Abstract
Automatic segmentation of the lungs in Chest X-ray images (CXRs) is a key step in the screening and diagnosis of related diseases. There are many opacities in the lungs in the CXRs of patients, which makes the lungs difficult to segment. In order to solve this problem, this paper proposes a segmentation algorithm based on U-Net. This article introduces variational auto-encoder (VAE) in each layer of the decoder-encoder. VAE can extract high-level semantic information, such as the symmetrical relationship between the left and right thoraxes in most cases. The fusion of the features of VAE and the features of convolution can improve the ability of the network to extract features. This paper proposes a three-terminal attention mechanism. The attention mechanism uses the channel and spatial attention module to automatically highlight the target area and improve the performance of lung segmentation. At the same time, the three-terminal attention mechanism uses the advanced semantics of high-scale features to improve the positioning and recognition capabilities of the attention mechanism, suppress background noise, and highlight target features. Experimental results on two different datasets show that the accuracy (ACC), recall (R), F1-Score and Jaccard values of the algorithm proposed in this paper are the highest on the two datasets, indicating that the algorithm in this paper is better than other state-of-the-art algorithms.
1. Introduction
The lungs are the primary sites of diseases such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, emphysema, and lung cancer [1,2,3]. In order to be able to obtain the lung lesions of different patients, the corresponding image information can be obtained through X-ray medical imaging technology [4]. CXRs, as a tool for visualization of thoracic cavity tissues, are fast, convenient and simple in technology. CXRs can clearly reveal a large amount of information about lung diseases, improving the basis for accurate diagnosis and treatment. CXRs can help physicians to judge the type and condition of the disease and propose the corresponding treatment plan [5]. Due to the poor diagnostic sensitivity of CXRs, only experienced physicians can analyze and interpret CXRs with time and effort. A typical CXRs analysis process includes the following steps: extracting the region of interest (ROI), extracting the typical features in the ROI, and performing diagnosis based on the typical features [6]. The ROI is the lung region within the bony thorax and its correct identification is a crucial prerequisite. In most cases, the left and right thoraxes are symmetrical. When analyzing the CXRs, the physicians first obtain the lung structure to make an accurate diagnosis. At present, the extraction structure of the lungs is still mainly based on the physician’s experience, and manual marking is the main method. Manual labeling is time-consuming and labor-intensive, which increases the burden on physicians. At the same time, manual labeling has a subjective bias, which is not conducive to discussing the condition between physicians [7]. Therefore, the development of an algorithm for automatic lung segmentation has great clinical application value.
Segmenting lungs is a critical step for diagnosing diseases such as pneumonia, tuberculosis [8]. Many authors have pointed out that segmenting lungs is very important for other processes. The authors of [9] segment lungs before detecting on COVID-19. When the authors of [10] detect rotation in CXRs, they report that poor lung segmentation causes the accuracy of the model to drop rapidly. The authors of [11] propose a technique for the detection of pulmonary abnormalities and show that lung segmentation is a critical step for subsequent classification.
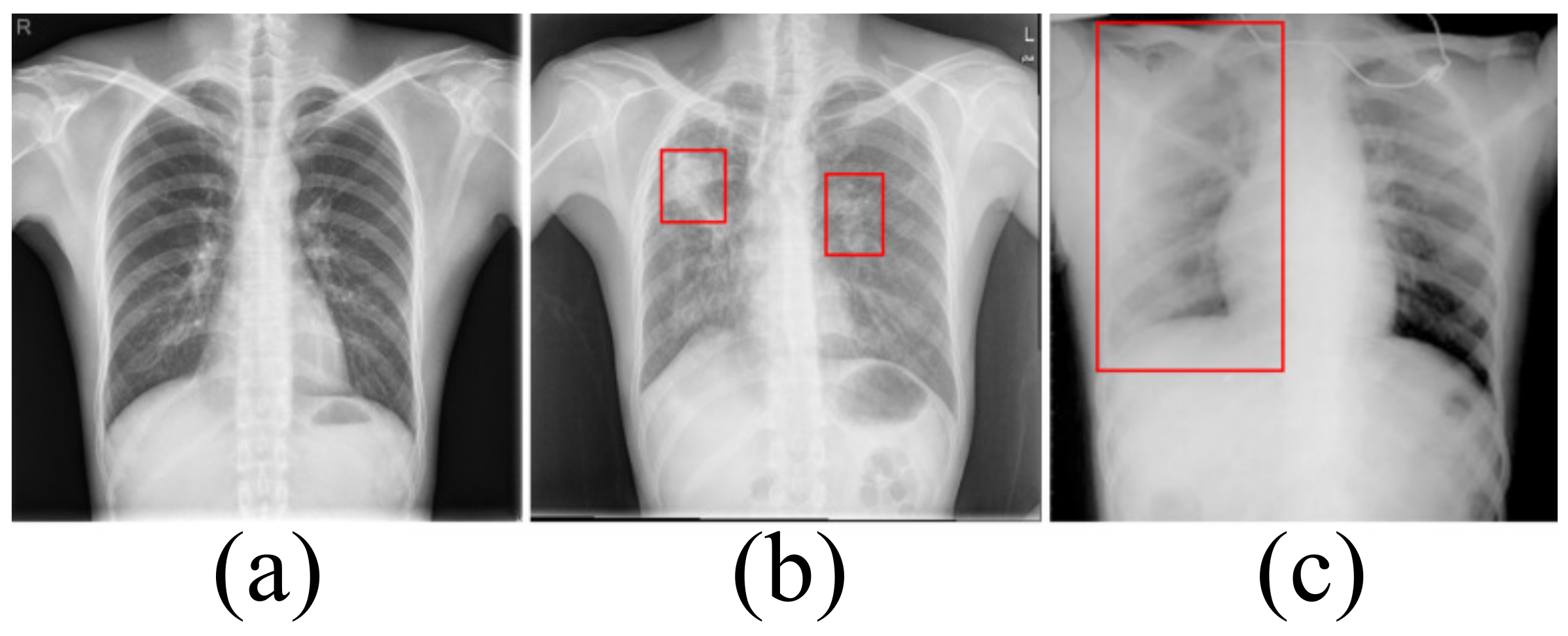
Accurately segmenting the lungs is a challenging image processing task [12]. The lungs have a strong transmittance to X-rays, and the gray value in the corresponding area of CXR is low. The surrounding tissues have low transmittance to X-rays and the gray value in the corresponding area of CXR is high. Figure 1 lists the CXRs of healthy people, patients with a small number of opacities and patients with a large number of opacities. In healthy people’s CXRs, the boundary between the lung and the surrounding tissues is obvious, clear and prominent. There are slight opacities in the lungs of CXRs in patients with a small number of opacities, especially at the edges of the lungs. The slight opacities reduce the contrast between the edge of the lung and the surrounding tissues and make segmentation difficult. For CXRs in patients with a large number of opacities, the boundary between the lungs and surrounding tissues is blurred. To a large extent, it is necessary to rely on the rich experience of physicians to correctly segment the lungs.
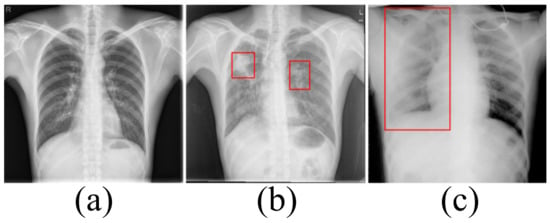
Figure 1.
(a) The chest X-ray image for healthy people. (b) The chest X-ray image in patients with a small number of opacities. (c) The chest X-ray image in patients with a large number of opacities.
Artificial intelligence has made many outstanding achievements in the medical field [13,14]. Algorithms based on artificial intelligence can automatically extract target features and resist the influence of interference such as noise. These algorithms are robust and effective. To overcome the effects of opacities and completely segment the lungs, this paper proposes a new lung segmentation algorithm based on U-Net [15]. Because U-Net can not extract sufficient features from the data affected by opacities, this paper proposes a structure based on the fusion of VAE [16] and convolutional layer. VAE is an effective encoder that fits the distribution of training data and uses resampling to obtain latent spatial characteristics. These latent spatial features as high-level semantic information can effectively promote the segmentation task. the fusion VAE (FVAE) can effectively extract rich features and obtain good segmentation results. In the encoder, the max-pooling indices is recorded during the maximum pooling in the max-pooling step, so that the up-sampling operation of the decoder retains accurate position information. In order to identify useful features from the data interfered by opacities to improve the segmentation effect of the model, this paper proposes a three-terminal attention mechanism. The three-terminal attention mechanism uses the spatial and channel attention mechanism [17] to correct the input features, suppress background noise and highlight the target area. At the same time, the use of high-scale features, which have the characteristics of paying attention to high-level semantics such as position and contour while ignoring information such as noise, improves the network’s ability to locate and recognize targets in low-scale features.
The main contributions of our work can be summarized as follows:
1. In the encoder-decoder structure, this paper introduces VAE into the convolutional layer to improve the ability of the network to extract features. Simultaneously, the network records the max-pooling indices computed in the max-pooling step and uses the he max-pooling indices to perform accurate upsampling during upsampling.
2. This paper proposes a three-terminal attention mechanism. While suppressing background noise and highlighting the target through the attention mechanism, the high-level semantic information of high-scale features is used to improve the network’s ability to locate and recognize target features in low-scale features.
2. Related Work
The ability to extract features automatically has enabled deep learning to achieve satisfactory results in image segmentation tasks. Image semantic segmentation is pixel level. Because the traditional Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) for classification loses image details during convolution and pooling, the feature map size gradually becomes smaller. So it is impossible to indicate which object each pixel belongs to, and achieve accurate segmentation. In order to use CNN for image segmentation tasks, scholars propose different methods.
Long converts the traditional fully connected CNN into a deconvolution layer to achieve end-to-end image segmentation and proposes a Fully convolutional network (FCN) [18]. FCN has become the basic framework of semantic segmentation. FCN has the problem of ignoring advanced semantic information, which leads to the loss of edge information. In order to solve this problem, Kendall proposes SegNet [19] based on FCN. Kendall introduces an encoding-decoding network structure to deep learning for the first time. Compared with FCN, the decoding network in the encoding-decoding network structure uses deconvolution to gradually restore the feature map to the same size as the segmentation result. This decoding process can extract more advanced semantic information, which is conducive to the restoration of detailed information. Downsampling destroys the integrity of high-frequency information. SegNet stores the max-pooling indices computed in the max-pooling step and use the max-pooling indices for upsampling in the decoder. Although the max-pooling indices helps maintain the integrity of high-frequency information, it also ignores neighboring information during upsampling.
Compared with natural images, medical images have regular shapes and simple textures, and it is difficult to obtain a large number of medical images. According to the characteristics of medical images, Ronneberger proposes U-Net [15] with a U-shaped encoding-decoding network structure. The encoder can gradually extract the contextual semantic information of the segmentation target in the entire image through convolution and downsampling. The decoder gradually recovers the detailed information that provides the basis for accurate segmentation and positioning through convolution and upsampling. At the same time, the skip connection transfers the low-level features of the encoder to the decoder to achieve feature fusion and solve the problem of insufficient details of the decoder. Inspired by the application of the attention mechanism in other fields, Oktay proposed AttU-Net [20]. Oktay proposes an attention model and adds it to the end of the jump connection. The attention model makes the network pay more attention to the useful information for the segmentation task, and the segmentation result is more accurate. Zhou introduces nested and dense skip connections to U-Net to enhance the connection between encoder and decoder, and proposes U-Net++ [21]. With the widespread use of U-Net networks, U-Net is combined with other modules to obtain lots of U-Net-based networks, such as R2Unet [22].
Based on the above work, many scholars apply deep learning to the lung segmentation task of CXR images. Inspired by FCN, Hooda proposed VFCN [23] to fuse all the features of the decoder and then directly use two upsampling to restore the output size. Simply upsampling twice cannot effectively extract advanced semantic features, resulting in the same problem as FCN. Mittal [24] introduces the skip connection to SegNet and proposes LF_Seg. In LF_Seg, the features of each layer are not only passed to the next layer, but also fused with the output of the next layer to achieve a dense connection. Inspired by the idea of adversarial networks, Dai [25] introduces a discriminant network into the segmented network and proposes Scan. The discriminant network can learn the physiological structure of the human body in the CXRs and guide the segmentation network to achieve accurate segmentation. For abnormal CXRs, the boundary between the lung and surrounding tissue is not clear. In order to achieve precise segmentation, context information or some immutable hidden features are required. On the one hand, Tang [26] uses Multimodal Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation [27] (MUNIT) to synthesize abnormal CXR images to increase the complexity of training samples. On the other hand, Tang uses Criss-cross Network [28] (CCNet) to extract contextual information. Based on CCNet, Tang proposes the XLSor network. Instead of using the attention mechanism, Selvan attempts to obtain latent spatial features such as thoracic contours to locate the lung area. Selvan [29] proposes VAEU-Net to extract latent spatial features from low-scale features through VAE and improve the segmentation ability of the U-Net network. However, this method of extracting the latent spatial features of low-scale features has limited improvement in the segmentation performance of U-Net. Souza [30] divides the segmentation task into two steps. First, Souza divides the CXRs into image blocks and classifies the image blocks through the classification network to obtain the rough segmentation result. Then Souza uses the reconstruction network to correct the coarse segmentation result and fuses the corrected result with the coarse segmentation result to obtain the lung area. All of the above deep learning algorithms, except XLsor, are trained and tested on simple data sets and are not evaluated on complex data sets.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset
This article uses four public datasets for training and testing: (1) Montgomery dataset [31] includes 138 CXR images with a resolution of 4020 × 4892, where 80 CXR images are from normal patients, and 58 CXR images are from patients with manifested tuberculosis (TB). Segmentation results are divided into left and right lungs; (2) Shenzhen Hospital (SH) dataset [31] includes 662 images, 336 images of which are from unhealthy people. Stirenko et al. provide the segmentation results of this dataset [32]; (3) Tang et al. selecte 100 abnormal CXRs with many opacities in the lung area from the Chest X-Ray dataset to create the Small NIH (SNIH) dataset [26]; (4) The Japanese Society of Radiological Technology(JRST) dataset [33] is released by the Japanese Society of Radiological Technology. It comprises 154 images of patients with lung nodules and 93 images of people without the disease.
We use the Montgomery dataset and Shenzhen Hospital (SH) dataset for training, and then compare the method of this paper with other segmentation methods on the SNIH dataset and the JRST dataset, respectively. For training and testing, we scale the images in the training and test sets to 512 × 512.
Data Enhancement
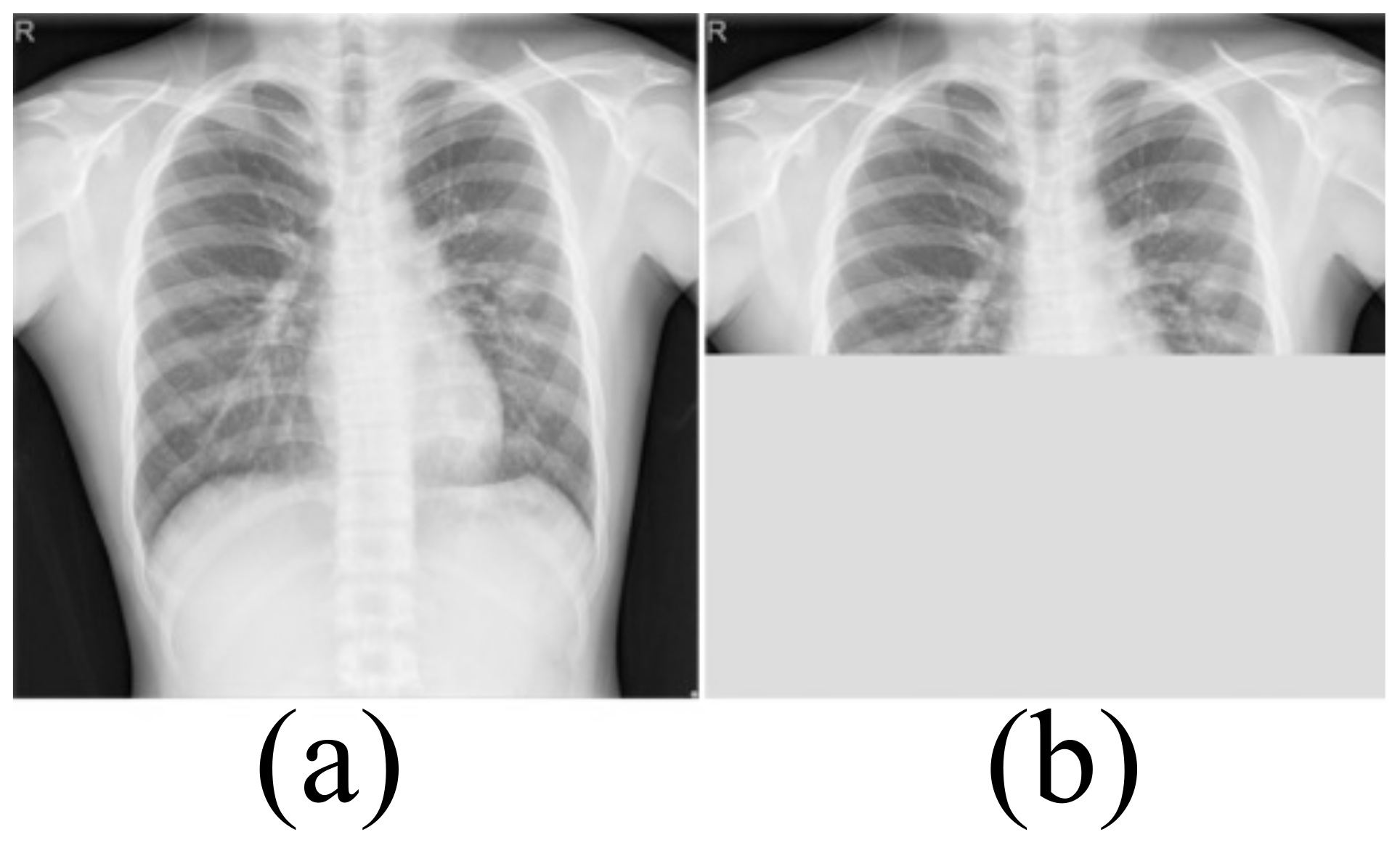
Medical image datasets contain fewer samples and often require data enhancement to increase the number and complexity of training samples. Data enhancement can make the training samples contain the type of test samples as much as possible, and improve the generalization ability of the network. We first perform a horizontal flip of the training sample and a rotation transformation between −20 degrees and 20 degrees with an interval of 5 degrees. These basic transformations can simulate the different postures of the person when doing the examination. The Montgomery dataset and Shenzhen Hospital (SH) dataset only include CXRs of healthy people and patients with moderate pneumonia. In order to simulate the presence of a large number of opacities in the lungs, we use block masking. We think of a large number of opacities in the lungs as missing data. As shown in Figure 2, the block masking simulates the opacities, increasing the complexity and diversity of the samples. If the width of the block masking is equal to the width of the image, the height of the block masking is half or one-third of the image’s height. If the height of the block masking is equal to the height of the image, the width of the block masking is half or one-third of the image’s width.
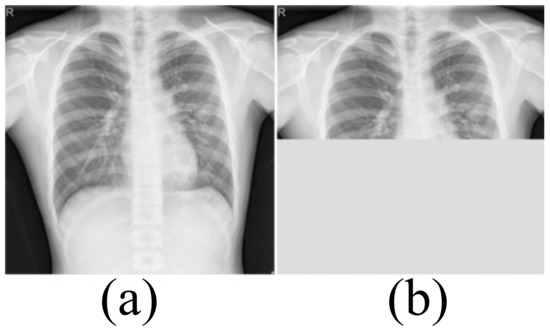
Figure 2.
The block masking. (a) Original image (b) With block masking.
3.2. Model Architecture
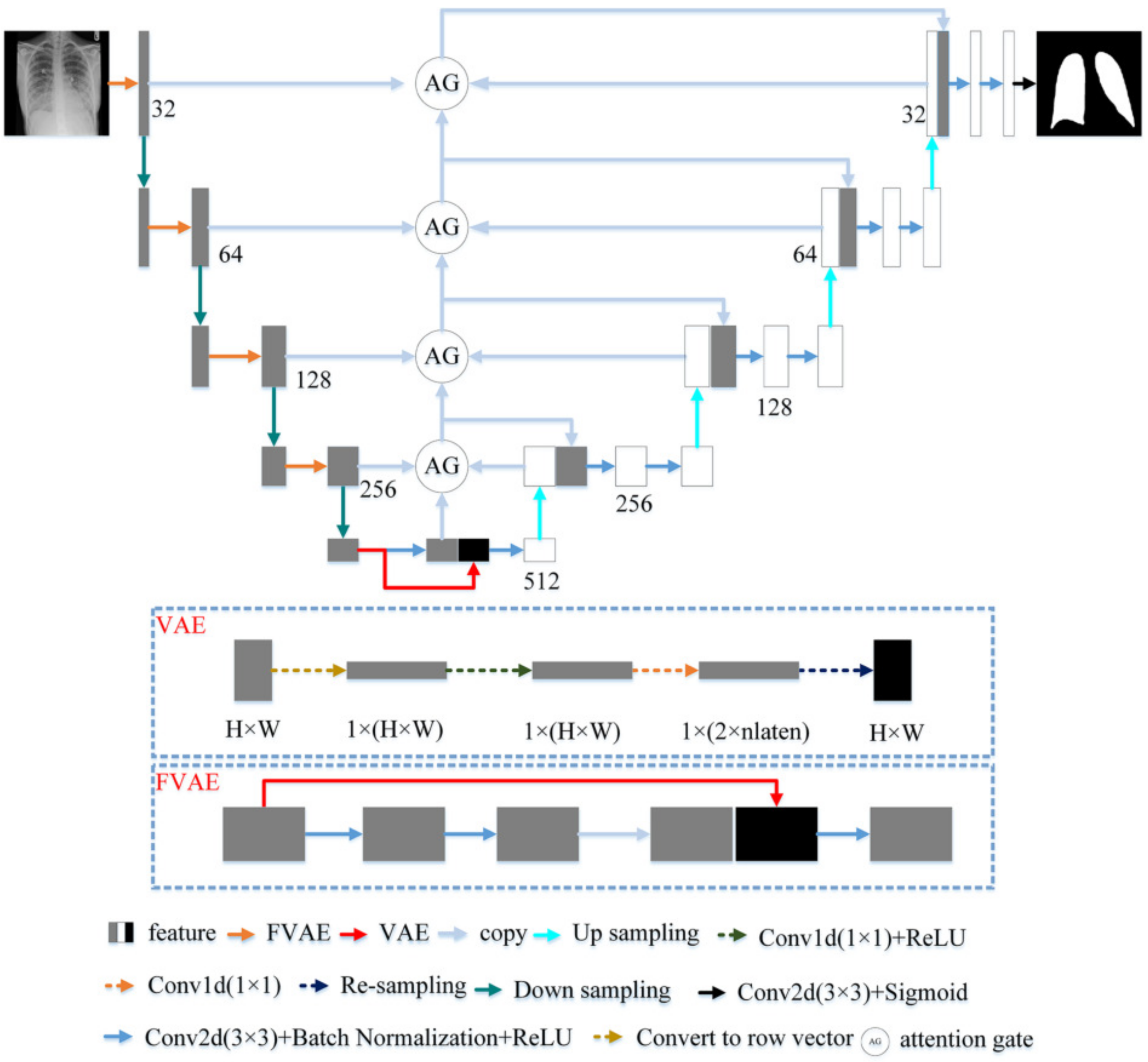
U-Net with a U-shaped structure and jump connection is very suitable for segmenting medical images. This article uses U-Net as the network skeleton. The network architecture of this article is shown in Figure 3. The encoder of the model in this paper includes five layers. The first four layers are composed of FVAE and downsampling. This article uses maximum pooling to down-sampling and records the max-pooling indices computed in the max-pooling step. Compared with the previous four layers, the fifth layer of the encoder consists of two convolutions with a convolution kernel size of 3 × 3 and a stride of 1. Each convolution is followed by Batch Normalization and ReLU. The number of channels of the encoder is a multiple of 32. The decoder of the model in this paper has four layers. Each layer includes two convolutions and the parameter settings of the convolutions are the same as the fifth layer of the encoder. The reverse operation of maximum pooling is used in the decoder for up-sampling. We use the maximum pooling sampling position for accurate up-sampling during upsampling.
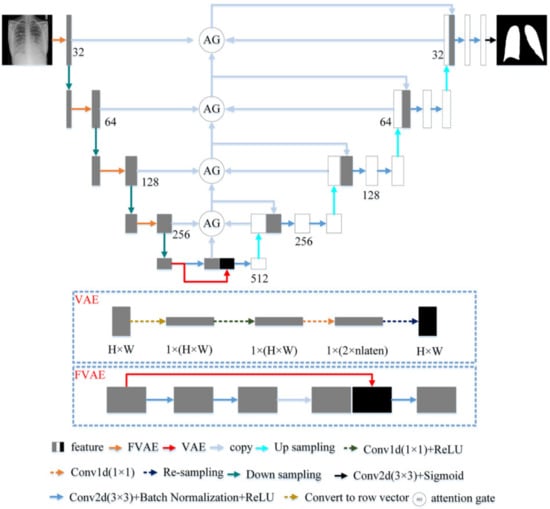
Figure 3.
The proposed architecture.
3.2.1. Fusion Variational Autoencoder
In the encoder, we proposed FVAE to replace the convolutional layer of U-Net. The structure of FVAE is shown in Figure 3. FVAE first includes two convolutions with a convolution kernel size of 3 × 3 and a stride of 1. Each convolution is followed by Batch Normalization and ReLU. After two convolutions, we use VAE to extract features. The structure of VAE is shown in Figure 3. VAE first converts the input features into one-dimensional features, and then performs a convolution with a kernel 1 × 1 and a stride of 1 and ReLU to obtain 2 × parameters. These 2 × are the and of the Gaussian functions. We set to 32. Then VAE obtains the space features through resampling.
High level semantic features , such as the relative position between the left and right lungs and the symmetrical relationship between the left and right thoraxes, are helpful for accurate lung segmentation. In order to effectively learn the features , this paper assumes that the features conform to the Gaussian distribution . For the input , it is not easy to obtain the posterior probability of the feature . VAE combines variational Bayes and neural networks to learn the parameters derived by variational neural networks and then obtains the likelihood of posterior inference . The network can predict the parameters of the Gaussian function. After the parameters of the Gaussian function are obtained, this paper performs resampling in the hidden space as shown in Figure 3 to get the latent space features . Because VAE can obtain rich characteristics, VAE has been widely used in generating networks. For the l-th layer of the encoder, VAE extracts the features by minimizing the posterior probability and the feature distribution function . The optimization objective of a VAE is the evidence lower bound (ELBO) [34,35] by
The is the KL divergence between and . Where represents the input feature.
For U-Net, the convolutional layer of each layer can extract plenty of detailed information related to the task. However, opacities make the background and the target less distinguishable, and the convolutional layers are too few. As a result, U-Net cannot extract sufficient high-level semantic features, such as position and edge information. The segmentation results are not ideal. VAE can obtain high-level semantic information in the data by estimating the data distribution, such as the relative position of the lungs and surrounding organs. This high-level semantic information is beneficial for locating the contours of the lungs and performing accurate segmentation. However, the features extracted by VAE are not refined enough, and a great deal of detailed information is lost. In order to achieve the complementary advantages of the convolutional layer and VAE, we splice the features of the convolutional layer with the features of the VAE. We then use the convolutional layer with a convolution kernel of 3 × 3 to perform feature fusion and channel number shrinking. Through feature fusion, the convolutional layer and VAE can complement each other’s advantages. Therefore, FVAE can extract both detailed information and high-level semantic information, which improves the model’s ability to extract features.
3.2.2. Three-Terminal Attention Mechanism
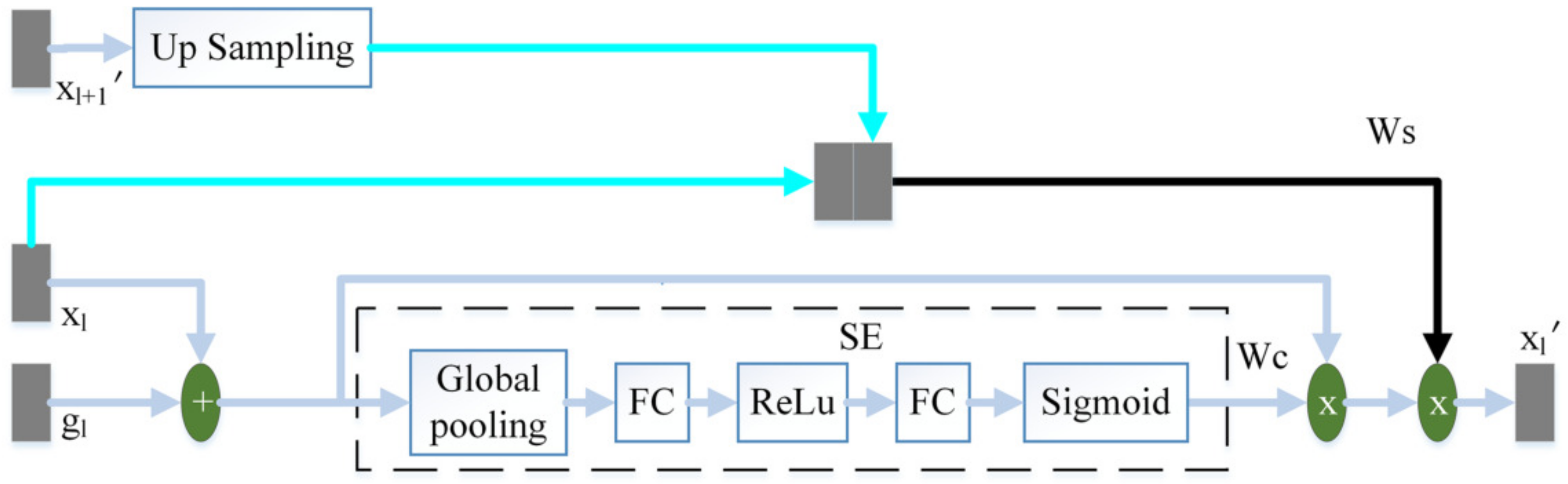
The attention mechanism enables the model to learn where to look and what is essential. The improvement of the attention mechanism has attracted the attention of many scholars. In order to increase the attention to task-related features and reduce the influence of interference information such as background noise during the jump connection, this paper proposes a three-terminal attention mechanism. The structure of the three-terminal attention mechanism is shown in Figure 4.
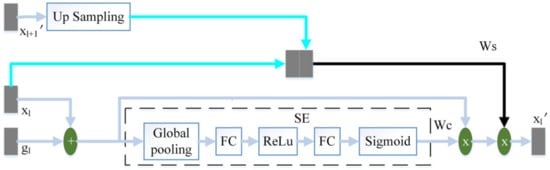
Figure 4.
The schematic diagram of the three-terminal attention mechanism.
The output feature of the l-th layer of the encoder and the output feature of the corresponding layer of the decoder are added to perform feature fusion. Then this article uses the SE module to calculate the channel attention coefficient . The SE module [17] is composed of global pooling (GP), fully connected layer (FC), ReLu and Sigmoid. uses the same two convolutions as the decoder to obtain preliminary features, where the number of channels is 32. We then use a convolution with the number of channels of 1 and the convolution kernel of 3 × 3, and the sigmoid to obtain the spatial attention coefficient . from the output of the adjacent high-scale attention mechanism or the feature of the convolutional layer is up-sampling to obtain the same size as . obtains the spatial attention coefficient in the same way as . and are spliced by channel. We then use a convolution with a convolution kernel size of 3 × 3 and channel number of 1, and sigmoid to perform feature fusion and obtain the final spatial attention coefficient . Finally, the fusion feature of and is multiplied by and to obtain the final output .
The channel attention mechanism captures the interaction between channels in a very light way, effectively increasing the channel’s attention. performs adaptive channel correction on the fusion feature of and by weighting the channels. The spatial attention mechanism can modify features to highlight useful features and weaken useless features. This paper uses to enhance the spatial attention coefficient of and improve the model’s attention to space. The high-scale feature, , contains high-level semantic information. pays more attention to large-scale information such as target contour and location, while ignoring detailed information such as noise. On the one hand, strengthens the model’s attention to the target area. On the other hand, guides the model to suppress interference information such as background noise in .
3.3. Objective Function
For the segmentation task in this paper, we use focal loss () [36] and dice loss () [37] as the loss function. The loss function in this paper, combined with the segmentation task and multi-scale latent space feature extraction task, is defined as:
3.4. Implementation Environment
After data enhancement, we train our model for 500 epochs. The equipment used in all experiments is a PC with an NVIDIA GeForce GTX 2080Ti GPU and Intel Xeon E5 CPU @2.5 GHz. The following hyperparameters are used in the training process of this article and the comparison algorithms: the number of epochs = 500, batch size = 3, = 32. ADAM optimization is used with a learning rate of 0.001. All the implementation is done in PyTorch 1.5.0 platform (https://pytorch.org/ (accessed on 20 January 2021)).
3.5. Evaluation Metrics
During the experiment, we selected the following six evaluation indicators to evaluate the segmentation effect.
1. Accuracy [3]: accuracy reflects the model’s ability to distinguish all samples correctly.
where indicates the number of positive samples correctly classified as positive samples. refers to the number of negative samples correctly classified. is the number of negative samples that are incorrectly classified as positive samples. represents the number of negative samples correctly classified as positive samples.
2. RECALL [3]: recall represents the percentage of correctly classified positive samples to all positive samples.
3. SPECIFICITY [3]: specificity indicates the proportion of negative samples that are correctly classified
4. PRECISION [3]: precision describes the percentage of samples that are classified as positive samples among the correctly classified samples
5. F1-SCORE [3]: when precision is large, recall is small. Precision and recall contradict each other. F1-Score is the arithmetic average of precision and recall and can better evaluate the segmentation effect.
where P represents the precision. R presents the recall.
6. JACCARD [12]: Jaccard measures the similarity between two sets.
For the six evaluation indexes, a large value corresponds to a good segmentation effect. At the same time, this article records and compares the running time.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Algorithms
This article tests the model of this article on the SNIH dataset and the JRST dataset. This paper compares the algorithm in this article with FCN [18], SegNet [19], U-Net [15], AttU-Net [20], LF_Seg [24] and VAEUNet [29] to evaluate the effectiveness and advanced nature of the proposed algorithm. All comparison algorithms adopt the network structure and parameters of the corresponding paper. FCN uses the pre-trained VGG16 as the feature extraction network.
4.1.1. Statistical Results
The statistical results are shown in Table 1 and Table 2. The maximum values of the corresponding index in the tables are marked in bold. As can be seen from Table 1, the ACC, R, SP, P, F1-Score and Jaccard of U-Net are 0.9673, 0.9062, 0.9861, 0.9479, 0.9244 and 0.8344, respectively. These indicators of U-Net are better than those of FCN, SegNet and LF_Seg. Compared with U-Net, AttU-Net introduces the spatial attention mechanism to U-Net. AttU-Net is better than U-Net. VAEU-Net integrates VAE and U-Net to improve the segmentation effect of U-Net. Although VAEU-Net also introduced VAE, it only uses VAE as a part of the last layer of the decoder. VAEU-NET is only higher in ACC than U-Net. The ACC, R, SP, P, F1-Score and Jaccard of our algorithm are 0.9731, 0.9178, 0.9886, 0.9573,0.9358 and 0.8817, respectively. All indicators of our algorithm are better than those of the comparison algorithms. In terms of average running time, our algorithm takes the longest time. The longest time is caused by the complexity of our network structure. The results show that our algorithm achieves the best segmentation effect on the SNIH dataset.

Table 1.
Comparison with other state-of-the-art algorithms on the SNIH dataset.

Table 2.
Comparison with other state-of-the-art algorithms on the JRST dataset.
Table 2 lists the statistical results of different algorithms on the JRST dataset. FCN has the shortest average running time. Except for P, other indicators of FCN are lower than that of other algorithms. For FCN, insufficient detail information in the decoding process leads to poor segmentation results. Compared with FCN, SegNet records the max-pooling indices computed in the max-pooling step and performs accurate upsampling during the upsampling process. The operation makes the segmentation performance of SegNet better than FCN. The SP of SegNet is the maximum value. The ACC, R, SP, P, F1-Score and Jaccard of U-Net are 0.9658, 0.9325, 0.9802, 0.9534, 0.9397 and 0.8915, respectively. UNET’s statistical results are overall better than FCN and SegNet. Compared with U-Net, the indicators of AttU-Net, LF_Seg and VAEU-Net are improved. The P of AttU-Net is the maximum value. The algorithm in this paper achieves the best on ACC R, F1-Score and Jaccard. The SP of our algorithm is second only to the maximum. Although the P of our algorithm is not the highest, F1-Score, a comprehensive indicator of P and R, achieves the best. These indicate that the segmentation effect of our algorithm compared with other algorithms on the JRST dataset is greatly improved.
It can be seen from the above results that the ACC, R, F1-Score and Jaccard of our algorithm achieve the maximum value on both datasets. It shows that our algorithm has better robustness and stability. At the same time, the average running time of our algorithm is also the largest. Adding modules will inevitably increase the amount of calculation. The increase in average running time is expected. The average running time of our algorithm are 44.36 ms and 44.38 ms on the SNIH dataset and the JRST dataset, respectively. The average running time of our algorithm is acceptable in the application.
4.1.2. Segmentation Results
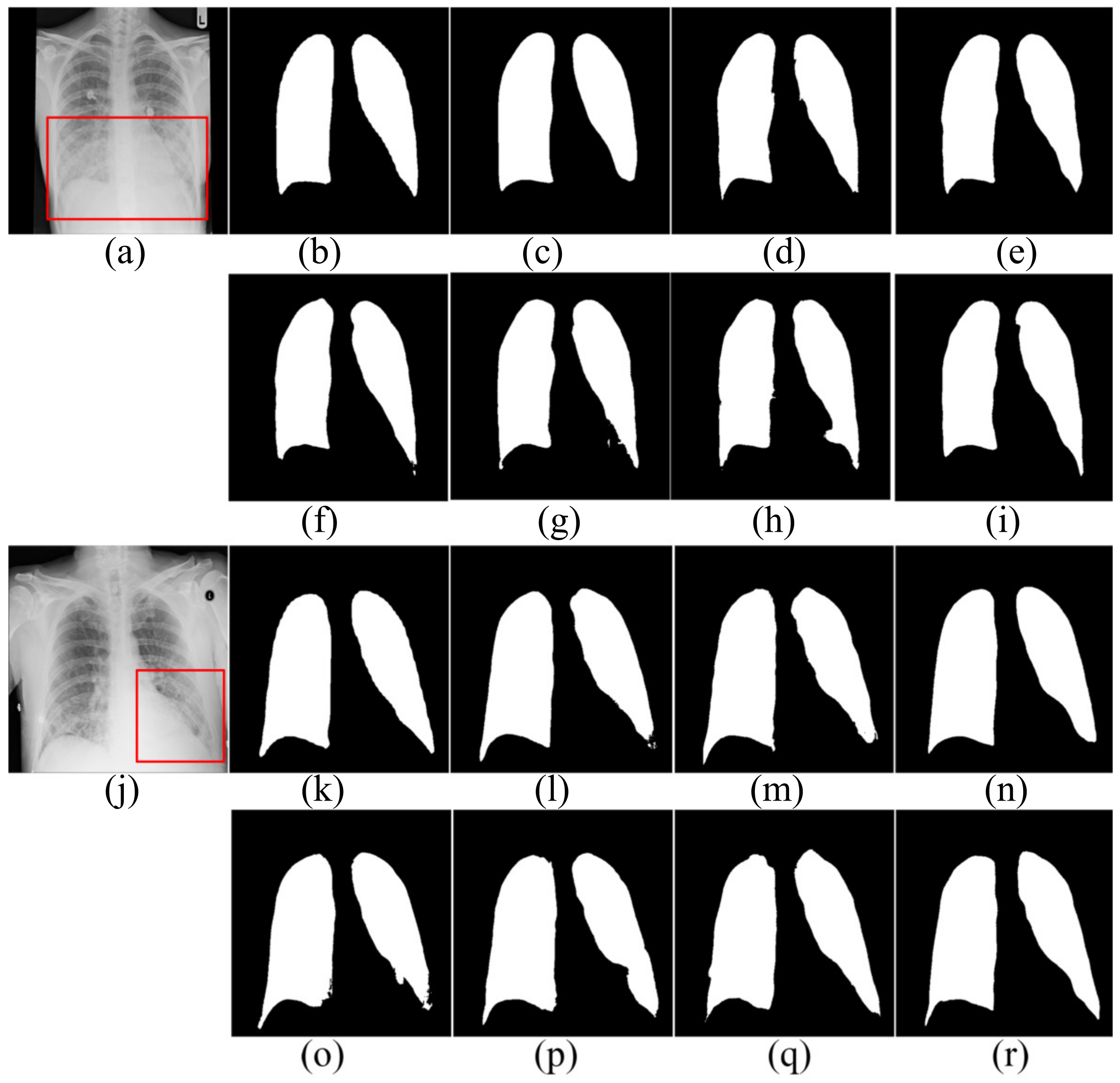
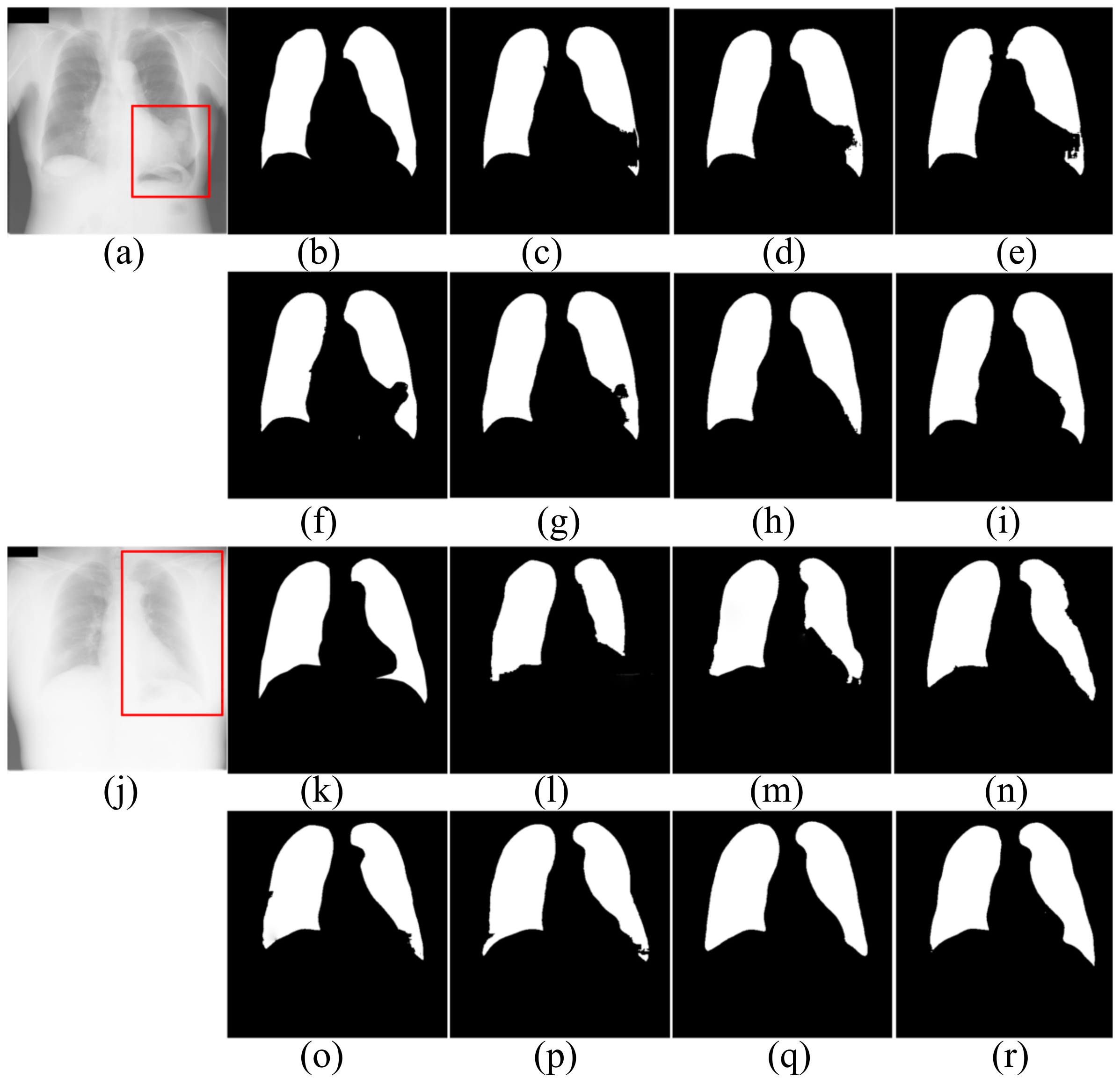
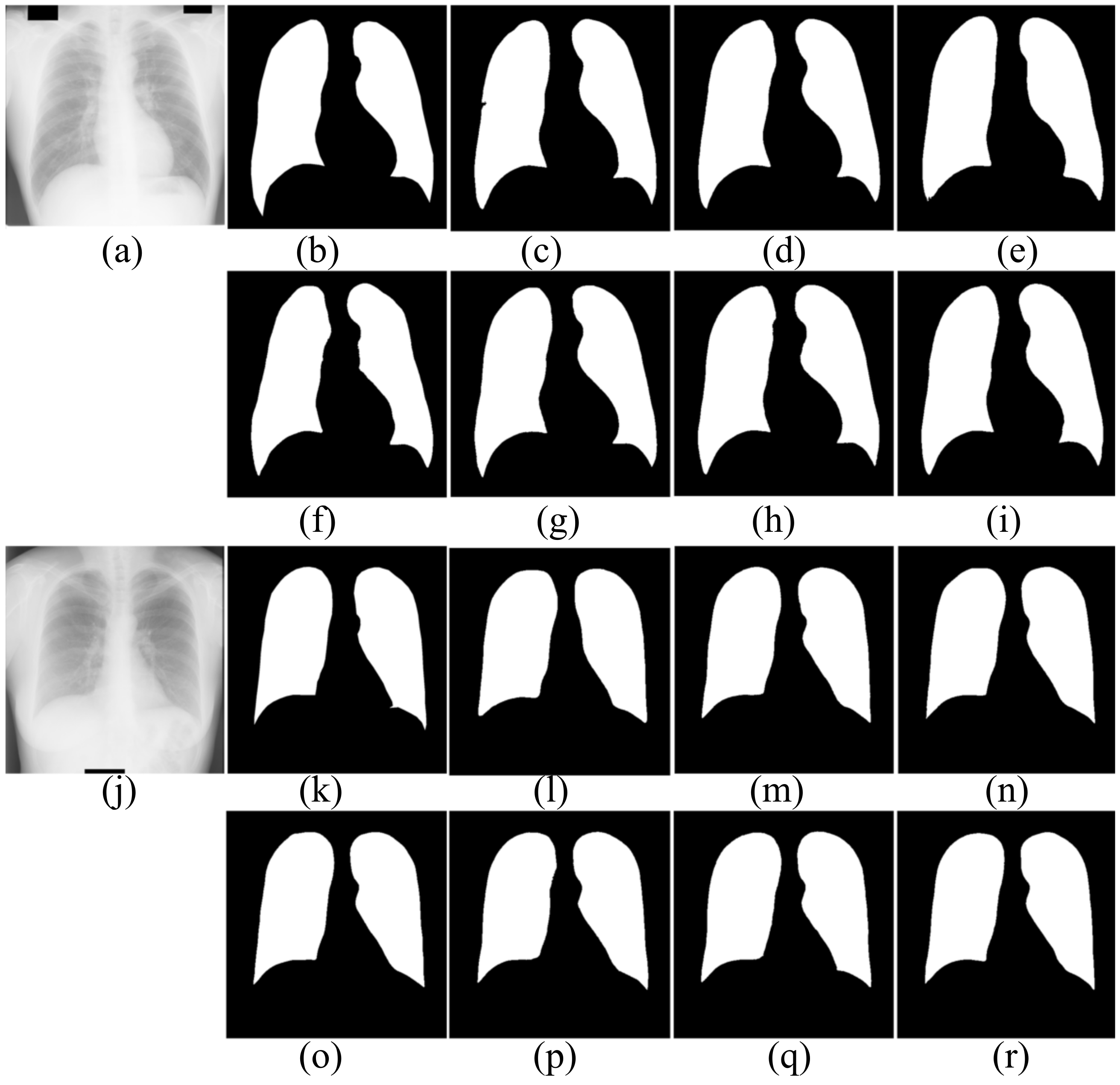
For further comparison, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7 show the segmentation results. Figure 5 and Figure 6 show the CXRS of patients. The red boxes in Figure 5 and Figure 6 are the areas with opacities for comparison. Figure 7 shows the CXRS of healthy people.
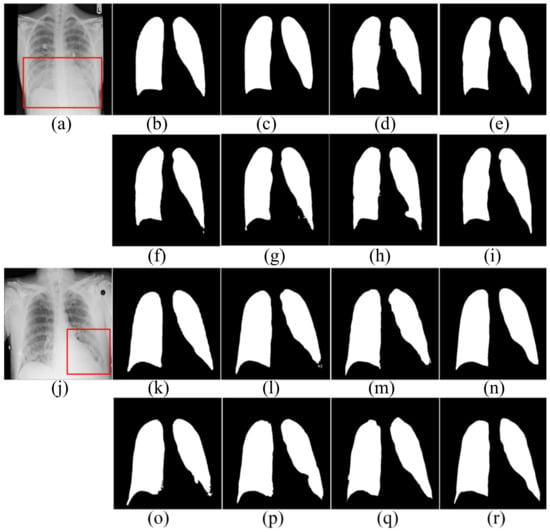
Figure 5.
The segmentation results in the SNIH dataset. (a,j) input images; (b,k) ground truth; (c,l) FCN; (d,m) SegNet; (e,n) U-Net; (f,o) AttU-Net; (g,p) LF_Seg; (h,q) VAEU-Net; (i,r) OUR.
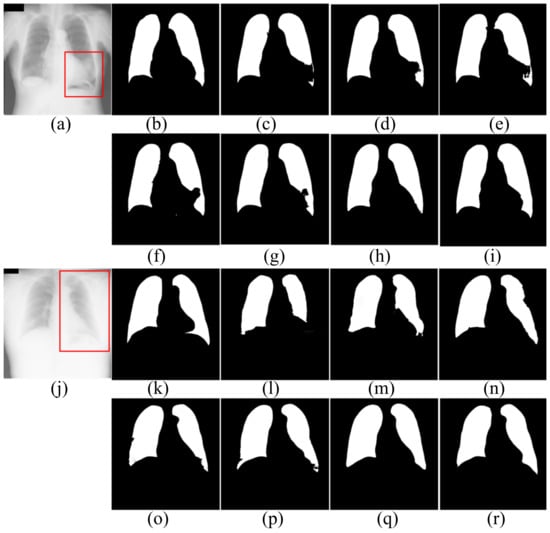
Figure 6.
The segmentation results of patients in JRST dataset. (a,j) input images; (b,k) ground truth; (c,l) FCN; (d,m) SegNet; (e,n) U-Net; (f,o) AttU-Net; (g,p) LF_Seg; (h,q) VAEU-Net; (i,r) OUR.
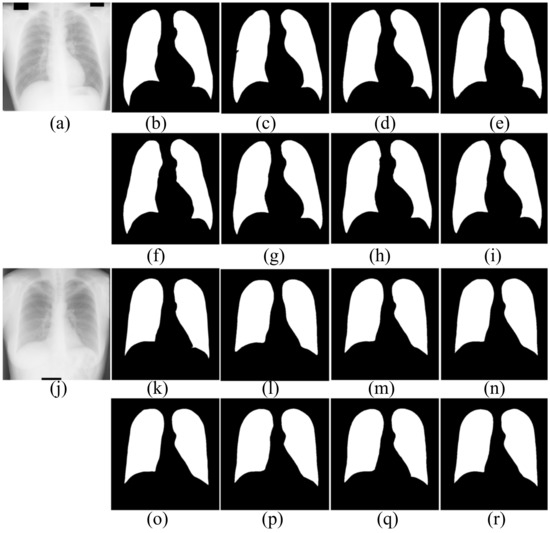
Figure 7.
The segmentation results of healthy people in JRST dataset. (a,j) input images; (b,k) ground truth; (c,l) FCN; (d,m) SegNet; (e,n) U-Net; (f,o) AttU-Net; (g,p) LF_Seg; (h,q) VAEU-Net; (i,r) OUR
The segmentation results on the NIH dataset are shown in Figure 5. There are a lot of opacities at the junction of lung and diaphragm. Opacities make the boundary between the lung and the diaphragm difficult to identify. FCN and SegNet lose a multitude of the details in the decoding process. The lack of detail makes the obtained contours smooth and incorrectly divides the bottom area of the lungs. Since the jump connection makes up for the detailed information in the decoding process, the segmentation accuracy of U-Net is improved to a certain extent. Compared with U-Net, the segmentation results of AttU-Net, LF_Seg and VAEU-Net improve the segmentation results of most regions of the lung, except for the regions that are hard-to-separate. Our algorithm has a strong ability to extract features and overcomes the problem of indistinguishability between the target and the background caused by opacities. Our algorithm achieves the best segmentation effect. For the segmentation results of the left lungs of two patients, the segmentation results obtained by the algorithm in this paper are the most complete among all the algorithms.
The segmentation results of the patient’s CXRs in the JRST dataset are shown in Figure 6. There is a severely blurred area in the left lung of the original image in the first row. The opacity makes the heart and lung tissues indistinguishable. For the area, FCN, SegNet, U-Net, AttU-Net and LFSeg misclassify most of the pixels in this area belonging to the lungs. Except for the bottom of the left lung, the accuracy of VAEU-Net for lungs is very high. Our algorithm not only overcomes the influence of the fuzzy region mentioned before, but also accurately segments the boundary between lung and diaphragm. In the original image on the third line, a large area of the left lung is covered by a large amount of opacities. The boundary between the left lung and surrounding tissue is very blurred. FCN, SegNet and U-Net have poor segmentation effects on the left lung, especially the bottom of the left lung. Although the segmentation results are still incomplete, AttU-Net and LF_Seg improve the the ability to segment the bottom of the lung. VAEU-Net and our algorithm obtain the best segmentation results.
The segmentation results of CXRs for healthy people in the JRST dataset are shown in Figure 7. In the two original images, the boundary between the lung and the surrounding tissue is clearly visible and the contrast is high. The proposed algorithm and other algorithms can achieve good segmentation results. The results are very close to the ground truths. The above results shows that the proposed algorithm and the comparison algorithms can segment the lungs of healthy people very well.
4.1.3. Limitation
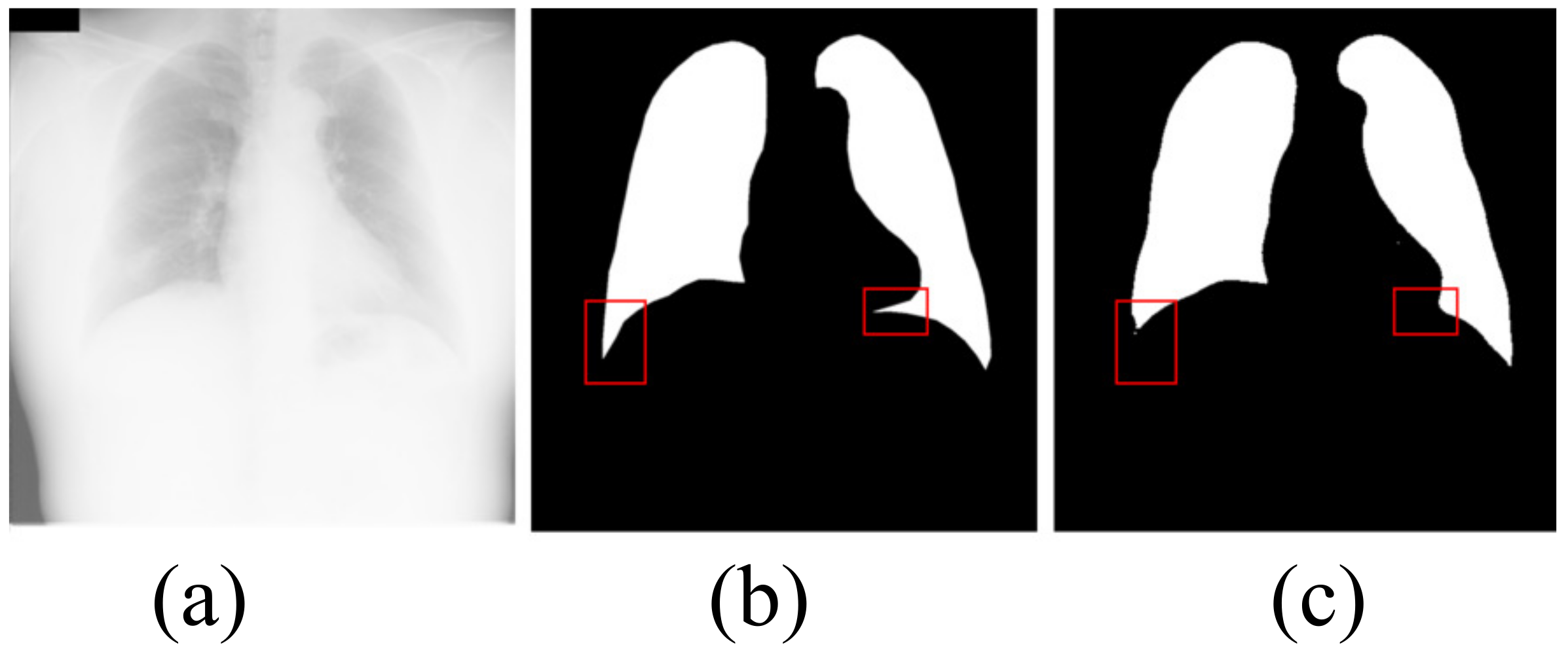
Although our algorithm achieves the best segmentation effect, our algorithm still has some limitations. As shown in Figure 8, the extremely large number of opacities makes it difficult to distinguish between the lung and the diaphragm. Although our algorithm correctly segments most lung regions, our algorithm fails to correctly segment the lung area in the red box. It can be seen that, when there are very many opacities in the lung area, our algorithm fails to correctly identify the local lung area and mistakenly divides part of the lung area into the background. The defect is a problem that we need to work hard to solve in the future.
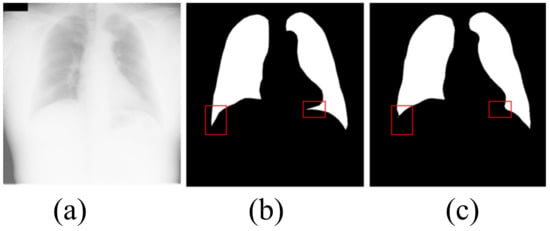
Figure 8.
The shortcoming of the algorithm in this paper. (a) input image; (b) ground truth; (c) OUR.
4.2. Ablation Study
In order to further illustrate that the FVAE and three-terminal attention mechanism proposed in this article have the ability to improve the segmentation effect of U-Net, this article conducts the following comparative experiments. This article compares U-Net, U-Net+FVAE and the algorithm of this article on the NIH dataset and JRST dataset. U-Net+FVAE indicates that FVAE is used to replace the convolutional layer of U-Net.
As shown in Table 3, all indicators of U-Net + FVAE on the two data sets have been significantly improved. Compared with U-Net, the R, P, F1-Score and Jaccard of U-NET + FVAE are improved by about 1% and 2% on the SNIH dataset and the JRST dataset, respectively. These indicate that the introduction of VAE into the convolutional layer in this paper is effective, and the proposed FVAE improves the segmentation performance of the U-Net network.

Table 3.
Comparison with other state-of-the-art algorithms on the SNIH and JRST dataset.
Compared with U-Net + FVAE, the algorithm of this paper, which combines FVAE and the three-terminal attention mechanism, gets a certain improvement in statistical results. The improvement of segmentation performance illustrates the effectiveness and reliability of the three-terminal attention mechanism proposed in this paper.
As FVAE and the three-terminal attention mechanism are gradually added to the U-Net network, the average running time is gradually increasing. It is due to the increase in the number of network parameters. The performance improvement of our algorithm comes at the cost of an increase in average running time. The average running time is still within the acceptable range.
At the same time, this article computes t-test between U-Net and two other algorithms. The results of the t-test show that the p-value is less than 0.05, which is statistically significant. The above results show that the FVAE and three-terminal attention mechanism proposed in this paper can effectively improve the effect of U-Net on lung segmentation in CXRs.
5. Conclusions
Automatic lung segmentation is critical for many subsequent tasks. CXRs of patients with opacities makes it challenging to segment the lungs. To overcome the influence of opacities, this paper proposes a new segmentation algorithm based on U-Net. In order to solve the insufficient feature extraction ability of U-Net when segmenting lungs in CXRs with opacities, this paper introduces VAE into the convolution layer and proposes FVAE. By combining the features of the convolutional layer with the features of the VAE, FVAE can simultaneously obtain detailed local information and global information, thereby improving the ability of the model to extract features. Because opacities weaken U-Net’s ability to locate and recognize the edges of the lungs, this paper proposes a three-terminal attention mechanism. Through the channel attention mechanism and the spatial attention mechanism modified by high-scale features, the three-terminal attention mechanism enhances the ability of the network to locate and recognize targets, and improves the segmentation performance of the model. By testing on the SNIH and JRST datasets, the ACC, R and F1-Score values of our algorithm are the best. The algorithm in this paper can completely segment the lungs in CXRs of healthy people. Our algorithm can still achieve the best segmentation effect for CXRs with varying degrees of opacities. Simultaneously, through the ablation study, it is verified that FVAE and the three-terminal attention mechanism can improve the segmentation performance of U-Net. Our future work will further improve the algorithm of this paper and solve the problem that local areas are difficult to segment when there is a large number of opacities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.C.; methodology, F.C.; software, F.C.; validation, F.C.; formal analysis, F.C.; investigation, F.C.; data curation, F.C.; writing—original draft preparation, F.C.; writing—review and editing, F.C.; visualization, F.C.; supervision, H.Z.; funding acquisition, H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by The National Natural Science Foundation of China grant number 62041302.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The analysed datasets are publicly available. Related references are reported in the References section.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| VAE | variational auto-encoder |
| FVAE | fusin variational auto-encoder |
References
- Rigby, D.M.; Hacking, L. Interpreting the chest radiograph. Anaesth Intensive Care 2018, 19, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilham, A.; Ginneken, B.; Loog, M. A computer- aided diagnosis system for detection of lung nodules in chest radiographs with an evaluation on a public database. Med. Image Anal. 2006, 10, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Hooda, R.; Sofat, S. Lung field segmentation in chest radiographs: A historical review, current status, and expectations from deep learning. IET Image Process 2017, 11, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoof, S.; Feigin, D.; Sung, A.; Irugulpati, L.; Rosenow, E.C. Interpretation of Plain Chest Roentgenogram. Chest 2012, 141, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reamaroon, N.; Sjoding, M.W.; Derksen, H.; Sabeti, E.; Najarian, K. Robust segmentation of lung in chest X-ray: Applications in analysis of acute respiratory distress syndrome. BMC Med. Imaging 2020, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candemir, S.; Antani, S. A review on lung boundary detection in chest X-rays. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019, 14, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, A.P. Error and discrepancy in radiology: Inevitable or avoidable? Insights Imaging 2016, 8, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, K. Computer-aided diagnosis in medical imaging: Historical review, current status and future potential. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2007, 31, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajinikanth, V.; Dey, N.; Raj, A.N.J.; Hassanien, A.E.; Santosh, K.C.; Raja, N. Harmony-search and otsu based system for coronavirus disease (COVID-19) detection using lung CT scan images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.03431. [Google Scholar]
- Zohora, F.T.; Santosh, K.C. Foreign circular element detection in chest X-rays for effective automated pulmonary abnormality screening. Int. J. Comput. Vis. Image Process. (IJCVIP) 2017, 7, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosh, K.C.; Vajda, S.; Antani, S.; Thoma, G.R. Edge map analysis in chest X-rays for automatic pulmonary abnormality screening. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2016, 9, 1637–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosdelekidis, V.; Ioakeimidis, N.S. Lung Field Segmentation in Chest X-rays: A Deformation-Tolerant Procedure Based on the Approximation of Rib Cage Seed Points. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlol, A.T.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Tariq, J.A.; Damaševičius, R.; Farouk, H.O. A novel method for detection of tuberculosis in chest radiographs using artificial ecosystem-based optimisation of deep neural network features. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifi, A.; Hafsa, N.E.; Ali, M.A.; Alhumam, A.; Alsalman, S. An Ensemble of Global and Local-Attention Based Convolutional Neural Networks for COVID-19 Diagnosis on Chest X-ray Images. Symmetry 2021, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-encoding variational bayes. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Banff, AB, Canada, 14–16 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 8–10 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention U-Net: Learning Where to Look for the Pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 4th Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis (DLMIA) Workshop, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Alom, M.Z.; Yakopcic, C.; Hasan, M. Recurrent residual U-Net for medical image segmentation. J. Med. Imaging 2019, 6, 014006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooda, R.; Mittal, A.; Sofat, S. An efficient variant of fully-convolutional network for segmenting lung fields from chest radiographs. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2018, 101, 1559–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Hooda, R.; Sofat, S. LF-SegNet: A fully convolutional encoder-decoder network for segmenting lung fields from chest radiographs. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2013, 101, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Doyle, J.; Liang, X.; Zhang, H.; Dong, N.; Li, Y.; Xing, E.P. Scan: Structure correcting adversarial network for organ segmentation in chest X-rays. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.08770. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Summers, R.M. XLSor: A robust and accurate lung segmentor on chest X-rays using criss-cross attention and customized radiorealistic abnormalities generation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.09229. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Liu, M.Y.; Belongie, S.; Jan, K. Multimodal unsupervised image-to-image translation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 172–189. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W.C. Ccnet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 603–612. [Google Scholar]
- Selvan, R.; Dam, E.B.; Rischel, S.; Sheng, K.; Nielsen, M.; Pai, A. Lung Segmentation from Chest X-rays using Variational Data Imputation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.10052. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, J.C.; Diniz, J.; Ferreira, J.L.; Silva, G.; Paiva, A. An automatic method for lung segmentation and reconstruction in chest x-ray using deep neural networks. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 177, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, S.; Candemir, S.; Antani, S.; Wang, Y.X.J.; Lu, P.X.; Thoma, G. Two public chest X-ray datasets for computer-aided screening of pulmonary diseases. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2014, 4, 475. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger, S.; Karargyris, A.; Candemir, S.; Folio, L.; Siegelman, J.; Callaghan, F.; McDonald, C. Automatic tuberculosis screening using chest radiographs. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2014, 33, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiraishi, J.; Katsuragawa, S.; Ikezoe, J.; Matsumoto, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Komatsu, K.I.; Doi, K. Development of a digital image database for chest radiographs with and without a lung nodule: Receiver operating characteristic analysis of radiologists’ detection of pulmonary nodules. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 174, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazabal, A.; Olmos, P.M.; Ghahramani, Z.; Valera, I. Handling incomplete heterogeneous data using vaes. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 107, 107501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S.A.V. V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision, Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2015; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).