Geochemical Background for Potentially Toxic Elements in Forested Soils of the State of Pará, Brazilian Amazon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
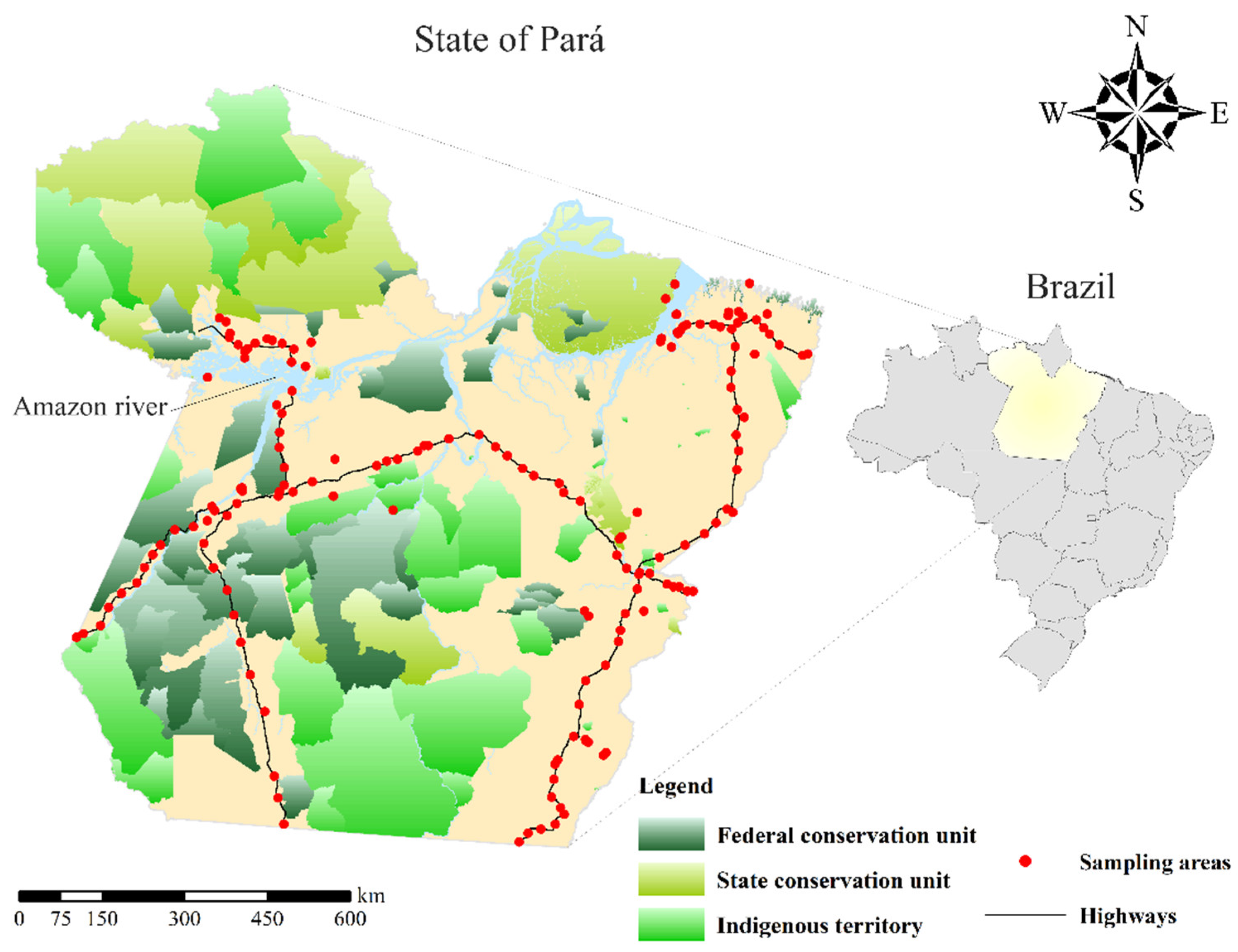
2.1. Soil Sampling
2.2. Characterization of Soil Attributes
2.3. Quantification of PTE Concentrations
2.4. Data Treatment and Statistics
2.5. Concentrations and Geochemical Backgrounds
2.6. Environmental Thresholds
3. Results
3.1. Soil Chemical Attributes
3.2. Factor Analysis of the Behavior of PTEs
3.3. Concentrations and Geochemical Backgrounds
3.4. Environmental Thresholds
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Chemical Attributes
4.2. Factor Analysis of the PTE Behavior
4.3. Concentrations and Geochemical Backgrounds
4.4. Environmental Thresholds
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; ISBN 9781420093704. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, A.R.; Souza, E.S.; Braz, A.M.d.S.; Birani, S.M.; Alleoni, L.R.F. Quality reference values and background concentrations of potentially toxic elements in soils from the Eastern Amazon, Brazil. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 190, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, T.A.R.; Abreu-Junior, C.H.; Alleoni, L.R.F.; He, Z.; Soares, M.R.; Vieira, C.d.S.; Lessa, L.G.F.; Capra, G.F. Background concentrations and quality reference values for some potentially toxic elements in soils of São Paulo State, Brazil. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 221, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution; Appelo, C.A.J., Postma, D., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; ISBN 9780429152320. [Google Scholar]
- Fuoco, I.; Marini, L.; de Rosa, R.; Figoli, A.; Gabriele, B.; Apollaro, C. Use of reaction path modelling to investigate the evolution of water chemistry in shallow to deep crystalline aquifers with a special focus on fluoride. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, I.; De Rosa, R.; Barca, D.; Figoli, A.; Gabriele, B.; Apollaro, C. Arsenic polluted waters: Application of geochemical modelling as a tool to understand the release and fate of the pollutant in crystalline aquifers. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachada, A.; Rocha-Santos, T.; Duarte, A.C. Soil and Pollution. In Soil Pollution; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Marins, R.V.; Machado, W.; Paraquetti, H.H.M.; Bidone, E.D.; Lacerda, L.D.; Molisani, M.M. Environmental changes in Sepetiba Bay, SE Brazil. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2004, 4, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, M.W.; Pereira, W.V.d.S.; de Souza, E.S.; Teixeira, R.A.; Palheta, D.d.C.; Faial, K.d.C.F.; Costa, H.F.; Fernandes, A.R. Bioaccumulation and human health risks of potentially toxic elements in fish species from the southeastern Carajás Mineral Province, Brazil. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konhauser, K.O.; Fyfe, W.S.; Zang, W.; Bird, M.I.; Kronberg, B.I. Advances in Amazonian Biogeochemistry. In Chemistry of the Amazon; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 208–247. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, L.J.D.; Silva, E.B.; Fontes, M.P.F.; Liu, X.; Ma, L.Q. Speciation, bioaccessibility and potential risk of chromium in Amazon forest soils. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M.W.; Hamid, S.S.; de Souza, E.S.; Teixeira, R.A.; Palheta, D.d.C.; Faial, K.d.C.F.; Fernandes, A.R. Geochemical background concentrations of potentially toxic elements in soils of the Carajás Mineral Province, southeast of the Amazonian Craton. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wei, F.; Zheng, C.; Wu, Y.; Adriano, D.C. Background concentrations of elements in soils of China. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 1991, 57, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crommentuijn, T.; Sijm, D.; de Bruijn, J.; van den Hoop, M.; van Leeuwen, K.; van de Plassche, E. Maximum permissible and negligible concentrations for metals and metalloids in the Netherlands, taking into account background concentrations. J. Environ. Manag. 2000, 60, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, W.; Nascimento, C.W.A.; Biondi, C.M.; Junior, V.S.d.S.; da Silva, W.R.; Ferreira, H.A. Valores de referência de qualidade para metais pesados em solos do Rio Grande do Norte. R. Bras. Ci. Solo 2014, 38, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.J.; McGrath, S.P.; Merrington, G. Estimates of ambient background concentrations of trace metals in soils for risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 148, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bini, C.; Sartori, G.; Wahsha, M.; Fontana, S. Background levels of trace elements and soil geochemistry at regional level in NE Italy. J. Geochem. Explor. 2011, 109, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, M.R.; Montero, A.; Ugarte, O.M.; do Nascimento, C.W.A.; Accioly, A.M.d.A.; Biondi, C.M.; da Silva, Y.J.A.B. Background concentrations and reference values for heavy metals in soils of Cuba. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; de Caritat, P. Establishing geochemical background variation and threshold values for 59 elements in Australian surface soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos-Miras, J.J.; Díaz-Férnandez, P.; SanJosé-Wery, A.; Rodríguez-Martin, J.A.; Roca, N.; Bech, J.; Roca-Perez, L.; Boluda, R.; Gil, C. Influence of parent material and soil use on arsenic forms in soils: A case study in the Amblés Valley (Castilla-León, Spain). J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 147, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, W.V.d.S.; Teixeira, R.A.; Souza, E.S.d.; Moraes, A.L.F.d.; Campos, W.E.O.; Amarante, C.B.d.; Martins, G.C.; Fernandes, A.R. Chemical fractionation and bioaccessibility of potentially toxic elements in area of artisanal gold mining in the Amazon. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 267, 110644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, H.F.d.S.; Pereira, W.V.d.S.; Dias, Y.N.; de Souza, E.S.; Teixeira, R.A.; de Lima, M.W.; Ramos, S.J.; do Amarante, C.B.; Fernandes, A.R. Environmental and human health risks of arsenic in gold mining areas in the eastern Amazon. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, R.A.; Pereira, W.V.d.S.; de Souza, E.S.; Ramos, S.J.; Dias, Y.N.; de Lima, M.W.; Neto, H.F.d.S.; de Oliveira, E.S.; Fernandes, A.R. Artisanal gold mining in the eastern Amazon: Environmental and human health risks of mercury from different mining methods. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, E.S.; Texeira, R.A.; da Costa, H.S.C.; Oliveira, F.J.; Melo, L.C.A.; Faial, K.d.C.F.; Fernandes, A.R. Assessment of risk to human health from simultaneous exposure to multiple contaminants in an artisanal gold mine in Serra Pelada, Pará, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, G.H.C.; Monteiro, L.V.S.; Moreto, C.P.N.; Xavier, R.P.; Silva, M.A.D. Paragenesis and evolution of the hydrothermal Bacuri iron oxide-copper-gold deposit, Carajás Province (PA). Braz. J. Geol. 2014, 44, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; Garrett, R.G. Geochemical background—Concept and reality. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 350, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimann, C.; Fabian, K.; Birke, M.; Filzmoser, P.; Demetriades, A.; Négrel, P.; Oorts, K.; Matschullat, J.; de Caritat, P.; Albanese, S.; et al. GEMAS: Establishing geochemical background and threshold for 53 chemical elements in European agricultural soil. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 88, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schobbenhaus, C.; Neves, B.B.d.B. The Geology of Brazil in the Context of the South American Platform. In Geology, Tectonics and Mineral Resources of Brazil; Bizzi, L.A., Schobbenhaus, C., Vidotti, R.M., Gonçalves, J.H., Eds.; CPRM—Serviço Geológico do Brasil: Brasília, Brazil, 2003; pp. 5–54. ISBN 85-230-0790-3. [Google Scholar]
- Werkenthin, M.; Kluge, B.; Wessolek, G. Metals in European roadside soils and soil solution—A review. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 189, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, P.C.; Donagemma, G.K.; Fontana, A.; Teixeira, W.G. Manual de Métodos de Análise de Solo, 3rd ed.; Embrapa: Brasília, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gee, G.W.; Bauder, J.W. Particle-size analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Klute, A., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 383–411. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, S.P.; Cunliffe, C.H. A simplified method for the extraction of the metals Fe, Zn, Cu, Ni, Cd, Pb, Cr, Co and Mn from soils and sewage sludges. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1985, 36, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F. Multivariate Data Analysis; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- CONAMA. Resolução No 420 de 28 de Dezembro de 2009; Diário Official da União: Brasilia, Brazil, 2009.
- Reimann, C.; Filzmoser, P.; Garrett, R.G. Background and threshold: Critical comparison of methods of determination. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 346, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ander, E.L.; Johnson, C.C.; Cave, M.R.; Palumbo-Roe, B.; Nathanail, C.P.; Lark, R.M. Methodology for the determination of normal background concentrations of contaminants in English soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 454, 604–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filzmoser, P. Package ‘StatDA’; R Package Version 1.9; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Venegas, V.H.A.; Novais, R.F.; Barros, N.F.; Cantarutti, R.B.; Lopes, A.S. Interpretation of soil analysis results. In Recommendations for the Use of Correctives and Fertilizers in Minas Gerais; Comissão de Fertilidade do Solo do Estado de Minas Gerais: Viçosa, Brazil, 1999; pp. 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, H.G.; Jacomine, P.K.T.; Anjos, L.H.C.; Oliveira, V.A.; Lumbreras, J.F.; Coelho, M.R.; Almeida, J.A.; Araujo-Filho, J.C.; Oliveira, J.B.; Cunha, T.J.F. Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos, 5th ed.; Embrapa Solos: Brasília, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Quesada, C.A.; Lloyd, J.; Schwarz, M.; Patiño, S.; Baker, T.R.; Czimczik, C.; Fyllas, N.M.; Martinelli, L.; Nardoto, G.B.; Schmerler, J.; et al. Variations in chemical and physical properties of Amazon forest soils in relation to their genesis. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 1515–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fadigas, F.S.; Sobrinho, N.M.B.d.A.; dos Cunha, L.H.A.; Mazur, N. Background levels of some trace elements in weathered soils from the Brazilian Northern region. Sci. Agric. 2010, 67, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza, E.S.; Fernandes, A.R.; Braz, A.M.d.S.; Sabino, L.L.L.; Alleoni, L.R.F. Potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in soils from the surroundings of the Trans-Amazonian Highway, Brazil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birani, S.M.; Fernandes, A.R.; Braz, A.M.d.S.; Pedroso, A.J.S.; Alleoni, L.R.F. Available contents of potentially toxic elements in soils from the Eastern Amazon. Geochemistry 2015, 75, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braz, A.M.d.S.; Fernandes, A.R.; Alleoni, L.R.F. Soil attributes after the conversion from forest to pasture in the Amazon. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradl, H.B. Sources and origins of heavy metals. In Heavy Metals in the Environment; Bradl, H.B., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 1–27. ISBN 1573-4285. [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo, P.K.; Dall’Agnol, R.; Salomão, G.N.; Junior, J.d.S.F.; Silva, M.S.; Filho, P.W.M.d.S.; da Costa, M.L.; Angélica, R.S.; Filho, C.A.M.; da Costa, M.F.; et al. Regional-scale mapping for determining geochemical background values in soils of the Itacaiúnas River Basin, Brazil: The use of compositional data analysis (CoDA). Geoderma 2020, 376, 114504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodyanitskii, Y.N. Arsenic, lead, and zinc compounds in contaminated soils according to EXAFS spectroscopic data: A review. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2006, 39, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejón, P. Barium. In Heavy Metals in Soils: Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability; Alloway, B.J., Ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2013; pp. 507–514. [Google Scholar]
- Oorts, K. Copper. In Heavy Metals in Soils: Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability; Alloway, B.J., Ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2013; pp. 367–394. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, B.A. Dos Recursos minerais da Amazônia. Estud. Avançados 2002, 16, 123–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonelli, C.; Renella, G. Chromium & Nickel. In Heavy Metals in Soils: Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability; Environmental Pollution; Alloway, B.J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 22, pp. 313–334. ISBN 978-94-007-4469-1. [Google Scholar]
- Alloway, B.J. Heavy Metals in Soils; Environmental Pollution; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 22, ISBN 978-94-007-4469-1. [Google Scholar]
- Biondi, C.M.; Nascimento, C.W.A.; Neta, A.B.F.; Neta, F.; Ribeiro, M.R. Teores de Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu, Ni e Co em solos de referência de Pernambuco. Rev. Bras. Ciência Do Solo 2011, 35, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Lima, D.P.; Santos, C.; Silva, R.d.S.; Yoshioka, E.T.O.; Bezerra, R.M. Contaminação por metais pesados em peixes e água da bacia do rio Cassiporé, Estado do Amapá, Brasil. Acta Amaz. 2015, 45, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iyaka, Y.A. Nickel in soils: A review of its distribution and impacts. Sci. Res. Essays 2011, 6, 6774–6777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, M.L.; Rosa-Costa, L.T. Geologia e Recursos Minerais do Estado do Pará; CPRM—Serviço Geológico do Brasil: Brasília, Brazil, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- De Almeida, A.B., Jr.; do Nascimento, C.W.A.; Biondi, C.M.; de Souza, A.P.; Barros, F.M.d.R. Background and Reference Values of Metals in Soils from Paraíba State, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Ciência Do Solo 2016, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Souza, E.S.; Fernandes, A.R.; Braz, A.M.d.S.; de Oliveira, F.J.; Alleoni, L.R.F.; Campos, M.C.C. Physical, chemical, and mineralogical attributes of a representative group of soils from the eastern Amazon region in Brazil. Soil 2018, 4, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonçalves, D.A.M.; de Matos, G.S.B.; Fernandes, A.R.; Barros, K.R.M.; Campinas, D.d.S.N.; do Amarante, C.B. Adsorption of cadmium and copper in representative soils of Eastern Amazonia, Brazil. Semin. Ciências Agrárias 2016, 37, 3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braz, A.M.S.; Fernandes, A.R.; Ferreira, J.R.; Alleoni, L.R.F. Prediction of the distribution coefficients of metals in Amazonian soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 95, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, W.W. Arsenic. In Heavy Metals in Soils: Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability; Environmental Pollution; Alloway, B.J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 22, pp. 241–282. ISBN 978-94-007-4469-1. [Google Scholar]
- Robles-Camacho, J.; Armienta, M. Natural chromium contamination of groundwater at León Valley, México. J. Geochem. Explor. 2000, 68, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantoni, D.; Brozzo, G.; Canepa, M.; Cipolli, F.; Marini, L.; Ottonello, G.; Zuccolini, M. Natural hexavalent chromium in groundwaters interacting with ophiolitic rocks. Environ. Geol. 2002, 42, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apollaro, C.; di Curzio, D.; Fuoco, I.; Buccianti, A.; Dinelli, E.; Vespasiano, G.; Castrignanò, A.; Rusi, S.; Barca, D.; Figoli, A.; et al. A multivariate non-parametric approach for estimating probability of exceeding the local natural background level of arsenic in the aquifers of Calabria region (Southern Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysochoou, M.; Theologou, E.; Bompoti, N.; Dermatas, D. Occurrence, Origin and Transformation Processes of Geogenic Chromium in Soils and Sediments. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2016, 2, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gäbler, H.-E.; Glüh, K.; Bahr, A.; Utermann, J. Quantification of vanadium adsorption by German soils. J. Geochem. Explor. 2009, 103, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, M.A.; Baken, S.; Gustafsson, J.P.; Hadialhejazi, G.; Smolders, E. Vanadium bioavailability and toxicity to soil microorganisms and plants. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 2266–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guagliardi, I.; Cicchella, D.; de Rosa, R.; Ricca, N.; Buttafuoco, G. Geochemical sources of vanadium in soils: Evidences in a southern Italy area. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 184, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, J.; Smolders, E. Zinc. In Heavy Metals in Soils: Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability; Environmental Pollution; Alloway, B.J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 22, pp. 465–495. ISBN 978-94-007-4469-1. [Google Scholar]

| Attributes | Minimum | Maximum | Median | Mean | SD a | CV b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH (in water) | 2.9 | 7.4 | 4.4 | 4.5 | 0.8 | 16.7 |
| OC (g kg−1) | 0.7 | 44.2 | 6.0 | 7.8 | 5.8 | 74.0 |
| CEC (cmolc dm−3) | 2.4 | 25.0 | 7.3 | 8.6 | 4.6 | 53.8 |
| m (%) | 0.1 | 97.9 | 41.2 | 43.1 | 28.1 | 65.1 |
| SiO2 (g kg−1) | 7.0 | 319.0 | 95.0 | 113.8 | 77.6 | 46.7 |
| Al2O3 (g kg−1) | 4.0 | 284.7 | 82.6 | 99.9 | 68.6 | 81.2 |
| Fe2O3 (g kg−1) | 1.0 | 325.3 | 25.9 | 43.7 | 53.1 | 60.6 |
| TiO2 (g kg−1) | 0.2 | 420.4 | 4.3 | 24.1 | 61.2 | 68.2 |
| Sand (g kg−1) | 17 | 940 | 543 | 530 | 248 | 121 |
| Silt (g kg−1) | 8 | 785 | 135 | 170 | 138 | 254 |
| Clay (g kg−1) | 30 | 859 | 290 | 299 | 182 | 276 |
| Elements | n a | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Median b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al (g kg−1) | 501 | 1.32 | 60.3 | 8.2 | 9.1 |
| Fe (g kg−1) | 491 | 1.41 | 40.7 | 9.3 | 9.3 |
| As (mg kg−1) | 144 | 0.12 | 8.3 | 0.8 | 0.7 |
| Ba (mg kg−1) | 503 | 1.02 | 251.2 | 16.7 | 20.9 |
| Cd (mg kg−1) | 267 | 0.01 | 1.7 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Co (mg kg−1) | 112 | 0.19 | 47.9 | 1.6 | 1.2 |
| Cr (mg kg−1) | 480 | 2.88 | 166 | 14.3 | 12.6 |
| Cu (mg kg−1) | 467 | 1.55 | 27.5 | 6 | 5.6 |
| Mn (mg kg−1) | 484 | 2.51 | 588.8 | 40.7 | 38 |
| Ni (mg kg−1) | 318 | 0.12 | 40.7 | 1.4 | 1.8 |
| Pb (mg kg−1) | 489 | 2.09 | 41.7 | 10.4 | 11 |
| V (mg kg−1) | 236 | 2.63 | 95.5 | 26.1 | 24 |
| Zn (mg kg−1) | 483 | 1.91 | 30.2 | 7 | 6.9 |
| Elements | TIF | 75th | 90th | 95th | 98th | PV a | IV b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 31,058.75 | 14,800.00 | 24,087.98 | 29,020.98 | 34,211.58 | - | - |
| Fe | 38,575.00 | 17,800.00 | 31,344.92 | 38,926.01 | 86,304.67 | - | - |
| Ba | 119.23 | 49.5 | 85.42 | 122.50 | 184.06 | 150 | 300 |
| Cr | 40.54 | 22.1 | 35.90 | 41.75 | 53.21 | 75 | 150 |
| Mn | 295.48 | 101 | 370.57 | 735.08 | 1073.45 | - | - |
| Pb | 33.38 | 17.8 | 21.76 | 27.53 | 33.04 | 72 | 180 |
| Zn | 24.94 | 10.1 | 24.25 | 45.19 | 56.17 | 300 | 450 |
| As | 4.18 | 1.9 | 3.51 | 5.40 | 7.17 | 15 | 35 |
| Cd | 0.72 | 0.3 | 0.55 | 0.77 | 1.22 | 1.3 | 3.0 |
| Co | 12.10 | 4.8 | 10.69 | 18.81 | 49.57 | 25 | 35 |
| Cu | 23.27 | 9.8 | 27.40 | 86.92 | 112.06 | 60 | 200 |
| Hg | 0.52 | 0.22 | 0.32 | 0.44 | 0.55 | 0.5 | 12 |
| Mo | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 30 | 50 |
| Ni | 10.92 | 4.5 | 7.55 | 10.43 | 20.16 | 30 | 70 |
| V | 124.13 | 57.2 | 74.41 | 88.39 | 94.72 | - | 1000 c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonçalves, D.A.M.; Pereira, W.V.d.S.; Johannesson, K.H.; Pérez, D.V.; Guilherme, L.R.G.; Fernandes, A.R. Geochemical Background for Potentially Toxic Elements in Forested Soils of the State of Pará, Brazilian Amazon. Minerals 2022, 12, 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060674
Gonçalves DAM, Pereira WVdS, Johannesson KH, Pérez DV, Guilherme LRG, Fernandes AR. Geochemical Background for Potentially Toxic Elements in Forested Soils of the State of Pará, Brazilian Amazon. Minerals. 2022; 12(6):674. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060674
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonçalves, Deyvison Andrey Medrado, Wendel Valter da Silveira Pereira, Karen H. Johannesson, Daniel Vidal Pérez, Luiz Roberto Guimarães Guilherme, and Antonio Rodrigues Fernandes. 2022. "Geochemical Background for Potentially Toxic Elements in Forested Soils of the State of Pará, Brazilian Amazon" Minerals 12, no. 6: 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060674
APA StyleGonçalves, D. A. M., Pereira, W. V. d. S., Johannesson, K. H., Pérez, D. V., Guilherme, L. R. G., & Fernandes, A. R. (2022). Geochemical Background for Potentially Toxic Elements in Forested Soils of the State of Pará, Brazilian Amazon. Minerals, 12(6), 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060674










