacheco, G.A.; Bueno, S.M.; Kalergis, A.M. Antibody development for preventing the human respiratory syncytial virus pathology. Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nath Neerukonda, S.; Vassell, R.; Weiss, C.D. Neutralizing Antibodies Targeting the Conserved Stem Region of Influenza Hemagglutinin. Vaccines 2020, 8, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieselmann, L.; Kreer, C.; Ercanoglu, M.S.; Lehnen, N.; Zehner, M.; Schommers, P.; Potthoff, J.; Gruell, H.; Klein, F. Effective high-throughput isolation of fully human antibodies targeting infectious pathogens. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Sun, Q. Antibodies and Vaccines Target RBD of SARS-CoV-2. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 671633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.C.; Adams, A.C.; Hufford, M.M.; de la Torre, I.; Winthrop, K.; Gottlieb, R.L. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminelli, G.; Garcia-Mandico, S. COVID-19 in Italy: An Analysis of Death Registry Data. J. Public Health 2020, 42, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senni, M. COVID-19 experience in Bergamo, Italy. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 1783–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fagiuoli, S.; Lorini, F.L.; Remuzzi, G.; Covid-19 Bergamo Hospital Crisis, U. Adaptations and Lessons in the Province of Bergamo. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, D.H.; Barlow, M.J.; Harrison, J.F.; Winger, L.; Huehns, E.R. Production of human monoclonal antibody to rhesus D antigen. Lancet 1983, 1, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahler, D.W.; Campbell, M.J.; Hart, S.; Miller, R.A.; Levy, S.; Levy, R. Ig VH gene expression among human follicular lymphomas. Blood 1991, 78, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tiller, T.; Meffre, E.; Yurasov, S.; Tsuiji, M.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; Wardemann, H. Efficient generation of monoclonal antibodies from single human B cells by single cell RT-PCR and expression vector cloning. J. Immunol. Methods 2008, 329, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rondinone, V.; Pace, L.; Fasanella, A.; Manzulli, V.; Parisi, A.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Ostuni, A.; Chironna, M.; Caprioli, E.; Labonia, M.; et al. VOC 202012/01 Variant Is Effectively Neutralized by Antibodies Produced by Patients Infected before Its Diffusion in Italy. Viruses 2021, 13, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozbor, D.; Steinitz, M.; Klein, G.; Koskimies, S.; Makela, O. Establishment of anti-TNP antibody-producing human lymphoid lines by preselection for hapten binding followed by EBV transformation. Scand. J. Immunol. 1979, 10, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurawski, V.R., Jr.; Haber, E.; Black, P.H. Production of antibody to tetanus toxoid by continuous human lymphoblastoid cell lines. Science 1978, 199, 1439–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, D.H.; Huehns, E.R.; Epstein, M.A. Therapeutic use of human monoclonal antibodies. Lancet 1983, 1, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, K.R.; Watanabe, A.; Kuraoka, M.; Do, K.T.; McGee, C.E.; Sempowski, G.D.; Kepler, T.B.; Schmidt, A.G.; Kelsoe, G.; Harrison, S.C. Memory B Cells that Cross-React with Group 1 and Group 2 Influenza A Viruses Are Abundant in Adult Human Repertoires. Immunity 2018, 48, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Traggiai, E.; Becker, S.; Subbarao, K.; Kolesnikova, L.; Uematsu, Y.; Gismondo, M.R.; Murphy, B.R.; Rappuoli, R.; Lanzavecchia, A. An efficient method to make human monoclonal antibodies from memory B cells: Potent neutralization of SARS coronavirus. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecetta, S.; Finco, O.; Seubert, A. Quantum leap of monoclonal antibody (mAb) discovery and development in the COVID-19 era. Semin. Immunol. 2020, 50, 101427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, J.M.; Cornacchione, V.; Sathe, A.; Be, C.; Srinivas, H.; Riquet, E.; Leber, X.C.; Hein, A.; Wrobel, M.B.; Scharenberg, M.; et al. Human Memory B Cells Harbor Diverse Cross-Neutralizing Antibodies against BK and JC Polyomaviruses. Immunity 2019, 50, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinna, D.; Corti, D.; Jarrossay, D.; Sallusto, F.; Lanzavecchia, A. Clonal dissection of the human memory B-cell repertoire following infection and vaccination. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byazrova, M.; Yusubalieva, G.; Spiridonova, A.; Efimov, G.; Mazurov, D.; Baranov, K.; Baklaushev, V.; Filatov, A. Pattern of circulating SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody-secreting and memory B-cell generation in patients with acute COVID-19. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2021, 10, e1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, G.E.; Edwards, E.S.J.; Aui, P.M.; Varese, N.; Stojanovic, S.; McMahon, J.; Peleg, A.Y.; Boo, I.; Drummer, H.E.; Hogarth, P.M.; et al. Rapid generation of durable B cell memory to SARS-CoV-2 spike and nucleocapsid proteins in COVID-19 and convalescence. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugan, H.L.; Stamper, C.T.; Li, L.; Changrob, S.; Asby, N.W.; Halfmann, P.J.; Zheng, N.Y.; Huang, M.; Shaw, D.G.; Cobb, M.S.; et al. Profiling B cell immunodominance after SARS-CoV-2 infection reveals antibody evolution to non-neutralizing viral targets. Immunity 2021, 54, 1290–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Uchil, P.D.; Li, W.; Zheng, D.; Terry, D.S.; Gorman, J.; Shi, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, T.; Ding, S.; et al. Real-Time Conformational Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Spikes on Virus Particles. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 880–891.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 183, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sempowski, G.D.; Saunders, K.O.; Acharya, P.; Wiehe, K.J.; Haynes, B.F. Pandemic Preparedness: Developing Vaccines and Therapeutic Antibodies For COVID-19. Cell 2020, 181, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.X.; Levesque, M.C.; Nagel, A.; Dixon, A.; Zhang, R.; Walter, E.; Parks, R.; Whitesides, J.; Marshall, D.J.; Hwang, K.K.; et al. High-throughput isolation of immunoglobulin genes from single human B cells and expression as monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. Methods 2009, 158, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Doria-Rose, N.A.; Longo, N.S.; Laub, L.; Lin, C.L.; Turk, E.; Kang, B.H.; Migueles, S.A.; Bailer, R.T.; Mascola, J.R.; et al. Isolation of human monoclonal antibodies from peripheral blood B cells. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1907–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wrammert, J.; Smith, K.; Miller, J.; Langley, W.A.; Kokko, K.; Larsen, C.; Zheng, N.Y.; Mays, I.; Garman, L.; Helms, C.; et al. Rapid cloning of high-affinity human monoclonal antibodies against influenza virus. Nature 2008, 453, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brouwer, P.J.M.; Caniels, T.G.; van der Straten, K.; Snitselaar, J.L.; Aldon, Y.; Bangaru, S.; Torres, J.L.; Okba, N.M.A.; Claireaux, M.; Kerster, G.; et al. Potent neutralizing antibodies from COVID-19 patients define multiple targets of vulnerability. Science 2020, 369, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreano, E.; Nicastri, E.; Paciello, I.; Pileri, P.; Manganaro, N.; Piccini, G.; Manenti, A.; Pantano, E.; Kabanova, A.; Troisi, M.; et al. Extremely potent human monoclonal antibodies from COVID-19 convalescent patients. Cell 2021, 184, 1821–1835.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakkenbos, M.J.; Diehl, S.A.; Yasuda, E.; Bakker, A.Q.; van Geelen, C.M.; Lukens, M.V.; van Bleek, G.M.; Widjojoatmodjo, M.N.; Bogers, W.M.; Mei, H.; et al. Generation of stable monoclonal antibody-producing B cell receptor-positive human memory B cells by genetic programming. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunert, R.; Reinhart, D. Advances in recombinant antibody manufacturing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 3451–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dejnirattisai, W.; Zhou, D.; Ginn, H.M.; Duyvesteyn, H.M.E.; Supasa, P.; Case, J.B.; Zhao, Y.; Walter, T.S.; Mentzer, A.J.; Liu, C.; et al. The antigenic anatomy of SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain. Cell 2021, 184, 2183–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Pan, Z.; Yue, S.; Yu, F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, B.; Yang, X.; Gao, L.; et al. Disease severity dictates SARS-CoV-2-specific neutralizing antibody responses in COVID-19. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, T.F.; Zhao, F.; Huang, D.; Beutler, N.; Burns, A.; He, W.T.; Limbo, O.; Smith, C.; Song, G.; Woehl, J.; et al. Isolation of potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies and protection from disease in a small animal model. Science 2020, 369, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheid, J.F.; Barnes, C.O.; Eraslan, B.; Hudak, A.; Keeffe, J.R.; Cosimi, L.A.; Brown, E.M.; Muecksch, F.; Weisblum, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. B cell genomics behind cross-neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants and SARS-CoV. Cell 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.O.; West, A.P., Jr.; Huey-Tubman, K.E.; Hoffmann, M.A.G.; Sharaf, N.G.; Hoffman, P.R.; Koranda, N.; Gristick, H.B.; Gaebler, C.; Muecksch, F.; et al. Structures of Human Antibodies Bound to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Reveal Common Epitopes and Recurrent Features of Antibodies. Cell 2020, 182, 828–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.D.; Lian, C.; Yeap, L.S.; Meng, F.L. The development of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and their common features. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 12, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makdasi, E.; Levy, Y.; Alcalay, R.; Noy-Porat, T.; Zahavy, E.; Mechaly, A.; Epstein, E.; Peretz, E.; Cohen, H.; Bar-On, L.; et al. Neutralizing Monoclonal Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Isolated from Immunized Rabbits Define Novel Vulnerable Spike-Protein Epitope. Viruses 2021, 13, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, A.J.; Turner, J.S.; Liu, Z.; Aziati, I.D.; Chen, R.E.; Joshi, A.; Bricker, T.L.; Darling, T.L.; Adelsberg, D.C.; Alsoussi, W.B.; et al. A public vaccine-induced human antibody protects against SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerutti, G.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, T.; Gorman, J.; Lee, M.; Rapp, M.; Reddem, E.R.; Yu, J.; Bahna, F.; Bimela, J.; et al. Potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies directed against spike N-terminal domain target a single supersite. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Wang, R.; Ju, B.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, P.; Zhou, B.; et al. Structural basis for bivalent binding and inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infection by human potent neutralizing antibodies. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wec, A.Z.; Wrapp, D.; Herbert, A.S.; Maurer, D.P.; Haslwanter, D.; Sakharkar, M.; Jangra, R.K.; Dieterle, M.E.; Lilov, A.; Huang, D.; et al. Broad neutralization of SARS-related viruses by human monoclonal antibodies. Science 2020, 369, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Sun, Y.; Feng, R.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Deng, Y.Q.; Wang, L.; Cui, Z.; Cao, L.; et al. Structure-based development of human antibody cocktails against SARS-CoV-2. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asarnow, D.; Wang, B.; Lee, W.H.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.W.; Faust, B.; Ng, P.M.L.; Ngoh, E.Z.X.; Bohn, M.; Bulkley, D.; et al. Structural insight into SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies and modulation of syncytia. Cell 2021, 184, 3192–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, M.M.; Tortorici, M.A.; Park, Y.J.; Walls, A.C.; Homad, L.; Acton, O.J.; Bowen, J.E.; Wang, C.; Xiong, X.; de van der Schueren, W.; et al. Structural basis for broad coronavirus neutralization. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2021, 28, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Su, B.; Guo, X.; Sun, W.; Deng, Y.; Bao, L.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Geng, C.; et al. Potent Neutralizing Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Identified by High-Throughput Single-Cell Sequencing of Convalescent Patients’ B Cells. Cell 2020, 182, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabll, A.A.; Shahein, Y.E.; Omran, M.M.; Elnakib, M.M.; Ragheb, A.A.; Amer, K.E. A review on monoclonal antibodies in COVID-19: Role in immunotherapy, vaccine development and viral detection. Hum. Antibodies 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Donor | Supernatant Tested | Spike S1/S2 IgG Test | Nucleocapsid Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n. pos./n. Tested | % pos (Titer) | n. pos./n. Tested | n. pos. (Titer) | ||
| Donor A | Clones | 0/91 | 0% | 0/18 | 0% |
| Pool | 0/1 | 0% | 0/1 | 0% | |
| Donor B | Clones | 2/29 | 6.9% 72.7 + 71.5 UA/mL *) | 0/29 | 0% |
| Pool | 1/1 | 100% (14.9 UA/mL *) | 1/1 | 100% (29.9 COI **) | |
| V Gene | J Gene | D Gene | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allele | % Identity | Allele | % Identity | Allele | |
| MB5 heavy chain | IGHV5-51*01 | 96.18% | IGHJ6*02 | 85.48% | IGHD3-3*01 |
| MB5 light chain | IGKV2-28*01 | 99.66% | IGKJ2*01 | 100.00% | NA |
| MC8 heavy chain | IGHV3-23*01 | 94.79% | IGHJ4*02 | 89.58% | IGHD1-14*01 |
| MC8 light chain | IGKV3-11*01 | 98.11% | IGKJ2*01 | 100.00% | NA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valgardsdottir, R.; Cattaneo, I.; Napolitano, G.; Raglio, A.; Spinelli, O.; Salmoiraghi, S.; Castilletti, C.; Lapa, D.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Farina, C.; et al. Identification of Human SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibodies from Convalescent Patients Using EBV Immortalization. Antibodies 2021, 10, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib10030026
Valgardsdottir R, Cattaneo I, Napolitano G, Raglio A, Spinelli O, Salmoiraghi S, Castilletti C, Lapa D, Capobianchi MR, Farina C, et al. Identification of Human SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibodies from Convalescent Patients Using EBV Immortalization. Antibodies. 2021; 10(3):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib10030026
Chicago/Turabian StyleValgardsdottir, Rut, Irene Cattaneo, Gavino Napolitano, Annibale Raglio, Orietta Spinelli, Silvia Salmoiraghi, Concetta Castilletti, Daniele Lapa, Maria Rosaria Capobianchi, Claudio Farina, and et al. 2021. "Identification of Human SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibodies from Convalescent Patients Using EBV Immortalization" Antibodies 10, no. 3: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib10030026
APA StyleValgardsdottir, R., Cattaneo, I., Napolitano, G., Raglio, A., Spinelli, O., Salmoiraghi, S., Castilletti, C., Lapa, D., Capobianchi, M. R., Farina, C., & Golay, J. (2021). Identification of Human SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibodies from Convalescent Patients Using EBV Immortalization. Antibodies, 10(3), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib10030026









