1. Introduction
In 1978, Rivest, Shamir and Adleman [
1] proposed the first asymmetric-key cryptosystem (RSA) for encryptions and digital signatures. Its security is based on the difficulty of factoring a large integer
that is a product of two large prime numbers
and
with
of the same bit-sizes, i.e.,
. Although there is a quantum algorithm that factors integers in polynomial time [
2], there is no polynomial time algorithm for factoring integers in classical computers.
The RSA encryption process of a message x is computing where is the RSA public key. The RSA decryption process of the ciphertext y is computing where d is the private key and satisfies that for some integer where is Euler’s totient function. The RSA encryption and decryption processes take times and respectively.
In order to speed up the decryption process, one might be tempted to use a small private exponent
, i.e.,
is small. Wiener [
3] showed that if
i.e.,
then
d is one of the denominators of the convergents of the continued fraction expansion of
and thus RSA is insecure. Boneh and Durfee [
4] used the lattice reduction to improve the bound of
d to be
where their method is based on Coppersmith’s [
5] technique to find small roots of modular polynomial equations.
Many other strategies [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10] for improving the bound of
d were inspired by Wiener’s result. They mainly try to find an approximation of
better than
n or to find a better lattice to recover large
For example, de Weger [
6] used
as an estimation of
to recover
d when
where
Maitra and Sarkar [
9] used
as an estimation of
to recover
d when
is small. Note that if
then Fermat’s factoring method [
6,
11,
12,
13] factorizes
n in polynomial time.
In order to unify small private exponent attacks on RSA and to determine a universal attack using continued fractions or lattices, the authors in [
14,
15] proposed concepts of the Wiener and Coppersmith intervals using continued fractions and lattices, respectively. An integer interval
I is called Wiener’s interval if each
satisfies Wiener’s attack, i.e.,
While an interval
I is called Coppersmith’s interval if each
satisfies that the tuple
is a root of the polynomial
In this paper, we are interested in improving the bound of d by:
Proposing an interval
I that contains
Section 3. The proposed interval is not necessary a Wiener or Coppersmith interval. It is sufficient to find an approximation
of
such that
i.e., Wiener’s attack using continued fraction succeeds.
Proposing a new strategy to search for such that
Using multicore systems to accelerate finding such that The interval I is divided into subintervals of the same length approximately. Then each core searches for such m in one subinterval. We choose that the number of subintervals is equal to the number of available cores.
We use the proposed strategy to study practically the possibility of attacking RSA when
Estimating a small interval that contains
is not simple. Therefore, we estimate the interval based on some conditions on the primes factors of
n as we will see in
Section 3. The practical study of the proposed method shows that we succeed to factor
n with
greater than previously discovered using continued fractions.
The organization of this paper is as follows.
Section 2 includes a brief background on continued fractions and a review of some results on small private exponent attacks on RSA. In
Section 3, we propose three intervals that contain
for three attacks on RSA. Each attack has different conditions on the prime factors
and/or
In
Section 4, we present a new technique to search for
m in the estimated intervals to find a good approximation of
Section 5 includes using multicore systems to study practically how the proposed technique can improve three attacks on RSA, i.e., extend the bound of
in three attacks. The theoretical study of the complexity of the proposed attacks is presented in
Section 6. The conclusion and future works are given in
Section 7.
2. Preliminaries
This section presents a definition of continued fractions, how to calculate continued fractions and some theorems and lemmas necessary in this paper.
Given a non-negative rational number
a (finite) continued fraction expansion [
16,
17] of
r (or simply we write
is an expression of the form:
This expansion is denoted by of non-negative integers
The following steps are a polynomial time algorithm [
18] of order
for computing a unique
for the rational number
where
are two positive integers such that
Compute where is the smallest value of i such that
Return where
The
is
infinite in case of
r is irrational number, i.e.,
In this case, we write the expansion as
Theorem 1.
((Legendre) [
19])
Let λ be a real number, and v be two positive integers such that Ifthen is a convergent of Lemma 1 ([
20,
21]).
If n is a product of two primes and of the same size, then Theorem 2.
([
6])
Let be a product of two primes of the same size, with Suppose that satisfy and . Given n and the integer n can be factored in polynomial time in ifwhere Proposition 1.
([
9])
Suppose that l is a positive integer, and is a product of two primes and If then Theorem 3.
([
9])
Let l be a positive integer, and be a product of two primes and with and Then n can be factored in polynomial time in whenwhere Theorem 4 ([
14]).
Let and be the public and private keys of RSA, respectively, where and If is an approximation for such thatThen is a Wiener’s interval for where 3. Estimation of
The main problem of using CFs in small private exponent attacks of RSA is to find a good approximation of to use it in Theorem 1. In this section, we estimate an interval I that contains i.e., determine the lower and upper bounds of In fact, estimating a small interval that contains is not easy. It is known that computing is computationally equivalent to factoring Thus, we try to estimate I based on some conditions on the prime factors and of
In the following, we consider three cases for the prime factors and
Attack 1: In [
6], if
,
then
Attack 2: Using Proposition 1 and Theorem 3 if for a positive integer
l,
and
then
It is clear that if
for a small value
then
Attack 3: Based on the result in [
22], an approximation
of the prime factor
may be obtained by some expectations in side-channel attacks. In [
14], if
and
be an approximation of the prime factor
where
then
can be estimated to be in the interval
The proof is as follows:
Let Then where . We have
Since we have either or .
If
then
Therefore,
Furthermore, if
then
Therefore,
Therefore, either
or
we have
4. The Proposed Strategy
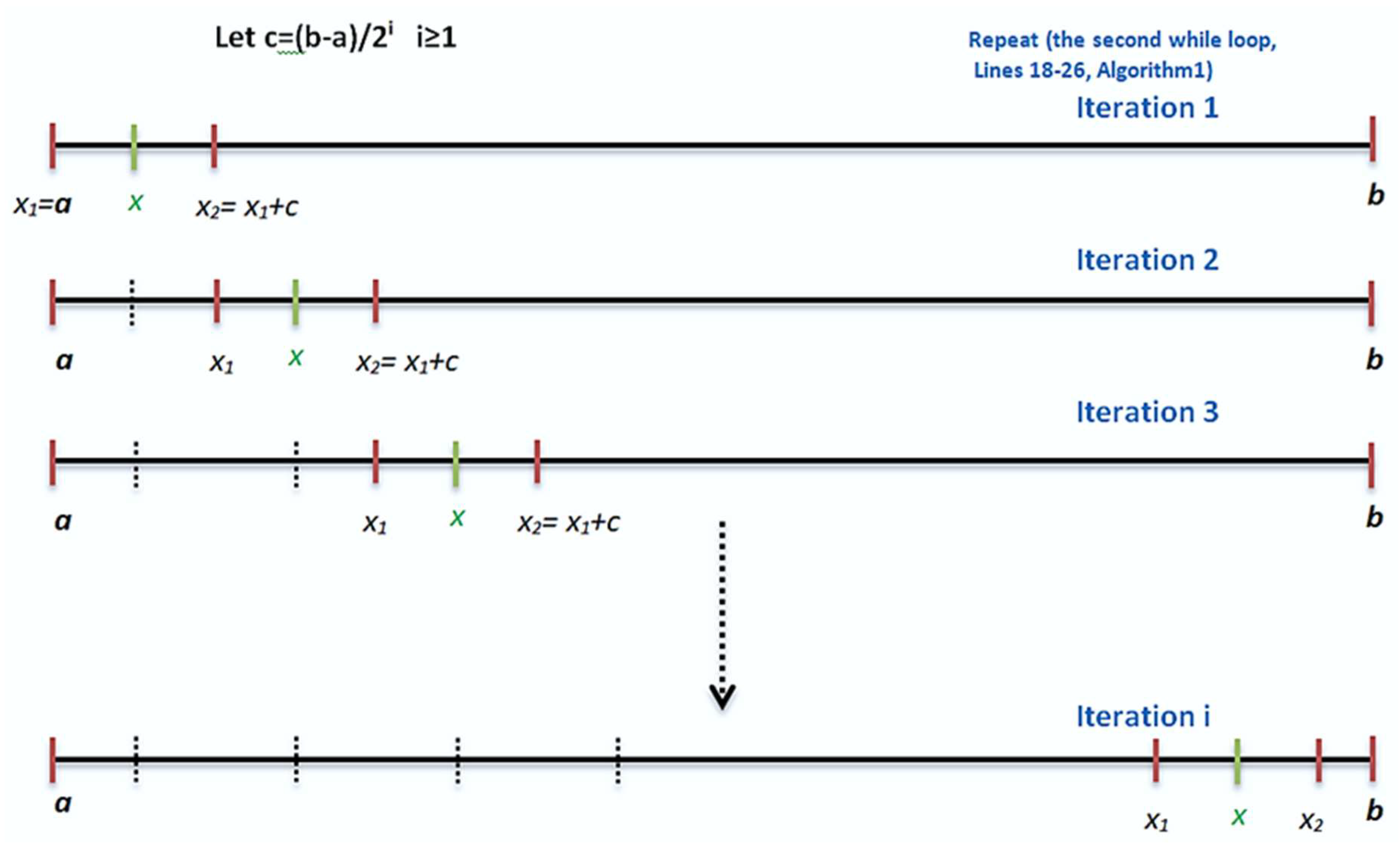
In this section, we propose a new strategy to search for such that In general, the proposed interval that contain are large. Since I is large, it is not feasible in polynomial time to test all integers in The main problem is to determine the number of tested points, i.e., how many points are sufficient to find or to stop the search. Testing a fixed number L of points in I has a problem: if L is small, then we may not find the solution. Otherwise, i.e., if L is very large, then the distance between two consecutive points may be small and the time to find a solution may be large if the solution is in the last parts of For this reason, we propose a new method to generate test points in I as follows (see Algorithm 1):
We first test whether is a convergent of or If is not a convergent of or we set the length , and then we repeat taking x as the midpoint between and i.e., and check whether is a convergent of If not, we repeat the previous steps with the length change to be and to be until the midpoint x is greater than For each new midpoint the counter is increased by 1 as long as it does not exceed the maximum number of iterations The loop is terminated either by:
Finding a solution, Lines 19–20 in Algorithm 1.
Exceed the maximum number of generated test points Line 13 in Algorithm 1. This number can be replaced by a maximum time to find a solution.
The number of round
i.e., number of iterations in the first while loop (Line 13 in Algorithm 1), is
i.e.,
In this case, we exhausted most points in the interval and the total number of tested points is about
which is large when
is large.
Figure 1 shows the idea of generating uniformly distributed
test points in
I for a round
where
For example, let
be an RSA modulus. We have
I = [800218, 800326].
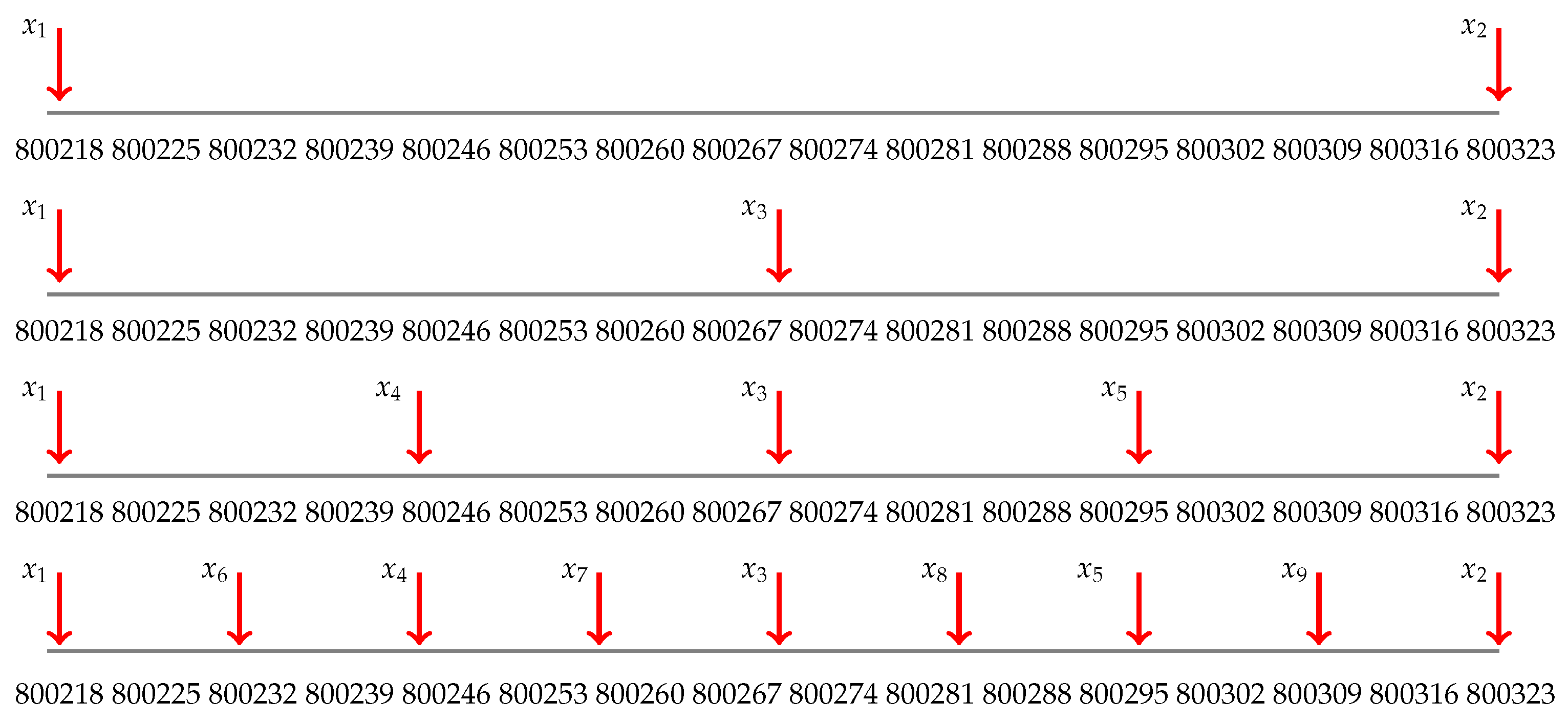
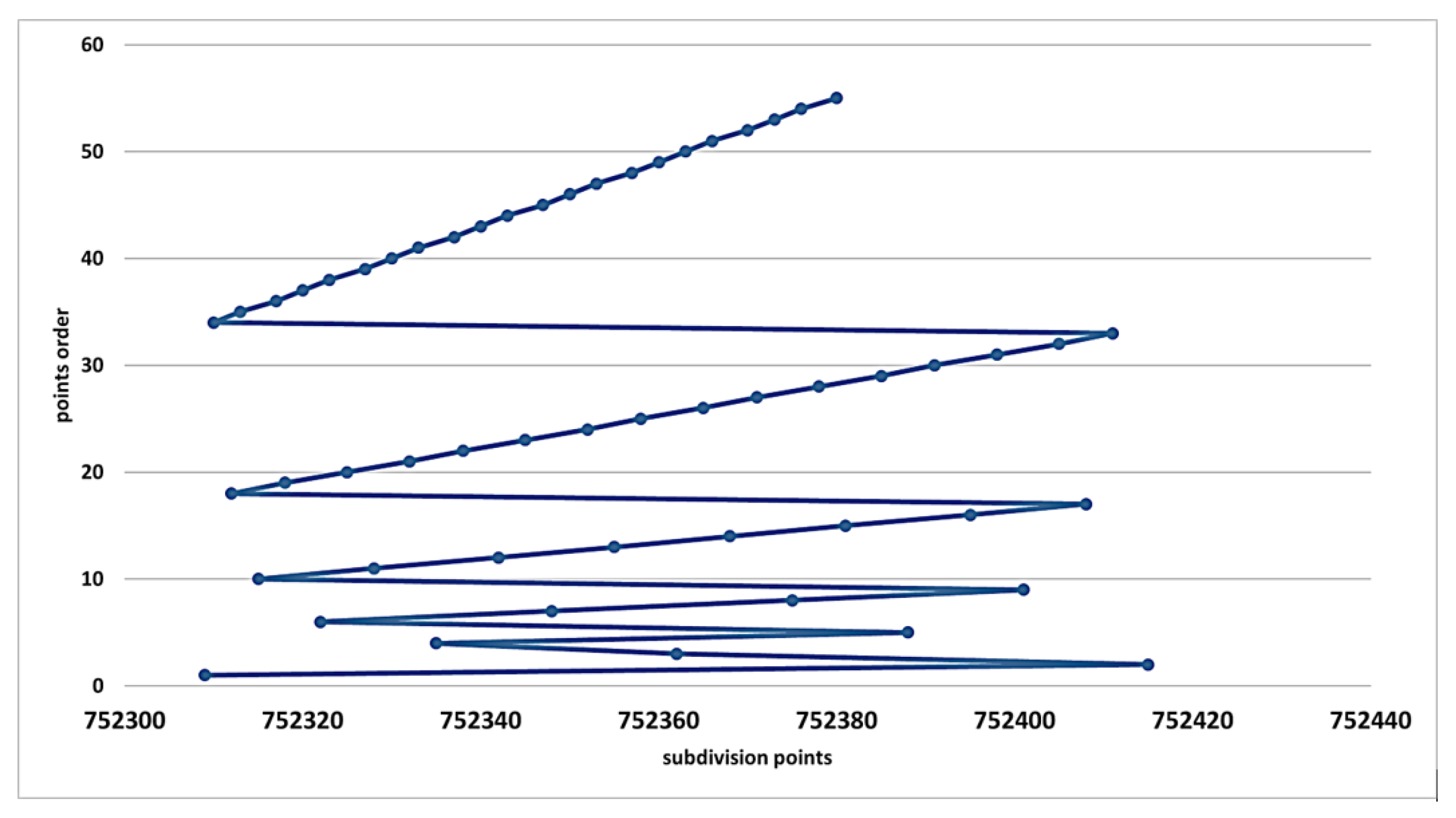
Figure 2 shows the generated test points in
I for rounds
and
i.e., we repeat the second while loop (Lines 17–25) of Algorithm 1 three times
In
Figure 3, we show the generation of the first fifty-five test points in the first 6 rounds (the sixth round is not completed).
| Algorithm 1: Search for d |
![Symmetry 14 01897 i001]() |
5. Implementation
In this section, we present the implementation of the proposed attack. The implementation is written in C/C++, compiled with GNU C++ Compiler, and run on an Intel(R) Xeon(R) E5645 CPU 2.40GHz running the Ubuntu operating system. We used GMP package [
23], a free library for arbitrary precision arithmetic, and OpenMP (Open Multi-Processing) [
24] to support multiprocessing programming in C.
The implementation considers the three attacks described in
Section 3. If
is expected to be in an interval
, then we distribute I on 20 threads. Let
be the set of end points of the 20 sub-intervals of
. Then thread number
independently runs Algorithm 1 on the sub-interval
. The size of the RSA modulus
n conducted in the experimental study was 1024 bits, where each prime factor has 512 bits and was generated randomly. For most studied cases, the number of tested
n is
The maximum value of test points was
The First Attack: We consider the first attack in
Section 3. We assume that
,
and
i.e.,
Based on Equations (
1) and (
2), we study the performance of using the proposed technique to attack RSA when
in the range
For each selected value of
we study the possibility of attack for different values of
Table 1 shows the average execution time and the (ceiling of) the average number of tested points of running the attack using single core and 20-cores. For
and
we study
in the ranges 0.256∼0.268, 0.296∼0.308, 0.316∼0.328, 0.356∼0.368, 0.396∼0.408, respectively. All values of
in the table are greater than the bound of de Weger [
6] using continued fractions, Equation (
1). This means that the proposed method using continued fractions and 20 cores succeeded to extend the bound of
Furthermore, the results in the table show that
is in the range of de Weger’s results [
6] using lattice, Equation (
2) The parallel (multicore) implementation of the attack speeds up the sequential implementation by
on average.
The Second Attack: We consider the second attack in
Section 3. We assume that
,
and
i.e.,
Based on Equation (
3), we study the performance of using multicore systems to attack RSA when
in the range
For each selected values of
we study the possibility of attack for different values of
Table 2 shows the average execution time and the (ceiling of the) average number of tested points of running the attack using single core and 20-cores. For
and
we study
in the ranges 0.296∼0.308, 0.316∼0.328, 0.356∼0.368 and 0.396∼0.408, respectively.
All values of
in the table are greater than the bound of Maitra-Sarkar [
9] using continued fractions, i.e.,
This means that the proposed method using continued fractions and 20 cores succeeded to extend the bound of
The parallel (multicore) implementation of the attack speeds up the sequential implementation by
on average
The Third Attack: we consider the third attack in
Section 3. We assume that an approximation
of
is obtained where
i.e.,
We study the performance of using multicore systems to attack RSA when
, and and
as in Equation (
4). We choose
in the range 0.36∼0.46. For each selected value of
we study the possibility of the attack for different values of
Table 3 shows the average execution time and the (ceiling of the) average number of tested points of running the attack using single core and 20-cores. For
and
we study
in the ranges 0.274∼0.286, 0.284∼0.296, 0.304∼0.316, and 0.324∼0.336, respectively.
All values of
in the table are greater than the bound of Equation (
4) using continued fractions. This means that the proposed method using continued fractions and 20 cores succeeded to extend the bound of
The parallel (multicore) implementation of the attack speeds up the sequential implementation by
on average.
Table 4 shows the upper bound of
for the proposed attacks and previous attacks [
6,
9,
14] using continued fractions. The proposed attack raises the previous bound of
by
As we can see from
Table 1,
Table 2 and
Table 3, the value of
depends on the number of generated test points in
The execution times required to complete the attacks depend on the number of cores, type of attack, and
For example, if
then the execution time to find the private key for the third attack (
Table 3) is 44 min on average, while the execution times are
h for the first attack (
Table 1) and
h for the second attack (
Table 2).
6. Complexity Analysis
Let be an approximation for . In the following lemma, we show the relationship between the difference and the upper bounds of e and d.
Lemma 2. Let n be a positive composite integer, , and where If and where , then is a convergent of i.e., Proof. We have
Also, we have
,
. Therefore, Equation (
5) leads to
□
Suppose that is in an interval , i.e., . We show, in the following theorem, the relationship between the length of this interval and the running time to retrieve the private exponent
Theorem 5. Let be a public key of RSA and be the corresponding private exponent. Suppose that we can estimate for two known values a and b and we divide into subintervals of the same size such thatfor a small value Then d can be obtained in time in . Proof. Let
be points of a subdivision for the interval
where
for
. We test for every
whether
is a convergent of
Let
satisfies that
Thus,
. Thus, we have
Let
for some real number
Then, we have
. By Lemma 2,
is a convergent of
Since computing
takes a polynomial time in
, so to test all
we need a time of order
□
Theorem 5 shows that the complexity of the proposed method depends on the size of S besides the length of
7. Conclusions and Future Works
The RSA cryptosystem is used in the most popular security products and protocols in use today. We have presented a new technique to improve a small private exponent attack on RSA. We have successfully raised the upper bound of the private exponent
d by
using continued fractions and multicore systems for three small private exponent attacks in RSA: de Weger [
6], Maitra-Sarkar [
9], and Nassr et al. [
14]. The average execution times for the attacks are 7.67 h, 2.7 h, and 44 min, respectively. These results were obtained using 20 cores and for
n with 1024 bits. The execution time and the value of
can be improved by
Finding a shorter interval for , i.e., finding better lower and upper bounds of In particular, when the prime factors and satisfy some conditions as in the three attacks.
Improving test points generation to find a value close to We have presented a new strategy (Algorithm 1) to generate such points.
Increasing the number of cores.
Increasing the number of cores is necessary to complete the attack in a reasonable time, but it is expected that increasing the number of cores only will not increase dramatically since the proposed interval for is not small.
The results presented in the paper can be extended to different variations of RSA such as [
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30]. The results can also be applied to different attacks [
4,
31] on the private exponent of RSA that use lattices instead of continued fractions. It is also possible to use cloud systems (with thousands of cores) to implement the attacks.
Thus, interesting research questions raised by this study are (1) how to get better lower and upper bounds of ? (2) how to improve test point generation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.M.B. (Hatem M. Bahig) and D.I.N.; methodology, H.M.B. (Hatem M. Bahig), D.I.N. and H.M.B. (Hazem M. Bahig); software, D.I.N. and M.A.M.; validation, H.M.B. (Hatem M. Bahig), D.I.N. and H.M.B. (Hazem M. Bahig); formal analysis, H.M.B. (Hatem M. Bahig) and D.I.N.; data curation, D.I.N. and H.M.B. (Hatem M. Bahig); writing—original draft preparation, H.M.B. (Hatem M. Bahig) and D.I.N.; writing—review and editing, H.M.B. (Hazem M. Bahig); visualization, H.M.B. (Hatem M. Bahig), D.I.N. and M.A.M.; supervision, H.M.B. (Hazem M. Bahig); project administration, H.M.B. (Hazem M. Bahig); funding acquisition, H.M.B. (Hazem M. Bahig). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been funded by Scientific Research Deanship at University of Ha’il—Saudi Arabia through project number RG-21 124.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the referees for their valuable comments and remarks. The authors would like to acknowledge the support provided by Scientific Research Deanship at University of Ha’il—Saudi Arabia through project number RG-21 124.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rivest, R.; Shamir, A.; Adleman, L. A Method for Obtaining Digital Signatures and Public-Key Cryptosystems. Commun. ACM 1978, 21, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shor, P. Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM J. Comput. 1997, 26, 1484–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, M. Cryptanalysis of short RSA secret exponents. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1990, 36, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boneh, D.; Durfee, G. Cryptanalysis of RSA with private key d less than N0.292. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2000, 46, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppersmith, D. Small Solutions to Polynomial Equations, and Low Exponent RSA Vulnerabilities. J. Cryptol. 1997, 10, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Weger, B. Cryptanalysis of RSA with Small Prime Difference. Appl. Algebra Eng. Commun. Comput. 2002, 13, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blömer, J.; May, A. A Generalized Wiener Attack on RSA. In Public Key Cryptography—PKC 2004, Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Theory and Practice in Public Key Cryptography, Singapore, 1–4 March 2004; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Volume 2947); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Jochemsz, E.; May, A. A Strategy for Finding Roots of Multivariate Polynomials with New Applications in Attacking RSA Variants. In Advances in Cryptology—ASIACRYPT 2006, Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Shanghai, China, 3–7 December 2006; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Volume 4284); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 267–282. [Google Scholar]
- Maitra, S.; Sarkar, S. Revisiting Wiener’s Attack—New Weak Keys in RSA. In Information Security, Proceedings of the 11th International Conference, ISC 2008, Taipei, Taiwan, 15–18 September 2008; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Volume 5222); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 228–243. [Google Scholar]
- Nitaj, A.; Ariffin, M.R.K.; Nassr, D.I.; Bahig, H.M. New Attacks on the RSA Cryptosystem. In Progress in Cryptology—AFRICACRYPT 2014, Proceedings of the P7th International Conference on Cryptology in Africa, Marrakesh, Morocco, 28–30 May 2014; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 178–198. [Google Scholar]
- Bahig, H.M.; Mahdi, M.A.; Alutaibi, K.A.; AlGhadhban, A.; Bahig, H.M. Performance Analysis of Fermat Factorization Algorithms. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2020, 11, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahig, H.M.; Bahig, H.M.; Kotb, Y. Fermat Factorization using a Multi-Core System. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahig, H.M. Speeding Up Fermat’s Factoring Method using Precomputation. Ann. Emerg. Technol. Comput. 2022, 6, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassr, D.I.; Bahig, H.M.; Bhery, A.; Daoud, S.S. A new RSA vulnerability using continued fractions. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/ACS International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications, Doha, Qatar, 31 March–4 April 2008; pp. 694–701. [Google Scholar]
- Bahig, H.M.; Nassr, D.I.; Bhery, A.; Nitaj, A. A Unified Method for Private Exponent Attacks on RSA Using Lattices. Int. J. Found. Comput. Sci. 2020, 31, 207–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, W.B.; Thron, W.J. Continued Fractions: Analytic Theory and Applications. In Encyclopedia of Mathematics and Its Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1984; pp. 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Cuyt, A.A.; Petersen, V.; Verdonk, B.; Waadeland, H.; Jones, W.B. Handbook of Continued Fractions for Special Functions, 1st ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Steinfeld, R.; Contini, S.; Pieprzyk, J.; Wang, H. Converse Results to the Wiener Attack on RSA; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 184–198. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, W. Elementary Number Theory: Primes, Congruences, and Secrets: A Computational Approach; Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dujella, A. Continued fractions and RSA with small secret exponent. Tatra Mt. Math. Publ. 2004, 29, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- May, A. New RSA Vulnerabilities Using Lattice Reduction Methods. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Paderborn, Paderborn, Germany, 2003. Available online: http://www.cs.uni-paderborn.de/uploads/tx_sibibtex/bp.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2022).
- Kaedi, S.; Doostari, M.; Ghaznavi-Ghoushchi, M.B.; Yusefi, H. A New Side-Channel Attack on Reduction of RSA CRT Montgomery Method Based. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2020, 30, 2150038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GNU, MP. The GNU Multiple Precision Arithmetic Library, 6.2.1 ed. 2020. Available online: http://gmplib.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- OpenMP Architecture Review Board. OpenMP Application Program Interface Version 5.2. 2021. Available online: https://www.openmp.org/wp-content/uploads/OpenMP-API-Specification-5-2.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Bahig, H.; Bhery, A.; Nassr, D. Cryptanalysis of Multi-Prime RSA with Small Prime Difference. In Information and Communications Security, Proceedings of the 14th International Conference, ICICS 2012, Hong Kong, China, 29–31 October 2012; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Volume 7618); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 33–44. [Google Scholar]
- Nassr, D.I.; Anwar, M.; Bahig, H.M. Improving small private exponent attack on the Murru-Saettone cryptosystem. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2022, 923, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunder, M.; Nitaj, A.; Susilo, W.; Tonien, J. A generalized attack on RSA type cryptosystems. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2017, 704, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitaj, A.; Kamel Ariffin, M.R.; Hanisah Adenan, N.N.; Azman Abu, N. Classical Attacks on a Variant of the RSA Cryptosystem. In Progress in Cryptology—LATINCRYPT 2021, Proceeding of the 7th International Conference on Cryptology and Information Security in Latin America, Bogotá, Colombia, 6–8 October 2021; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Volume 12912); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 151–167. [Google Scholar]
- Nitaj, A.; Kamel Ariffin, M.R.; Hanisah Adenan, N.N.; Chien Lau, T.S.; Chen, J. Security Issues of Novel RSA Variant. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 53788–53796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Ghafar, A.H.; Kamel Ariffin, M.R.; Asbullah, M.A. A New LSB Attack on Special-Structured RSA Primes. Symmetry 2020, 12, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durfee, G. Cryptanalysis of RSA Using Algebraic and Lattice Methods. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 2002. Available online: http://theory.stanford.edu/~gdurf/durfee-thesis-phd.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2022).
| Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).