Glycoprotein Profile Measured by a 1H-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Based on Approach in Patients with Diabetes: A New Robust Method to Assess Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Associations of 1H-NMR-Derived Glycoprotein Variables with the Clinical and the Liposcale® Test Variables
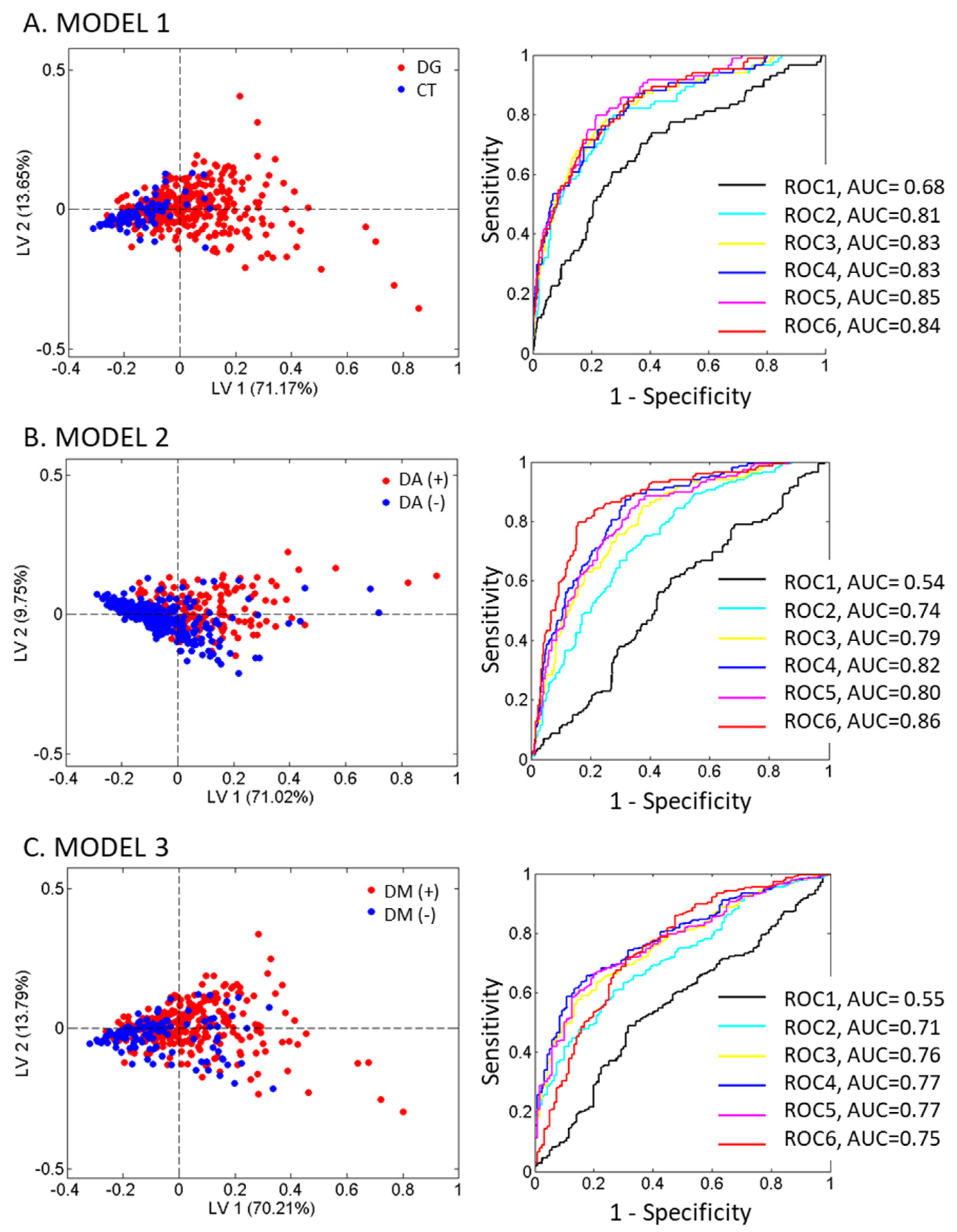
2.2. Analysis of Glycoproteins and CRP in the Study Population Groups
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maffi, P.; Secchi, A. The Burden of Diabetes: Emerging Data. Dev. Ophthalmol. 2017, 60, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, J.D.; Schwartzbard, A.Z.; Weintraub, H.S.; Goldberg, I.J.; Berger, J.S. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Mellitus. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoria, P.C.; Chopra, H.K.; Parashar, S.K.; Dutta, A.L.; Pinto, B.; Mullasari, A.; Prajapati, S. The Nuances of Atherogenic Dyslipidemia in Diabetes: Focus on Triglycerides and Current Management Strategies. Indian Heart J. 2013, 65, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haffner, S.M. American Diabetes Association. Management of Dyslipidemia in Adults with Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003, 26 (Suppl. S1), S83–S86. [Google Scholar]
- Mooradian, A.D. Dyslipidemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2009, 5, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A.; Klip, A.; Haddad, P.; Cole, D.E.; Bailo, B.G.; El-Sohemy, A.; Karmali, M. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Inflammation: Prospects for Biomarkers of Risk and Nutritional Intervention. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2010, 3, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karstoft, K.; Pedersen, B.K. Exercise and Type 2 Diabetes: Focus on Metabolism and Inflammation. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2016, 94, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, S.C.; Würtz, P.; Nath, A.P.; Abraham, G.; Havulinna, A.S.; Fearnley, L.G.; Sarin, A.-P.; Kangas, A.J.; Soininen, P.; Aalto, K.; et al. The Biomarker GlycA Is Associated with Chronic Inflammation and Predicts Long-Term Risk of Severe Infection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziegler, D. Type 2 Diabetes as an Inflammatory Cardiovascular Disorder. Curr. Mol. Med. 2005, 5, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, B.B.; Schmidt, M.I.; Pankow, J.S.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Couper, D.; Vigo, A.; Hoogeveen, R.; Folsom, A.R.; Heiss, G. Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Low-Grade Systemic Inflammation and the Development of Type 2 Diabetes: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1799–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation and Metabolic Disorders. Nature 2006, 444, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinkuolie, A.O.; Buring, J.E.; Ridker, P.M.; Mora, S. A Novel Protein Glycan Biomarker and Future Cardiovascular Disease Events. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e001221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGarrah, R.; Craig, D.; Haynes, C.; Dowdy, Z.E.; Shah, S.; Kraus, W. GlycA, a Novel Biomarker of Systemic Inflammation, Improves Cardiovascular Risk Prediction in a High-Risk Coronary Catheterization Cohort. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, A1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otvos, J.D.; Shalaurova, I.; Wolak-Dinsmore, J.; Connelly, M.A.; Mackey, R.H.; Stein, J.H.; Tracy, R.P. GlycA: A Composite Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Biomarker of Systemic Inflammation. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fuertes-Martín, R.; Taverner, D.; Vallvé, J.-C.; Paredes, S.; Masana, L.; Correig Blanchar, X.; Amigó Grau, N. Characterization of 1H NMR Plasma Glycoproteins as a New Strategy To Identify Inflammatory Patterns in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 3730–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesh, J.; Wheeler, J.G.; Hirschfield, G.M.; Eda, S.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Rumley, A.; Lowe, G.D.O.; Pepys, M.B.; Gudnason, V. C-Reactive Protein and Other Circulating Markers of Inflammation in the Prediction of Coronary Heart Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes-Martín, R.; Correig, X.; Vallvé, J.C.; Amigó, N. Human serum/plasma glycoprotein analysis by 1H-NMR, an emerging method of inflammatory assessment. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malo, A.I.; Girona, J.; Ibarretxe, D.; Rodríguez-Borjabad, C.; Amigó, N.; Plana, N.; Masana, L. Serum glycoproteins A and B assessed by 1H-NMR in familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis 2021, 330, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabré, N.; Gil, M.; Amigó, N.; Luciano-Mateo, F.; Baiges-Gaya, G.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Rodríguez-Tomàs, E.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; Castañé, H.; París, M.; et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy alters 1 H-NMR-measured lipoprotein and glycoprotein profile in patients with severe obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Maurici, J.; Amigó, N.; Cuello, E.; Bermúdez, M.; Baena-Fustegueras, J.A.; Peinado-Onsurbe, J.; Pardina, E. Bariatric surgery decreases oxidative stress and protein glycosylation in patients with morbid obesity. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 50, e13320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna, A.; Xicoy, H.; Tolosa, E.; Serradell, M.; Vilas, D.; Gaig, C.; Fernández, M.; Yanes, O.; Santamaria, J.; Amigó, N.; et al. Serum metabolic biomarkers for synucleinopathy conversion in isolated REM sleep behavior disorder. NPJ Parkinson’s Dis. 2021, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malo, A.I.; Peraire, J.; Ruiz-Mateos, E.; Masip, J.; Amigó, N.; Alcamí, J.; Moreno, S.; Girona, J.; García-Pardo, G.; Reig, R.; et al. Evolution of Serum Acute-Phase Glycoproteins Assessed by 1H-NMR in HIV Elite Controllers. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 730691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Carrio, J.; Alperi-López, M.; López, P.; Pérez-Álvarez, Á.I.; Gil-Serret, M.; Amigó, N.; Ulloa, C.; Benavente, L.; Ballina-García, F.J.; Suárez, A. GlycA Levels during the Earliest Stages of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Potential Use as a Biomarker of Subclinical Cardiovascular Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncayo, S.; Insenser, M.; Martínez-García, M.Á.; Fuertes-Martín, R.; Amigó-Grau, N.; Álvarez-Blasco, F.; Luque-Ramírez, M.; Correig-Blanchar, X.; Escobar-Morreale, H.F. Acute-phase glycoprotein profile responses to different oral macronutrient challenges: Influence of sex, functional hyperandrogenism and obesity. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardikar, S.; Song, X.; Kratz, M.; Anderson, G.L.; Blount, P.L.; Reid, B.J.; Vaughan, T.L.; White, E. Intraindividual Variability over Time in Plasma Biomarkers of Inflammation and Effects of Long-Term Storage. Cancer Causes Control 2014, 25, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dierckx, T.; Verstockt, B.; Vermeire, S.; van Weyenbergh, J. GlycA, a Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Measure for Protein Glycosylation, Is a Viable Biomarker for Disease Activity in IBD. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2018, 13, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gruppen, E.G.; Connelly, M.A.; Vart, P.; Otvos, J.D.; Bakker, S.J.; Dullaart, R.P. GlycA, a Novel Proinflammatory Glycoprotein Biomarker, and High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Are Inversely Associated with Sodium Intake after Controlling for Adiposity: The Prevention of Renal and Vascular End-Stage Disease Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gruppen, E.G.; Connelly, M.A.; Dullaart, R.P.F. Higher Circulating GlycA, a pro-Inflammatory Glycoprotein Biomarker, Relates to Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2 Mass in Nondiabetic Subjects but Not in Diabetic or Metabolic Syndrome Subjects. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2016, 10, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dullaart, R.P.F.; Gruppen, E.G.; Connelly, M.A.; Lefrandt, J.D. A Pro-Inflammatory Glycoprotein Biomarker Is Associated with Lower Bilirubin in Metabolic Syndrome. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 1045–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dullaart, R.P.F.; Gruppen, E.G.; Connelly, M.A.; Otvos, J.D.; Lefrandt, J.D. GlycA, a Biomarker of Inflammatory Glycoproteins, Is More Closely Related to the Leptin/Adiponectin Ratio than to Glucose Tolerance Status. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Use of Glycated Haemoglobin (HbA1c) in the Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus: Abbreviated Report of a WHO Consultation; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Morgner, F.; Lecointre, A.; Charbonnière, L.J.; Löhmannsröben, H.-G. Detecting Free Hemoglobin in Blood Plasma and Serum with Luminescent Terbium Complexes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krauss, R.M. Lipids and Lipoproteins in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amigó, N.; Mallol, R.; Heras, M.; Martínez-Hervás, S.; Blanco-Vaca, F.; Escolà-Gil, J.C.; Plana, N.; Yanes, Ó.; Masana, L.; Correig, X. Lipoprotein Hydrophobic Core Lipids Are Partially Extruded to Surface in Smaller HDL: “Herniated” HDL, a Common Feature in Diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wurtz, P.; Tiainen, M.; Makinen, V.-P.; Kangas, A.J.; Soininen, P.; Saltevo, J.; Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Mantyselka, P.; Lehtimaki, T.; Laakso, M.; et al. Circulating Metabolite Predictors of Glycemia in Middle-Aged Men and Women. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1749–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akinkuolie, A.O.; Pradhan, A.D.; Buring, J.E.; Ridker, P.M.; Mora, S. Novel Protein Glycan Side-Chain Biomarker and Risk of Incident Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dungan, K.; Binkley, P.; Osei, K. GlycA Is a Novel Marker of Inflammation Among Non-Critically Ill Hospitalized Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Inflammation 2015, 38, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Connelly, M.A.; Shimizu, C.; Winegar, D.A.; Shalaurova, I.; Pourfarzib, R.; Otvos, J.D.; Kanegaye, J.T.; Tremoulet, A.H.; Burns, J.C. Differences in GlycA and Lipoprotein Particle Parameters May Help Distinguish Acute Kawasaki Disease from Other Febrile Illnesses in Children. BMC Pediatr. 2016, 16, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorenzo, C.; Festa, A.; Hanley, A.J.; Rewers, M.J.; Escalante, A.; Haffner, S.M. Novel Protein Glycan–Derived Markers of Systemic Inflammation and C-Reactive Protein in Relation to Glycemia, Insulin Resistance, and Insulin Secretion. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bell, J.D.; Brown, J.C.C.; Nicholson, J.K.; Sadler, P.J. Assignment of Resonances for ‘Acute-Phase’ Glycoproteins in High Resolution Proton NMR Spectra of Human Blood Plasma. FEBS Lett. 1987, 215, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mallol, R.; Amigó, N.; Rodríguez, M.A.; Heras, M.; Vinaixa, M.; Plana, N.; Rock, E.; Ribalta, J.; Yanes, O.; Masana, L.; et al. Liposcale: A Novel Advanced Lipoprotein Test Based on 2D Diffusion-Ordered 1H NMR Spectroscopy. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ballabio, D.; Consonni, V. Classification Tools in Chemistry. Part 1: Linear Models. PLS-DA. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| AD (+) DM (+) n = 129 | DM (−) AD (+) n = 38 | DM (+) AD (−) n = 222 | CT n = 115 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 58 ± 14 | 54 ± 15 | 65 ± 10.75 | 58 ± 13.50 | 0.00 ** (A-B, A-D, B-C, C-D) |
| Gender (% male) | 50 | 33.3 | 49.5 | 61.4 | 0.02 * |
| BMI (kg/m) | 31.85 ± 5.87 | 31.76 ± 2.86 | 30.20 ± 6.22 | 26.90 ± 4.49 | 0.00 ** (A-D, B-D, C-D) |
| Smoking (%) | 25.3 | 25 | 18 | 4.7 | 0.00 ** |
| Total-C | 215.37 ± 70.81 | 223.84 ± 47.54 | 197.19 ± 66.92 | 206.38 ± 43 | 0.00 ** (A-C, B-C, C-D) |
| LDL-C | 117.89 ± 59.25 | 125.14 ± 46.16 | 111.57 ± 46.27 | 107.79 ± 46.14 | >0.05 |
| HDL-C | 41.04 ± 15.75 | 40.63 ± 16.53 | 51.54 ± 18.84 | 56.16 ± 22.93 | 0.00 ** (A-C, A-D, B-C, B-D) |
| TG | 215.56 ±127.62 | 217.10 ± 134.97 | 111.35 ± 57 | 71.48 ± 42.84 | 0.00 ** (A-C, A-D, B-C) |
| Glucose | 158.50 ± 57 | 114 ± 22 | 151.50 ± 62.25 | 101.50 ± 18 | 0.00 ** (A-B, A-D, B-C, C-D) |
| Hb1AC (%) | 6.70 ± 1.50 | 5.20 ± 0.60 | 6.90 ± 1.67 | 5.23 ± 0.31 | 0.00 ** (A-B, A-D, B-C, B-D, C-D) |
| AREA GLYCB | AREA GLYCF | AREA GLYCA | H/W GLYCB | H/W GLYCA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| CLINICAL VARIABLES | ||||||||||
| AGE | −0.03 | 0.46 | −0.01 | 0.84 | −0.05 | 0.31 | 0.02 | 0.75 | −0.02 | 0.66 |
| BMI | 0.30 | 0.00 ** | 0.30 | 0.00 ** | 0.34 | 0.00 ** | 0.29 | 0.00 ** | 0.32 | 0.00 ** |
| GLUCOSE | 0.38 | 0.00 ** | 0.44 | 0.00 ** | 0.42 | 0.00 ** | 0.39 | 0.00 ** | 0.44 | 0.00 ** |
| CRP | 0.37 | 0.00 ** | 0.32 | 0.00 ** | 0.31 | 0.00 ** | 0.42 | 0.00 ** | 0.39 | 0.00 ** |
| HBA1C | 0.10 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.00 ** | 0.16 | 0.04 * |
| LIPOSCALE® VARIABLES | ||||||||||
| VLDL-C | 0.61 | 0.00 ** | 0.76 | 0.00 ** | 0.88 | 0.00 ** | 0.42 | 0.00 ** | 0.74 | 0.00 ** |
| IDL-C | 0.49 | 0.00 ** | 0.48 | 0.00 ** | 0.55 | 0.00 ** | 0.31 | 0.00 ** | 0.49 | 0.00 ** |
| LDL-C | 0.04 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 0.04 * | 0.13 | 0.00 ** | −0.02 | 0.66 | 0.10 | 0.02 * |
| HDL-C | −0.40 | 0.00 ** | −0.47 | 0.00 ** | −0.56 | 0.00 ** | −0.34 | 0.00 ** | −0.49 | 0.00 ** |
| VLDL-TG | 0.60 | 0.00 ** | 0.79 | 0.00 ** | 0.89 | 0.00 ** | 0.44 | 0.00 ** | 0.75 | 0.00 ** |
| IDL-TG | 0.59 | 0.00 ** | 0.61 | 0.00 ** | 0.70 | 0.00 ** | 0.40 | 0.00 ** | 0.63 | 0.00 ** |
| LDL-TG | 0.41 | 0.00 ** | 0.35 | 0.00 ** | 0.42 | 0.00 ** | 0.25 | 0.00 ** | 0.39 | 0.00 ** |
| HDL-TG | 0.42 | 0.00 ** | 0.52 | 0.00 ** | 0.58 | 0.00 ** | 0.24 | 0.00 ** | 0.48 | 0.00 ** |
| VLDL-P (nmol/L) | 0.60 | 0.00 ** | 0.79 | 0.00 ** | 0.89 | 0.00 ** | 0.44 | 0.00 ** | 0.75 | 0.00 ** |
| Large VLDL-P (nmol/L) | 0.59 | 0.00 ** | 0.76 | 0.00 ** | 0.88 | 0.00 ** | 0.44 | 0.00 ** | 0.75 | 0.00 ** |
| Medium VLDL-P (nmol/L) | 0.61 | 0.00 ** | 0.78 | 0.00 ** | 0.90 | 0.00 ** | 0.44 | 0.00 ** | 0.75 | 0.00 ** |
| Small VLDL-P (nmol/L) | 0.60 | 0.00 ** | 0.79 | 0.00 ** | 0.89 | 0.00 ** | 0.44 | 0.00 ** | 0.74 | 0.00 ** |
| LDL-P (nmol/L) | 0.14 | 0.00 ** | 0.19 | 0.00 ** | 0.23 | 0.00 ** | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.00 ** |
| Large LDL-P (nmol/L) | 0.03 | 0.53 | −0.01 | 0.89 | 0.06 | 0.17 | −0.06 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.54 |
| Medium LDL-P (nmol/L) | 0.01 | 0.88 | 0.03 | 0.47 | 0.07 | 0.10 | −0.03 | 0.50 | 0.06 | 0.15 |
| Small LDL-P (nmol/L) | 0.24 | 0.00 ** | 0.31 | 0.00 ** | 0.35 | 0.00 ** | 0.14 | 0.00 ** | 0.31 | 0.00 ** |
| HDL-P (μmol/L) | −0.09 | 0.03 * | −0.06 | 0.17 | −0.09 | 0.03 * | −0.14 | 0.00 ** | −0.10 | 0.02 * |
| Large HDL-P (μmol/L) | 0.19 | 0.00 ** | 0.17 | 0.00 ** | 0.27 | 0.00 ** | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.00 ** |
| Medium HDL-P (μmol/L) | −0.36 | 0.00 ** | −0.46 | 0.00 ** | −0.55 | 0.00 ** | −0.31 | 0.00 ** | −0.48 | 0.00 ** |
| Small HDL-P (μmol/L) | 0.10 | 0.01 * | 0.21 | 0.00 ** | 0.23 | 0.00 ** | 0.00 | 0.96 | 0.17 | 0.00 ** |
| VLDL-Z (nm) | −0.27 | 0.00 ** | −0.44 | 0.00 ** | −0.40 | 0.00 ** | −0.21 | 0.00 ** | −0.33 | 0.00 ** |
| LDL-Z (nm) | −0.38 | 0.00 ** | −0.53 | 0.00 ** | −0.51 | 0.00 ** | −0.35 | 0.00 ** | −0.47 | 0.00 ** |
| HDL-Z (nm) | −0.45 | 0.00 ** | −0.62 | 0.00 ** | −0.74 | 0.00 ** | −0.34 | 0.00 ** | −0.61 | 0.00 ** |
| NON-HDL-P (nmol/L) | 0.29 | 0.00 ** | 0.37 | 0.00 ** | 0.43 | 0.00 ** | 0.17 | 0.00 ** | 0.38 | 0.00 ** |
| TOTAL-P/HDL-P | 0.28 | 0.00 ** | 0.32 | 0.00 ** | 0.39 | 0.00 ** | 0.21 | 0.00 ** | 0.35 | 0.00 ** |
| LDL-P/HDL-P | 0.17 | 0.00 ** | 0.19 | 0.00 ** | 0.25 | 0.00 ** | 0.13 | 0.00 ** | 0.23 | 0.00 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amigó, N.; Fuertes-Martín, R.; Malo, A.I.; Plana, N.; Ibarretxe, D.; Girona, J.; Correig, X.; Masana, L. Glycoprotein Profile Measured by a 1H-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Based on Approach in Patients with Diabetes: A New Robust Method to Assess Inflammation. Life 2021, 11, 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121407
Amigó N, Fuertes-Martín R, Malo AI, Plana N, Ibarretxe D, Girona J, Correig X, Masana L. Glycoprotein Profile Measured by a 1H-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Based on Approach in Patients with Diabetes: A New Robust Method to Assess Inflammation. Life. 2021; 11(12):1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121407
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmigó, Núria, Rocío Fuertes-Martín, Ana Irene Malo, Núria Plana, Daiana Ibarretxe, Josefa Girona, Xavier Correig, and Lluís Masana. 2021. "Glycoprotein Profile Measured by a 1H-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Based on Approach in Patients with Diabetes: A New Robust Method to Assess Inflammation" Life 11, no. 12: 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121407
APA StyleAmigó, N., Fuertes-Martín, R., Malo, A. I., Plana, N., Ibarretxe, D., Girona, J., Correig, X., & Masana, L. (2021). Glycoprotein Profile Measured by a 1H-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Based on Approach in Patients with Diabetes: A New Robust Method to Assess Inflammation. Life, 11(12), 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121407






