Cosmological Reflection of Particle Symmetry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cosmological Pattern of Particle Physics
2.1. Cosmoarcheology of New Physics
2.2. Cosmophenomenology of New Stable Particles
2.2.1. Freezing out
2.2.2. Stable Relics: Decoupling
2.2.3. Stable Relics: SuperWIMPs
2.2.4. Self-Interacting Dark Matter
2.2.5. Subdominant Dark Matter
2.2.6. Charged Stable Relics: Dark Atoms
2.3. Cosmophenomenology of Metastable Particles
2.3.1. Decaying Dark Matter
2.3.2. Charge Asymmetry of Dark Matter
2.3.3. Unstable Particles
2.4. Phase Transitions
2.4.1. Large Scale Correlations of Axion Field
2.4.2. Primordial Seeds for Active Galactic Nuclei
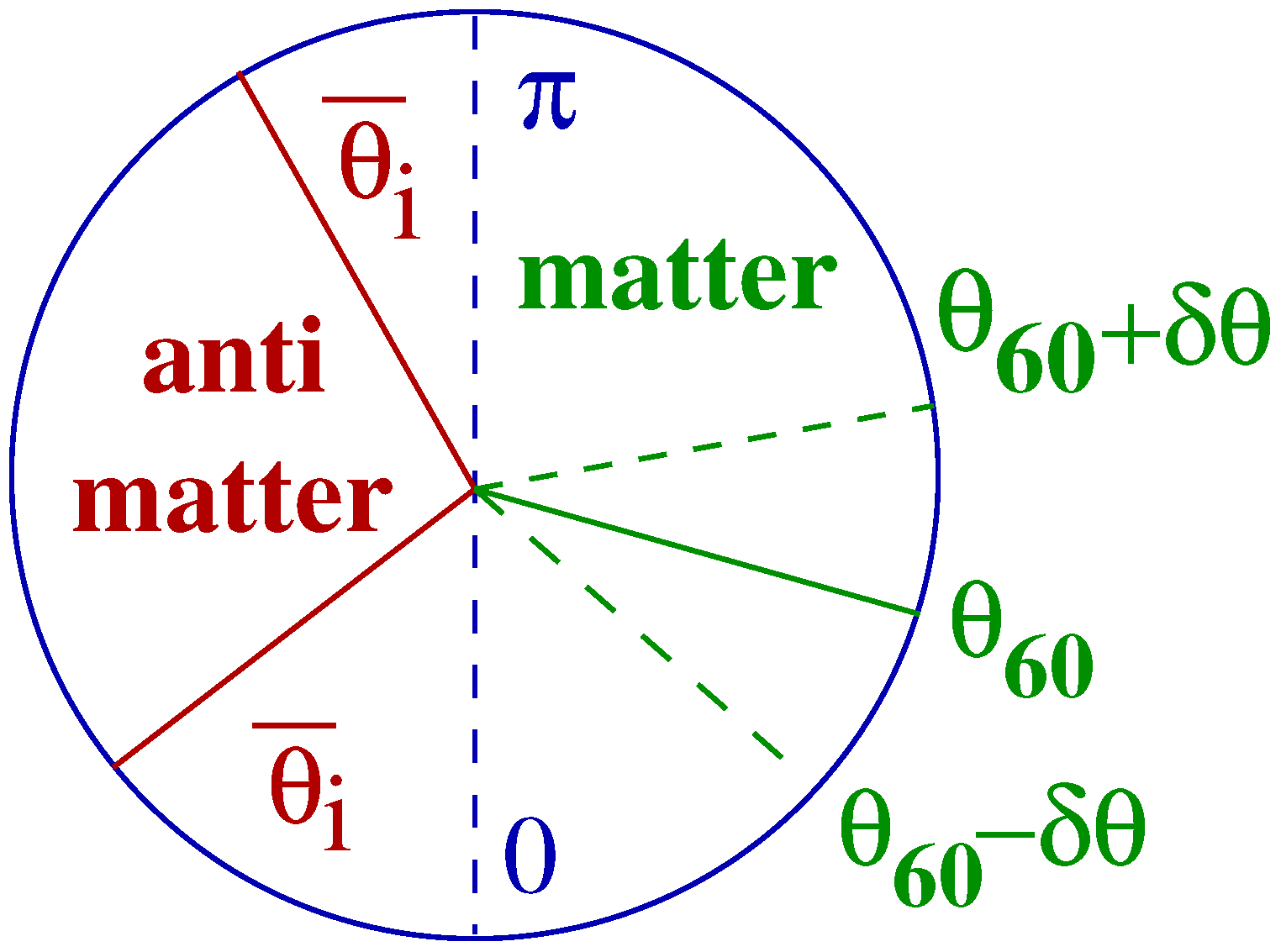
2.4.3. Antimatter in Baryon Asymmetric Universe?
3. Primordial Black Holes as a Cosmological Reflection of Particle Structure
3.1. PBHs from Early Dust-Like Stages
3.1.1. Dominance of Superheavy Particles in the Early Universe
3.1.2. Direct PBH Formation
3.1.3. Evolutional Formation of PBHs
3.2. Spikes from Phase Transitions in the Inflationary Stage
3.3. First Order Phase Transitions as a Source of Black Holes in the Early Universe
3.4. PBH Evaporation as Universal Particle Accelerator
4. Dark Matter from Flavor Symmetry
4.1. Symmetry of Known Families
4.1.1. Horizontal Hierarchy
4.1.2. Horizontal Unification
4.2. Stable Charged Constituents of Dark Atoms
4.2.1. Problem of Tera-Fermion Composite Dark Matter
4.2.2. Composite Dark Matter from Almost Commutative Geometry
4.2.3. Stable Charged Techniparticles in Walking Technicolor
4.2.4. Stable Particles of Fourth Generation Matter
5. Dark Atoms with Helium Shell
5.1. OHe Atoms and Their Interaction with Nuclei
5.2. Large Scale Structure Formation by OHe Dark Matter
5.3. Anomalous Component of Cosmic Rays
5.4. Positron Annihilation and Gamma Lines in Galactic Bulge
5.5. O-Helium Solution for Dark Matter Puzzles
5.5.1. O-Helium in the Terrestrial Matter
5.5.2. OHe in the Underground Detectors
5.6. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khlopov, M.Y. Cosmoparticle Physics; World Scientific: Singapore, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y. Fundamentals of Cosmoparticle Physics; CISP-Springer: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y. Cosmoparticle physics: Cross-disciplinary study of physics beyond the standard model. Bled Workshops Phys. 2006, 7, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y. Direct and indirect astrophysical effects of hypothetical particles and fields. In Cosmion-94; Editions Frontieres: Moscow, Russia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Mankoc-Borstnik, N.S. Proceedings to the 10th workshop ’what comes beyond the standard models. Bled Workshops Phys. 2007, 8, 114–131. [Google Scholar]
- Bertone, G. Particle Dark Matter: Observations, Models and Searches; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Frenk, C.S.; White, S.D.M. Dark matter and cosmic structure. Ann. Phys. 2012, 524, 507–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelmini, G.B. Search for dark matter. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2008, 23, 4273–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprile, E.; Profumo, S. Focus on dark matter and particle physics. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 105002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.L. Dark matter candidates from particle physics and methods of detection. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 48, 495–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S. Gravitation and Cosmology; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Zeldovich, Y.B.; Novikov, I.D. Structure and Evolution of the Universe; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Starobinsky, A. A new type of isotropic cosmological models without singularity. Phys. Lett. 1980, 91B, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, A.H. The inflationary universe: A possible solution to the horizon and flatness problems. Phys. Rev. D 1981, 23, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, A.D. A new inflationary universe scenario: A possible solution of the horizon, flatness, homogeneity, isotropy and primordial monopole problems. Phys. Lett. B 1982, 108, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, A.; Steinhardt, P.J. Cosmology for grand unified theories with radiatively induced symmetry breaking. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 48, 1220–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, A.D. Chaotic inflation. Phys. Lett. B 1983, 129, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakharov, A.D. Violation of CP invariance, c asymmetry, and baryon asymmetry of the universe. JETP Lett. 1967, 5, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzmin, V.A. CP-noninvariance and baryon asymmetry of the universe. JETP Lett. 1970, 12, 228–230. [Google Scholar]
- Linde, A.D. Particle Physics and Inflationary Cosmology; Harwood: Chur, Switzerland, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Kolb, E.W.; Turner, M.S. The Early Universe; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Gorbunov, D.S.; Rubakov, V.A. Introduction to the Theory of the Early Universe Hot Big Bang Theory; World Scientific: Singapore, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gorbunov, D.S.; Rubakov, V.A. Introduction to the Theory of the Early Universe. Cosmological Perturbations and Inflationary Theory; World Scientific: Singapore, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco, J.J.M.; Kallosh, R.; Linde, A. Minimal supergravity inflation. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 061301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopov, M.Y. Fundamental particle structure in the cosmological dark matter. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2013, 28, 1330042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T’Hooft, G. Magnetic monopoles in unified gauge theories. Nucl. Phys. B 1974, 79, 276–284. [Google Scholar]
- Polyakov, A.M. Particle spectrum in quantum field theory. JETP Lett. 1974, 20, 194–195. [Google Scholar]
- Zeldovich, Y.B.; Khlopov, M.Y. On the concentration of relic magnetic monopoles in the universe. Phys. Lett. 1978, B79, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopov, M.Y. Primordial magnetic monopoles. Priroda 1979, 12, 99–101. [Google Scholar]
- Preskill, J.P. Cosmological production of superheavy magnetic monopoles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1979, 43, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopov, M.Y. On the concentration of magnetic monopoles in the universe. In Magnetic Stars; Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1988; p. 201. [Google Scholar]
- Zeldovich, Y.B. Cosmological fluctuations produced near a singularity. Mon. Not. Roy. Astr. Soc. 1980, 192, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilenkin, A. Cosmological density fluctuations produced by vacuum strings. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1981, 46, 1169–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeldovich, Y.B.; Kobzarev, I.Y.; Okun, L.B. Cosmological consequences of the spontaneous breakdown of discrete symmetry. Sov. Phys. JETP 1975, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y. Primordial black holes. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 10, 495–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezhiani, Z.; Khlopov, M.Y. Theory of broken gauge symmetry of families. Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 1990, 51, 739–746. [Google Scholar]
- Berezhiani, Z.; Khlopov, M.Y. Physical and astrophysical consequences of breaking of the symmetry of families. Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 1990, 51, 935–942. [Google Scholar]
- Berezhiani, Z.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Khomeriki, R.R. On the possible test of quantum flavor dynamics in the searches for rare decays of heavy particles. Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 1990, 52, 344–347. [Google Scholar]
- Sakharov, A.S.; Khlopov, M.Y. Horizontal unification as the phenomenology of the theory of “everything”. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 1994, 57, 651–658. [Google Scholar]
- Jungman, G.; Kamionkowski, M.; Griest, K. Supersymmetric dark matter. Phys. Rept. 1996, 267, 195–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeldovich, Y.B.; Klypin, A.A.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Chechetkin, V.M. Astrophysical bounds on the mass of heavy stable neutral leptons. Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 1980, 31, 664–669. [Google Scholar]
- Fargion, D.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Konoplich, R.V.; Mignani, R. Bounds on very heavy relic neutrinos by their annihilation in galactic halo. Phys. Rev. D 1995, 52, 1828–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, A. keV neutrino model building. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2013, 22, 1330020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Linde, A.D. Is it easy to save gravitino? Phys. Lett. B 1984, 138, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestra, F. Annihilation of antiprotons with Helium-4 at low energies and its relationship with the problems of the modern cosmology and models of grand unification. Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 1984, 39, 626–631. [Google Scholar]
- Levitan, Y.L.; Sobol, I.M.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Chechetkin, V.M. Production of light elements in cascades from energetic antiprotons in early Universe and problems of nuclear cosmoarcheology. Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 1988, 47, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Levitan, Y.L.; Sedel’Nikov, E.V.; Sobol’, I.M. Nonequilibrium cosmological nucleosynthesis of light elements: Calculations by the Monte Carlo method. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 1994, 57, 1393–1397. [Google Scholar]
- Sedel’nikov, E.V.; Filippov, S.S.; Khlopov, M.Y. Kinetic theory of nonequilibrium cosmological nucleosynthesis. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 1995, 58, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Jedamzik, K. Did something decay, evaporate, or annihilate during Big Bang nucleosynthesis? Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 063524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, M.; Kohri, K.; Moroi, T. Hadronic decay of late-decaying particles and Big-Bang nucleosynthesis. Phys. Lett. 2005, B625, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.D.; Yang, C.N. Question of parity conservation in weak interactions. Phys. Rev. 1956, 104, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobzarev, I.Y.; Okun, L.B.; Pomeranchuk, I.Y. On the possibility of experimental observation of mirror particles. Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 1966, 3, 837–841. [Google Scholar]
- Zeldovich, Y.B.; Khlopov, M.Y. The neutrino mass in elementary particle physics and in big Bang cosmology. Sov. Phys. Uspekhi 1981, 24, 755–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foot, R.; Volkas, R.R. Neutrino physics and the mirror world: How exact parity symmetry explains the solar neutrino deficit, the atmospheric neutrino anomaly and the LSND experiment. Phys. Rev. D 1995, 52, 6595–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinnikov, S.I.; Khlopov, M.Y. On possible effects of mirror particles. Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 1982, 36, 472–474. [Google Scholar]
- Blinnikov, S.I.; Khlopov, M.Y. Possible astronomical effects of mirror particles. Sov. Astron. J. 1983, 27, 371–375. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, E.D.; Glashow, S.L. Nucleosynthesis versus the mirror universe. Phys. Lett. B 1987, 193, 168–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foot, R.; Volkas, R.R. The Exact parity symmetric model and big bang nucleosynthesis. Astropart. Phys. 1997, 7, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezhiani, Z.; Comelli, D.; Villante, F. The Early mirror universe: Inflation, baryogenesis, nucleosynthesis and dark matter. Phys. Lett. B 2001, 503, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezhiani, Z. Mirror world and its cosmological consequences. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2004, 19, 3775–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, E.W.; Seckel, D.; Turner, M.S. The shadow world. Nature 1985, 314, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopov, M.Y. Observational physics of mirror world. Sov. Astron. 1991, 35, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Okun, L.B. Mirror particles and mirror matter: 50 years of speculations and search. Phys. Usp. 2007, 50, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarcelluti, P. Cosmology with mirror dark matter. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2010, 19, 2151–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, A. Über die beugung und bremsung der elektronen. Ann. Phys. 1931, 11, 257–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakharov, A.D. Interaction of an electron and positron in pair production. Sov.Phys.Usp. 1991, 34, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotsky, K.M.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Shibaev, K.I. Sakharov’s enhancement in the effect of 4th generation neutrino. Gravit. Cosmol. Suppl. 2000, 6, 140–150. [Google Scholar]
- Bernabei, R.; Bellia, P.; Cerullia, R.; Montecchiaa, F.; Amatob, M.; Ignestib, G.; Incicchittib, A.; Prosperib, D.; Daic, C.J.; He, H.L. Search for WIMP annual modulation signature: Results from DAMA/NaI-3 and DAMA/NaI-4 and the global combined analysis. Phys. Lett. B 2000, 480, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabei, R.; Bellia, P.; Cappella, F.; Cerullia, R.; Montecchiaa, F.; Nozzoli, F.; Incicchitti, A.; Prosperib, D.; Daic, C.J.; Kuang, H.H. Dark matter search. Riv. Nuovo Cim. 2003, 26, 1–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabei, R.; Bellia, P.; Cappella, F.; Cerullia, R.; Dai, C.J.; d’Angelo, A.; He, H.L.; Incicchitti, A.; Kuang, H.H.; Ma, J.M. First results from DAMA/LIBRA and the combined results with DAMA/NaI. Eur. Phys. J. C 2008, 56, 333–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabei, R.; Bellia, P.; d’Angelo, S.; Di Marco, A.; Montecchia, F.; Cappella, F.; d’Angelo, A.; Incicchitti, A.; Caracciolo, V.; Castellano, S. Dark Matter investigation by DAMA at Gran Sasso. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2013, 28, 1330022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, D.; Akerib, D.S.; Barnes, P.D., Jr. Exclusion limits on the WIMP nucleon cross-section from the cryogenic dark matter search. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 122003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerib, D.S.; Armel-Funkhouser, M.S.; Attisha, M.J.; Young, B.A. Exclusion limits on the WIMP-nucleon cross section from the first run of the cryogenic dark matter search in the soudan underground laboratory. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 052009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Akerib, D.S.; Arrenberg, S. Search for weakly interacting massive particles with the first five-tower data from the cryogenic dark matter search at the soudan underground laboratory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 011301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aprile, E.; Arisaka, K.; Arneodo, F. First dark matter results from the XENON100 experiment. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 131302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalseth, C.E.; Barbeau, P.S.; Bowden, N.S. Results from a search for light-mass dark matter with a p-type point contact germanium detector. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 131302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golubkov, Y.A.; Khlopov, M.Y. Possible effects of the existence of the fourth generation neutrino. JETP Lett. 1999, 69, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargion, D.; Konoplich, R.V.; Grossi, M.; Khlopov, M.Y. Galactic gamma halo by heavy neutrino annihilations? Astropart. Phys. 2000, 12, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotsky, K.M.; Khlopov, M.Y. Astrophysical Signature of the 4th Neutrino. Gravit. Cosmol. Suppl. 2002, 8, 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Belotsky, K.M.; Fargion, D.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Konoplich, R.V. May heavy neutrinos solve underground and cosmic ray puzzles? Phys. Atomn. Nucl. 2008, 71, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotsky, K.M.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Shibaev, K.I. Monochromatic neutrinos from massive fourth generation neutrino annihilation in the Sun and in the Earth. Part. Nucl. Lett. 2001, 108, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotsky, K.M.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Shibaev, K.I. Monochromatic neutrinos from the annihilation of fourth-generation massive stable neutrino in the Sun and in the Earth. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 2002, 65, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotsky, K.M.; Damour, T.; Khlopov, M.Y. Implications of a solar-system population of massive 4th generation neutrinos for underground searches of monochromatic neutrino-annihilation signals. Phys. Lett. 2002, B529, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargion, D.; Khlopov, M.Y. Tera-leptons shadows over sinister universe. Gravit. Cosmol. 2013, 19, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotsky, K.M.; Khlopov, M.Y. Cosmoparticle physics of the 4th generation neutrino. Gravit. Cosmol. 2001, 7, 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Belotsky, K.M.; Fargion, D.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Konoplich, R.V.; Ryskin, M.G.; Shibaev, K.I. Heavy hadrons of 4th family hidden in our universe and close to detection? Grav. Cosm. Suppl. 2005, 11, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Fargion, D.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Stephan, C.A. Cold dark matter by heavy double charged leptons? Class. Quantum Grav. 2006, 23, 7305–7354. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y. Composite dark matter from 4th generation. JETP Lett. 2006, 83, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotsky, K.M.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Shibaev, K.I. Composite dark matter and its charged constituents. Gravit. Cosmol. 2006, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y. Physics of dark matter in the light of aark atoms. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2011, 26, 2823–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, A.; Tran, D.; Weniger, C. Indirect searches for decaying dark matter. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2013, 28, 1330040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriani, O.; Barbarino, G.C.; Bazilevskaya, G.A.; Bellotti, R.; Boezio, M.; Bogomolov, E.A.; Bonechi, L.; Bongi, M.; Bonvicini, V.; Bottai, S. An anomalous positron abundance in cosmic rays with energies 1.5–100 GeV. Nature 2009, 458, 607–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Allafort, A. Measurement of separate cosmic-ray electron and positron spectra with the Fermi Large Area Telescope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 011103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, M.; Alberti, G.; Alpat, B. First result from the alpha magnetic spectrometer on the international space station: Precision measurement of the positron fraction in primary cosmic rays of 0.5–350 GeV. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 141102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kounine, A. The alpha magnetic spectrometer on the international space station. Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 2012, 21, 1230005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petraki, K.; Volkas, R.R. Review of asymmetric dark matter. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2013, 28, 1330028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glashow, S.L. A Sinister Extension of the Standard Model to SU(3) x SU(2) x SU(2) x U(1), 2005. Available online: http://arXiv:hep-ph/0504287 (accessed on 29 April 2005).
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Chechetkin, V.M. Antiprotons in the universe as a cosmological test of grand unification. Sov. J. Part. Nucl. 1987, 18, 267–288. [Google Scholar]
- Doroshkevich, A.G.; Khlopov, M.Y. On the physical nature of dark matter of the Universe. Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 1984, 39, 551–553. [Google Scholar]
- Doroshkevich, A.G.; Khlopov, M.Y. Formation of structure in the universe with unstable neutrinos. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1984, 211, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroshkevich, A.G.; Klypin, A.A.; Khlopov, M.Y. Cosmological Models with Unstable Neutrinos. Sov. Astron. 1988, 32, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Doroshkevich, A.G.; Klypin, A.A.; Khlopov, M.Y. Large-scale structure formation by decaying massive neutrinos. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1989, 239, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezhiani, Z.G.; Khlopov, M.Y. Physics of cosmological dark matter in the theory of broken family symmetry. Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 1990, 52, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Berezhiani, Z.G.; Khlopov, M.Y. Cosmology of spontaneously broken gauge family symmetry with axion solution of strong CP-problem. Z. Phys. C Part. Fields 1991, 49, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.S.; Steigman, G.; Krauss, L.M. Flatness of the universe-Reconciling theoretical prejudices with observational data. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1984, 52, 2090–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelmini, G.; Schramm, D.N.; Valle, J.W.F. Majorons: A simultaneous solution to the large and small scale dark matter problems. Phys. Lett. B 1984, 146, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedelnikov, E.V.; Khlopov, M.Y. Cosmic rays as an additional source of information about nonequilibrium processes in the Universe. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 1996, 59, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Dimopoulos, S.; Esmailzadeh, R.; Starkman, G.D.; Hall, L.J. Is the universe closed by baryons? Nucleosynthesis with a late decaying massive particle. Astrophys. J. 1988, 330, 545–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroshkevich, A.G.; Khlopov, M.Y. Fluctuations of the cosmic background temperature in unstable-particle Cosmologies. Sov. Astron. Lett 1985, 11, 236–238. [Google Scholar]
- Polnarev, A.G.; Khlopov, M.Y. Cosmology, primordial black Holes, and supermassive particles. Sov. Phys. Uspekhi 1985, 28, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Polnarev, A.G. Primordial black holes as a cosmological test of grand unification. Phys. Lett. B 1980, 97, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polnarev, A.G.; Khlopov, M.Y. Primordial black holes and the ERA of superheavy particle dominance in the early universe. Sov. Astron. 1981, 25, 406–411. [Google Scholar]
- Konoplich, R.V.; Rubin, S.G.; Sakharov, A.S.; Khlopov, M.Yu. Formation of black holes in the first order phase transitions as cosmological test of mechanisms of symmetry breaking. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 1999, 62, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Rubin, S.G. Cosmological Pattern of Microphysics in Inflationary Universe; Springer Science Business Media: Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sakharov, A.S.; Khlopov, M.Y. The nonhomogeneity problem for the primordial axion field. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 1994, 57, 485–487. [Google Scholar]
- Sakharov, A.S.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Sokoloff, D.D. Large scale modulation of the distribution of coherent oscillations of a primordial axion field in the Universe. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 1996, 59, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Sakharov, A.S.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Sokoloff, D.D. The nonlinear modulation of the density distribution in standard axionic CDM and its cosmological impact. Nucl. Phys. B Proc. Suppl. 1999, 72, 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeckel, J.; Ringwald, A. The low-energy frontier of particle physics. Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 2010, 60, 405–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E. Light pseudoscalars, particle physics and cosmology. Phys. Rept. 1987, 150, 1–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilenkin, A.; Shellard, E.P.S. Cosmic Strings and Other Topological Defects; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, S.G.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Sakharov, A.S. Primordial black holes from non-equilibrium second order phase transitions. Gravit. Cosmol. Suppl. 2000, 6, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Rubin, S.G.; Sakharov, A.S. Strong primordial nonhomogeneities and galaxy formation. Gravit. Cosmol. Suppl. 2002, 8, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, S.G.; Sakharov, A.S.; Khlopov, M.Y. Formation of primordial galactic nuclei at phase transitions in the early Universe. JETP 2001, 92, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokuchaev, V.; Eroshenko, Y.; Rubin, S. Quasars formation around clusters of primordial black holes. Grav. Cosmol. 2005, 11, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Rubin, S.G.; Sakharov, A.S. Primordial structure of massive black hole clusters. Astropart. Phys. 2005, 23, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chechetkin, V.M.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Sapozhnikov, M.G.; Zeldovich, Y.B. Astrophysical aspects of antiproton interaction with He (Antimatter in the Universe). Phys. Lett. B 1982, 118, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgov, A.D. Matter and antimatter in the universe. Nucl. Phys. Proc. Suppl. 2002, 113, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgov, A.; Silk, J. Baryon isocurvature fluctuations at small scales and baryonic dark matter. Phys. Rev. D 1993, 47, 4244–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgov, A.D.; Kawasaki, M.; Kevlishvili, N. Inhomogeneous baryogenesis, cosmic antimatter, and dark matter. Nucl. Phys. B 2009, 807, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Rubin, S.G.; Sakharov, A.S. Possible origin of antimatter regions in the baryon dominated universe. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 62, 083505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopov, M.Y. An antimatter globular cluster in our galaxy: A probe for the origin of matter. Gravit. Cosmol. 1998, 4, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Golubkov, Y.A.; Khlopov, M.Y. Anti-protons annihilation in the galaxy as a source of diffuse gamma background. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 2001, 64, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotsky, K.M.; Golubkov, Y.A.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Konoplich, R.V.; Sakharov, A.S. Anti-helium flux as a signature for antimatter globular clusters in our galaxy. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 2000, 63, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargion, D.; Khlopov, M.Y. Antimatter bounds by anti-asteroids annihilations on planets and sun. Astropart. Phys. 2003, 19, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinnikov, S.I.; Dolgov, A.D.; Postnov, K.A. Antimatter and antistars in the universe and in the Galaxy. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 023516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopov, M.Y. Primordial nonlinear structures and massive black holes from early Universe. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 66, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, J.R.; Sneider, H. On continued gravitational contraction. Phys. Rev. 1939, 56, 455–459. [Google Scholar]
- Zeldovich, Y.B.; Novikov, I.D. Relativistic Astrophysics: Stars and Relativity; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1971; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Zeldovich, Y.B.; Novikov, I.D. The hypothesis of cores retarded during expansion and the hot cosmological model. Sov. Astron. 1967, 10, 602–609. [Google Scholar]
- Hawking, S.W. Gravitationally collapsed objects of very low mass. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1971, 152, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, B.J.; Hawking, S.W. Black holes in the early Universe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1974, 168, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, J.S.; Primack, J.R. NonGaussian fluctuations and primordial black holes from inflation. Phys. Rev. D 1997, 55, 7423–7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carr, B.J. The primordial black hole mass spectrum. Astroph. J. 1975, 201, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polnarev, A.G.; Khlopov, M.Y. Dustlike stages in the early universe and constraints on the primordial black-hole spectrum. Sov. Astron. 1982, 26, 391–395. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Polnarev, A.G. Superheavy particles in cosmology and evolution of inhomogeneities in the early Universe. In The Very Early Universe; Gibbons, G., Hawking, S., Siclos, E., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1983; pp. 407–432. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Malomed, B.A.; Zel’dovich, Y.B. Gravitational instability of scalar fields and formation of primordial black holes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1985, 215, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeldovich, Y.B.; Podurets, M.A. The evolution of a system of gravitationally interacting point masses. Sov. Astron. 1965, 9, 742–748. [Google Scholar]
- Gurzadian, V.G.; Savvidi, G.K. Collective relaxation of stellar systems. Astrophys. J. 1986, 160, 203–210. [Google Scholar]
- Kalashnikov, O.K.; Khlopov, M.Y. On the possibility of checking the cosmology of asymptotically free SU(5) theory. Phys. Lett. 1983, 127B, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadnikov, A.F.; Maslyankin, V.I.; Khlopov, M.Y. Modelling of evolution of quasi-stellar systems, formed by particles and antiparticles in early Universe. Astrophysics 1990, 31, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofman, L.A.; Linde, A.D. Generation of density perturbations in the inflationary cosmology. Nucl. Phys. B 1987, 282, 555–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakharov, A.S.; Khlopov, M.Y. Cosmological signatures of family symmetry breaking in multicomponent inflation models. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 1993, 56, 412–417. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, R.; Widrow, M. Aspects of reheating in first order inflation. Nucl. Phys. B 1992, 374, 446–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawking, S.W.; Moss, I.G.; Stewart, J.M. Bubble collisions in the very early universe. Phys. Rev. D 1982, 26, 2681–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, I.G. Singularity formation from colliding bubbles. Phys. Rev. D 1994, 50, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konoplich, R.V.; Rubin, S.G.; Sakharov, A.S.; Khlopov, M.Y. Formation of black holes in first-order phase transitions in the Universe. Astron. Lett. 1998, 24, 413–417. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Konoplich, R.V.; Rubin, S.G.; Sakharov, A.S. First-order phase transitions as a source of black holes in the early universe. Gravit. Cosmol. 2000, 6, 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- La, D.; Steinhardt, P.J. Extended inflationary cosmology. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1989, 62, 376–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, R.; Kolb, E.W.; Wang, Y. Gravitational couplings of the inflaton in extended inflation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1990, 62, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, R.; Kolb, E.W.; Vadas, S.L.; Wang, Y. Scale invariant extended inflation. Phys. Rev. D 1991, 43, 3833–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, F.C.; Freese, K. Double field inflation. Phys. Rev. D 1991, 43, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, E.J.; Liddle, A.R.; Lyth, D.H.; Stewart, E.D.; Wands, D. False vacuum inflation with Einstein gravity. Phys. Rev. D 1994, 49, 6410–6433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occhionero, F.; Amendola, L. Primordial bubbles from quadratic gravity. Phys. Rev. D 1994, 50, 4846–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Baccigalupi, C.; Konoplich, R. Reconstruction of the bubble nucleating potential. Phys. Rev. D 1996, 54, 7199–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.S.; Weinberg, E.J.; Widrow, L.M. Bubble nucleation in first order inflation and other cosmological phase transitions. Phys. Rev. D 1992, 46, 2384–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawking, S.W. Particle creation by black holes. Comm. Math. Phys. 1975, 43, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawking, S.W. Black hole explosions. Nature 1974, 248, 30–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, B.J.; Gilbert, J.H.; Lidsey, J.E. Black hole relics and inflation: Limits on blue perturbation spectra. Phys. Rev. D 1994, 50, 4853–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, J.D.; Copeland, E.J.; Liddle, A.R. The cosmology of black hole relics. Phys. Rev. D 1992, 46, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexeyev, S.O.; Pomazanov, M.V. Black hole solutions with dilatonic hair in higher curvature gravity. Phys. Rev. D 1997, 55, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dymnikova, I.G. De sitter-schwarzschild black hole: Its particlelike core and thermodynamical properties. Int. Jour. Mod. Phys. D 1996, 5, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyama, S.; Sato, K. The upper bound of the number density of primordial black holes from the big bang nucleosynthesis. Prog. Theor. Phys. 1978, 59, 1012–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeldovich, Y.B.; Starobinsky, A.A. Possibility of a cold cosmological singularity in the spectrum of primordial black holes. JETP Lett. 1976, 24, 571–573. [Google Scholar]
- Naselsky, P.D. Hydrogen recombination kinetics in the presence of low-mass primordial black holes. Sov. Astron. Lett. 1978, 4, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindley, D. Primordial black holes and the deuterium abundance. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1980, 193, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeldovich, Y.B.; Starobinskii, A.A.; Khlopov, M.I.; Chechetkin, V.M. Primordial black holes and the deuterium problem. Sov. Astron. Lett. 1977, 3, 110–112. [Google Scholar]
- Rothman, T.; Matzner, R. Upper limits on micro-mini black holes. Astrophys. Space. Sci. 1981, 75, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGibbon, J.H.; Carr, B.J. Cosmic rays from primordial black holes. Astrophys. J. 1991, 371, 447–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, I.D.; Polnarev, A.G.; Starobinskii, A.A.; Zeldovich, I.B. Primordial black holes. Astron. Astrophys. 1979, 80, 104–109. [Google Scholar]
- Chechetkin, V.M.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Sapozhnikov, M.G. Antiproton interactions with light elements as a test of GUT cosmology. Riv. Nuovo Cim. 1982, 5, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGibbon, J.H.; Carr, B.J. Cosmic rays from primordial black holes and constraints on the early universe. Phys. Rept. 1998, 307, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddle, A.R.; Green, A.M. Cosmological constraints from primordial black holes. Phys. Rept. 1998, 307, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, M. Moduli constraints on primordial black holes. Phys. Lett. B 2000, 481, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.M. Supersymmetry and primordial black hole abundance constraints. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 60, 063516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Barrau, A.; Grain, J. Gravitino production by primordial black hole evaporation and constraints on the inhomogeneity of the early Universe. Class. Quantum Grav. 2006, 23, 1875–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, B.J. Primordial black holes as a probe of cosmology and high energy physics. Lect. Notes Phys. 2003, 631, 301–321. [Google Scholar]
- Blais, D.; Kiefer, C.; Polarski, D. Can primordial black holes be a significant part of dark matter? Phys. Lett. B 2002, 535, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshordi, N.; McDonald, P.; Spergel, D.N. Primordial black holes as dark matter: The power spectrum and evaporation of early structures. Astrophys. J. 2003, 594, L71–L74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelquist, T.; Bai, Y.; Piai, M. SU(3) family gauge symmetry and the axion. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 073005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelquist, T.; Bai, Y.; Piai, M. Neutrinos and SU(3) family gauge symmetry. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 076001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelquist, T.; Bai, Y.; Piai, M. Quark mass ratios and mixing angles from SU(3) family gauge symmetry. Phys. Lett. B 2006, 637, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chkareuli, J.L. Quark-Lepton families: From SU(5) to SU(8) symmetry. JETP Lett. 1980, 32, 671–674. [Google Scholar]
- Berezhiani, Z.G.; Chkareuli, J.L. Mass of the T quark and the number of quark lepton generations. JETP Lett. 1982, 35, 612–615. [Google Scholar]
- Berezhiani, Z.G.; Chkareuli, J.L. Neutrino oscillations in grand unified models with a horizontal symmetry. JETP Lett. 1983, 37, 338–341. [Google Scholar]
- Berezhiani, Z.G. The weak mixing angles in gauge models with horizontal symmetry: A new approach to quark and lepton masses. Phys. Lett. B 1983, 129, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotsky, K.M.; Fargion, D.; Khlopov, M.Y. Heavy hadrons of 4th family hidden in our universe and close to detection? Gravit. Cosmol. 2005, 11, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Belotsky, K.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Shibaev, K.I. The Physics of Quarks: New Research; Watson, N.L., Grant, T.M., Eds.; NOVA Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2009; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Connes, A. Noncommutative Geometry; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Kouvaris, C. Strong interactive massive particles from a strong coupled theory. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 065002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannino, F.; Tuominen, K. Orientifold theory dynamics and symmetry breaking. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 051901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.K.; Hsu, S.D.H.; Sannino, F. Composite higgs from higher representations. Phys. Lett. B 2004, 597, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, D.D.; Sannino, F.; Tuominen, K. Light composite higgs from higher representations versus electroweak precision measurements: Predictions for LHC. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 055001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, D.D.; Sannino, F.; Tuominen, K. Light composite higgs and precision electroweak measurements on the Z resonance: An update. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 037701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudnason, S.B.; Kouvaris, C.; Sannino, F. Towards working technicolor: Effective theories and dark matter. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 115003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudnason, S.B.; Kouvaris, C.; Sannino, F. Dark matter from new technicolor theories. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 095008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankoč Borštnik, N.S. The spin-charge-family theory is explaining the origin of families, of the Higgs and the Yukawa couplings. Bled Workshops Phys. 2010, 11, 105–129. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Mayorov, A.G.; Soldatov, E.Y. Dark atoms of the universe: towards OHe nuclear physics. Bled Workshops Phys. 2010, 11, 73–88. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Kouvaris, C. Composite dark matter from a model with composite Higgs boson. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 065040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopov, M.Y. The puzzles of dark matter searches. AIP Conf. Proc. 2010, 1241, 388–397. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Mayorov, A.G.; Soldatov, E.Y. Composite dark matter and puzzles of dark matter searches. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2010, 19, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopov, M.Y. Composite Dark Matter from Stable Charged Constituents. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/0806.3581 (accessed on 22 June 2008).
- Maltoni, M.; Novikov, V.A.; Okun, L.B.; Rozanov, A.N.; Vysotsky, M.I. Extra quark lepton generations and precision measurements. Phys. Lett. B 2000, 476, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Shibaev, R.M. Probes for 4th generation constituents of dark atoms in Higgs boson studies at the LHC. Adv. High Energy Phys. 2014, 2014, 406458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotsky, K.M.; Fargion, D.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Konoplich, R.V.; Shibaev, K.I. Heavy neutrinos of 4th generation in searches for dark matter. Gravit. Cosmol. 2005, 11, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Mayorov, A.G.; Soldatov, E.Y. Puzzles of dark matter in the light of dark atoms. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 309, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopov, M.Y. Dark Matter from Stable Charged Particles? Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/0801.0167 (accessed on 30 December 2007).
- Khlopov, M.Y. Primordial Heavy Elements in Composite Dark Matter Models. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/0801.0169 (accessed on 31 December 2007).
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Mayorov, A.G.; Soldatov, E.Y. Puzzles of dark matter-more light on dark atoms? Bled Workshops Phys. 2010, 11, 186–193. [Google Scholar]
- Dover, C.B.; Gaisser, T.K.; Steigman, G. Cosmological constraints on new stable hadrons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1979, 42, 1117–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfram, S. Abundances of stable particles produced in the early universe. Phys. Lett. B 1979, 82, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkman, G.D.; Gould, A.; Esmailzadeh, R.; Dimopoulos, S. Opening the window on strongly interacting dark matter. Phys. Rev. D 1990, 41, 3594–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javorsek, D.; Elmore, D.; Fischbach, E.; Granger, D.; Miller, T.; Oliver, D.; Teplitz, V. New experimental limits on strongly interacting massive particles at the TeV scale. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 231804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S. Uranus’s anomalously low excess heat constrains strongly interacting dark matter. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 103517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, G.D.; Beacom, J.F.; Bertone, G. Towards closing the window on strongly interacting dark matter: Far-reaching constraints from Earth’s heat flow. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 043523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandelt, B.D.; Dave, R.; Farrar, G.R.; McGuire, P.C.; Spergel, D.N.; Steinhardt, P.J. Self-Interacting Dark Matter. Available online: http://arXiv:astro-ph/0006344 (accessed on 24 June 2000).
- McGuire, P.C.; Steinhardt, P.J. Cracking Open the Window for Strongly Interacting Massive Particles as the Halo Dark Matter. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0105567 (accessed on 31 May 2001).
- Zaharijas, G.; Farrar, G.R. A window in the aark matter exclusion limits. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 083502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahn, R.N.; Glashow, S.L. Chemical signatures for superheavy elementary particles. Science 1981, 213, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pospelov, M. Particle physics catalysis of thermal big bang nucleosynthesis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 231301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohri, K.; Takayama, F. Big bang nucleosynthesis with long-lived charged massive particles. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 063507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudell, J.-R.; Khlopov, M.Y.; Wallemacq, Q. The nuclear physics of OHe. Bled Workshops Phys. 2012, 13, 10–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wallemacq, Q. Milli-interacting Dark Matte. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 063516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotsky, K.M.; Mayorov, A.G.; Khlopov, M.Y. Charged particles of dark matter in cosmic rays. In Scientific Session NRNU MEPhI-2010; V.4, P.127; World Scientific Publishing Company: Singapore, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Finkbeiner, D.P.; Weiner, N. Exciting dark matter and the INTEGRAL/SPI 511 keV signal. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 083519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teegarden, B.J.; Watanabe, K.; Jean, P.; Knödlseder, J.; Lonjou, V.; Roques, J.P.; Skinner, G.K.; von Ballmoos, P.; Weidenspointner, G.; Bazzano, A.; et al. INTEGRAL SPI limits on electron-positron annihilation radiation from the galactic plane. Astrophys. J. 2005, 621, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCammon, D.; Almy, R.; Deiker, S.; Morgenthaler, J.; Kelley, R.L.; Marshall, F.J.; Moseley, S.H.; Stahle, C.K.; Szymkowiak, A.E. A sounding rocket payload for X-ray astronomy employing high-resolution microcalorimeters. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 1996, 370, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCammon, D.; Almy, R.; Apodaca, E.; Tiest, W.B.; Cui, W.; Deiker, S.; Galeazzi, M.; Juda, M.; Lesser, A.; Miharaet, T. A high spectral resolution observation of the soft X-ray diffuse background with thermal detectors. Astrophys. J. 2002, 576, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotsky, K.; Bunkov, Y.; Godfrin, H.; Khlopov, M.; Konoplich, R. He-3 Experimentum Crucis for Dark Matter Puzzles. Available online: http://arXiv:astro-ph/0606350 (accessed on 14 June 2006).
- Angloher, G.; Bauer, M.; Bavykina, I.; Bento, A.; Bucci, C.; Ciemniak, C.; Deuter, G.; von Feilitzsch, F.; Hauff, D.; Huffet, P. Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter search. Eur. Phys. J. C 2012, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopov, M.Y.; Mayorov, A.G.; Soldatov, E.Y. Low energy binding of composite dark matter with nuclei as a solution for the puzzles of dark matter searches. Bled Workshops Phys. 2009, 10, 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Bernabei, R.; Belli, P.; Bussolotti, A.; Cappella, F.; Cerulli, R.; Dai, C.J.; d’Angelo, A.; He, H.L.; Incicchitti, A.; Kuang, H.H.; et al. The DAMA/LIBRA apparatus. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 2008, 592, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakharov, A.D. Cosmoparticle physics-a multidisciplinary science. Vestnik AN SSSR 1989, 4, 39–40. [Google Scholar]
- Khlopov, M.Y. Fundamental cross-disciplinary studies of microworld and Universe. Vestnik Russ. Acad. Sci. 2001, 71, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar]


© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khlopov, M. Cosmological Reflection of Particle Symmetry. Symmetry 2016, 8, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym8080081
Khlopov M. Cosmological Reflection of Particle Symmetry. Symmetry. 2016; 8(8):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym8080081
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhlopov, Maxim. 2016. "Cosmological Reflection of Particle Symmetry" Symmetry 8, no. 8: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym8080081
APA StyleKhlopov, M. (2016). Cosmological Reflection of Particle Symmetry. Symmetry, 8(8), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym8080081





