A Novel Safe Life Extension Method for Aircraft Main Landing Gear Based on Statistical Inference of Test Life Data and Outfield Life Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
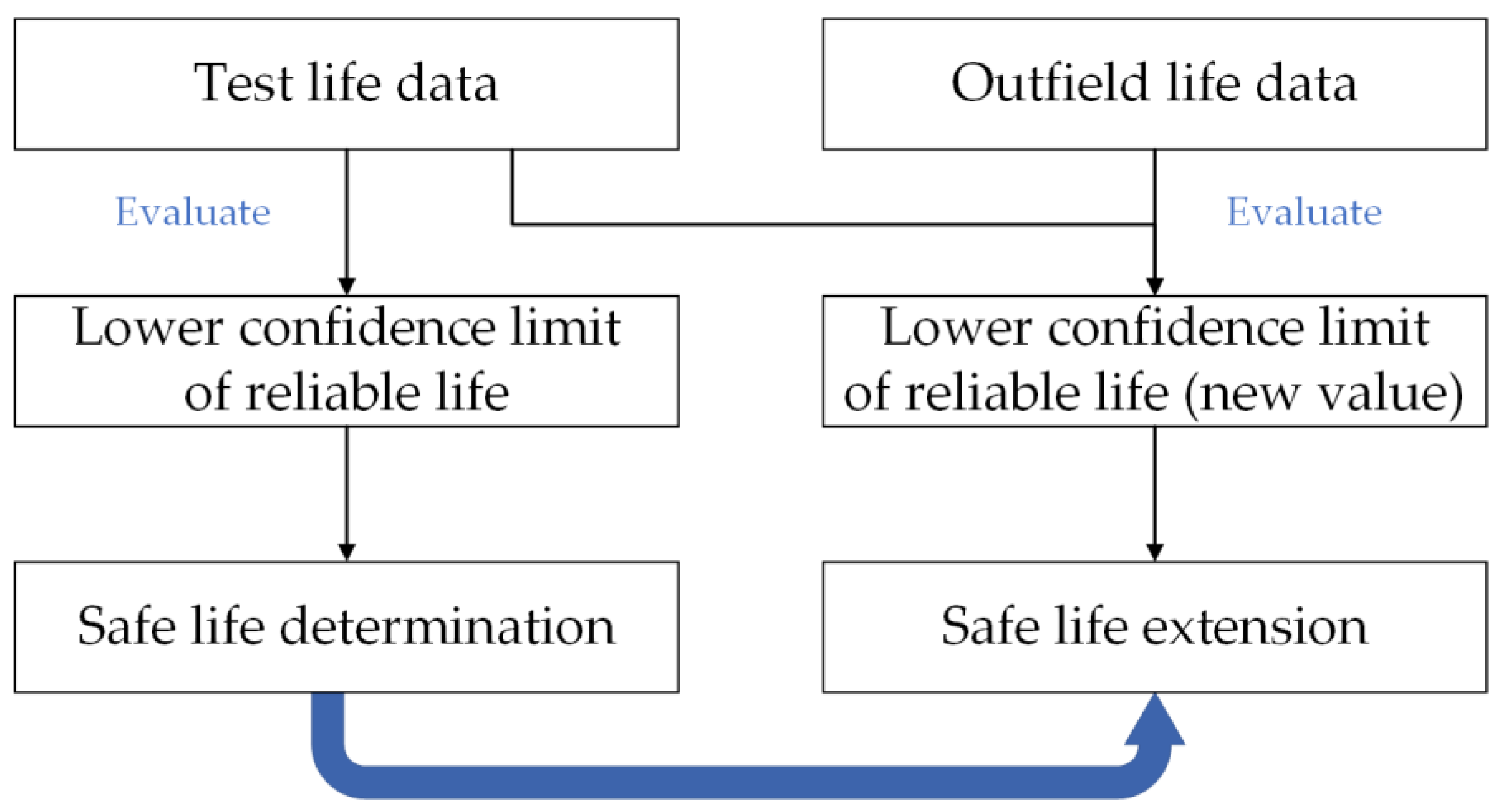
2. Safe Life Extension Method for MLG
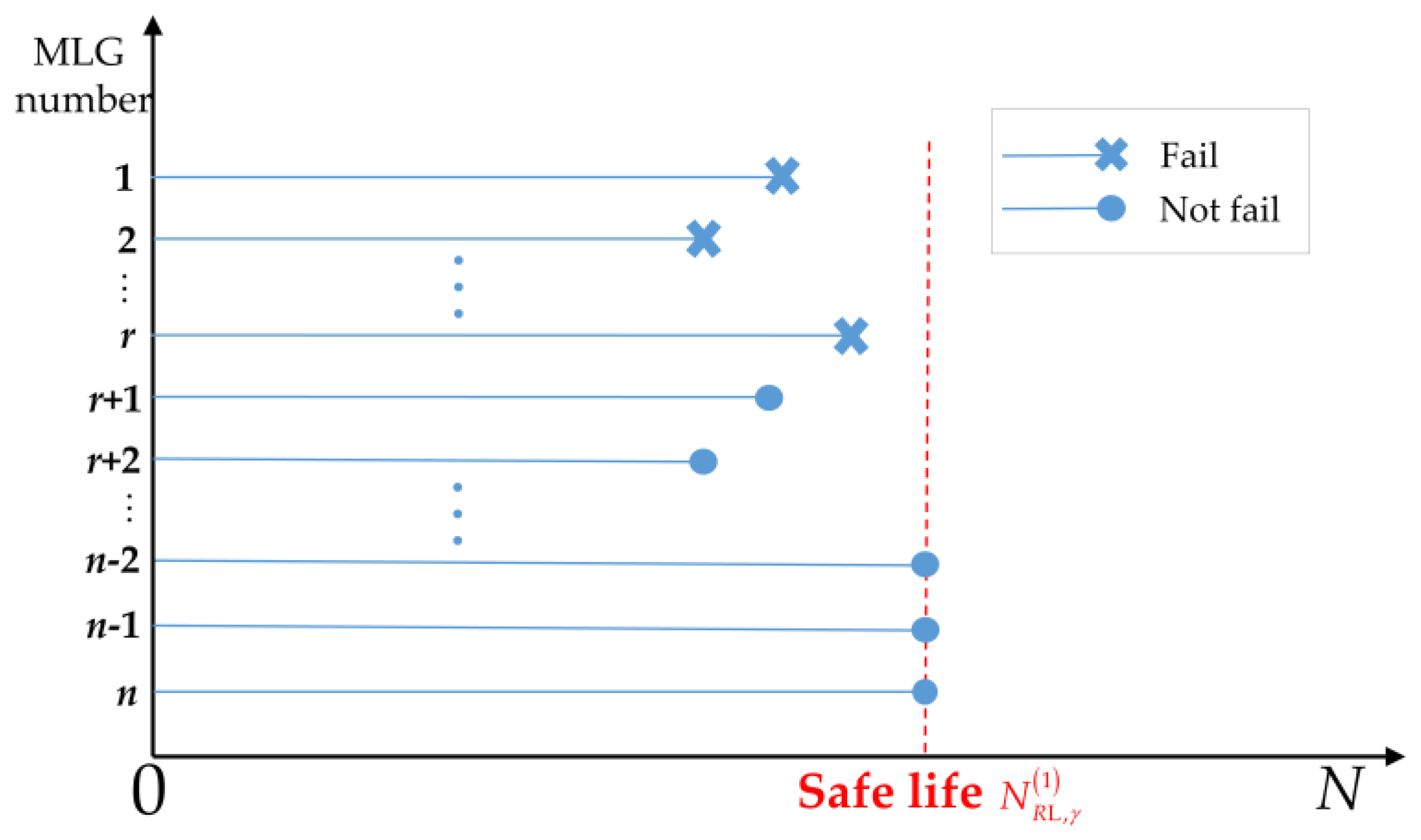
2.1. MLG’s Safe Life Determination by Test Life Data
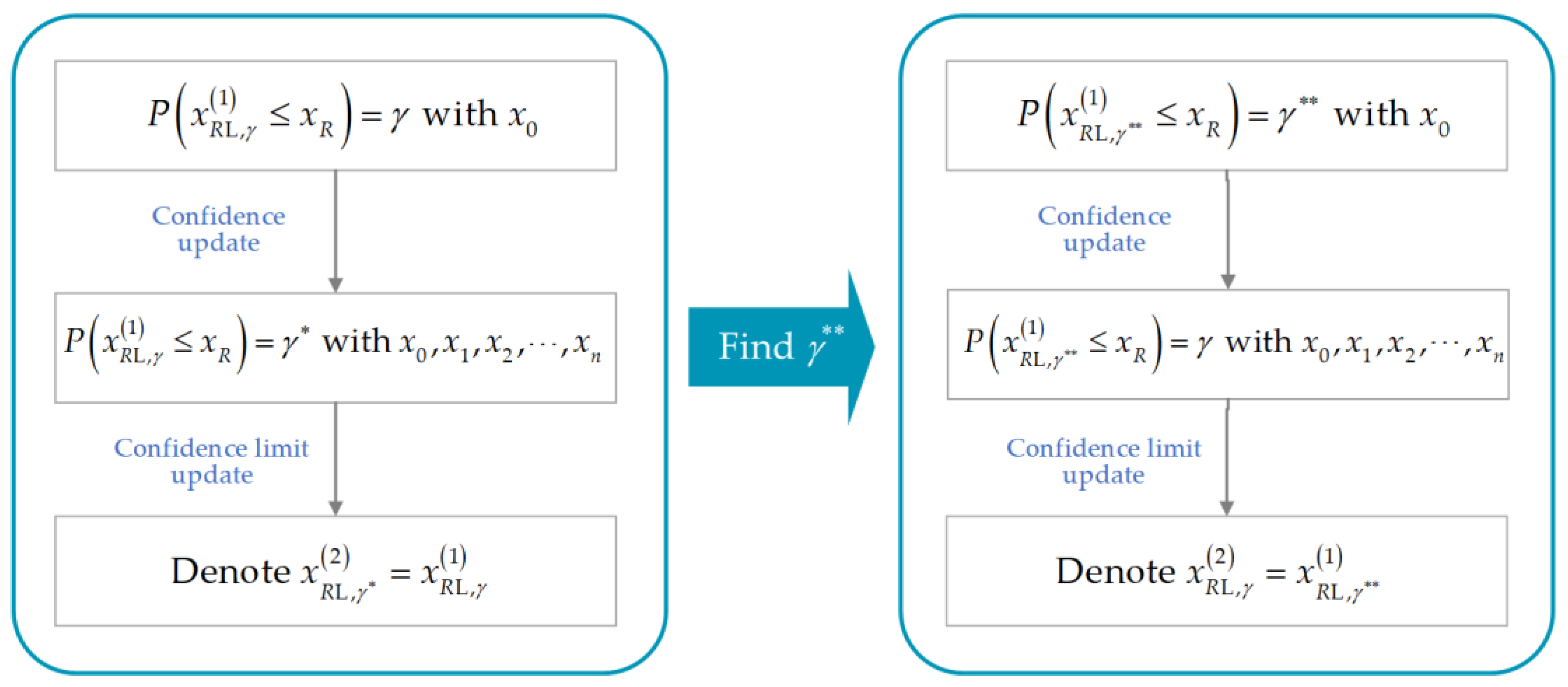
2.2. MLG’s Safe Life Extension by Outfield Life Data
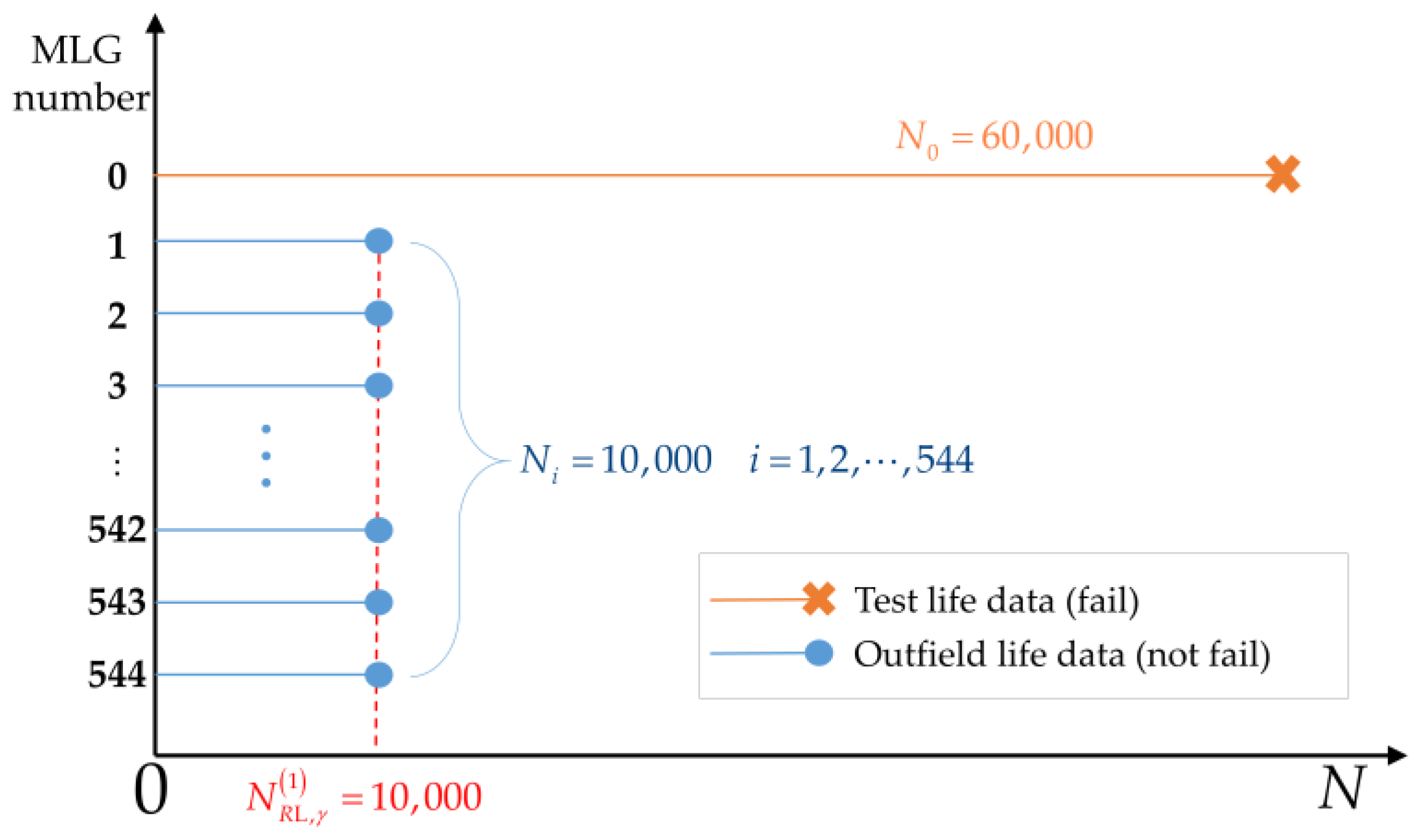
3. Safe Life Extension Example for MLG
4. Simulation Verification for MLG’s Safe Life Extension
- (1)
- Randomly simulate the MLG’s full-scale fatigue life test data via MC;
- (2)
- Determine the MLG’s safe life using the test life and Equation (1);
- (3)
- Randomly simulate the MLG’s outfield life data , , which should be censored at the determined safe life to match the engineering practice;
- (4)
- Extend the MLG’s safe life to via the proposed safe life extension method in Section 2.2;
- (5)
- Judge and record whether and are less than ;
- (6)
- Repeat Steps 1–5 50,000 times and count the frequencies of and in the MC simulations. That is, record the coverage probability for safe life determination and for safe life extension.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Confidence Updating Process Derivation of Equations (8)–(12)
Appendix B. The Mathematical Proof of Equations (18) and (19)
References
- Yan, C.L.; Liu, K.G. Theory of Economic Life Prediction and Reliability Assessment of Aircraft Structures. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2011, 24, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab, S.G.; Sirajuddin; Sreedhara, B.; Ganesh, E.; Babu, N.R.; Aithal, S.K. Finite Element Analysis of a Passenger Aircraft Landing Gear for Structural and Fatigue Safety. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 54, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnoli, F.; Dolce, F.; Colavita, M.; Bernabei, M. Fatigue Fracture of a Main Landing Gear Swinging Lever in a Civil Aircraft. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2008, 15, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, L.A.L.; Lourenco, N.J.; Graca, M.L.A.; Silva, O.M.M.; de Campos, P.P.; von Dollinger, C.F.A. Fatigue Fracture of a Nose Landing Gear in a Military Transport Aircraft. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2006, 13, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.J.; Dai, J.H.; Wei, T.; Liu, B.; Deng, Y.Q.; Ma, J. Structural Optimization of a Nose Landing Gear Considering Its Fatigue Life. J. Aircr. 2012, 49, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insley, J.; Turkoglu, C. A Contemporary Analysis of Aircraft Maintenance-Related Accidents and Serious Incidents. Aerospace 2020, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.L.; Su, K.X. Design of Safe Life and Damage Tolerance for Aircraft Landing Gear; Aviation Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2011; ISBN 978-7-80243-894-1. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.X.; Smith, S.; Duff, A. The Effect of Overloading Sequences on Landing Gear Fatigue Damage. Int. J. Fatigue 2009, 31, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandt, F., Jr. Damage Tolerant Design and Nondestructive Inspection—Keys to Aircraft Airworthiness. Procedia Eng. 2011, 17, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, S.M.O.; De Castro, P.M.S.T. An Overview of Fatigue in Aircraft Structures. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2017, 40, 1510–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuegel, E.J.; Bell, R.P.; Berens, A.P.; Brussat, T.; Cardinal, J.W.; Gallagher, J.P.; Rudd, J. Aircraft Structural Reliability and Risk Analysis Handbook Volume 1: Basic Analysis Methods; Air Force Research Laboratory Headquarters: Wright-Patterson AFB, OH, USA, 2013; pp. 1–104. [Google Scholar]
- Glista, S.M.; Postema, W.; Arcusa, L.; Clark, B. F-22 MECSIP Lessons Learned: Risk Based Fatigue Scatter Factors High Durability Margin Analysis Using Miner’s Rule and Weibull Analysis. In Proceedings of the ASME 2011 International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition; ASMEDC: Denver, CO, USA, 2011; pp. 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brot, A. Weibull or Log-Normal Distribution to Characterize Fatigue Life Scatter—Which Is More Suitable? In Proceedings of the ICAF 2019—Structural Integrity in the Age of Additive Manufacturing; Niepokolczycki, A., Komorowski, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, J.F. Maintenance Reliability Analysis for Increasing Parts Availability and Reducing Operations and Maintenance Costs. Ph.D. Thesis, The George Washington University, Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dziendzikowski, M.; Kurnyta, A.; Reymer, P.; Kurdelski, M.; Klysz, S.; Leski, A.; Dragan, K. Application of Operational Load Monitoring System for Fatigue Estimation of Main Landing Gear Attachment Frame of an Aircraft. Materials 2021, 14, 6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, D.L.; Gross, P.C.; Burt, R.J. F-35 Full Scale Durability Modeling and Test. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 891–892, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaisarje, G.; Khapli, R.P. Fatigue Crack Growth (FCG) Studies on Landing Gear (LG) Actuating Cylinder of Fighter Aircraft for Life Extension. In Proceedings of the Fatigue, Durability, and Fracture Mechanics; Seetharamu, S., Jagadish, T., Malagi, R., Eds.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2021; pp. 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.L.; Liu, K.G. Fatigue Scatter Factor of Whole Life and Reliability of Aircraft Structure Service Life. Adv. Mater. Res. 2008, 44–46, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Armament Department of the People’s Liberation Army of China. GJB 67.6A-2008; Military Airplane Structural Strength Specification Part6: Repeated Loads, Durability and Damage Tolerance. General Equipment Department Military Standard Publishing and Distribution Department: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese)
- Chen, Z.W. Structural Reliable Life and Spectrum Difference Factor. Int. J. Fatigue 1993, 15, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorupka, Z.; Tywoniuk, A. Health Monitoring in Landing Gears. J. KONES Powertrain Transp. 2019, 26, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfingstl, S.; Steinweg, D.; Zimmermann, M.; Hornung, M. On the Potential of Extending Aircraft Service Time Using Load Monitoring. J. Aircr. 2022, 59, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorupka, Z. Dynamic Fatigue Tests of Landing Gears. Fatigue Aircr. Struct. 2020, 2020, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, N.S.; Fu, Y.Z.; Hu, Z. Summary of determination of structures fatigue life for Y8 aircraft series. Aeronaut. Sci. Technol. 2006, 2006, 40–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iele, A.; Leone, M.; Consales, M.; Persiano, G.V.; Brindisi, A.; Ameduri, S.; Concilio, A.; Ciminello, M.; Apicella, A.; Bocchetto, F.; et al. Load Monitoring of Aircraft Landing Gears Using Fiber Optic Sensors. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2018, 281, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, G.; Sartor, P.; Reed, S.; Southern, P.; Worden, K.; Cross, E. Prediction of Landing Gear Loads Using Machine Learning Techniques. Struct. Health Monit.-Int. J. 2016, 15, 568–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Gui, W.H. Corrected Maximum Likelihood Estimations of the Lognormal Distribution Parameters. Symmetry 2020, 12, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaras, Z.; Lukosevicius, V. Statistical Assessment of Low-Cycle Fatigue Durability. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuti, A.; Bertini, F.; Cipolla, V.; Di Rito, G. Design of a Fuselage-Mounted Main Landing Gear of a Medium-Size Civil Transport Aircraft. Aerotec. Missili Spaz. 2018, 97, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Cai, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z. A Bayesian Proportional Hazards Model for General Interval-Censored Data. Lifetime Data Anal. 2015, 21, 470–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.B.; Li, X.Y.; Li, F.R.; Kang, R. Belief Reliability Evaluation with Uncertain Right Censored Time-to-Failure Data under Small Sample Situation. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2022, 38, 3099–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, N.; Ling, M.H. Gamma Lifetimes and One-Shot Device Testing Analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2014, 126, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.W. Weibull Parameter Estimation and Reliability Analysis with Zero-Failure Data from High-Quality Products. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 207, 107321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.P.; Lodhi, C.; Tripathi, Y.M.; Wang, L. Inference for Two-Parameter Rayleigh Competing Risks Data under Generalized Progressive Hybrid Censoring. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2021, 37, 1210–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannig, J.; Iyer, H.; Lai, R.C.S.; Lee, T.C.M. Generalized Fiducial Inference: A Review and New Results. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2016, 111, 1346–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Singh, K. Confidence Distribution, the Frequentist Distribution Estimator of a Parameter: A Review. Int. Stat. Rev. 2013, 81, 3–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.L.; Li, H.H.; Tian, W.Z.; Yang, Y.T. Confidence Interval, Prediction Interval and Tolerance Interval for the Skew Normal Distribution: A Pivotal Approach. Symmetry 2022, 14, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Scatter factor Lf | 4.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 |
| Confidence γ | 0.90 | 0.95 | 0.90 | 0.95 | 0.90 | 0.95 |
| Standard deviation σ0 | 0.138 | 0.127 | 0.160 | 0.148 | 0.178 | 0.164 |
| Simulation No. | Scatter Factor Lf | Required Confidence γ | Outfield Amount n |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.0 | 0.90 | 200, 500, 1000 |
| 2 | 4.0 | 0.95 | |
| 3 | 5.0 | 0.90 | |
| 4 | 5.0 | 0.95 | |
| 5 | 6.0 | 0.90 | |
| 6 | 6.0 | 0.95 |
| Simulation No. | Scatter Factor Lf | Required Confidence γ | Coverage Probability γ(1) | Respective Coverage Probabilities γ(2) with n = 200, 500, 1000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.0 | 0.90 | 0.899 | 0.899, 0.899, 0.900 |
| 2 | 4.0 | 0.95 | 0.950 | 0.949, 0.950, 0.950 |
| 3 | 5.0 | 0.90 | 0.900 | 0.899, 0.899, 0.898 |
| 4 | 5.0 | 0.95 | 0.949 | 0.950, 0.950, 0.950 |
| 5 | 6.0 | 0.90 | 0.898 | 0.900, 0.901, 0.898 |
| 6 | 6.0 | 0.95 | 0.951 | 0.951, 0.949, 0.949 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Fu, H.; Zhang, S. A Novel Safe Life Extension Method for Aircraft Main Landing Gear Based on Statistical Inference of Test Life Data and Outfield Life Data. Symmetry 2023, 15, 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15040880
Fu Y, Fu H, Zhang S. A Novel Safe Life Extension Method for Aircraft Main Landing Gear Based on Statistical Inference of Test Life Data and Outfield Life Data. Symmetry. 2023; 15(4):880. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15040880
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yueshuai, Huimin Fu, and Sheng Zhang. 2023. "A Novel Safe Life Extension Method for Aircraft Main Landing Gear Based on Statistical Inference of Test Life Data and Outfield Life Data" Symmetry 15, no. 4: 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15040880
APA StyleFu, Y., Fu, H., & Zhang, S. (2023). A Novel Safe Life Extension Method for Aircraft Main Landing Gear Based on Statistical Inference of Test Life Data and Outfield Life Data. Symmetry, 15(4), 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15040880







