Longitudinal Observation of Asymmetric Iron Deposition in an Intracerebral Hemorrhage Model Using Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Intracerebral Hemorrhage
1.2. Imaging Techniques for ICH
1.3. QSM
2. Materials and Methods
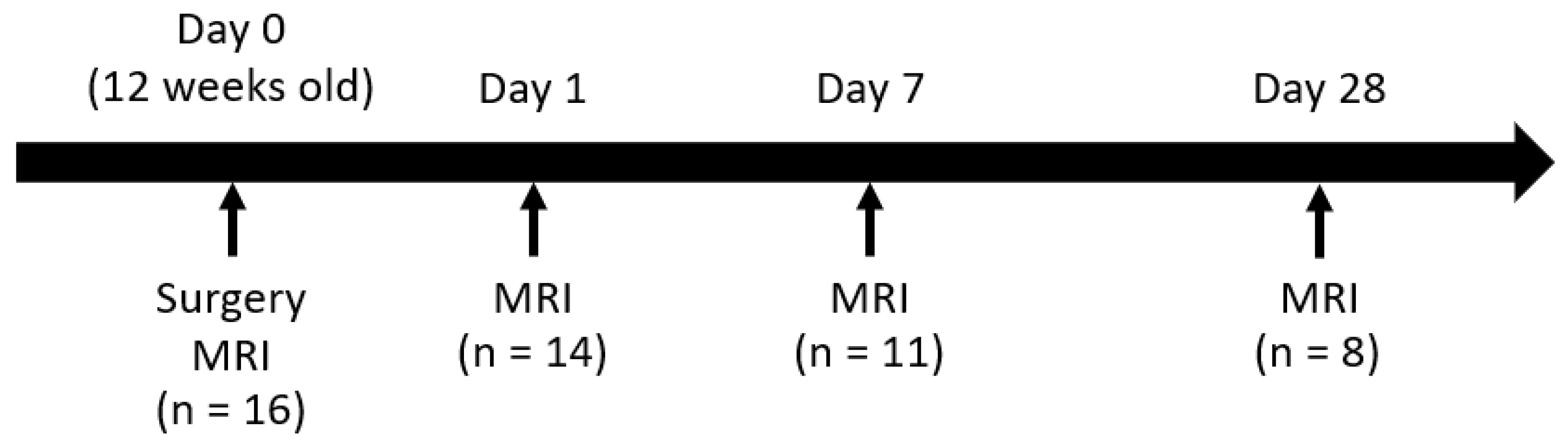
2.1. Animals
2.2. ICH Models
2.3. MRI
2.4. MRI Analysis
2.5. Histological Studies
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. MRI Observation
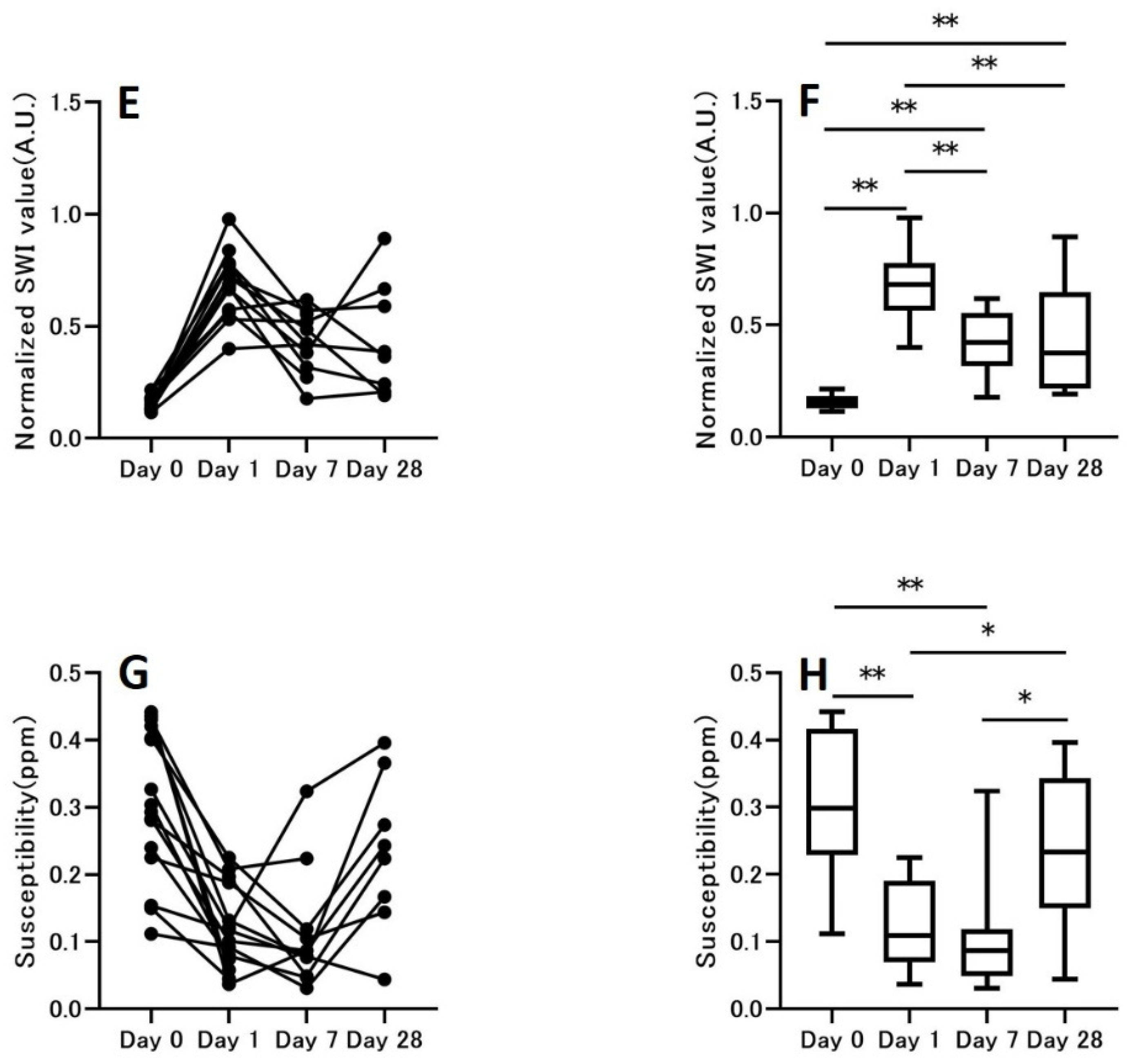
3.2. Hemorrhage Signal
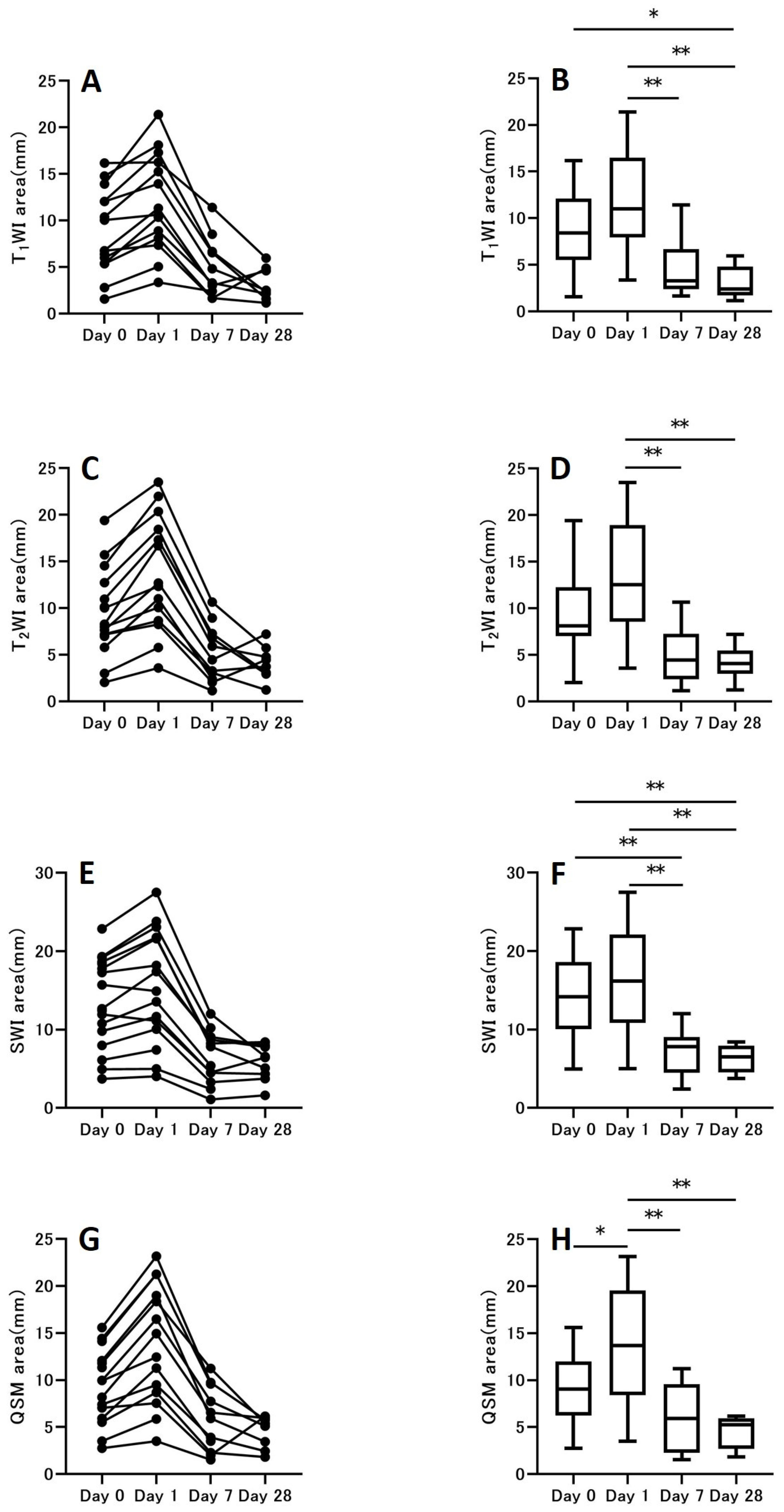
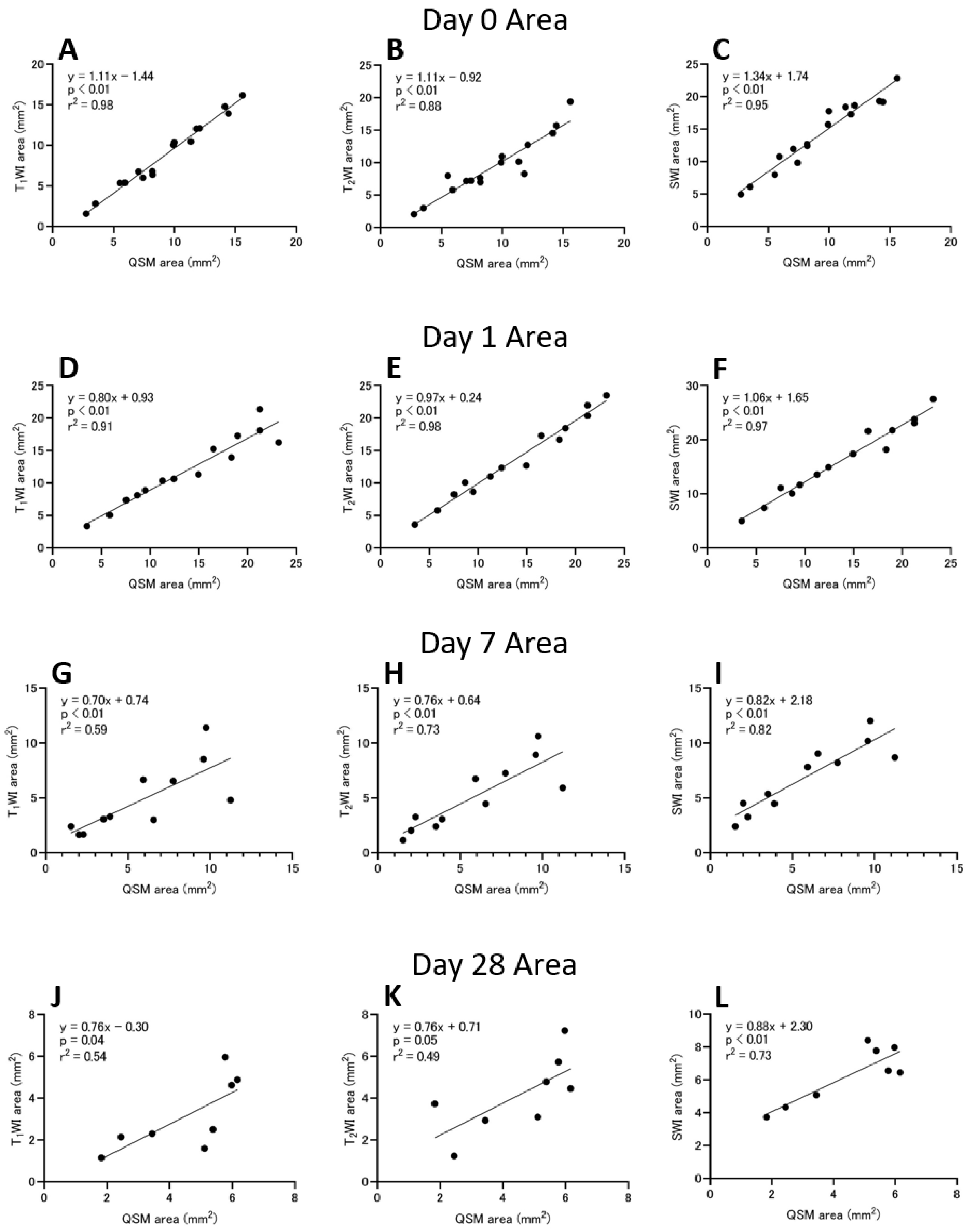
3.3. Hemorrhage Area
3.4. Histological Studies
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Previous Studies of ICH Models
4.2. Contrast Mechanism of Bleeding
4.3. ICH Area
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Lawes, C.M.; Bennett, D.A.; Barker-Collo, S.L.; Parag, V. Worldwide stroke incidence and early case fatality reported in 56 population-based studies: A systematic review. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, S.; Totaro, R.; Toni, D.; Marini, C.; Cerone, D.; Carolei, A. Incidence, case-fatalities and 10-year survival of subarachnoid hemorrhage in a population-based registry. Eur. Neurol. 2009, 62, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keep, R.F.; Hua, Y.; Xi, G. Intracerebral haemorrhage: Mechanisms of injury and therapeutic targets. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, G.; Keep, R.F.; Hoff, J.T. Mechanisms of brain injury after intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.Y.; Wang, J.; Qian, Z.M.; Yang, Q.W. Iron and intracerebral hemorrhage: From mechanism to translation. Transl. Stroke Res. 2014, 5, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.Y.; Yang, Q.W. Rethinking the roles of inflammation in the intracerebral hemorrhage. Transl. Stroke Res. 2015, 6, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selim, M.; Sheth, K.N. Perihematoma edema: A potential translational target in intracerebral hemorrhage? Transl. Stroke Res. 2015, 6, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, S.; Hua, Y.; Keep, R.F.; Hoff, J.T.; Xi, G. A new hippocampal model for examining intracerebral hemorrhage-related neuronal death: Effects of deferoxamine on hemoglobin-induced neuronal death. Stroke 2007, 38, 2861–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua, Y.; Schallert, T.; Keep, R.F.; Wu, J.; Hoff, J.T.; Xi, G. Behavioral tests after intracerebral hemorrhage in the rat. Stroke 2002, 33, 2478–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, G.; Keep, R.F.; Hoff, J.T. Erythrocytes and delayed brain edema formation following intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 89, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkman, M.A.; Allan, S.M.; Parry-Jones, A.R. Experimental intracerebral hemorrhage: Avoiding pitfalls in translational research. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2011, 31, 2135–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weingarten, K.; Zimmerman, R.D.; Deo-Narine, V.; Markisz, J.; Cahill, P.T.; Deck, M.D. MR imaging of acute intracranial hemorrhage: Findings on sequential spin-echo and gradient-echo images in a dog model. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1991, 12, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hakimi, R.; Garg, A. Imaging of Hemorrhagic Stroke. Continuum 2016, 22, 1424–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta-Cabronero, J.; Williams, G.B.; Cardenas-Blanco, A.; Arnold, R.J.; Lupson, V.; Nestor, P.J. In vivo quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gauthier, S.A.; Gupta, A.; Comunale, J.; Liu, T.; Wang, S.; Pei, M.; Pitt, D.; Wang, Y. Quantitative susceptibility mapping of multiple sclerosis lesions at various ages. Radiology 2014, 271, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eskreis-Winkler, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Dimov, A.; Gupta, A.; Wang, Y. The clinical utility of QSM: Disease diagnosis, medical management, and surgical planning. NMR Biomed. 2017, 30, e3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Kakeda, S.; Watanabe, K.; Ueda, I.; Ogasawara, A.; Moriya, J.; Ide, S.; Futatsuya, K.; Sato, T.; Okada, K.; et al. Usefulness of quantitative susceptibility mapping for the diagnosis of Parkinson disease. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schweitzer, A.D.; Liu, T.; Gupta, A.; Zheng, K.; Seedial, S.; Shtilbans, A.; Shahbazi, M.; Lange, D.; Wang, Y.; Tsiouris, A.J. Quantitative susceptibility mapping of the motor cortex in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and primary lateral sclerosis. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, G.E.C.; Leyland, L.A.; Schrag, A.E.; Lees, A.J.; Acosta-Cabronero, J.; Weil, R.S. Brain iron deposition is linked with cognitive severity in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradley, W.G., Jr. MR appearance of hemorrhage in the brain. Radiology 1993, 189, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, R.; Rossi, C.; Cordonnier, C. Diagnostic evaluation for nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurol. Clin. 2015, 33, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgenstern, L.B.; Hemphill, J.C., III; Anderson, C.; Becker, K.; Broderick, J.P.; Connolly, E.S., Jr.; Greenberg, S.M.; Huang, J.N.; MacDonald, R.L.; Messe, S.R.; et al. Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2010, 41, 2108–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Li, W.; Tong, K.A.; Yeom, K.W.; Kuzminski, S. Susceptibility-weighted imaging and quantitative susceptibility mapping in the brain. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 42, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Liu, J.; de Rochefort, L.; Spincemaille, P.; Khalidov, I.; Ledoux, J.R.; Wang, Y. Morphology enabled dipole inversion (MEDI) from a single-angle acquisition: Comparison with COSMOS in human brain imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 66, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLellan, C.L.; Davies, L.M.; Fingas, M.S.; Colbourne, F. The influence of hypothermia on outcome after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Stroke 2006, 37, 1266–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohki, A.; Saito, S.; Hirayama, E.; Takahashi, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Tsuji, M.; Higuchi, T.; Fukuchi, K. Comparison of Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer Imaging with Diffusion-weighted Imaging and Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in a Rat Model of Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2020, 19, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saito, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Ohki, A.; Shintani, Y.; Higuchi, T. Early detection of elevated lactate levels in a mitochondrial disease model using chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) at 7T-MRI. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2019, 12, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, T.; de Rochefort, L.; Ledoux, J.; Khalidov, I.; Chen, W.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Wisnieff, C.; Spincemaille, P.; Prince, M.R.; et al. Morphology enabled dipole inversion for quantitative susceptibility mapping using structural consistency between the magnitude image and the susceptibility map. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 2560–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Xu, W.; Spincemaille, P.; Avestimehr, A.S.; Wang, Y. Accuracy of the morphology enabled dipole inversion (MEDI) algorithm for quantitative susceptibility mapping in MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2012, 31, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peeling, J.; Del Bigio, M.R.; Corbett, D.; Green, A.R.; Jackson, D.M. Efficacy of disodium 4-[(tert-butylimino)methyl]benzene-1,3-disulfonate N-oxide (NXY-059), a free radical trapping agent, in a rat model of hemorrhagic stroke. Neuropharmacology 2001, 40, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeling, J.; Yan, H.J.; Chen, S.G.; Campbell, M.; Del Bigio, M.R. Protective effects of free radical inhibitors in intracerebral hemorrhage in rat. Brain Res. 1998, 795, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeling, J.; Yan, H.J.; Corbett, D.; Xue, M.; Del Bigio, M.R. Effect of FK-506 on inflammation and behavioral outcome following intracerebral hemorrhage in rat. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 167, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tone, O.; Ito, U.; Tomita, H.; Masaoka, H.; Tominaga, B. High colloid oncotic therapy for brain edema with cerebral hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 1994, 60, 568–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belayev, L.; Obenaus, A.; Zhao, W.; Saul, I.; Busto, R.; Wu, C.; Vigdorchik, A.; Lin, B.; Ginsberg, M.D. Experimental intracerebral hematoma in the rat: Characterization by sequential magnetic resonance imaging, behavior, and histopathology. Effect of albumin therapy. Brain Res. 2007, 1157, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Park, J.; Shin, J.I.; Kim, H.J.; Jung, D.I.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, G.; Chang, D.W.; Sur, J.H.; Yang, M.P.; et al. Temporal Evolution of MRI Characteristics in Dogs with Collagenase-Induced Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Comp. Med. 2015, 65, 517–525. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, G.; Yang, Y.; Wu, G.; Hua, Y.; Keep, R.F.; Xi, G. Early Erythrolysis in the Hematoma after Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Transl. Stroke Res. 2017, 8, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Klahr, A.C.; Kate, M.; Gioia, L.C.; Emery, D.J.; Butcher, K.S.; Wilman, A.H. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping for Following Intracranial Hemorrhage. Radiology 2018, 288, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, T.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Shou, J.; Nguyen, T.; Leifer, D.; Wang, Y.; Kovanlikaya, I. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping of Intracerebral Hemorrhages at Various Stages. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 44, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santin, M.D.; Didier, M.; Valabregue, R.; Yahia Cherif, L.; Garcia-Lorenzo, D.; Loureiro de Sousa, P.; Bardinet, E.; Lehericy, S. Reproducibility of R2 * and quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) reconstruction methods in the basal ganglia of healthy subjects. NMR Biomed. 2017, 30, e3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chang, S.; Liu, T.; Wang, Q.; Cui, D.; Chen, X.; Jin, M.; Wang, B.; Pei, M.; Wisnieff, C.; et al. Reducing the object orientation dependence of susceptibility effects in gradient echo MRI through quantitative susceptibility mapping. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 68, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, T. Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM): Decoding MRI data for a tissue magnetic biomarker. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heier, L.A.; Amster, J.L.; Zimmerman, R.D.; Deck, M.D. Focal recurrent hemorrhage on magnetic resonance at 0.5 tesla. An aid to the diagnosis of cryptic cerebral vascular malformations. Acta Radiol. Suppl. 1986, 369, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Surapaneni, K.; Lou, M.; Cheng, L.; Spincemaille, P.; Wang, Y. Cerebral microbleeds: Burden assessment by using quantitative susceptibility mapping. Radiology 2012, 262, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zimmerman, R.D.; Heier, L.A.; Snow, R.B.; Liu, D.P.; Kelly, A.B.; Deck, M.D. Acute intracranial hemorrhage: Intensity changes on sequential MR scans at 0.5 T. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1988, 150, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLellan, C.L.; Silasi, G.; Poon, C.C.; Edmundson, C.L.; Buist, R.; Peeling, J.; Colbourne, F. Intracerebral hemorrhage models in rat: Comparing collagenase to blood infusion. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2008, 28, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, J.P.; Brott, T.G.; Duldner, J.E.; Tomsick, T.; Huster, G. Volume of intracerebral hemorrhage. A powerful and easy-to-use predictor of 30-day mortality. Stroke 1993, 24, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, S.M.; Broderick, J.; Hennerici, M.; Brun, N.C.; Diringer, M.N.; Mayer, S.A.; Begtrup, K.; Steiner, T.; Recombinant Activated Factor, V.I.I.I.H.T.I. Hematoma growth is a determinant of mortality and poor outcome after intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 2006, 66, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, H.K.; Huang, L.C.; Yang, H.I.; Peng, H.F.; Li, K.W.; Tsai, A.P.; Chen, S.Y.; Kuo, J.S.; Pang, C.Y. Therapeutic effects of human urocortin-1, -2 and -3 in intracerebral hemorrhage of rats. Neuropeptides 2015, 52, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orakcioglu, B.; Becker, K.; Sakowitz, O.W.; Unterberg, A.; Schellinger, P.D. Serial diffusion and perfusion MRI analysis of the perihemorrhagic zone in a rat ICH model. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2008, 103, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orakcioglu, B.; Fiebach, J.B.; Steiner, T.; Kollmar, R.; Juttler, E.; Becker, K.; Schwab, S.; Heiland, S.; Meyding-Lamade, U.K.; Schellinger, P.D. Evolution of early perihemorrhagic changes—ischemia vs. edema: An MRI study in rats. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 193, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hong, X.; Chang, C.F.; Li, Q.; Ma, B.; Zhang, H.; Xiang, S.; Heo, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Simultaneous detection and separation of hyperacute intracerebral hemorrhage and cerebral ischemia using amide proton transfer MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 74, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Khatibi, N.H.; Chen, H.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H. History of preclinical models of intracerebral hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2011, 111, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsuji, K.; Onishi, R.; Sawaya, R.; Arihara, N.; Ueda, J.; Saito, S. Longitudinal Observation of Asymmetric Iron Deposition in an Intracerebral Hemorrhage Model Using Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping. Symmetry 2022, 14, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14020350
Tsuji K, Onishi R, Sawaya R, Arihara N, Ueda J, Saito S. Longitudinal Observation of Asymmetric Iron Deposition in an Intracerebral Hemorrhage Model Using Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping. Symmetry. 2022; 14(2):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14020350
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsuji, Keiho, Ryutarou Onishi, Reika Sawaya, Narumi Arihara, Junpei Ueda, and Shigeyoshi Saito. 2022. "Longitudinal Observation of Asymmetric Iron Deposition in an Intracerebral Hemorrhage Model Using Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping" Symmetry 14, no. 2: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14020350
APA StyleTsuji, K., Onishi, R., Sawaya, R., Arihara, N., Ueda, J., & Saito, S. (2022). Longitudinal Observation of Asymmetric Iron Deposition in an Intracerebral Hemorrhage Model Using Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping. Symmetry, 14(2), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14020350




