Modeling the Dynamics of Heavy-Ion Collisions with a Hydrodynamic Model Using a Graphics Processor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Initial Conditions
3.2. Hypersurface Extraction Methods
3.3. Hydrodynamics and Kinematic Description
3.4. Simulation of Pb-Pb Collisions at TeV
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kliemant, M.; Sahoo, R.; Schuster, T.; Stock, R. Global Properties of Nucleus-Nucleus Collisions. In The Physics of the Quark-Gluon Plasma; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 785, pp. 23–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satz, H. The Thermodynamics of Quarks and Gluons. Lect. Notes Phys. 2010, 785, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirano, T.; van der Kolk, N.; Bilandzic, A. Hydrodynamics and Flow. Lect. Notes Phys. 2010, 785, 139–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schenke, B.; Jeon, S.; Gale, C. (3 + 1) D hydrodynamic simulation of relativistic heavy-ion collisions. Phys. Rev. C 2010, 82, 014903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.G.; Petersen, H.; Wang, X.N. Pseudorapidity distribution and decorrelation of anisotropic flow within CLVisc hydrodynamics. Phys. Rev. C 2018, 97, 064918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen, H.; Steinheimer, J.; Burau, G.; Bleicher, M.; Stöcker, H. Fully integrated transport approach to heavy ion reactions with an intermediate hydrodynamic stage. Phys. Rev. C 2008, 78, 044901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhard, J.; Lindenstruth, V.; Bleicher, M. Relativistic hydrodynamics on graphic cards. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2013, 184, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karpenko, I.; Huovinen, P.; Bleicher, M. A 3 + 1 dimensional viscous hydrodynamic code for relativistic heavy ion collisions. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2014, 185, 3016–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alqahtani, M.; Nopoush, M.; Ryblewski, R.; Strickland, M. (3+ 1) D quasiparticle anisotropic hydrodynamics for ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 042301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Z.W.; Ko, C.M.; Li, B.A.; Zhang, B.; Pal, S. Multiphase transport model for relativistic heavy ion collisions. Phys. Rev. C 2005, 72, 064901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schenke, B.; Tribedy, P.; Venugopalan, R. Fluctuating Glasma initial conditions and flow in heavy ion collisions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 252301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreland, J.S.; Bernhard, J.E.; Bass, S.A. Alternative ansatz to wounded nucleon and binary collision scaling in high-energy nuclear collisions. Phys. Rev. C 2015, 92, 011901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donoho, D.L.; Grimes, C. Hessian eigenmaps: Locally linear embedding techniques for high-dimensional data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5591–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boris, J.P.; Book, D.L. Flux-corrected transport. I. SHASTA, a fluid transport algorithm that works. J. Comput. Phys. 1973, 11, 38–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraposhin, M.; Bovtrikova, A.; Strijhak, S. Adaptation of Kurganov-Tadmor numerical scheme for applying in combination with the PISO method in numerical simulation of flows in a wide range of Mach numbers. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 66, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huovinen, P.; Petersen, H. Particlization in hybrid models. Eur. Phys. J. A 2012, 48, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weil, J.; Steinberg, V.; Staudenmaier, J.; Pang, L.; Oliinychenko, D.; Mohs, J.; Kretz, M.; Kehrenberg, T.; Goldschmidt, A.; Bäuchle, B.; et al. Particle production and equilibrium properties within a new hadron transport approach for heavy-ion collisions. Phys. Rev. C 2016, 94, 054905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierog, T.; Werner, K. EPOS model and ultra high energy cosmic rays. Nucl. Phys. B-Proc. Suppl. 2009, 196, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bleicher, M.; Zabrodin, E.; Spieles, C.; Bass, S.A.; Ernst, C.; Soff, S.; Bravina, L.; Belkacem, M.; Weber, H.; Stöcker, H.; et al. Relativistic hadron-hadron collisions in the ultra-relativistic quantum molecular dynamics model. J. Phys. G Nucl. Part. Phys. 1999, 25, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.L.; Reygers, K.; Sanders, S.J.; Steinberg, P. Glauber modeling in high energy nuclear collisions. Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 2007, 57, 205–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gelis, F.; Iancu, E.; Jalilian-Marian, J.; Venugopalan, R. The Color Glass Condensate. Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 2010, 60, 463–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Słodkowski, M.; Marcinkowski, P.; Gawryszewski, P.; Kikoła, D.; Porter-Sobieraj, J. Modeling of modifications induced by jets in the relativistic bulk nuclear matter. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1085, 052001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słodkowski, M.; Gawryszewski, P.; Marcinkowski, P.; Setniewski, D.; Porter-Sobieraj, J. Simulations of Energy Losses in the Bulk Nuclear Medium Using Hydrodynamics on the Graphics Cards (GPU). Proceedings 2019, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcinkowski, P.; Słodkowski, M.; Kikoła, D.; Gawryszewski, P.; Sikorski, J.; Porter-Sobieraj, J.; Zygmunt, B. Jet-induced modifications of the characteristic of the bulk nuclear matter. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Strangeness in Quark Matter (SQM2015), Dubna, Russia, 6–11 July 2015; Volume 668, p. 012115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porter-Sobieraj, J.; Słodkowski, M.; Kikoła, D.; Sikorski, J.; Aszklar, P. A MUSTA-FORCE algorithm for solving partial differential equations of relativistic hydrodynamics. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2018, 19, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter-Sobieraj, J.; Cygert, S.; Kikoła, D.; Sikorski, J.; Słodkowski, M. Optimizing the computation of a parallel 3D finite difference algorithm for graphics processing units. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2015, 27, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nvidia, CUDA C++ Programming Guide; PG-02829-001_v11.2; Nvidia Corporation. Available online: https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/pdf/CUDA_C_Programming_Guide.pdf (accessed on 19 March 2020).
- Słodkowski, M.; Gawryszewski, P.; Setniewski, D. Study of the influence of initial-state fluctuations on hydrodynamic simulations. EPJ Web Conf. 2020, 245, 06005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, S. Accounting for backflow in hydrodynamic-Boltzmann interfaces. Phys. Rev. C 2014, 89, 024910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adam, J.; Adamová, D.; Aggarwal, M.M.; Rinella, G.A.; Agnello, M.; Agrawal, N.; Ahammed, Z.; Ahmad, S.; Ahn, S.; Aiola, S.; et al. Anisotropic flow of charged particles in Pb-Pb collisions at s N N= 5.02 TeV. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 132302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romatschke, P. New developments in relativistic viscous hydrodynamics. Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 2010, 19, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romatschke, P.; Romatschke, U. Relativistic Fluid Dynamics in and out of Equilibrium: And Applications to Relativistic Nuclear Collisions; Cambridge Monographs on Mathematical Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Burrage, K.; Butcher, J.C.; Chipman, F. An implementation of singly-implicit Runge-Kutta methods. BIT Numer. Math. 1980, 20, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.D.; Osher, S.; Chan, T. Weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 1994, 115, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, F.; Frye, G. Comment on the Single Particle Distribution in the Hydrodynamic and Statistical Thermodynamic Models of Multiparticle Production. Phys. Rev. D 1974, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huovinen, P.; Holopainen, H. Cornelius—User’s Guide. Available online: https://itp.uni-frankfurt.de/~huovinen/cornelius/guide.pdf (accessed on 19 March 2020).
- Lorensen, W.; Cline, H. Marching Cubes: A High Resolution 3D Surface Construction Algorithm. ACM SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 1987, 21, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielson, G.M.; Hamann, B. The asymptotic decider: Resolving the ambiguity in Marching Cubes. IEEE Vis. 1991, 91, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montani, C.; Scateni, R.; Scopigno, R. A modified look-up table for implicit disambiguation of Marching Cubes. Vis. Comput. 1994, 10, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaniramka, P.; Wenger, R.; Crawfis, R. Isosurface construction in any dimension using convex hulls. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2004, 10, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacki, M.; Kisiel, A.; Florkowski, W.; Broniowski, W. THERMINATOR 2: THERMal heavy IoN generATOR 2. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2012, 183, 746–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernhard, J.E. Bayesian Parameter Estimation for Relativistic Heavy-Ion Collisions. Ph.D. Thesis, Duke University, Durham, NC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, C.W. WENO methods. Scholarpedia 2011, 6, 9709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.W. The special relativistic shock tube. J. Fluid Mech. 1986, 171, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinyukov, Y.M.; Karpenko, I.A. Ellipsoidal flows in relativistic hydrodynamics of finite systems. Acta Phys. Hung. Ser. A Heavy Ion Phys. 2006, 25, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chojnacki, M.; Florkowski, W.; Csörgö, T. Formation of Hubble-like flow in little bangs. Phys. Rev. C 2005, 71, 044902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazavov, A.; Bhattacharya, T.; DeTar, C.; Ding, H.-T.; Gottlieb, S.; Gupta, R.; Hegde, P.; Heller, U.M.; Karsch, F.; Laermann, E.; et al. Equation of state in ( 2+1 )-flavor QCD. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 094503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bożek, P. Effect of bulk viscosity on interferometry correlations in ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions. Phys. Rev. C 2017, 95, 054909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bożek, P.; Broniowski, W.; Rybczynski, M.; Stefanek, G. GLISSANDO 3: GLauber Initial-State Simulation AND mOre..., ver. 3. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2019, 245, 106850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernhard, J. Frzout -Particlization Model (Cooper-Frye Sampler) for Relativistic Heavy-Ion Collisions. Available online: http://qcd.phy.duke.edu/frzout/index.html (accessed on 19 March 2020).
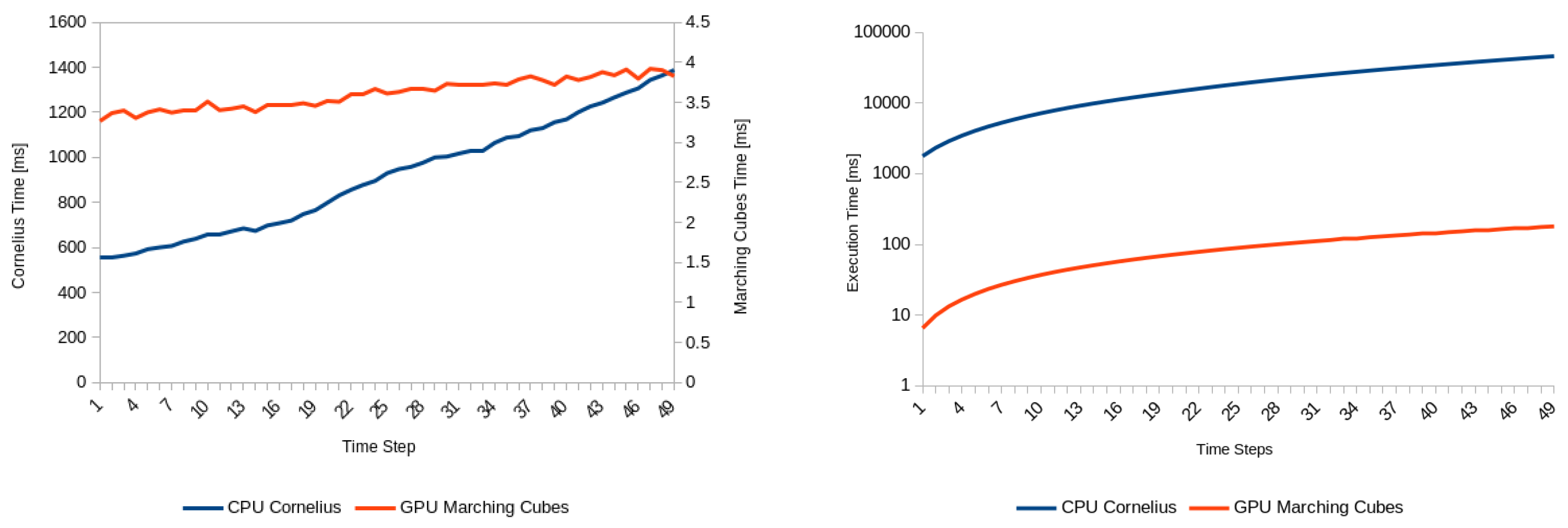
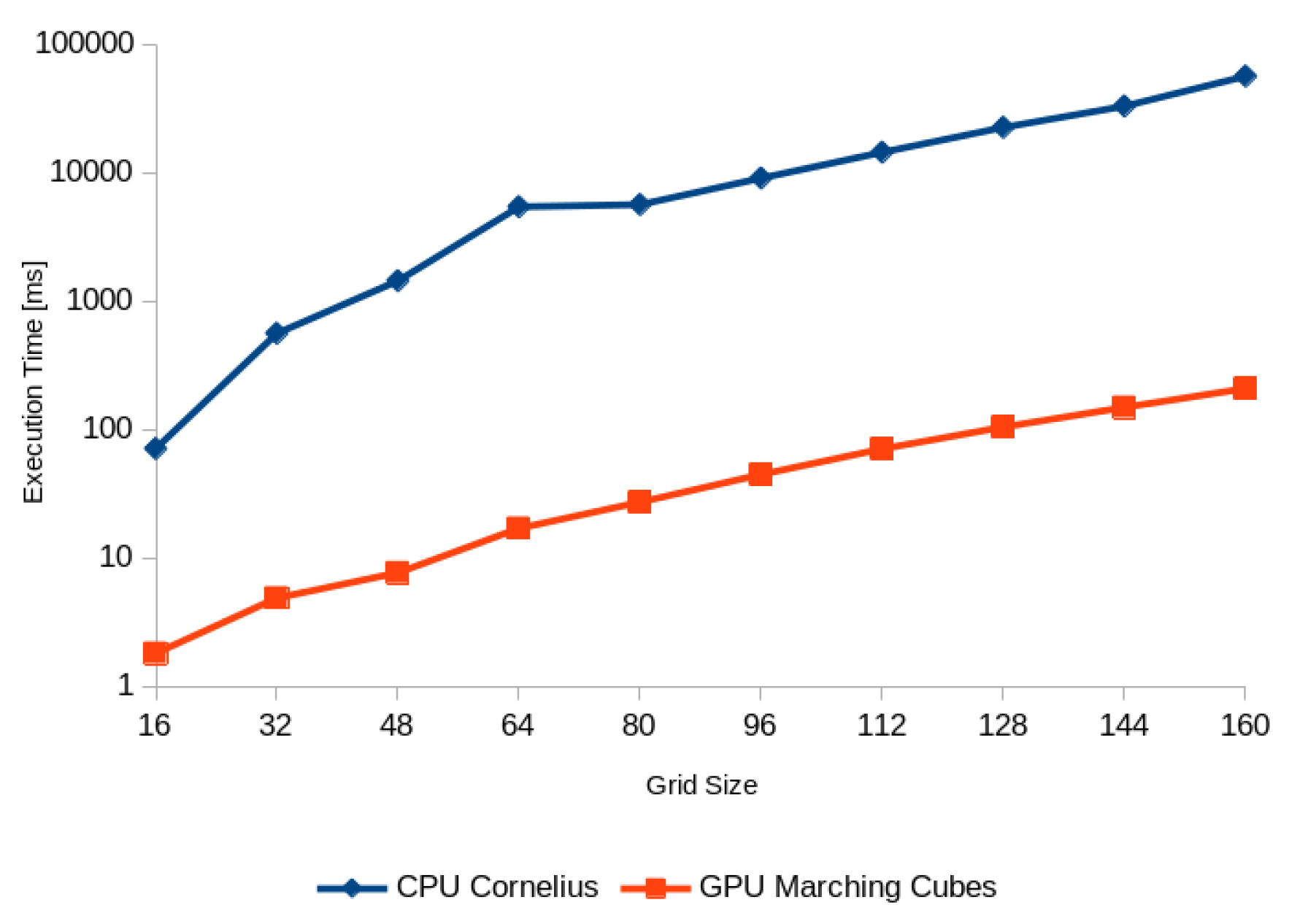






| Method | Time (s) (w/Copy Overhead) | Cells Intersections | Hypersurface Elements | % of Program Runtime (w/Copy Overhead) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cornelius (single-threded) | 46 (46.2) | 6296765 | 6606727 | 89.1% (89.3%) |
| Marching cubes (parallel) | 0.18 | 6296765 | 6669758 | 3.2% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Słodkowski, M.; Setniewski, D.; Aszklar, P.; Porter-Sobieraj, J. Modeling the Dynamics of Heavy-Ion Collisions with a Hydrodynamic Model Using a Graphics Processor. Symmetry 2021, 13, 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13030507
Słodkowski M, Setniewski D, Aszklar P, Porter-Sobieraj J. Modeling the Dynamics of Heavy-Ion Collisions with a Hydrodynamic Model Using a Graphics Processor. Symmetry. 2021; 13(3):507. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13030507
Chicago/Turabian StyleSłodkowski, Marcin, Dominik Setniewski, Paweł Aszklar, and Joanna Porter-Sobieraj. 2021. "Modeling the Dynamics of Heavy-Ion Collisions with a Hydrodynamic Model Using a Graphics Processor" Symmetry 13, no. 3: 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13030507
APA StyleSłodkowski, M., Setniewski, D., Aszklar, P., & Porter-Sobieraj, J. (2021). Modeling the Dynamics of Heavy-Ion Collisions with a Hydrodynamic Model Using a Graphics Processor. Symmetry, 13(3), 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13030507






