Bending Analysis of Symmetrical Porous Functionally Graded Sandwich Panels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model Establishment and Formula
2.1. FMG Sandwich Panel
2.2. Material Properties
2.3. Displacement and Shape Function
2.4. Constitutive Equation
- depends on
- obtains
- while
2.5. Governing Equations
2.6. Closed-Form Solution of Functionally Graded Sandwich Panels
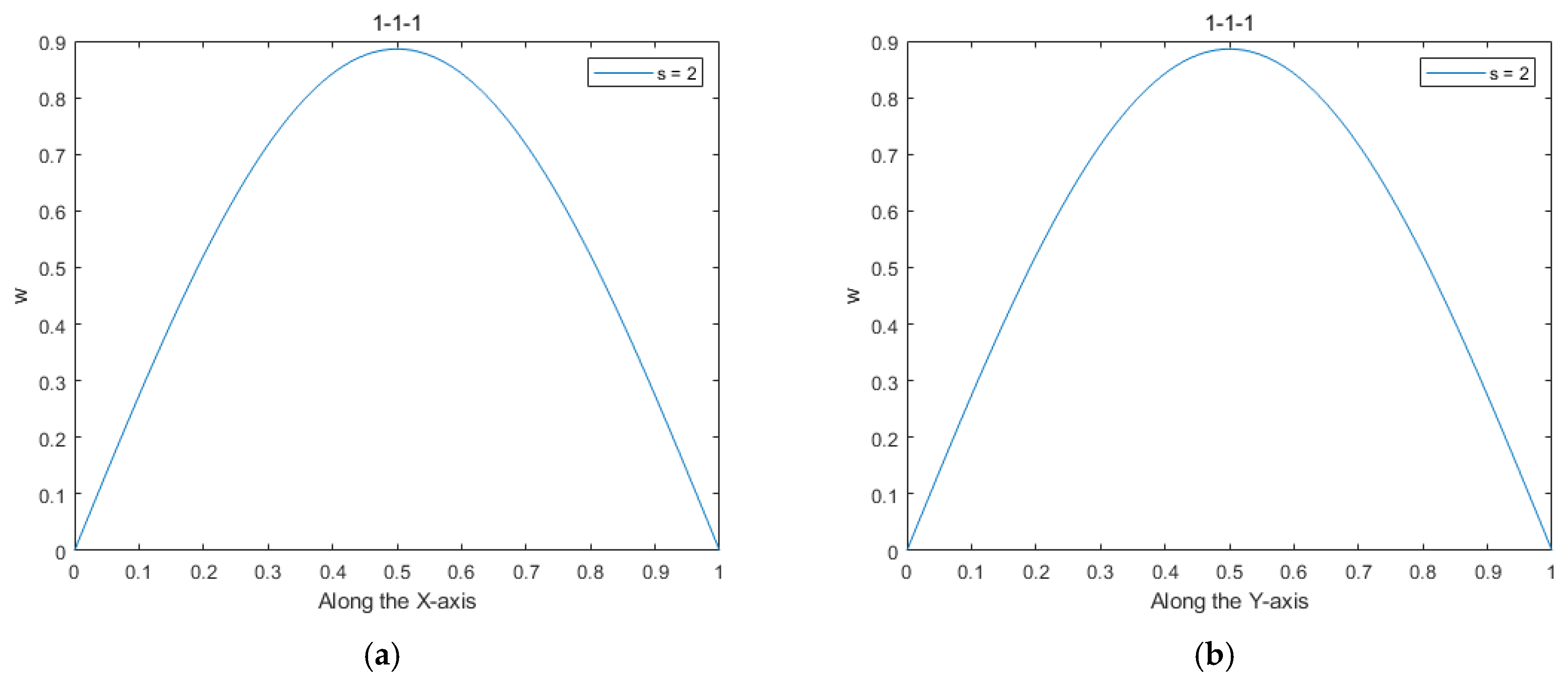
3. Model Validation and Numerical Results
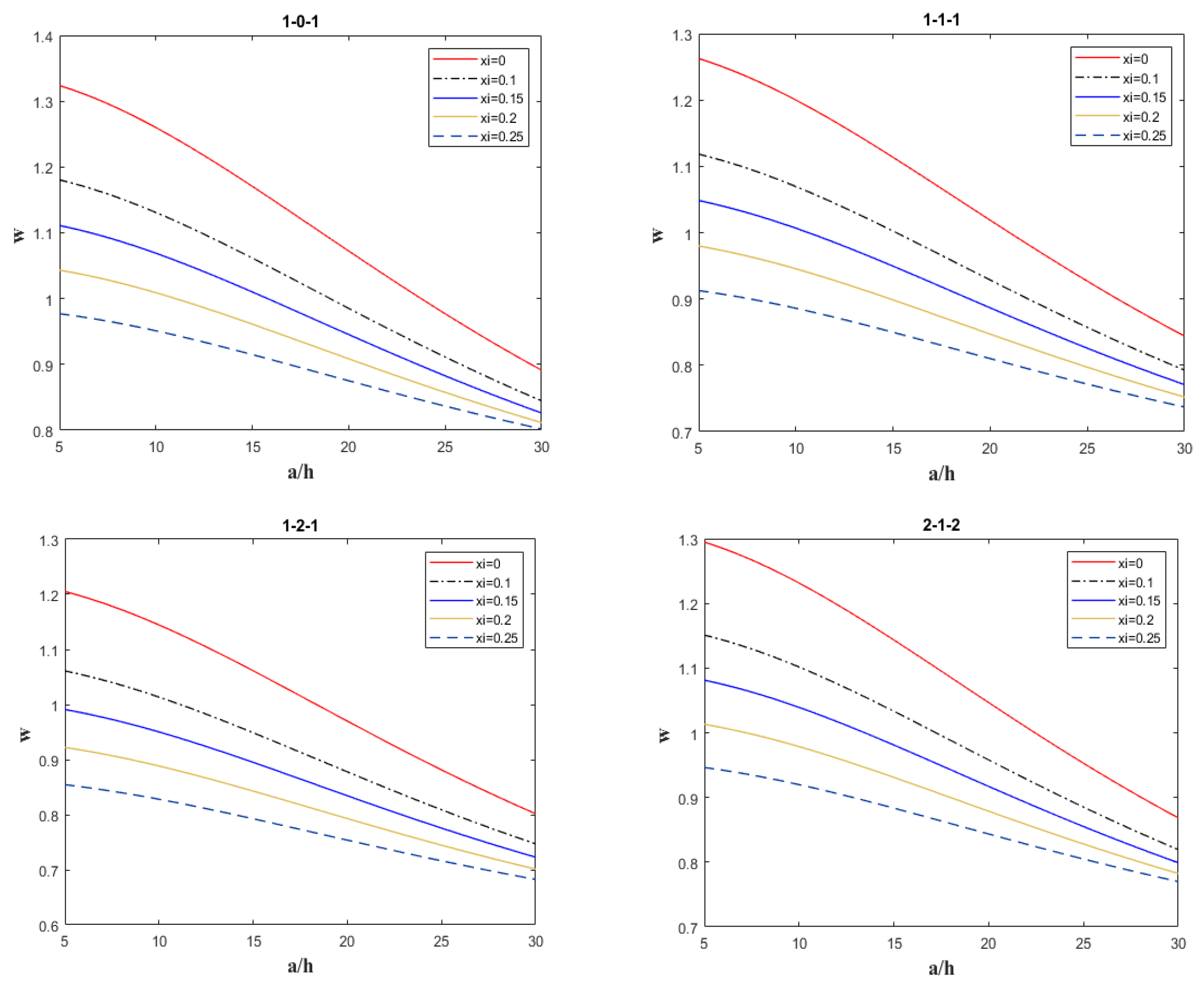
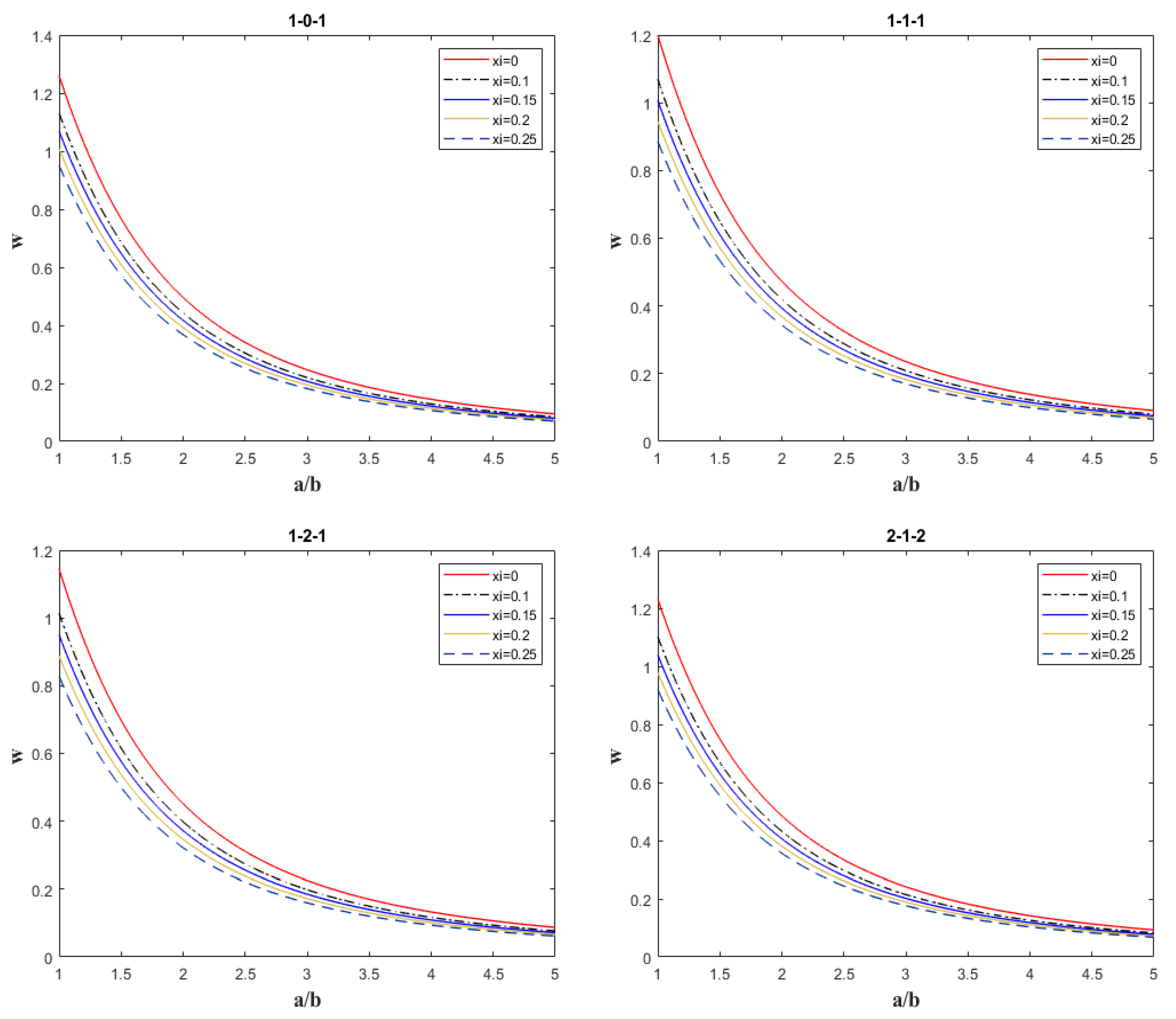
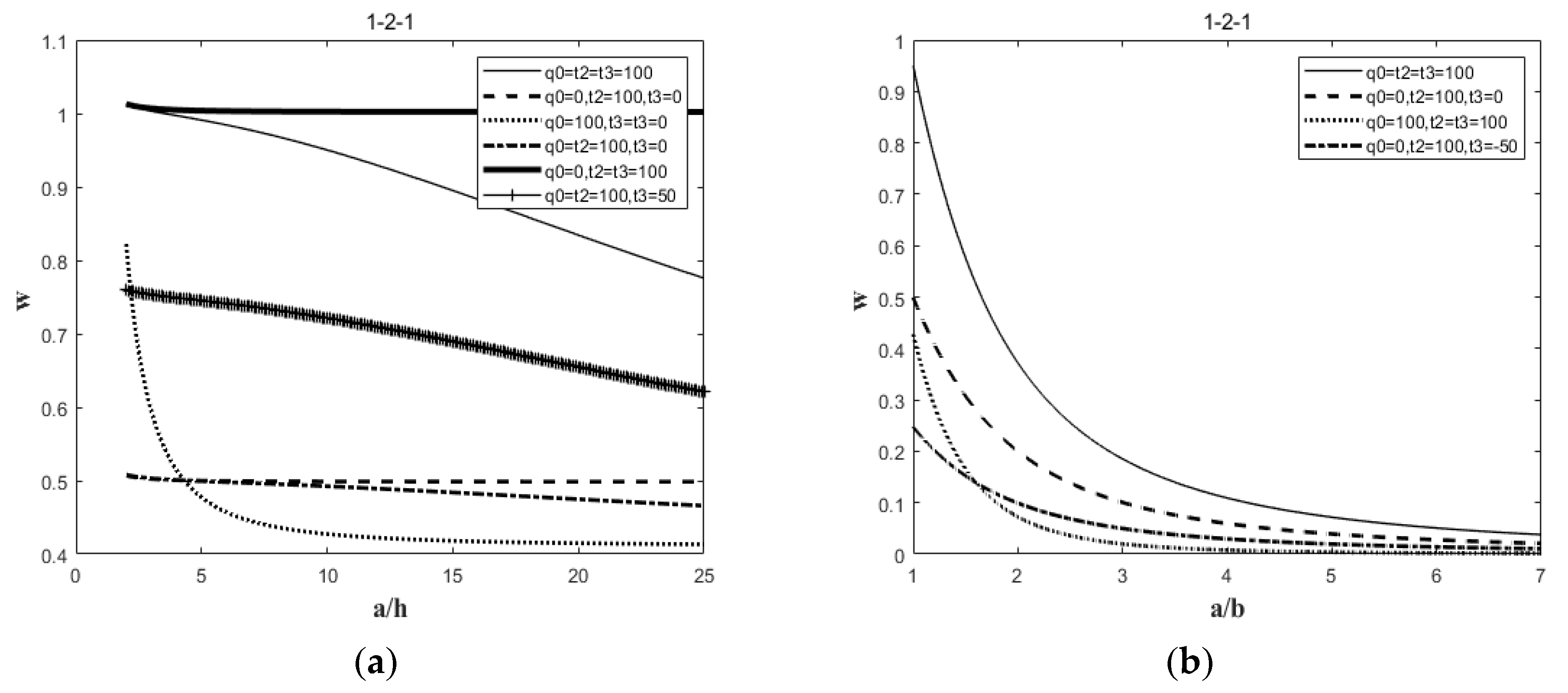
Parameter Analysis
4. Conclusions
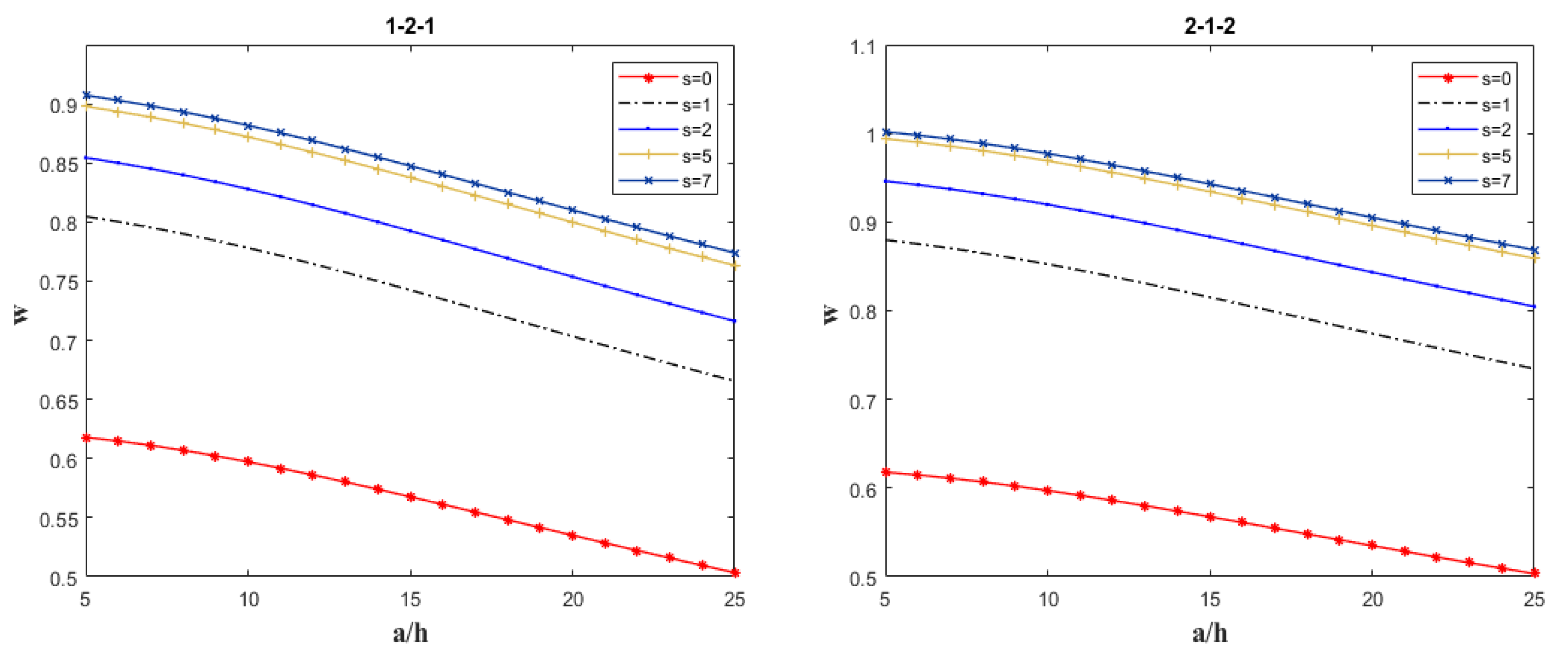
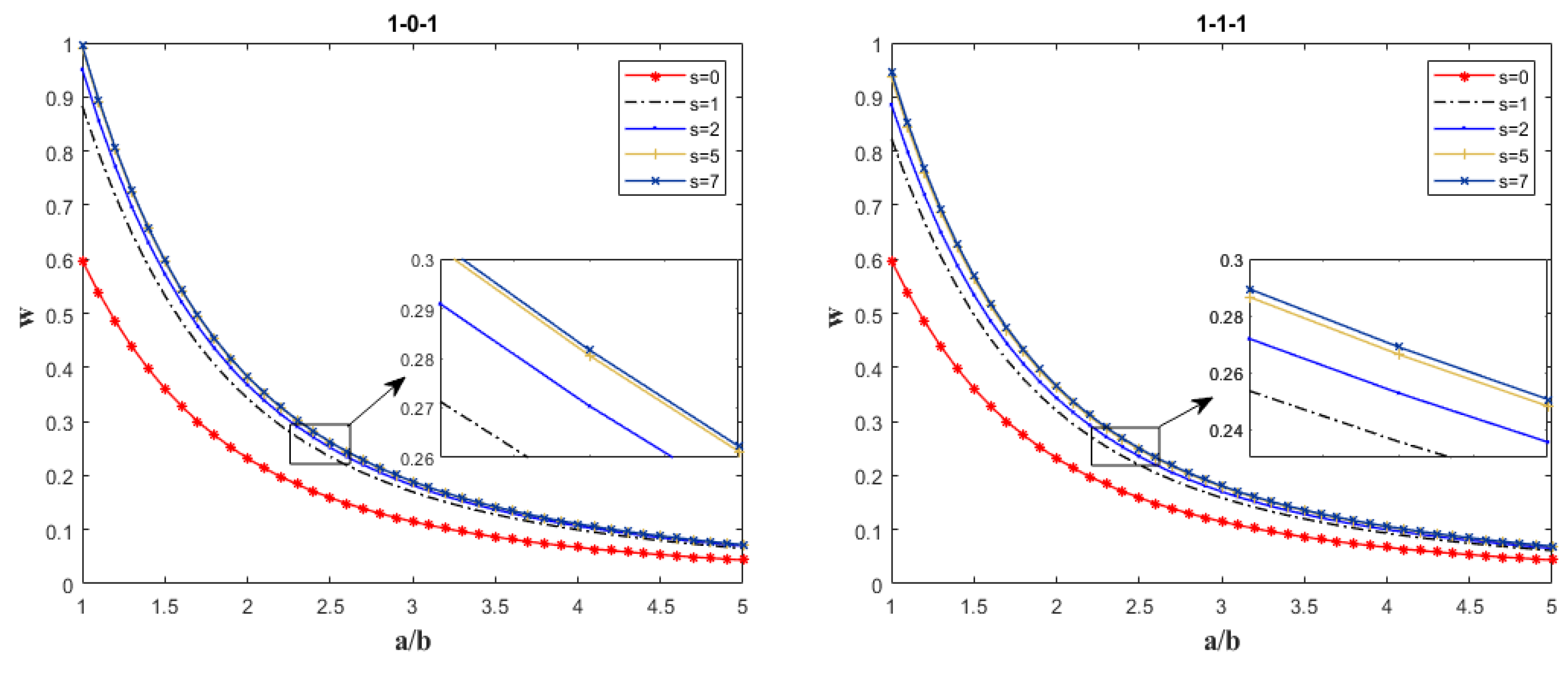
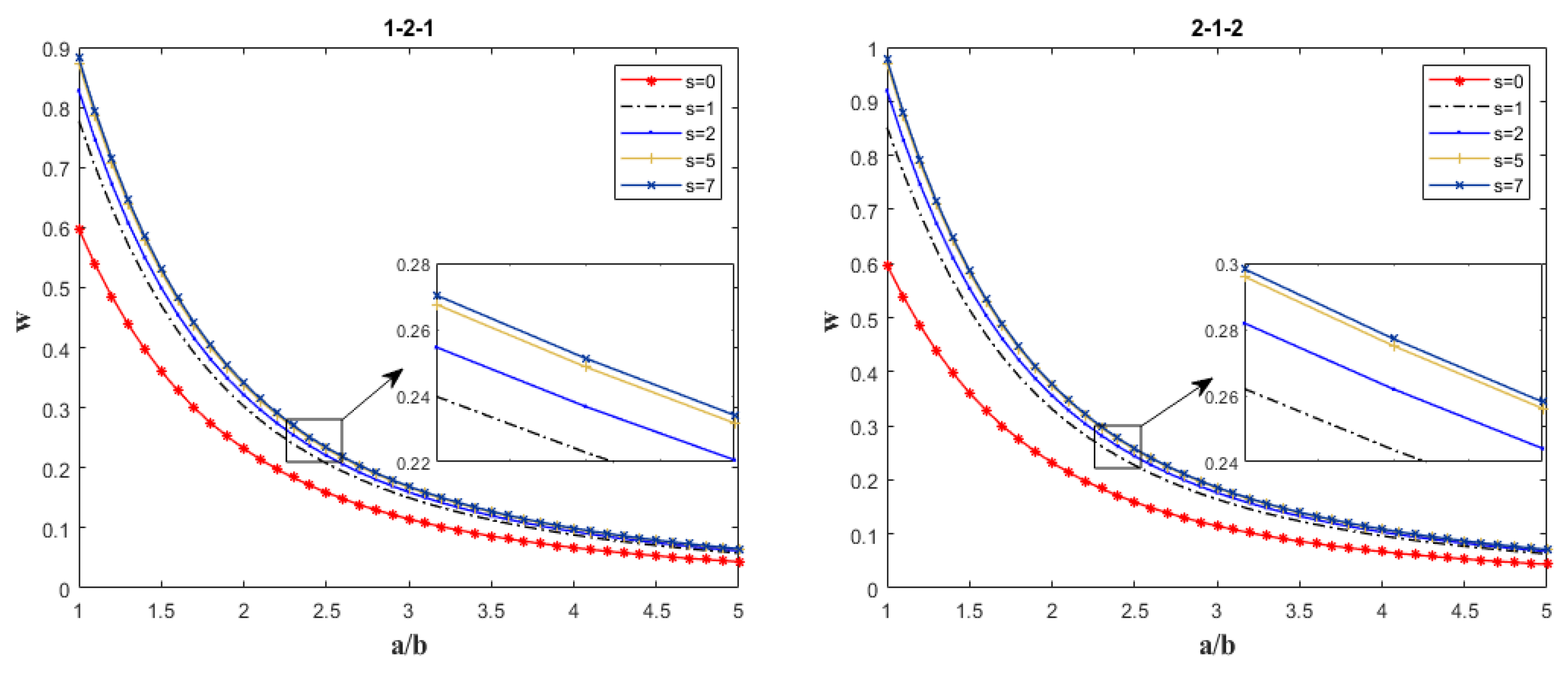
- Under a given layer thickness ratio, the dimensionless deflection of the functionally graded sandwich plate increases with the rise in the gradient index s.
- For a given volume fraction and identical layer thickness ratio, the deflection trends of different pore structures vary with increasing porosity. Specifically, the dimensionless deflection of Pore Type 1 decreases as porosity increases, whereas the dimensionless deflections of Pore Type 2 and Pore Type 3 exhibit an increasing trend with higher porosity.
- At a given porosity level, regardless of the specific value of the volume fraction index s, the dimensionless deflection w of the sandwich plate decreases with increasing edge thickness ratio or aspect ratio.
- For a fixed gradient index, irrespective of the porosity xi within the range [0, 0.3], the dimensionless deflection w of the sandwich plate decreases as the edge thickness ratio or aspect ratio increases.
- Compared to mechanical loading and thermal loading, the dimensionless deflection under thermal loading alone is greater than that under mechanical loading alone.
- Under thermo-mechanical loading, the deflection of the functionally graded sandwich plate is significantly more sensitive to changes in the aspect ratio than to variations in the edge thickness ratio.
- By adjusting the gradient index and porosity of the sandwich panel, the bending stiffness of the structure can be improved without significantly increasing the weight. For example, in aerospace applications, the optimized design of the gradient index can effectively alleviate thermal stress concentration while reducing the amount of material used; in new energy vehicle battery brackets, the gradient porosity design can balance structural strength and heat dissipation efficiency, thereby extending battery life.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, H.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, J.; Ruan, D. Review of sandwich structures under impact loadings: Experimental, numerical and theoretical analysis. Thin Walled Struct. 2024, 196, 111541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkunte, S.; Fidan, I.; Naikwadi, V.; Gudavasov, S.; Ali, M.A.; Mahmudov, M.; Hasanov, S.; Cheepu, M. Advancements and Challenges in Additively Manufactured Functionally Graded Materials: A Comprehensive Review. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2024, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Van, V.; Peng, C.; Liu, J.; Tran, P.; Nguyen-Xuan, H. Performance evaluations of functionally graded porous structures. In Machine Learning Aided Analysis Design and Additive Manufacturing of Functionally Graded Porous Composite Structures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 315–346. [Google Scholar]
- Mechab, I.; Mechab, B.; Benaissa, S.; Serier, B.; Bouiadjra, B.B. Free vibration analysis of FGM nanoplate with porosities resting on Winkler Pasternak elastic foundations based on two-variable refined plate theories. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2016, 38, 2193–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenkour, A.M. Hygrothermal effects on the bending of angle-ply composite plates using a sinusoidal theory. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 3685–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, H.T.; Vo, T.P. A new sinusoidal shear deformation theory for bending, buckling, and vibration of functionally graded plates. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 37, 3269–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahi, A.; Tounsi, A. A new hyperbolic shear deformation theory for bending and free vibration analysis of isotropic, functionally graded, sandwich and laminated composite plates. Appl. Math. Model. 2015, 39, 2489–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantari, J.L.; Granados, E.V. A refined FSDT for the static analysis of functionally graded sandwich plates. Thin Walled Struct. 2015, 90, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, C.H.; Kulasegaram, S.; Tran, L.V.; Nguyen-Xuan, H. Generalized shear deformation theory for functionally graded isotropic and sandwich plates based on isogeometric approach. Comput. Struct. 2014, 141, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantari, J.L.; Monge, J.C. Buckling, free vibration and bending analysis of functionally graded sandwich plates based on an optimized hyperbolic unified formulation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2016, 119, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Thai, C.H.; Nguyen-Xuan, H. A novel computational approach for functionally graded isotropic and sandwich plate structures based on a rotation-free meshfree method. Thin Walled Struct. 2016, 107, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, K.; Hirannaiah, S.; Rajanna, T. Vibration and stability characteristics of functionally graded sandwich plates with/without porosity subjected to localized edge loadings. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 2023, 51, 6254–6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertenli, M.F.; Esen, İ. The effect of the various porous layers on thermomechanical buckling of FGM sandwich plates. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2024, 31, 10935–10961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.C.; Tran, H.Q.; Pham, V.V. Nonlinear static analysis of bi-directional functionally graded sandwich plates in thermal environments by a higher-order finite element model. Thin Walled Struct. 2023, 188, 110819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenkour, A.M.; Alghamdi, N.A. Bending analysis of functionally graded sandwich plates under the effect of mechanical and thermal loads. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2010, 17, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantari, J.L.; Granados, E.V. Thermoelastic behavior of advanced composite sandwich plates by using a new 6 unknown quasi-3D hybrid type HSDT. Compos. Struct. 2015, 126, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantari, J.L.; Granados, E.V. Thermoelastic analysis of advanced sandwich plates based on a new quasi-3D hybrid type HSDT with 5 unknowns. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 69, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Shen, H.S. Nonlinear analysis of sandwich plates with FGM face sheets resting on elastic foundations. Compos. Struct. 2011, 93, 2521–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liew, K.M.; Kitipornchai, S. Dynamic stability of laminated FGM plates based on higher-order shear deformation theory. Comput. Mech. 2004, 33, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadji, L.; Tounsi, A. Static deflections and stress distribution of functionally graded sandwich plates with porosity. Smart Struct. Syst. Int. J. 2021, 28, 343–354. [Google Scholar]
- Sah, S.K.; Ghosh, A. Effect of porosity on the thermal buckling analysis of power and sigmoid law functionally graded material sandwich plates based on sinusoidal shear deformation theory. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2022, 22, 2250063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Talha, M. Influence of porosity on the flexural and free vibration responses of functionally graded plates in thermal environment. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2018, 18, 1850013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavari, D.; Shahsavari, M.; Li, L.; Karami, B. A novel quasi-3D hyperbolic theory for free vibration of FG plates with porosities resting on Winkler/Pasternak/Kerr foundation. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2018, 72, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanasakulpong, N.; Ungbhakorn, V. Linear and nonlinear vibration analysis of elastically restrained ends FGM beams with porosities. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, J.N. A simple higher-order theory for laminated composite plates. J. Appl. Mech. 1984, 51, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reissner, E. On tranverse bending of plates, including the effect of transverse shear deformation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1975, 11, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touratier, M. An efficient standard plate theory. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 1991, 29, 901–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tounsi, A.; Houari MS, A.; Benyoucef, S. A refined trigonometric shear deformation theory for thermoelastic bending of functionally graded sandwich plates. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2013, 24, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houari MS, A.; Tounsi, A.; Bég, O.A. Thermoelastic bending analysis of functionally graded sandwich plates using a new higher order shear and normal deformation theory. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2013, 76, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Material | (/K) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 70 | 0.3 | 23 |
| ZrO2 | 117 | 1/3 | 7.11 |
| Type | 1-0-1 | 1-1-1 | 1-2-1 | 2-1-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ||||
| 0 | ||||
| s | theory | 1-0-1 | 1-1-1 | 2-1-2 | 3-1-3 |
| 0 | paper [29] (SSDPT) | 0.79678 | 0.79678 | 0.79678 | 0.79678 |
| paper [29] (FSDPT) | 0.89573 | 0.89573 | 0.89573 | 0.89573 | |
| Reissner | 0.89543 | 0.89543 | 0.89543 | 0.89543 | |
| Reddy | 0.80817 | 0.80817 | 0.80817 | 0.80817 | |
| Touratier | 0.79678 | 0.79678 | 0.79678 | 0.79678 | |
| 1 | paper [29] (SSDPT) | 1.06284 | 1.01126 | 1.03621 | 1.04502 |
| paper [29] (FSDPT) | 1.19072 | 1.13244 | 1.16056 | 1.17053 | |
| Reissner | 1.19411 | 1.13626 | 1.16425 | 1.17414 | |
| Reddy | 1.07769 | 1.02537 | 1.05067 | 1.05961 | |
| Touratier | 1.06284 | 1.01126 | 1.03621 | 1.04503 | |
| 2 | paper [29] (SSDPT) | 1.12160 | 1.06809 | 1.09609 | 1.10517 |
| paper [29] (FSDPT) | 1.25730 | 1.19570 | 1.22776 | 1.23823 | |
| Reissner | 1.25988 | 1.19991 | 1.23130 | 1.24148 | |
| Reddy | 1.13730 | 1.08291 | 1.11135 | 1.12058 | |
| Touratier | 1.12161 | 1.06809 | 1.09609 | 1.10517 | |
| 3 | paper [29] (SSDPT) | 1.14165 | 1.09231 | 1.11979 | 1.12808 |
| paper [29] (FSDPT) | 1.28074 | 1.22323 | 1.25504 | 1.26472 | |
| Reissner | 1.28228 | 1.22701 | 1.25781 | 1.26709 | |
| Reddy | 1.15769 | 1.10748 | 1.13542 | 1.14386 | |
| Touratier | 1.14166 | 1.09231 | 1.11979 | 1.12808 | |
| 5 | paper [29] (SSDPT) | 1.15441 | 1.11266 | 1.13799 | 1.14485 |
| paper [29] (FSDPT) | 1.29610 | 1.24683 | 1.27649 | 1.28462 | |
| Reissner | 1.29653 | 1.24976 | 1.27816 | 1.28584 | |
| Reddy | 1.17072 | 1.12815 | 1.15395 | 1.16095 | |
| Touratier | 1.15441 | 1.11266 | 1.13799 | 1.14485 |
| Volume Fraction | Type Function | Pore 1 | Pore 2 | Pore 3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xi = 0 | xi = 0.1 | xi = 0.15 | xi = 0.2 | xi = 0.1 | xi = 0.15 | xi = 0.2 | xi = 0.1 | xi = 0.15 | xi = 0.2 | ||
| 1-0-1 | Reissner | 1.25988 | 1.13080 | 1.06891 | 1.00894 | 1.34635 | 1.74373 | 2.10809 | 1.69370 | 1.93663 | 2.19699 |
| Reddy | 1.13730 | 1.02173 | 0.96640 | 0.91285 | 1.23730 | 1.59340 | 1.92076 | 1.52665 | 1.74501 | 1.97919 | |
| Touratier | 1.12161 | 1.00781 | 0.95335 | 0.90065 | 1.21230 | 1.56145 | 1.88216 | 1.50507 | 1.72012 | 1.95071 | |
| 1-1-1 | Reissner | 1.19991 | 1.06955 | 1.00671 | 0.94549 | 1.96094 | 2.53031 | 3.14298 | 1.95532 | 2.41580 | 2.93388 |
| Reddy | 1.08291 | 0.96610 | 0.90985 | 0.85512 | 1.77430 | 2.28917 | 2.84568 | 1.76210 | 2.17677 | 2.64404 | |
| Touratier | 1.06809 | 0.95305 | 0.89766 | 0.84377 | 1.74727 | 2.25191 | 2.79569 | 1.73655 | 2.14463 | 2.60409 | |
| 1-2-1 | Reissner | 1.14440 | 1.01349 | 0.95018 | 0.88834 | 2.27972 | 3.14814 | 4.21453 | 2.22296 | 2.96961 | 4.31152 |
| Reddy | 1.03269 | 0.91533 | 0.85863 | 0.80328 | 2.05833 | 2.84445 | 3.83492 | 2.00441 | 2.67823 | 3.95517 | |
| Touratier | 1.01858 | 0.90298 | 0.84713 | 0.79263 | 2.02737 | 2.79849 | 3.75552 | 1.97388 | 2.63628 | 3.85594 | |
| 2-1-2 | Reissner | 1.23130 | 1.10156 | 1.03918 | 0.97856 | 1.74183 | 2.19808 | 2.66548 | 1.82628 | 2.17166 | 2.54937 |
| Reddy | 1.11135 | 0.99514 | 0.93934 | 0.88517 | 1.58252 | 1.99484 | 2.41851 | 1.64575 | 1.95646 | 2.29660 | |
| Touratier | 1.09609 | 0.98166 | 0.92671 | 0.87340 | 1.55618 | 1.95974 | 2.37354 | 1.62233 | 1.92825 | 2.26299 | |
| a/h | 1-0-1 | 1-1-1 | 1-2-1 | 2-1-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0.97698 | 0.91263 | 0.85449 | 0.94628 |
| 10 | 0.95104 | 0.88597 | 0.82799 | 0.91982 |
| 15 | 0.91489 | 0.84979 | 0.79257 | 0.88346 |
| 20 | 0.87513 | 0.81010 | 0.75378 | 0.84352 |
| 25 | 0.83659 | 0.77166 | 0.71623 | 0.80482 |
| a/b | 1-0-1 | 1-1-1 | 1-2-1 | 2-1-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.95100 | 0.88600 | 0.82800 | 0.91980 |
| 2 | 0.36770 | 0.34340 | 0.32150 | 0.35610 |
| 3 | 0.18190 | 0.17030 | 0.15960 | 0.17640 |
| 4 | 0.10670 | 0.10010 | 0.09401 | 0.10360 |
| 5 | 0.06973 | 0.06564 | 0.06177 | 0.06780 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Chu, F. Bending Analysis of Symmetrical Porous Functionally Graded Sandwich Panels. Symmetry 2025, 17, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17030327
Huang Z, Chen Y, Wang X, Chu F. Bending Analysis of Symmetrical Porous Functionally Graded Sandwich Panels. Symmetry. 2025; 17(3):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17030327
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Zhicheng, Yingjie Chen, Xingguo Wang, and Fulei Chu. 2025. "Bending Analysis of Symmetrical Porous Functionally Graded Sandwich Panels" Symmetry 17, no. 3: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17030327
APA StyleHuang, Z., Chen, Y., Wang, X., & Chu, F. (2025). Bending Analysis of Symmetrical Porous Functionally Graded Sandwich Panels. Symmetry, 17(3), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17030327






