Estimation of the Potential Antimony Resource in Southern China with the Geochemical Block Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
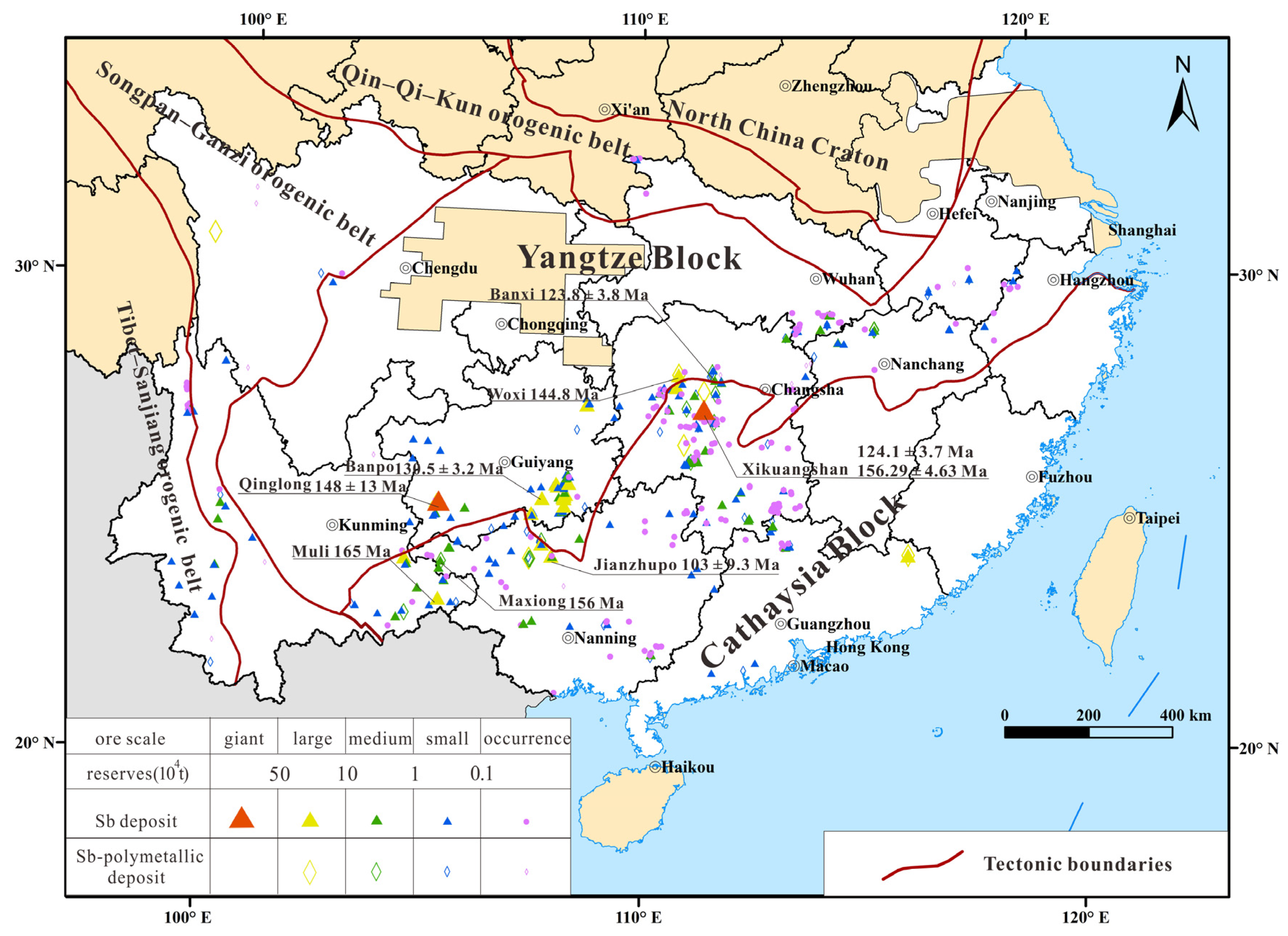
2. Overview of Sb Deposits in Southern China
| Provinces | Deposits | Ages (Ma) | Methods | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hunan | Xikuangshan | 124.1 ± 3.7 | Calcite Sm-Nd | [55] |
| 156.3 ± 12 | Calcite and Stibnite Sm-Nd | [56] | ||
| 156.29 ± 4.63 | Stibnite Sm-Nd | [57] | ||
| 117~156 | Zircon (U-Th)/He | [58] | ||
| Banxi | 120~130 | Zircon (U-Th)/He | [58] | |
| 123.8 ± 3.8 | Zircon (U-Th)/He | [59] | ||
| Woxi | 144.8 | Quartz fluid Rb-Sr | [60] | |
| Guizhou | Qinglong | 142~148 | Fluorite Sm-Nd | [55] |
| 148 ± 13 | Calcite Sm-Nd | [61] | ||
| Banpo | 130.5 ± 3.2 | Calcite Sm-Nd | [62] | |
| Banian | 128.2 ± 3.2 126.4 ± 2.7 | Calcite Sm-Nd | [63] | |
| Weizhai | 115.3 ± 1.5 | Calcite LA-ICP-MS | [64] | |
| Guangxi | Maxiong | 141 | Quartz fluid Ar-Ar | [65] |
| 156 | Quartz fluid Rb-Sr | |||
| Jianzhupo | 103 ± 9.3 | Cassiterite LA-ICP-MS | [66] | |
| Yunnan | Muli | 165 | Quartz fluid Ar-Ar | [67] |
3. Methods and Materials
3.1. Sample Collection and Laboratory Analysis
3.2. Geochemical Map and Geochemical Blocks of Sb
3.3. Potential Resource of Sb Reckoned on Geochemical Block Theory
3.3.1. Metal Supply of Geochemical Blocks
3.3.2. Mineralization Coefficient of Geochemical Blocks
4. Geochemical Blocks and Potential Resources of Sb in Southern China
4.1. General Statistical Distribution of Sb in Southern China
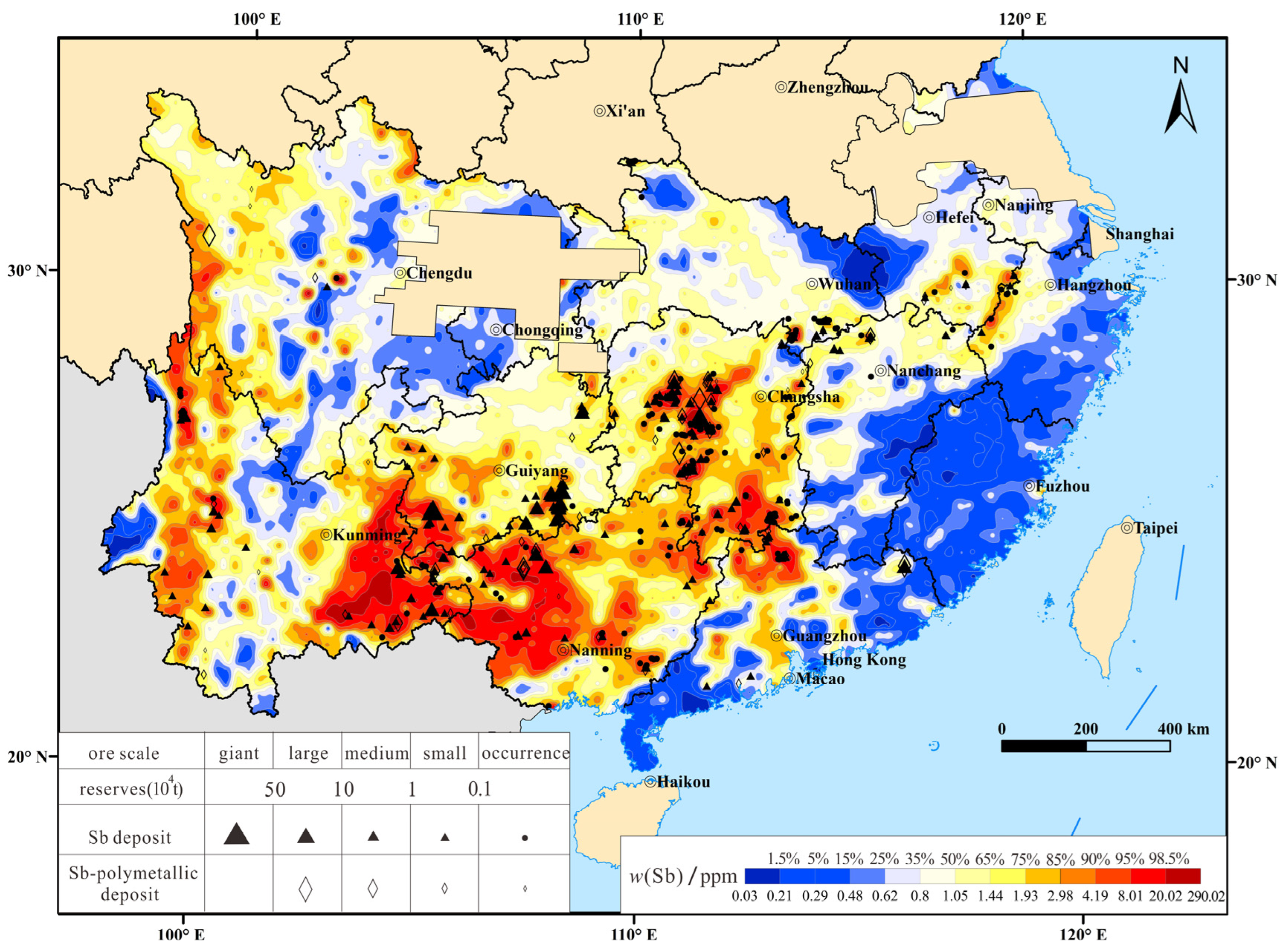
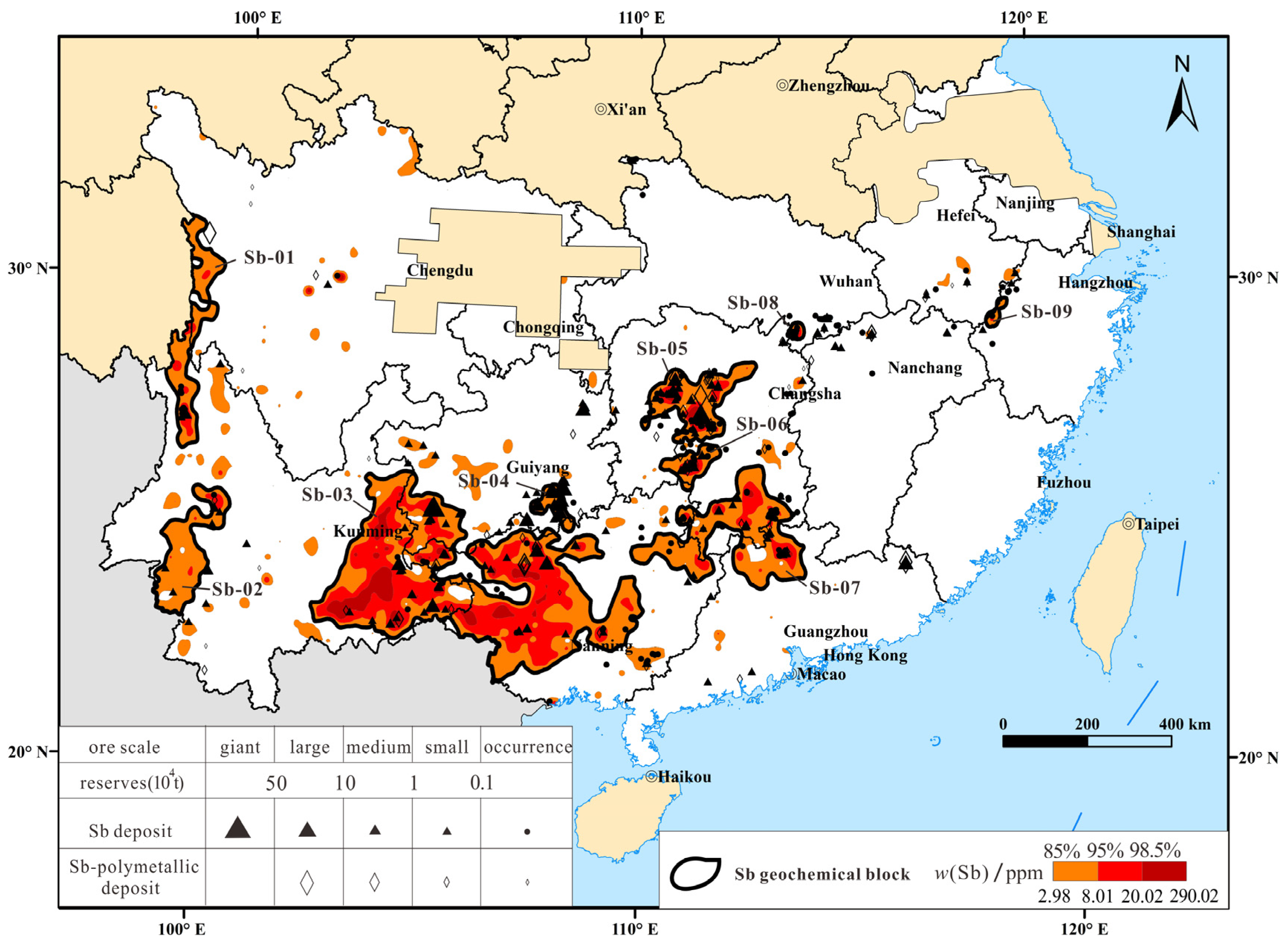
4.2. Spatial Relationship between Sb Geochemical Blocks and Sb Deposits
4.3. Geochemical Blocks and the Potential Resource of Sb in Southern China
- (1)
- Sanjiang Sb block (Sb-01)
- (2)
- Southwestern Yunnan Sb geochemical block (Sb-02)
- (3)
- Dian–Qian–Gui Sb block (Sb-03)
- (4)
- Southeastern Guizhou Sb block (Sb-04)
- (5)
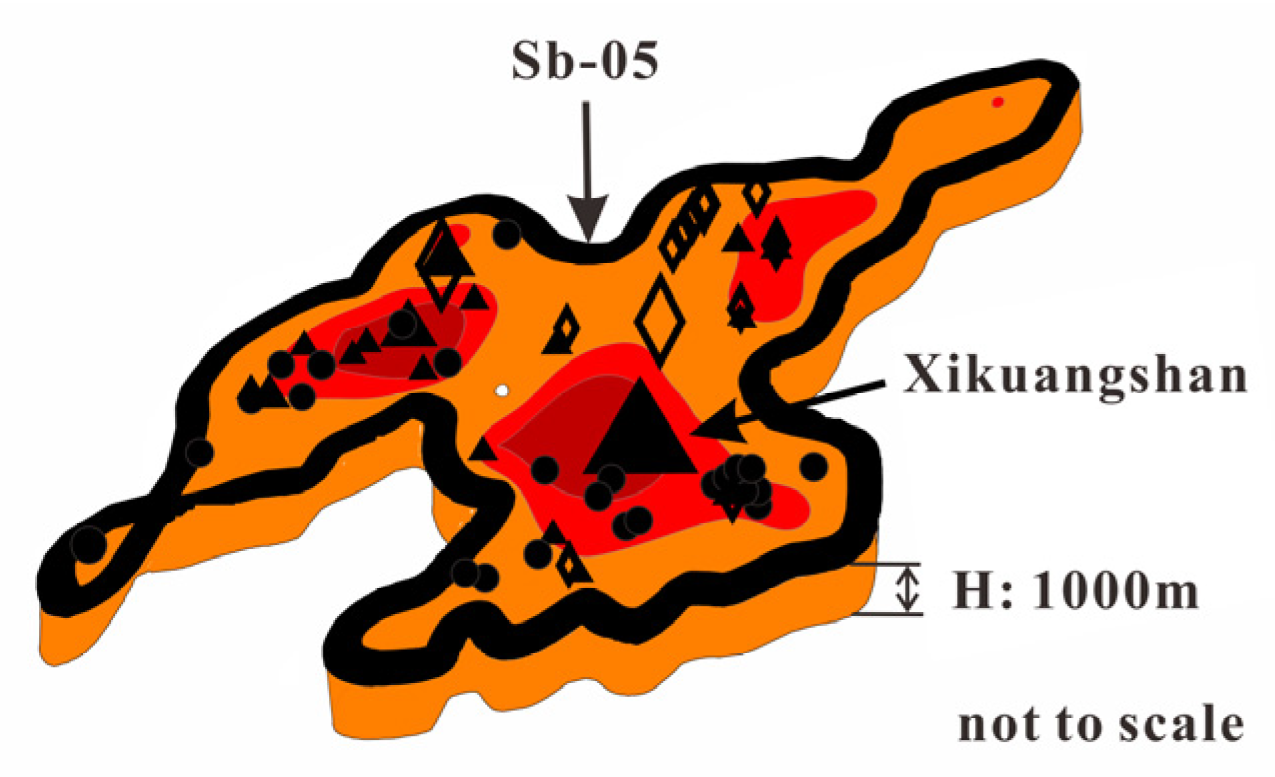
- Central Hunan Sb block (Sb-05)
- (6)
- Southern Hunan Sb block (Sb-06)
- (7)
- Nanling Sb geochemical block (Sb-07)
- (8)
- Southern Hubei Sb geochemical block (Sb-08)
- (9)
- Sb geochemical block in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River (Sb-09)
5. Discussion
5.1. The Predicted Potential Resources of Sb at Different Threshold Values
5.2. Limitations and Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Huang, F. Summary of Metallogenic Regularities of Antimony Deposits in China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2014, 88, 2208–2215, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Natural Resources. National Mineral Resources Planning (2016–2020); Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese)
- European Commission. Report on Critical Raw Materials in the Circular Economy; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Critical Mineral Resources of the United States Economic and Environmental Geology and Prospects for Future Supply; U. S. Geological Survey Professional: New York, NY, USA, 2017.
- Zaw, K.; Peters, S.; Cromie, P.; Burrett, C.; Hou, Z. Nature, diversity of deposit types and metallogenic relations of South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2007, 31, 3–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2022; Mineral Commodity Summaries: Reston, VA, USA, 2022; p. 202.
- Wu, Q.; Lv, Z.; Cao, J. Distribution and Supply of Antimony Resources in China and Abroad and Development Status of Antimony Industry Chain. Multipurp. Util. Miner. Resour. 2022, 43, 76–81, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Peng, S. Current situation of antimony ore resources and analysis of supply and demand situation of antimony ore in China. West. Resour. 2018, 15, 201–203, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Xiang, W.; Jiang, J.; Melka, H.; Degu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y. Application of geochemical block method in the evaluation of gold resources in Ethiopia. China Min. Mag. 2022, 31, 203–211, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Yang, G.; Xiao, G.; Gong, P.; Xiong, R.; Zhao, B. Application of Geochemical Blocks Method to Strata-Bound Copper Resources Assessment in the Central Yunnan Province. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2012, 31, 33–39, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, Y. Geochemical prognosis method of mineral deposits: A case study of the geochemical block in Gansu. Geol. China 2003, 30, 192–198, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, Q. Prediction of Resource Potential and Discussion about Prospecting-Directions of gold Mineral Resources by Geochemical Blocks Theory in Xinjiang. Xinjiang Geol. 2003, 21, 298–302, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, Z.; Liu, F.; Yan, T.; Wang, Q.; Wu, H. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of lithium geochemistry and prospecting prediction in the key resource prospecting new area of Yunnan, Guizhou, and Guangxi in Southwest China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2023, 97, 1828–1847, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Gong, J.; Zhang, J. Lead-zinc source beds and geochemical blocks in Hebei Province. Miner. Depos. 2010, 29, 276–282, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Liu, X.; He, S.; Gong, P.; Xu, K.; Ren, J.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, L. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediment in Tanzania and prospective analysis of gold resources. Geol. Bull. China 2022, 42, 1–22, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, W.; Chi, Q.; Zhou, J.; Yan, T. China’s Uranium Geochemical Blocks: Lmplications for Delineation of Uranium Prospective Areas. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2020, 41, 785–796, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, S.; Nie, L.; Liu, D.; Han, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Chi, Q. The Geochemical lndicator and Prognosis of Large Gold Ore Districts in nner Mongolia. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2020, 41, 818–826, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X. Searching for mega deposits with new concepts and technologies. Sci. Chin. 1995, 5, 15–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X. Surficial geochemical expressions of giant ore deposits. In Giant ore Deposits II; Clark, A.H., Ed.; Queen’s University Press: Kingston, ON, Canada, 1995; pp. 475–485. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Liu, D.; Xiang, Y.; Yan, G. Geochemical Blocks-Development of concept and methodology. Geol. China 2002, 29, 225–233, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Xie, X. Evaluation of China’s tin resources potential based on the geochemical block concept. Geol. China 2005, 32, 25–32, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Xie, X.; Yan, G.; Lian, C.; Wang, Q. The Application of Geochemical Blocks Methods to Gold Resources Assessment in Shandong Province. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2002, 23, 169–174, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Lv, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Xing, G.; Yan, J.; Yuan, L.; Chen, C. Multi-element geochemical data mining: Implications for block boundaries and deposit distributions in South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 133, 104063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, X. Investigating the spatial distribution of antimony geochemical anomalies located in the Yunnan-Guizhou-Guangxi region, China. Geochemistry 2021, 81, 125829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Yang, Y.; Deng, F. Resource potential and metallogenic prognosis of antimony deposits in China. Geol. China 2013, 40, 846–858, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Xie, X.; Yao, W.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, J. Multi-element geochemical mapping in Southern China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 139, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T. Metallogenic characteristics and resource potential of antimony in China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 230, 106834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Huang, F. Quantitative research on spatial distribution of antimony deposits in China based on geological big data. Geol. China 2021, 48, 52–67, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Chen, W.; Xu, D.; Zhou, M. Reviews and new metallogenic models of mineral deposits in South China: An introduction. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 137, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, H.; Yonezu, K.; Imai, A.; Tindell, T. In-situ trace elements and sulfur isotopic analyses of stibnite: Constraints on the genesis of Sb/Sb-polymetallic deposits in southern China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2023, 247, 107177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, G.; Santosh, M. Cenozoic tectono-magmatic and metallogenic processes in the Sanjiang region, southwestern China. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 138, 268–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, G.; Mao, Y.; Mao, Q.; Xia, T. Tectonic Evolution and Metallogeny in The West South Area of Nujiang-Lancang-Jinsha Rivers, China. Mineral. Petrol. 2017, 37, 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, H.; Xiong, X.; Gao, L.; Xu, Z.; Sheng, Y.; Xu, J.; Yuan, Z.; Bai, G. Division for Prospecting Types of Important Mineral Resources in China; Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Song, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Yan, B. Study on the evolution of ore-formation fluids for Au-Sb ore deposits and the mechanism of Au-Sb paragenesis and differentiation in the southwestern part of Guizhou Province, China. Chin. J. Geochem. 2013, 32, 056–068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Pan, J.; Xie, Q.; He, J. Ore Source of Sb(Au) Deposits in Central Hunan: I. Evidences of Trace Elements and Experimental Geochemistry. Miner. Depos. 2002, 3, 366–376, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.; Pan, J.; Xie, Q. Ore Sources of Sb(Au) Deposits in Central Hunan: II. Evidence of lsotopic Geochemistry. Miner. Depos. 2003, 22, 78–87, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, Q.; Evans, N.J.; Zhou, Z.; Kong, H.; Xi, X.; Lin, Z. Geochemistry and geochronology of the Banxi Sb deposit: Implications for fluid origin and the evolution of Sb mineralization in central-western Hunan, South China. Gondwana Res. 2018, 55, 112–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, R.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, J.; Oyebamiji, A. Genesis of gold and antimony deposits in the Youjiang metallogenic province, SW China: Evidence from in situ oxygen isotopic and trace element compositions of quartz. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 116, 103257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, D.; Mathur, R.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Godfrey, L.; Wang, K.; Xu, J.; Vervoort, J. Antimony isotope fractionation in hydrothermal systems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2021, 306, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Z.; Yang, R.; Du, L.; Liao, M. Gold and antimony metallogenic relations and ore-forming process of Qinglong Sb(Au) deposit in Youjiang basin, SW China: Sulfide trace elements and sulfur isotopes. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 605–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Wang, T.; Yan, J.; Pan, L.; Wei, L.; Lan, Q.; Fu, S. Formation of the Banxi Sb deposit in Eastern Yangtze Block: Evidence from individual fluid inclusion analyses, trace element chemistry, and He-Ar-S isotopes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 146, 104949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Zhang, J.; Hu, R.; Luo, K.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, R. Mercury isotope constraints on the genesis of late Mesozoic Sb deposits in South China. Sci. China Earth Sci. Sci. Sin. (Terrae) 2022, 52, 327–339, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ni, X.; Du, L.; Gao, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, L.; Ji, Y.; Yang, R. Gold, antimony and mercury ore formation and metallogenic link in the Sandu-Danzhai area, Jiangnan Orogen, SW China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 156, 105–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yan, S. A Preliminary Discussion on Some Problems of Antimony Deposits. Miner. Depos. 2000, 19, 166–172, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. 4.1—Composition of the Continental Crust. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Yang, R.; Du, L.; Gao, J.; Zheng, L.; Huang, Z. Multistage fluid sources and evolution of Qinglong Sb-(Au) deposit in northern margin of Youjiang basin, SW China: REE geochemistry and Sr-H-O isotopes of ore-related jasperoid, quartz and fluorite. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 127, 103851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Hu, R.; Su, W.; Wen, H.; Liu, S.; Fu, Y. A Study on the Large-Scale Low-Temperature Metallogenic Domain in Southwestern China—Significance, History and New Progress. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2011, 31, 309–314, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D. Geochemical indications of mineralization in low and medium temperature fluids and their significance for mineral searching. In Proceedings of the Abstracts of the 4th World Chinese Conference of Geological Science, Nanjing, China, 22–23 May 2002; pp. 338–339. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Fu, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Fu, S.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Bi, X.; Xiao, J. The giant South China Mesozoic low-temperature metallogenic domain: Reviews and a new geodynamic model. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 137, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Peng, J. Infrared microthermometric and noble gas isotope study of fluid inclusions in ore minerals at the Woxi orogenic Au–Sb–W deposit, western Hunan, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 65, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Peng, J. Fluid inclusions and ore precipitation mechanism in the giant Xikuangshan mesothermal antimony deposit, South China: Conventional and infrared microthermometric constraints. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 95, 49–64. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Fu, S.; Liu, S.; Wei, L.; Wang, T. Giant Sb metallogenic belt in South China: A product of Late Mesozoic flat-slab subduction of paleo-Pacific plate. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 142, 104697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Ghaderi, M.; Ouyang, L. Geochronology and geochemistry of ore-hosted zircon reveal the genesis of typical Sb-(Au-W) deposits in South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 155, 105358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kong, H.; Guo, B.; Tamehe, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Xi, X. Fluid inclusion, H–O–S isotope and rare earth element constraints on the mineralization of the Dong’an Sb deposit, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 126, 103759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Hu, R.; Jiang, G. Samarium-Neodymium isotope system of fluorites from the Qinglong antimony deposit, Guizhou Province: Constraints on the mineralizing age and ore-forming materials’ sources. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2003, 19, 785–791, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Pei, R.; Zhou, S. Sm-Nd dating for antimony mineralization in the Xikuangshan deposit, Hunan, China. Shigen-Chishitsu 1996, 46, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L. Xikuangshan mica-plagioclase lamprophyre and its granite inclusions, Hunan Province. Geol. Geochem. 2000, 28, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.; Hu, R.; Yan, J.; Lan, Q.; Gao, W. The mineralization age of the Banxi Sb deposit in Xiangzhong metallogenic province in southern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 112, 103033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Danišík, M.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, W.; Wu, J. Integrated U–Pb, Lu–Hf and (U–Th)/He analysis of zircon from the Banxi Sb deposit and its implications for the low-temperature mineralization in South China. Geosci. Front. 2020, 11, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Fu, B.; Jin, X.; Zhou, X. Antimony Metallogeny in Central Part of Hunan Province; Hunan Press of Science and Technology: Changsha, China, 1993; p. 1150. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Ying, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Li, L.; Qin, Y.; et al. New Data of the Rock-Forming and Ore-Forming Chronology for China’s lmportant Mineral Resources Areas. Acta Geol. Sin. 2010, 84, 1030–1040, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X. Geochronology, Ore Geochemistry and Genesis of the Banpo Antimony Deposit, Guizhou Province, China; Kunming University of Science and Technology: Kunming, China, 2014; (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. The Metallogenesis, Time and Geodynamic Research of Low Temperature Metallogenic Province in Southwest China. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guiyang, China, 2012; pp. 1–116. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, K.; Zhou, J.; Feng, Y.; Uysal, I.T.; Nguyen, A.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J. In situ U-Pb Dating of Calcite from the South China Antimony Metallogenic Belt. iScience 2020, 23, 101575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X. Geological characteristics of Maxiong Sb deposit, Southwest China. Miner. Geol. 1993, 2, 8–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S. Study on the Geological Characteristics and Genesis of the Main Deposits in the Wuxu ore field, Guangxi; Guangxi University: Nanning, China, 2020; (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R. Epoch of large-scale low temperature mineralizations in southwestern Yangtze massif. Miner. Depos. 2007, 26, 583–596, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; Jiang, C.; Niu, B.; Li, J.; Xie, G.; He, Z.; Liu, Z. The Tectonics of China from a Global View—A Guide to the Tectonic Map of China and Adjacent Regions; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1999; p. 32. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, T.; Huang, H. Preparation of Geochemical Reference Materials of Stream Sediments. Rock Miner. Anal. 2011, 30, 714–722, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H.; Gong, C.; Bao, Q.; Sun, Z.; You, H.; Jin, X.; Gao, F. A Comparison of Several Threshold Determination Methods in Geochemical Data Processing: A case study of Stream Sediments in Chabaqi Area of Inner Mongolia. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 34, 782–786, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y. Comparative Study on the Geochemical Exploration Data Processing Method: A Case of Wurinitu W-Mo Deposit; China University of Geosciences: Beijing, China, 2015; (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X. The Information Extraction, Interpretation and Evaluation of Geochemical Anomalies in Maqu Area of Gansu Province; Jilin University: Changchun, China, 2018; (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Tan, J.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Gan, J. A comparative study of several regional geochemical data processing methods and extraction effects of anomalies: A case study of stream system sediments in Xiaoheba area of Qinghai Province. Miner. Explor. 2019, 10, 321–331, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Liu, D.; Xiang, Y.; Yan, G.; Lian, C. Geochemical blocks for predicting large ore deposits—Concept and methodology. J. Geochem. Explor. 2004, 84, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Lei, J.; Xu, H.; Zen, K. Spatial distribution characteristics of ore bodies and prospecting prediction in the deep and edge area of Daocaowan antimony mining area, Central Hunan. Miner. Resour. Geol. 2024, 2, 219–230, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zou, L.; Tang, D.; Shi, J.; Zhou, X.; Lei, J.; Wei, J.; Xiao, L. First discovery of No. IV Antimony Ore Body North. Mine Xikuangshan, Hunan Province. J. Geol. 2024, 48, 9–17, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X. Improvement practice of deep mining equipment and technology in South Mine of Xikuangshan. Sci. Technol. Vis. 2015, 14, 262+294, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Department of Natural Resources of Hunan Province. Hunan Antimony Mining Overview; Department of Natural Resources of Hunan Province: Changsha, China, 2022. (In Chinese)
- Chi, Q.; Yan, M. Handbook of Elemental Abundance for Applied Geochemistry; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2007; (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- De Vos, W.; Tarvainen, T.; Salminen, R.; Reeder, S.; De Vivo, B.; Lima, A. Geochemical atlas of Europe. In Part 2. Interpretation of Geochemical Maps, Additional Tables, Figures, Maps, and Related Publications; Geological Survey of Finland: Espoo, Finland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, J.; Gu, X. Time and Spatial Distribution Regularities and Deposit Types of Antimony in China. Miner. Resour. Geol. 1998, 5, 19–25, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Liu, J.; Gu, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, F.; Wang, D.; Xu, L.; Li, J. The Relationship of Tectonic Evolution and Au-Sb Mineralization in Nanpanjiang–Youjiang Basin. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2020, 41, 280–292, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, D.; Wan, G.; Hou, B. Characteristics of structurally superimposed geochemical haloes at the polymetallic Xiasai silver-lead-zinc ore deposit in Sichuan Province, SW China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 169, 100–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Chen, M.; Fu, B.; Xue, Z. Comparative Study of Gacun and Youre Silver–Lead–Zinc–Copper Deposits in Sichuan, SW China, and their Mineralization Significance. Acta Geol. Sin.-Eng. Ed. 2018, 92, 162–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K. On the Genesis of Bijiashan Sb Deposit in Weishan, Yunnan. Yunnan Geol. 2007, 26, 197–206, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Yang, R.; Du, L.; Zheng, L.; Gao, J.; Laai, C.; Wei, H.; Yuan, M. Mineralogy, geochemistry and fluid inclusions of the Qinglong Sb-(Au) deposit, Youjiang basin (Guizhou, SW China). Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 92, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T. Analysis on Characteristics of Provenance of Antimony in Western Guizhou, China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 300, 022062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Chen, Q. Geological characteristics and metallogenic conditions of gold—Antimony polymetallic deposit in qiubei, Yunnan province. World Nonferrous Met. 2019, 1, 89–91, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, W.; Liang, H.; Wu, J.; Chen, X. Genesis of the Jianzhupo Sb–Pb–Zn–Ag deposit and formation of an ore shoot in the Wuxu ore field, Guangxi, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 102, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Fu, S.; Sullivan, N.; Lan, J.; Wei, L. Deciphering the ore-forming process of Sb-W deposits through scheelite and stibnite trace element geochemistry. J. Geochem. Explor. 2024, 257, 107367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Lai, J.; Song, X.; He, H.; Zhang, L.; Shi, J.; Zhou, X.; Liao, J.; Cao, Y.; et al. Genetic significance of trace elements in hydrothermal quartz from the Xiangzhong metallogenic province, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 152, 105229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Gao, Z.; Jin, J.; Zeng, L. The Xikuangshan Sb deposit hosted by the Upper Devonian black shale series, Hunan, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2004, 24, 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhu, D.; Shen, L.; Algeo, T.; Elatikpo, S. A general ore formation model for metasediment-hosted Sb-(Au-W) mineralization of the Woxi and Banxi deposits in South China. Chem. Geol. 2022, 607, 121020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xie, G.; Olin, P. Texture, in-situ geochemical, and S isotopic analyses of pyrite and arsenopyrite from the Longshan Sb-Au deposit, southern China: Implications for the genesis of intrusion-related Sb-Au deposit. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 143, 104781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xiao, K.; Luo, X.; An, J.; Wen, C. Metallogenic prospective area division and quantified research on antimony potential in Hu’nan Province. Geol. Bull. China 2015, 34, 1386–1390, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. An analysis of the origin of antimony ore mineralization in E’nan region. Resour. Environ. Eng. 2013, 27, 59–64, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]

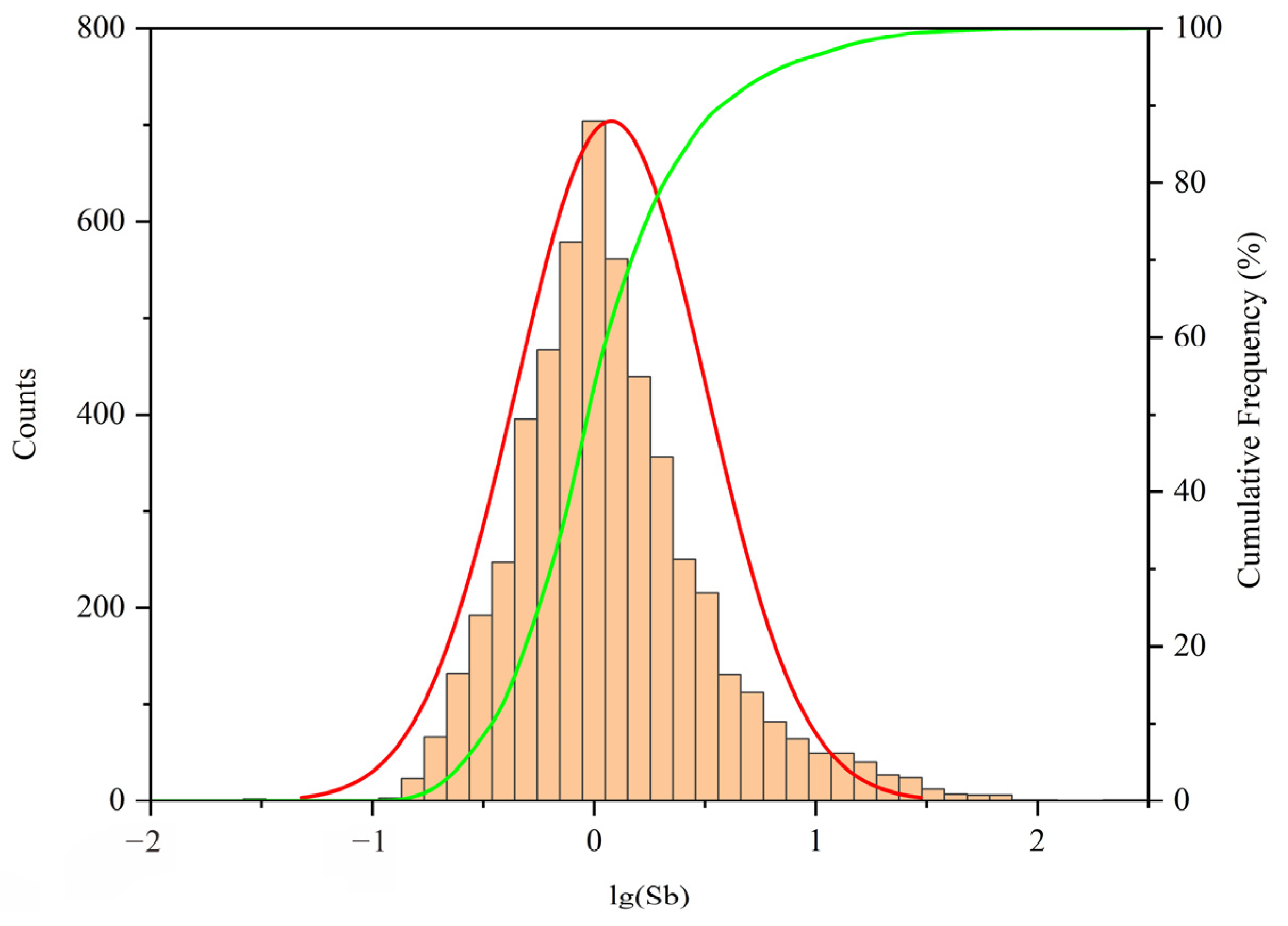


| Number | Min | 25% | 50% | 75% | 85% | 97.5% | Max | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5244 | 0.03 | 0.62 | 1.05 | 1.93 | 2.98 | 14.4 | 290 | 2.41 | 7.22 |
| Antimony Reserves (ton) | Number of Sb Deposits | The Number of Sb Deposits Located in Geochemical Block | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Occurrence | 217 | 144 | 66% |
| Small (<10,000) | 144 | 94 | 65% |
| Medium (10,000~100,000) | 55 | 41 | 75% |
| Large (100,000~1,000,000) | 28 | 23 | 82% |
| Giant (≥1,000,000) | 2 | 2 | 100% |
| In total | 446 | 304 | 68% |
| Number | Location | Area /km2 | Average Sb Content (ppm) | Standard Deviation (ppm) | Anomaly Intensity | Predicted Resources /104 tons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sb-01 | Western Sichuan | 23,813 | 5.68 | 3.20 | 5.41 | 116.5 |
| Sb-02 | Southwestern Yunnan | 24,294 | 4.61 | 1.83 | 4.39 | 96.44 |
| Sb-03 | Yunnan–Guizhou–Guangxi (Dian–Qian–Gui) | 171,247 | 9.71 | 6.96 | 9.25 | 1432 |
| Sb-04 | Southeastern Guizhou | 4982 | 5.51 | 4.48 | 5.24 | 23.63 |
| Sb-05 | Central Hunan | 23,523 | 9.81 | 15.42 | 9.34 | 198.7 |
| Sb-06 | Southern Hunan | 7079 | 8.44 | 9.51 | 8.04 | 51.48 |
| Sb-07 | Hunan–Guangdong (Nanling) | 48,747 | 6.19 | 4.75 | 5.89 | 259.7 |
| Sb-08 | Southern Hubei | 1196 | 2.84 | 6.52 | 8.80 | 9.51 |
| Sb-09 | Northwestern Zhejiang | 1563 | 4.34 | 5.50 | 4.14 | 5.85 |
| Province | Anomalous Area /km2 | Average Sb Content (ppm) | Predicted Resources /104 tons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Huanan | 52,024 | 8.44 | 375.89 |
| Yunnan | 112,508 | 5.41 | 908.64 |
| Guangxi | 110,073 | 4.72 | 785.06 |
| Guizhou | 28,379 | 4.76 | 144.96 |
| Geochemical Blocks/Threshold Value at 2.98 ppm | Area/km2 | Predicted Resources/104 tons | Geochemical Blocks/Threshold Value at 4.19 ppm | Area/km2 | Predicted Resources/104 tons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sb-01 | 23,813 | 116.5 | Sb-01 | 10,098 | 75.15 |
| Sb-02 | 24,294 | 96.44 | Sb-02 | 4029 | 26.44 |
| Sb-03 | 1715 | 8.35 | |||
| Sb-04 | 5162 | 26.88 | |||
| Sb-03 | 171,247 | 1432 | Sb-05 | 136,329 | 1480.63 |
| Sb-06 | 1734 | 12.79 | |||
| Sb-07 | 3002 | 17.88 | |||
| Sb-08 | 3864 | 18.44 | |||
| Sb-04 | 4982 | 23.63 | Sb-09 | 2558 | 17.78 |
| Sb-05 | 23,523 | 198.7 | Sb-10 | 15,967 | 192.77 |
| Sb-06 | 7079 | 51.48 | Sb-11 | 3367 | 44.73 |
| Sb-07 | 48,747 | 259.7 | Sb-12 | 29,815 | 223.87 |
| Sb-08 | 1196 | 9.51 | |||
| Sb-09 | 1563 | 5.85 | |||
| Total | 306,444 | 2193.81 | Total | 217,640 | 2145.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Y.; Han, Z.; Zhang, B.; Dong, Z.; Wei, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H. Estimation of the Potential Antimony Resource in Southern China with the Geochemical Block Method. Minerals 2024, 14, 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14080830
Du Y, Han Z, Zhang B, Dong Z, Wei X, Zhao H, Wang X, Zhang M, Liu H. Estimation of the Potential Antimony Resource in Southern China with the Geochemical Block Method. Minerals. 2024; 14(8):830. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14080830
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Yude, Zhixuan Han, Bimin Zhang, Zhengnan Dong, Xiaocheng Wei, Haonan Zhao, Xiaolong Wang, Man Zhang, and Hanliang Liu. 2024. "Estimation of the Potential Antimony Resource in Southern China with the Geochemical Block Method" Minerals 14, no. 8: 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14080830
APA StyleDu, Y., Han, Z., Zhang, B., Dong, Z., Wei, X., Zhao, H., Wang, X., Zhang, M., & Liu, H. (2024). Estimation of the Potential Antimony Resource in Southern China with the Geochemical Block Method. Minerals, 14(8), 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14080830







