An Emergency Decision-Making Method for Probabilistic Linguistic Term Sets Extended by D Number Theory
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Linguistic Term Set
2.2. Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Term Set
2.3. Probabilistic Linguistic Term Set
2.4. Dempster–Shafer Evidence Theory
2.5. D Number Theory
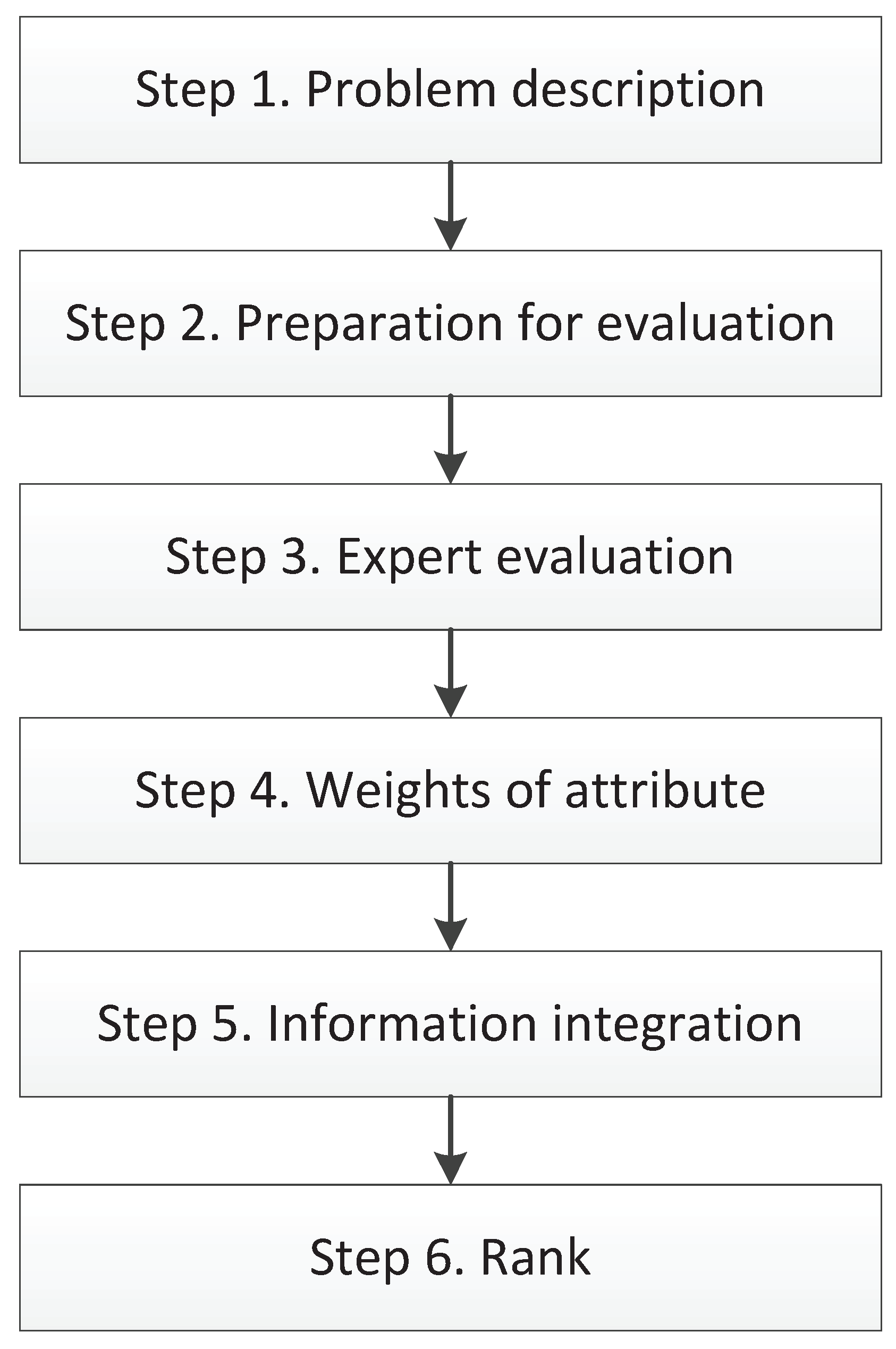
3. Proposed Method
4. Case Study and Discussion
4.1. Case Study
4.2. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kowalski-Trakofler, K.M.; Vaught, C.; Scharf, T. Judgment and decision-making under stress: An overview for emergency managers. Int. J. Emerg. Manag. 2003, 1, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Lai, K.K. A distance-based group decision-making methodology for multi-person multi-criteria emergency decision support. Decis. Support Syst. 2011, 51, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wei, C. An emergency decision-making method based on DS evidence theory for probabilistic linguistic term sets. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 37, 101178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, E.W.; Grot, R.A. Rapid Fire Emergency Response for Minimizing Human Casualties within a Facility. U.S. Patent 6,496,110, 17 December 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, J.K.; Hartmann, J.; Li, K.W.; An, Y.; Asgary, A. Multi-criteria decision support systems for flood hazard mitigation and emergency response in urban watersheds. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.F.; Dong, X.M.; Wang, S.Y. Emergency management of Yushu earthquake tests the Wenchuan experience. J. Evid.-Based Med. 2010, 10, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Liu, J.; Jiang, G. The mechanism of the emergency rescue response during coal mine gas explosion. J. China Coal Soc. 2006, 31, 697–700. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Wu, X.; Xu, Z.; Fujita, H. Emergency decision-making for natural disasters: An overview. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2018, 27, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, W.; Herrera, F. A group decision-making approach considering self-confidence behaviors and its application in environmental pollution emergency management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keshavarz Ghorabaee, M.; Amiri, M.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Antucheviciene, J. Supplier evaluation and selection in fuzzy environments: A review of MADM approaches. Econ. Res.-Ekon. Istraživanja 2017, 30, 1073–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Wu, X.; Mi, X.; Herrera, F. An integrated method for cognitive complex multiple experts multiple criteria decision-making based on ELECTRE III with weighted Borda rule. Omega 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Deng, Y. Multi-criteria decision-making in Pythagorean fuzzy environment. Appl. Intell. 2020, 50, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janis, I.L.; Mann, L. Emergency decision-making: A theoretical analysis of responses to disaster warnings. J. Hum. Stress 1977, 3, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.Y.; Cao, P.P. Extended TODIM method for multi-attribute risk decision-making problems in emergency response. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 135, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xuan, J.; Chen, H.; Mei, L. Crowdsourcing based social media data analysis of urban emergency events. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 11567–11584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, W.E.; Orr, M.F.; Wattigney, W.A. Surveillance of hazardous substance emergency events: Identifying areas for public health prevention. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2005, 208, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, D.; Prade, H. Operations on fuzzy numbers. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 1978, 9, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P. Modeling of variability and uncertainty in human health risk assessment. MethodsX 2017, 4, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Hazarika, G. Construction of families of probability boxes and corresponding membership functions at different fractiles. Expert Syst. 2017, 34, e12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F. A distance measure for intuitionistic fuzzy sets and its application to pattern classification problems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Cao, Y.; Deng, X. A novel Z-network model based on Bayesian network and Z-number. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Garg, H.; Deng, Y. A new uncertainty measure of discrete Z-numbers. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Xia, M. On distance and correlation measures of hesitant fuzzy information. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2011, 26, 410–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Lin, C.T. Inherent fuzzy entropy for the improvement of EEG complexity evaluation. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 26, 1032–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Z.; Lin, C.T.; Lai, K.L.; Ko, L.W.; King, J.T.; Liao, K.K.; Fuh, J.L.; Wang, S.J. Extraction of SSVEPs-based inherent fuzzy entropy using a wearable headband EEG in migraine patients. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera, F.; Herrera-Viedma, E. Linguistic decision analysis: Steps for solving decision problems under linguistic information. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2000, 115, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Deng, Y. The maximum Deng entropy. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 120758–120765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Deng, Y. The Pseudo-Pascal triangle of maximum Deng entropy. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control 2020, 15, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seiti, H.; Hafezalkotob, A. Developing the R-TOPSIS methodology for risk-based preventive maintenance planning: A case study in rolling mill company. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 128, 622–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loia, V.; Orciuoli, F. Understanding the composition and evolution of terrorist group networks: A rough set approach. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 101, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, S.; Pan, X.; Li, C. Shadowed sets-based linguistic term modeling and its application in multi-attribute decision-making. Symmetry 2018, 10, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, M.; Bashir, Z.; Rashid, T.; Ali, J. Probabilistic hesitant intuitionistic linguistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision-making. Symmetry 2018, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Gao, H.; Wei, G.; Wei, Y.; Wei, C. Evaluation based on distance from average solution method for multiple criteria group decision-making under picture 2-tuple linguistic environment. Mathematics 2019, 7, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera, F.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Verdegay, J.L. A sequential selection process in group decision-making with a linguistic assessment approach. Inf. Sci. 1995, 85, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.; Verdegay, J.L.; Vila, M. Linguistic decision-making models. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 1992, 7, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.M.; Martinez, L.; Herrera, F. Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision-making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2011, 20, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Liao, H.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z. Nature disaster risk evaluation with a group decision-making method based on incomplete hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, C.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Li, P. Note on entropies of hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and their applications. Inf. Sci. 2020, 512, 352–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, L.; Wei, C. The consistency measures and priority weights of hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 65, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Extended hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and their aggregation in group decision-making. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2015, 8, 14–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Q.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z. Probabilistic linguistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision making. Inf. Sci. 2016, 369, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Chen, Z.; Liao, H.; Xu, Z. ELECTRE II method to deal with probabilistic linguistic term sets and its application to edge computing. Nonlinear Dyn. 2019, 96, 2125–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, G. A large-scale group decision-making with incomplete multi-granular probabilistic linguistic term sets and its application in sustainable supplier selection. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2019, 70, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, H.; Liao, H. Consistency-based risk assessment with probabilistic linguistic preference relation. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 49, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Cloud decision support model for selecting hotels on TripAdvisor.com with probabilistic linguistic information. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2018, 68, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xu, Z.; Liang, Z.; Liao, H. Expected consistency-based emergency decision-making with incomplete probabilistic linguistic preference relations. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2019, 176, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Long, Y.; Liao, H.; Xu, Z. Inclusion measures of probabilistic linguistic term sets and their application in classifying cities in the Economic Zone of Chengdu Plain. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liao, H.; Xu, Z.; Hafezalkotob, A.; Herrera, F. Probabilistic linguistic MULTIMOORA: A multicriteria decision-making method based on the probabilistic linguistic expectation function and the improved Borda rule. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 26, 3688–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liao, H. A consensus-based probabilistic linguistic gained and lost dominance score method. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 272, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liao, H. Mixed fuzzy least absolute regression analysis with quantitative and probabilistic linguistic information. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, A.P. Upper and lower probabilities induced by a multivalued mapping. Ann. Math. Stat. 1967, 38, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafer, G. A Mathematical Theory of Evidence; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1976; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, R.; Tang, M.; Wang, H.; Li, H. A reliability analysis method of accelerated performance degradation based on Bayesian strategy. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 169047–169054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F. Multi-sensor data fusion based on the belief divergence measure of evidences and the belief entropy. Inf. Fusion 2019, 46, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F. A new divergence measure for belief functions in D-S evidence theory for multisensor data fusion. Inf. Sci. 2019, 514, 462–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Deng, Y. An association coefficient of belief function and its application in target recognition system. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2020, 35, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Huang, C.; Deng, X. A new probability transformation method based on a correlation coefficient of belief functions. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2019, 34, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Ding, L. Improved fuzzy Bayesian network-based risk analysis with interval-valued fuzzy sets and DS evidence theory. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F. EFMCDM: Evidential fuzzy multicriteria decision-making based on belief entropy. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Li, S.; Deng, Y. Determining weights in multi-criteria decision-making based on negation of probability distribution under uncertain environment. Mathematics 2020, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, D.; Li, Y.; Zhu, S.P.; Hu, Z.; Xie, T.; Fan, Z. Collaborative maritime design using sequential optimisation and reliability assessment. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Marit. Eng. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Zang, T.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, T.; Wei, X.; Li, C. A fault diagnosis method for power transmission networks based on spiking neural P systems with self-updating rules considering biological apoptosis mechanism. Complexity 2020, 2020, 2462647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Yuan, R.; Fu, J. A reliability modeling for multi-component systems considering random shocks and multistate degradation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 168805–168814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Liu, M.; Yang, S.; Zhang, H.; Ding, R. A fluid–structure analysis approach and its application in the uncertainty-based multidisciplinary design and optimization for blades. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Xiao, F. DCM: D number extended cognitive map: Application on location selection in SCM. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control 2019, 14, 753–771. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Deng, Y. Performer selection in human reliability analysis: D numbers approach. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control 2019, 14, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, F. A novel multi-criteria decision-making method for assessing health-care waste treatment technologies based on D numbers. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 71, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Li, C.; Xu, F.; Liu, D.; Liu, J. Risk identification and analysis for new energy power system in China based on D numbers and decision-making trial and evaluation laboratory (DEMATEL). J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Deng, Y. Risk evaluation in failure mode and effects analysis based on D numbers theory. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control 2019, 14, 672–691. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Jiang, W. Evaluating green supply chain management practices under fuzzy environment: A novel method based on D number theory. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 21, 1389–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, R.; Choudhary, D.; Jharkharia, S. An integrated risk assessment model: A case of sustainable freight transportation systems. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 63, 662–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wei, D. A modified D numbers methodology for environmental impact assessment. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2018, 24, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, X.; Wei, D. A modified D numbers’ integration for multiple attributes decision making. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 20, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F. A multiple-criteria decision-making method based on D numbers and belief entropy. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 21, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, X. A multicriteria decision-making approach with linguistic D numbers based on the choquet integral. Cogn. Comput. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, X. D-intuitionistic hesitant fuzzy sets and their application in multiple attribute decision-making. Cogn. Comput. 2018, 10, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yu, H. Emergency alternative selection based on an E-IFWA approach. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 44431–44440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Garg, H. Algorithms for interval-valued fuzzy soft sets in emergency decision making based on WDBA and CODAS with new information measure. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 119, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xu, Z.; Ren, P.; Liao, H. An emergency decision-making method based on the multiplicative consistency of probabilistic linguistic preference relations. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2019, 10, 1613–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Wang, A. Emergency alternative evaluation under group decision-makers: A method of incorporating DS/AHP with extended TOPSIS. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z. Deviation measures of linguistic preference relations in group decision-making. Omega 2005, 33, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennes, R.; Smets, P. Fast algorithms for Dempster–Shafer theory. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Processing and Management of Uncertainty in Knowledge-Based Systems, Paris, France, 2–6 July 1990; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; pp. 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Lin, Y.; Hong, L.; Zetao, L. Improved method to D-S evidence theory based on weight and matrix. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2012, 48, 150–153. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, L.A. A simple view of the Dempster–Shafer theory of evidence and its implication for the rule of combination. AI Mag. 1986, 7, 85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xing, X. Probabilistic linguistic VIKOR method to evaluate green supply chain initiatives. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Mutually Exclusive | Completeness Constraint | Independence Constraint | Computational Complexity | One-vote-veto | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D-S theory | Must be | Must be | Must be | O() | Exists |
| D number | Not necessary | Not necessary | Not necessary | O(mn) | Does not exist |
| Experts | Experts | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | VH | F | F | VH | L | ||||
| VH | - | H | VH | F | H | ||||
| H | H | VH | H | H | VH | ||||
| VH | VL | H | VH | VL | H | ||||
| F | VH | L | F | VH | L | ||||
| VH | F | VH | P | F | VH | ||||
| H | H | VH | H | H | VH | ||||
| VH | VL | H | VH | VL | H | ||||
| H | VH | L | H | VH | L | ||||
| P | F | VH | P | F | VH | ||||
| H | H | VH | H | VH | VH | ||||
| - | L | H | P | F | H | ||||
| H | VH | L | H | VH | L | ||||
| P | F | P | P | - | P | ||||
| H | VH | P | H | VH | P | ||||
| P | F | H | P | H | H | ||||
| H | VH | F | H | VH | L | ||||
| P | F | P | P | F | P | ||||
| H | VH | P | H | VH | P | ||||
| - | H | H | P | H | - |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mo, H. An Emergency Decision-Making Method for Probabilistic Linguistic Term Sets Extended by D Number Theory. Symmetry 2020, 12, 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12030380
Mo H. An Emergency Decision-Making Method for Probabilistic Linguistic Term Sets Extended by D Number Theory. Symmetry. 2020; 12(3):380. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12030380
Chicago/Turabian StyleMo, Hongming. 2020. "An Emergency Decision-Making Method for Probabilistic Linguistic Term Sets Extended by D Number Theory" Symmetry 12, no. 3: 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12030380
APA StyleMo, H. (2020). An Emergency Decision-Making Method for Probabilistic Linguistic Term Sets Extended by D Number Theory. Symmetry, 12(3), 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12030380





