Variable Distribution of DOCK-D Proteins between Cytosol and Nucleoplasm in Cell Lines, Effect of Interleukin-4 on DOCK10 in B-Cell Lymphoid Neoplasms, and Validation of a New DOCK10 Antiserum for Immunofluorescence Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Patients
2.3. HeLa Stable Cells with Regulatable Expression of DOCK10
2.4. Cytosolic and Nuclear Protein Extraction
2.5. Western Blot (WB) Analysis
2.6. Immunofluorescence (IF) Microscopy
3. Results
3.1. Expression of the DOCK-D Proteins in Cytosolic and Nuclear Fractions of Cell Lines
3.2. Induction of Expression of DOCK10 by IL-4 in B-Cell Neoplasms and Distribution between Cytosolic and Nuclear Fractions in a CLL Patient
3.3. Localization of DOCK10 in PM Ruffles and Filopodia in Transfected HeLa Cells Using a DOCK10 Antiserum
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rossman, K.L.; Der, C.J.; Sondek, J. GEF means go: Turning on RHO GTPases with guanine nucleotide-exchange factors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 6, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meller, N.; Merlot, S.; Guda, C. CZH proteins: A new family of Rho-GEFs. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 4937–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gadea, G.; Blangy, A. Dock-family exchange factors in cell migration and disease. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 93, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heasman, S.J.; Ridley, A.J. Mammalian Rho GTPases: New insights into their functions from in vivo studies. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 9, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meller, N.; Irani-Tehrani, M.; Kiosses, W.B.; Del Pozo, M.A.; Schwartz, M.A. Zizimin1, a novel Cdc42 activator, reveals a new GEF domain for Rho proteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikimi, A.; Meller, N.; Uekawa, N.; Isobe, K.; Schwartz, M.A.; Maruyama, M. Zizimin2: A novel, DOCK180-related Cdc42 guanine nucleotide exchange factor expressed predominantly in lymphocytes. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Q.; Yang, W.; Baird, D.; Feng, Q.; Cerione, R.A. Identification of a DOCK180-related guanine nucleotide exchange factor that is capable of mediating a positive feedback activation of Cdc42. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 35253–35262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaudon, F.; Raynaud, F.; Wehrlé, R.; Bellanger, J.M.; Doulazmi, M.; Vodjdani, G.; Gasman, S.; Fagni, L.; Dusart, I.; Debant, A.; et al. The RhoGEF DOCK10 is essential for dendritic spine morphogenesis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 2112–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Lafuente, N.; Alcaraz-García, M.J.; García-Serna, A.M.; Sebastián-Ruiz, S.; Moya-Quiles, M.R.; García-Alonso, A.M.; Parrado, A. Dock10, a Cdc42 and Rac1 GEF, induces loss of elongation, filopodia, and ruffles in cervical cancer epithelial HeLa cells. Biol. Open 2015, 4, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Côté, J.F.; Motoyama, A.B.; Bush, J.A.; Vuori, K. A novel and evolutionarily conserved PtdIns(3,4,5)P3-binding domain is necessary for DOCK180 signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, Y.; Tsuda, M.; Ichihara, S.; Watanabe, T.; Sakai, M.; Sawa, H.; Nagashima, K.; Hatakeyama, S.; Tanaka, S. Elmo1 inhibits ubiquitylation of Dock180. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frank, S.R.; Köllmann, C.P.; van Lidth de Jeude, J.F.; Thiagarajah, J.R.; Engelholm, L.H.; Frödin, M.; Hansen, S.H. The focal adhesion-associated proteins DOCK5 and GIT2 comprise a rheostat in control of epithelial invasion. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1816–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikimi, A.; Fukuhara, H.; Su, W.; Hongu, T.; Takasuga, S.; Mihara, H.; Cao, Q.; Sanematsu, F.; Kanai, M.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. Sequential regulation of DOCK2 dynamics by two phospholipids during neutrophil chemotaxis. Science 2009, 324, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caspi, E.; Rosin-Arbesfeld, R. A novel functional screen in human cells identifies MOCA as a negative regulator of Wnt signaling. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 4660–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiramoto-Yamaki, N.; Takeuchi, S.; Ueda, S.; Harada, K.; Fujimoto, S.; Negishi, M.; Katoh, H. Ephexin4 and EphA2 mediate cell migration through a RhoG-dependent mechanism. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 190, 461–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerikan, B.; Schiebel, E. Mechanism of cell-intrinsic adaptation to Adams-Oliver Syndrome gene DOCK6 disruption highlights ubiquitin-like modifier ISG15 as a regulator of RHO GTPases. Small GTPases 2019, 10, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Lafuente, N.; Minguela, A.; Parrado, A. DOCK9 induces membrane ruffles and Rac1 activity in cancer HeLa epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2018, 14, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Haney, L.; Walk, S.; Zhou, S.; Ravichandran, K.S.; Wang, W. Nuclear localization of the DOCK180/ELMO complex. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 429, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yelo, E.; Bernardo, M.V.; Gimeno, L.; Alcaraz-García, M.J.; Majado, M.J.; Parrado, A. Dock10, a novel CZH protein selectively induced by interleukin-4 in human B lymphocytes. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 3411–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parrado, A. Expression of DOCK10.1 protein revealed with a specific antiserum: Insights into regulation of first exon isoforms of DOCK10. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 3003–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz-García, M.J.; Ruiz-Lafuente, N.; Sebastián-Ruiz, S.; Majado, M.J.; González-García, C.; Bernardo, M.V.; Alvarez-López, M.R.; Parrado, A. Human and mouse DOCK10 splicing isoforms with alternative first coding exon usage are differentially expressed in T and B lymphocytes. Hum. Immunol. 2011, 72, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrado, A. Expression of DOCK9 and DOCK11 analyzed with commercial antibodies: Focus on regulation of mutually exclusive first exon isoforms. Antibodies 2020, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, J.J.; Narayan, P.; Padmanabhan, R.A.; Joseph, S.; Kumar, P.G.; Laloraya, M. Silencing of dedicator of cytokinesis (DOCK180) obliterates pregnancy by interfering with decidualization due to blockage of nuclear entry of autoimmune regulator (AIRE). Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2018, 80, e12844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Zhang, L.; Chiorazzi, N.; Rothstein, T.L. IL-4 rescues surface IgM expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2016, 128, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapman, E.A.; Oates, M.; Mohammad, I.S.; Davies, B.R.; Stockman, P.K.; Zhuang, J.; Pettitt, A.R. Delineating the distinct role of AKT in mediating cell survival and proliferation induced by CD154 and IL-4/IL-21 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 102948–102964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Falco, F.; Del Papa, B.; Baldoni, S.; Sabatini, R.; Falzetti, F.; Di Ianni, M.; Martelli, M.P.; Mezzasoma, F.; Pelullo, M.; Marconi, P.; et al. IL-4-dependent Jagged1 expression/processing is associated with survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells but not with Notch activation. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Lafuente, N.; Alcaraz-García, M.J.; Sebastián-Ruiz, S.; Gómez-Espuch, J.; Funes, C.; Moraleda, J.M.; García-Garay, M.C.; Montes-Barqueros, N.; Minguela, A.; Álvarez-López, M.R.; et al. The gene expression response of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells to IL-4 is specific, depends on ZAP-70 status and is differentially affected by an NFκB inhibitor. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Lafuente, N.; Alcaraz-García, M.J.; Sebastián-Ruiz, S.; García-Serna, A.M.; Gómez-Espuch, J.; Moraleda, J.M.; Minguela, A.; García-Alonso, A.M.; Parrado, A. IL-4 up-regulates miR-21 and the miRNAs hosted in the CLCN5 gene in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Namekata, K.; Enokido, Y.; Iwasawa, K.; Kimura, H. MOCA induces membrane spreading by activating Rac1. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 14331–14337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, M.; Harada, K.; Negishi, M.; Katoh, H. Dock4 forms a complex with SH3YL1 and regulates cancer cell migration. Cell Signal. 2014, 26, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, E.; Tohme, M.; Hedayat, M.; Leick, M.; Kumari, S.; Ramesh, N.; Massaad, M.J.; Ullas, S.; Azcutia, V.; Goodnow, C.C.; et al. A DOCK8-WIP-WASp complex links T cell receptors to the actin cytoskeleton. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3837–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
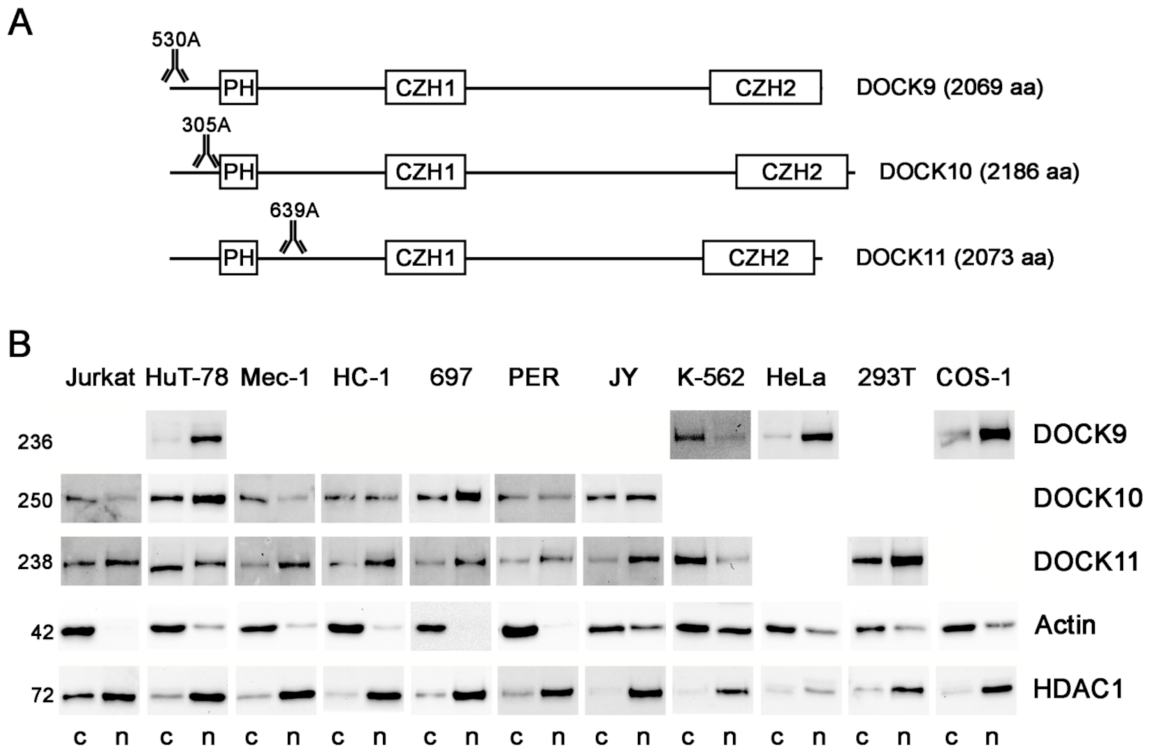

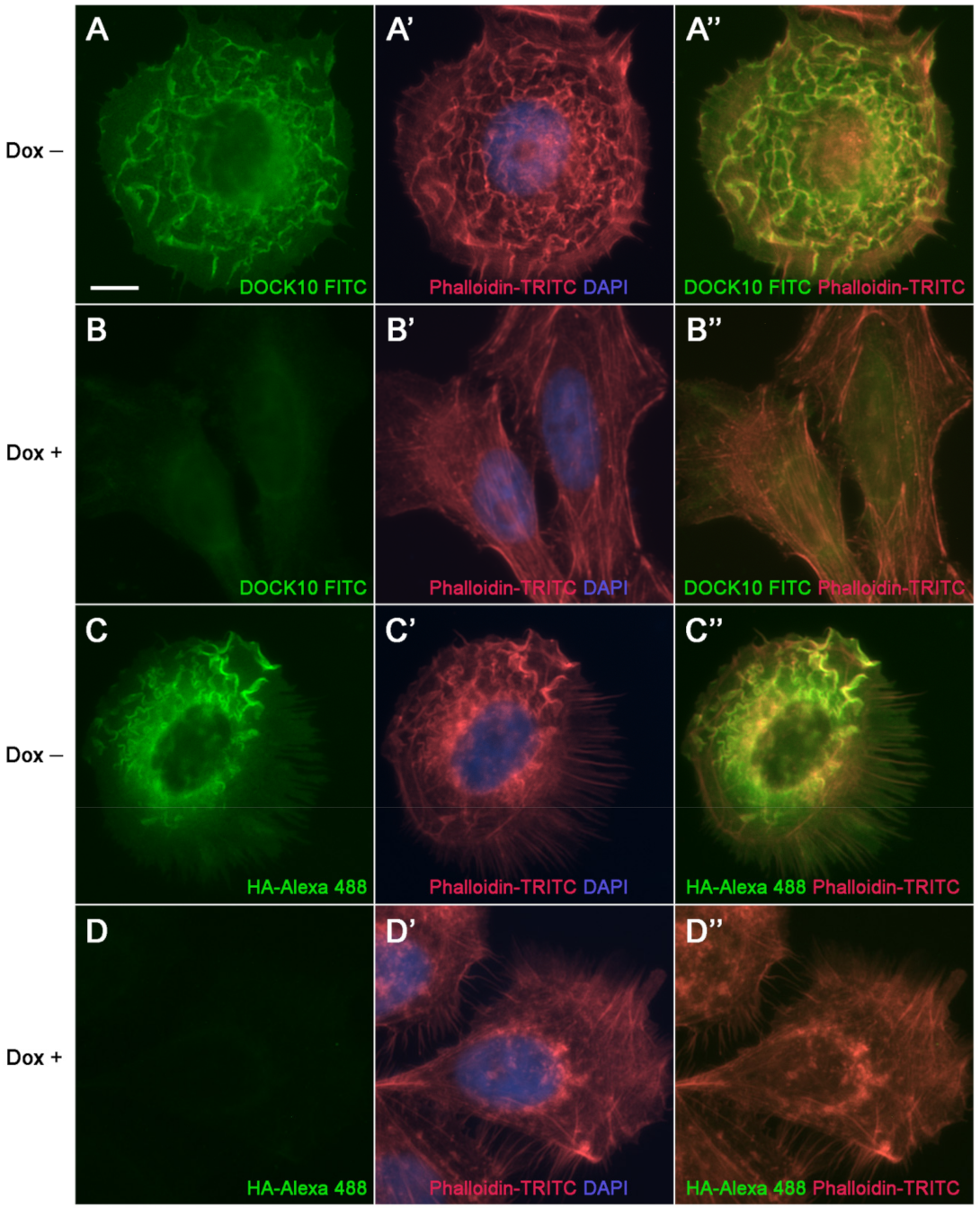
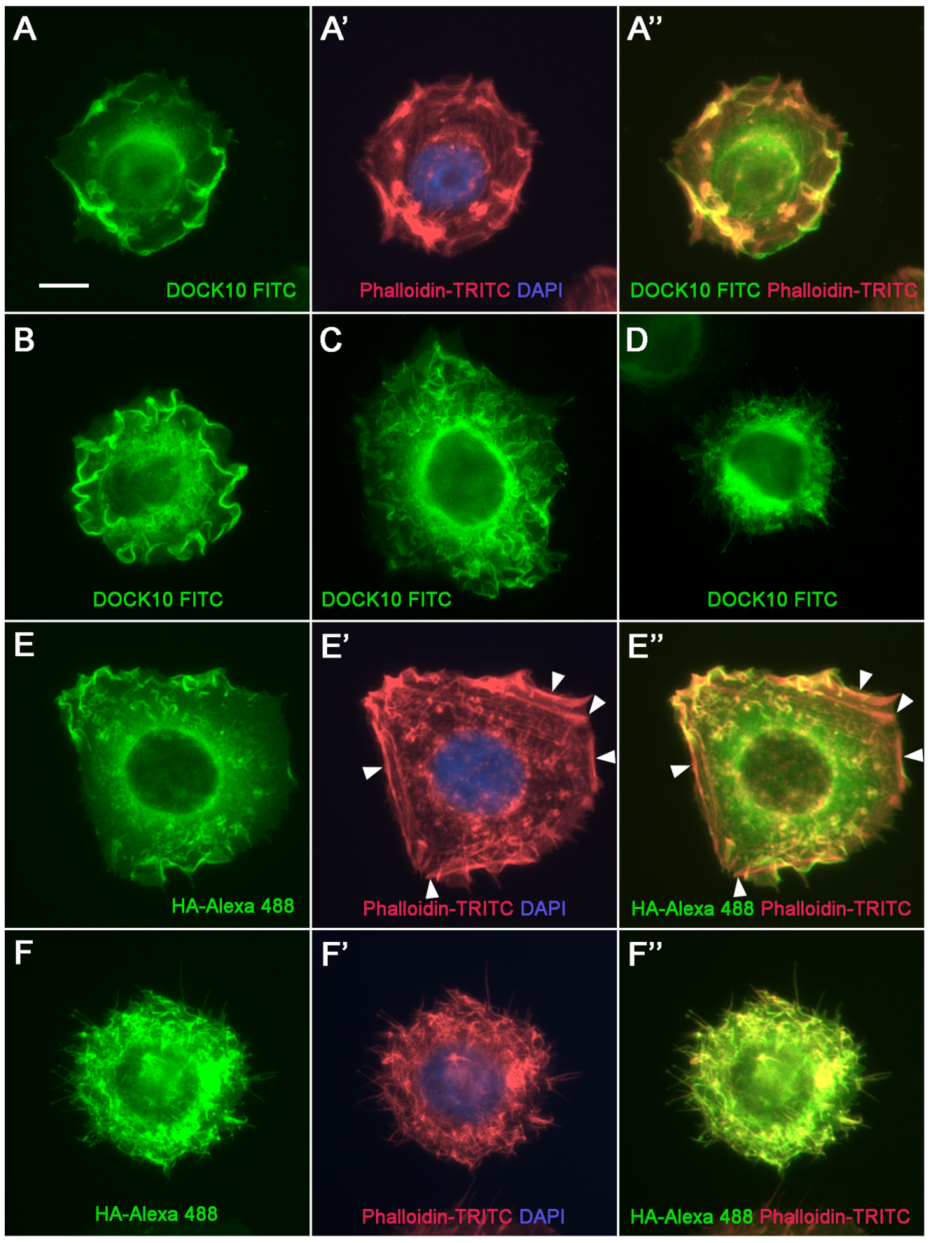
| Cell Line | Cell Lineage | Cell Origin | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jurkat | T lymphocytes | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia | 1 |
| HuT-78 | T lymphocytes | Sezary syndrome | 2 |
| Mec-1 | B lymphocytes | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | 3 |
| HC-1 | B lymphocytes | Hairy cell leukemia | 4 |
| 697 | B lymphocytes | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia | 5 |
| PER | B lymphocytes | Epstein-Barr virus-transformed lymphoblasts | 6 |
| JY | B lymphocytes | Epstein-Barr virus-transformed lymphoblasts | 7 |
| K-562 | Myeloid | Chronic myeloid leukemia | 1 |
| HeLa | Epithelial | Cervix carcinoma | 8 |
| 293T | Uncertain (fibroblastic, epithelial, neuronal…) | Embryonic kidney | 1 |
| COS-1 | Uncertain (fibroblast-like) | Cercopithecus aethiops kidney | 1 |
| Protein Target (Clone) | Dilution (Ratio) | Used For | Source | Used As | Catalog No. | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOCK9 | 1:2000 | WB | Rabbit | 1ary | A300-530A | 1 |
| DOCK10 | 1:5000 | WB | Rabbit | 1ary | A301-305A | 1 |
| DOCK11 | 1:5000 | WB | Rabbit | 1ary | A301-639A | 1 |
| DOCK10.2 | 1:5000 | WB | Rabbit | 1ary | Non applicable | 2 |
| Actin (C-2) | 1:1000 | WB | Mouse | 1ary | sc-8432 | 3 |
| HDAC1 (C-19) | 1:1000 | WB | Goat | 1ary | sc-6298 | 3 |
| Rabbit Igs-HRP | 1:2000 | WB | Swine | 2ary | P0399 | 4 |
| Mouse Igs-HRP | 1:2000 | WB | Goat | 2ary | P0447 | 4 |
| Goat Igs-HRP | 1:2000 | WB | Donkey | 2ary | sc-2020 | 3 |
| DOCK10.1 | 1:100 | IF | Rabbit | 1ary | Non applicable | 5 |
| HA (3F10) | 1:100 | IF | Rat | 1ary | 11 867 423 001 | 6 |
| Rabbit Igs-FITC | 1:100 | IF | Swine | 2ary | F0054 | 4 |
| Rat Igs-Alexa Fluor 488 | 1:100 | IF | Goat | 2ary | A11006 | 7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz-Lafuente, N.; Minguela, A.; Moraleda, J.M.; Muro, M.; Parrado, A. Variable Distribution of DOCK-D Proteins between Cytosol and Nucleoplasm in Cell Lines, Effect of Interleukin-4 on DOCK10 in B-Cell Lymphoid Neoplasms, and Validation of a New DOCK10 Antiserum for Immunofluorescence Studies. Antibodies 2021, 10, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib10030033
Ruiz-Lafuente N, Minguela A, Moraleda JM, Muro M, Parrado A. Variable Distribution of DOCK-D Proteins between Cytosol and Nucleoplasm in Cell Lines, Effect of Interleukin-4 on DOCK10 in B-Cell Lymphoid Neoplasms, and Validation of a New DOCK10 Antiserum for Immunofluorescence Studies. Antibodies. 2021; 10(3):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib10030033
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz-Lafuente, Natalia, Alfredo Minguela, Jose M. Moraleda, Manuel Muro, and Antonio Parrado. 2021. "Variable Distribution of DOCK-D Proteins between Cytosol and Nucleoplasm in Cell Lines, Effect of Interleukin-4 on DOCK10 in B-Cell Lymphoid Neoplasms, and Validation of a New DOCK10 Antiserum for Immunofluorescence Studies" Antibodies 10, no. 3: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib10030033
APA StyleRuiz-Lafuente, N., Minguela, A., Moraleda, J. M., Muro, M., & Parrado, A. (2021). Variable Distribution of DOCK-D Proteins between Cytosol and Nucleoplasm in Cell Lines, Effect of Interleukin-4 on DOCK10 in B-Cell Lymphoid Neoplasms, and Validation of a New DOCK10 Antiserum for Immunofluorescence Studies. Antibodies, 10(3), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib10030033







