Antibody Fragments and Their Purification by Protein L Affinity Chromatography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
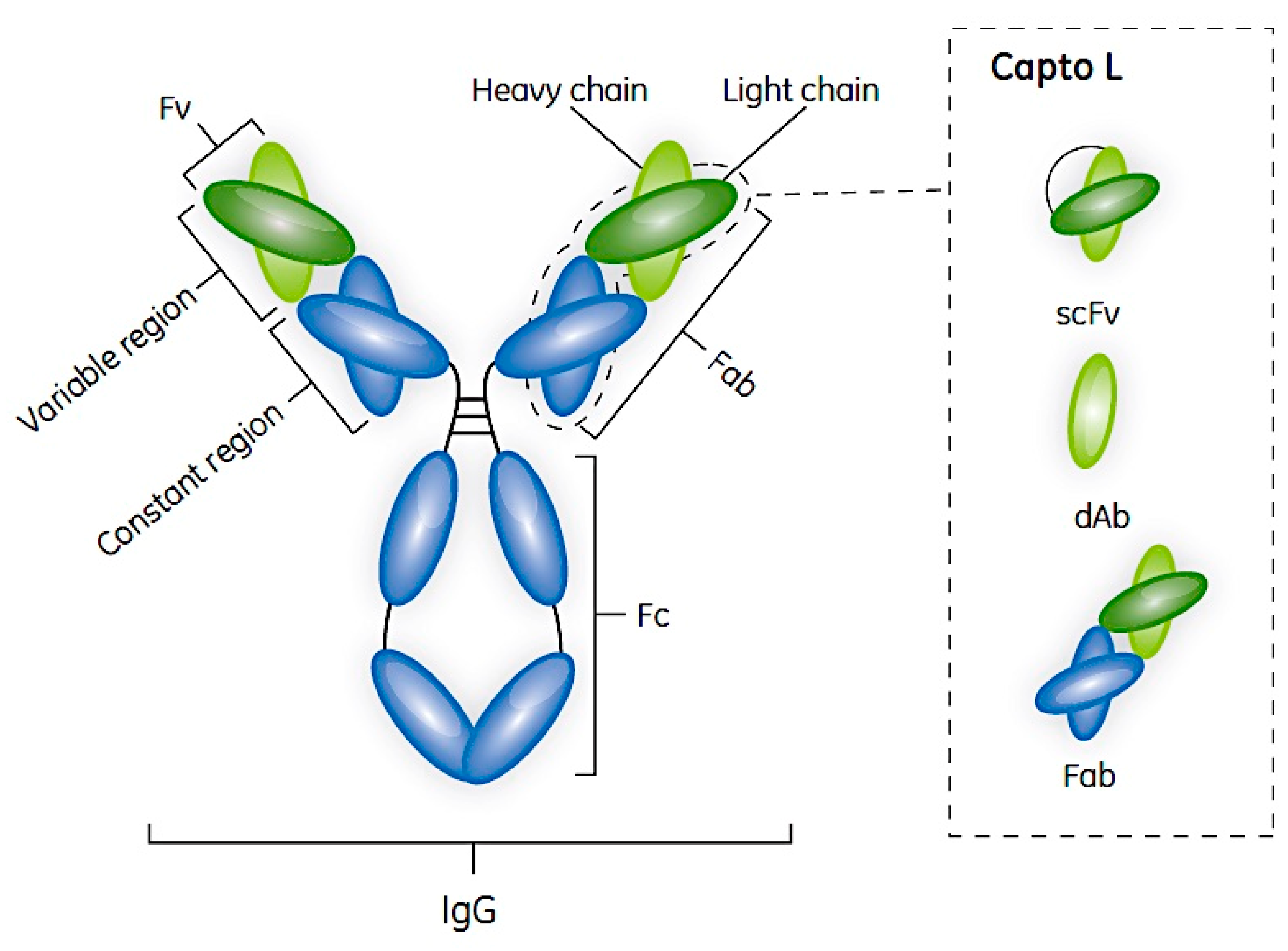

2. Antibodies and Their Fragments
3. mAbs and Their Fragments as Therapeutic Agents
4. Antibody Fragment Production and Purification
5. Protein L and Its Use in Antibody Fragment Bioprocessing
| Species and Antibody Class | Protein A * | Protein G * | Protein L |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. General Kappa LC 1, 3, 4 Lambda LC Heavy chain ** Fab, ScFv, Dab | None None Strong Weak *** | None None Strong Strong | Strong None None Strong |
| 2. Human IgG1, IgG2 IgG3 IgG4 IgA, IgM IgE IgD | Strong Weak Strong Weak Weak None | Strong Strong Strong None None None | Strong Strong Strong Strong Strong Strong |
| 3. Mouse IgG1 IgG2a, IgG22b IgG3, IgM | Weak Strong Strong | Weak Strong Strong | Strong Strong Strong |
| 4. Rat IgG1 IgG2a, IgG22b IgG2c | Weak None Strong | Weak Strong Weak | Strong Strong Strong |
| 5. Pig total IgG | Strong | Weak | Strong |
| 6. Dog total IgG | Strong | Weak | Weak |
| 7. Chicken IgG | None | ||
| 8. Cow IgG1 IgG2 | Weak Strong | Strong Strong | None None |
| 9. Goat IgG1 IgG2 | Weak Strong | Strong trong | None None |
| 10. Sheep IgG1 IgG2 | Weak Strong | Strong Strong | None None |
6. Alternatives to Protein L: Peptide Tags and Mimetics
| Criteria | rTag | Protein L |
|---|---|---|
| Effective | Yes | Yes |
| Alters Ab Fragment | Possibly | No |
| Requires Tag Cleavage | Maybe | No |
| Bioprocess Resins Available | Yes | Yes |
| Typical Dynamic Capacity (g/L) + | NK | 25 g Fab |
| Working pH stability | 3–12 | 2–10 |
| Effective cleaning in place | Yes ++ | Yes +++ |
| Available Ligand or Tag Assays | Perhaps | Yes |
| Regulatory Support | Yes | Yes |
7. Protein L Bioprocess Resins
| Criteria | MabSelect | Capto L |
|---|---|---|
| Rigid 85 µm Matrix | Yes | Yes |
| ≤500 cm/h in 20 cm high bed | Yes | Yes |
| rProtein Ligand (non-animal) | Yes | Yes |
| Typical Dynamic Capacity (g/L) + | 30 g IgG | 25 g Fab |
| Working pH | 3–10 | 2–10 |
| Standard cleaning in place ++ | Yes | Yes |
| Leached Ligand Assays | Yes ** | Yes *** |
| Regulatory Support | Yes | Yes |
8. Examples of Protein L-based Purifications
9. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ab | antibody |
| Ab-fragment | antigen-binding antibody fragment |
| mAb | monoclonal antibody |
| CHO | Chinese hamster ovary |
| CIP | cleaning-in-place |
| ELISA | enzyme linked immunosorbent assay |
| Fc | crystallizable Ab fragment which may bind to protein A |
| GMP | Good Manufacturing Process |
| GST-C | glutathione transferase (affinity tag) based chromatography |
| HCP | host cell protein |
| His | histidine |
| Ig | immunoglobulin |
| IMAC | immobilized metal affinity chromatography |
| LC | light chain |
| PEGylation | covalent modification with poly(ethylene glycol) polymers |
| Protein A | Fc-binding protein of bacterial surface origin |
| Protein G | Ab binding protein of bacterial surface origin |
| Protein L | Ab light chain-binding protein of bacterial surface origin |
| rTag | recombinant affinity tag such as 6His based tags for IMAC |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
References
- Lain, B. Protein A: The life of a disruptive technology. BioProcess Intl. 2013, 11, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Malpiedi, L.P.; Diaz, C.A.; Nerli, B.B.; Pessoa, A., Jr. Single-chain antibody fragments: Purification methodologies. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrington-Symes, A.P.; Farys, M.; Khalili, H.; Brocchini, S. Antibody fragments: Prolonging circulation half-life. Adv. Biosci. Biotech. 2013, 4, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, G. Biopharmaceutical benchmarks 2014. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therapeutic Antibody Data Base. Available online: tabs.craic.com (accessed on 25 May 2015).
- Socinski, M.A.; Curigliano, G.; Jacobs, I.; Gumbiner, B.; MacDonald, J.; Thomas, D. Clinical considerations for the development of biosimilars in oncology. mAbs 2015, 7, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elvin, J.G.; Couston, R.G.; van der Walle, C.F. Therapeutic antibodies: Market considerations, disease targets and bioprocessing. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 440, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.L. Antibody fragments: Hope and hype. mAbs 2010, 2, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.M.; Li, Y.H.; Jaiteh, L.E.; Han, C.L. Pexelizumab fails to inhibit assembly of the terminal complement complex in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Insight from a substudy of the Assessment of Pexelizumab in Acute Myocardial Infarction (APEX-AMI) trial. Am. Heart J. 2012, 164, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Spitali, M.; Symmons, J.; Whitcombe, R.; Pearce-Higgens, M.R. Protein Purification. Patent WO21201368A2, 2 February 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Holliger, P.; Hudson, P.J. Engineered antibody fragments and the rise of single domains. Nat. Biotech. 2005, 23, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuchowski, A.; McCoy, J.R.; Palczuk, N.C.; van Es, T.; Davis, F.F. Effect of covalent attachment of polyethylene glycol on immunogenicity and circulating life of bovine liver catalase. J. Biol. Chem. 1977, 252, 3582–3586. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karr, L.J.; Shafer, S.G.; Harris, J.M.; Van Alstine, J.M.; Snyder, R.S. Immuno-affinity partition of cells in aqueous polymer two-phase systems. J. Chromatogr. A 1986, 354, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Jain, S.K. PEGylation: An approach for drug delivery. A review. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Sys. 2008, 25, 403–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, A.P. PEGylated antibodies and antibody fragments for improved therapy: A review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, B. Industrialization of mAb production technology. The bioprocessing industry at a crossroads. mAbs 2009, 1, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalalirad, R. Efficient chromatographic processes for elevated purification of antibody fragment (Fab D1.3) from crude Escherichia coli culture. Biotechnology 2013, 12, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koussoroplis, S.-J.; Heywood, S.; Uyttenhove, C.; Barilly, C.; Van Snick, J.; Vanbever, R. Production, purification and biological characterization of mono-PEGylated anti IL-17 antibody fragments. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 454, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eifler, N.; Medaglia, G.; Anderka, O.; Laurin, L.; Hermans, P. Development of a novel affinity chromatography resin for platform purification of lambda Fabs. Biotechnol. Prog. 2014, 30, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlan, C.; Shumway, J.; Wagner, M.; Waghmare, R. Downstream purification and formulation of Fab antibody fragments. BioPharm. Intl. 2014, 27, 42–44. [Google Scholar]
- Weisser, N.E.; Hall, J.C. Applications of single-chain variable fragment antibodies in therapeutics and diagnostics. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 502–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camber, A.J.; Ward, E.S.; Winter, G.; Parnell, G.D.; Wawrzynczak, E.J. Comparative stabilities in vitro and in vivo of a recombinant mouse antibody fvcys fragment and a bisFvCys conjugate. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz, L.; Cuesta, A.M.; Compte, M.; Alvarez-Vallina, L. Antibody engineering: Facing new challenges in cancer therapy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.L.; Reichert, J.M. Development trends for therapeutic antibody fragments. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Shively, L.; Raubitschek, A.; Sherman, M.; Williams, L.E.; Wong, J.Y.; Shively, J.E.; Wu, A.M. Minibody: A novel engineered anti-carcinoembryonic antigen antibody fragment (single-chain Fv-CH3) which exhibits rapid, high-level targeting of xenografts. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 3055–3061. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roque, A.C.; Lowe, C.R.; Taipa, M.A. Antibodies and genetically engineered related molecules: Production and purification. Biotechnol. Prog. 2004, 20, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monnier, P.P.; Vigouroux, R.J.; Tassew, N.G. In vivo applications of single chain Fv (variable domain) (scFv) fragments. Antibodies 2013, 2, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, R.R. The hydrolysis of rabbit Υ-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem. J. 1959, 73, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inbar, D.; Hochman, J.; Givol, D. Localization of antibody-combining sites within the variable portions of heavy and light chains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1972, 69, 2659–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, A.P.; Antoniw, P.; Spitali, M.; West, S.; Stephens, S.; King, D.J. Therapeutic antibody fragments with prolonged in vivo half-lives. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, V.; Dernedde, J.; Petrausch, U.; Panjideh, H.; Fuchs, H.; Menzel, C.; Dübel, S.; Keilholz, U.; Thiel, E.; Deckert, P.M. Design, construction and in vitro analysis of A33scFv:CDy, a recombinant fusion protein for antibody-directed enzyme prodrug therapy in colon cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2007, 31, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.Y.; Stavrou, S.; Mathias, A.; Goodwin, K.J.; Thomas, J.M.; Neville, D.M. A fold-back single chain diabody format enhances the bioactivity of an anti-monkey CD3 recombinant diphtheria toxin-based immunotoxin. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2007, 20, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, P. Improving the efficacy of antibody-based cancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2001, 1, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, N.; Odaka, K.; Uehara, T.; Imanaka-Yoshida, K.; Kato, Y.; Oyama, H.; Tadokoro, H.; Akizawa, H.; Tanada, S.; Hiroe, M.; et al. Toward in vivo imaging of heart disease using a radiolabeled single-chain Fv fragment targeting tenascin-C. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9123–9130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, T.; Furumoto, S.; Higuchi, K.; Yokoyama, J.; Zhang, M.R.; Yanai, K.; Iwata, R.; Kigawa, T. Rapid biochemical synthesis of 11C-labelled single chain variable fragment antibody for immuno-PET by cell-free protein synthesis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 6579–6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarschler, K.; Prapainop, K.; Mahon, E.; Rocks, L.; Bramini, M.; Kelly, P.M.; Stephan, H.; Dawson, K.A. Diagnostic nanoparticle targeting of the EGF receptor in complex biological conditions using single-domain antibodies. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 6046–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saerens, D.; Frederix, F.; Reekmans, G.; Conrath, K.; Jans, K.; Brys, L.; Huang, L.; Bosmans, E.; Maes, G.; Borghs, G.; et al. Engineering camel single-domain antibodies and immobilization chemistry for human prostate-specific antigen sensing. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 7547–7555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hariri, G.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, A.; Han, Z.; Brechbiel, M.; Tantawy, M.N.; Peterson, T.E.; Mernaugh, R.; Hallahan, D. Radiation-guided P-selectin antibody targeted to lung cancer. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 36, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Shen, Z.; Mernaugh, R. Recombinant antibodies and their use in biosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 3027–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enever, C.; Batuwangala, T.; Plummer, C.; Sepp, A. Next generation immunotherapeutics—honing the magic bullet. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2009, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaux, C.; Moreau, E.; Goyffon, M.; Rochat, H.; Billiad, P. Construction and functional evaluation of a single-chain antibody fragment that neutralizes toxin AahI from the venom of the scorpion Androctonus australis hector. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaksen, M.L.; FitzGerald, K. Purification and analysis of antibody fragments using proteins L, A and LA. In Antibody Engineering; Kontermann, R., Dübel, S., Eds.; Springer Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2001; Chapter 21; pp. 282–291. [Google Scholar]
- McCafferty, J.; Griffiths, A.D.; Winter, G.; Chiswell, D.J. Phage antibodies: Filamentous phage displaying antibody variable domains. Nature 1990, 348, 552–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, J.D.; Hoogenboom, H.R.; Bonnert, T.P.; McCafferty, J.; Griffiths, A.D.; Winter, G. By-passing immunization: Human antibodies from V-gene libraries displayed on phage. J. Mol. Biol. 1991, 222, 581–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clackson, T.; Hoogenboom, H.R.; Griffiths, A.D.; Winter, G. Making antibody fragments using phage display libraries. Nature 1991, 352, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucca, M.B.; Bertolini, T.B.; Barbosa, J.E.; Galina, S.V.; Porto, G.S. Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies: scFv patents as a marker of a new class of potential biopharmaceuticals. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 47, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Fitting, J.; Blume, T.; Ten Haaf, A.; Blau, W.; Gottenlöhner, S.; Tur, M.K.; Barth, S. Phage display-based generation of novel internalizing antibody fragments for immunotoxin-based treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. mAbs 2015, 7, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ward, E.S.; Güssow, D.; Griffiths, A.D.; Jones, P.J.; Winter, G. Binding activities of a repertoire of single immunoglobulin variable domains secreted from Escherichia coli. Nature 1989, 341, 544–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, B.; Benedict, C.R.; Le, A.; Shapiro, S.S.; Thiagarajan, P. Cardiolipin binding a light chain from Lupus-prone mice. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmsen, M.M.; De Haard, H.J. Properties, production, and applications of camelid single-domain antibody fragments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 77, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, L.J.; Herring, C.; Jespers, L.S.; Woolven, B.P.; Tomlinson, I.M. Domain antibodies: Proteins for therapy. Trends Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossins, A.J.; Harrison, S.; Popplewell, A.G.; Gore, M.G. Recombinant production of a VL single domain antibody in Escherichia coli and analysis of its interaction with peptostreptococcal protein L. Protein Expr. Purif. 2007, 51, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumoulin, M.; Conrath, K.; Van Meirhaeghe, A.; Meersman, F.; Heremans, K.; Frenken, L.G.J.; Muyldermans, S.; Wyns, L.; Matagne, A. Single-domain antibody fragments with high conformational stability. Protein Sci. 2002, 11, 500–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendershot, K.; Bole, D.; Köhler, G.; Kearney, J.F. Assembly and secretion of heavy chains that do not associate post-translationally with immunoglobulin heavy-chain binding protein. J. Cell Biol. 1987, 104, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prelli, F.; Frangione, B. Franklin’s disease: Ig gamma2H chain mutant BUR. J. Immunol. 1992, 248, 949–952. [Google Scholar]
- Hilschmann, N.; Craig, L.C. Amino acid sequence studies with Bence-Jones proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1965, 531, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungar-Waron, H.; Elias, E.; Gluckman, A.; Trainin, Z. Dromedary IgG purification, characterization and quantitation in sera of dams and newborns. Israel J. Vet. Med. 1987, 43, 198–203. [Google Scholar]
- Arbabi Ghahroudi, M.; Desmyter, A.; Wyns, L.; Hamers, R.; Muyldermans, S. Selection and identification of single domain antibody fragments from camel heavy-chain antibodies. FEBS Lett. 1997, 414, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, K.H.; Greenberg, A.S.; Greene, L.; Strelets, L.; Avila, D.; McKinney, E.C.; Flajnik, M.F. Structural analysis of the nurse shark (new) antigen receptor (NAR), molecular convergence of NAR and unusual mammalian immunoglobulins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11804–11809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuttall, S.D.; Krishnan, U.V.; Hattarki, M.; De Gori, R.; Irving, R.A.; Hudson, P.J. Isolation of the new antigen receptor from wobbegong sharks, and use as a scaffold for the display of protein loop libraries. Mol. Immunol. 2001, 38, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, D.S. Therapeutic proteins. In Therapeutic Proteins, Methods in Molecular Biology; Voynov, V., Caravella, J.A., Eds.; Humana Press Clifton: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, R.K. Physiological barriers to delivery of monoclonal antibodies and other macromolecules in tumors. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 814S–819S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reichert, J.M. Monoclonal antibodies as innovative therapeutics. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2008, 9, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revets, H.; De Baetselier, P.; Myldermans, S. Nanobodies as novel agents for cancer therapy. Exp. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2005, 5, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Marco, A. Biotechnological applications of recombinant single-domain antibody fragments. Microb. Cell Fact. 2011, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahbarizadeh, F.; Ahmadvand, D.; Sharifzadeh, Z. Nanobody: An old concept and new vehicle for immunotargeting. Immunol. Invest. 2011, 4, 299–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Williams, R.L.; Rabbitts, T.H. Tumour prevention by a single antibody domain targeting the interaction of signal transduction proteins with RAS. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 3250–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibanez, L.I.; De Filette, M.; Hultberg, A.; Verrips, T.; Temperton, N.; Weiss, R.A.; Vandevelde, W.; Schepens, B.; Vanlandschoot, P.; Saelens, X. Nanobodies with in vitro neutralizing activity protect mice against H5N1 influenza virus infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, N.; Hultberg, A.; Zhao, Y.; Svensson, L.; Pan-Hammarstrom, Q.; Johansen, K.; Pouwels, P.H.; Ruggeri, F.M.; Hermans, P.; Frenken, L.; et al. Lactobacilli expressing variable domain of llama heavy-chain antibody fragments (lactobodies) confer protection against rotavirus-induced diarrhea. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, S.; Toussaint, W.; Panayotou, G.; de Wit, T.; Visser, P.; Grosveld, F.; Drabek, D. Intracellularly expressed single-domain antibody against p15 matrix protein prevents the production of porcine retroviruses. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 12132–12139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussack, G.; Arbabi-Ghahroudi, M.; van Faassen, H.; Songer, J.G.; Ng, K.K.; MacKenzie, R.; Tanha, J. Neutralization of Clostridium difficile toxin A with single-domain antibodies targeting the cell receptor binding domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 8961–8976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Feng, M.; Gao, W.; Phung, Y.; Chen, W.; Chaudhary, A.; St Croix, B.; Qian, M.; Dimitrov, D.S.; Ho, M. A human single-domain antibody elicits potent antitumor activity by targeting an epitope in mesothelin close to the cancer cell surface. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willems, A.; Leoen, J.; Schoonooghe, S.; Grooten, J.; Mertens, N. Optimizing expression and purification from cell culture medium of trispecific recombinant antibody derivatives. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 786, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.J.; Turner, A.; Farnsworth, A.P.; Adair, J.R.; Owens, R.J.; Pedley, R.B.; Baldock, D.; Proudfoot, K.A.; Lawson, A.D.; Beeley, N.R. Improved tumor targeting with chemically cross-linked recombinant antibody fragments. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 6176–6185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.C.; Reilly, D.E. Production technologies for monoclonal antibodies and their fragments. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2004, 15, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.C.; Carter, P.J. Therapeutic antibodies for autoimmunity and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, T.; Milenic, D.E.; Whitlow, M.; Schlom, J. Rapid tumor penetration of a single-chain Fv and comparison with other immunoglobulin forms. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 3402–3408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johdi, N.A.; Harman, R.; Sanjuan, I.; Kousparou, C.; Courtenay-Luck, N.; Deonarain, M.P. Production and binding analyses of a humanised scFv against a cryptic epitope on tumour-associated fibronectin. Protein Expr. Purif. 2013, 88, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, J.; Devoogdt, N.; Lahoutte, T.; Muyldermans, S. Camelid single-domain antibody-fragment engineering for (pre)clinical in vivo molecular imaging applications: Adjusting the bullet to its target. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2013, 13, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubrey, N.; Devaux, C.; Sizaret, P.Y.; Rochat, H.; Goyffon, M.; Billiad, P. Design and evaluation of a diabody to improve protection against a potent scorpion neurotoxin. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2003, 60, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorovska, A.; Roovers, R.C.; Dolezal, O.; Kortt, A.A.; Hoogenboom, H.R.; Hudson, P.J. Design and application of diabodies, triabodies and tetrabodies for cancer targeting. J. Immunol. Methods 2001, 248, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fee, C.J.; Van Alstine, J.M. PEG-proteins: Reaction engineering and separation issues. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 924–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, R.E.; Hardman, K.D.; Jacobson, J.W.; Johnson, S.; Kaufman, B.M.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, T.; Pope, S.H.; Riordan, G.S.; Whitlow, M. Single-chain antigen-binding proteins. Science 1988, 242, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewert, S.; Huber, T.; Honegger, A.; Plückthun, A. Biophysical properties of human antibody variable domains. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 325, 531–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenzel, A.; Hust, M.; Schirrmann, T. Expression of recombinant antibodies. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarschler, K.; Witecy, S.; Kapplusch, F.; Foerster, C.; Stephan, H. High yield production of functional soluble single-domain antibodies in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Cell Fact. 2013, 12, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljunglöf, A.; Lacki, K.M.; Mueller, J.; Harinarayan, C.; van Reis, R.; Fahrner, R.; Van Alstine, J.M. Ion exchange chromatography of antibody fragments. Biotech. Bioeng. 2009, 96, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Three step purification process for dAb expressed in periplasm of E. coli. GE Application Note 29-0655-41AA. Available online: www.gelifesciences.com (accessed on 14 August 2015).
- Das, D.; Allen, T.M.; Suresh, M.R. Comparative evaluation of two purification methods of anti-CD19-c-myc-His6-Cys ScFv. Protein Expr. Purif. 2005, 39, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitali, M. Downstream processing of antibody fragments. In Process Scale Purification of Antibodies; Gottschalk, U., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 349–372. [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson, Å.; Widehammar, J.; Rodrigo, G. Preparation and high resolution analysis of a Fab fragment. FASEB J. 2013, 27, Ib157. [Google Scholar]
- Franzreb, M.; Müller, E.; Vajda, J. Cost estimation for protein A chromatography: An in silico approach to Mab purification strategy. BioProcess Intl. 2014, 12, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren, A.; Sjöquist, J. “Protein A” from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma globulin. J. Immunol. 1966, 97, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Björck, L.; Protein, L. A novel bacterial cell wall protein with affinity for Ig L chains. J. Immunol. 1988, 140, 1194–1197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reis, K.J.; Ayoub, E.M.; Boyle, M.D. Streptococcal Fc receptors. I. Isolation and partial characterization of the receptor from a group C streptococcus. J. Immunol. 1984, 132, 3091–3097. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akerstrom, B.; Nilson, B.H.; Hoogenboom, H.R.; Björck, L. On the interaction between single chain Fv antibodies and bacterial immunoglobulin-binding proteins. J. Immunol. Methods 1994, 177, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protein G Sepharose Fast Flow 4 Instruction Document 71-7083-00 AI. Available online: www.gelifesciences.com (accessed on 14 August 2015).
- De Chateau, M.; Nilson, B.H.; Emtell, M.; Myhre, E.; Magnusson, C.G.; Åkerström, B.; Björck, L. On the interaction between protein L and immunoglobulins of various mammalian species. Scand. J. Immunol. 1993, 37, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hage, D.S.; Bian, M.; Burks, R.; Karle, E.; Ohnmacht, C.; Wa, C. Bioaffinity Chromatography. In Handbook of Affinity Chromatography, 2nd ed.; Hage, D.S., Cazes, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; p. 103. [Google Scholar]
- Enever, C.; Tomlinson, I.M.; Lund, J.; Levens, M.; Holliger, P. Engineering high affinity superantigens by phage display. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 347, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrick, J.P.; Wigley, D.B. The third IgG-binding domain from Streptococcal Protein G: An analysis by x-ray crystallography of the structure alone and in a complex with Fab. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 243, 906–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastern, W.; Holst, E.; Nielsen, E.; Sjobring, U.; Bjorck, L.; Protein, L. A bacterial immunoglobulin-binding protein and possible virulence determinant. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, J.P.; Duggleby, C.J.; Atkinson, M.A. The functional units of a peptostreptococcal protein L. Mol. Microbiol. 1994, 12, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastern, W.; Sjöbring, U.; Björck, L. Structure of peptostreptococcal protein L and identification of a repeated immunoglobulin light chain-binding domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 12820–12825. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kriangkum, J.; Xu, B.; Gervais, C.; Paquette, D.; Jacobs, F.A.; Martin, L.; Suresh, M.R. Development and characterization of a bi-specific single-chain antibody directed against T cells and ovarian carcinoma. Hybridoma 2000, 19, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouet, R.; Lowe, D.; Dudgeon, K.; Roome, B.; Schofield, P.; Langley, D.; Andrews, J.; Whitfeld, P.; Jermutus, L.; Christ, D. Expression of high-affinity human antibody fragments in bacteria. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.-G.; Jager, S.; Chau, D.; Mah, D.; Nagata, L.P. Generation of a recombinant full-length human antibody binding to botulinum neurotoxin A. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 1206–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouki, T.; Inui, T.; Okabe, H.; Ochi, Y.; Kajita, Y. Separation method of IgG fragments using protein L. Immunol. Invest. 1997, 26, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Housden, N.G.; Harrison, S.; Roberts, S.E.; Beckingham, J.A.; Graille, M.; Stura, E.; Gore, M.G. Immunoglobulin-binding domains: Protein L from Peptostreptococcus magnus. Sci. Trans. 2003, 31, 716–718. [Google Scholar]
- Nilson, B.H.K.; Solomon, A.; Björck, L.; Åkerstöm, B. Protein L from Peptostreptococcus magnus binds to the kappa light chain variable domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 2234–2239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nilson, B.H.; Lögberg, L.; Kastern, W.; Björck, L.; Åkerström, B. Purification of antibodies using protein L-binding framework structures in the light chain variable domain. J. Immunol. Methods 1993, 164, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Loyau, S.; Bouabdelli, M.; Aubrey, N.; Jandrot-Perrus, M.; Billiald, P. Design and reshaping of an scFv directed against human platelet glycoprotein VI with diagnostic potential. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 417, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boes, A.; Spiegel, H.; Delbrück, H.; Fisher, R.; Schillberg, S.; Sack, M. Affinity purification of a framework 1 engineered mouse/human chimeric IgA2 antibody from tobacco. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 2804–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzard, J.; Adi-Bessalem, S.; Juste, M.; Laraba-Djebari, F.; Aubrey, N.; Billiad, P. Grafting protein L-binding activity onto recombinant antibody fragments. Anal. Biochem. 2009, 388, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kihlberg, B.-M.; Sjöbring, U.; Kastern, W.; Björck, L. Protein LG: A hybrid molecule with unique immunoglobulin binding properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 2676, 25583–25588. [Google Scholar]
- Vola, R.; Lombardi, A.; Tarditi, L.; Björck, L.; Mariani, M. Recombinant proteins L and LG: Efficient tools for purification of murine immunoglobulin G fragments. J. Chromatogr. B 1995, 668, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, H.G.; Hoogenboom, H.R.; Sjöbring, U.; Protein, L.A. A novel hybrid protein with unique single-chain Fv antibody- and Fab-binding properties. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 258, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, H.G.; Hoogenboom, H.R.; Sjöbring, U. The ultimate Ig-binding protein. BIA J. 1999, 2, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lichty, L.L.; Malecki, J.L.; Agnew, H.D.; Michelson-Horowitz, D.J.; Tan, S. Comparison of affinity tags for protein purification. Protein Expr. Purif. 2005, 4, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, D.; Colcher, D.; Koo, J.S.; Booth, B.J.; Pavlinkova, G.; Batra, S.K. Relative position of the hexahistidine tag affects binding properties of a tumor-associated single-chain Fv construct. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1523, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeisser, H.; Kontsek, P.; Esposito, D.; Gillette, W.; Schreiber, G.; Zoon, K.C. Binding characteristics of IFN-alpha subvariants to IFNAR2-EC and influence of the 6-histidine tag. J. Interf. Cytok. Res. 2006, 26, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, C.R. Combinatorial approaches to affinity chromatography. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2001, 5, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roque, A.C.; Taipa, M.A.; Lowe, C.R. An artificial protein L for the purification of immunoglobulins and fab fragments by affinity chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1064, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roque, A.C.; Lowe, C.R. Rationally designed ligands for use in affinity chromatography: An artificial protein L. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 421, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hober, S.; Nord, K.; Linhult, M. Protein A chromatography for antibody purification. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 848, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabst, T.M.; Palmgren, R.; Forss, A.; Hunter, A.K. Engineering of novel Staphylococcal protein A ligands to enable milder elution pH and high dynamic binding capacity. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1362, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, H.; Matsumaru, H.; Ooishi, A.; Feng, Y.; Odahara, T.; Suto, K.; Honda, S. Optimizing pH response of affinity between protein G and IgG Fc. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 12373–12383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protein L–Agarose from Peptostreptococcus magnus. Available online: www.sigmaaldrich.com (accessed on 14 August 2015).
- Thermo Scientific™ Pierce™ Protein Biology. (http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink" xlink:href="https://www.thermofisher.com/se/en/home/brands/thermo-scientific/pierce-protein-biology.html). Available online: www.piercenet.com (accessed on 14 August 2015).
- Gagnon, P.S. Enhanced purification of antibodies and antibody fragments by apatite chromatography. US8093364 B2, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- A platform approach for the purification of antibody fragments (Fabs). Application Note 20-0320-66AA, GE Healthcare Life Sciences, 2013. Available online: www.gelifesciences.com (accessed on 14 August 2015).
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigo, G.; Gruvegård, M.; Van Alstine, J.M. Antibody Fragments and Their Purification by Protein L Affinity Chromatography. Antibodies 2015, 4, 259-277. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib4030259
Rodrigo G, Gruvegård M, Van Alstine JM. Antibody Fragments and Their Purification by Protein L Affinity Chromatography. Antibodies. 2015; 4(3):259-277. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib4030259
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigo, Gustav, Mats Gruvegård, and James M. Van Alstine. 2015. "Antibody Fragments and Their Purification by Protein L Affinity Chromatography" Antibodies 4, no. 3: 259-277. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib4030259
APA StyleRodrigo, G., Gruvegård, M., & Van Alstine, J. M. (2015). Antibody Fragments and Their Purification by Protein L Affinity Chromatography. Antibodies, 4(3), 259-277. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib4030259





