An Outline of Renal Artery Stenosis Pathophysiology—A Narrative Review
Abstract
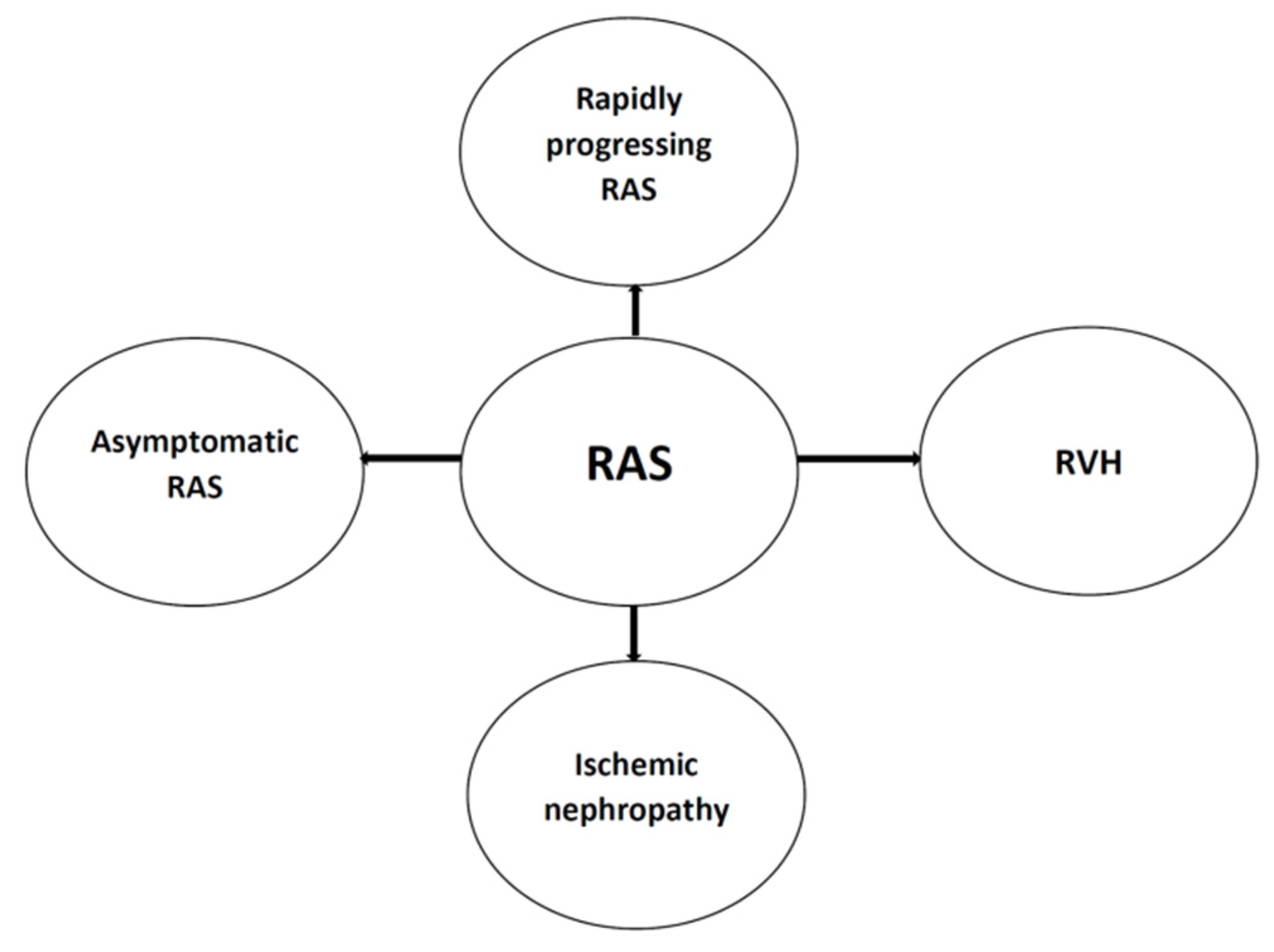
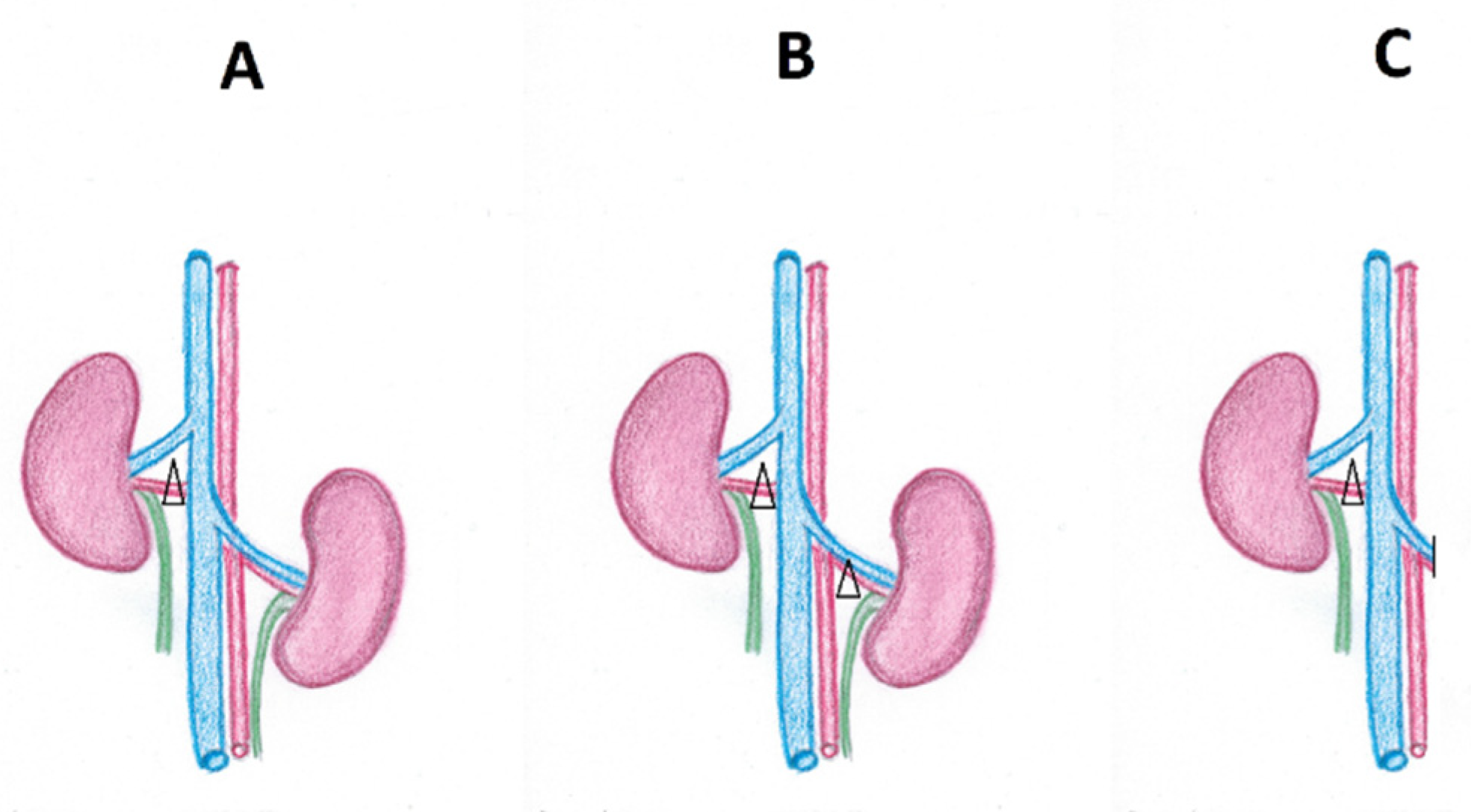
:1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology of Renovascular Hypertension
2.1. The Role of the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System
2.2. The Participation of Functional Mechanisms Functionally Associated with RAAS
2.3. The Sympathetic Nervous System
2.4. The Recruitment of Additional Mechanisms
3. Ischemic Nephropathy
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | angiotensin converting enzyme |
| ACEI | angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors |
| AII | angiotensin II |
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| ARAS | atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis |
| ARB | angiotensin II AT1 receptor blockers |
| BK | bradykinin |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| COX-2 | cyclooxygenase-2 |
| ET | endothelin |
| ETA/ETB | endothelin A or B receptors |
| FMD | fibromuscular dysplasia |
| GFR | glomerular filtration rate |
| JG | juxtaglomerular apparatus |
| KKS | kallikrein-kinin system |
| NA | noradrenaline |
| PVN | paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus |
| RAAS | renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system |
| RAS | renal artery stenosis |
| RBF | renal blood flow |
| RVH | renovascular hypertension |
| RVLM | rostral ventrolateral medulla |
| SNS | sympathetic nervous system |
References
- Herrmann, S.M.; Textor, S.C. Renovascular hypertension. Endocrinol. Metabol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 48, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safian, R.D.; Textor, S.C. Renal-Artery Stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadian, F.; Dalili, N.; Jamalian, A. New insights into pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of renovascular hyper-tension. Iran. J. Kid Dis. 2017, 11, 79–89. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, M.A. Renovascular hypertension and ischemic nephropathy. In Atlas of Diseases of the Kidney. Hypertension and the Kidney; Schrier, R.W., Wilcox, C.S., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1999; Volume 3, pp. 3.1–3.21. [Google Scholar]
- Bruni, K.R. Renovascular Hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2001, 15, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rohani, M. Renovascular hypertension. Saudi. J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 2003, 14, 497–510. [Google Scholar]
- Di Monaco, S.; Georges, A.; Lengelé, J.-P.; Vikkula, M.; Persu, A. Genomics of Fibromuscular Dysplasia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marks, S.D.; Gullett, A.M.; Brennan, E.; Tullus, K.; Jaureguiberry, G.; Klootwijk, E.; Stanescu, H.C.; Kleta, R.; Woolf, A.S. Renal FMD may not confer a familial hypertensive risk nor is it caused by ACTA2 mutations. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2011, 26, 1857–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Wu, M.C.; Lin, X. Optimal tests for rare variant effects in sequencing association studies. Biostatistics 2012, 13, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiando, S.R.; Tucker, N.R.; Castro-Vega, L.-J.; Katz, A.; D’Escamard, V.; Tréard, C.; Fraher, D.; Albuisson, J.; Kadian-Dodov, D.; Ye, Z.; et al. PHACTR1 Is a Genetic Susceptibility Locus for Fibromuscular Dysplasia Supporting Its Complex Genetic Pattern of Inheritance. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gornik, H.L.; Persu, A.; Adlam, D.; Aparicio, L.S.; Azizi, M.; Boulanger, M.; Bruno, R.M.; De Leeuw, P.; Fendrikova-Mahlay, N.; Froehlich, J.; et al. First International Consensus on the diagnosis and management of fibromuscular dysplasia. Vasc. Med. 2019, 24, 164–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Missouris, C.G.; Barley, J.; Jeffery, S.; Carter, N.D.; Singer, D.R.; MacGregor, G.A. Genetic risk for renal artery stenosis: Association with deletion polymorphism in angiotensin 1-converting enzyme gene. Kidney Int. 1996, 49, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Onna, M.; Kroon, A.A.; Houben, A.J.; Koster, D.; Zeegers, M.P.; Henskens, L.H.; Plat, A.W.; Stoffers, H.E.; de Leeuw, P.W. Genetic risk of atherosclerotic renal artery disease: The candidate gene approach in a renal angiography cohort. Hypertension 2004, 44, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Senitko, M.; Fenves, A.Z. An Update on Renovascular Hypertension. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2005, 7, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, W.J. Renovascular Hypertension: An Update. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2008, 10, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, L.; Triscott, J.; Dobbs, B. Secondary Hypertension: Discovering the Underlying Cause. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 453–461. [Google Scholar]
- Dieter, R.S.; Weber, B.R. Renal artery stenosis: Epidemiology and treatment. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2014, 7, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colyer, W.R.; Eltahawy, E.; Cooper, C.J. Renal Artery Stenosis: Optimizing Diagnosis and Treatment. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2011, 54, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manaktala, R.; Tafur-Soto, J.D.; White, C.J. Renal Artery Stenosis in the Patient with Hypertension: Prevalence, Impact and Management. Integr. Blood Press. Control. 2020, 13, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Textor, S.C.; McKusick, M.M. Renal artery stenosis: If and when to intervene. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2016, 25, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, D.; Kalra, P.A. Atherosclerotic renovascular disease—Epidemiology, treatment and current challenges. Adv. Interv. Cardiol. 2017, 13, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prince, M.; Tafur, J.D.; White, C.J. When and how should we revascularize patients with atherosclerotic renal artery steno-sis? JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 12, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, S.M.; Textor, S.C. Current Concepts in the Treatment of Renovascular Hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2018, 31, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossier, B.C.; Bochud, M.; Devuyst, O. The Hypertension Pandemic: An Evolutionary Perspective. Physiology 2017, 32, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyton, A.C.; Coleman, T.G.; Cowley, A.V., Jr.; Scheel, K.W.; Manning, R.D., Jr.; Norman, R.A., Jr. Arterial pressure regula-tion. Overriding dominance of the kidneys in long-term regulation and in hypertension. Am. J. Med. 1972, 52, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Epps, H.L. Harry Goldblatt and the discovery of renin. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glodny, B.; Glodny, D.E. John Loesch, discoverer of renovscular hypetension and Harry Goldblatt: Two great pioneers in circulation research. Ann. Int. Med. 2006, 144, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, N.; Terragno, N.A. History About the Discovery of the Renin-Angiotensin System. Hypertension 2001, 38, 1246–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riordan, J.F. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme and its relatives. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montani, J.P.; Van Vliet, B.N. General Physiology and Pathophysiology of the Renin-Angiotensin System. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Unger, T., Schölkens, B.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004; Volume 163/1, pp. 3–29. [Google Scholar]
- Atlas, S.A. The Renin-Angiotensin Aldosterone System: Pathophysiological Role and Pharmacologic Inhibition. J. Manag. Care Pharm. 2007, 13, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaszczewska-Markowska, M.; Sagan, M.; Bogunia-Kubik, K. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)—Physiology and molecular mechanisms of functioning. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2016, 70, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Červenka, L.; Horáček, V.; Vaněčková, I.; Hubáček, J.A.; Oliverio, M.I.; Coffman, T.M.; Navar, L.G. Essential Role of AT 1A Receptor in the Development of 2K1C Hypertension. Hypertension 2002, 40, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navar, L.G.; Zou, L.; Von Thun, A.; Tarng Wang, C.; Imig, J.D.; Mitchell, K.D. Unraveling the Mystery of Goldblatt Hyper-tension. News Physiol. Sci. 1998, 13, 170–176. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, M.K.; Ramos, S.P.; Geary, K.M.; Norling, L.L.; Peach, M.J.; Gomez, R.A.; Carey, R.M. Colocalization and release of angiotensin and renin in renal cortical cells. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1992, 263, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagami, T.; Mizuno, K.; Naruse, K.; Okamura, T.; Kawamura, M. Intracellular formation and release of angiotensins from juxtaglomerular cells. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1990, 30, S33–S37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ingelfinger, J.R.; Zuo, W.M.; Fon, E.A.; Ellison, K.E.; Dzau, V.J. In situ hybridization evidence for angiotensinogen messen-ger RNA in the rat proximal tubule. An hypothesis for the intrarenal renin angiotensin system. J. Clin. Invest. 1990, 85, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reckelhoff, J.F.; Romero, J.C. Role of oxidative stress in angiotensin-induced hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2003, 284, R893–R912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Navar, L.G.; Harrison-Bernard, L.M. Intrarenal Angiotensin II Augmentation in Angiotensin II Dependent Hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2000, 23, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Kats, J.P.; Schalekamp, M.A.; Verdouw, P.D.; Duncker, D.J.; Danser, A.H. Intrarenal angiotensin II: Interstitial and cellular levels and site of production. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 2311–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vío, C.P.; Jeanneret, V.A. Local induction of angiotensin-converting enzyme in the kidney as a mechanism of progressive renal diseases. Kidney Int. 2003, 64, S57–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dahl, L.K.; Heine, M. Primary role of renal homgrafts in setting chronic blood pressure levels in rats. Circ. Res. 1975, 36, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zicha, J.; Dobešová, Z.; Vokurková, M.; Rauchová, H.; Hojná, S.; Kadlecová, M.; Behuliak, M.; Vaněčková, I.; Kuneš, J. Age-dependent salt hypertension in Dahl rats: Fifty years of research. Physiol. Res. 2012, 61, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohan, D.E. Endothelin, hypertension and chronic kidney disease: New insights. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2010, 19, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, R.; Chauvin, A.; Chakraborty, R.; Nair, N.; Shah, H.; Krishnappa, V.; Kusumi, K. The role of endothelin and endo-thelin antagonists in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Dis. 2020, 6, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anguiano, L.; Riera, M.; Pascual, J.; Soler, M.J. Endothelin Blockade in Diabetic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 4, 1171–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davenport, A.P.; Hyndman, K.A.; Dhaun, N.; Southan, C.; Kohan, D.E.; Pollock, J.S.; Pollock, D.M.; Webb, D.J.; Maguire, J.J. Endothelin. Pharmacol. Rev. 2016, 68, 357–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawanabe, Y.; Nauli, S.M. Endothelin. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignon-Zellweger, N.; Heiden, S.; Miyauchi, T.; Emoto, N. Endothelin and endothelin receptors in the renal and cardiovas-cular systems. Life Sci. 2012, 91, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masaki, T.; Sawamura, T. Endothelin and endothelial dysfunction. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B. 2006, 82, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nandagopal, A.; Shamsia, M.U. A Review on Endothelins: An Update. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2018, 11, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maguire, J.J.; Davenport, A.P. Endothelin Receptors and Their Antagonists. Semin. Nephrol. 2015, 35, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enevoldsen, F.C.; Sahana, J.; Wehland, M.; Grimm, D.; Infanger, M.; Krüger, M. Endothelin Receptor Antagonists: Status Quo and Future Perspectives for Targeted Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, G.P.; Sacchetto, A.; Cesari, M.; Pessina, A.C. Interactions between endothelin-1 and the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system. Cardiovasc. Res. 1999, 43, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan, D.E.; Barton, M. Endothelin and endothelin antagonists in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kittikulsuth, W.; Pollock, J.S.; Pollock, D.M. Loss of renal medullary endothelin B receptor function during salt deprivation is regulated by angiotensin II. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2012, 303, F659–F666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bryant, J.W.; Shariat-Madar, Z. Human plasma kallikrein-kinin system: Physiological and biochemical parameters. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents Med. Chem. 2009, 7, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhaleb, N.-E.; Yang, X.-P.; Carretero, O.A. The Kallikrein-Kinin System as a Regulator of Cardiovascular and Renal Function. Compr. Physiol. 2011, 1, 971–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, J.B. Different cross-talk sites between the renin–angiotensin and the kallikrein–kinin systems. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2013, 15, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kashuba, E.; Bailey, J.; Allsup, D.; Cawkwell, L. The kinin–kallikrein system: Physiological roles, pathophysiology and its relationship to cancer biomarkers. Biomarkers 2013, 18, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcondes, S.; Antunes, E. The Plasma and Tissue Kininogen-kallikrein-kinin System: Role in the Cardiovascular System. Curr. Med. Chem. Hematol. Agents 2005, 3, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.N.; Al-Sherif, G.J. The Kinin System: Present and Future Pharmacological Targets. Am. J. Biomed. Sci. 2011, 3, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, M.E.; Garbacki, N.; Molinaro, G.; Brown, N.J.; Marceau, F.; Adam, A. The kallikrein-kinin system: Current and future pharmacological targets. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 99, 6–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmaier, A.H. The kallikrein-kinin and the renin-angiotensin systems have a multilayered interaction. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2003, 285, R1–R13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oparil, S. The sympathetic nervous system in clinical and experimental hypertension. Kidney Int. 1986, 30, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grisk, O.; Rettig, R. Interactions between the sympathetic nervous system and the kidneys in arterial hypertension. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 61, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genova, G.C.; Veglio, F.; Rabbia, F.; Milan, A.; Grosso, T.; Chiandussi, L. Baroreflex Sensitivity in Secondary Hypertension. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2001, 23, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, R.R.; Nishi, E.E.; Paton, J.F.R.; Bergamaschi, C.T.; Oliveira-Sales, E.B. Mechanisms of renal sympathetic activation in renovascular hypertension. Exp. Physiol. 2015, 100, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grassi, G.; Esler, M. The sympathetic nervous system in renovascular hypertension: Lead actor or “bit” player? J. Hypertens. 2002, 20, 1071–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.M.; Strawn, W.B. Role of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and proinflammatory mediators in cardio-vascular disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 98, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, B.M.; Mehta, A.A. Aldosterone and angiotensin: Role in diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 697, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüster, C.; Wolf, G. Angiotensin II as a Morphogenic Cytokine Stimulating Renal Fibrogenesis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, S.I.; Choi, M.E. Therapeutic targets for treating fibrotic kidney diseases. Transl. Res. 2015, 165, 512–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vanhove, T.; Goldschmeding, R.; Kuypers, D. Kidney fibrosis: Origins and interventions. Transplantation 2017, 101, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawrys, J.; Gawrys, K.; Szahidewicz-Krupska, E.; Derkacz, A.; Mochol, J.; Doroszko, A. Interactions between the Cyclooxygenase Metabolic Pathway and the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Systems: Their Effect on Cardiovascular Risk, from Theory to the Clinical Practice. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.C.; Zhang, M.-Z.; Cheng, H.-F. Cyclooxygenase-2 and the renal renin-angiotensin system. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2004, 181, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komhoff, M.; Jeck, N.D.M.; Seyberth, H.W.; Grone, H.J.; Nusing, R.M.; Breyer, M.D. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is associ-ated with the renal macula densa of patients with Bartter-like syndrome. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 2420–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovacs, G.; Peti-Peterdi, J.; Rosivall, L.; Bell, P.D. Angiotensin II directly stimulates macula densa Na-2Cl-K cotransport via apical AT1 receptors. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2002, 282, F301–F306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuhki, K.; Kashiwagi, H.; Kojima, F.; Kawabe, J.; Ushikubi, F. Roles of prostanoids in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases. Int. Angiol. 2010, 29, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fujino, T.; Nakagawa, N.; Yuhki, K.-I.; Hara, A.; Yamada, T.; Takayama, K.; Kuriyama, S.; Hosoki, Y.; Takahata, O.; Taniguchi, T.; et al. Decreased susceptibility to renovascular hypertension in mice lacking the prostaglandin I2 receptor IP. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schweda, F.; Klar, J.; Narumiya, S.; Nüsing, R.M.; Kurtz, A. Stimulation of renin release by prostaglandin E2 is mediated by EP2 and EP4 receptors in mouse kidneys. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2004, 287, F427–F433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quadri, S.S.; Culver, S.A.; Li, C.; Siragy, H.M. Interaction of the renin angiotensin and COX systems in the kidney. Front. Biosci. 2016, 8, 215–226. [Google Scholar]
- Moro, M.G.; Sanchez, P.K.V.; Lupepsa, A.C.; Baller, E.M.; Franco, G.C.N. Cyclooxygenase biology in renal function—Literature review. Rev. Colomb. Nefrol. 2017, 4, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xia, W.; Zhao, F.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, A.; Huang, S.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, Y. Prostaglandins in the pathogenesis of kidney diseases. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 26586–26602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jakubczyk, K.; Dec, K.; Kałduńska, J.; Kawczuga, D.; Kochman, J.; Janda, K. Reactive oxygen species—Sources, functions, oxidative damage. Pol. Med. J. 2020, 48, 124–127. [Google Scholar]
- Manisha, N.; Wahidul, H.; Richa, R.; Deepali, J. Oxidative stress and antioxidants: An overview. IJARR 2017, 2, 110–119. [Google Scholar]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D.; et al. Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campos, R.R.; Oliveira-Sales, E.B.; Nishi, E.E.; Boim, M.A.; Dolnikoff, M.S.; Bergamaschi, C.T. The role of oxidative stress in renovascular hypertension. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2011, 38, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doughan, A.K.; Harrison, D.G.; Dikalov, S.I. Molecular mechanisms of angiotensin II-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction: Linking mitochondrial oxidative damage and vascular endothelial dysfunction. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirofumi, H.; Hideyasu, K.; Akira, N. Angiotensin II and oxidative stress. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2007, 22, 311–315. [Google Scholar]
- Textor, S.C. Renovascular hypertension in 2007: Where are we now? Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2007, 9, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, O.; Schreiber, J.; Geiger, H.; Pedrazzini, T.; Busse, R.; Brandes, R. gp91phox-Containing NADPH Oxidase Mediates Endothelial Dysfunction in Renovascular Hypertension. Circulation 2004, 109, 1795–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Welch, W.J.; Mendonca, M.; Aslam, S.; Wilcox, C.S. Roles of Oxidative Stress and AT 1 Receptors in Renal Hemodynamics and Oxygenation in the Postclipped 2K,1C Kidney. Hypertension 2003, 41, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parildar, M.; Parildar, Z.; Oran, I.; Kabaroglu, C.; Memis, A.; Bayindir, O. Nitric Oxide and Oxidative Stress in Atherosclerotic Renovascular Hypertension: Effect of Endovascular Treatment. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2003, 14, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Textor, S.C.; Lerman, L. Renovascular hypertension and ischemic nephropathy. Am. J. Hypertens. 2010, 23, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epstein, F.H. Oxygen and renal metabolism. Kidney Int. 1997, 51, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gloviczki, M.L.; Glockner, J.F.; Lerman, L.O.; McKusick, M.A.; Misra, S.; Grande, J.P.; Textor, S.C. Preserved Oxygenation Despite Reduced Blood Flow in Poststenotic Kidneys in Human Atherosclerotic Renal Artery Stenosis. Hypertension 2010, 55, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garovic, V.D.; Textor, S.C. Renovascular Hypertension and Ischemic Nephropathy. Circulation 2005, 112, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Saad, A.; Herrmann, S.M.; Massat, A.E.; McKusick, M.A.; Misra, S.; Lerman, L.O.; Textor, S.C. Changes in inflammatory biomarkers after renal revascularization in atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Textor, S.C. Renal Arterial Disease and Hypertension. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 101, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanjwal, K.; Figueredo, V.M. Controversies in the management of the renal artery stenosis. Cardiol. J. 2013, 20, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Textor, S.; Mailloux, L.U. Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease Resulting from Atherosclerotic Renal Artery Stenosis. Literature Review Current Through October 2020. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-manifestations-and-diagnosis-of-chronic-kidney-disease-resulting-from-atherosclerotic-renal-artery-stenosis?source=related_link (accessed on 14 January 2020).

| Unilateral Stenosis | Bilateral Stenosis | |
|---|---|---|
| Lesion of renal vessels (renal artery or its branches or renal veins) | Unilateral atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis Unilateral fibromuscular dysplasia of renal artery (medial, perimedial, intimal) Renal artery aneurysm Renal arterial embolus Posttraumatic segmental arterial occlusion | Bilateral atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis Stenosis to a solitary functioning kidney |
| Renal parenchymal diseases | Intrarenal compression (carcinoma, sarcoma, metastasis) Extrarenal compression (aortic aneurysm, retroperitoneal hematoma, peripelvic cyst) | |
| Other clinical entities | Arteriovenous malformations Congenital narrowing Systemic vasculitis Arterial nephrosclerosis Rare diseases (type 1 neurofibromatosis, tuberous sclerosis, Ehler’s-Danlos syndrome, Marfan syndrome) | |
| Hypertension characteristics | Onset of hypertension in young patients (<30 years); suggestive of FMD Onset of hypertension at and after about 50 years of age; suggestive of ARAS Abrupt onset of hypertension Acceleration of previously well-controlled hypertension Hypertension refractory to an appropriate 3-drug regimen Features of malignant hypertension No family history of hypertension |
| Renal abnormalities | Unexplained and unprovoked acute kidney injury with/or hypokalemia Acute kidney injury induced by treatment with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II AT1 receptor blockers Unilateral small kidney (asymmetric kidneys with more than 1.5 cm of difference in the size) |
| Other findings | Continuous, high-pitched holosystolic with diastolic component abdominal bruit or flank Recurrent, unexplained flash pulmonary edema even in the absence of severe congestive heart failure Severe retinopathy (Keith-Wagener-Barker grade III or IV optic fundi) Carotid, coronary vascular disease (suggestive of ARAS) History of cigarette smoking |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dobrek, L. An Outline of Renal Artery Stenosis Pathophysiology—A Narrative Review. Life 2021, 11, 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11030208
Dobrek L. An Outline of Renal Artery Stenosis Pathophysiology—A Narrative Review. Life. 2021; 11(3):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11030208
Chicago/Turabian StyleDobrek, Lukasz. 2021. "An Outline of Renal Artery Stenosis Pathophysiology—A Narrative Review" Life 11, no. 3: 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11030208
APA StyleDobrek, L. (2021). An Outline of Renal Artery Stenosis Pathophysiology—A Narrative Review. Life, 11(3), 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11030208






