Effect of Pressure, H2/CO Ratio and Reduction Conditions on Co–Mn/CNT Bimetallic Catalyst Performance in Fischer–Tropsch Reaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Carbon Nanotube Support Functionalization
2.2. Determination of PZC, Catalyst Uptake on CNT Support and Catalyst Synthesis
2.3. Catalyst Characterization and Equations
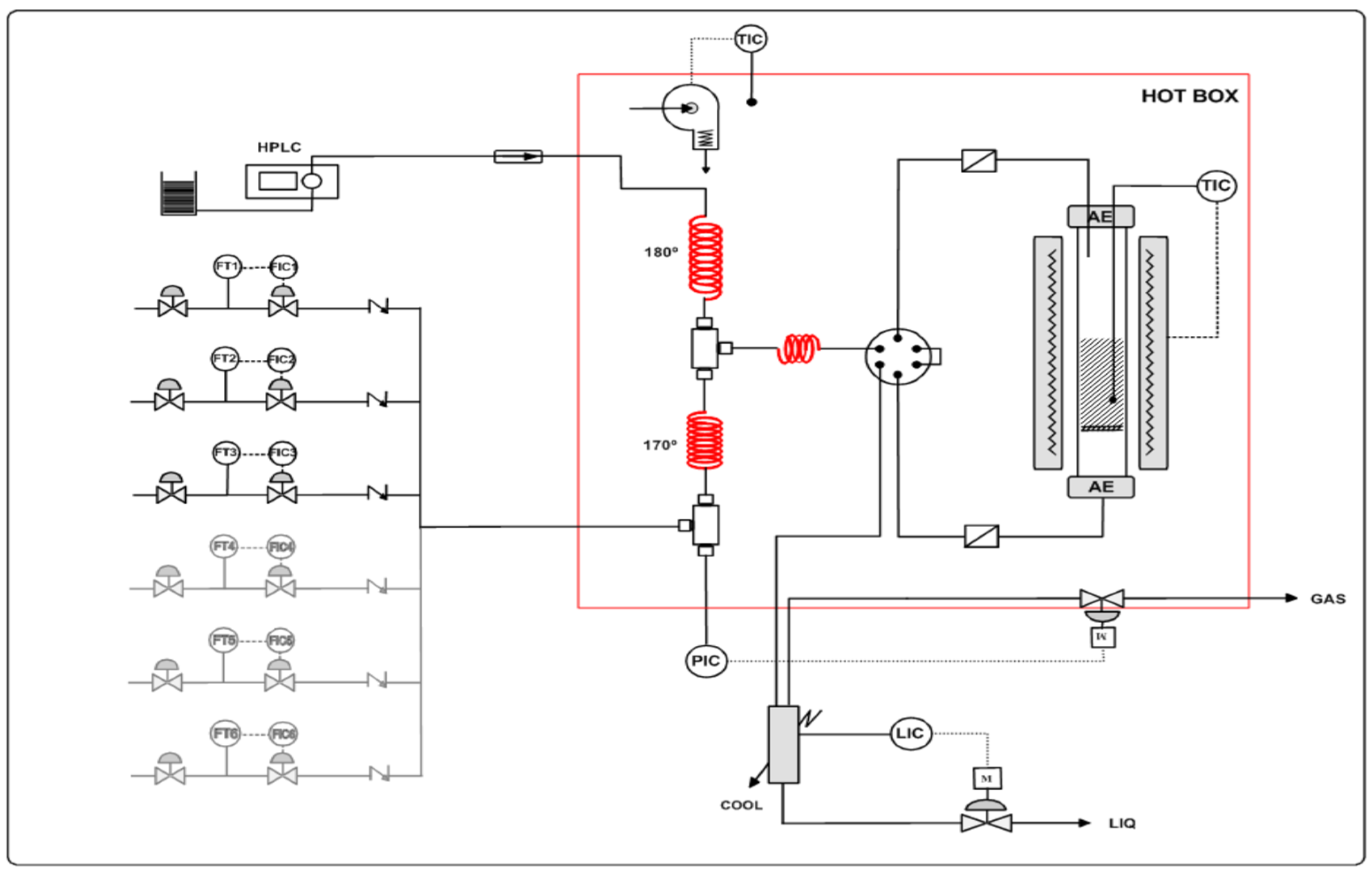
2.4. Microreactor Setup, Sampling, and Composition Analysis
3. Process Studies
3.1. Effect of Pressure on Catalytic Performance
3.2. Effects of H2/CO Feed Ratio on Catalytic Performance
3.3. Effect of Reduction Time Period and Temperature on Catalytic Performance
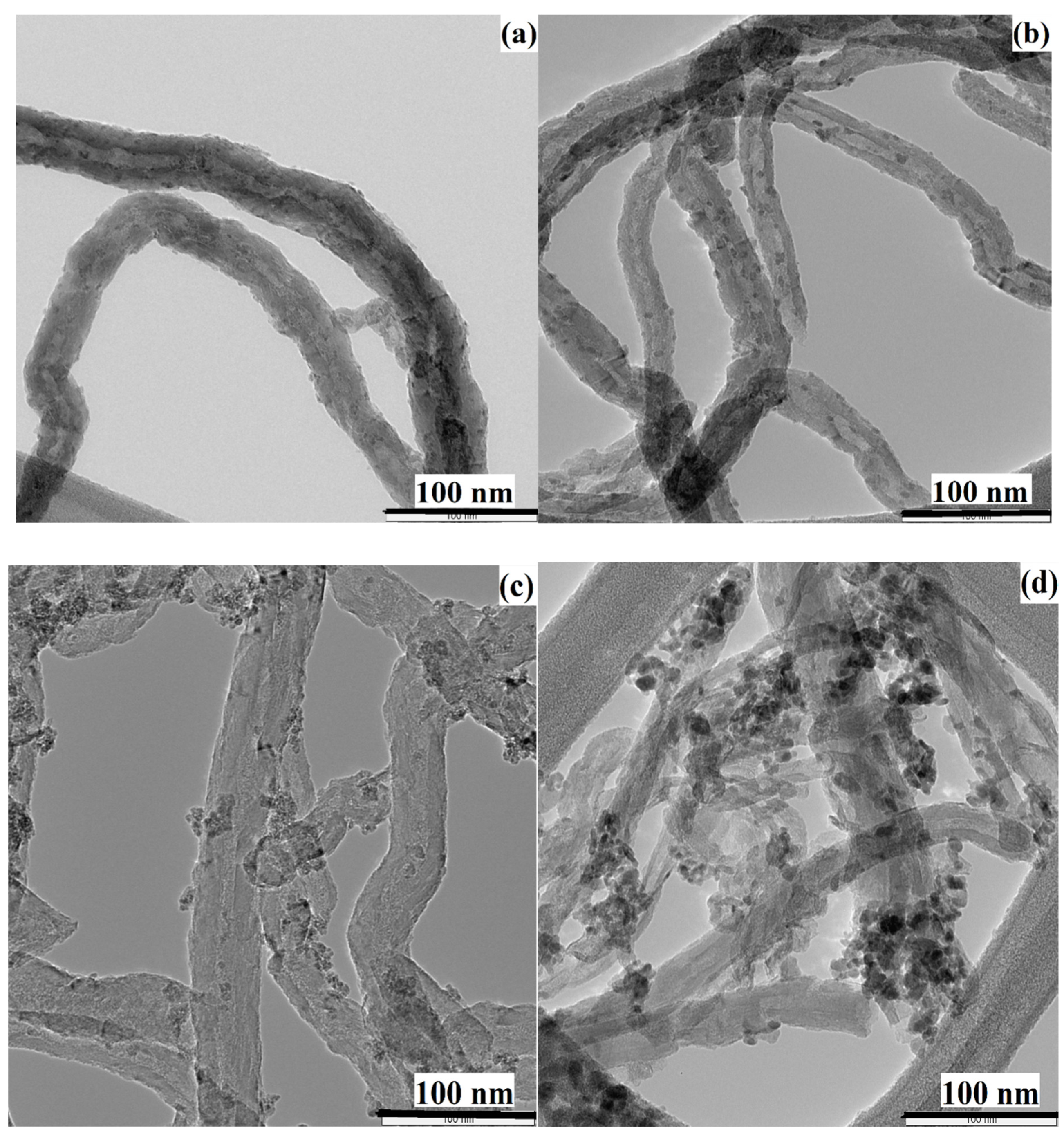
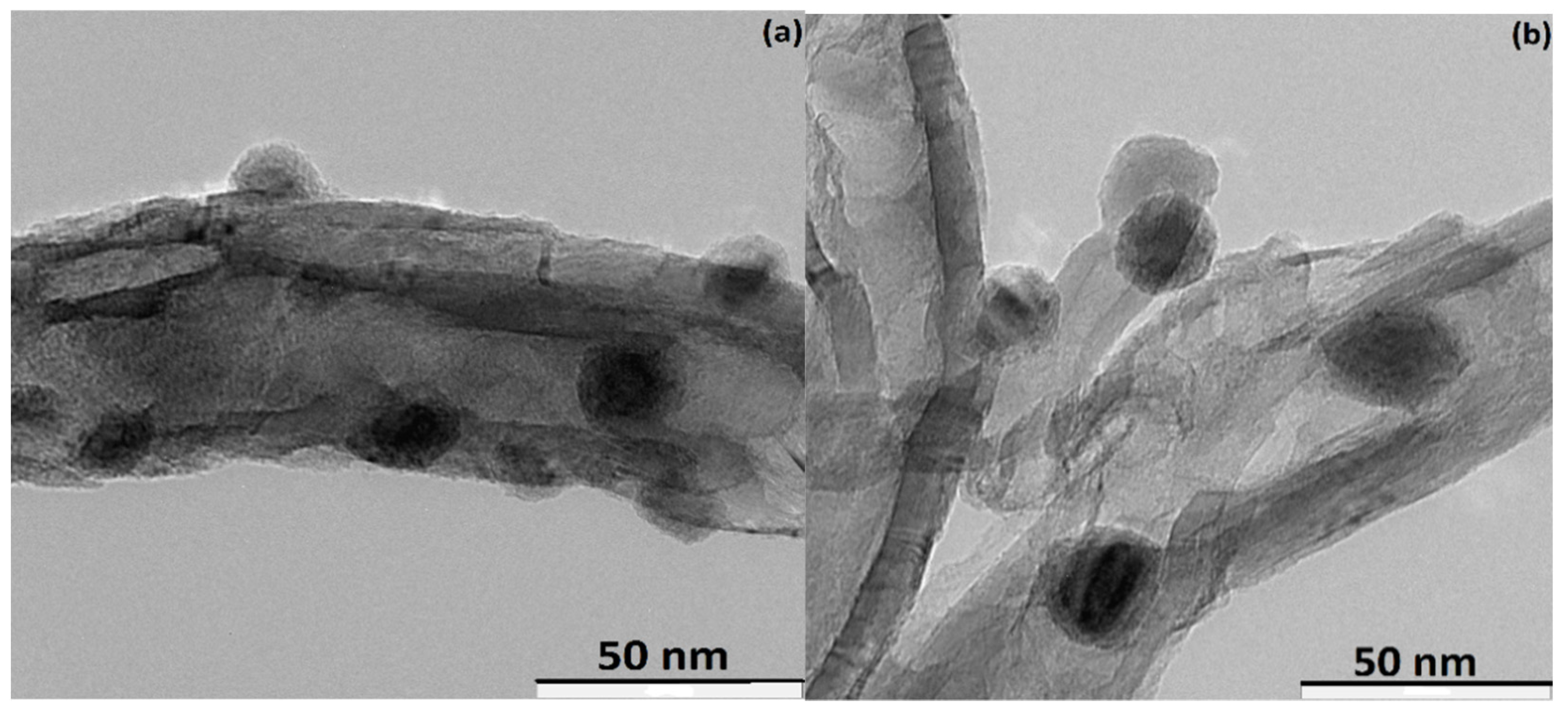
3.4. Characterization of Spent Catalyst
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shokouhimehr, M.; Asl, M.S.; Mazinani, B. Modulated large-pore mesoporous silica as an efficient base catalyst for the Henry reaction. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesia, E. Design, synthesis, and use of cobalt-based Fischer–Tropsch synthesis catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1997, 161, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.A.; Shirzadi, B.; Atashi, H.; Mansouri, M. Modeling and operating conditions optimization of Fischer–Tropsch synthesis in a fixed-bed reactor. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyzi, M.; Irandoust, M.; Mirzaei, A.A. Effects of promoters and calcination conditions on the catalytic performance of iron–manganese catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.A.; Babaei, A.B.; Galavy, M.; Youssefi, A. A silica supported Fe–Co bimetallic catalyst prepared by the sol/gel technique: Operating conditions, catalytic properties and characterization. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashi, H.; Siami, F.; Mirzaei, A.A.; Sarkari, M. Kinetic study of Fischer–Tropsch process on titania-supported cobalt–manganese catalyst. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2010, 16, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, L.C.P.F.; de Miguel, S.; Fierro, J.L.G.; do Carmo Rangel, M. Evaluation of Pd/La2O3 catalysts for dry reforming of methane. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Bellot Noronha, F., Schmal, M., Falabella Sousa-Aguiar, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 167, pp. 499–504. [Google Scholar]
- Gheitanchi, R.; Khodadadi, A.A.; Taghizadeh, M.; Mortazavi, Y. Effects of ceria addition and pre-calcination temperature on performance of cobalt catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2006, 88, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Teng, B.-T.; Guo, X.-H.; Li, Y.; Chang, J.; Tian, L.; Hao, X.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, H.-W.; Xu, Y.-Y.; et al. Effect of reaction conditions on the catalytic performance of Fe-Mn catalyst for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2007, 272, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, F.; de Smit, E.; de Groot, F.M.F.; Visser, T.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Effects of manganese oxide promoter on the CO and H2 adsorption properties of titania-supported cobalt Fischer–Tropsch catalysts. J. Catal. 2007, 246, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.-H.; Yang, Y.; Teng, B.-T.; Li, T.-Z.; Zheng, H.-Y.; Xiang, H.-W.; Li, Y.-W. Study of an iron-manganese Fischer–Tropsch synthesis catalyst promoted with copper. J. Catal. 2006, 237, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsalanfar, M.; Mirzaei, A.A.; Bozorgzadeh, H.R.; Atashi, H. Effect of process conditions on the surface reaction rates and catalytic performance of MgO supported Fe–Co–Mn catalyst for CO hydrogenation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 2092–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-M.; Bae, J.W.; Lee, Y.-J.; Jun, K.-W. Effect of CO2 in the feed stream on the deactivation of Co/γ-Al2O3 Fischer–Tropsch catalyst. Catal. Commun. 2008, 9, 2269–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, O.; Mohd Zabidi, N.; Abdul Wahab, Y.; Hamizi, N.; Chowdhury, Z.; Merican Aljunid Merican, Z.; Ab Rahman, M.; Akhter, S.; Rasouli, E.; Johan, M. Effect of Cobalt Catalyst Confinement in Carbon Nanotubes Support on Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis Performance. Symmetry 2018, 10, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akbarzadeh, O.; Mohd Zabidi, N.; Hamizi, N.; Abdul Wahab, Y.; Aljunid Merican, Z.; Yehya, W.; Akhter, S.; Shalauddin, M.; Rasouli, E.; Johan, M. Effect of pH, Acid and Thermal Treatment Conditions on Co/CNT Catalyst Performance in Fischer–Tropsch Reaction. Symmetry 2019, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akbarzadeh, O.; Mohd Zabidi, N.; Abdul Wahab, Y.; Hamizi, N.; Chowdhury, Z.; Aljunid Merican, Z.; Ab Rahman, M.; Akhter, S.; Shalauddin, M.; Johan, M. Effects of Cobalt Loading, Particle Size, and Calcination Condition on Co/CNT Catalyst Performance in Fischer–Tropsch Reactions. Symmetry 2018, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akbarzadeh, O.; Mohd Zabidi, N.A.; Aljunid Merican, Z.M.; Sagadevan, S.; Kordijazi, A.; Das, S.; Amani Babadi, A.; Ab Rahman, M.; Hamizi, N.A.; Abdul Wahab, Y.; et al. Effect of Manganese on Co–Mn/CNT Bimetallic Catalyst Performance in Fischer–Tropsch Reaction. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akbarzadeh, O.; Zabidi, N.A.M.; Abdullah, B.; Subbarao, D. Synthesis and Characterization of Co/CNTs Catalysts Prepared by Strong Electrostatic Adsorption (SEA) Method. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 625, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, O.; Zabidi, N.A.M.; Abdullah, B.; Subbarao, D. Dispersion of Co/CNTs via strong electrostatic adsorption method: Thermal treatment effect. AIP Conf. Proc. 2015, 1669, 020052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, O.; Mohd Zabidi, N.A.; Abdullah, B.; Subbarao, D. Synthesis of Co/CNTs Catalyst via Strong Electrostatic Adsorption: Effect of Calcination Condition. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1109, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, O.; Mohd Zabidi, N.A.; Abdullah, B.; Subbarao, D. Synthesis of Co/CNTs via Strong Electrostatic Adsorption: Effect of Metal Loading. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1043, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, O.; Mohd Zabidi, N.A.; Abdullah, B.; Subbarao, D. Influence of Acid and Thermal Treatments on Properties of Carbon Nanotubes. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 832, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbashir, N.O.; Roberts, C.B. Enhanced incorporation of α-olefins in the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis chain-growth process over an alumina-supported cobalt catalyst in near-critical and supercritical hexane media. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitlis, P.M.; Zanotti, V. The role of electrophilic species in the Fischer–Tropsch reaction. Chem. Commun. 2009, 1619–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dry, M. Chemical concepts used for engineering purposes. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2004, 152, 196–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hexana, W.M. A Systematic Study of the Effect of Chemical Promoters on the Precipitated Fe-Based Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis Catalyst. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Science, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Regalbuto, J.R. A simple, accurate determination of oxide PZC and the strong buffering effect of oxide surfaces at incipient wetness. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1995, 175, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, D.; Nóbrega, J.A. Interferences in Thermospray Flame Furnace AAS: Co and Mn Behavior. Spectrosc. Lett. 2008, 41, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tony, K.A.; Kartikeyan, S.; Vijayalakshmy, B.; Prasada Rao, T.; Padmanabha Iyer, C.S. Flow injection on-line preconcentration and flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination of iron, cobalt, nickel, manganese and zinc in sea-water. Analyst 1999, 124, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, Z.; Tavasoli, A.; Tabyar, S.; Pour, A.N. Enhancement of bimetallic Fe-Mn/CNTs nano catalyst activity and product selectivity using microemulsion technique. J. Energy Chem. 2014, 23, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, G.; Das, T.K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Racoillet, G.; Davis, B.H. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: Support, loading, and promoter effects on the reducibility of cobalt catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2002, 233, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, G.; Patterson, P.M.; Das, T.K.; Luo, M.; Davis, B.H. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: Effect of water on Co/Al2O3 catalysts and XAFS characterization of reoxidation phenomena. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 270, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavasoli, A.; Mortazavi, Y.; Khodadadi, A.A.; Mousavian, M.A.; Sadagiani, K.; Karimi, A. Effects of different loadings of Ru and Re on physico-chemical properties and performance of 15% Co/Al2O3 FTS catalysts. Iran. J. Chem. 2005, 24, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Mukenz, T.M. Graphical Methods for the Representation of the Fischer–Tropsch Reaction: Towards Understanding the Mixed Iron-Cobalt Catalyst Systems; University of the Witwatersrand: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Jacobs, G.; Das, T.; Zhang, Y.; Davis, B. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: Effect of water on the catalytic properties of a Co/SiO2 catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2002, 236, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Pena O’Shea, V.; Alvarez-Galvan, M.; Campos-Martin, J.; Fierro, J. Strong dependence on pressure of the performance of a Co/SiO2 catalyst in Fischer–Tropsch slurry reactor synthesis. Catal. Lett. 2005, 100, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Berge, P.; Everson, R. Natural gas conversion IV. Stud. Surf. Sci. Cat 1997, 107, 207. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, F.A. Polymerization Kinetics of Fischer-Tropsch Reaction on Iron Based Catalysts and Product Grade Optimization. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2005, 28, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tristantini, D.; Lögdberg, S.; Gevert, B.; Borg, Ø.; Holmen, A. The effect of synthesis gas composition on the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis over Co/γ-Al2O3 and Co–Re/γ-Al2O3 catalysts. Fuel Process. Technol. 2007, 88, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, H.; Nie, Z.; Ousmanov, F. Construction of the Fischer–Tropsch regime with cobalt catalysts. Catal. Today 2002, 71, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, I.C.; Satterfield, C.N. Intrinsic kinetics of the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis on a cobalt catalyst. Energy Fuels 1991, 5, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetty, R.; Xia, W.; Kundu, S.; Bron, M.; Reinecke, T.; Schuhmann, W.; Muhler, M. Effect of reduction temperature on the preparation and characterization of Pt−Ru nanoparticles on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Langmuir 2009, 25, 3853–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahome, M.C.; Jewell, L.L.; Hildebrandt, D.; Glasser, D.; Coville, N.J. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis over iron catalysts supported on carbon nanotubes. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2005, 287, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, U.; Dozier, A.; Khatri, R.; Bahome, M.; Jewell, L.; Mhlanga, S.; Coville, N.; Davis, B. Carbon nanotube docking stations: A new concept in catalysis. Catal. Lett. 2009, 129, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CO Conversion | 1 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co/CNT | 32.2 | 50.4 | 53.7 | 55.6 | 58.7 | 61.5 |
| 95Co5Mn/CNT | 49.4 | 78.5 | 81.7 | 84.4 | 86.6 | 89.5 |
| 90Co10Mn/CNT | 44.6 | 75.8 | 77.0 | 78.1 | 79.8 | 83.9 |
| 85Co15Mn/CNT | 42.2 | 68.6 | 70.1 | 72.2 | 73.2 | 77.7 |
| 80Co20Mn/CNT | 38.9 | 58.1 | 62.6 | 64.9 | 66.3 | 68.2 |
| C1 Selectivity | ||||||
| Co/CNT | 16.6 | 15.2 | 14.5 | 13.8 | 9.5 | 12.7 |
| 95Co5Mn/CNT | 15.5 | 13.2 | 12.4 | 11.9 | 11.8 | 6.1 |
| 90Co10Mn/CNT | 14.1 | 13.7 | 12.2 | 11.4 | 8.3 | 11.3 |
| 85Co15Mn/CNT | 14.7 | 14.1 | 13.1 | 12.3 | 9.1 | 11.4 |
| 80Co20Mn/CNT | 15.1 | 14.6 | 13.8 | 13.2 | 10.0 | 12.1 |
| C2–C4 selectivity | ||||||
| Co/CNT | 42.1 | 33.6 | 30.6 | 25.6 | 13.4 | 21.8 |
| 95Co5Mn/CNT | 26.2 | 16.3 | 11.3 | 8.6 | 6.7 | 6.5 |
| 90Co10Mn/CNT | 32.7 | 25.8 | 20.5 | 15.4 | 8.4 | 9.3 |
| 85Co15Mn/CNT | 37.5 | 30.7 | 26.7 | 21.3 | 9.4 | 13.6 |
| 80Co20Mn/CNT | 41.5 | 35.2 | 31.4 | 25.5 | 10.5 | 18.1 |
| C5+ selectivity | ||||||
| Co/CNT | 27.3 | 36.2 | 39.5 | 45.4 | 59.1 | 50.5 |
| 95Co5Mn/CNT | 55.3 | 66.7 | 72.3 | 76.1 | 81.5 | 76.3 |
| 90Co10Mn/CNT | 48.2 | 56.2 | 62.3 | 68.2 | 78.0 | 74.6 |
| 85Co15Mn/CNT | 43.3 | 50.2 | 55.2 | 61.4 | 76.5 | 70.7 |
| 80Co20Mn/CNT | 38.4 | 45.2 | 49.8 | 56.5 | 74.5 | 64.8 |
| CO Conversion | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co/CNT | 25.6 | 46.7 | 53.3 | 58.7 | 55.8 |
| 95Co5Mn/CNT | 41.7 | 62.6 | 69.7 | 86.6 | 74.7 |
| 90Co10Mn/CNT | 36.6 | 57.3 | 65.6 | 79.8 | 70.5 |
| 85Co15Mn/CNT | 33.8 | 52.8 | 59.8 | 73.2 | 65.3 |
| 80Co20Mn/CNT | 28.3 | 49.7 | 56.9 | 66.3 | 61.7 |
| C1 selectivity | |||||
| Co/CNT | 16.5 | 16.0 | 15.5 | 9.5 | 14.3 |
| 95Co5Mn/CNT | 13.5 | 13.1 | 12.5 | 11.8 | 11.3 |
| 90Co10Mn/CNT | 14.5 | 14.0 | 13.5 | 13.3 | 12.2 |
| 85Co15Mn/CNT | 15.5 | 15.0 | 14.5 | 14.1 | 13.3 |
| 80Co20Mn/CNT | 16.4 | 15.5 | 15.1 | 15.0 | 13.7 |
| C2–C4 selectivity | |||||
| Co/CNT | 45.7 | 33.7 | 26.5 | 13.4 | 28.8 |
| 95Co5Mn/CNT | 35.6 | 23.6 | 15.5 | 6.7 | 4.4 |
| 90Co10Mn/CNT | 38.8 | 29.8 | 21.5 | 8.4 | 9.6 |
| 85Co15Mn/CNT | 42.6 | 33.8 | 24.5 | 9.4 | 13.7 |
| 80Co20Mn/CNT | 45.5 | 35.5 | 29.6 | 10.5 | 16.5 |
| C5+ selectivity | |||||
| Co/CNT | 30.2 | 41.3 | 48.8 | 59.1 | 54.5 |
| 95Co5Mn/CNT | 50.6 | 64.4 | 72.7 | 81.5 | 78.1 |
| 90Co10Mn/CNT | 45.7 | 57.8 | 65.6 | 78.0 | 76.5 |
| 85Co15Mn/CNT | 42.3 | 52.6 | 61.3 | 76.5 | 71.5 |
| 80Co20Mn/CNT | 38.9 | 49.2 | 56.8 | 74.5 | 67.5 |
| CO Conversion | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co/CNT | 21.5 | 35.7 | 46.2 | 58.7 | 58.8 |
| 95Co5Mn/CNT | 30.4 | 67.9 | 83.1 | 86.6 | 86.7 |
| 90Co10Mn/CNT | 28.9 | 65.7 | 70.5 | 83.8 | 83.8 |
| 85Co15Mn/CNT | 25.7 | 52.6 | 60.6 | 73.2 | 73.3 |
| 80Co20Mn/CNT | 23.9 | 48.7 | 52.8 | 66.3 | 66.5 |
| C1 selectivity | |||||
| Co/CNT | 16.2 | 14.1 | 11.7 | 9.5 | 9.6 |
| 95Co5Mn/CNT | 17.3 | 15.6 | 13.9 | 11.8 | 11.7 |
| 90Co10Mn/CNT | 19.6 | 17.7 | 15.6 | 13.3 | 13.4 |
| 85Co15Mn/CNT | 21.8 | 19.9 | 17.4 | 14.1 | 14.5 |
| 80Co20Mn/CNT | 23.7 | 20.4 | 17.7 | 15.0 | 15.4 |
| C2–C4 selectivity | |||||
| Co/CNT | 70.8 | 65.6 | 34.4 | 13.4 | 13.5 |
| 95Co5Mn/CNT | 60.6 | 48.8 | 27.9 | 6.7 | 6.8 |
| 90Co10Mn/CNT | 63.5 | 52.7 | 29.7 | 8.4 | 8.5 |
| 85Co15Mn/CNT | 66.9 | 55.6 | 33.9 | 9.4 | 9.5 |
| 80Co20Mn/CNT | 69.6 | 57.4 | 37.6 | 10.5 | 10.6 |
| C5+ selectivity | |||||
| Co/CNT | 15.3 | 30.3 | 35.7 | 59.1 | 59.3 |
| 95Co5Mn/CNT | 25.4 | 34.2 | 40.6 | 81.5 | 81.5 |
| 90Co10Mn/CNT | 23.9 | 31.6 | 37.3 | 78.0 | 78.2 |
| 85Co15Mn/CNT | 21.7 | 29.8 | 35.1 | 76.5 | 76.6 |
| 80Co20Mn/CNT | 18.6 | 26.4 | 32.6 | 74.5 | 74.7 |
| CO Conversion | 340 | 380 | 420 | 460 | 500 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co/CNT | 31.4 | 40.8 | 58.7 | 37.7 | 29.4 |
| 95Co5Mn/CNT | 46.6 | 62.6 | 86.6 | 56.9 | 43.6 |
| 90Co10Mn/CNT | 45.7 | 58.7 | 79.8 | 52.8 | 40.7 |
| 85Co15Mn/CNT | 37.6 | 51.8 | 73.2 | 47.7 | 35.9 |
| 80Co20Mn/CNT | 35.8 | 46.6 | 66.3 | 42.4 | 32.5 |
| C1 selectivity | |||||
| Co/CNT | 25.5 | 22.3 | 9.5 | 20.7 | 29.4 |
| 95Co5Mn/CNT | 15.3 | 12.7 | 11.8 | 12.6 | 18.7 |
| 90Co10Mn/CNT | 18.6 | 15.9 | 13.3 | 14.7 | 20.6 |
| 85Co15Mn/CNT | 21.9 | 17.4 | 14.1 | 16.6 | 23.4 |
| 80Co20Mn/CNT | 22.4 | 19.5 | 15.0 | 18.4 | 26.3 |
| C2–C4 selectivity | |||||
| Co/CNT | 40.4 | 37.2 | 13.4 | 40.2 | 41.9 |
| 95Co5Mn/CNT | 37.5 | 33.3 | 6.7 | 31.7 | 38.6 |
| 90Co10Mn/CNT | 38.6 | 35.4 | 8.4 | 34.8 | 39.4 |
| 85Co15Mn/CNT | 41.7 | 38.6 | 9.4 | 37.9 | 40.5 |
| 80Co20Mn/CNT | 42.2 | 38.8 | 10.5 | 38.6 | 40.2 |
| C5+ selectivity | |||||
| Co/CNT | 30.5 | 41.3 | 59.1 | 40.7 | 30.7 |
| 95Co5Mn/CNT | 42.9 | 55.5 | 81.5 | 57.4 | 44.3 |
| 90Co10Mn/CNT | 39.4 | 50.6 | 78.0 | 52.6 | 41.7 |
| 85Co15Mn/CNT | 35.6 | 45.8 | 76.5 | 47.5 | 37.1 |
| 80Co20Mn/CNT | 32.5 | 43.4 | 74.5 | 44.8 | 34.4 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akbarzadeh, O.; Mohd Zabidi, N.A.; Wang, G.; Kordijazi, A.; Sadabadi, H.; Moosavi, S.; Amani Babadi, A.; Hamizi, N.A.; Abdul Wahab, Y.; Ab Rahman, M.; et al. Effect of Pressure, H2/CO Ratio and Reduction Conditions on Co–Mn/CNT Bimetallic Catalyst Performance in Fischer–Tropsch Reaction. Symmetry 2020, 12, 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12050698
Akbarzadeh O, Mohd Zabidi NA, Wang G, Kordijazi A, Sadabadi H, Moosavi S, Amani Babadi A, Hamizi NA, Abdul Wahab Y, Ab Rahman M, et al. Effect of Pressure, H2/CO Ratio and Reduction Conditions on Co–Mn/CNT Bimetallic Catalyst Performance in Fischer–Tropsch Reaction. Symmetry. 2020; 12(5):698. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12050698
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkbarzadeh, Omid, Noor Asmawati Mohd Zabidi, Guangxin Wang, Amir Kordijazi, Hamed Sadabadi, Seyedehmaryam Moosavi, Arman Amani Babadi, Nor Aliya Hamizi, Yasmin Abdul Wahab, Marlinda Ab Rahman, and et al. 2020. "Effect of Pressure, H2/CO Ratio and Reduction Conditions on Co–Mn/CNT Bimetallic Catalyst Performance in Fischer–Tropsch Reaction" Symmetry 12, no. 5: 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12050698
APA StyleAkbarzadeh, O., Mohd Zabidi, N. A., Wang, G., Kordijazi, A., Sadabadi, H., Moosavi, S., Amani Babadi, A., Hamizi, N. A., Abdul Wahab, Y., Ab Rahman, M., Sagadevan, S., Chowdhury, Z. Z., & Johan, M. R. (2020). Effect of Pressure, H2/CO Ratio and Reduction Conditions on Co–Mn/CNT Bimetallic Catalyst Performance in Fischer–Tropsch Reaction. Symmetry, 12(5), 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12050698









