A Two-Stream CNN Model with Adaptive Adjustment of Receptive Field Dedicated to Flame Region Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
- (1)
- We construct a two-stream network to utilize spatial and temporal features for flame region detection. The spatial features represent color features, texture features, and so on. The temporal features represent dynamic characteristics such as blinking characteristics.
- (2)
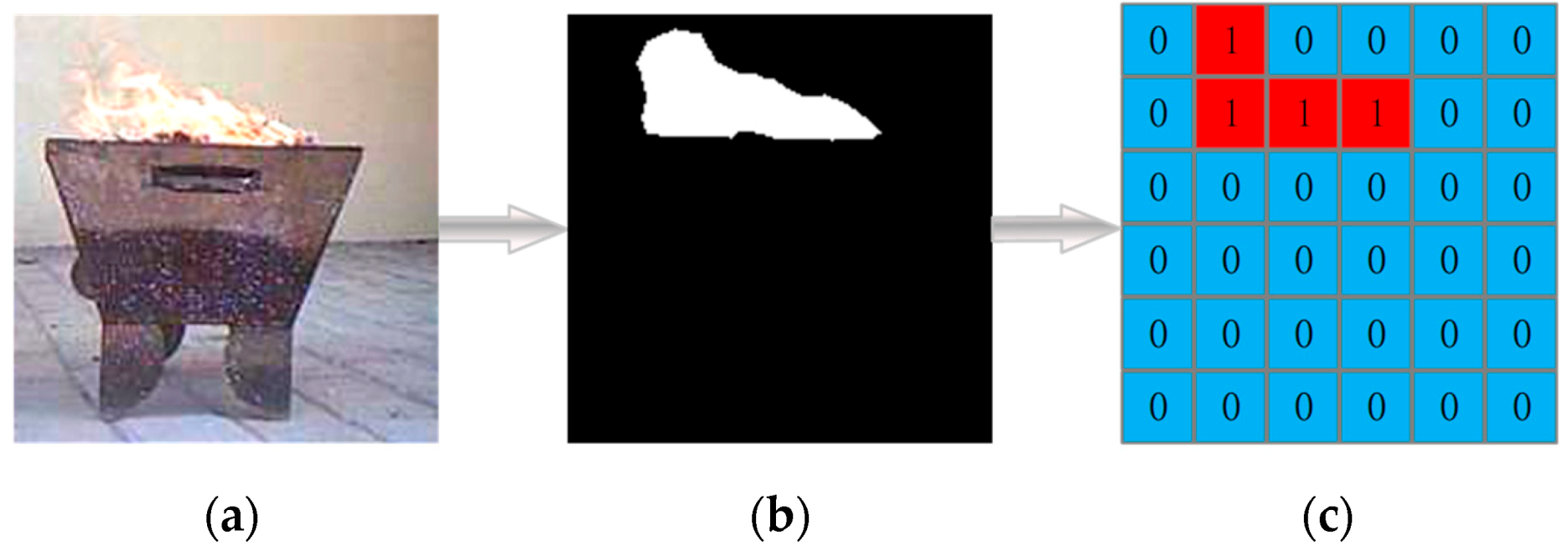
- We pre-divide the input video frame into several equal cells and design a lightweight network that can identify all flame cells through one-stage detection, thus avoiding the complex units of the segmentation network designed to adapt to multiple targets.
- (3)
- We replace the convolutional layers by the convolutional block combining SKnet and ShuffleNet V2. The SK convolution is integrated into the deep convolutional layer of ShuffleNet V2 to achieve the adaptive ability of the convolutional block in adjusting the size of receptive fields, which is of great significance for some very small flame areas captured on a distant view or some small fragment-like flame regions.
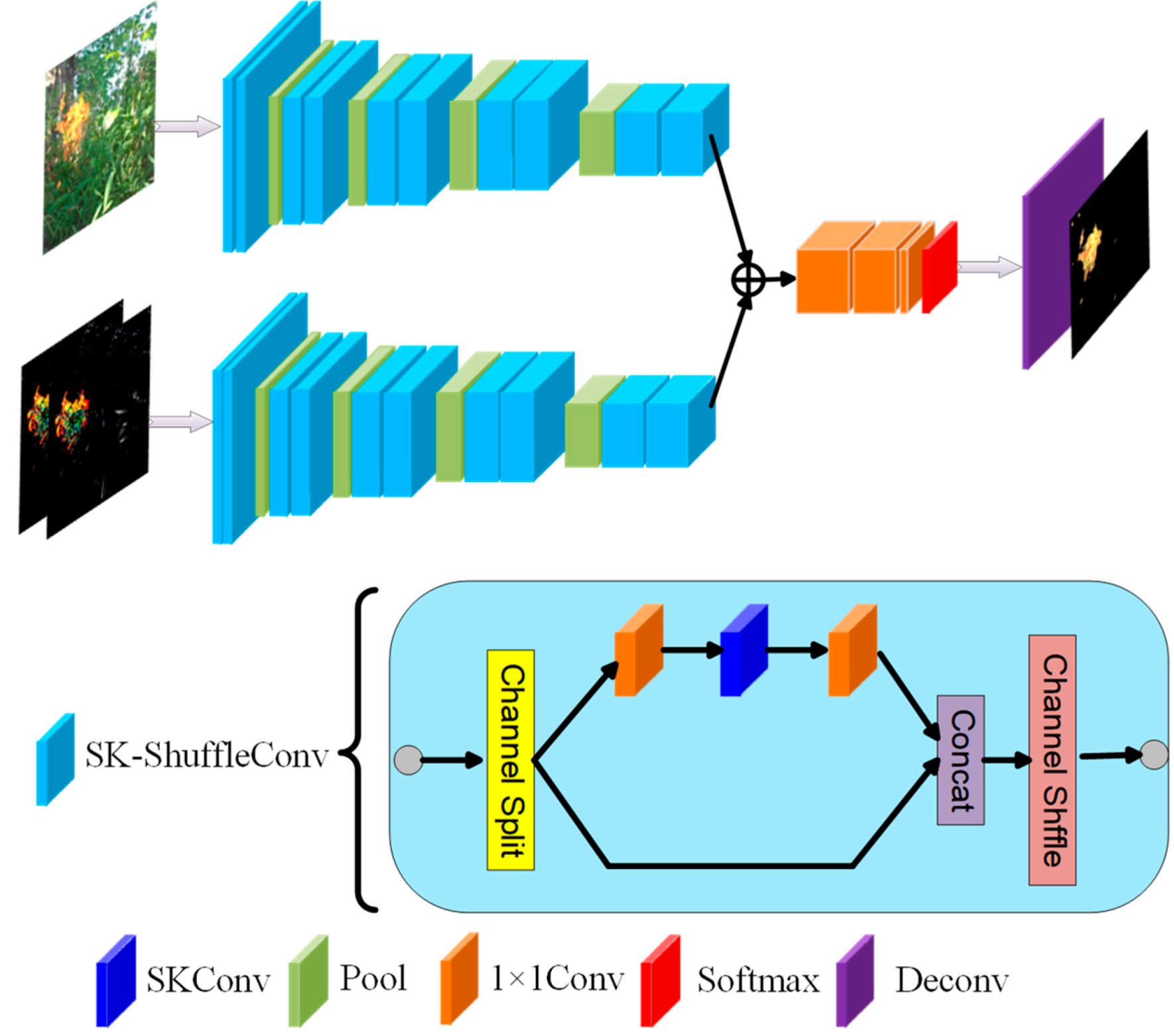
3. The Proposed Model
3.1. Pipeline Overview
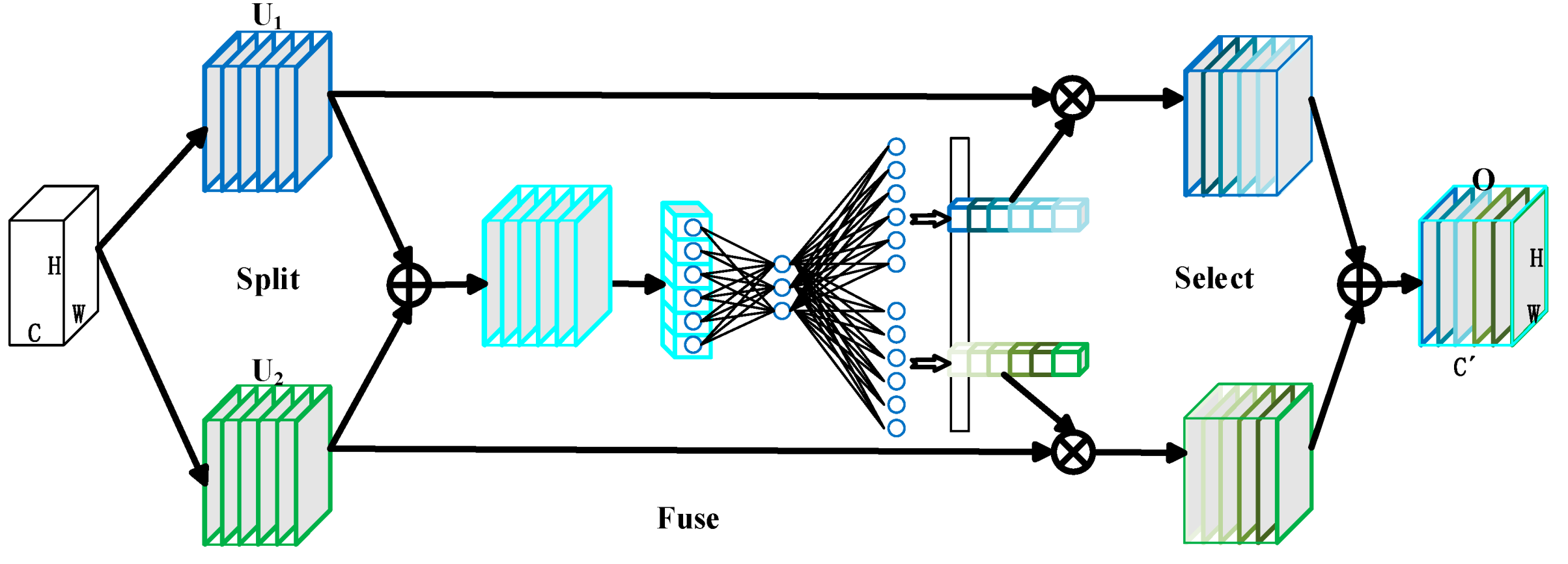
3.2. Adaptive Adjustment of the Receptive Field Based on SKnet
3.3. Lighten the Network by ShuffleNet
4. Experiments and Analysis
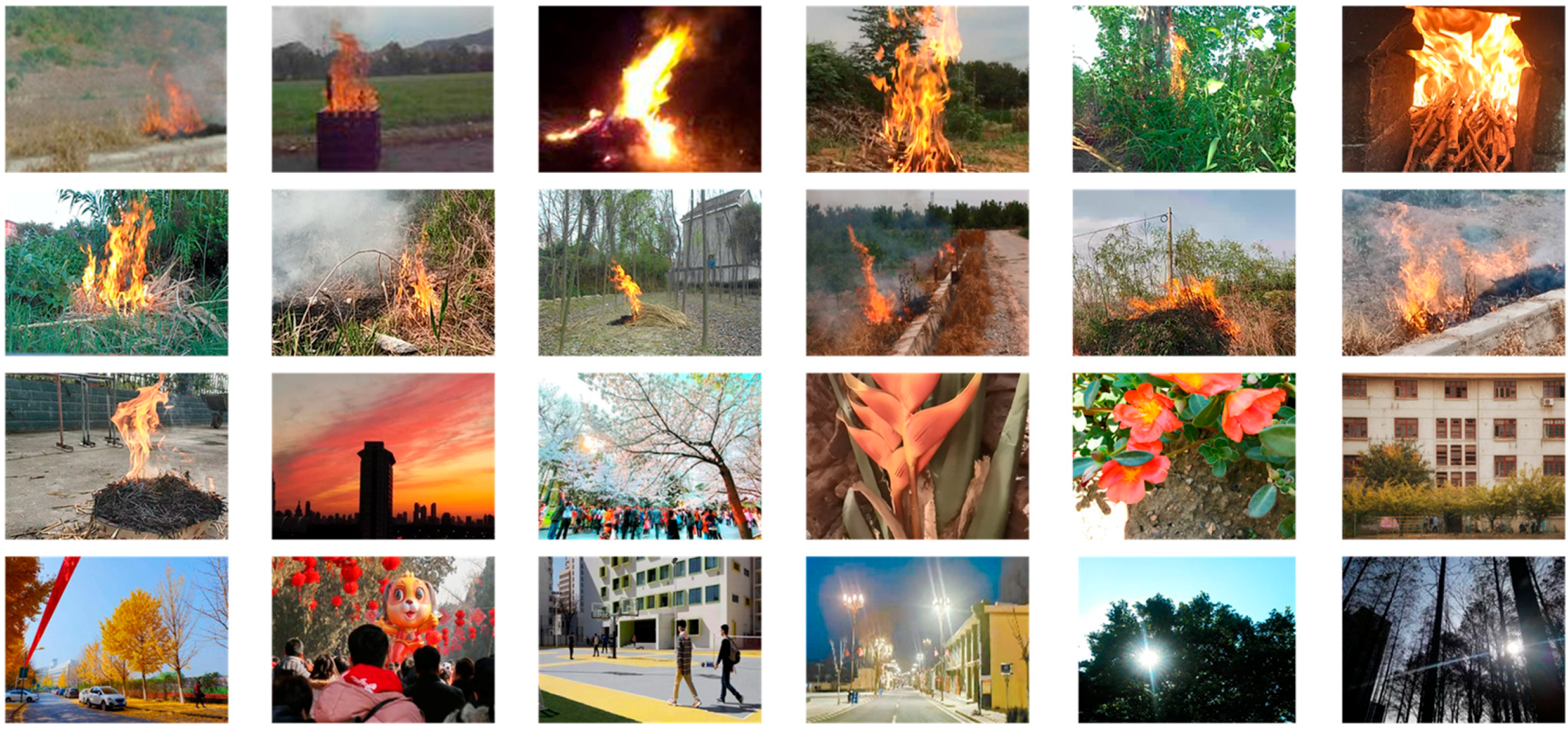
4.1. Experimental Settings
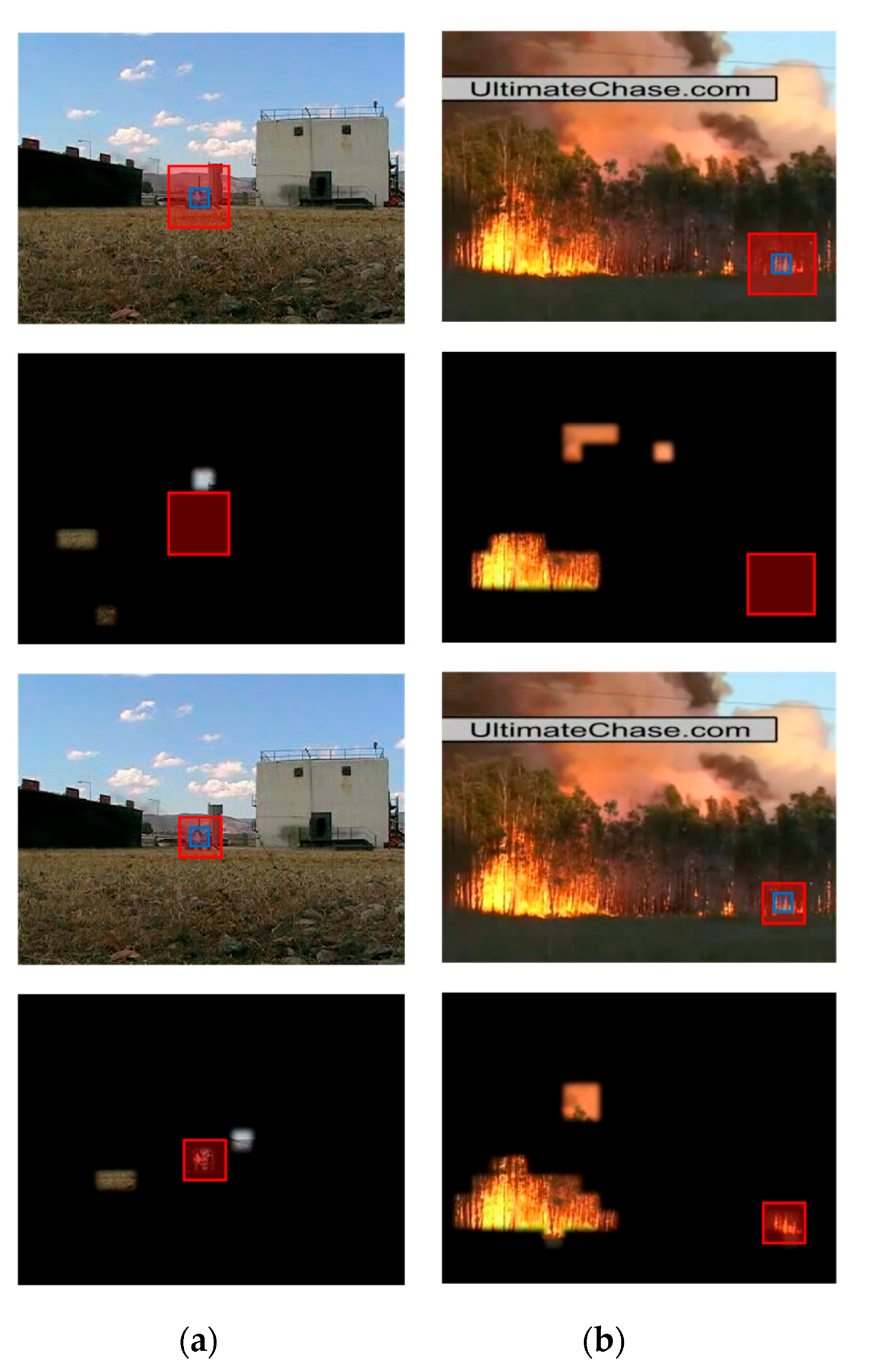
4.2. Adaptive Adjustment of the Receptive Field
4.3. Comparison of Recognition Performance
4.3.1. Comparison of Recognition Accuracy
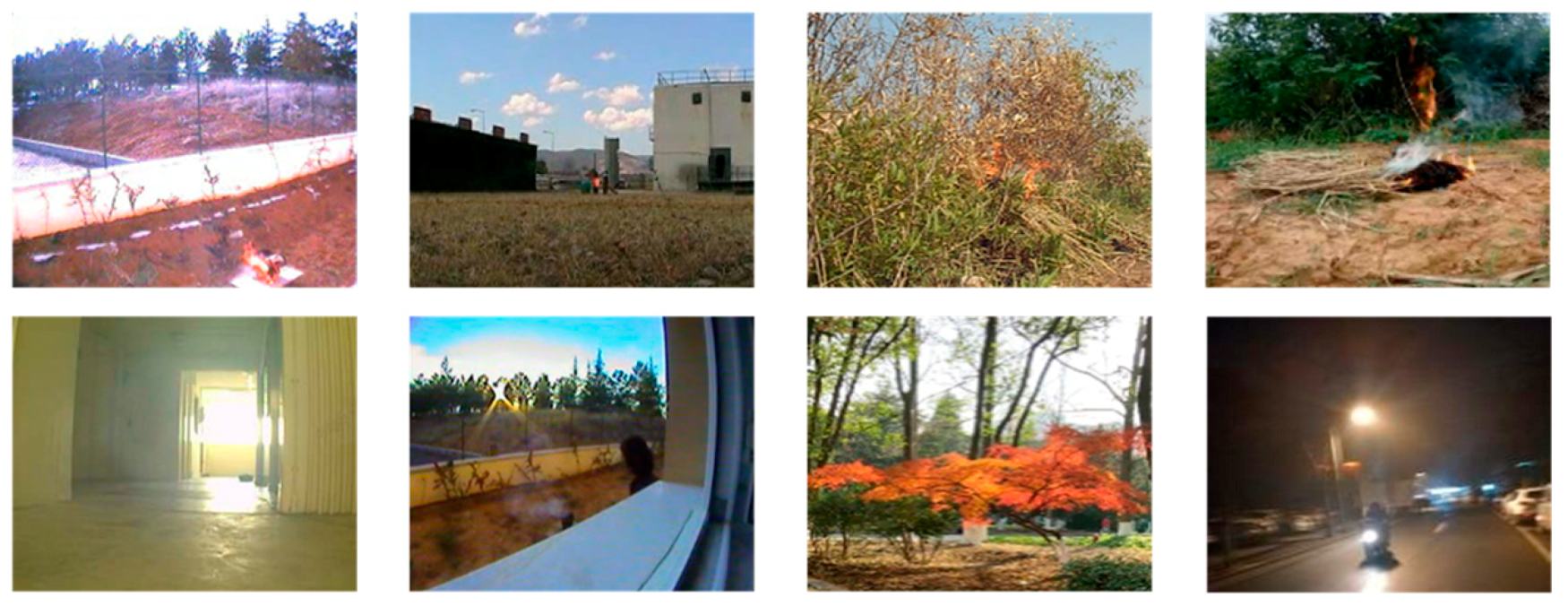
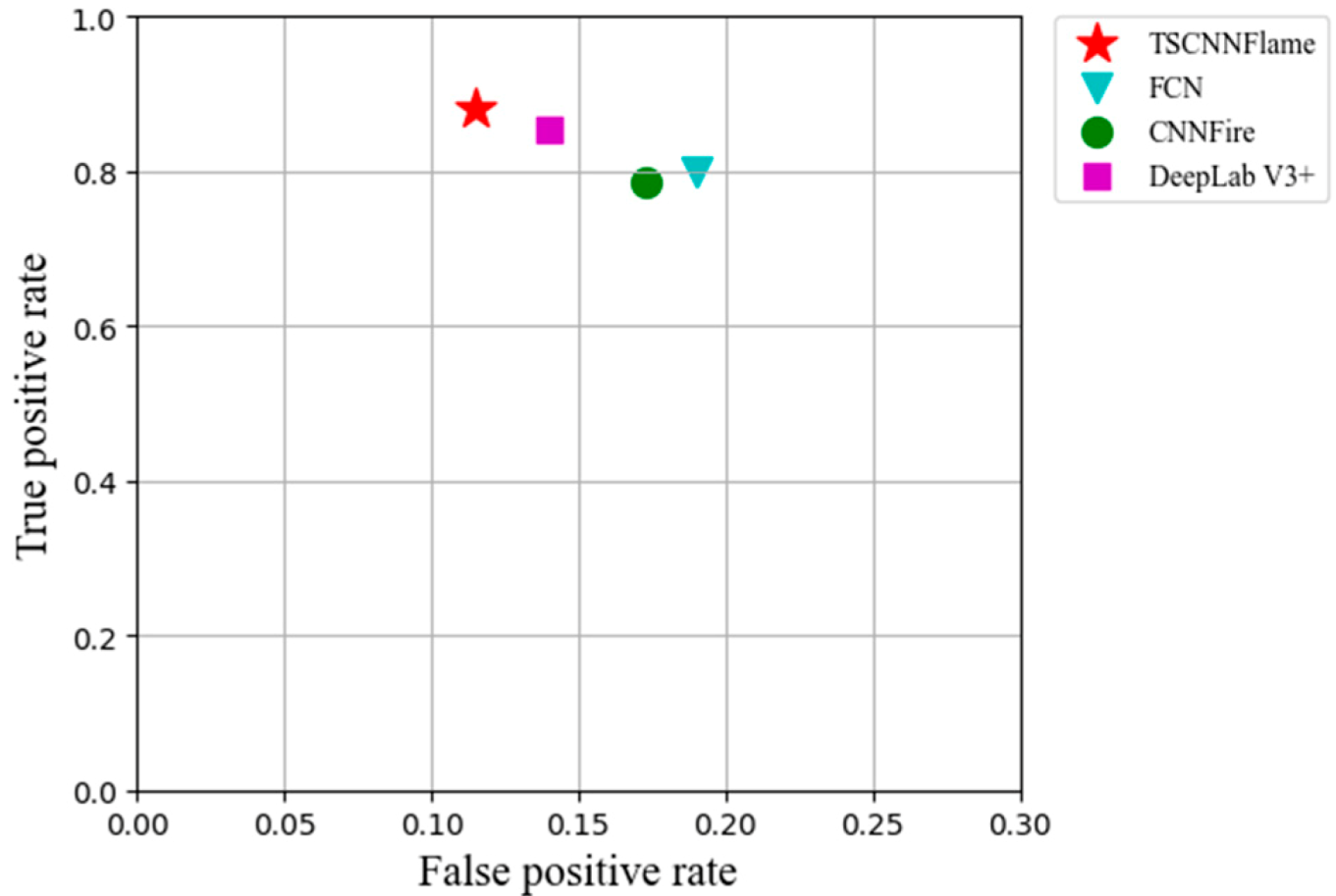
4.3.2. Comparison of Anti-Interference
4.4. Running Time
5. Conclusions and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Çelik, T.; Demirel, H. Fire Detection in Video Sequences Using a Generic Color Model. Fire Saf. J. 2009, 44, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chino, D.Y.; Avalhais, L.P.; Rodrigues, J.F.; Traina, A.J. Detection of Fire in Still Images by Integrating Pixel Color and Texture Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2015 28th SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images, Salvador, Brazil, 26–29 August 2015; pp. 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, M.; Karasev, P.; Kolesov, I.; Tannenbaum, A. Optical Flow Estimation for Flame Detection in Videos. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 2786–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lascio, R.; Greco, A.; Saggese, A.; Vento, M. Improving fire detection reliability by a combination of videoanalytics. In Proceedings of the International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 477–484. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitropoulos, K.; Barmpoutis, P.; Grammalidis, N. Spatio-temporal flame modeling and dynamic texture analysis for automatic video-based fire detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2015, 25, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yuan, P.; Liu, X.; Zhou, H. Street tree segmentation from mobile laser scanning data. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2020, 41, 7145–7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kima, B.-G.; Roy, P.P.; Jeong, D.-M. Efficient Facial Expression Recognition Algorithm Based on Hierarchical Deep Neural Network Structure. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 41273–41285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frizzi, S.; Kaabi, R.; Bouchouicha, M.; Ginoux, J.-M.; Moreau, E.; Fnaiech, F. Convolutional Neural Network for Video Fire and Smoke Detection. In Proceedings of the IECON 2016—42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Florence, Italy, 23–26 October 2016; pp. 877–882. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, J.; Granmo, O.-C.; Goodwin, M.; Fidje, J.T. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Fire Detection in Images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering Applications of Neural Networks; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 183–193. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.; Wang, M.; Shi, Y.; Gao, W. A Convolutional Neural Network-Based Flame Detection Method in Video Sequence. Signal Image Video Process. 2018, 12, 1619–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Chen, Y. Video Flame Detection Method Based on TwoStream Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 8th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC), Chongqing, China, 24–26 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, K.; Ahmad, J.; Lv, Z.; Bellavista, P.; Yang, P.; Baik, S.W. Efficient Deep CNN-Based Fire Detection and Localization in Video Surveillance Applications. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2018, 49, 1419–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-H.; Wu, P.-H.; Chiou, Y.-C. An Early Fire-Detection Method Based on Image Processing. In Proceedings of the 2004 International Conference on Image Processing, 2004. ICIP ’04, Singapore, 24–27 October 2004; Volume 3, pp. 1707–1710. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Finn, A.; Erdinc, O.; Vincitore, A. Spatial-Temporal Structural and Dynamics Features for Video Fire Detection. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Clearwater Beach, FL, USA, 15–17 January 2013; pp. 513–519. [Google Scholar]
- Töreyin, B.U.; Dedeoğlu, Y.; Güdükbay, U.; Cetin, A.E. Computer Vision Based Method for Real-Time Fire and Flame Detection. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, J.; Xu, L.; Guo, H. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Forest Fire Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Forum on Management, Education and Information Technology Application; Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2016; pp. 568–575. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, K.; Khan, S.; Elhoseny, M.; Ahmed, S.H.; Baik, S.W. Efficient Fire Detection for Uncertain Surveillance Environment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 3113–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunnings, A.J.; Breckon, T.P. Experimentally Defined Convolutional Neural Network Architecture Variants for Non-Temporal Real-Time Fire Detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Athens, Greece, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 1558–1562. [Google Scholar]
- Chaoxia, C.; Shang, W.; Zhang, F. Information-Guided Flame Detection Based on Faster R-CNN. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 58923–58932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Lee, J. A Video-Based Fire Detection Using Deep Learning Models. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhao, W. Image Fire Detection Algorithms Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2020, 19, 100625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, K.; Ahmad, J.; Mehmood, I.; Rho, S.; Baik, S.W. Convolutional Neural Networks Based Fire Detection in Surveillance Videos. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 18174–18183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets and Fully Connected CRFs. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.00915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 833–851. [Google Scholar]
- Benitez-Garcia, G.; Prudente-Tixteco, L.; Castro-Madrid, L.C.; Toscano-Medina, R.; Olivares-Mercado, J.; Sanchez-Perez, G.; Villalba, L.J.G. Improving Real-Time Hand Gesture Recognition with Semantic Segmentation. Sensors 2021, 21, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Selective Kernel Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 510–519. [Google Scholar]
- Dumoulin, V.; Visin, F. A Guide to Convolution Arithmetic for Deep Learning. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.07285. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet: An Extremely Efficient Convolutional Neural Network for Mobile Devices. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.01083. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.-T.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet V2: Practical Guidelines for Efficient CNN Architecture Design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 122–138. [Google Scholar]
- Foggia, P.; Saggese, A.; Vento, M. Real-Time Fire Detection for Video-Surveillance Applications Using a Combination of Experts Based on Color, Shape, and Motion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2015, 25, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmpoutis, P.; Stathaki, T.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Grammalidis, N. Early Fire Detection Based on Aerial 360-Degree Sensors, Deep Convolution Neural Networks and Exploitation of Fire Dynamic Textures. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








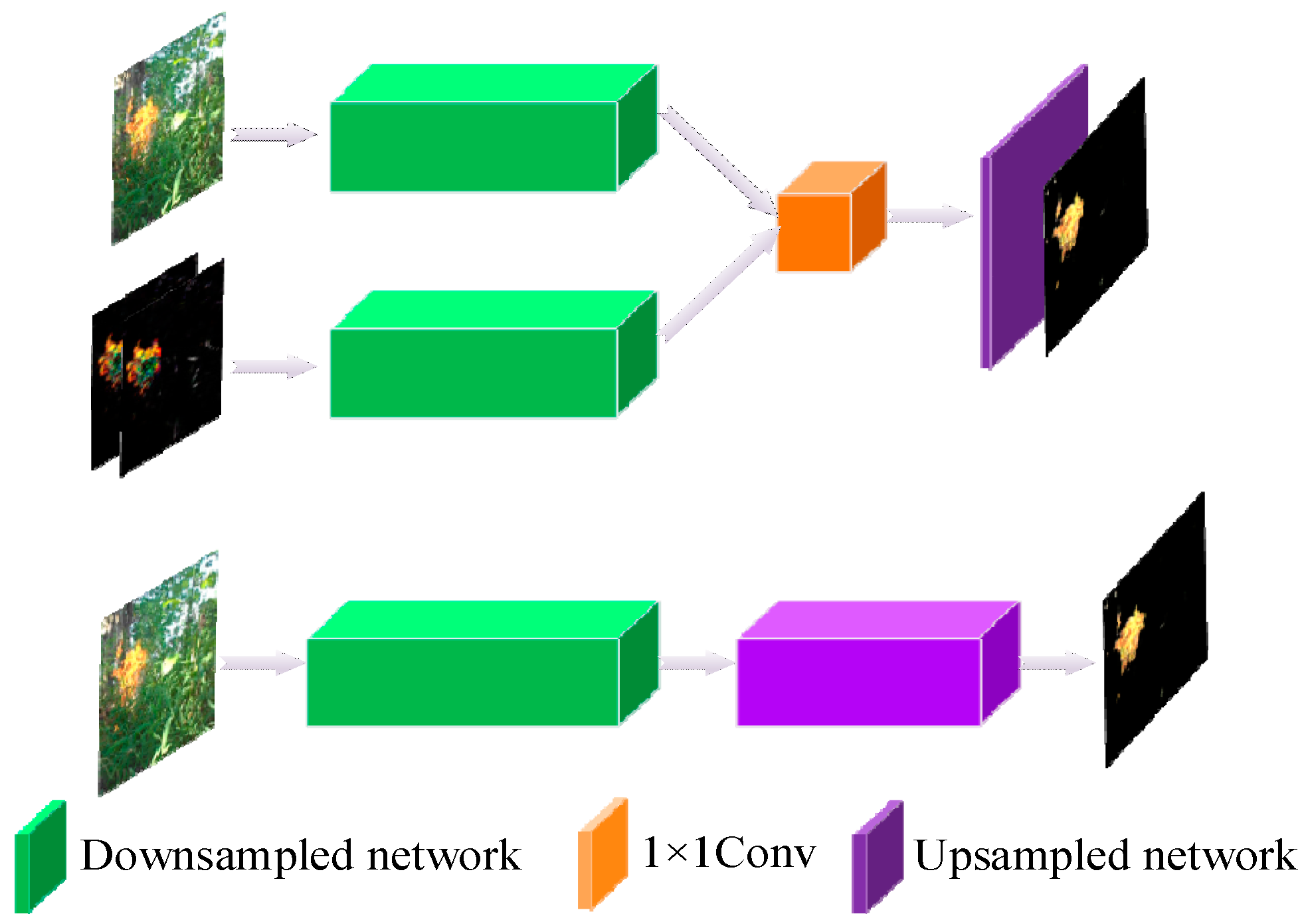
| Input | Spatial stream/Temporal Stream | Output |
|---|---|---|
| W × H × 3 | [3 × 3, 64, Stride:1] × 2 | W × H × 64 |
| W × H × 3 | 2 × 2 max pool, stride 2 | W/2 × H/2 × 64 |
| W/2 × H/2 × 64 | × 2 | W/2 × H/2 × 128 |
| W/2 × H/2 × 128 | 2 × 2 max pool, stride 2 | W/4 × H/4 × 128 |
| W/4 × H/4 × 128 | × 2 | W/4 × H/4 × 256 |
| W/4 × H/4 × 256 | 2 × 2 max pool, stride 2 | W/8 × H/8 × 256 |
| W/8 × H/8 × 256 | × 2 | W/8 × H/8 × 512 |
| W/16 × H/16 × 512 | 2 × 2 max pool, stride 2 | W/16 × H/16 × 512 |
| W/16 × H/16 × 512 | × 2 | W/16 × H/16 × 512 |
| W/16 × H/16 × 512 | fusion | W/16 × H/16 × 1024 |
| W/16 × H/16 × 1024 | 1 × 1, 1024, Stride:1 | W/16 × H/16 × 1024 |
| W/16 × H/16 × 1024 | 1 × 1, 512, Stride:1 | W/16 × H/16 × 512 |
| W/16 × H/16 × 512 | 1 × 1, 2, Stride:1, softmax | W/16 × H/16 × 2 |
| Video1 | Video2 | Video3 | Video4 | Video5 | Video6 | Video7 | Video8 | Avg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCN | 86.2% | 66.5% | 90.8% | 76.7% | 89.8% | 89.4% | 63.1% | 71.5% | 79.25% |
| CNNFire | 82.3% | 68.9% | 85.4% | 72.2% | 92.1% | 87.5% | 69.3% | 76.4% | 79.26% |
| DeepLab V3+ | 87.4% | 74.2% | 91.3% | 78.7% | 84.3% | 90.7% | 63.7% | 74.1% | 80.55% |
| TSCNNFlame | 87.6% | 75.4% | 89.2% | 83.5% | 85.2% | 91.1% | 73.0% | 78.6% | 82.95% |
| Video1 | Video2 | Video3 | Video4 | Video5 | Video6 | Video7 | Video8 | Avg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCN | 75.3% | 64.9% | 92.2% | 74.7% | 90.9% | 84.0% | 70.2% | 69.3% | 77.69% |
| CNNFire | 71.0% | 62.1% | 81.7% | 77.3% | 93.5% | 82.2% | 78.4% | 72.2% | 77.30% |
| DeepLab V3+ | 83.4% | 58.1% | 92.8% | 79.5% | 91.3% | 85.2% | 70.7% | 71.1% | 79.01% |
| TSCNNFlame | 84.7% | 71.2% | 88.5% | 84.7% | 89.8% | 85.9% | 82.1% | 73.4% | 82.54% |
| Method | Fps |
|---|---|
| FCN | 5 |
| CNNFire | 39 |
| DeepLab V3+ | 14 |
| TSCNNFlame | 35 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, P.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y. A Two-Stream CNN Model with Adaptive Adjustment of Receptive Field Dedicated to Flame Region Detection. Symmetry 2021, 13, 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13030397
Lu P, Zhao Y, Xu Y. A Two-Stream CNN Model with Adaptive Adjustment of Receptive Field Dedicated to Flame Region Detection. Symmetry. 2021; 13(3):397. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13030397
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Peng, Yaqin Zhao, and Yuan Xu. 2021. "A Two-Stream CNN Model with Adaptive Adjustment of Receptive Field Dedicated to Flame Region Detection" Symmetry 13, no. 3: 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13030397
APA StyleLu, P., Zhao, Y., & Xu, Y. (2021). A Two-Stream CNN Model with Adaptive Adjustment of Receptive Field Dedicated to Flame Region Detection. Symmetry, 13(3), 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13030397







