Soil Geochemistry Combined with Particulate Gold Microchemistry Provides Evidence of Eluvial Gold Genesis and Anthropogenic Hg Use in Eastern Cameroon Goldfields
Abstract
1. Introduction
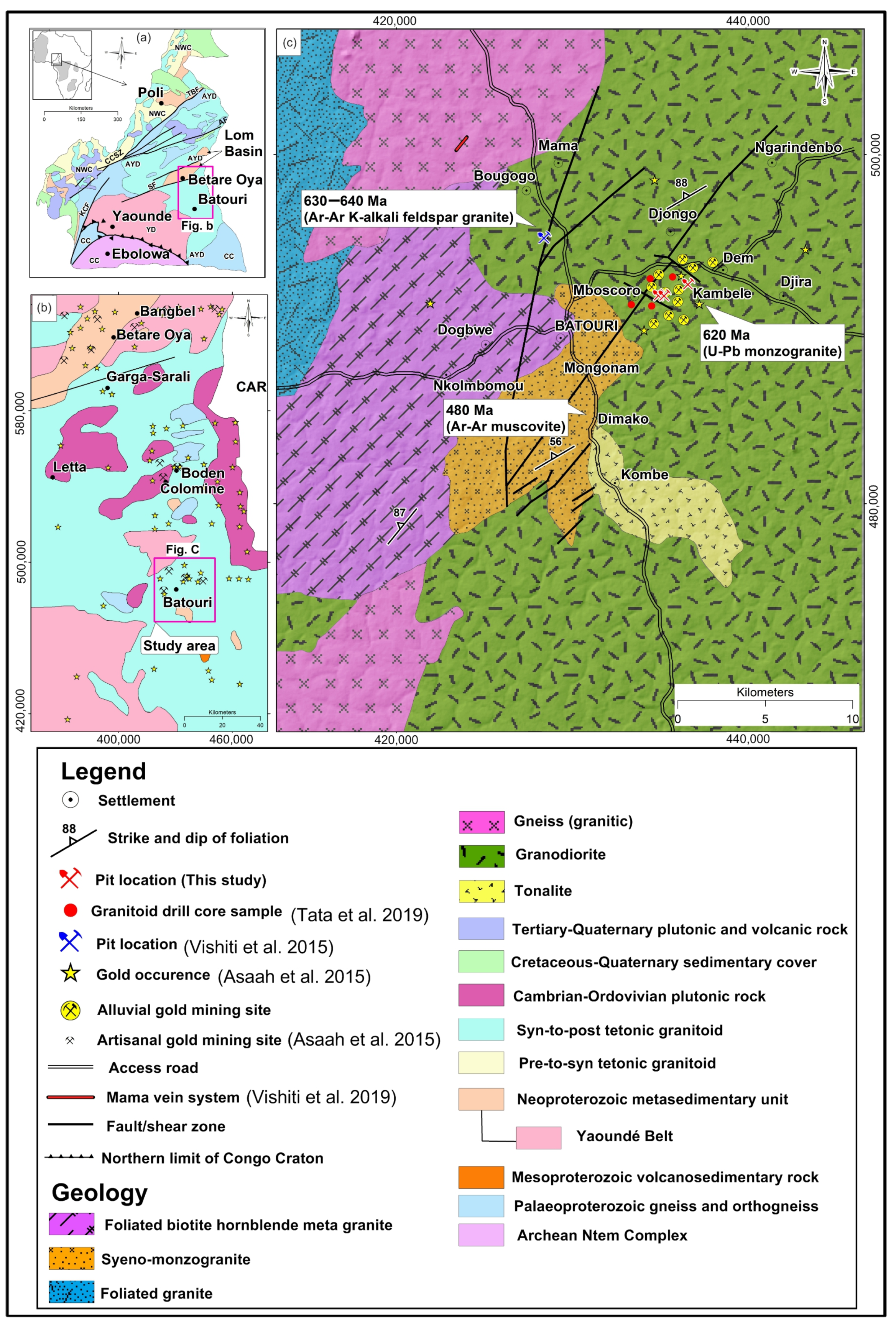
2. Regional and Local Geology
3. Materials and Methods
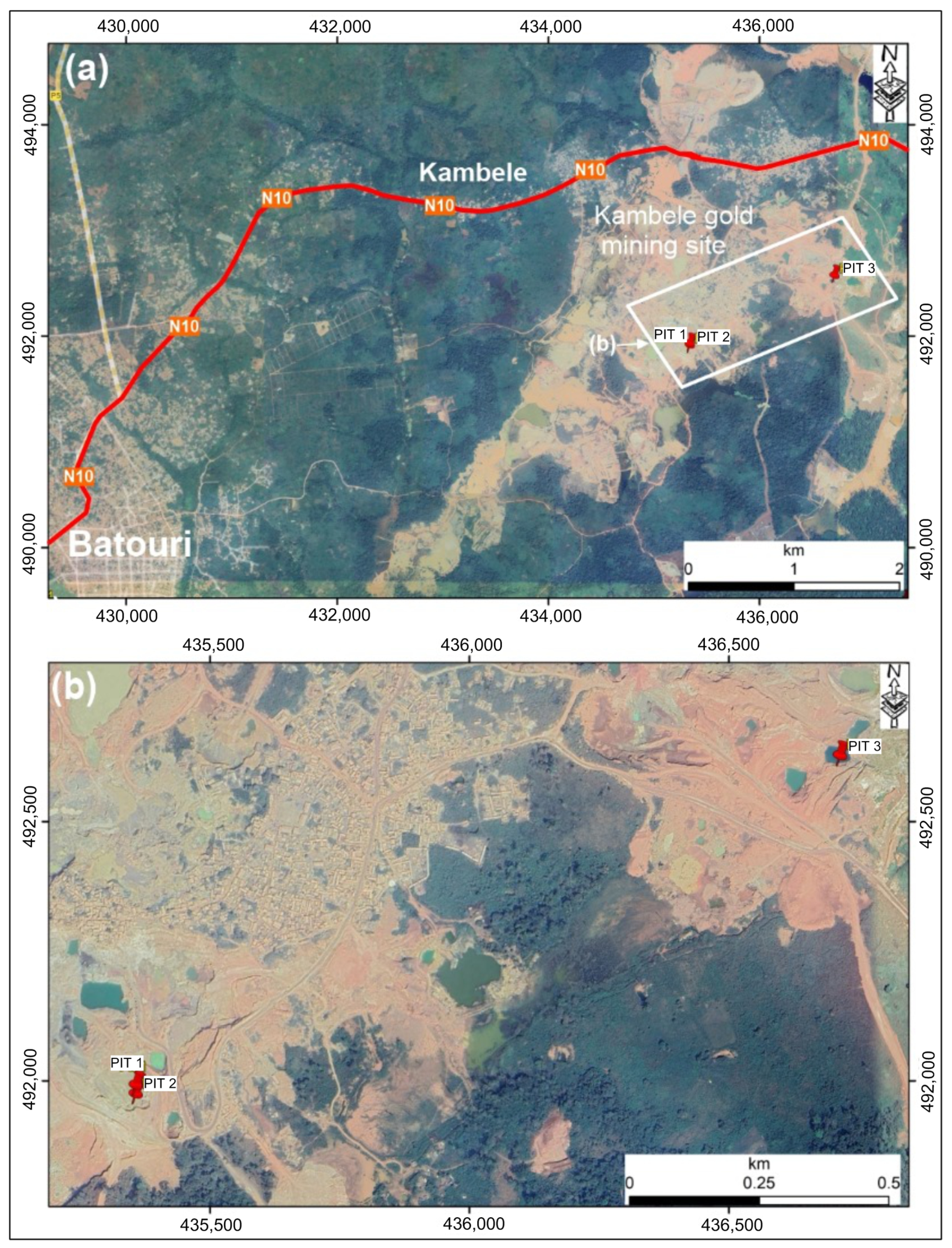
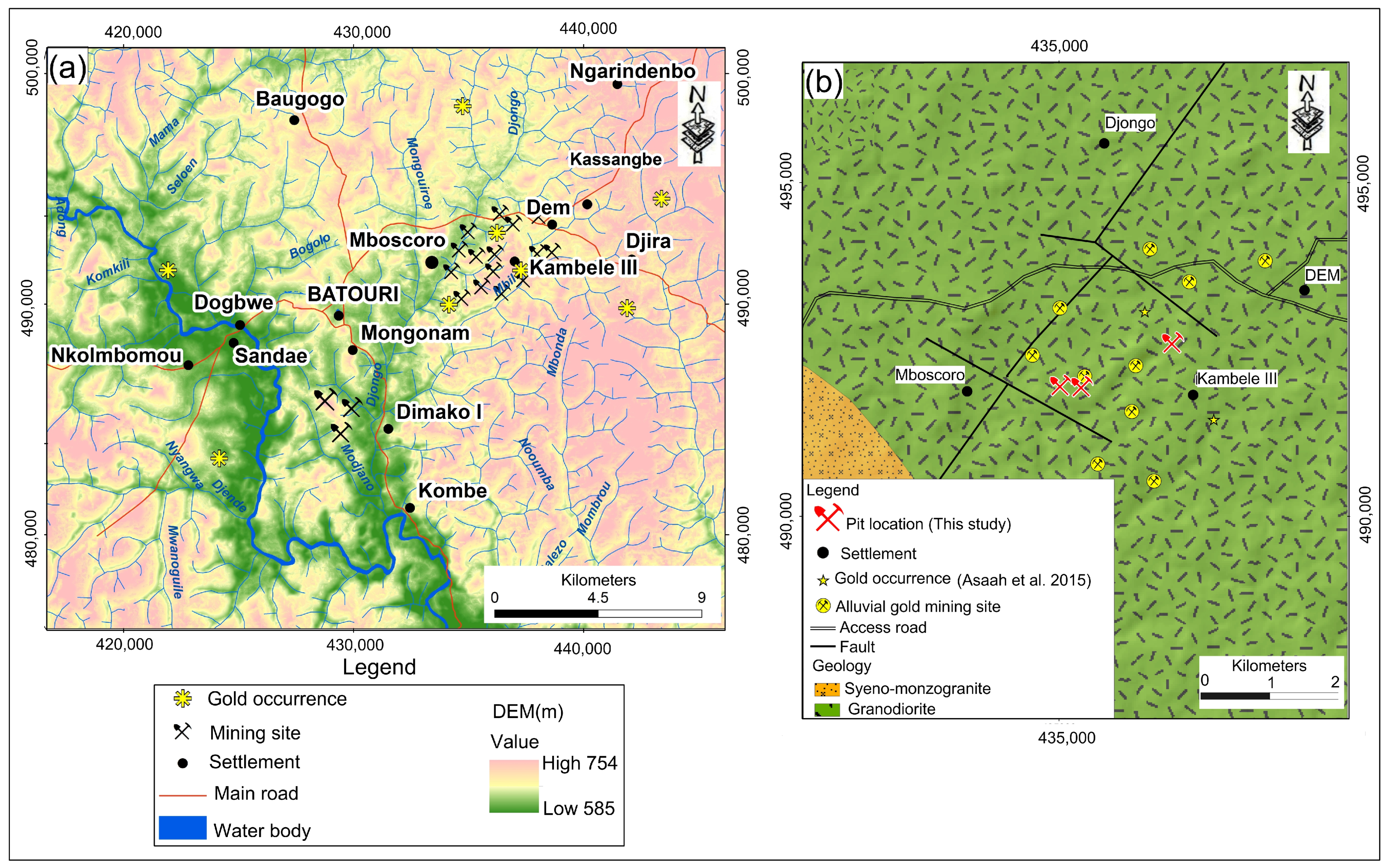
3.1. Sample Collection
3.2. Panning, Gold Grain Morphology and Microchemical Characterization
3.3. Bulk Geochemistry
4. Results
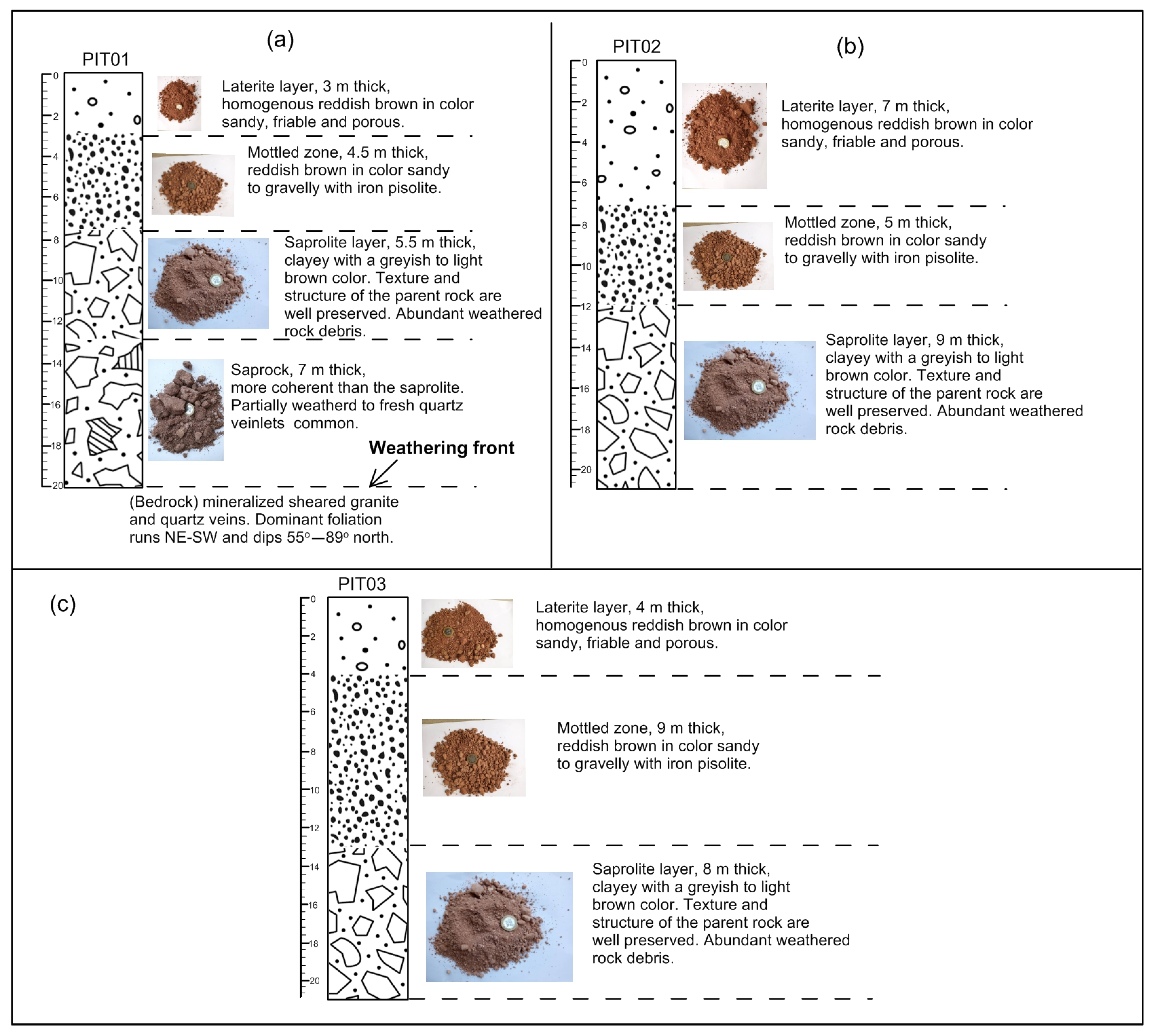
4.1. Description of the Soil Profile
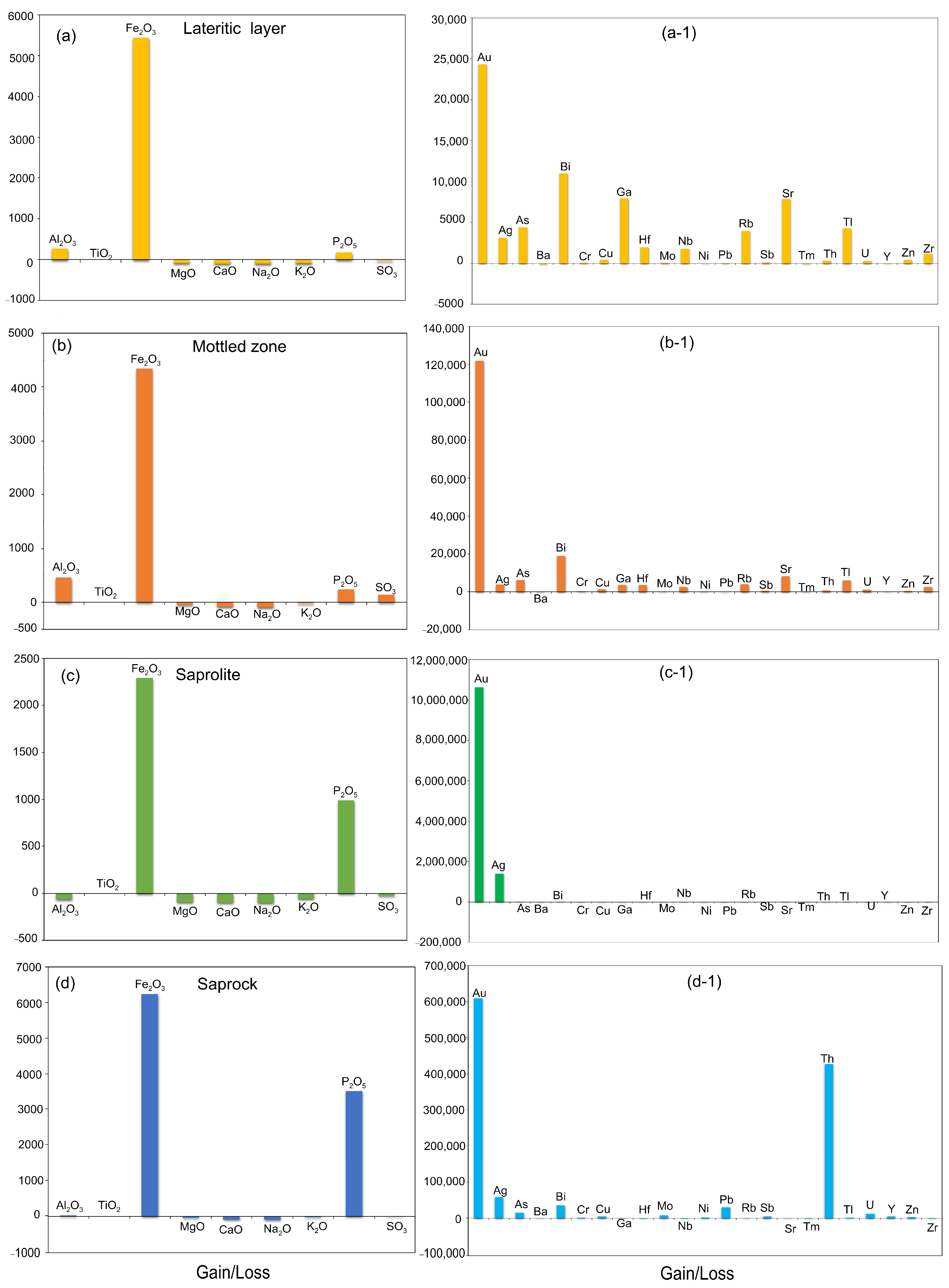
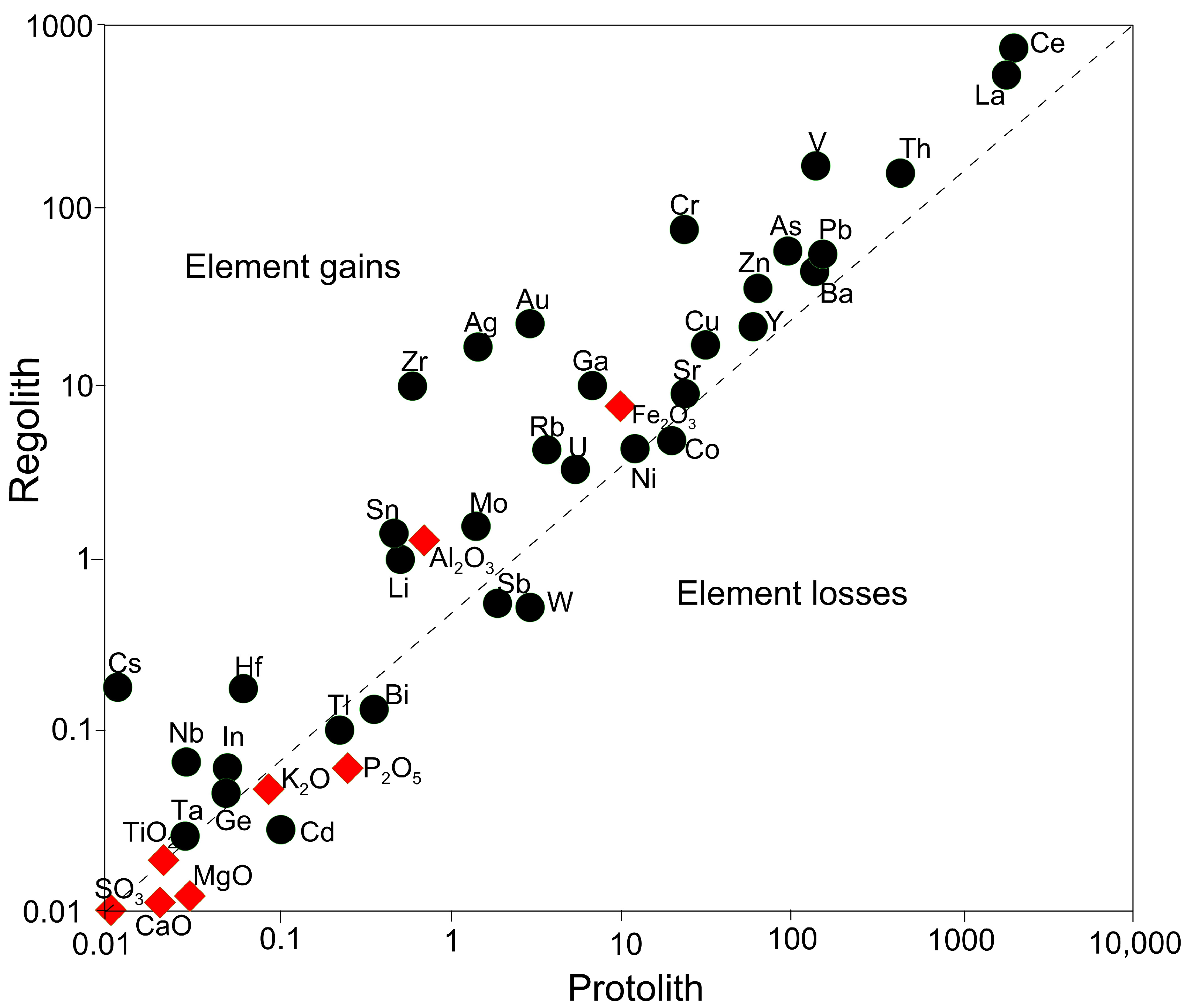
4.2. Chemical Trends and Element Mobility in the Weathering Blanket
4.3. Gold Concentrations along the Weathering Profile
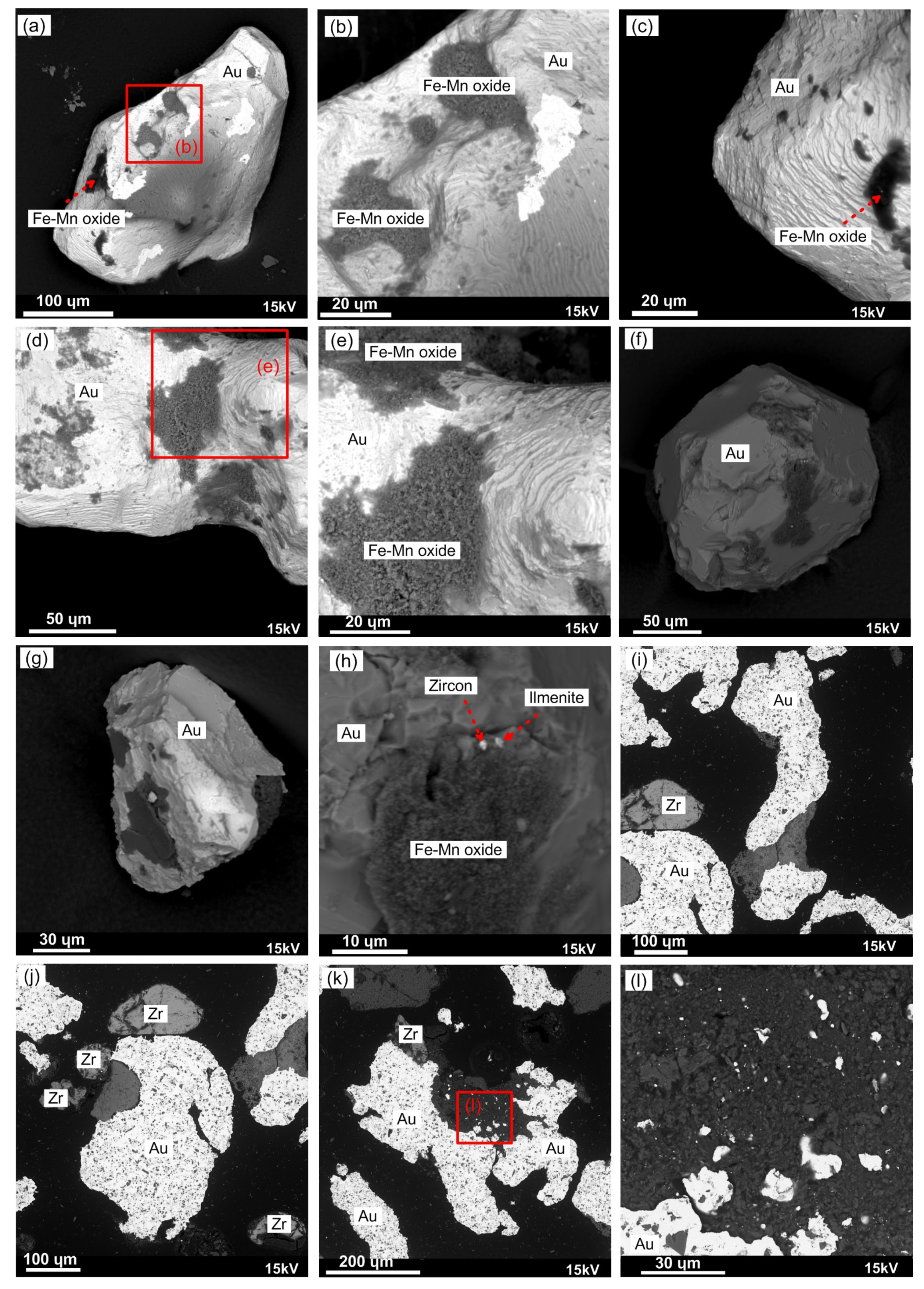
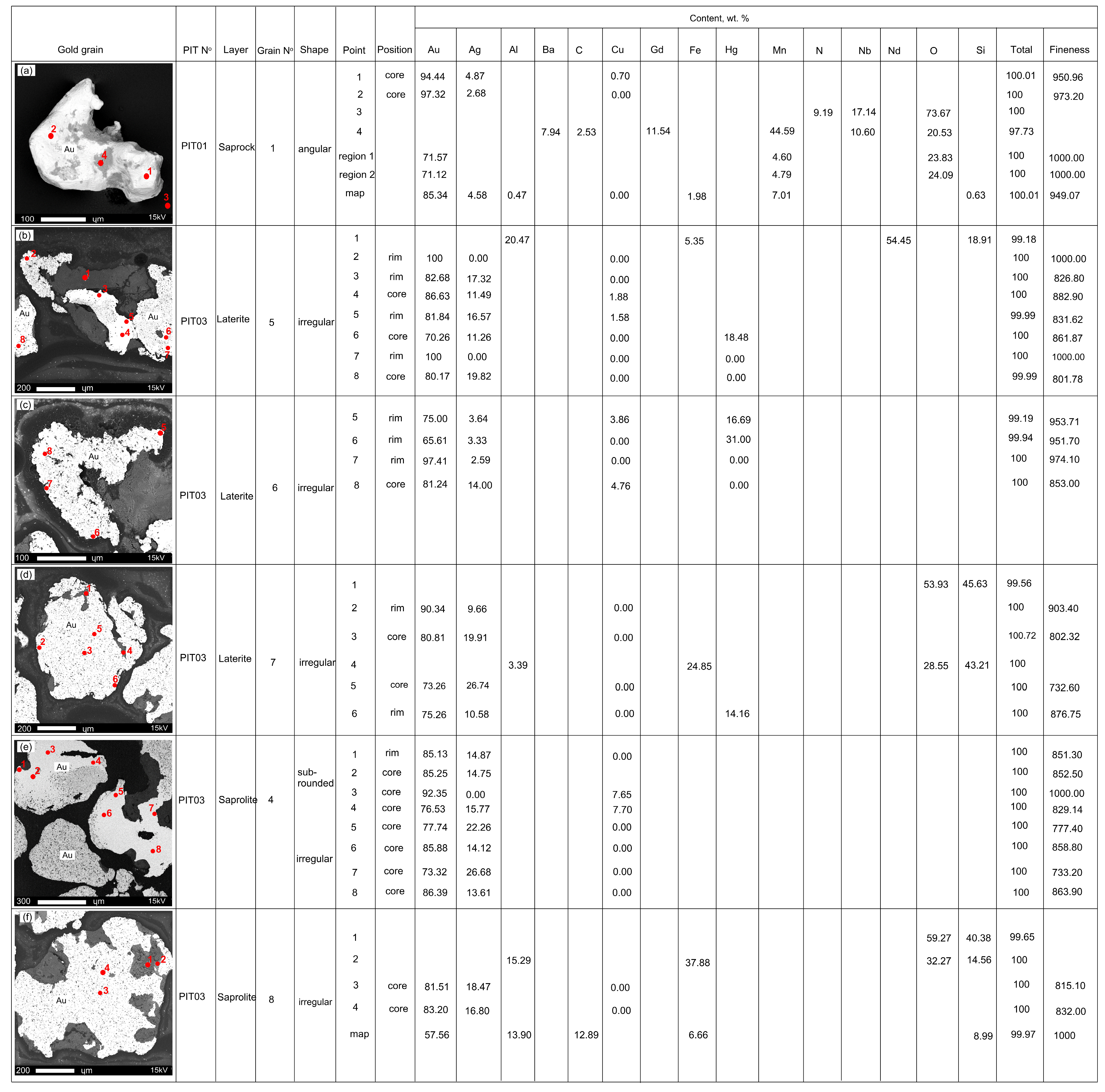
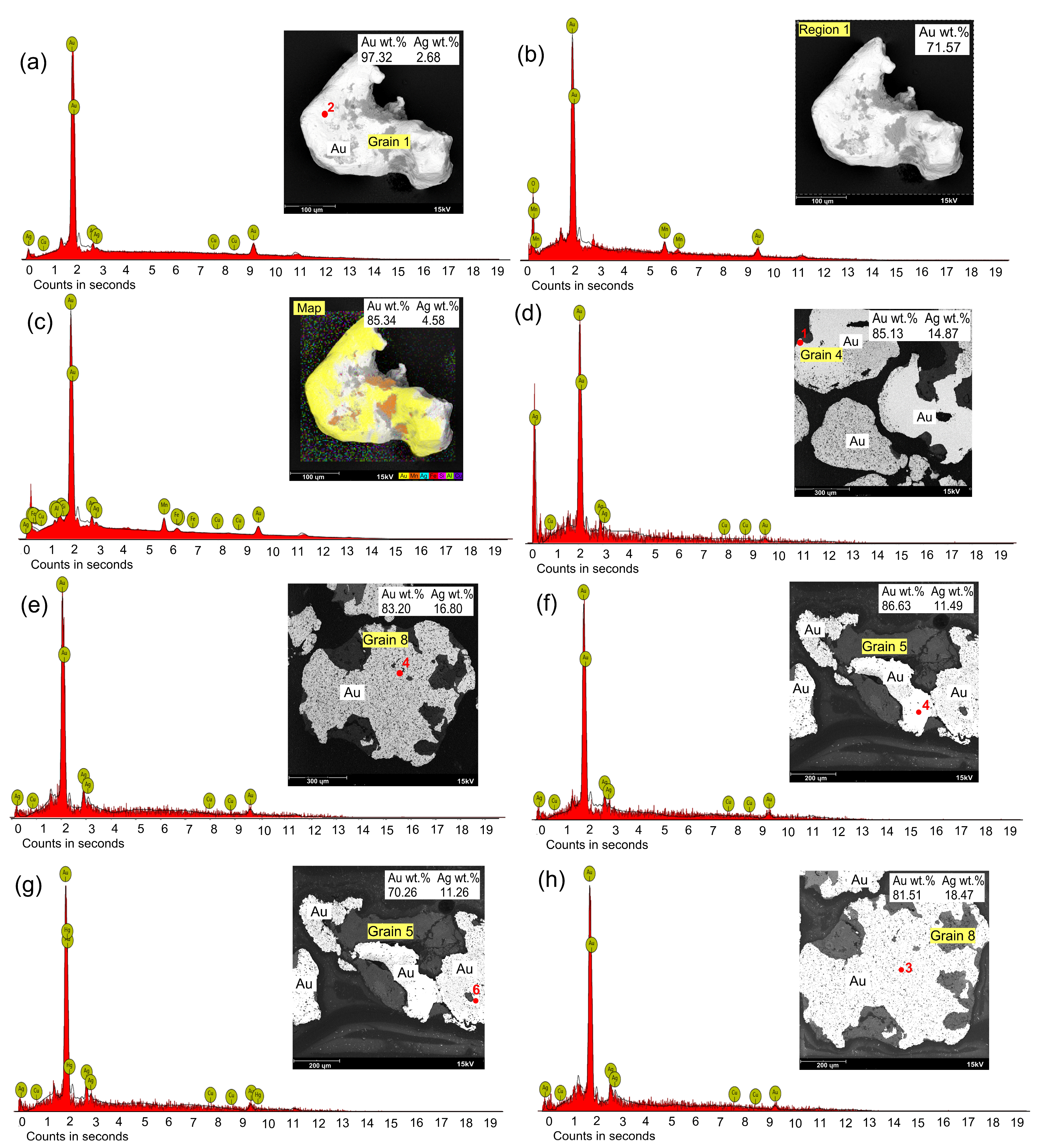
4.4. Gold Grain Morphology, Surface Characteristics and Microchemistry
4.5. Characterization of Inclusion Signatures
5. Discussion
5.1. Geochemical Characterization of the Weathering Blanket
5.2. Gold Grain Distribution along the Weathering Blanket
5.3. Gold Microchemical Signature and Grain Transportation
5.4. Impact of Anthropogenic Activities
5.5. Implication to Gold Exploration in the Regolith
6. Conclusions
- Pits dug in the Batouri goldfield exposed an in situ profile comprising various layers from the bottom to top as follows: saprock layer, saprolite, mottled zone and the laterite layer. It is clear that the lateritic layer has been reworked. The saprock layer in PIT01 is characterized by quartz veins that show gold flakes.
- The soil samples define a single weathering array corresponding to intermediate weathering evolving towards the kaolinitic end.
- Regolith evolution involved the development of laterite with elevated Fe content and enriched in Au-As-Ba-Ce-Cu-Pb-Rb-Sr-Y-Zn, pointing to inputs from the felsic basement, while Cr-V are related to mafic lithologies. High concentrations of chemically unstable Ba in the weathering blanket (e.g., PIT01) also affirm the proximity to the primary source.
- Gold grains show surface features that attest to their derivation from proximal sources. They are associated with inclusions of gangue minerals such as quartz, silicates, zircon and ilmenite inferred to be inherited from the underlying granitic basement rock.
- All horizons identified show the presence of gold; however, the concentration varies from top to bottom in a non-systematic manner. Gold essentially survived the rigors of the weathering cycle in the particulate form as explained by the 3 ppm Au in the saprock and 100 ppm Au in the saprolite. All the soil layers should therefore be taken into account during succinct regolith exploration efforts in this area.
- The gold grains are not authigenic in origin, and the concentration of Au is uniform along the core, solution fissures and rims, while that of Ag increases towards the core. These grains are alloyed with Ag and define a single compositional population similar to grains from the bedrock.
- Gold grains from the lateritic horizon show a Au-Ag-Hg assemblage. The Hg high is identified for the first time in the Batouri goldfield. Such elevated contents of Hg indicate modification due to human activities especially with the use of hazardous Hg-based products in the gold extraction process.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Orji, O.U.; Ibiam, U.A.; Awoke, J.N.; Obasi, O.D.; Uraku, A.J.; Alum, E.U.; Eze, A.G. Assessment of levels and health risks of trace metals in soils and food crops cultivated on farm lands near enyigba mining sites, Ebonyi state, Nigeria. J. Food Protect. 2021, 84, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvine Paternie, E.D.; Hakkou, R.; Ekengele Nga, L.; Bitom Oyono, L.D.; Ekoa Bessa, A.Z.; Oubaha, S.; Khalil, A. Geochemistry and geostatistics for the assessment of trace elements contamination in soil and stream sediments in abandoned artisanal small-scale gold mining (Bétaré-Oya, Cameroon). Appl. Geochem. 2023, 150, 105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, A.S.; Jamieson, H.E.; Radkova, A.B. Geochemical characterization of dust from arsenic-bearing tailings, Giant Mine, Canada. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 135, 105119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, A.; Cuevas, J.; Fuentes, B.; Fernandez, E.; Arce, W.; Guerrero, M.; Letelier, M.V. Distribution of potentially toxic elements in soils surrounding abandoned mining waste located in Taltal, Northern Chile. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 220, 106653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, D.M.; Craw, D.; Youngson, J.H.; Faure, K. Gold and sulphide minerals in tertiary quartz pebble conglomerate gold placers, Southland, New Zealand. Ore Geol. Rev. 2006, 28, 525–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetlitskaya, T.V.; Nevolko, P.A.; Kolpakov, V.V.; Tolstykh, N.D. Native gold from the Inagli Pt–Au placer deposit (the Aldan Shield, Russia): Geochemical characteristics and implications for possible bedrock sources. Miner. Depos. 2018, 53, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazel, J.; Gérard, G. Carte Géologique de Reconnaissance du Cameroun au 1/500,000, Feuille Batouri-Est avec Notice Explicative; Mémoire Direction des Mines et de la Géologie, Yaoundé, Cameroon; Science and Education Publishing: Newark, DE, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Vishiti, A.; Etame, J.; Suh, C.E. Features of gold-bearing quartz veins in an artisanal mining dominated terrain, Batouri Gold District, Eastern region of Cameroon. Episodes 2019, 42, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tata, E.; Suh, C.E.; Vishiti, A.; Shemang, E.M.; Fon, A.N.; Ateh, K.I.; Chombong, N.N. Wallrock alteration categories and theirgeochemical signatures in gold-bearing Neoproterozoic granitoids, Batouri Gold District, southeastern Cameroon. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2019, 19, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaah, A.V.; Zoheir, B.; Lehmann, B.; Frei, D.; Burgess, R.; Suh, C.E. Geochemistry and geochronology of the ~620 Magold-associated Batouri granitoids, Cameroon. Inter. Geol. Rev. 2015, 57, 1485–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.R.; Hough, R.M.; Salama, W.; Aspandiar, M.F.; Butt, C.R.M.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, I.; Metelka, V. Gold and pathfinder elements in ferricrete gold deposits of the Yilgarn Craton of Western Australia: A review with new concepts. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 104, 294–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, V.; Teitler, Y.; Eglinger, A.; André-Mayer, A.-S.; Heuret, A.; Pochon, A.; Cathelineau, M.; Gibert, P. Diversity of supergene gold expressions and implications for gold targeting in an equatorial regolith (AMG’s Couriège Exploration Prospect, French Guiana). The Geological Society of London Recent Advances in Understanding Gold Deposits: From Orogeny to Alluvium. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2022, 516, SP516-2021-40. [Google Scholar]
- Vishiti, A.; Suh, C.E.; Lehmann, B.; Egbe, J.A.; Shemang, E.M. Gold grade variation and particle microchemistry in exploration pits of the Batouri Gold District, SE Cameroon. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 111, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etutu, M.E.M.; Mafany, G.T.; Suh, C.E. Application of multi-element soil geochemistry and particulate gold exploration in the Kambele plain, Batouri Gold District, Southeast Cameroon. In Recent Research on Geomorphology, Sedimentology, Marine Geosciences and Geochemistry, Advances in Science, Technology & Innovation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Craw, D.; Kerr, G. Geochemistry and mineralogy of contrasting supergene gold alteration zones, southern New Zealand. J. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 5, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamba, O.; Parisot, J.C.; Grandin, G.; Beauvais, G. Ferricrete genesis and supergene gold behavior in Burkina Faso, West Africa. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2002, 2, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larizzatti, H.; Oliveria, S.M.B.; Butt, C.R.M. Morphology and composition of gold in a lateritic profile, Fazenda Pison Garimpo, Amazon, Brazil. J. South Am. Earth Sci. 2008, 25, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, D.M.; Craw, D. Supergene gold mobility: A textural and geochemical study from gold placers in southern New Zealand. Econ. Geol. Spec. Publ. 2009, 14, 77–93. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, C.E.; Lehmann, B. Morphology and electron-probe micro analysis of residual gold-grains at Dimako, southeast Cameroon. Neues Jahrb. Für Mineral. Monatshefte 2003, 6, 225–275. [Google Scholar]
- Freyssinet, P.H.; Butt, C.R.M.; Morris, R.C.; Piantone, P. Ore-forming processes related to lateritic weathering. In Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume; Hedenquist, J.W., Thomson, J.F.H., Goldfarb, R.J., Richards, J.P., Eds.; Society of Economic Geologists Inc.: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005; pp. 681–722. [Google Scholar]
- Zotov, A.; Kuzmin, N.; Reukov, V.; Tagirov, B. Stability of AuCl2—From 25 to 1000 °C at pressures to 5000 bar and consequences for hydrothermal gold mobilization. Minerals 2018, 8, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.P.; Silva, E.F.; Sousa, A.J.; Patinha, C.; Martins, E.; Guimaraes, C.; Azevedo, M.R.; Nogueira, P. Geochemical associations and their spatial patterns of variation in soil tungsten deposit: A pilot analysis data from the Marrancos gold. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2009, 9, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuster, J.; Reith, F.; Cornelis, G.; Parsons, J.E.; Parsons, J.M.; Southam, G. Secondary gold structures: Relics of past biogeochemical transformations and implications for colloidal gold dispersion in sub tropical environments. Chem. Geol. 2017, 450, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toteu, S.F.; Penaye, J.; Djomani, Y.P. Geodynamic evolution of the Pan-African belt in central Africa with special reference toCameroon. Can. J. Earth Sci. 2004, 41, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schmus, W.R.; Oliveira, E.P.; Da Silva Filho, A.F.; Toteu, S.F.; Penaye, J.; Guimaraes, I.P. Proterozoic links between the Borborema Province, NE Brazil, and the Central African Fold Belt. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2008, 294, 69–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toteu, S.F.; Van Schmus, R.W.; Penaye, J.; Michard, A. New U-Pb and Sm-Nd data from north central Cameroon and its bearing on the Pre-Pan-African history of Central Africa. Precambrian Res. 2001, 108, 45–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milesi, J.P.; Toteu, S.F.; Deschamps, Y.; Feybesse, J.L.; Lerouge, C.; Cocherie, A.; Penaye, J.; Tchameni, R.; Moloto-A-Kenguemb, G.; Kampunzu, H.A.B.; et al. An overview of the geology and major ore deposits of Central Africa: Explanatory note for the 1:4,000,000 map “geology and major ore deposits of Central Africa”. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2006, 44, 571–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njiekak, G.; Dorr, W.; Tchouankoue, J.-P.; Zulauf, G. U–Pb zircon and microfabric data of (meta) granitoids of western Cameroon: Constraints on the timing of pluton emplacement and deformation in the Pan-African belt of central Africa. Lithos 2008, 102, 460–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchameni, R.; Pouclet, A.; Penaye, J.; Ganwa, A.A.; Toteu, S.F. Petrography and geochemistry of the Ngaoundéré Pan-African granitoids in Central North Cameroon: Implications for their sources and geological setting. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2006, 44, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateh, K.I.; Suh, C.E.; Shemang, E.M.; Vishiti, A.; Tata, E.; Chombong, N.N. New LA-ICP MS U-Pb Ages, Lu-Hf Systematics and REE Characterization of Zircons from a Granitic Pluton in the Betare Oya Gold District, SE Cameroon. J. Geosci. Geomat. 2017, 5, 267–283. [Google Scholar]
- Ngatcha, R.B.; Okunlola, O.A.; Suh, C.E.; Ateh, K.I.; Hofmann, A. Petrochemical characterization of Neoproterozoic Colomine granitoids, SE Cameroon: Implications for gold mineralization. Lithos 2019, 344–345, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganwa, A.A.; Siebel, W.; Frisch, W.; Shang, K.C.; Ekodeck, E.G. Geochemistry and geochronology of the Meiganga metadiorite: Implication on the timing of D2 deformational phase in Adamawa-Yade Domain in Cameroon. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2011, 5, 1754–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakounte, J.N.; Eglinger, A.; Toteu, S.F.; Zeh, A.; Nkoumbou, C.; Mvondo-Ondoa, J.; Penaye, J.; Wit, M.; Barbey, P. The Adamawa-Yade domain, a piece of Archaean crust in the Neoproterozoic Central African Orogenic belt (Bafia area, Cameroon). Precambrian Res. 2017, 299, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngatcha, R.B.; Suh, C.E.; Okunlola, O.A.; Nunoo, S.; Ateh, K.I.; Elburg, M.; Hofmann, A. Crustal modeling from Pan-African granites of the Colomine Gold District, SE Cameroon: Insights from zircon U-Pb dating and Lu-Hf isotope systematic. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2022, 187, 104441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, C.E.; Lehmann, B.; Mafany, G.T. Geology and geochemical aspects of lode gold mineralization at Dimako-Mboscorro, SE Cameroon. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2006, 6, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaah, A.V. Lode Gold Mineralization in the Neoproterozoic Granitoids of Batouri. Ph.D. Dissertation, Southeastern Cameroon, Technische Universität Clausthal, Clausthal-Zellerfeld, Germany, 2010; 187p. [Google Scholar]
- Ndonfack, K.I.A.; Xie, Y.; Zhong, R.; Yomeun, B.S.; Cui, K.; Shan, X. Tectonic evolution of Neoproterozoic rocks, eastern Cameroon: Implication for gold mineralization in the Bétaré Oya and Woumbou-Colomine-Kette districts. Precambrian Res. 2022, 368, 106475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchameni, R.; Doumnang, J.C.; Deudibaye, M.; Branquet, Y. On the occurrence of gold mineralization in the Pala Neoproterozoic formations, South-Western Chad. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2013, 84, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large, R.R.; Allen, R.L.; Blake, M.D.; Herrmann, W. Hydrothermal alteration and volatile element halos for the Rosebery Klens volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposit, western Tasmania. Econ. Geol. 2001, 96, 1055–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, S.; Amponsah, P.O.; Siebenaller, L.; Béziat, D.; Baratoux, L.; Jessell, M. Shear related gold mineralization in Northwest Ghana: The Julie deposit. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 78, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElMonsef, M.A.; Slobodník, M.; Salem, I.A. Hydrothermal evolution of granitoid hosted gold mineralization in gidami area: An example for orogenic-gold deposits in Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 146, 132–149. [Google Scholar]
- Frimmel, H.E. Earth’s continental crustal gold endowment. Earth Plan. Sci. Lett. 2008, 267, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipson, R. The promise and perils of porphyry deposits in the future of gold production. SEG Discov. 2014, 98, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchiorre, E.B.; Henderson, J. Topographic gradients and lode gold sourcing recorded by placer gold morphology, geochemistry, and mineral inclusions in the east fork San Gabriel River, California, USA. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 109, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallbaer, D.K.; Utter, T. Geochemical and morphological characteristics of gold particles from recent river deposits and the fossil placer of the Witwatersrand. Miner. Depos. 1977, 12, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Formation and diagenesis of weathering profiles. J. Geol. 1989, 97, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, W.H.; Kranidiotis, P. Immobile elements as monitors of mass transfer in hydrothermal alteration: Phelps Dodge massive sulfide deposit, Matagami, Quebec. Econ. Geol. 1987, 82, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.A. Isocon analysis: A brief review of the method and applications. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2005, 30, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollinson, H.R. Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation; Routledge: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fon, A.N.; Suh, C.E.; Vishiti, A.; Ngatcha, R.B.; Ngang, T.C.; Shemang, E.M.; Egbe, J.A.; Lehmann, B. Gold dispersion in tropical weathering profiles at the Belikombone gold anomaly(Bétaré Oya gold district), east Cameroon. Geochemistry 2021, 81, 125770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchiorre, E.B.; Orwin, P.M.; Reith, F.; Rea, M.A.D.; Yahn, J.; Allison, R. Biological and geochemical development of placergold deposits at Rich Hill, Arizona, USA. Minerals 2018, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Guchhait, S. Characterization and evolution of primary and secondary laterites in north western Bengal Basin, West Bengal, India. J. Palaeogeogr. 2015, 4, 203–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzabakurikiza, A.; Onana, V.L.; ZeA, N.; Mvindi, A.T.Z.; Ekodeck, G.E. Geological, geotechnical, and mechanical characterization of lateritic gravels from Eastern Cameroon for road construction purposes. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2016, 76, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doum, J.M.; Fuh, G.C.; Fadil-Djenabou, S.; Onana, V.L.; Ndjigui, P.D.; Armstrong-Altrin, J.S. Characterization and potential application of gley sols and feral sols for ceramic industry: A case study from Dimako (Eastern Cameroon). Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongmo, F.W.N.; Chapman, R.J.; Bolarinwa, A.T.; Yongue, R.F.; Banks, D.A.; Olajide-Kayodea, J.O. Microchemical characterization of placer gold grains from the Meyos Essabikoula area, Ntem complex, southern Cameroon. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 151, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moles, N.R.; Chapman, R.J. Integration of detrital gold microchemistry, heavy mineral distribution, and sediment geochemistry to clarify regional metallogeny in glaciated terrains: Application in the Caledonides of southeast Ireland. Econ. Geol. 2019, 114, 207–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.G.; Mann, A.W. The influence of climate, geomorphology and primary geology on the supergene migration of gold and silver. J. Geochem. Explor. 1984, 22, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, C.R.M. The development of regolith exploration geochemistry in the tropics and sub-tropics. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 73, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyssinet, P. Gold dispersion related to ferricrete pedogenesis in South Mali: Application to geochemical exploration. Chron. Miner. Res. Explor. 1993, 510, 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Reith, F.; Fairbrother, L.; Nolze, G.; Wilhelmi, O.; Clode, P.L.; Gregg, A.; Parsons, J.E.; Wakelin, S.A.; Pring, A.; Hough, R.; et al. Nano particle factories: Biofilms hold key to gold dispersion and nugget formation. Geology 2010, 38, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, R.J.; Leake, R.C.; Moles, N.R.; Earls, G.; Cooper, C.; Harrington, K.; Berzins, R. The application of microchemical analysis of gold grains to the understanding of complex local and regional gold mineralization: A case study in Ireland and Scotland. Econ. Geol. 2000, 95, 1753–1773. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, R.J.; Leake, R.C.; Moles, N.R. The use of microchemical analysis of alluvial gold grains in mineral exploration: Experiences in Britain and Ireland. J. Geochem. Explor. 2000, 71, 241–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townley, B.K.; Hérail, G.; Maksaev, V.; Palacios, C.; de Parseval, P.; Sepulveda, F.; Orellana, R.; Rivas, P.; Ulloa, C. Gold grain morphology and composition as an exploration tool: Application to gold exploration in covered areas. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2003, 3, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, R.J.; Moles, N.R.; Bluemel, B.; Walshaw, R.D. Detrital gold as an indicator mineral. In Recent Advances in Understanding Gold Deposits: From Orogeny to Alluvium; Torvela, T., Lambert-Smith, J.S., Chapman, R.J., Eds.; Geological Society, London, Special Publications; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2022; p. 516. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, R.J.; Mortensen, J.K.; Allan, M.M.; Walshaw, R.D.; Bond, J.; MacWilliam, K.A. New approach to characterizing deposit type using mineral inclusion assemblages in gold particles. Econ. Geol. 2022, 117, 361–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, R.J.; Mortensen, J.K. Application of microchemical characterization of placer gold grains to exploration for epithermal gold mineralization in regions of poor exposure. J. Geochem. Explor. 2006, 91, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moles, N.R.; Chapman, R.J.; Warner, R.B. The significance of copper concentrations in natural gold alloy for reconnaissance exploration and understanding gold-depositing hydrothermal systems. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2013, 13, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, S.; Lima, A.; Noronha, F. Characterization of heavy mineral concentrates and detrital gold particles from the Bigorne granite-hosted gold deposit in the Iberian Variscan Belt. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2021, 516, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, A.H.; Lavin, O.P.; Nicol, I. The morphology and chemistry of transported grains as an exploration tool. J. Geochem. Explor. 1991, 40, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubé, B.; Gosselin, P. Greenstone-hosted quartz carbonate vein deposits. In Mineral Deposits of Canada: A Synthesis of Major Deposit-Types, District Metallogeny, the Evolution of Geological Provinces, and Exploration Methods; Good fellow, W.D., Ed.; Geological Association of Canada, Mineral Deposits Division, Special Publication; Geological Association of Canada: St. John’s, NL, Canada, 2007; Volume 5, pp. 49–73. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, I.M.; Gignoux, T. Distribution, characteristics, and genesis of high fineness gold placers, Nine mile Valley, Central-Western Montana. Econ. Geol. 1999, 94, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb, R.J.; Pitcairn, I. Orogenic gold: Is a genetic association with magmatism realistic? Miner. Depost. 2023, 58, 5–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisabeth Sylvie, N.M.; Ekoa Bessa, A.Z.; Ayissi Mbomo, R.E.; Akono, J.V.; Dairou, B.; Pierre, K. Evaluation of surface water contamination and its impacts on health in the mining districts of Kambélé and Bétaré-Oya (Eastern-Cameroon). Heliyon 2024, 10, 29189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hylander, L.D.; Meili, M. 500 years of mercury production: Global annual inventory by region until 2000 and associate demissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 304, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP Reducing Mercury Use in Artisanal and Small Scale; United Nations Environmental Program, United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2012; p. 76.
- Sousa, R.; Veiga, V.; Zyl, V.D.; Telmer, K.; Spiegel, S.; Selder, J. Policies and regulations for Brazil’s artisanal gold mining sector: Analysis and recommendations. J. Clean Prod. 2011, 19, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, M.J. Future strategies for tackling mercury pollution in artisanal gold mining sector: Making the Minamata convention work. Futures 2014, 62, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchiorre, E.B.; Mathur, R.; Kamenov, G.; Paredes, J. Geochemical Overprinting and Secondary Placer Crystal Formation in the La Cholla District, Quartzsite, Arizona, USA: Evidence from Copper Isotopes, Morphology, and Trace Elements. Minerals 2023, 13, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, C.R.M.; Lintern, M.; Anand, R.R. Evolution of regoliths and landscapes in deeply weathered terrain—Implications for geochemical exploration. Ore Geol. Rev. 2000, 16, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawadogo, B.; Bamba, O.; Chardon, D. Landform-regolith mapping in the West African context. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 126, 103782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkari, E.D.; Appiah-Twum, M.; Lermi, A. Spatial distribution and trace element geochemistry of laterites in Kunche area: Implication for gold exploration targets in NW, Ghana. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 158, 103519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| SOIL | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DL | PIT01 | PIT02 | PIT03 | ||||||||
| LAT | MOT | SAP | SAPROCK | LAT | MOT | SAP | LAT | MOT | SAP | ||
| Elements | |||||||||||
| Al2O3wt% | 0.01 | 2.76 | 1.70 | 0.18 | 0.60 | 2.15 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 2.79 | 0.82 | 0.22 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.01 | 17.15 | 4.06 | 1.38 | 9.71 | 10.04 | 1.96 | 0.32 | 8.97 | 2.92 | 12.88 |
| MgO | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | bdl | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | bdl | 0.01 | bdl | bdl |
| CaO | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | bdl | 0.01 | bdl | bdl |
| Na2O | 0.001 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | bdl | 0.01 | bdl | bdl | bdl | <0.01 |
| K2O | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| TiO2 | 0.001 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.02 | <0.01 | bdl | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| P2O5 | 0.001 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.12 |
| SO3 | 0.02 | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl |
| CIA | 99 | 98 | 85 | 72 | 97 | 93 | 74 | 99 | 94 | 80 | |
| ppm | |||||||||||
| Au | 0.0002 | <1 | <1 | >100 | 3 | <1 | 1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | >100 |
| Ag | 0.002 | <1 | <1 | 53 | 1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | 85 |
| As | 0.1 | 19 | 4 | bdl | 100 | 40 | 21 | 9 | 67 | 30 | 253 |
| Ba | 0.5 | 7 | 10 | 165 | 151 | 14 | 15 | 22 | 7 | 9 | 19 |
| Be | 0.1 | 1 | <1 | 1 | 3 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | 1 |
| Bi | 0.02 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| B | 20 | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl |
| Co | 0.1 | 1 | 1 | 14 | 20 | 1 | 1 | <1 | 1 | <1 | 7 |
| Cs | 0.02 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | 1 | <1 | <1 |
| Cr | 0.5 | 250 | 23 | 12 | 25 | 132 | 17 | 3 | 106 | 32 | 112 |
| Cu | 0.01 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 31 | 27 | 17 | 10 | 22 | 6 | 22 |
| Cd | 0.01 | bdl | bdl | <1 | <1 | <1 | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | <1 |
| Ga | 0.1 | 23 | 13 | bdl | 8 | 16 | 7 | 1 | 20 | 7 | 3 |
| Ge | 0.1 | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl |
| Hf | 0.02 | <1 | <1 | <1 | bdl | <1 | <1 | <1 | 1 | <1 | <1 |
| Hg | 0.005 | <1 | <1 | 4 | 10 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | 3 |
| In | 0.02 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | bdl | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Li | 0.1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | <1 |
| Mo | 0.01 | 2 | 1 | <1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | <1 | 2 | 1 | 4 |
| Mn | 1 | 100 | 110 | 695 | 762 | 94 | 35 | 13 | 104 | 40 | 242 |
| Nb | 0.02 | <1 | <1 | bdl | <1 | <1 | <1 | bdl | <1 | <1 | bdl |
| Ni | 0.1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 12 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 10 |
| Pb | 0.01 | 47 | 22 | 136 | 157 | 36 | 15 | 8 | 15 | 6 | 39 |
| Pd | 0.01 | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl |
| Pt | 0.002 | bdl | bdl | <1 | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | <1 |
| Rb | 0.1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| Re | 0.001 | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl |
| Sb | 0.02 | <1 | <1 | 1 | 2 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | 2 |
| Sc | 0.1 | 13 | 8 | 13 | 17 | 10 | 5 | 1 | 13 | 4 | 12 |
| Se | 0.1 | 1 | bdl | bdl | 1 | 1 | bdl | bdl | <1 | <1 | bdl |
| Sn | 0.1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | <1 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Sr | 0.5 | 2 | 3 | 28 | 25 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 12 |
| Ta | 0.05 | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl |
| Te | 0.02 | <1 | bdl | bdl | <1 | <1 | bdl | bdl | <1 | bdl | bdl |
| Th | 0.1 | 38 | 13 | 626 | 431 | 21 | 9 | 7 | 21 | 13 | 265 |
| Tl | 0.02 | <1 | <1 | 1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | bdl |
| U | 0.1 | 3 | 2 | 7 | 6 | 2 | 1 | <1 | 3 | 1 | 7 |
| V | 1 | 537 | 88 | 30 | 145 | 259 | 41 | 5 | 232 | 74 | 227 |
| W | 0.1 | <1 | bdl | bdl | 3 | 1 | <1 | bdl | bdl | bdl | 1 |
| Y | 0.01 | 3 | 7 | 82 | 59 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 22 |
| Zn | 0.1 | 10 | 10 | 154 | 66 | 24 | 14 | 5 | 15 | 3 | 21 |
| Zr | 0.1 | 22 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 14 | 5 | 2 | 24 | 9 | 3 |
| La | 0.5 | 10 | 38 | 2438 | 1968 | 20 | 41 | 56 | 22 | 26 | 1288 |
| Ce | 0.1 | 70 | 136 | >2000 | >2000 | 75 | 82 | 88 | 57 | 67 | >2000 |
| Au | Ag | As | Ba | Ce | Co | Cr | Cu | Mo | Mn | Pb | Rb | Sb | Sr | Th | V | W | Zn | Zr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ag | 0.97 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||||
| As | 0.51 | 0.69 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| Ba | 0.44 | 0.28 | −0.02 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||
| Ce | 0.78 | 0.75 | 0.57 | 0.78 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||
| Co | 0.46 | 0.39 | 0.31 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||
| Cr | −0.07 | 0.02 | 0.20 | −0.38 | −0.20 | −0.26 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| Cu | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.54 | 0.23 | 0.36 | 0.44 | 0.04 | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| Mo | 0.34 | 0.52 | 0.87 | −0.27 | 0.29 | 0.05 | 0.64 | 0.43 | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| Mn | 0.49 | 0.37 | 0.18 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 0.98 | −0.25 | 0.34 | −0.05 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| Pb | 0.40 | 0.27 | 0.09 | 0.95 | 0.80 | 0.95 | −0.13 | 0.34 | −0.06 | 0.98 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| Rb | −0.64 | −0.64 | −0.34 | −0.28 | −0.55 | −0.35 | −0.04 | 0.41 | −0.26 | −0.36 | −0.28 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Sb | 0.53 | 0.57 | 0.69 | 0.67 | 0.92 | 0.89 | −0.05 | 0.60 | 0.46 | 0.80 | 0.77 | −0.37 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Sr | 0.62 | 0.50 | 0.22 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.96 | −0.28 | 0.30 | −0.03 | 0.98 | 0.95 | −0.41 | 0.80 | 1.00 | |||||
| Th | 0.73 | 0.60 | 0.23 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.91 | −0.25 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.95 | 0.90 | −0.49 | 0.76 | 0.99 | 1.00 | ||||
| V | −0.12 | −0.04 | 0.21 | −0.29 | −0.14 | −0.14 | 0.98 | 0.10 | 0.63 | −0.14 | −0.02 | −0.07 | 0.05 | −0.20 | −0.19 | 1.00 | |||
| W | −0.01 | 0.04 | 0.45 | 0.54 | 0.60 | 0.78 | −0.09 | 0.72 | 0.25 | 0.65 | 0.67 | 0.03 | 0.83 | 0.57 | 0.46 | 0.06 | 1.00 | ||
| Zn | 0.64 | 0.44 | −0.09 | 0.90 | 0.72 | 0.75 | −0.28 | 0.06 | −0.26 | 0.85 | 0.83 | −0.32 | 0.48 | 0.90 | 0.92 | −0.26 | 0.20 | 1.00 | |
| Zr | −0.39 | −0.37 | −0.18 | −0.50 | −0.57 | −0.52 | 0.74 | −0.06 | 0.26 | −0.44 | −0.37 | 0.20 | −0.47 | −0.50 | −0.49 | 0.71 | −0.38 | −0.35 | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vishiti, A.; Suh, C.E.; Ngatcha, R.B.; Melchiorre, E.B.; Shemang, E.M.; Omang, B.O.; Ngang, T.C.; Valdez, F.C.; Sekem, S.G. Soil Geochemistry Combined with Particulate Gold Microchemistry Provides Evidence of Eluvial Gold Genesis and Anthropogenic Hg Use in Eastern Cameroon Goldfields. Minerals 2024, 14, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14060567
Vishiti A, Suh CE, Ngatcha RB, Melchiorre EB, Shemang EM, Omang BO, Ngang TC, Valdez FC, Sekem SG. Soil Geochemistry Combined with Particulate Gold Microchemistry Provides Evidence of Eluvial Gold Genesis and Anthropogenic Hg Use in Eastern Cameroon Goldfields. Minerals. 2024; 14(6):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14060567
Chicago/Turabian StyleVishiti, Akumbom, Cheo Emmanuel Suh, Ralain Bryan Ngatcha, Erik B. Melchiorre, Elisha Mutum Shemang, Benjamin Odey Omang, Terence Cho Ngang, Fernando Castro Valdez, and Sharila Gillian Sekem. 2024. "Soil Geochemistry Combined with Particulate Gold Microchemistry Provides Evidence of Eluvial Gold Genesis and Anthropogenic Hg Use in Eastern Cameroon Goldfields" Minerals 14, no. 6: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14060567
APA StyleVishiti, A., Suh, C. E., Ngatcha, R. B., Melchiorre, E. B., Shemang, E. M., Omang, B. O., Ngang, T. C., Valdez, F. C., & Sekem, S. G. (2024). Soil Geochemistry Combined with Particulate Gold Microchemistry Provides Evidence of Eluvial Gold Genesis and Anthropogenic Hg Use in Eastern Cameroon Goldfields. Minerals, 14(6), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14060567








