Ischemic Heart Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis—Two Conditions, the Same Background
Abstract
:1. Introduction
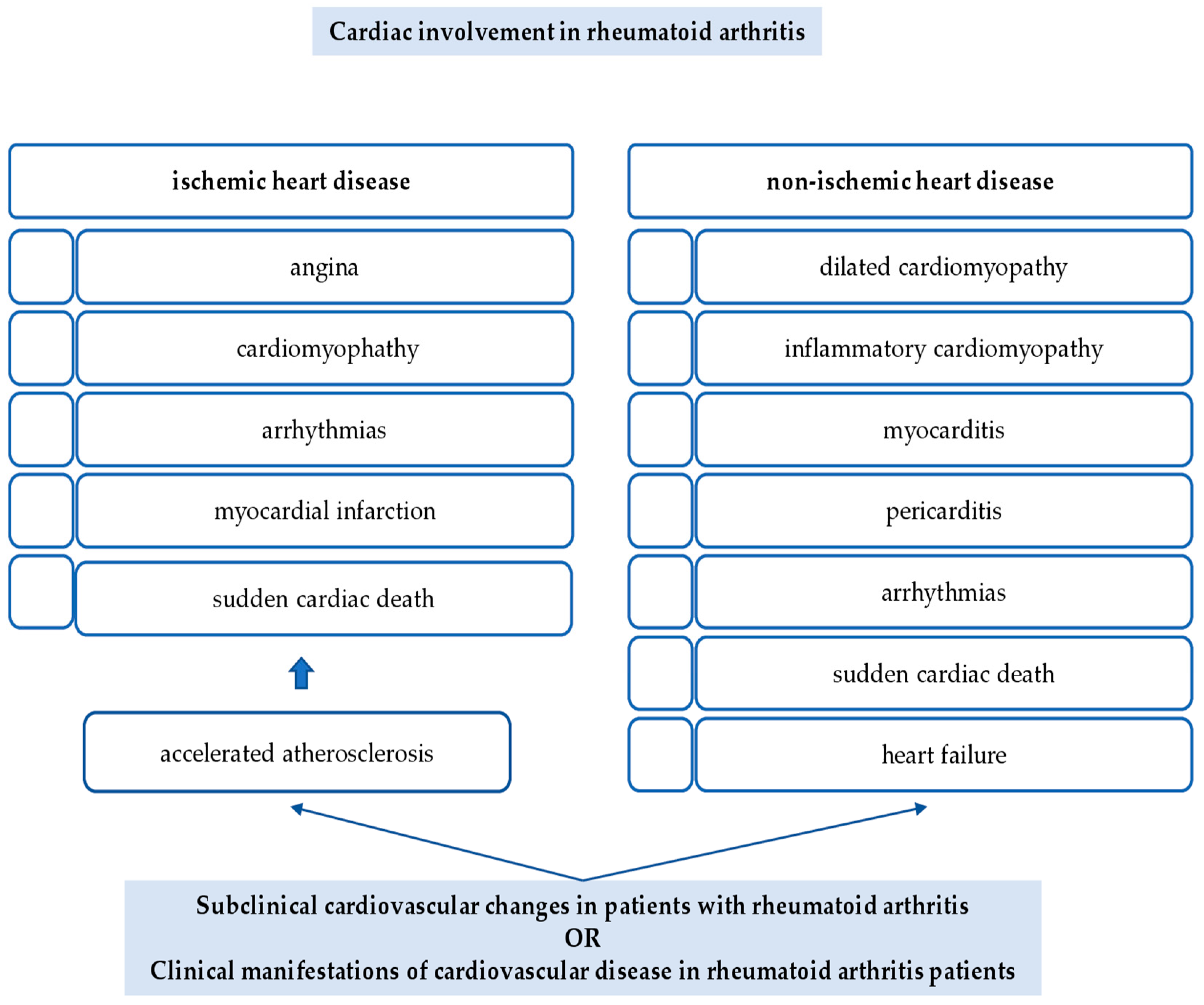
2. Cardiac Involvement in Rheumatoid Arthritis
2.1. Ischemic Heart Disease
2.2. Non-Ischemic Heart Disease
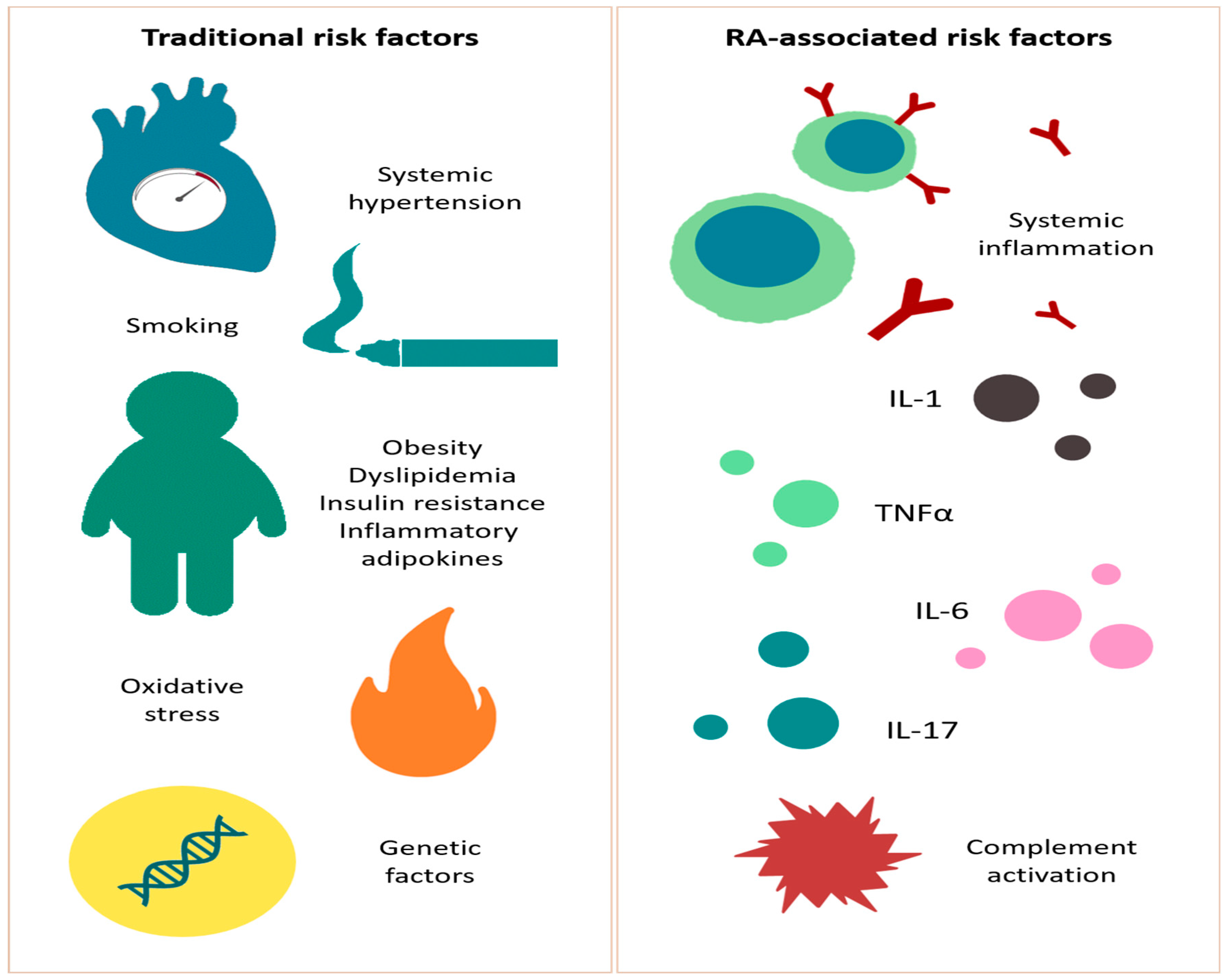
3. Cardiovascular Risk Factors in the Rheumatoid Arthritis Population
3.1. Traditional Risk Factors
3.1.1. Smoking
3.1.2. Hypertension
3.1.3. Dyslipidemia
3.1.4. Obesity
3.1.5. Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome
3.1.6. Reactive Oxygen Species
3.1.7. Genetic Risk Factor
3.2. RA-Associated Risk Factors
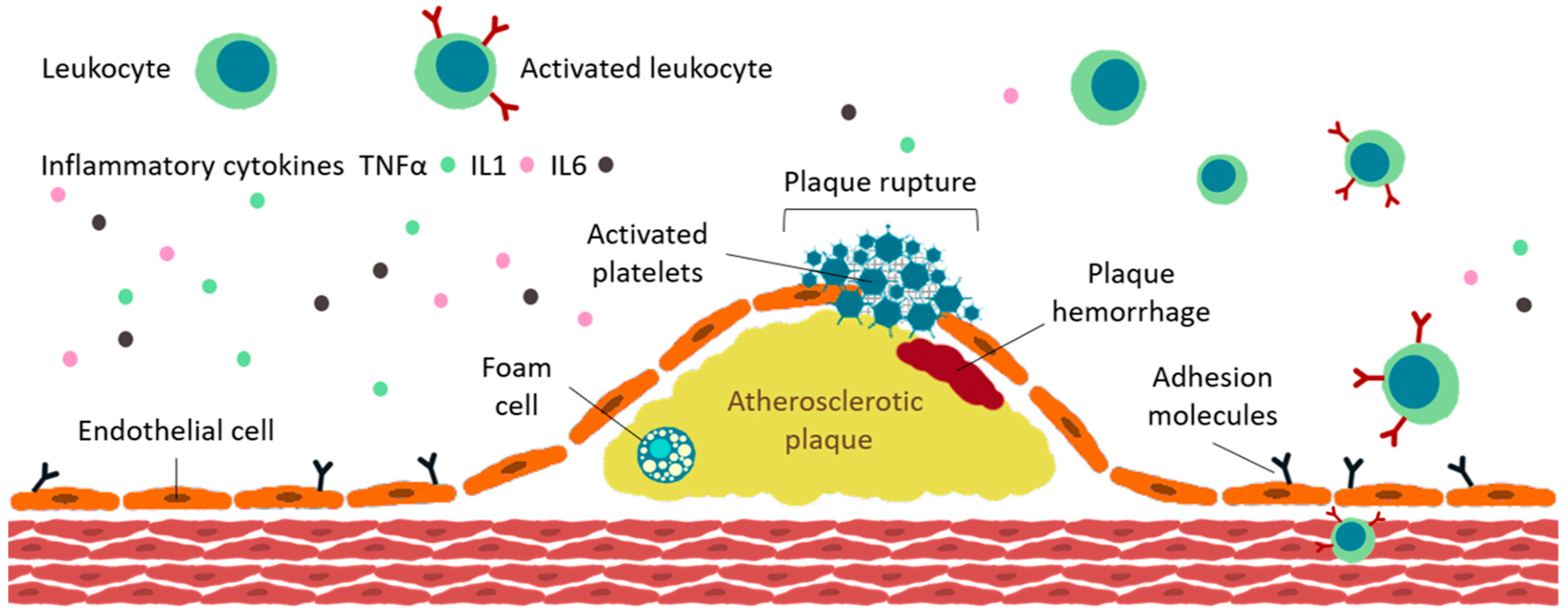
4. Inflammation and Atherosclerotic Burden in Rheumatoid Arthritis
4.1. Accelerated ATS in RA
4.2. Endothelial Dysfunction
4.3. Plaque Development
4.4. Plaque Destabilization
4.5. Lipid Metabolism
4.6. Micro- and Macrovascular Involvement in RA
4.6.1. Macrovascular Involvement in RA
4.6.2. Microvascular Involvement in RA
5. Impact of Medication on Development of Ischemic Heart Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis
5.1. NSAIDs and CS
5.2. csDMARDs
5.3. bDMARDs
5.3.1. Anti-TNFα
5.3.2. Anti-IL-6
5.3.3. Anti-CD-20
5.3.4. Anti-IL-1
5.3.5. Anti-CD80/86
5.4. tsDMARDs—JAK Inhibitors
6. Assessing Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis
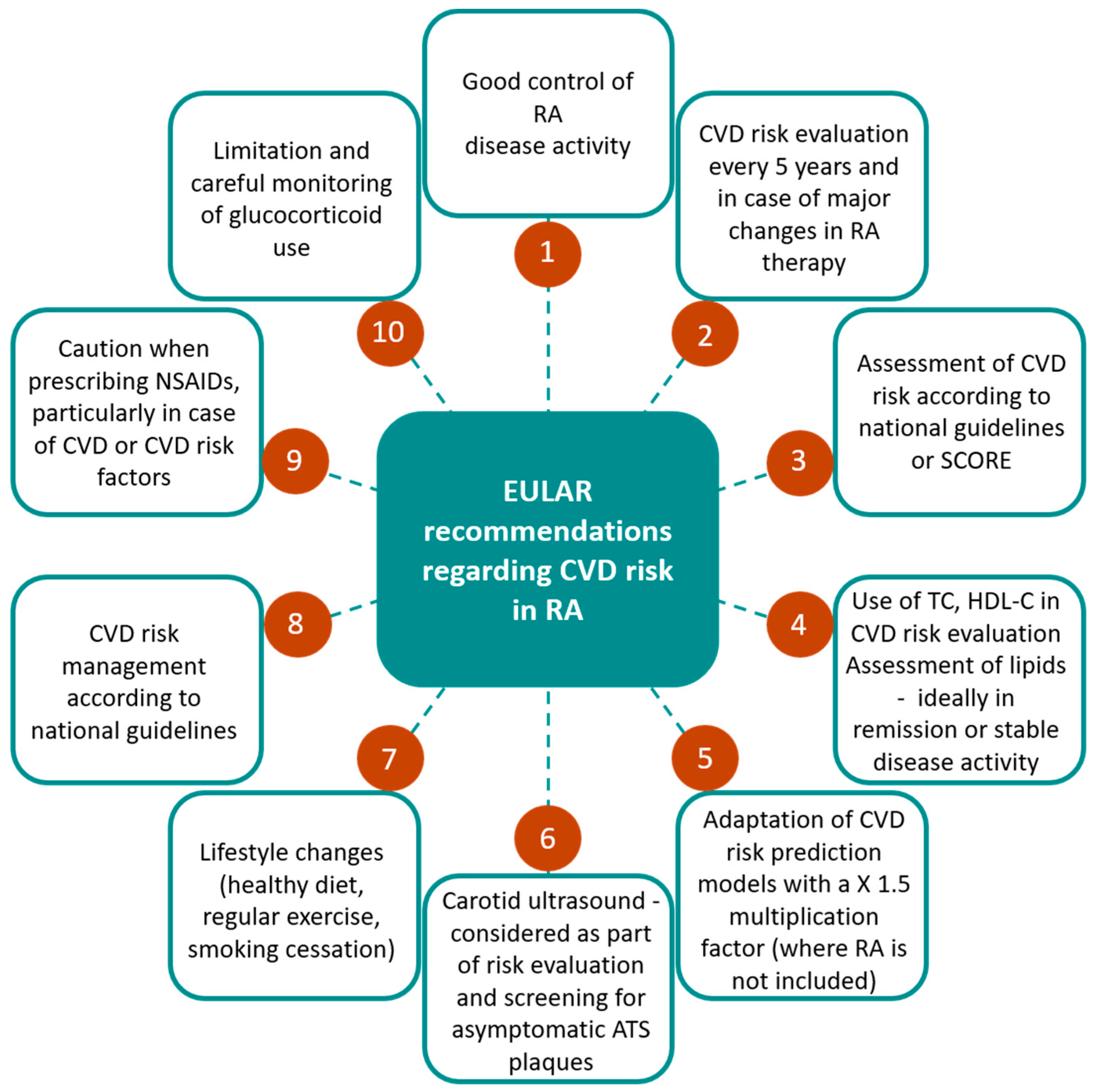
6.1. CVD Risk Scores
6.2. Imaging Modalities
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Safiri, S.; Kolahi, A.; Hoy, D.; Smith, E.; Bettampadi, D.; Mansournia, M.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; ashrafi-asgarabad, A.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; Qorbani, M.; et al. Global, Regional and National Burden of RheumaToid Arthritis 1990–2017: A Systematic analysis of The Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2019, 78, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.; Karlson, E.; Rimm, E.; Cannuscio, C.; Mandl, L.; Manson, J.; Stampfer, M.; Curhan, G. Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality in Women Diagnosed with RheumaToid Arthritis. Circulation 2003, 107, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solomon, D.; Avorn, J.; Katz, J.; Weinblatt, M.; SeToguchi, S.; Levin, R.; Schneeweiss, S. Immunosuppressive Medications and Hospitalization for Cardiovascular Events in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. Off. J. Am. Coll. Rheumatol. 2006, 54, 3790–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahtta, D.; Gupta, A.; Ramsey, D.; Rifai, M.; Mehta, A.; Krittanawong, C.; Lee, M.; Nasir, K.; Samad, Z.; Blumenthal, R.; et al. AuToimmune Rheumatic Diseases and Premature Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: An analysis from The VITAL Registry. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, 1424–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Błyszczuk, P.; Szekanecz, Z. Pathogenesis of Ischaemic and Non-Ischaemic Heart Diseases in RheumaToid Arthritis. RMD Open 2020, 6, e001032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visseren, F.; Mach, F.; Smulders, Y.; Carballo, D.; Koskinas, K.; Bäck, M.; BeneTos, A.; Biffi, A.; Boavida, J.; Capodanno, D.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3227–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMizio, D.; Geraldino-Pardilla, L. AuToimmunity and inflammation Link to Cardiovascular Disease Risk in RheumaToid Arthritis. Rheumatol. Ther. 2019, 7, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, M.; van Halm, V.; Voskuyl, A.; Smulders, Y.; Boers, M.; Lems, W.; Visser, M.; Stehouwer, C.; Dekker, J.; Nijpels, G.; et al. Does RheumaToid Arthritis Equal Diabetes Mellitus as an independent Risk FacTor for Cardiovascular Disease? A Prospective Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2009, 61, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Halm, V.; Peters, M.; Voskuyl, A.; Boers, M.; Lems, W.; Visser, M.; Stehouwer, C.; Spijkerman, A.; Dekker, J.; Nijpels, G.; et al. RheumaToid Arthritis Versus Diabetes as A Risk FacTor for Cardiovascular Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study, The CARRÉ investigation. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 68, 1395–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kryvenko, O. Positive surgical margins increase risk of recurrence after partial nephrecTomy for high risk renal tumors. Shah, PH, Moreira DM, Okhunov Z, Patel VR, Chopra S, Razmaria AA, Alom M, George AK, Yaskiv O, Schwartz MJ, Desai M, Vira MA, Richstone L, Landman J, Shalhav AL, Gill, I., Kavoussi LR. J. Urol. 2016 Aug;196(2):327-34. Urol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 449–450. [Google Scholar]
- Avina-Zubieta, J.; Thomas, J.; Sadatsafavi, M.; Lehman, A.; Lacaille, D. Risk of incident Cardiovascular Events in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis: A Meta-analysis of Observational Studies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1524–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowson, C.; Rollefstad, S.; Ikdahl, E.; Kitas, G.; van Riel, P.; Gabriel, S.; Matteson, E.; Kvien, T.; Douglas, K.; Sandoo, A.; et al. Impact of Risk FacTors associated with Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2017, 77, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Hoek, J.; Boshuizen, H.; Roorda, L.; Tijhuis, G.; Nurmohamed, M.; van den Bos, G.; Dekker, J. Mortality in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis: A 15-Year Prospective Cohort Study. Rheumatol. Int. 2016, 37, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bacon, P.; Stevens, R.; Carruthers, D.; Young, S.; Kitas, G. Accelerated Atherogenesis in AuToimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2002, 1, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agca, R.; Heslinga, S.; Rollefstad, S.; Heslinga, M.; Mcinnes, I.; Peters, M.; Kvien, T.; Dougados, M.; Radner, H.; Atzeni, F.; et al. EULAR Recommendations for Cardiovascular Disease Risk Management in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis and Other forms of inflammaTory Joint Disorders: 2015/2016 Update. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2016, 76, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mason, J.; Libby, P. Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Chronic inflammation: Mechanisms Underlying Premature Cardiovascular Events in Rheumatologic Conditions. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 36, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- von Hundelshausen, P.; Weber, C. Chronische Entzündung Und Atherosklerose. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2013, 138, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theander, L.; Nyhäll-Wåhlin, B.; Nilsson, J.; Willim, M.; Jacobsson, L.; Petersson, I.; Turesson, C. Severe Extraarticular Manifestations in A Community-Based Cohort of Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis: Risk FacTors and incidence in Relation to Treatment with Tumor Necrosis FacTor inhibiTors. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Giles, J.; Hirano, M.; Yokoe, I.; Nakajima, Y.; Bathon, J.; Lima, J.; Kobayashi, H. Assessment of Myocardial Abnormalities in RheumaToid Arthritis Using A Comprehensive Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Approach: A Pilot Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masoud, S.; Lim, P.; Kitas, G.; Panoulas, V. Sudden Cardiac Death in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis. World J. Cardiol. 2017, 9, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, H.; Kitas, G. InflammaTory Arthritis as A Novel Risk FacTor for Cardiovascular Disease. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 23, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrengül, H.; Dursunoglu, D.; Cobankara, V.; Polat, B.; Seleci, D.; Kabukçu, S.; Kaftan, A.; Semiz, E.; Kilic, M. Heart Rate Variability in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2003, 24, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzerini, P.; Capecchi, P.; Acampa, M.; Galeazzi, M.; Laghi-Pasini, F. Arrhythmic Risk in RheumaToid Arthritis: The Driving Role of Systemic inflammation. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowson, C.; Nicola, P.; Kremers, H.; O’Fallon, W.; Therneau, T.; Jacobsen, S.; Roger, V.; Ballman, K.; Gabriel, S. How Much of the increased incidence of Heart Failure in RheumaToid Arthritis Is Attributable to Traditional Cardiovascular Risk FacTors and Ischemic Heart Disease? Arthritis Rheum. Off. J. Am. Coll. Rheumatol. 2005, 52, 3039–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trelle, S.; Reichenbach, S.; Wandel, S.; Hildebrand, P.; Tschannen, B.; Villiger, P.; Egger, M.; Juni, P. Cardiovascular Safety of Non-Steroidal anti-inflammaTory Drugs: Network Meta-analysis. Brit. Med. J. 2011, 342, c7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, J.; Roger, V.; Crowson, C.; Kremers, H.; Therneau, T.; Gabriel, S. The Presentation and Outcome of Heart Failure in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis Differs from That in The General Population. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 2603–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Del Buono, M.; Abbate, A.; Toldo, S. interplay of inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Cardiovascular Disease in RheumaToid Arthritis. Heart 2018, 104, 1991–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maradit-Kremers, H.; Crowson, C.; Nicola, P.; Ballman, K.; Roger, V.; Jacobsen, S.; Gabriel, S. Increased Unrecognized Coronary Heart Disease and Sudden Deaths in RheumaToid Arthritis: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Arthritis Rheum. Off. J. Am. Coll. Rheumatol. 2005, 52, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigues, I.; Tugcu, A.; Russo, C.; Giles, J.; Morgenstein, R.; ZarToshti, A.; Schulze, C.; Flores, R.; Bokhari, S.; Bathon, J. Myocardial inflammation, Measured Using 18-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography with Computed Tomography, Is Associated with Disease Activity in RheumaToid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amigues, I.; Russo, C.; Giles, J.; Tugcu, A.; Weinberg, R.; Bokhari, S.; Bathon, J. Myocardial Microvascular Dysfunction in RheumaToid Arthritis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, e007495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mavrogeni, S.; Dimitroulas, T.; Sfikakis, P.; Kitas, G. Heart involvement in RheumaToid Arthritis: Multimodality Imaging and The Emerging Role of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 43, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrao, S.; Messina, S.; Pistone, G.; Calvo, L.; Scaglione, R.; Licata, G. Heart involvement in RheumaToid Arthritis: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 2031–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanvivadhanakul, P.; Buakhamsri, A. Disease Activity Is Associated With LV Dysfunction In Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Without Clinical Cardiovascular Disease. Adv. Rheumatol. 2019, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mantel, Ä.; Holmqvist, M.; Andersson, D.; Lund, L.; Askling, J. Association Between RheumaToid Arthritis and Risk of Ischemic and Nonischemic Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Gong, G. Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Co-Existing Coronary Artery Disease and RheumaToid Arthritis. Medicine 2020, 99, e19658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicola, P.; Maradit-Kremers, H.; Roger, V.; Jacobsen, S.; Crowson, C.; Ballman, K.; Gabriel, S. The Risk Of Congestive Heart Failure In Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Population-Based Study Over 46 Years. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myasoedova, E.; Chandran, A.; Ilhan, B.; Major, B.; Michet, C.; Matteson, E.; Crowson, C. The Role of RheumaToid Arthritis (RA) Flare and Cumulative Burden of RA Severity in The Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2015, 75, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arts, E.; Fransen, J.; Den Broeder, A.; van Riel, P.; Popa, C. Low Disease Activity (DAS28 ≤ 3.2) Reduces the Risk of First Cardiovascular Event in RheumaToid Arthritis: A Time-Dependent Cox Regression analysis in A Large Cohort Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2017, 76, 1693–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, L.; Woodman, R.; Shanahan, E.; Mangoni, A. The Impact of Traditional Cardiovascular Risk FacTors on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, A.; Kremers, H.; Crowson, C.; Ballman, K.; Roger, V.; Jacobsen, S.; O’Fallon, W.; Gabriel, S. Do Cardiovascular Risk FacTors Confer the Same Risk for Cardiovascular Outcomes in RheumaToid Arthritis Patients as in Non-RheumaToid Arthritis Patients? Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2008, 67, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, J.; Gourraud, P.; Cantagrel, A.; Davignon, J.; Constantin, A. Traditional Cardiovascular Risk FacTors in RheumaToid Arthritis: A Meta-analysis. Jt. Bone Spine 2011, 78, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Oeser, A.; Solus, J.; Avalos, I.; Gebretsadik, T.; Shintani, A.; Raggi, P.; Sokka, T.; Pincus, T.; Stein, C. Prevalence of The Metabolic Syndrome Is increased in RheumaToid Arthritis and Is associated with Coronary Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2008, 196, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikonomidis, I.; Lekakis, J.; Vamvakou, G.; Andreotti, F.; Nihoyannopoulos, P. Cigarette Smoking Is associated with increased Circulating ProinflammaTory and Procoagulant Markers in Patients with Chronic Coronary Artery Disease. Am. Heart J. 2005, 149, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Serrano, J.; Pérez, L.; García, C.; Moctezuma, F.; Álvarez-Hernández, E.; Vázquez-Mellado, J.; Montiel, J.; Burgos-Vargas, R. Current Smoking Status Is associated to A Non-ACR 50 Response in Early RheumaToid Arthritis. A Cohort Study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 30, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baka, Z.; Buzás, E.; Nagy, G. RheumaToid Arthritis and Smoking: Putting the Pieces Together. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breitling, L.; Yang, R.; Korn, B.; Burwinkel, B.; Brenner, H. Tobacco-Smoking-Related Differential DNA Methylation: 27K Discovery and Replication. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dougados, M.; Soubrier, M.; antunez, A.; Balint, P.; Balsa, A.; Buch, M.; Casado, G.; Detert, J.; El-zorkany, B.; Emery, P.; et al. Prevalence of Comorbidities in RheumaToid Arthritis and Evaluation of Their MoniToring: Results of an international, Cross-Sectional Study (COMORA). Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2013, 73, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gullick, N.; Scott, D. Co-Morbidities In Established Rheumatoid Arthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 25, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergstrom, U.; Jacobsson, L.; Nilsson, J.; Berglund, G.; Turesson, C. Pulmonary Dysfunction, Smoking, Socioeconomic Status and The Risk of Developing RheumaToid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 2005–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rawla, P. Cardiac and Vascular Complications in RheumaToid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2019, 57, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alemao, E.; Cawston, H.; Bourhis, F.; Al, M.; Rutten-van Mölken, M.; Liao, K.; Solomon, D. Cardiovascular Risk FacTor Management in Patients with RA Compared to Matched Non-RA Patients. Rheumatology 2015, 55, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- an, J.; Cheetham, T.; Reynolds, K.; Alemao, E.; Kawabata, H.; Liao, K.; Solomon, D. Traditional Cardiovascular Disease Risk FacTor Management in RheumaToid Arthritis Compared to Matched NonrheumaToid Arthritis in A US Managed Care Setting. Arthritis Care Res. 2016, 68, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boersma, P.; McElwee, M.; Hashmi, H.; Schreiner, P.; Demmer, R.; Shmagel, A. Blood Pressure Trends in Patients with Seropositive RheumaToid Arthritis Compared with Controls without RheumaToid Arthritis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Open Rheumatol. J. 2019, 1, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toms, T.E.; Symmons, D.P.; Kitas, G.D. Dyslipidaemia in RheumaToid Arthritis: The Role of inflammation, Drugs, Lifestyle and Genetic FacTors. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2010, 8, 301–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, J.; Wasko, M.; Chung, C.; Szklo, M.; Blumenthal, R.; Kao, A.; Bokhari, S.; ZarToshti, A.; Stein, C.; Bathon, J. Exploring the Lipid Paradox Theory in RheumaToid Arthritis: Associations of Low Circulating Low-Density Lipoprotein Concentration with Subclinical Coronary Atherosclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1426–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, L.; Xiong, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Li, H.; et al. Recognition of H3K9 Methylation by GLP Is Required for Efficient Establishment of H3K9 Methylation, Rapid Target Gene Repression, and Mouse Viability. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, K.; Cai, T.; Gainer, V.; Cagan, A.; Murphy, S.; Liu, C.; Churchill, S.; Shaw, S.; Kohane, I.; Solomon, D.; et al. Lipid and Lipoprotein Levels and Trend in RheumaToid Arthritis Compared to The General Population. Arthritis Care Res. 2013, 65, 2046–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myasoedova, E.; Crowson, C.; Kremers, H.; Fitz-Gibbon, P.; Therneau, T.; Gabriel, S. Total Cholesterol and LDL Levels Decrease Before RheumaToid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2009, 69, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robertson, J.; Peters, M.; Mcinnes, I.; Sattar, N. Changes in Lipid Levels with inflammation and Therapy in RA: A Maturing Paradigm. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegkos, T.; Kitas, G.; Dimitroulas, T. Cardiovascular Risk in RheumaToid Arthritis: Assessment, Management and Next Steps. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2016, 8, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mcinnes, I.; Thompson, L.; Giles, J.; Bathon, J.; Salmon, J.; Beaulieu, A.; Codding, C.; Carlson, T.; Delles, C.; Lee, J.; et al. Effect of interleukin-6 RecepTor Blockade On Surrogates of Vascular Risk in RheumaToid Arthritis: MEASURE, A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2013, 74, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles-Schoeman, C.; Fleischmann, R.; Davignon, J.; Schwartz, H.; Turner, S.; Beysen, C.; Milad, M.; Hellerstein, M.; Luo, Z.; Kaplan, I.; et al. Potential Mechanisms Leading to The Abnormal Lipid Profile in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis Versus Healthy Volunteers and Reversal By Tofacitinib. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, F.; Michaud, K. Effect of Body Mass index On Mortality and Clinical Status in RheumaToid Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escalante, A.; Haas, R.; del Rincón, I. Paradoxical Effect of Body Mass index On Survival in RheumaToid Arthritis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 1624–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baker, J.; Billig, E.; Michaud, K.; Ibrahim, S.; Caplan, L.; Cannon, G.; STokes, A.; Majithia, V.; Mikuls, T. Weight Loss, The Obesity Paradox, and The Risk of Death in RheumaToid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1711–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerekes, G.; Nurmohamed, M.; González-Gay, M.; Seres, I.; Paragh, G.; Kardos, Z.; Baráth, Z.; Tamási, L.; Soltész, P.; Szekanecz, Z. RheumaToid Arthritis and Metabolic Syndrome. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, R.; Conde, J.; Scotece, M.; Gómez-Reino, J.; Lago, F.; Gualillo, O. What’s New in Our Understanding of The Role of Adipokines in Rheumatic Diseases? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Hong, S.; Hahm, D.; Choi, S.; Yang, H.; Yoo, M.; Kim, K. Adiponectin May Contribute to Synovitis and Joint Destruction in RheumaToid Arthritis by Stimulating Vascular Endothelial Growth FacTor, Matrix Metalloproteinase-1, and Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 Expression in Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes More Than ProinflammaTory MediaTors. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R161. [Google Scholar]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A. AdipocyTokines: MediaTors Linking Adipose Tissue, inflammation and Immunity. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2006, 6, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, M.; Lago, R.; Gomez, R.; Lago, F.; Dieguez, C.; Gomez-Reino, J.; Gualillo, O. Changes in Plasma Levels of Fat-Derived Hormones Adiponectin, Leptin, Resistin and Visfatin in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2006, 65, 1198–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamaluddin, M.; Weakley, S.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Resistin: Functional Roles and Therapeutic Considerations for Cardiovascular Disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fadaei, R.; Parvaz, E.; Emamgholipour, S.; Moradi, N.; Vatannejad, A.; Najafi, M.; Doosti, M. The Mrna Expression and Circulating Levels of Visfatin and Their Correlation with Coronary Artery Disease Severity and 25-Hydroxyvitamin D. Horm. Metab. Res. 2015, 48, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Versari, D.; Daghini, E.; Virdis, A.; Ghiadoni, L.; Taddei, S. Endothelial Dysfunction as A Target for Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, S314–S321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barton, A.; Worthington, J. Genetic Susceptibility to RheumaToid Arthritis: An Emerging Picture. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2009, 61, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roses, A. Genetic Susceptibility to Cardiovascular Diseases. Am. Heart J. 2000, 140, S45–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkamani, A.; Topol, E.; Schork, N. Pathway analysis of Seven Common Diseases assessed By Genome-Wide association. Genomics 2008, 92, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karczewski, K.; Dudley, J.; Kukurba, K.; Chen, R.; Butte, A.; Montgomery, S.; Snyder, M. Systematic Functional RegulaTory assessment of Disease-associated Variants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9607–9612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toms, T.; Panoulas, V.; Smith, J.; Douglas, K.; Metsios, G.; Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou, A.; Kitas, G. RheumaToid Arthritis Susceptibility Genes associate with Lipid Levels in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2011, 70, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maehlen, M.; Provan, S.; de Rooy, D.; van der Helm-van Mil, A.; Krabben, A.; Saxne, T.; Lindqvist, E.; Semb, A.; Uhlig, T.; van der Heijde, D.; et al. associations Between APOE Genotypes and Disease Susceptibility, Joint Damage and Lipid Levels in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palomino-Morales, R.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, C.; Vazquez-Rodriguez, T.; Rodriguez, L.; Miranda-Filloy, J.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, B.; Llorca, J.; Martin, J.; Gonzalez-Gay, M. A1298C Polymorphism in The MTHFR Gene Predisposes to Cardiovascular Risk in RheumaToid Arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallvé, J.; Girona, J.; Paredes, S.; Hurt-Camejo, E.; Masana, L. We-P12:310 TNF Alpha -1031 T>C Polymorphism Is associated with Elevated Markers of Oxidation and with Smaller LDL Size in Subjects with RheumaToid Arthritis. Atheroscler. Suppl. 2006, 7, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowes, J.; Barton, A. Recent Advances in The Genetics of RA Susceptibility. Rheumatology 2007, 47, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ajeganova, S.; andersson, M.; Frostegård, J.; Hafström, I. Disease FacTors in Early RheumaToid Arthritis Are associated with Differential Risks for Cardiovascular Events and Mortality Depending on Age at Onset: A 10-Year Observational Cohort Study. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 40, 1958–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Delzell, E.; Muntner, P.; Hillegass, W.; Safford, M.; Millan, I.; Crowson, C.; Curtis, J. The association Between inflammaTory Markers, Serum Lipids and The Risk of Cardiovascular Events in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2014, 73, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, L.; Sattar, N.; Mcinnes, I. Managing Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Rheumatic Disease. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 105, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P. Role of inflammation in Atherosclerosis associated with RheumaToid Arthritis. Am. J. Med. 2008, 121, S21–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, L.; Siebert, S.; Mcinnes, I.; Sattar, N. Cardiometabolic Comorbidities in RA and Psa: Lessons Learned and Future Directions. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, F.; Dalbeth, N. Disease Modification and Cardiovascular Risk Reduction: Two Sides of The Same Coin? Rheumatology 2005, 44, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peiró, C.; Lorenzo, Ó.; Carraro, R.; Sánchez-Ferrer, C. IL-1Β inhibition in Cardiovascular Complications associated to Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6 Biology Is Coordinated by Membrane-Bound and Soluble RecepTors: Role in inflammation and Cancer. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 80, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terrell, A.; CrisosTomo, P.; Wairiuko, G.; Wang, M.; Morrell, E.; Meldrum, D. Jak/STAT/SOCS signaling circuits and associated cytokine-mediated inflammation and hypertrophy in the heart. Shock 2006, 26, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Blüml, S. Therapeutic Implications of AuToantibodies in RheumaToid Arthritis. RMD Open 2016, 2, e000009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marder, W.; Khalatbari, S.; Myles, J.; Hench, R.; Yalavarthi, S.; Lustig, S.; Brook, R.; Kaplan, M. Interleukin 17 as A Novel PredicTor of Vascular Function in RheumaToid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2011, 70, 1550–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlaicu, S.; TaTomir, A.; Boodhoo, D.; Vesa, S.; Mircea, P.; Rus, H. The Role of Complement System in Adipose Tissue-Related inflammation. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 64, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.; Fernández-Real, J. The Complement System Is Dysfunctional in Metabolic Disease: Evidences in Plasma and Adipose Tissue from Obese and insulin Resistant Subjects. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 85, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, K.; Mollnes, T.; Eidet, J.; Mikkelsen, K.; Almdahl, S.; Bottazzi, B.; Lyberg, T.; Manzi, S.; Ahearn, J.; Hollan, I. Plasma Complement and Vascular Complement Deposition in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease with and without inflammaTory Rheumatic Diseases. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoenfeld, Y.; Sherer, Y.; Harats, D. Atherosclerosis as an infectious, inflammaTory and AuToimmune Disease. Trends Immunol. 2001, 22, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Zhu, J.; Halcox, J.; Waclawiw, M.; Epstein, S.; Quyyumi, A. Predisposition to Atherosclerosis By infections. Circulation 2002, 106, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Libby, P.; Lichtman, A.; Hansson, G. Immune EffecTor Mechanisms Implicated in Atherosclerosis: From Mice to Humans. Immunity 2013, 38, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mudau, M.; Genis, A.; Lochner, A.; Strijdom, H. Endothelial Dysfunction : The Early PredicTor of Atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2012, 23, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ToToson, P.; Maguin-Gaté, K.; Prati, C.; Wendling, D.; Demougeot, C. Mechanisms of Endothelial Dysfunction in RheumaToid Arthritis: Lessons from animal Studies. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prati, C.; Berthelot, A.; Kantelip, B.; Wendling, D.; Demougeot, C. Treatment with The Arginase inhibiTor Nw-Hydroxy-Nor-L-Arginine ResTores Endothelial Function in Rat Adjuvant-induced Arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, K.; Tabas, I. The Response-To-Retention Hypothesis of Early Atherogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1995, 15, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Armstrong, S.; Sugiyama, M.; Fung, K.; Gao, Y.; Wang, C.; Levy, A.; Azizi, P.; Roufaiel, M.; Zhu, S.; Neculai, D.; et al. A Novel assay Uncovers an Unexpected Role for SR-BI in LDL TranscyTosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 108, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raggi, P.; Genest, J.; Giles, J.; Rayner, K.; Dwivedi, G.; Beanlands, R.; Gupta, M. Role of inflammation in The Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis and Therapeutic interventions. Atherosclerosis 2018, 276, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frostegård, J. Immunity, Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Disease. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navarro-Hernández, R.; Oregon-Romero, E.; Vázquez-Del Mercado, M.; Rangel-Villalobos, H.; Palafox-Sánchez, C.; Muñoz-Valle, J. Expression of ICAM1 and VCAM1 Serum Levels in RheumaToid Arthritis Clinical Activity. association with Genetic Polymorphisms. Dis. Markers 2009, 26, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tall, A.; Yvan-Charvet, L. Cholesterol, inflammation and innate Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansson, G. Inflammation, Atherosclerosis, and Coronary Artery Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, L.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Chang, C.; Song, B.; Chang, T.; Li, B. TNF-Alpha Stimulates the ACAT1 Expression in Differentiating Monocytes to Promote The CE-Laden Cell formation. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, R.; Svenungsson, E.; Gunnarsson, I.; andersson, B.; Lundberg, I.; Elinder, L.; Frostegård, J. antibodies Against Lysophosphatidylcholine and Oxidized LDL in Patients with SLE. Lupus 1999, 8, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjadi, M.; Rezvanie Sichanie, Z.; Totonchi, H.; Karami, J.; Rezaei, R.; Aslani, S. Atherosclerosis and AuToimmunity: A Growing Relationship. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 908–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grainger, D. High titres of serum antinuclear antibodies, mostly directed against nucleolar antigens, are associated with the presence of Coronary Atherosclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2002, 61, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shankman, L.; Gomez, D.; Cherepanova, O.; Salmon, M.; Alencar, G.; Haskins, R.; Swiatlowska, P.; Newman, A.; Greene, E.; Straub, A.; et al. KLF4-Dependent Phenotypic Modulation of Smooth Muscle Cells Has A Key Role in Atherosclerotic Plaque Pathogenesis. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falk, E.; Nakano, M.; Bentzon, J.; Finn, A.; Virmani, R. Update on Acute Coronary Syndromes: The Pathologists’ View. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 34, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Charles-Schoeman, C.; Lee, Y.; Grijalva, V.; Amjadi, S.; FitzGerald, J.; Ranganath, V.; Taylor, M.; McMahon, M.; Paulus, H.; Reddy, S. Cholesterol Efflux by High Density Lipoproteins Is Impaired in Patients with Active RheumaToid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2012, 71, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkolfinopoulou, C.; Stratikos, E.; TheofilaTos, D.; Kardassis, D.; Voulgari, P.; Drosos, A.; Chroni, A. Impaired antiatherogenic Functions of High-Density Lipoprotein in Patients with ankylosing Spondylitis. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshyna, I.; Modayil, S.; Littlefield, M.; Belilos, E.; BelosTocki, K.; Bonetti, L.; Rosenblum, G.; Carsons, S.; Reiss, A. Plasma from RheumaToid Arthritis Patients Promotes Pro-Atherogenic Cholesterol Transport Gene Expression in THP-1 Human Macrophages. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013, 238, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahmoudi, M.; aslani, S.; Fadaei, R.; Jamshidi, A. New insights to The Mechanisms Underlying Atherosclerosis in RheumaToid Arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandoo, A.; Carroll, D.; Metsios, G.; Kitas, G.; Veldhuijzen van Zanten, J. The association Between Microvascular and Macrovascular Endothelial Function in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noorwali, A.; Omran, N.; Elmedany, S.; El-Barbary, A. Risk FacTors for Acute Coronary Events in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis. Egypt. Rheumatol. Rehabil. 2017, 44, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, J.; Nevskaya, T.; Barra, L.; Parraga, G. Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis in Patients with Active RheumaToid Arthritis: PredicTors of Plaque Occurrence and Progression Over 24 Weeks. Open Rheumatol. J. 2016, 10, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dimitroulas, T.; Hodson, J.; Sandoo, A.; Smith, J.; Kitas, G. Endothelial injury in RheumaToid Arthritis: A Crosstalk Between Dimethylarginines and Systemic inflammation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skeoch, S.; Cristinacce, P.; Williams, H.; Pemberton, P.; Xu, D.; Sun, J.; James, J.; Yuan, C.; Hatsukami, T.; Hockings, P.; et al. Imaging Atherosclerosis in RheumaToid Arthritis: Evidence for increased Prevalence, Altered Phenotype and A Link Between Systemic and Localised Plaque inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erre, G.; Piga, M.; Fedele, A.; Mura, S.; Piras, A.; Cadoni, M.; Cangemi, I.; Dessi, M.; Di Sante, G.; Tolusso, B.; et al. Prevalence and Determinants of Peripheral Microvascular Endothelial Dysfunction in RheumaToid Arthritis Patients: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarraga, B.; Khan, F.; Kumar, P.; Pullar, T.; Belch, J. C-Reactive Protein: The Underlying Cause of Microvascular Dysfunction in RheumaToid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 1780–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mäki-Petäjä, K.; Cheriyan, J.; Booth, A.; Hall, F.; Brown, J.; Wallace, S.; Ashby, M.; McEniery, C.; Wilkinson, I. Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Activity Is increased in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis and Contributes to Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2008, 129, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgill, N.; Gow, P. Nailfold Capillaroscopy: A Blinded Study of Its DiscriminaTory Value in Scleroderma, Systemic Lupus ErythemaTosus, and RheumaToid Arthritis. Austr. N. Z. J. Public Health 1986, 16, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutolo, M.; Paolino, S.; Smith, V. Nailfold Capillaroscopy in Rheumatology: Ready for The Daily Use but with Care in Terminology. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 2293–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Figus, F.; Piga, M.; Azzolin, I.; McConnell, R.; Iagnocco, A. RheumaToid Arthritis: Extra-Articular Manifestations and Comorbidities. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGettigan, P.; Henry, D. Cardiovascular Risk and inhibition of Cyclooxygenase. JAMA 2006, 296, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varas-Lorenzo, C.; Riera-Guardia, N.; Calingaert, B.; Castellsague, J.; Pariente, A.; Scotti, L.; Sturkenboom, M.; Perez-Gutthann, S. Stroke Risk and Nsaids: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2011, 20, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grosser, T. Biological Basis for The Cardiovascular Consequences of COX-2 inhibition: Therapeutic Challenges and Opportunities. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 116, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, P.; Baigent, C.; Godwin, J.; Halls, H.; Emberson, J.; Patrono, C. Do Selective Cyclo-Oxygenase-2 inhibiTors and Traditional Non-Steroidal Anti-InflammaTory Drugs Increase the Risk of Atherothrombosis? Meta-Analysis of Randomised Trials. BMJ 2006, 332, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cipollone, F.; Fazia, M. COX-2 and Atherosclerosis. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 47, S26–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, S.; Berlin, J.; Reilly, M.; Jaskowiak, J.; Kishel, L.; Chittams, J.; Strom, B. The Effects of Nonselective Non-aspirin Non-Steroidal anti-inflammaTory Medications on The Risk of Nonfatal Myocardial infarction and Their interaction with aspirin. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; Tai, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhou, W.; Han, Y.; Wei, W.; Wang, Q. Triggers of Cardiovascular Diseases in RheumaToid Arthritis. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2021, 100853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panoulas, V.; Douglas, K.; Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou, A.; Metsios, G.; Nightingale, P.; Kita, M.; Elisaf, M.; Kitas, G. Long-Term Exposure to Medium-Dose Glucocorticoid Therapy associates with Hypertension in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roubille, C.; Richer, V.; Starnino, T.; McCourt, C.; McFarlane, A.; Fleming, P.; Siu, S.; Kraft, J.; Lynde, C.; Pope, J.; et al. The Effects of Tumour Necrosis FacTor inhibiTors, Methotrexate, Non-Steroidal anti-inflammaTory Drugs and Corticosteroids on Cardiovascular Events in RheumaToid Arthritis, Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2015, 74, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurmohamed, M.; Heslinga, M.; Kitas, G. Cardiovascular Comorbidity in Rheumatic Diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.; Symmons, D.; McCarey, D.; Dijkmans, B.; Nicola, P.; Kvien, T.; Mcinnes, I.; Haentzschel, H.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.; Provan, S.; et al. EULAR Evidence-Based Recommendations for Cardiovascular Risk Management in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis and Other forms of inflammaTory Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2009, 69, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezus, C.; Cardoneanu, A.; Dima, N.; Cumpata, A.J.F.; Rezus, E. Myocardial ischemia in rheumatic inflammaTory diseases. Rom. J. Cardiol. 2016, 26, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Smolen, J.; Aletaha, D.; Mcinnes, I. RheumaToid Arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Smolen, J. Diagnosis and Management of RheumaToid Arthritis. JAMA 2018, 320, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micha, R.; Imamura, F.; Wyler von Ballmoos, M.; Solomon, D.; Hernán, M.; Ridker, P.; Mozaffarian, D. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Methotrexate Use and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2011, 108, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, H.; Hernán, M.; Seeger, J.; Robins, J.; Wolfe, F. Methotrexate and Mortality in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis: A Prospective Study. Lancet 2002, 359, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzeni, F.; Turiel, M.; Caporali, R.; Cavagna, L.; Tomasoni, L.; Sitia, S.; Sarzi-Puttini, P. The Effect of Pharmacological Therapy on The Cardiovascular System of Patients with Systemic Rheumatic Diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2010, 9, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronda, N.; Greco, D.; Adorni, M.; Zimetti, F.; Favari, E.; Hjeltnes, G.; Mikkelsen, K.; Borghi, M.; Favalli, E.; Gatti, R.; et al. Newly Identified antiatherosclerotic Activity of Methotrexate and Adalimumab: Complementary Effects on Lipoprotein Function and Macrophage Cholesterol Metabolism. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Lee, C.; Hong, Y. Effects of Methotrexate on Carotid intima-Media Thickness in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marks, J.; Edwards, C. Protective Effect of Methotrexate in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis and Cardiovascular Comorbidity. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2012, 4, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suissa, S.; Bernatsky, S.; Hudson, M. Antirheumatic Drug Use and The Risk of Acute Myocardial infarction. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2006, 55, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.; Massarotti, E.; Garg, R.; Liu, J.; Canning, C.; Schneeweiss, S. Association Between Disease-Modifying antirheumatic Drugs and Diabetes Risk in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis and Psoriasis. JAMA 2011, 305, 2525–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathieu, S.; Pereira, B.; Tournadre, A.; Soubrier, M. Cardiovascular Effects of Hydroxychloroquine: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2017, 77, e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo, A.; Sokka, T.; Descalzo, M.; Calvo-Alén, J.; Hørslev-Petersen, K.; Luukkainen, R.; Combe, B.; Burmester, G.; Devlin, J.; Ferraccioli, G.; et al. Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis: Results from the QUEST-RA Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, R30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Halm, V.; Nurmohamed, M.; Twisk, J.; Dijkmans, B.; Voskuyl, A. Disease-Modifying antirheumatic Drugs Are associated with A Reduced Risk for Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis: A Case Control Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roubille, C.; Martel-Pelletier, J.; Haraoui, B.; Tardif, J.; Pelletier, J. Biologics and The Cardiovascular System: A Double-Edged Sword. Antiinflamm. Antiallergy Agents Med. Chem. 2013, 12, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feldmann, M.; Maini, R. TNF Defined as A Therapeutic Target for RheumaToid Arthritis and Other AuToimmune Diseases. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Saag, K.; Bridges, S.; Akl, E.; Bannuru, R.; Sullivan, M.; Vaysbrot, E.; McNaughton, C.; Osani, M.; Shmerling, R.; et al. 2015 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for The Treatment of RheumaToid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 68, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Bili, A.; Tang, X.; Pranesh, S.; Bozaite, R.; Morris, S.; anTohe, J.; Kirchner, H.; Wasko, M. Tumor Necrosis FacTor A inhibiTor Use and Decreased Risk for incident Coronary Events in RheumaToid Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agca, R.; Heslinga, S.; van Halm, V.; Nurmohamed, M. Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Chronic inflammaTory Joint Disorders. Heart 2016, 102, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daïen, C.; Duny, Y.; Barnetche, T.; Daurès, J.; Combe, B.; Morel, J. Effect of TNF inhibiTors On Lipid Profile in RheumaToid Arthritis: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2012, 71, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, B.; Thiele, G.; Anderson, D.; Mikuls, T. Increased Cardiovascular Risk in RheumaToid Arthritis: Mechanisms and Implications. BMJ 2018, 361, k1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljung, L.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; Jacobsson, L.; Askling, J. Response to Biological Treatment and Subsequent Risk of Coronary Events in RheumaToid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2016, 75, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Hong, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X. association Between anti-TNF Therapy for RheumaToid Arthritis and Hypertension. Medicine 2015, 94, e731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ursini, F.; Leporini, C.; Bene, F.; D’angelo, S.; Mauro, D.; Russo, E.; De Sarro, G.; Olivieri, I.; Pitzalis, C.; Lewis, M.; et al. Anti-TNF-Alpha Agents and Endothelial Function in RheumaToid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, L.; Kitas, G.; Gonzalez-Gay, M. Can Suppression of inflammation by anti-TNF Prevent Progression of Subclinical Atherosclerosis in inflammaTory Arthritis? Rheumatology 2014, 53, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szekanecz, Z.; Kerekes, G.; Végh, E.; Kardos, Z.; Baráth, Z.; Tamási, L.; Shoenfeld, Y. AuToimmune Atherosclerosis in 3D: How It Develops, How to Diagnose and What to Do. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmohamed, M.; Choy, E.; Lula, S.; Kola, B.; DeMasi, R.; Accossato, P. The Impact of Biologics and Tofacitinib On Cardiovascular Risk FacTors and Outcomes in Patients with Rheumatic Disease: A Systematic Literature Review. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2018, 41, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bacchiega, B.; Bacchiega, A.; Usnayo, M.; Bedirian, R.; Singh, G.; Pinheiro, G. interleukin 6 inhibition and Coronary Artery Disease in A High-Risk Population: A Prospective Community-Based Clinical Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcinnes, I.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Mandel, D.; Song, Y.; Connell, C.; Luo, Z.; Brosnan, M.; Zuckerman, A.; Zwillich, S.; et al. Open-Label Tofacitinib and Double-Blind ATorvastatin in RheumaToid Arthritis Patients: A Randomised Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2013, 73, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabay, C.; Mcinnes, I.; Kavanaugh, A.; Tuckwell, K.; Klearman, M.; Pulley, J.; Sattar, N. Comparison of Lipid and Lipid-associated Cardiovascular Risk Marker Changes After Treatment with Tocilizumab Or Adalimumab in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2015, 75, 1806–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, V.; Pavlov, A.; Klearman, M.; Musselman, D.; Giles, J.; Bathon, J.; Sattar, N.; Lee, J. An Evaluation of Risk FacTors for Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events During Tocilizumab Therapy. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Fumery, M.; Singh, A.; Singh, N.; Prokop, L.; Dulai, P.; Sandborn, W.; Curtis, J. Comparative Risk of Cardiovascular Events with Biologic and Synthetic Disease-Modifying antirheumatic Drugs in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Arthritis Care Res. 2020, 72, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, J.; Sattar, N.; Gabriel, S.; Ridker, P.; Gay, S.; Warne, C.; Musselman, D.; Brockwell, L.; Shittu, E.; Klearman, M.; et al. Cardiovascular Safety of Tocilizumab Versus Etanercept in RheumaToid Arthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 72, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yokoe, I.; Kitamura, N.; Nishiwaki, A.; Takei, M.; Giles, J. Heart Rate–Corrected QT interval Duration in RheumaToid Arthritis and Its Reduction with Treatment with the interleukin 6 inhibiTor Tocilizumab. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 45, 1620–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz-Amaro, I.; Hernández-Hernández, M.; Tejera-Segura, B.; Delgado-Frías, E.; Macía-Díaz, M.; Machado, J.; Diaz-González, F. Effect of IL-6 RecepTor Blockade on Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type-9 and Cholesterol Efflux Capacity in RheumaToid Arthritis Patients. Horm. Metab. Res. 2019, 51, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kume, K.; Amano, K.; Yamada, S.; Hatta, K.; Ohta, H.; Kuwaba, N. Tocilizumab Monotherapy Reduces Arterial Stiffness as Effectively as Etanercept Or Adalimumab Monotherapy in RheumaToid Arthritis: An Open-Label Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 2169–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Solomon, D.; Rogers, J.; Gale, S.; Klearman, M.; Sarsour, K.; Schneeweiss, S. Cardiovascular Safety of Tocilizumab Versus Tumor Necrosis FacTor inhibiTors in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis: A Multi-Database Cohort Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrold, L.; Reed, G.; Magner, R.; Shewade, A.; John, A.; Greenberg, J.; Kremer, J. Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Rituximab Versus Subsequent anti–Tumor Necrosis FacTor Therapy in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis with Prior Exposure to anti–Tumor Necrosis FacTor Therapies in The United States Corrona Registry. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benucci, M.; Saviola, G.; Manfredi, M.; Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Atzeni, F. FacTors Correlated with Improvement of Endothelial Dysfunction During Rituximab Therapy in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis. Biologics 2013, 7, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Hsue, P.; Scherzer, R.; Grunfeld, C.; Imboden, J.; Wu, Y.; del Puerto, G.; Nitta, E.; Shigenaga, J.; Schnell Heringer, A.; Ganz, P.; et al. Depletion of B-Cells with Rituximab Improves Endothelial Function and Reduces inflammation Among individuals with RheumaToid Arthritis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e001267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gottenberg, J.; Morel, J.; Perrodeau, E.; Bardin, T.; Combe, B.; Dougados, M.; Flipo, R.; Saraux, A.; Schaeverbeke, T.; Sibilia, J.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Rituximab, Abatacept, and Tocilizumab in Adults with RheumaToid Arthritis and inadequate Response to TNF inhibiTors: Prospective Cohort Study. BMJ 2019, 364, 167. [Google Scholar]
- Ridker, P.; Thuren, T.; Zalewski, A.; Libby, P. Interleukin-1Β inhibition and The Prevention of Recurrent Cardiovascular Events: Rationale and Design of The Canakinumab anti-inflammaTory Thrombosis Outcomes Study (CANTOS). Am. Heart J. 2011, 162, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.; Everett, B.; Thuren, T.; MacFadyen, J.; Chang, W.; Ballantyne, C.; Fonseca, F.; Nicolau, J.; Koenig, W.; Anker, S.; et al. antiinflammaTory Therapy with Canakinumab for Atherosclerotic Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikonomidis, I.; Tzortzis, S.; Andreadou, I.; Paraskevaidis, I.; Katseli, C.; Katsimbri, P.; Pavlidis, G.; Parissis, J.; Kremastinos, D.; Anastasiou-Nana, M.; et al. Increased Benefit of interleukin-1 inhibition On Vascular Function, Myocardial Deformation, and Twisting in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease and Coexisting RheumaToid Arthritis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Generali, E.; Carrara, G.; Kallikourdis, M.; Condorelli, G.; Bortoluzzi, A.; Scirè, C.; Selmi, C. Risk of Hospitalization for Heart Failure in RheumaToid Arthritis Patients Treated with Etanercept and Abatacept. Rheumatol. Int. 2018, 39, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Moe, S.; Myint, K.; Htet, A. Oral Janus Kinase inhibiTor for The Treatment of RheumaToid Arthritis: Tofacitinib. ISRN Rheumatol. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, J.; Genovese, M.; Keystone, E.; Taylor, P.; Zuckerman, S.; Ruotolo, G.; Schlichting, D.; Crotzer, V.; Nantz, E.; Beattie, S.; et al. Effects of Baricitinib On Lipid, Apolipoprotein, and Lipoprotein Particle Profiles in a Phase Iib Study of Patients with Active RheumaToid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.; Weinblatt, M.; Burmester, G.; Rooney, T.; Witt, S.; Walls, C.; Issa, M.; Salinas, C.; Saifan, C.; Zhang, X.; et al. Cardiovascular Safety During Treatment with Baricitinib in RheumaToid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1042–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charles-Schoeman, C.; DeMasi, R.; Valdez, H.; Soma, K.; Hwang, L.; Boy, M.; Biswas, P.; Mcinnes, I. Risk FacTors for Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Phase III and Long-Term Extension Studies of Tofacitinib in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conroy, R.; Pyörälä, K.; Fitzgerald, A.; Sans, S.; Menotti, A.; De Backer, G.; De Bacquer, D.; Ducimetière, P.; Jousilahti, P.; Keil, U.; et al. Estimation of Ten-Year Risk of Fatal Cardiovascular Disease in Europe: The SCORE Project. Eur. Heart J. 2003, 24, 987–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, R.; Vasan, R.; Pencina, M.; Wolf, P.; Cobain, M.; Massaro, J.; Kannel, W. General Cardiovascular Risk Profile for Use in Primary Care. Circulation 2008, 117, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rezus, E.; Dima, N.; Badescu, C.; Cardoneanu, A.; Rusu, R.G.; Rezus, C. Cardiovascular Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Case Report. Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat. 2017, 121, 523–527. [Google Scholar]
- De Backer, G. European Guidelines on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice Third Joint Task force of European and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (Constituted By Representatives of Eight Societies and by invited Experts). Eur. Heart J. 2003, 24, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hollan, I.; Dessein, P.; Ronda, N.; Wasko, M.; Svenungsson, E.; Agewall, S.; Cohen-Tervaert, J.; Maki-Petaja, K.; Grundtvig, M.; Karpouzas, G.; et al. Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in RheumaToid Arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2015, 14, 952–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasoedova, E.; Crowson, C.; Kremers, H.; Roger, V.; Fitz-Gibbon, P.; Therneau, T.; Gabriel, S. Lipid Paradox in RheumaToid Arthritis: The Impact of Serum Lipid Measures and Systemic inflammation On The Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2011, 70, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, K.; Diogo, D.; Cui, J.; Cai, T.; Okada, Y.; Gainer, V.; Murphy, S.; Gupta, N.; Mirel, D.; ananthakrishnan, A.; et al. Association Between Low Density Lipoprotein and RheumaToid Arthritis Genetic FacTors with Low Density Lipoprotein Levels in RheumaToid Arthritis and Non-RheumaToid Arthritis Controls. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2013, 73, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, E.; Sattar, N. Interpreting Lipid Levels in The Context of High-Grade inflammaTory States with A Focus on RheumaToid Arthritis: A Challenge to Conventional Cardiovascular Risk Actions. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2009, 68, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K.; Kastelein, J.; Matthijs Boekholdt, S.; Nicholls, S.; Khaw, K.; Ballantyne, C.; Catapano, A.; Reiner, E.; Luscher, T. The ACC/AHA 2013 Guideline on The Treatment of Blood Cholesterol to Reduce Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Adults: The Good the Bad and The Uncertain: A Comparison with ESC/EAS Guidelines for The Management of Dyslipidaemias 2011. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okano, T.; inui, K.; Tada, M.; Sugioka, Y.; Mamoto, K.; Wakitani, S.; Koike, T.; Nakamura, H. Loss of Lean Body Mass Affects Low Bone Mineral Density in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis—Results from The TOMORROW Study. Mod. Rheumatol. 2017, 27, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.; Buring, J.; Rifai, N.; Cook, N. Development and Validation of Improved Algorithms for the assessment of Global Cardiovascular Risk in Women. JAMA 2007, 297, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.; Paynter, N.; Rifai, N.; Gaziano, J.; Cook, N. C-Reactive Protein and Parental HisTory Improve Global Cardiovascular Risk Prediction. Circulation 2008, 118, 2243–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pencina, M.; D’Agostino, R.; Larson, M.; Massaro, J.; Vasan, R. Predicting The 30-Year Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2009, 119, 3078–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sen, D.; González-Mayda, M.; Brasington, R. Cardiovascular Disease in RheumaToid Arthritis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 40, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.; Greenberg, J.; Curtis, J.; Liu, M.; Farkouh, M.; Tsao, P.; Kremer, J.; Etzel, C. Derivation and internal Validation of an Expanded Cardiovascular Risk Prediction Score for RheumaToid Arthritis: A Consortium of Rheumatology Researchers of North America Registry Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1995–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowson, C.; Gabriel, S.; Semb, A.; van Riel, P.; Karpouzas, G.; Dessein, P.; Hitchon, C.; Pascual-Ramos, V.; Kitas, G.; Douglas, K.; et al. RheumaToid Arthritis-Specific Cardiovascular Risk Scores Are Not Superior to General Risk Scores: A Validation analysis of Patients from Seven Countries. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giles, J.; Allison, M.; Blumenthal, R.; Post, W.; Gelber, A.; Petri, M.; Tracy, R.; Szklo, M.; Bathon, J. Abdominal Adiposity in RheumaToid Arthritis: Association with Cardiometabolic Risk FacTors and Disease Characteristics. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2010, 62, 3173–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karpouzas, G.; Malpeso, J.; Choi, T.; Li, D.; Munoz, S.; Budoff, M. Prevalence, Extent and Composition of Coronary Plaque in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis without SympToms or Prior Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2013, 73, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Sijl, A.; Peters, M.; Knol, D.; de Vet, H.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.; Smulders, Y.; Dijkmans, B.; Nurmohamed, M. Carotid intima Media Thickness in RheumaToid Arthritis as Compared to Control Subjects: A Meta-analysis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 40, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, A.; González-Juanatey, C.; Peiró, M.; Blanco, R.; Llorca, J.; González-Gay, M. Carotid Ultrasound Is Useful for The Cardiovascular Risk Stratification of Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis: Results of A Population-Based Study. Ann. Rheum. Dis.. 2013, 73, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikdahl, E.; Rollefstad, S.; WibeToe, G.; Olsen, I.; Berg, I.; Hisdal, J.; Uhlig, T.; Haugeberg, G.; Kvien, T.; Provan, S.; et al. Predictive Value of Arterial Stiffness and Subclinical Carotid Atherosclerosis for Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 43, 1622–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannawi, S.; Hannawi, H.; Al Salmi, I. Cardiovascular Disease and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in RheumaToid Arthritis. Hypertens. Res. 2020, 43, 982–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedrakyan, S.; Fatima, T.; Khatun, M.; Awan, M.; Okam, N.; Jahan, N. Evaluation of The Risk of Getting Peripheral Artery Disease in RheumaToid Arthritis and The Selection of Appropriate Diagnostic Methods. Cureus 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatelopoulos, K.; Kitas, G.; Papamichael, C.; Kyrkou, K.; Zampeli, E.; Fragiadaki, K.; Panoulas, V.; Mavrikakis, M.; Sfikakis, P. Subclinical Peripheral Arterial Disease in RheumaToid Arthritis. Atherosclerosis 2010, 212, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehan, P.; Stewart, S.; Chuter, V.; Carroll, M.; Rutherfurd, K.; Brenton-Rule, A. Relationship Between Lower Limb Vascular Characteristics, Peripheral Arterial Disease and Gait in RheumaToid Arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, C.; Kim, N.; Kang, J.; Kim, J.; Kang, J.; Bae, G.; Nam, E.; Kang, Y. InflammaTory Burden interacts with Conventional Cardiovascular Risk FacTors for Carotid Plaque formation in RheumaToid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2014, 54, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Evans, M.; Escalante, A.; Battafarano, D.; Freeman, G.; O’Leary, D.; del Rincón, I. Carotid Atherosclerosis Predicts incident Acute Coronary Syndromes in RheumaToid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ajeganova, S.; de Faire,, U.; Jogestrand, T.; FrostegÅrd, J.; HafstrÖm, I. Carotid Atherosclerosis, Disease Measures, Oxidized Low-Density Lipoproteins, and Atheroprotective Natural antibodies for Cardiovascular Disease in Early RheumaToid Arthritis—An inception Cohort Study. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hannawi, S.; Haluska, B.; Marwick, T.; Thomas, R. Atherosclerotic Disease Is increased in Recent-Onset RheumaToid Arthritis: A Critical Role for inflammation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2007, 9, R116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hannawi, S.; Hannawi, H.; Alokaily, F.; Salmi, I. Variables associated with Subclinical Atherosclerosis Among RheumaToid Arthritis Patients of Gulf Cooperative Council Countries. Saudi Med. J. 2020, 41, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosino, P.; Tasso, M.; Lupoli, R.; Di Minno, A.; Baldassarre, D.; Tremoli, E.; Di Minno, M. Non-invasive assessment of Arterial Stiffness in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Literature Studies. Ann. Med. 2015, 47, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2013 ESC Guidelines On The Management of Stable Coronary Artery Disease. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 2949–3003. [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Lu, B.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Budoff, M. Prognostic Value of Coronary CT angiography and Calcium Score for Major Adverse Cardiac Events in Outpatients. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 5, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yiu, K.; Wang, S.; Mok, M.; Ooi, G.; Khong, P.; Lau, C.; Tse, H. Relationship Between Cardiac Valvular and Arterial Calcification in Patients with RheumaToid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus ErythemaTosus. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K.; Crowson, C.; Gabriel, S. Cardiovascular Comorbidity in Rheumatic Diseases. Heart Fail Clin. 2014, 10, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rudominer, R.; Roman, M.; Devereux, R.; Paget, S.; Schwartz, J.; Lockshin, M.; Crow, M.; Sammaritano, L.; Levine, D.; Salmon, J. independent association of RheumaToid Arthritis with increased Left Ventricular Mass but Not with Reduced Ejection Fraction. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2009, 60, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rezuș, E.; Floria, M.; Grigoriu, A.; Tamba, B.; Rezuș, C. Cardiovascular Risk FacTors in Chronic inflammaTory Rheumatic Diseases: Modern assessment and Diagnosis. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 13, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rezuș, E.; Macovei, L.A.; Burlui, A.M.; Cardoneanu, A.; Rezuș, C. Ischemic Heart Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis—Two Conditions, the Same Background. Life 2021, 11, 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11101042
Rezuș E, Macovei LA, Burlui AM, Cardoneanu A, Rezuș C. Ischemic Heart Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis—Two Conditions, the Same Background. Life. 2021; 11(10):1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11101042
Chicago/Turabian StyleRezuș, Elena, Luana Andreea Macovei, Alexandra Maria Burlui, Anca Cardoneanu, and Ciprian Rezuș. 2021. "Ischemic Heart Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis—Two Conditions, the Same Background" Life 11, no. 10: 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11101042
APA StyleRezuș, E., Macovei, L. A., Burlui, A. M., Cardoneanu, A., & Rezuș, C. (2021). Ischemic Heart Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis—Two Conditions, the Same Background. Life, 11(10), 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11101042






