Magnolol Induces the Extrinsic/Intrinsic Apoptosis Pathways and Inhibits STAT3 Signaling-Mediated Invasion of Glioblastoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Antibodies, and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture of GBM
2.3. MTT Assay
2.4. Flow Cytometry
2.5. GEPIA Analysis
2.6. Transwell Invasion Assay
2.7. Wound Healing Assay
2.8. Western Blotting Assay
2.9. Translocation Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Magnolol Effectively Induced Cytotoxicity and Activated the Extrinsic/Intrinsic Apoptosis Pathways of GBM Cells
3.2. Magnolol-Suppressed GBM Progression Is Associated with PKCδ/STAT3 Inactivation
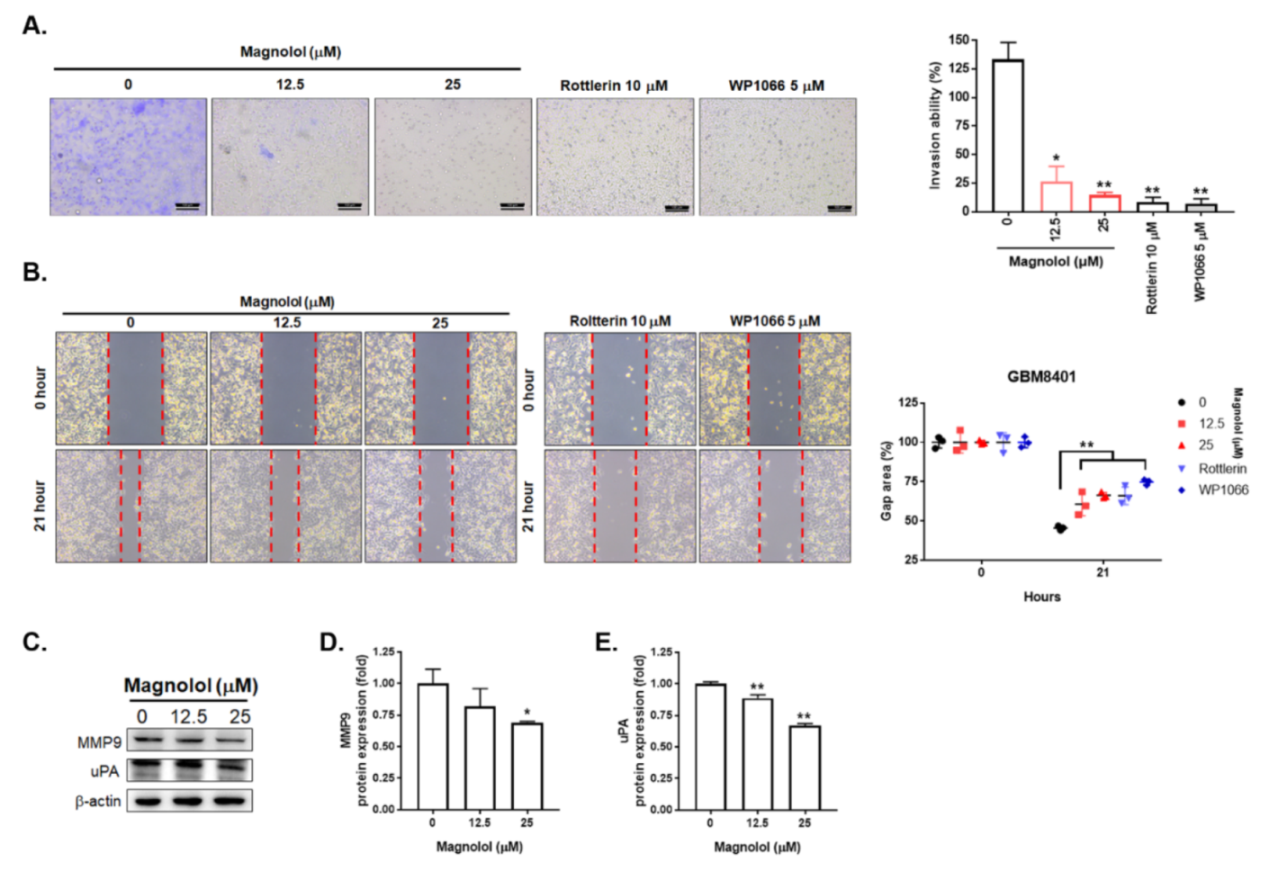
3.3. Magnolol-Diminished GBM Invasion and Migration Is Associated with PKCδ/STAT3 Suppression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arcella, A.; Oliva, M.A.; Staffieri, S.; Sanchez, M.; Madonna, M.; Riozzi, B.; Esposito, V.; Giangaspero, F.; Frati, L. Effects of aloe emodin on U87MG GBM cell growth: In vitro and in vivo study. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Chang, Y.M.; Wang, K.Y.; Chen, P.N.; Hseu, Y.C.; Chen, K.M.; Yeh, K.T.; Chen, C.J.; Hsu, L.S. Naringenin inhibited migration and invasion of GBM cells through multiple mechanisms. Environ. Toxicol. 2019, 34, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qi, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, N.; Huai, L.; Qu, S.; Zhao, L. A review of traditional Chinese medicine for treatment of GBM. Biosci. Trends 2020, 13, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trogrlić, I.; Trogrlić, D.; Trogrlić, D.; Trogrlić, A.K. Treatment of GBM with herbal medicines. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhai, K.; Siddiqui, M.; Abdellatif, B.; Liskova, A.; Kubatka, P.; Büsselberg, D. Natural Compounds in GBM Therapy: Preclinical Insights, Mechanistic Pathways, and Outlook. Cancers 2021, 13, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.C.; Lin, W.W.; Wu, C.C.; Hsu, S.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Chung, J.G.; Chiang, C.S. Lauryl Gallate Induces Apoptotic Cell Death through Caspase-dependent Pathway in U87 Human GBM Cells In Vitro. In Vivo 2018, 32, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.S.; Chien, C.C.; Liu, K.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Chiu, W.T. Evodiamine Prevents Glioma Growth, Induces GBM Cell Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest through JNK Activation. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2017, 45, 879–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szoka, L.; Palka, J. Capsaicin up-regulates pro-apoptotic activity of thiazolidinediones in GBM cell line. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, Z.G.; Lin, Y.; Qu, X.G.; Lv, W.; Wang, G.B.; Li, C.L. Effects of quercetin on proliferation and migration of human GBM U251 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.G.; Oliveira, K.A.; Lopes, R.G.; Poluceno, G.G.; Simioni, C.; Gabriel, D.S.P.; Bauer, C.M.; Maraschin, M.; Derner, R.B.; Garcez, R.C.; et al. Anti-cancer Effects of Fucoxanthin on Human GBM Cell Line. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 6799–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, C.M.; Singh, A.T.K. Apoptosis: A Target for Anticancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Zhao, X.; Wang, D. Sinomenine Hydrochloride Inhibits the Metastasis of Human GBM Cells by Suppressing the Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2/-9 and Reversing the Endogenous and Exogenous Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.E.; Patel, M.; Ruzevick, J.; Jackson, C.M.; Lim, M. STAT3 Activation in GBM: Biochemical and Therapeutic Implications. Cancers 2014, 6, 376–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindemann, C.; Hackmann, O.; Delic, S.; Schmidt, N.; Reifenberger, G.; Riemenschneider, M.J. SOCS3 promoter methylation is mutually exclusive to EGFR amplification in gliomas and promotes glioma cell invasion through STAT3 and FAK activation. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 122, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Y.; Lai, C.C.; Huang, P.H.; Yang, A.H.; Chiang, S.C.; Huang, P.C.; Tseng, K.W.; Huang, C.H. Magnolol Reduces Renal Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury via Inhibition of Apoptosis. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2017, 45, 1421–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, F.; Sun, W.; Gao, L.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, K.T.; Cai, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Y. Extracts of Magnolia Species-Induced Prevention of Diabetic Complications: A Brief Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Kuo, H.C.; Lee, K.F.; Tsai, T.H. Magnolol protects neurons against ischemia injury via the downregulation of p38/MAPK, CHOP and nitrotyrosine. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 279, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Liang, Y.C.; Ho, Y.S.; Lee, W.S. Magnolol inhibits human GBM cell proliferation through upregulation of p21/Cip1. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7331–7337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.C.; Tsao, M.J.; Chiu, C.Y.; Kan, P.C.; Chen, Y. Magnolol Inhibits Human GBM Cell Migration by Regulating N-Cadherin. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 77, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.Y.; Yang, S.T.; Shen, S.C.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Hsu, F.T.; Chen, C.Y.; Chiang, Y.H.; Chuang, J.Y.; Chen, K.Y.; Hsu, T.I.; et al. Serum amyloid A1 in combination with integrin αVβ3 increases GBM cells mobility and progression. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 756–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saggioro, F.P.; Neder, L.; Stávale, J.N.; Paixão-Becker, A.N.; Malheiros, S.M.; Soares, F.A.; Pittella, J.E.; Matias, C.C.; Colli, B.O.; Carlotti, C.G., Jr.; et al. Fas, FasL, and cleaved caspases 8 and 3 in GBMs: A tissue microarray-based study. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2014, 210, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shinoura, N.; Ohashi, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Kirino, T.; Asai, A.; Hashimoto, M.; Hamada, H. Adenovirus-mediated overexpression of Fas induces apoptosis of gliomas. Cancer Gene Ther. 2000, 7, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.B.; Li, T.; Ma, D.Z.; Ji, Y.X.; Zhi, H. Overexpression of FADD and Caspase-8 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of human GBM cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.C.; Hueng, D.Y.; Huang, H.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Chen, Y. Magnolol and honokiol exert a synergistic anti-tumor effect through autophagy and apoptosis in human GBMs. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 29116–29130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, I.T.; Chen, W.T.; Tseng, C.W.; Chen, Y.C.; Kuo, Y.C.; Chen, B.J.; Weng, M.C.; Lin, H.J.; Wang, W.S. Hyperforin Inhibits Cell Growth by Inducing Intrinsic and Extrinsic Apoptotic Pathways in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ou, A.; Ott, M.; Fang, D.; Heimberger, A.B. The Role and Therapeutic Targeting of JAK/STAT Signaling in GBM. Cancers 2021, 13, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senft, C.; Priester, M.; Polacin, M.; Schröder, K.; Seifert, V.; Kögel, D.; Weissenberger, J. Inhibition of the JAK-2/STAT3 signaling pathway impedes the migratory and invasive potential of human GBM cells. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2011, 101, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.S.; Yang, L.J.; Wang, X.F.; Chen, Y.P.; Tang, W.L.; Chen, L.; Lin, Z.X. STAT3 Tyr705 phosphorylation affects clinical outcome in patients with newly diagnosed supratentorial GBM. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, C.L.; Nuzzo, S.; Catuogno, S.; Romano, S.; de Nigris, F.; de Franciscis, V. STAT3 Gene Silencing by Aptamer-siRNA Chimera as Selective Therapeutic for GBM. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 10, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranaware, A.M.; Banik, K.; Deshpande, V.; Padmavathi, G.; Roy, N.K.; Sethi, G.; Fan, L.; Kumar, A.P.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Magnolol: A Neolignan from the Magnolia Family for the Prevention and Treatment of Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsai, J.J.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, C.H.; Chung, J.G.; Hsu, F.T. Apoptosis induction and ERK/NF-κB inactivation are associated with magnolol-inhibited tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo. Environ. Toxicol. 2020, 35, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shen, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Shan, T.; Li, J.; Xu, M.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Cao, G. Magnolol Suppresses Pancreatic Cancer Development In Vivo and In Vitro via Negatively Regulating TGF-β/Smad Signaling. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 597672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeown, B.T.; Hurta, R.A. Magnolol affects expression of IGF-1 and associated binding proteins in human prostate cancer cells in vitro. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 6333–6338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.H.; Ren, H.Y.; Shen, J.X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ye, H.M.; Shen, D.Y. Magnolol suppresses the proliferation and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma cells via inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geribaldi-Doldán, N.; Hervás-Corpión, I.; Gómez-Oliva, R.; Domínguez-García, S.; Ruiz, F.A.; Iglesias-Lozano, I.; Carrascal, L.; Pardillo-Díaz, R.; Gil-Salú, J.L.; Nunez-Abades, P.; et al. Targeting Protein Kinase C in GBM Treatment. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, J.A.; Pitarresi, J.R.; Sharma, N.; Palettas, M.; Cuitiño, M.C.; Sizemore, S.T.; Yu, L.; Sanderlin, A.; Rosol, T.J.; Mehta, K.D.; et al. Protein kinase C Beta in the tumor microenvironment promotes mammary tumorigenesis. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, E.; Yoo, K.C.; Kang, S.G.; Kim, R.K.; Cui, Y.H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, I.G.; Suh, Y.; et al. PKCδ activated by c-MET enhances infiltration of human GBM cells through NOTCH2 signaling. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 4890–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yueh, P.-F.; Lee, Y.-H.; Fu, C.-Y.; Tung, C.-B.; Hsu, F.-T.; Lan, K.-L. Magnolol Induces the Extrinsic/Intrinsic Apoptosis Pathways and Inhibits STAT3 Signaling-Mediated Invasion of Glioblastoma Cells. Life 2021, 11, 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121399
Yueh P-F, Lee Y-H, Fu C-Y, Tung C-B, Hsu F-T, Lan K-L. Magnolol Induces the Extrinsic/Intrinsic Apoptosis Pathways and Inhibits STAT3 Signaling-Mediated Invasion of Glioblastoma Cells. Life. 2021; 11(12):1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121399
Chicago/Turabian StyleYueh, Po-Fu, Yuan-Hao Lee, Chun-Yu Fu, Chun-Bin Tung, Fei-Ting Hsu, and Keng-Li Lan. 2021. "Magnolol Induces the Extrinsic/Intrinsic Apoptosis Pathways and Inhibits STAT3 Signaling-Mediated Invasion of Glioblastoma Cells" Life 11, no. 12: 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121399
APA StyleYueh, P.-F., Lee, Y.-H., Fu, C.-Y., Tung, C.-B., Hsu, F.-T., & Lan, K.-L. (2021). Magnolol Induces the Extrinsic/Intrinsic Apoptosis Pathways and Inhibits STAT3 Signaling-Mediated Invasion of Glioblastoma Cells. Life, 11(12), 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121399






