A Generalization of the Importance of Vertices for an Undirected Weighted Graph †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Basic Definitions
Graphs
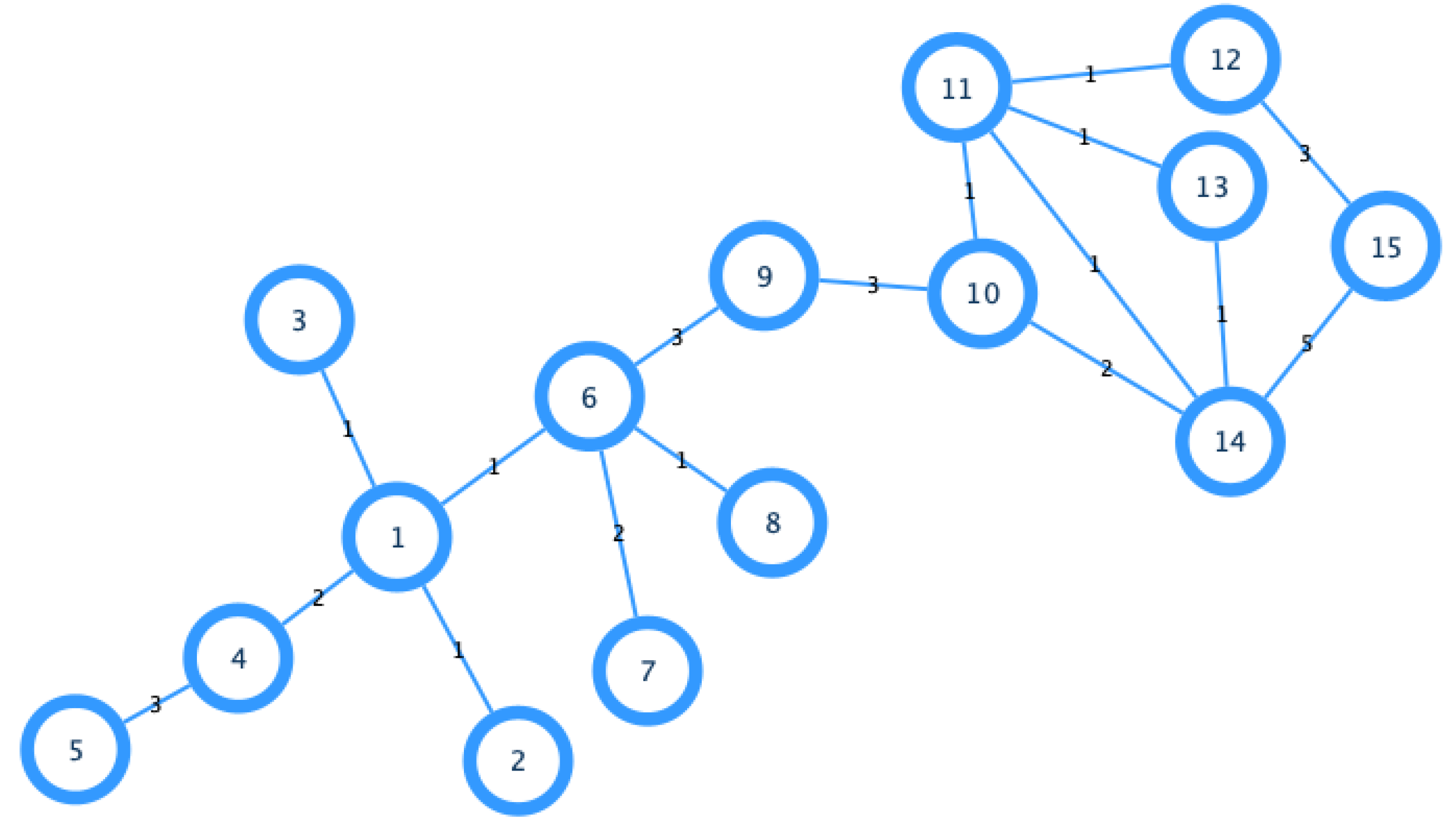
3. Measuring Vertex Importance on an Undirected Weighted Graph
4. Comparison and Analysis Results
4.1. Data and Source Code
4.2. Evaluation
4.3. Ranking DIL-W for Different Values of
4.4. Computational Complexity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newman, M. The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Rev. 2003, 45, 167–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almasi, S.; Hu, T. Measuring the importance of vertices in the weighted human disease network. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0205936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, X.L.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.Z.; Zhang, J.G. Synchronization analysis of complex networks with multi-weights and its application in public traffic network. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2014, 412, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manríquez, R.; Guerrero-Nancuante, C.; Martínez, F.; Taramasco, C. Spread of Epidemic Disease on Edge-Weighted Graphs from a Database: A Case Study of COVID-19. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossley, N.; Mechelli, A.; Vértes, P.; Winton-Brown, T.; Patel, A.; Ginestet, C.; McGuire, P.; Bullmore, E. Cognitive relevance of the community structure of the human brain functional coactivation network. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11583–11588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Cao, Y.; Bao, Z.Y.; Han, Z.X. A novel local-world evolving network model for power grid. Acta Phys. Sin. 2009, 6, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Montenegro, E.; Cabrera, E.; González, J.; Manríquez, R. Linear representation of a graph. Bol. Soc. Parana. Matemática 2019, 37, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pastor-Satorras, R.; Vespignani, A. Epidemic Spreading in Scale-Free Networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 3200–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lü, L.; Chen, D.; Ren, X.L.; Zhang, Q.M.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhou, T. Vital nodes identification in complex networks. Phys. Rep. 2016, 650, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinterbo, S.A. Privacy: A machine learning view. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2004, 16, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Lun, L. Node Importance Ranking of Complex Network based on Degree and Network Density. Int. J. Perform. Eng. 2019, 15, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiong, Q.; Shi, W.; Shi, X.; Wang, K. Evaluating the importance of nodes in complex networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2016, 452, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saxena, C.; Doja, M.N.; Ahmad, T. Group based centrality for immunization of complex networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 508, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magelinski, T.; Bartulovic, M.; Carley, K.M. Measuring Node Contribution to Community Structure with Modularity Vitality. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 8, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalmane, Z.; Hassouni, M.E.; Cherifi, H. Immunization of networks with non-overlapping community structure. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2019, 9, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghalmane, Z.; Cherifi, C.; Cherifi, H.; Hassouni, M.E. Centrality in complex networks with overlapping community structure. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, N.; Singh, A.; Cherifi, H. Community-based immunization strategies for epidemic control. In Proceedings of the 2015 7th International Conference on Communication Systems and Networks (COMSNETS), Bangalore, India, 6–10 January 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.W.; Rong, L.; Guo, T.Z. A new measure method of network node importance based on local characteristics. J. Dalian Univ. Technol. 2010, 50, 822–826. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Shao, F.; Liu, J.; Guo, Q.; Wang, B.H. Node importance measurement based on the degree and clustering coefficient information. Acta Phys. Sin. 2013, 62, 128901. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Y.; Kou, T. A novel method to evaluate node importance in complex networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 526, 121118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Yan, B.; Guo, J. Improved method of node importance evaluation based on node contraction in complex networks. Procedia Eng. 2011, 15, 1600–1604. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, H.; Deng, Y. Identifying node importance based on evidence theory in complex networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 529, 121538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrat, A.; Barthelemy, M.; Pastor-Satorras, R.; Vespignani, A. The architecture of complex weighted networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3747–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lü, L.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Q.M.; Stanley, H.E. The H-index of a network node and its relation to degree and coreness. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garas, A.; Schweitzer, F.; Havlin, S. A k-shell decomposition method for weighted networks. New J. Phys. 2012, 14, 083030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Liu, J.; Wei, D.; Gao, C.; Deng, Y. Weighted k-shell decomposition for complex networks based on potential edge weights. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2015, 420, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M. Scientific collaboration networks. II. Shortest paths, weighted networks, and centrality. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 016132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brandes, U. A faster algorithm for betweenness centrality. J. Math. Sociol. 2001, 25, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Q.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, T.; Wang, B.H.; Yin, B.Q. Power-law strength-degree correlation from resource-allocation dynamics on weighted networks. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 75, 021102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Opsahl, T.; Agneessens, F.; Skvoretz, J. Node centrality in weighted networks: Generalizing degree and shortest paths. Soc. Netw. 2010, 32, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, G.; Xie, J. Mining important nodes in directed weighted complex networks. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2017, 2017, 9741824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Fuller, E.; Wu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.Q. Laplacian centrality: A new centrality measure for weighted networks. Inf. Sci. 2012, 194, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Song, C.; Ding, W.; Ma, J.; Dong, J.; Huang, L. Research on the node importance of a weighted network based on the k-order propagation number algorithm. Entropy 2020, 22, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, T.; Bhatt, A. HWSMCB: A community-based hybrid approach for identifying influential nodes in the social network. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2020, 545, 123590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skibski, O.; Rahwan, T.; Michalak, T.; Yokoo, M. Attachment centrality: Measure for connectivity in networks. Artif. Intell. 2019, 274, 151–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnowska, J.; Skibski, O. Attachment Centrality for Weighted Graphs. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-17), Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 August 2017; pp. 416–422. [Google Scholar]
- Chartrand, G.; Lesniak, L. Graphs and Digraphs, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- West, D.B. Introduction to Graph Theory, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Musial, K.; Juszczyszyn, K. Properties of bridge nodes in social networks. In International Conference on Computational Collective Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 357–364. [Google Scholar]
- Zachary, W.W. An Information Flow Model for Conflict and Fission in Small Groups. J. Anthropol. Res. 1977, 33, 452–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colizza, V.; Pastor-Satorras, R.; Vespignani, A. Reaction–diffusion processes and metapopulation models in heterogeneous networks. Nat. Phys. 2007, 3, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mersch, D.P.; Crespi, A.; Keller, L. Tracking individuals shows spatial fidelity is a key regulator of ant social organization. Science 2013, 340, 1090–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Firth, J.A.; Sheldon, B.C. Experimental manipulation of avian social structure reveals segregation is carried over across contexts. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20142350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, R.; Ahmed, N.K. The Network Data Repository with Interactive Graph Analytics and Visualization. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Latora, V.; Nicosia, V.; Russo, G. Complex Networks: Principles, Methods and Applications, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rubinov, M.; Sporns, O. Complex network measures of brain connectivity: Uses and interpretations. NeuroImage 2010, 52, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latora, V.; Marchiori, M. Efficient Behavior of Small-World Networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 198701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, Y.; Motter, A.; Nishikawa, T. Attacks and cascades in complex networks. In Complex Networks; Lecture Notes in Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 650. [Google Scholar]
- Sciarra, C.; Chiarotti, G.; Laio, F.; Ridolfi, L. A change of perspective in network centrality. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Wild Birds Network | US Air Transport Network | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIL-W | DIL-W | DIL-W | DIL-W | |
| Ranking Position | ID | ID | ID | ID |
| 1 | 12 | 12 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 27 | 27 | 3 | 3 |
| 3 | 23 | 23 | 6 | 6 |
| 4 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 5 | 35 | 35 | 14 | 14 |
| 6 | 77 | 77 | 7 | 5 |
| 7 | 25 | 25 | 5 | 7 |
| 8 | 51 | 51 | 4 | 4 |
| 9 | 26 | 26 | 8 | 8 |
| 10 | 94 | 94 | 2 | 2 |
| 11 | 6 | 6 | 12 | 12 |
| 12 | 56 | 56 | 11 | 11 |
| 13 | 61 | 61 | 13 | 13 |
| 14 | 11 | 11 | 21 | 21 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manríquez, R.; Guerrero-Nancuante, C.; Martínez, F.; Taramasco, C. A Generalization of the Importance of Vertices for an Undirected Weighted Graph. Symmetry 2021, 13, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13050902
Manríquez R, Guerrero-Nancuante C, Martínez F, Taramasco C. A Generalization of the Importance of Vertices for an Undirected Weighted Graph. Symmetry. 2021; 13(5):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13050902
Chicago/Turabian StyleManríquez, Ronald, Camilo Guerrero-Nancuante, Felipe Martínez, and Carla Taramasco. 2021. "A Generalization of the Importance of Vertices for an Undirected Weighted Graph" Symmetry 13, no. 5: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13050902
APA StyleManríquez, R., Guerrero-Nancuante, C., Martínez, F., & Taramasco, C. (2021). A Generalization of the Importance of Vertices for an Undirected Weighted Graph. Symmetry, 13(5), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13050902







