The Effect of Media in Mitigating Epidemic Outbreaks: The Sliding Mode Control Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Modeling and Dynamical System Analysis
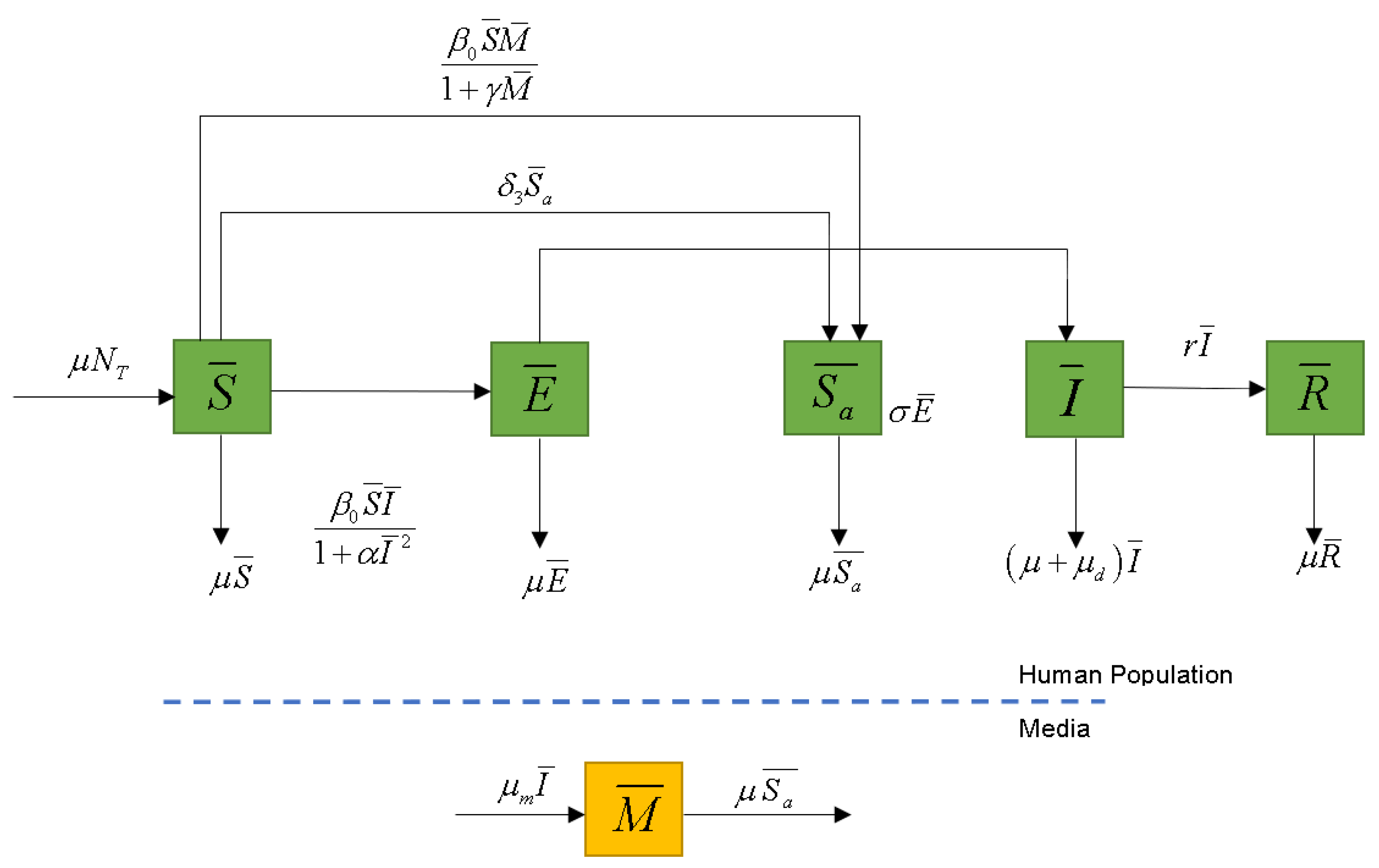
2.1. The Model
2.2. Equilibrium Analysis
2.3. Stability Analysis of Open Loop System
2.4. Numerical Analysis with Baseline Parameter Values
2.5. Sensitivity Analysis
3. Sliding Mode Control Designs
3.1. Policy 1: Governmental Interaction
Stability Analysis of Closed-Loop System
3.2. Policy 2: Vaccination Strategy
3.2.1. Relative Degree of the SEIRM System and Asymptotic Stability of the Zero Dynamics
3.2.2. Control Design
3.2.3. Stability Analysis of Closed-Loop System
4. Results and Discussion
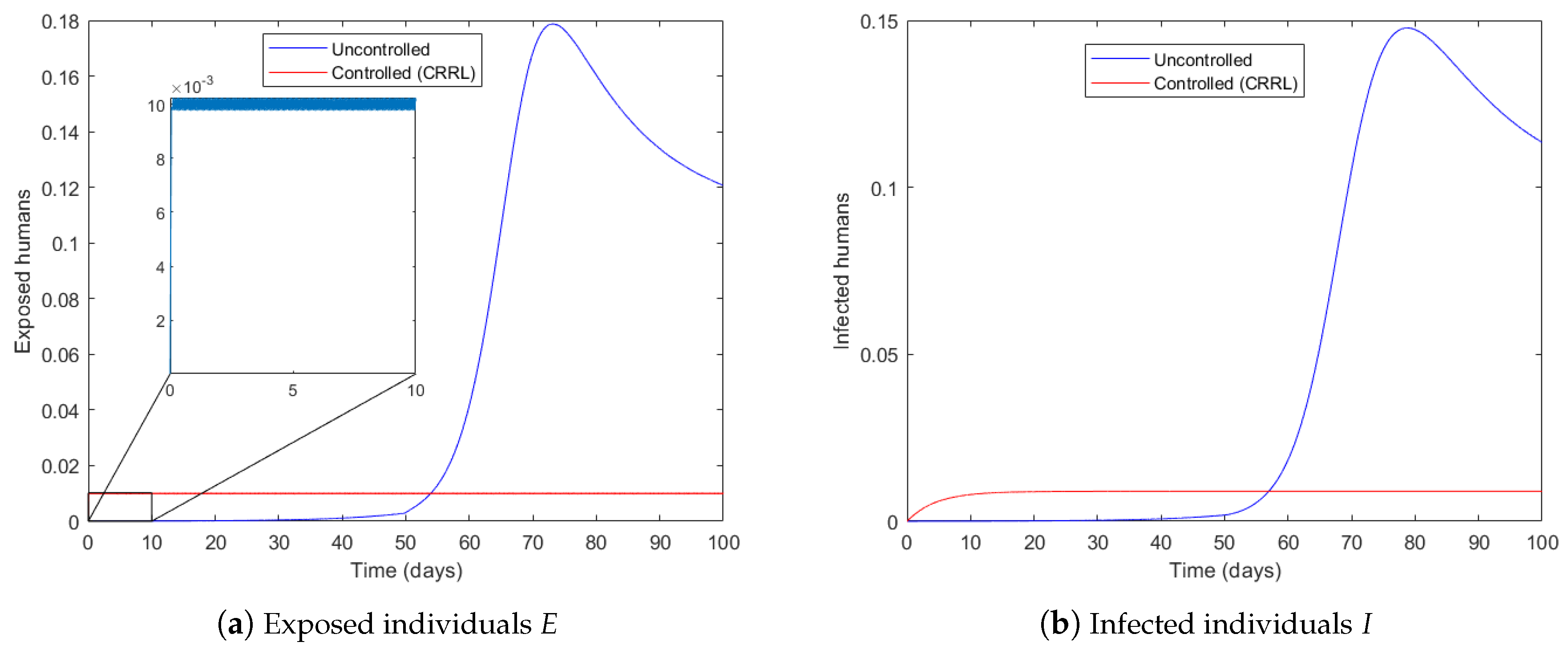
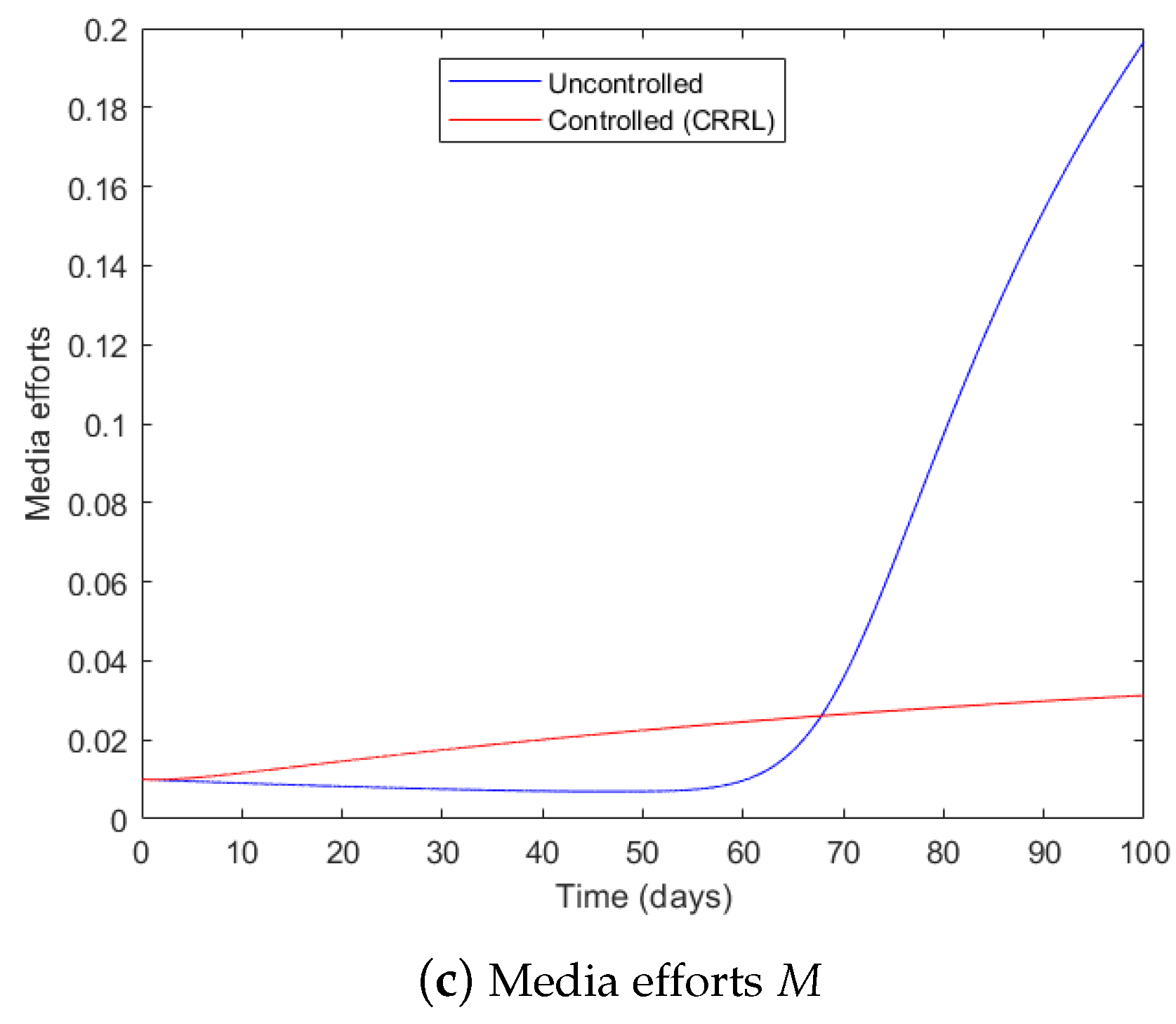
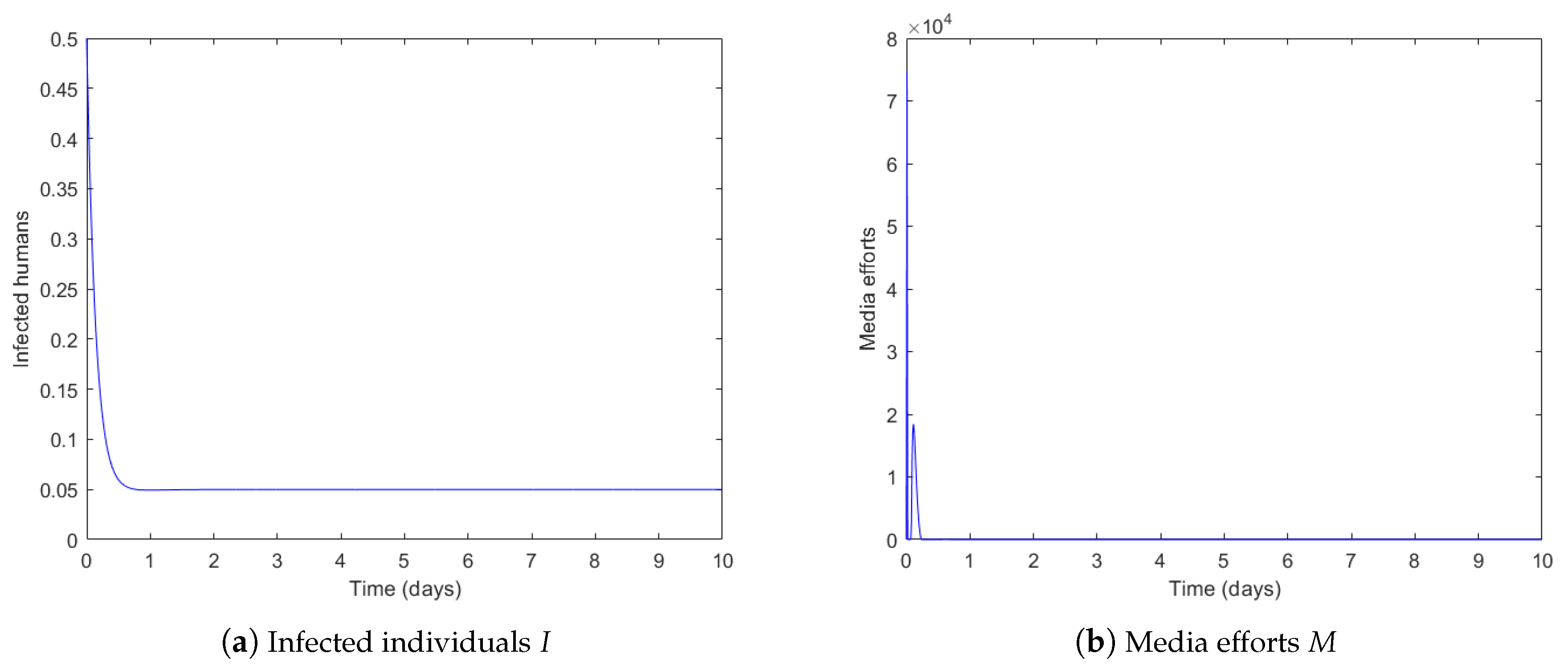
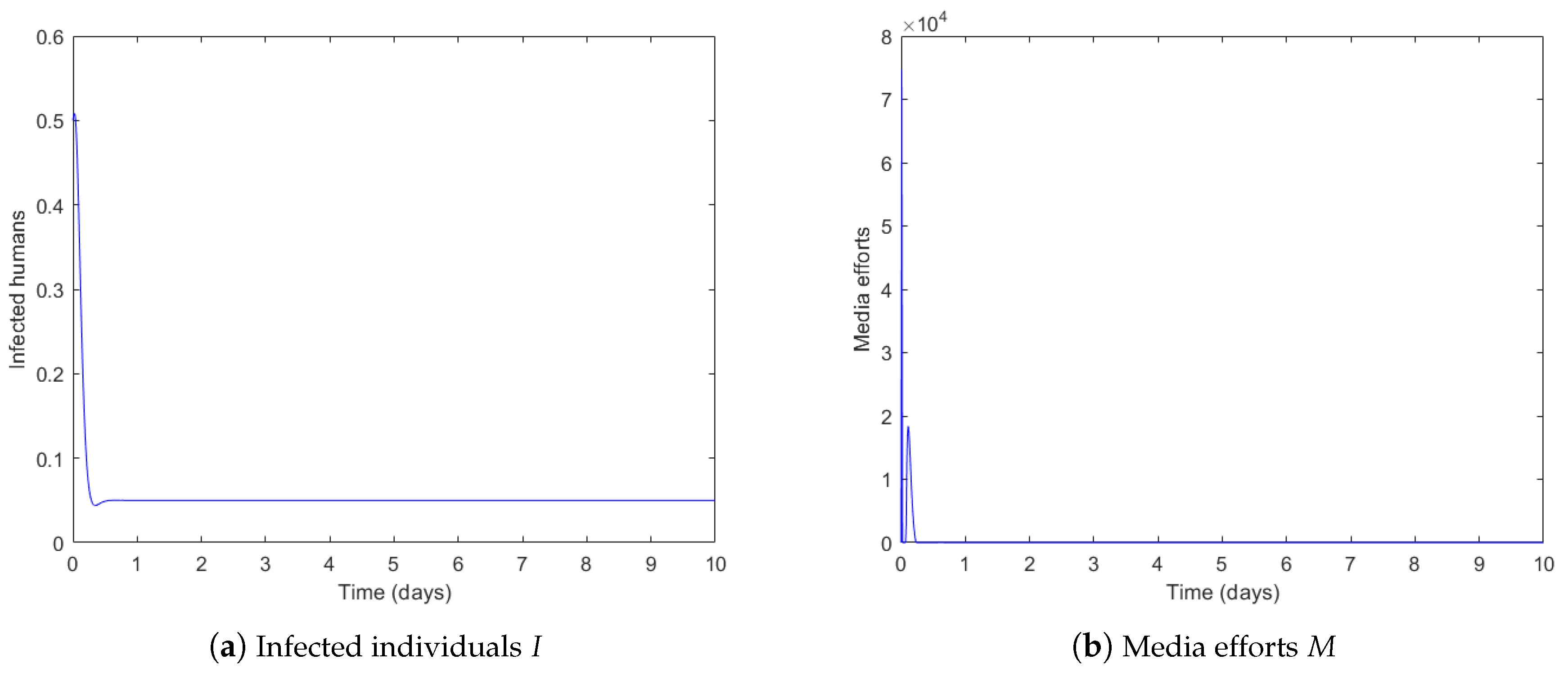
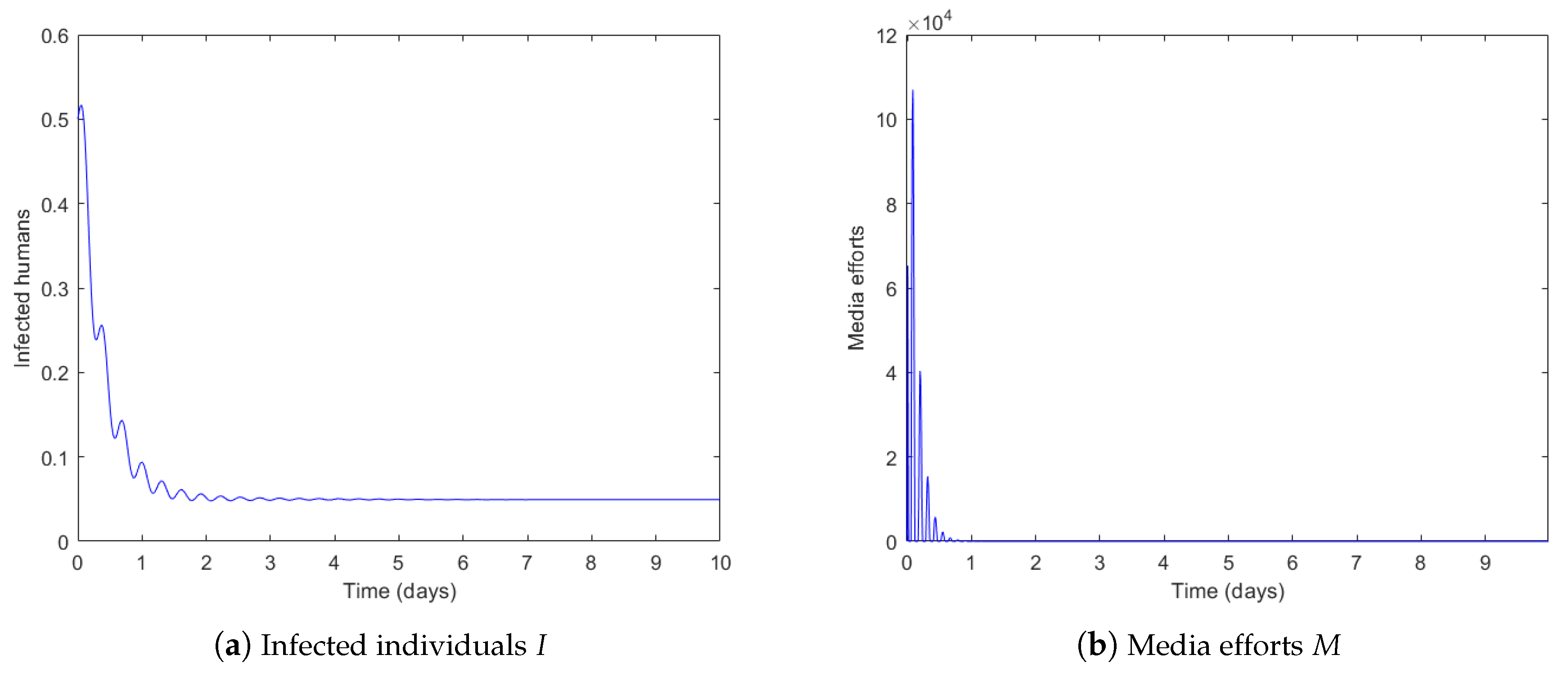
4.1. Governmental Interaction Strategy
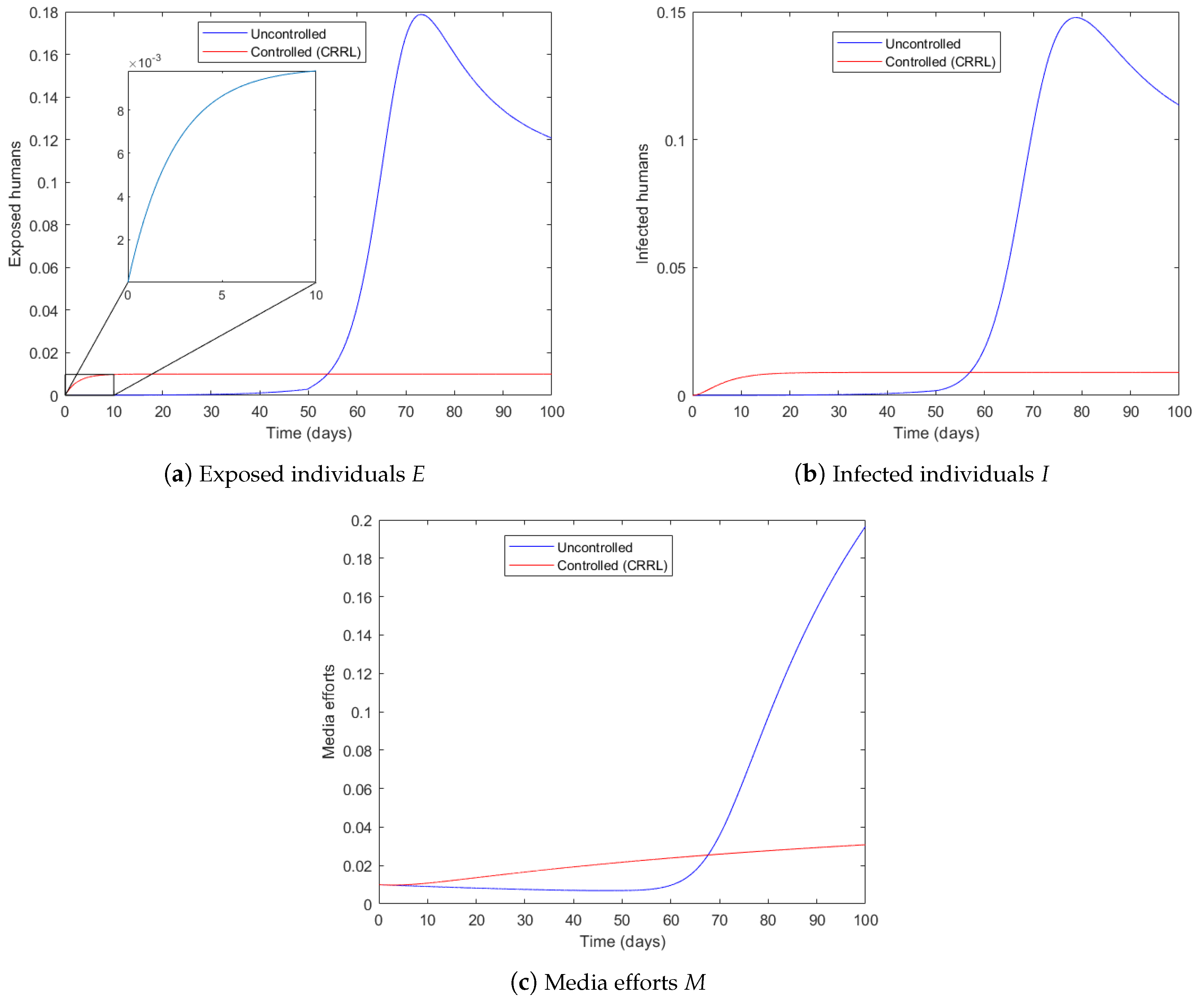
4.2. Vaccination Strategy
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Derivations and Proofs
Appendix A.1
Appendix A.2
References
- GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Diseases and Vaccines Included. Available online: www.cdc.gov (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Kermack, W.O.; McKendrick, A.G. A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1927, 115, 700–721. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.Z. A new SEIR epidemic model with applications to the theory of eradication and control of diseases, and to the calculation of R0. Math. Biosci. 2008, 215, 84–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pongsumpun, P.; Tang, I.M.; Wongvanich, N. Optimal control of the dengue dynamical transmission with vertical transmission. Adv. Diff. Eqn. 2019, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamwong, J.; Wongvanich, N.; Tang, I.M.; Changpuek, K.; Pongsumpun, P. Global Stability of the Transmission of Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease According to the Age Structure of the Population. Curr. Appl. Sci. Tech. 2021, 2, 351–369. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, D.; Ruan, S. Global analysis of an epidemic model with nonmonotone incidence rate. Math. Biosci. 2007, 208, 419–429. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, R.K.; Pal, A.K.; Kumari, S.; Roy, P. Dynamics of an SEIR epidemic model with nonlinear incidence and treatment rates. Nonlinear Dyn. 2019, 96, 2351–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.P.; Huang, N.J. Threshold dynamics of an SEIR epidemic model with a nonlinear incidence rate and a discontinuous treatment function. RACSAM 2020, 114, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wei, F. Study on a susceptible–exposed–infected–recovered model with nonlinear incidence rate. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2020, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagradi, R.; Bolzoni, L.; Levin, S.A.; Andreasen, V. The SIRC model and influenza A. Math. Biosci. 2006, 200, 152169. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, R.E.; Cunha, A., Jr. Embedded model discrepancy: A case study of Zika modeling. Chaos 2020, 30, 051103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsitch, M.; Cohen, T.; Cooper, B.; Robins, J.M.; Ma, S.; James, L.; Gopalakrishna, G.; Chew, S.K.; Tan, C.C.; Samore, M.H.; et al. Transmission dynamics and control of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Science 2003, 300, 19661970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ingemar, N. Stochastic models of some endemic infections. Math. Biosci. 2002, 179, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Guy, R.; Laredo, C.; Vergu, E. Approximation of epidemic models by diffusion processes and their statistical inference. J. Math. Biol. 2015, 70, 621–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, A.K.; Sharma, A.; Shukla, J.B. Modeling and analysis of effects of awareness programs by media on the spread of infectious diseases. Math. Comput. Model 2011, 53, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchuenche, J.M.; Dube, N.; Bhunu, C.P.; Smith, R.J.; Bauch, C.T. The impact of media coverage on the transmission dynamics of human influenza. BMC Publ. Health 2011, 11 (Suppl. S1), S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, B.; Dubey, P.; Dubey, U. Role of media and treatment on SIR model. Nonl. Anal. Model. Control. 2015, 21, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, X. Stationary Distribution and Extinction in a Stochastic SIQR Epidemic Model Incorporating Media Coverage and Markovian Switching. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, H.S.; Monteiro, M.T.; Torres, D.F.M. Dynamics of Dengue epidemics when using optimal control. Math. Comput. Model. 2010, 52, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imran, M.; Usman, M.; Malik, T.; Ansari, A.R. Mathematical analysis of the role of hospitalization/isolation in controlling the spread of Zika fever. Virus Res. 2018, 255, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momoh, A.A.; Fuegenschuh, A. Optimal control of intervention strategies and cost effectiveness analysis for a Zika virus model. Oper. Res. Health. Care 2018, 18, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongvanich, N.; Tang, I.-M.; Dubois, M.-A.; Pongsumpun, P. Mathematical Modeling and Optimal Control of the Hand Foot Mouth Disease Affected by Regional Residency in Thailand. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.P.; Mofarreh, F.; Shah, R.; Luangboon, W.; Nonlaopon, K. An Analytical Technique, Based on Natural Transform to Solve Fractional-Order Parabolic Equations. Entropy 2021, 23, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levant, A. Sliding order and sliding accuracy in sliding mode control. Int. J. Control. 1993, 58, 1247–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtessel, Y.; Edwards, C.; Fridman, L.; Levant, A. Sliding Mode Control and Observation. In Control Engineering; Springer Science+Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, X.; Zhao, D.; Spurgeon, S.K.; Yan, X. Sliding Mode Control for Nonlinear Manipulator Systems. IFAC-Pap. Online 2017, 50, 5127–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Fu, W.; An, C.; Yuan, Z.; Fei, J. Modelling, Simulation and Dynamic Sliding Mode Control of a MEMS Gyroscope. Micromachines 2021, 12, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Yuan, C.; Sun, D.; Jin, N.; Wu, X. Parameter adaptive terminal sliding mode control for full-bridge DC-DC converter. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, Z. Adaptive Sliding Mode Attitude Control of Quadrotor UAVs Based on the Delta Operator Framework. Symmetry 2022, 14, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Xia, Y.; Liu, G.P.; Rees, D. On designing of sliding-mode control for stochastic jump systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2006, 51, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Ho, D.W.C.; Wang, X. Sliding mode control for Itô stochastic systems with Markovian switching. Automatica 2007, 43, 1784–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shen, M. Sliding mode H-∞ control of time-varying delay Markov jump with quantized output. Optim. Control. Appl. Methods 2019, 40, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, H.; Park, J.H. Observer-based quantized sliding mode H-∞ control of Markov jump systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 92, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili Amirabadi, R.; Heydari, A.; Zarrabi, M. Analysis and control of SEIR epedemic model via sliding mode control. Adv. Model. Optim. 2016, 18, 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi, M.; Moradi, H. Nonlinear robust adaptive sliding mode control of influenza epidemic in the presence of uncertainty. J. Process Control 2017, 56, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Driessche, P.; Watmough, J. Reproduction number and subthreshold endemic equilibria for compartment models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 2002, 180, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohith, G.; Devika, K.B. Dynamics and control of COVID-19 pandemic with nonlinear incidence rates. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 101, 2013–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitnis, N.; Hyman, J.M.; Cushing, J.M. Determining important parameters in the spread of malaria through the sensitivity analysis of a mathematical model. Bullet. Math. Biol. 2008, 70, 1272–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.J.; Torres, D.F.M. Optimal control for a tuberculosis model with reinfection and post-exposure interventions. Math. Biosci. 2013, 244, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, W.; Hung, J.C. Variable structure control of nonlinear systems: A new approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1993, 40, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Spooner, J.T.; Maggione, M.; Ordonez, R.; Passino, K.M. Stable Adaptive Control and Estimation for Nonlinear Systems: Neural and Fuzzy Approximator Techniques, ser. In Adaptive and Cognitive Dynamic Systems: Signal Processing, Learning, Communications and Control; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 141–153. [Google Scholar]
- Hangos, K.; Bokor, J.; Szederkenyi, G. Analysis and Control of Nonlinear Process Systems, ser. Advanced Textbooks in Control and Signal Processing; Springer: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Brockett, R.W. Nonlinear systems and differential geometry. Proc. IEEE 1976, 64, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabczyk, J. Mathematical Control Theory: An Introduction, ser. Modern Birkhauser Classics; Birkhauser: Boston, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ledlord, H. Six months of COVID vaccines: What 1.7 billion doses have taught scientists. Nature 2021, 594, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hass, E.J.; Angulo, F.J.; McLaughlin, J.M.; Anis, E.; Singer, S.R.; Khan, F.; Brooks, N.; Smaja, M.; Mircus, G.; Pan, K.; et al. Impact and effectiveness of mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19 cases, hospitalisations, and deaths following a nationwide vaccination campaign in Israel: An observational study using national surveillance data. Lancet 2021, 397, 1819–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenck, R.W.; Klein, N.P.; Kitchin, N.; Gurtman, A.; Absalon, J.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Walter, E.B.; Senders, S.; Bailey, R.; et al. Safety, Immunogenicity, and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccine in Adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, J.L.; Andrews, N.; Gower, C.; Robertson, C.; Stowe, J.; Tessier, E.; Simmons, R.; Cottrell, S.; Roberts, R.; O’Doherty, M.; et al. Effectiveness of the Pfizer-BioNTech and Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccines on COVID-19 related symptoms, hospital admissions, and mortality in older adults in England: Test negative case-control study. Br. Med. J. 2021, 373, n1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Birth/death rate, | 0.08 |
| Contact rate, | 0.76 |
| Rate of transfer between the aware susceptible individuals back to susceptibles, | 0.18 |
| Governmental effort, | 10 |
| Media inhibition parameter, | 20 |
| Rate of transfer between the exposed and infected classes, | 0.20 |
| Disease recovery rate, r | 1/7 |
| Disease induced mortality rate, | 0.02 |
| Implementation rate of the awareness program, | 0.05 |
| Removal rate of the awareness program, | 0.02 |
| Parameter | Forward Sensitivity |
|---|---|
| −0.6151 | |
| 1 | |
| 0 | |
| 0 | |
| 0 | |
| 0.2857 | |
| r | −0.5882 |
| −0.082 | |
| 0 | |
| 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wongvanich, N. The Effect of Media in Mitigating Epidemic Outbreaks: The Sliding Mode Control Approach. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14051010
Wongvanich N. The Effect of Media in Mitigating Epidemic Outbreaks: The Sliding Mode Control Approach. Symmetry. 2022; 14(5):1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14051010
Chicago/Turabian StyleWongvanich, Napasool. 2022. "The Effect of Media in Mitigating Epidemic Outbreaks: The Sliding Mode Control Approach" Symmetry 14, no. 5: 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14051010
APA StyleWongvanich, N. (2022). The Effect of Media in Mitigating Epidemic Outbreaks: The Sliding Mode Control Approach. Symmetry, 14(5), 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14051010






