Tailoring a Behavioral Symmetry on KERMA, Mass Stopping Power and Projected Range Parameters against Heavy-Charged Particles in Zinc-Tellurite Glasses for Nuclear Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Background
2.2. SRIM and PAGEX Codes
2.3. Investigated Glass Samples
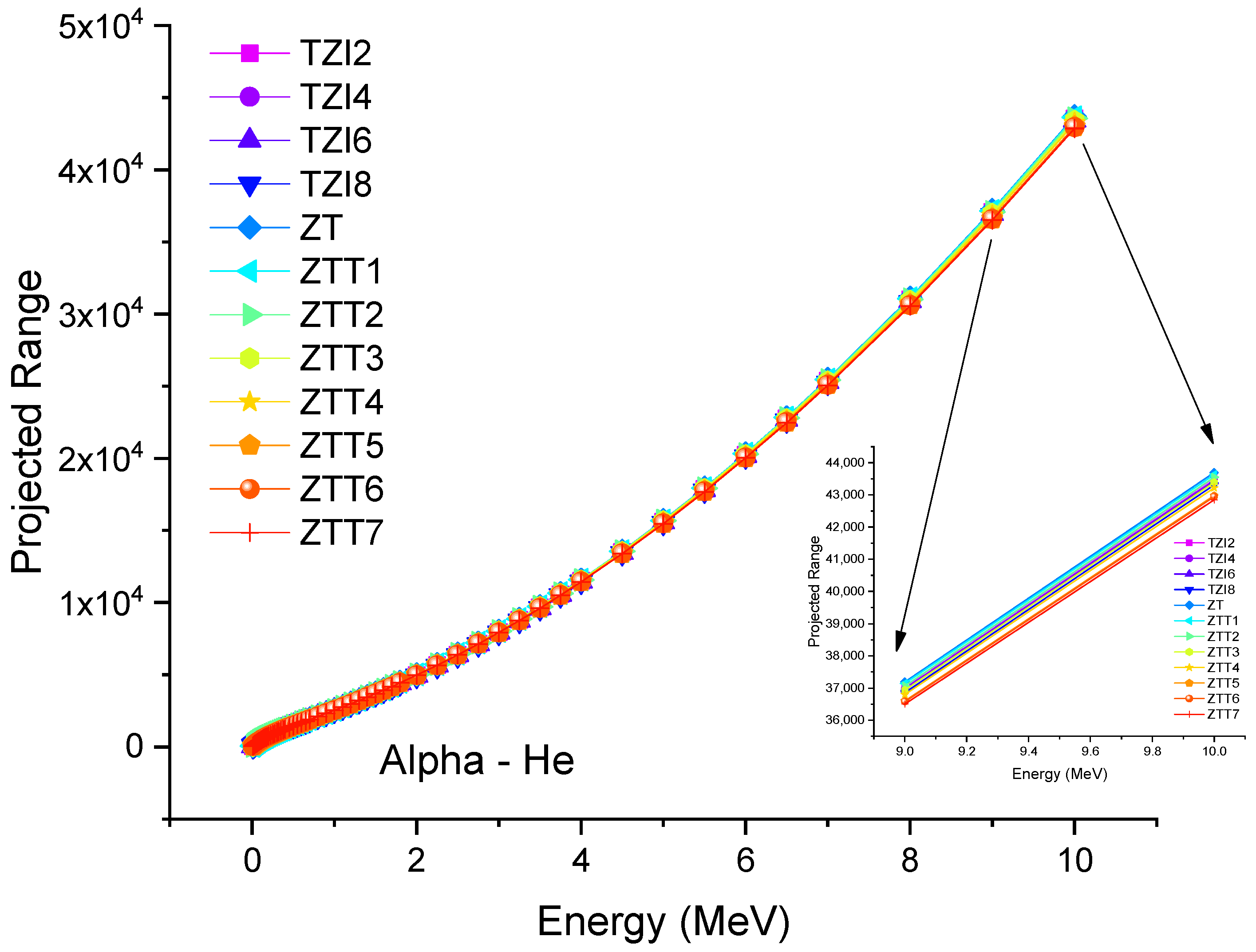
3. Results and Discussion
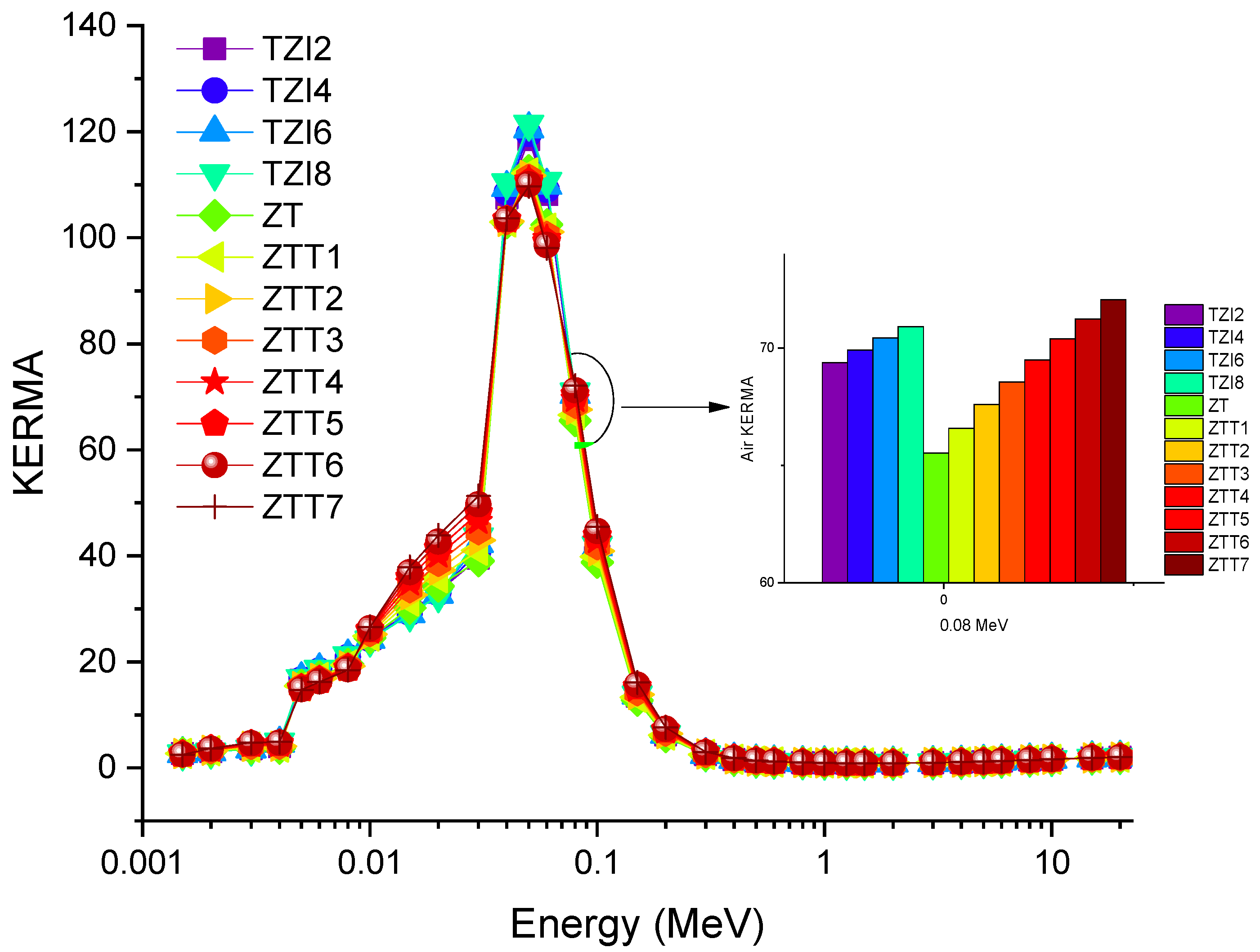
3.1. Assessment of KERMA Values for Glass Shields
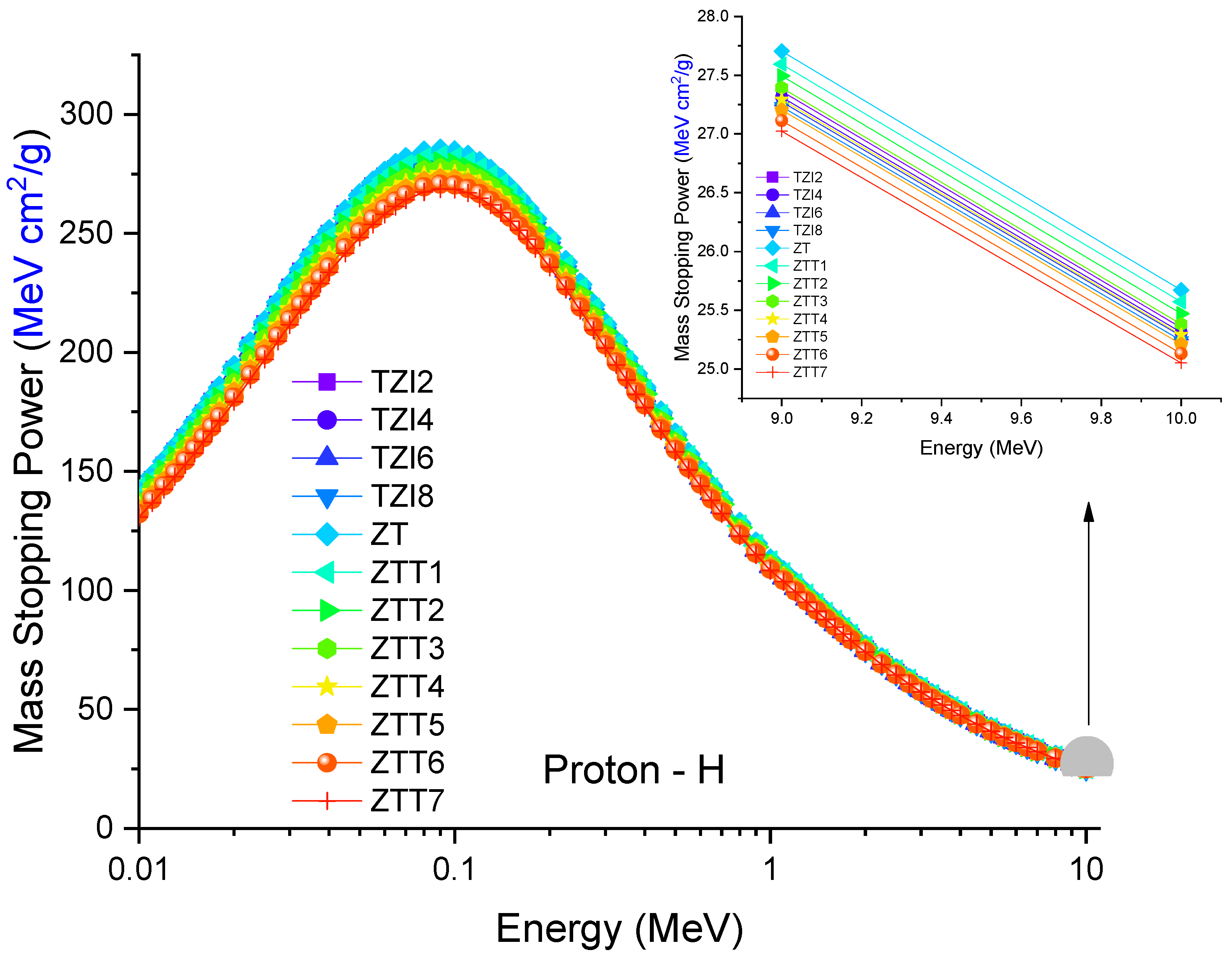
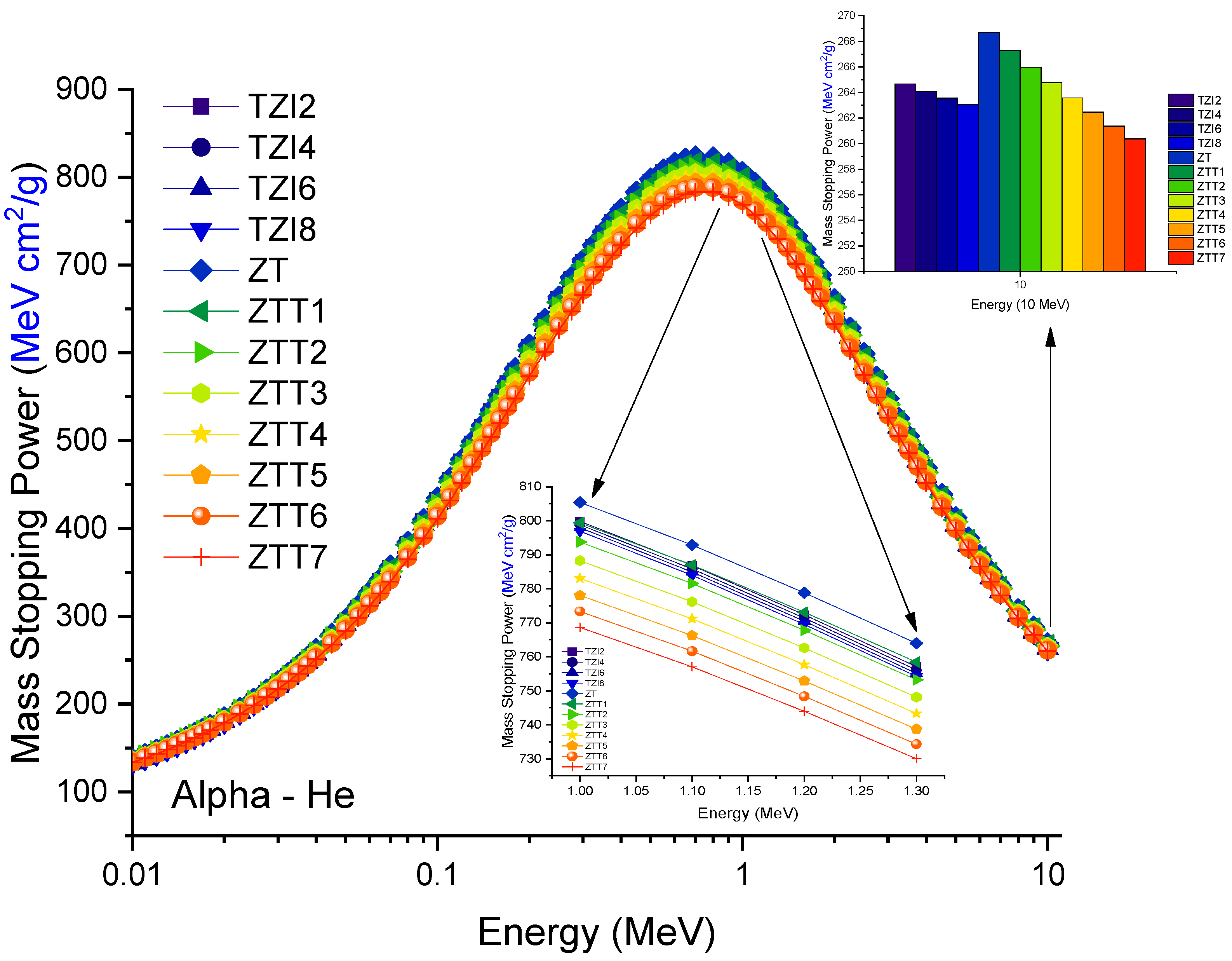
3.2. Assessment of Mass Stopping Power Values for Glass Shields
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flerov, G.N.; Barashenkov, V.S. Practical applications of heavy ion beams. Sov. Phys. Uspekhi 1975, 17, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghossain, M.O. Calculations of Stopping Power, and Range of Ions Radiation (Alpha Particles) Interaction with Different Materials and Human Body Parts. Int. J. Phys. 2017, 5, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Crnjac, A.; Jakšić, M.; Matijević, M.; Rodriguez-Ramos, M.; Pomorski, M.; Siketić, Z. Energy loss of MeV protons in diamond: Stopping power and mean ionization energy. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 132, 109621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, A.A. Calculating electronic stopping power in materials from first principles. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2018, 150, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SRIM - The Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter. Available online: http://www.srim.org/ (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Ziegler, J.F.; Ziegler, M.D.; Biersack, J.P. SRIM—The stopping and range of ions in matter. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 2010, 268, 1818–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Available online: https://github.com/sriharijayaram5/PAGEX (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Available online: https://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/Star/Text/ASTAR.html (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Available online: https://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/Star/Text/PSTAR.html (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Available online: https://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/Star/Text/ESTAR.html (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Kurudirek, M. Effective atomic number, energy loss and radiation damage studies in some materials commonly used in nuclear applications for heavy charged particles such as H, C, Mg, Fe, Te, Pb and U. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2016, 122, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhuo, W.; Shen, H.; Chen, B. Changes of the linear energy transfer (LET) and beam width of therapeutic carbon ion beam in density heterogeneous phantoms. J. Radiol. Prot. 2022, 42, 021518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıcoğlu, O.; Altunsoy, E.; Agar, O.; Kamislioglu, M.; Sayyed, M.; Tekin, H.; Tarhan, N. Synergistic effect of La2O3 on mass stopping power (MSP)/projected range (PR) and nuclear radiation shielding abilities of silicate glasses. Results Phys. 2019, 14, 102424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.; Jayaram, S.; Bubbly, S.; Gudennavar, S. A simple software for swift computation of photon and charged particle interaction parameters: PAGEX. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2021, 176, 109903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavaz, E.; Tekin, H.O.; Agar, O.; Altunsoy, E.E.; Kilicoglu, O.; Kamislioglu, M.; Abuzaid, M.M.; Sayyed, M.I. The Mass stopping power/projected range and nuclear shielding behaviors of barium bismuth borate glasses and influence of cerium oxide. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 15348–15357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaniwa, T.; Kanematsu, N. Effective particle energies for stopping power calculation in radiotherapy treatment planning with protons and helium, carbon, and oxygen ions. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, N542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geithner, O.; Andreo, P.; Sobolevsky, N.; Hartmann, G.; Jäkel, O. Calculation of stopping power ratios for carbon ion dosimetry. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, 2279–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegena, E.; Androulakaki, E.; Kokkoris, M.; Patronis, N.; Stamati, M. A comparative study of stopping power calculations implemented in Monte Carlo codes and compilations with experimental data. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2020, 467, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, M.; Machrafi, R. Development of a new code for stopping power and CSDA range calculation of incident charged particles, part A: Electron and positron. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2020, 161, 109145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bake, W.Y.; Braunroth, T.; Rosales, L.D.L.F.; Rahm, J.M.; Rabus, H. Stopping power of water for carbon ions with energies in the Bragg peak region. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 102, 062418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Ullah, N.; Rahman, A.U. Density-dependent Energy Loss of Protons in Pb and Be Targets and Percent Mass-Stopping Power from Bethe-Bloch Formula and Bichsel-Sternheimer Data within 1–12 MeV Energy Range: A Comparative Study Based on Bland-Altman Analysis. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Sci. 2019, 50, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palmer, G.; Bailey, B.; Wilkinson, C.; Duru, F. Radiation Shielding Capabilities of Glasses with Potential Applications in Spacecraft and Laboratories. In Proceedings of the APS March Meeting 2018 Volume 63, Number 1 Monday–Friday, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 5–9 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Brandt, W.; Kitagawa, M. Effective stopping-power charges of swift ions in condensed matter. Phys. Rev. B 1982, 25, 5631–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biersack, J.P.; Haggmark, L.G. A Monte Carlo computer program for the transport of energetic ions in amorphous targets. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 1980, 174, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, J.F.; Ziegler, M.D.; Biersack, J.P. The Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985; ISBN 978-0-08-021607-2. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, M.; Torrens, I. Computer simulation of atomic-displacement cascades in solids in the binary-collision approximation. Phys. Rev. B 1974, 9, 5008–5024, Bibcode: 1974PhRvB...9.5008R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Was, G. Fundamentals of Radiation Materials Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, R. Atomic & Ion Collisions in Solids and at Surfaces: Theory, Simulation and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997; ISBN 978-0-521-44022-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kilic, G.; Ilik, E.; Issa, S.A.; Issa, B.; Issever, U.; Zakaly, H.M.; Tekin, H. Fabrication, structural, optical, physical and radiation shielding characterization of indium (III) oxide reinforced 85TeO2-(15–x)ZnO-xIn2O3 glass system. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 27305–27315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, G.; Işsever, U.G.; Ilik, E. The synthesis and characterization of zinc-tellurite semiconducting oxide glasses containing Ta2O5. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 065907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekerek, S. Calculation of Air Kerma of CT Contrast Agents and Painkiller. J. Biomed. Res. Environ. Sci. 2021, 2, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Elemental Mass Fractions (wt.%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Te | Zn | In | Ta | O | Density (g/cm3) |
| TZI2 | 29.210 | 4.467 | 1.375 | 0.000 | 64.948 | 5.60 |
| TZI4 | 28.620 | 3.704 | 2.694 | 0.000 | 64.983 | 5.63 |
| TZI6 | 28.053 | 2.970 | 3.960 | 0.000 | 65.017 | 5.65 |
| TZI8 | 27.508 | 2.265 | 5.178 | 0.000 | 65.049 | 5.67 |
| ZT | 27.273 | 9.091 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 63.636 | 5.51 |
| ZTT1 | 26.589 | 8.863 | 0.000 | 0.716 | 63.832 | 5.55 |
| ZTT2 | 25.926 | 8.642 | 0.000 | 1.411 | 64.021 | 5.59 |
| ZTT3 | 25.282 | 8.427 | 0.000 | 2.085 | 64.205 | 5.64 |
| ZTT4 | 24.658 | 8.219 | 0.000 | 2.740 | 64.384 | 5.69 |
| ZTT5 | 24.051 | 8.017 | 0.000 | 3.376 | 64.557 | 5.75 |
| ZTT6 | 23.461 | 7.820 | 0.000 | 3.993 | 64.725 | 5.78 |
| ZTT7 | 22.888 | 7.629 | 0.000 | 4.594 | 64.889 | 5.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Susam, L.A.; Yilmaz, A.; ALMisned, G.; Yilmaz Alan, H.; Ozturk, G.; Kilic, G.; Tuysuz, B.; Topuzlar, S.E.; Akkus, B.; Ene, A.; et al. Tailoring a Behavioral Symmetry on KERMA, Mass Stopping Power and Projected Range Parameters against Heavy-Charged Particles in Zinc-Tellurite Glasses for Nuclear Applications. Symmetry 2023, 15, 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15061201
Susam LA, Yilmaz A, ALMisned G, Yilmaz Alan H, Ozturk G, Kilic G, Tuysuz B, Topuzlar SE, Akkus B, Ene A, et al. Tailoring a Behavioral Symmetry on KERMA, Mass Stopping Power and Projected Range Parameters against Heavy-Charged Particles in Zinc-Tellurite Glasses for Nuclear Applications. Symmetry. 2023; 15(6):1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15061201
Chicago/Turabian StyleSusam, Lidya Amon, Ayberk Yilmaz, Ghada ALMisned, Hatice Yilmaz Alan, Gizem Ozturk, Gokhan Kilic, Bahar Tuysuz, Selin Ece Topuzlar, Baki Akkus, Antoaneta Ene, and et al. 2023. "Tailoring a Behavioral Symmetry on KERMA, Mass Stopping Power and Projected Range Parameters against Heavy-Charged Particles in Zinc-Tellurite Glasses for Nuclear Applications" Symmetry 15, no. 6: 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15061201
APA StyleSusam, L. A., Yilmaz, A., ALMisned, G., Yilmaz Alan, H., Ozturk, G., Kilic, G., Tuysuz, B., Topuzlar, S. E., Akkus, B., Ene, A., & Tekin, H. O. (2023). Tailoring a Behavioral Symmetry on KERMA, Mass Stopping Power and Projected Range Parameters against Heavy-Charged Particles in Zinc-Tellurite Glasses for Nuclear Applications. Symmetry, 15(6), 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15061201









