DNA Structure and the Golden Ratio Revisited
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Length: Diameter
3.2. Major: Minor Groove
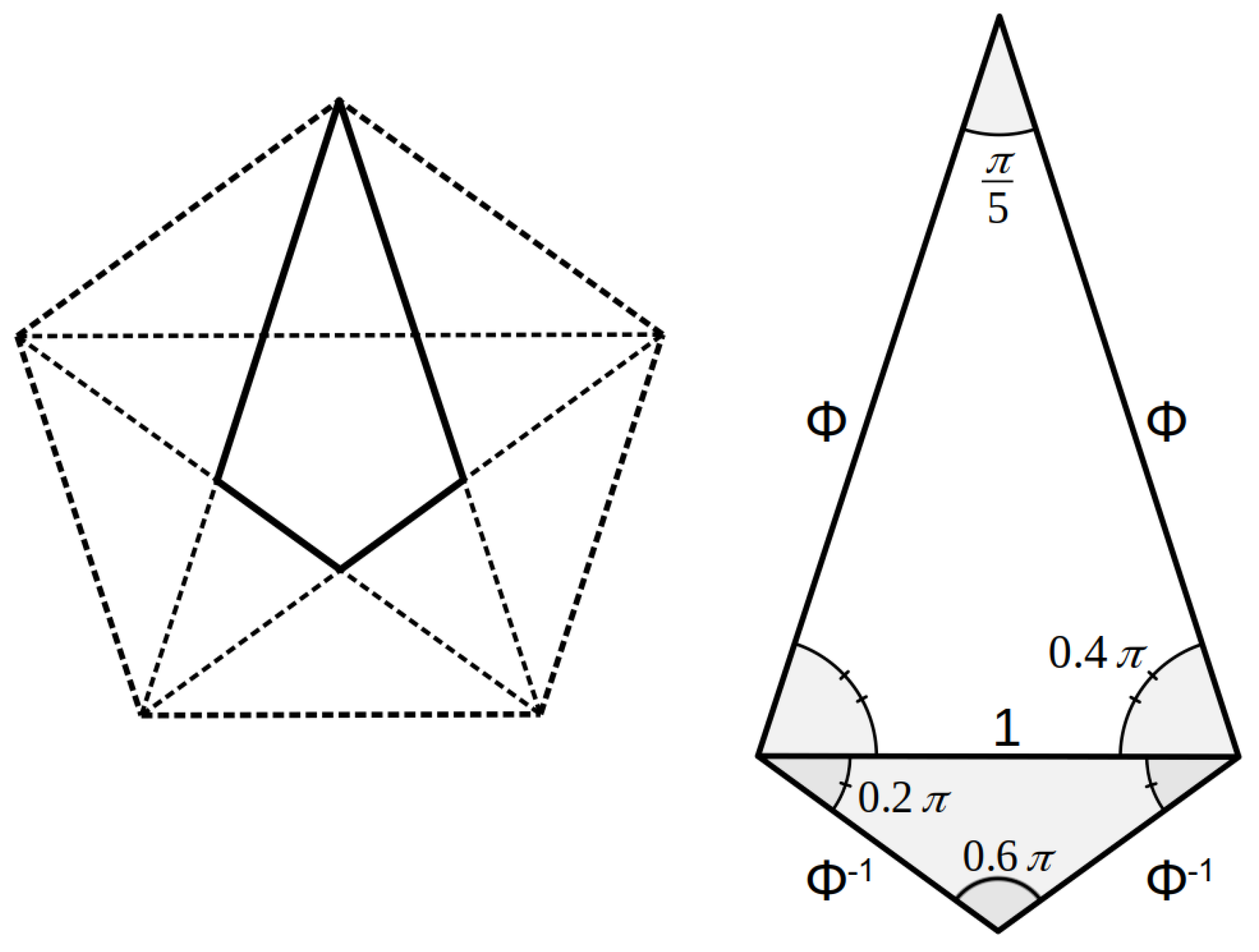
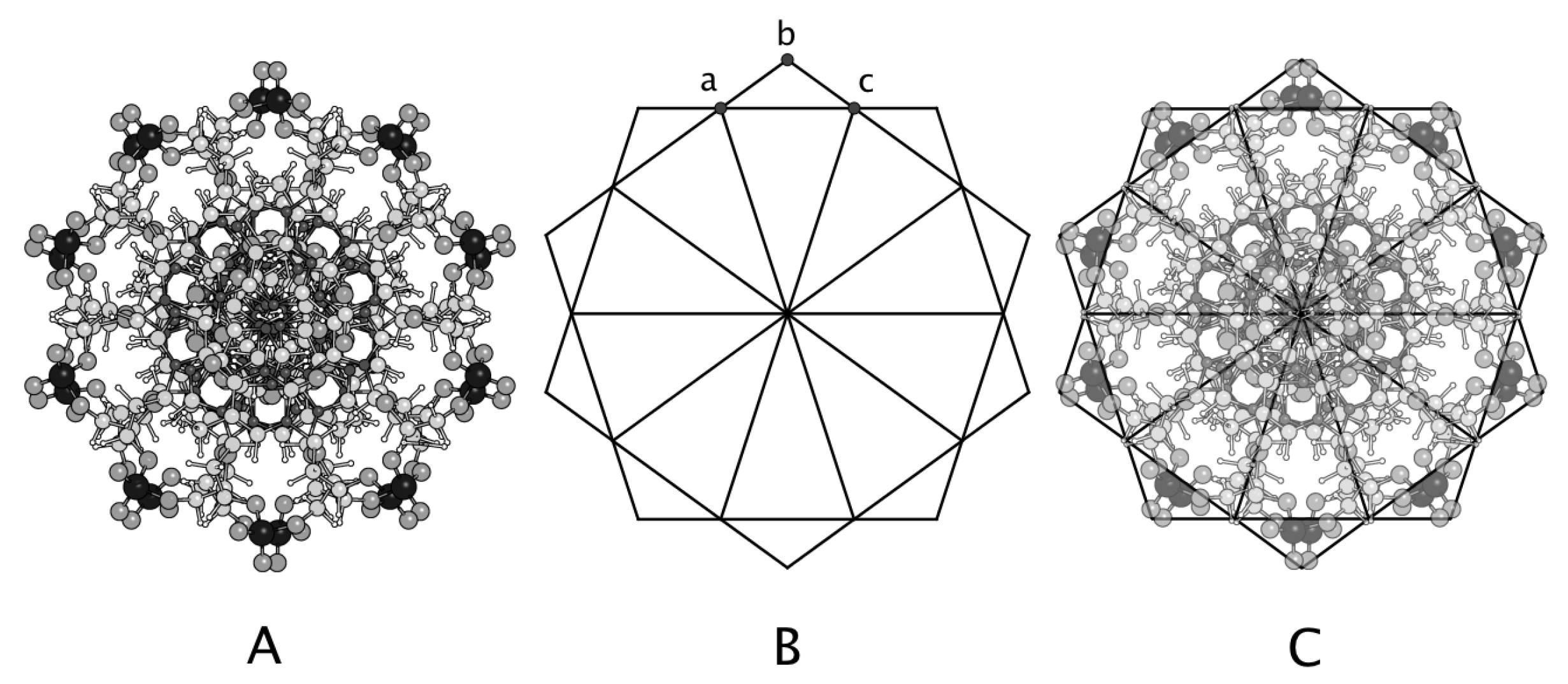
3.3. Axial Symmetry
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harel, D.; Unger, R.; Sussman, J. Beauty is in the genes of the beholder. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1986, 11, 155–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reichmann, W. The Spell of Mathematics; Methuen: London, UK, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Huntley, H.E. The Divine Proportion: A Study in Mathematical Beauty; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Posamentier, A.S.; Lehmann, I. The Glorious Golden Ratio; Prometheus Books: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Palais, R. π is wrong. Math. Intell. 2001, 23, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, M. How many base-pairs per turn does DNA have in solution and in chromatin? Some theoretical calculations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bates, A.D.; Maxwell, A. DNA Topology, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wynveen, A.; Lee, D.J.; Kornyshev, A.A.; Leikin, S. Helical coherence of DNA in crystals and solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 5540–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.J.; Olson, W.K. 3DNA: A software package for the analysis, rebuilding and visualization of three-dimensional nucleic acid structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 5108–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arnott, S.; Hukins, D.W.L. Refinement of the structure of B-DNA and implications for the analysis of X-ray diffraction data from fibers of biopolymers. J. Mol. Biol. 1973, 81, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, R.; Arnott, S. The structures of DNA and RNA helices in oriented fibers. In Landolt-Börnstein Numerical Data and Functional Relationships in Science and Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; Volume VII/1b, pp. 31–170. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran, R.; Arnott, S. The structure of B-DNA in oriented fibers. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 1996, 13, 1015–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickerson, R.E.; Drew, H.R. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer II. Influence of base sequence on helix structure. J. Mol. Biol. 1981, 149, 761–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, C.S.; Harvey, S.C. Base sequence, local helix structure, and macroscopic curvature of A-DNA and B-DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 3700–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger, L.L.C. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.8.6.0. Available online: https://pymol.org (accessed on 9 October 2021).
- Franklin, R.E.; Gosling, R.G. Molecular configuration in sodium thymonucleate. Nature 1953, 171, 740–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, K.J.; Beveridge, D.L. DNA structure: What’s in charge? J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 304, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojzsis, S.J.; Arrhenius, G.; McKeegan, K.D.; Harrison, T.M.; Nutman, A.P.; Friend, C.R.L. Evidence for life on Earth before 3800 million years ago. Nature 1996, 384, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano, A.; Miller, S.L. The origin and early evolution of life: Prebiotic chemistry, the pre-RNA world, and time. Cell 1996, 85, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bell, E.A.; Boehnke, P.; Harrison, T.M.; Mao, W.L. Potentially biogenic carbon preserved in a 4.1 billion-year-old zircon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14518–14521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tashiro, T.; Ishida, A.; Hori, M.; Igisu, M.; Koike, M.; Méjean, P.; Takahaya, N.; Sano, Y.; Komiya, T. Early trace of life from 3.95 Ga sedimentary rocks in Labrador, Canada. Nature 2017, 549, 516–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benner, S.A.; Karalkar, N.B.; Hoshika, S.; Laos, R.; Shaw, R.W.; Matsuura, M.; Fajardo, D.; Moussatche, P. Alternative Watson-Crick synthetic genetic systems. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a023779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falbo, C. The Golden Ratio—A contrary viewpoint. Coll. Math. J. 2005, 36, 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- Markowsky, G. Misconceptions about the Golden Ratio. Coll. Math. J. 1992, 23, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anosova, I.; Kowal, E.A.; Dunn, M.R.; Chaput, J.C.; Van Horn, W.D.; Egli, M. The structural diversity of artificial genetic polymers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 1007–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higgs, P.; Lehman, N. The RNA world: Molecular cooperation at the origins of life. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, P.P.; Holland, B.R.; Moulton, V.; Hendy, M.; Penny, D. Optimal alphabets for an RNA world. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2003, 270, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swinton, J.; Ochu, E.; The MSI Turing’s Sunflower Consortium. Novel Fibonacci and non-Fibonacci structure in the sunflower: Results of a citizen science experiment. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 3, 160091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larsen, S.H. Geometry of Braarudosphaera bigelowii (Prymnesiophyceae) nannoliths. Phycologia 2018, 57, 705–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meléndez-Hevia, E.; Waddel, T.G.; Cascante, M. The puzzle of the Krebs citric acid cycle: Assembling the pieces of chemically feasible reactions, and opportunism in the design of metabolic pathways during evolution. J. Mol. Evol. 1996, 43, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazcano, A.; Guerrero, R.; Margulis, L.; Oró, J. The evolutionary transition from RNA to DNA in early cells. J. Mol. Evol. 1988, 27, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, A.C.; Tor, Y. On the origin of the canonical nucleobases: An assessment of selection pressures across chemical and early biological evolution. Isr. J. Chem. 2013, 53, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saenger, W. Principles of Nucleic Acid Structure; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, M.; Miller, S.L. The stability of the RNA bases: Implications for the origin of life. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7933–7938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernhardt, H.S. The RNA world hypothesis: The worst theory of the early evolution of life (except for all the others). Biol. Direct 2012, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larralde, R.; Robertson, M.P.; Miller, S.L. Rates of decomposition of ribose and other sugars: Implications for chemical evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8158–8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ricardo, A.; Carrigan, M.A.; Olcott, A.N.; Benner, S.A. Borate minerals stabilize ribose. Science 2004, 303, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Becker, S.; Feldmann, J.; Wiedemann, S.; Okamura, H.; Schneider, C.; Iwan, K.; Crisp, A.; Rossa, M.; Amatov, T.; Carell, T. Unified prebiotically plausible synthesis of pyrimidine and purine RNA ribonucleotides. Science 2019, 366, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dhuime, B.; Wuestefeld, A.; Hawkesworth, C.J. Emergence of modern continental crust about 3 billion years ago. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, P. Gravitational potential energy per unit area as a constraint on Archean sea level. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2018, 19, 4063–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.W.; Wing, B.A. Limited Archaean continental emergence reflected in an early Archaean 18O-enriched ocean. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grew, E.S.; Bada, J.L.; Hazen, R.M. Borate minerals and origin of the RNA world. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 2011, 41, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, M.P.; Joyce, G.F. The origins of the RNA World. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a003608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, A.M.; Jeffares, D.C.; Penny, D. The path from the RNA world. J. Mol. Evol. 1998, 46, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, K.E.; Levy, M.; Miller, S.L. Peptide nucleic acids rather than RNA may have been the first genetic molecule. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3868–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hud, N.V.; Cafferty, B.J.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Williams, L.D. The origin of RNA and “My Grandfather’s Axe”. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biondi, E.; Furukawa, Y.; Kawai, J.; Benner, S.A. Adsorption of RNA on mineral surfaces and mineral precipitates. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Mao, C. Regulating self-assembly by DNA-surface interactions. ChemBioChem 2017, 18, 2404–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, J.P. Montmorillonite-catalysed formation of RNA oligomers: The possible role of catalysis in the origins of life. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B. 2006, 361, 1777–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- James Cleaves, H., II; Michalkova Scott, A.; Hill, F.C.; Leszczynski, J.; Sahai, N.; Hazen, R. Mineral-organic interfacial processes: Potential roles in the origins of life. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5502–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shechtman, D.; Blech, I.; Gratias, D.; Cahn, J.W. Metallic phase with long-range orientational order and no translational symmetry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1984, 53, 1951–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levine, D.; Steinhardt, P.J. Quasicrystals: A new class of ordered substances. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1984, 53, 2477–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caspar, D.L.D.; Fontano, E. Five-fold symmetry in crystalline quasicrystal lattices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14271–14278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, H.R.; Nozawa, K.; Smerdon, J.A.; Nugent, P.J.; McLeod, I.; Dhanak, V.R.; Shimoda, M.; Ishii, Y.; Tsai, A.P.; McGrath, R. Templated three-dimensional growth of quasicrystalline lead. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bindi, L.; Lin, C.; Ma, C.; Steinhardt, P.J. Collisions in outer space produced an icosahedral phase in the Khatyrka meteorite never observed previously in the laboratory. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Larsen, S.H. DNA Structure and the Golden Ratio Revisited. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1949. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101949
Larsen SH. DNA Structure and the Golden Ratio Revisited. Symmetry. 2021; 13(10):1949. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101949
Chicago/Turabian StyleLarsen, Stuart Henry. 2021. "DNA Structure and the Golden Ratio Revisited" Symmetry 13, no. 10: 1949. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101949
APA StyleLarsen, S. H. (2021). DNA Structure and the Golden Ratio Revisited. Symmetry, 13(10), 1949. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101949





