The Role of Systems Biology in Deciphering Asthma Heterogeneity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Etiology of Asthma
2.1. Genetic Factors
2.2. Environmental and Toxicogenomic Factors
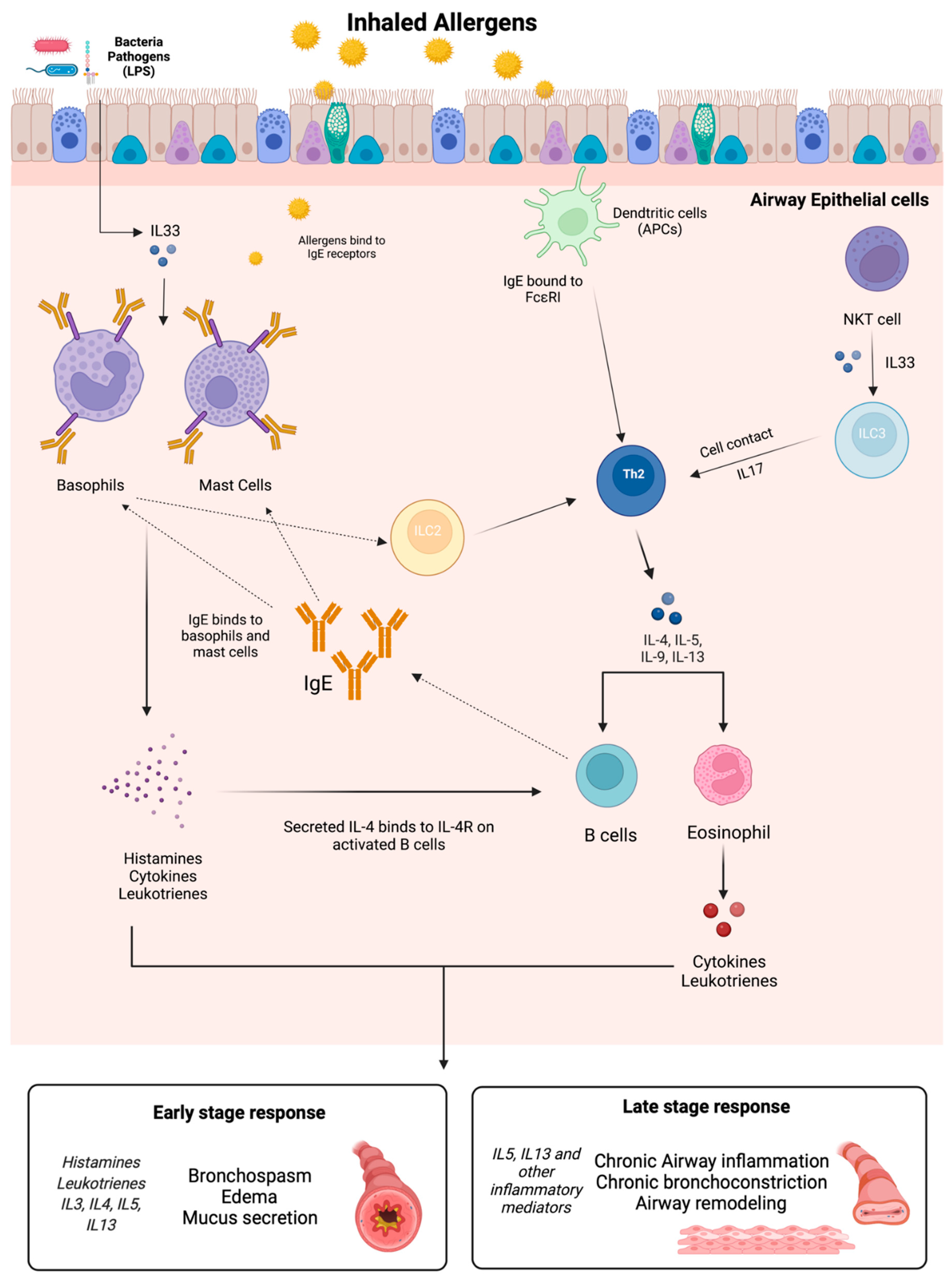
2.3. The Immune System in Asthma
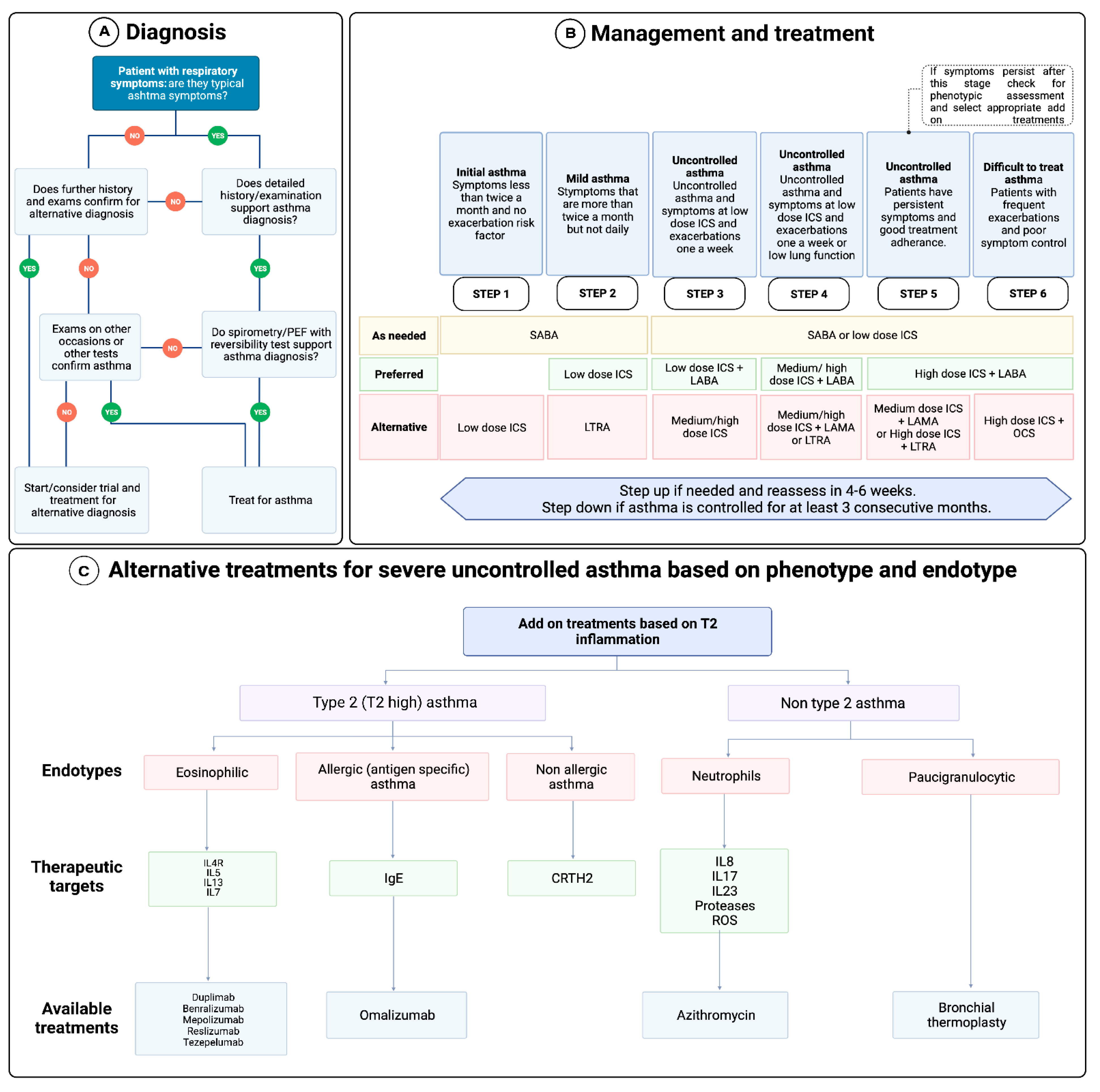
3. Diagnosis and Management
4. Systems Biology
4.1. Why Systems Biology Approach Is Needed in Asthma?
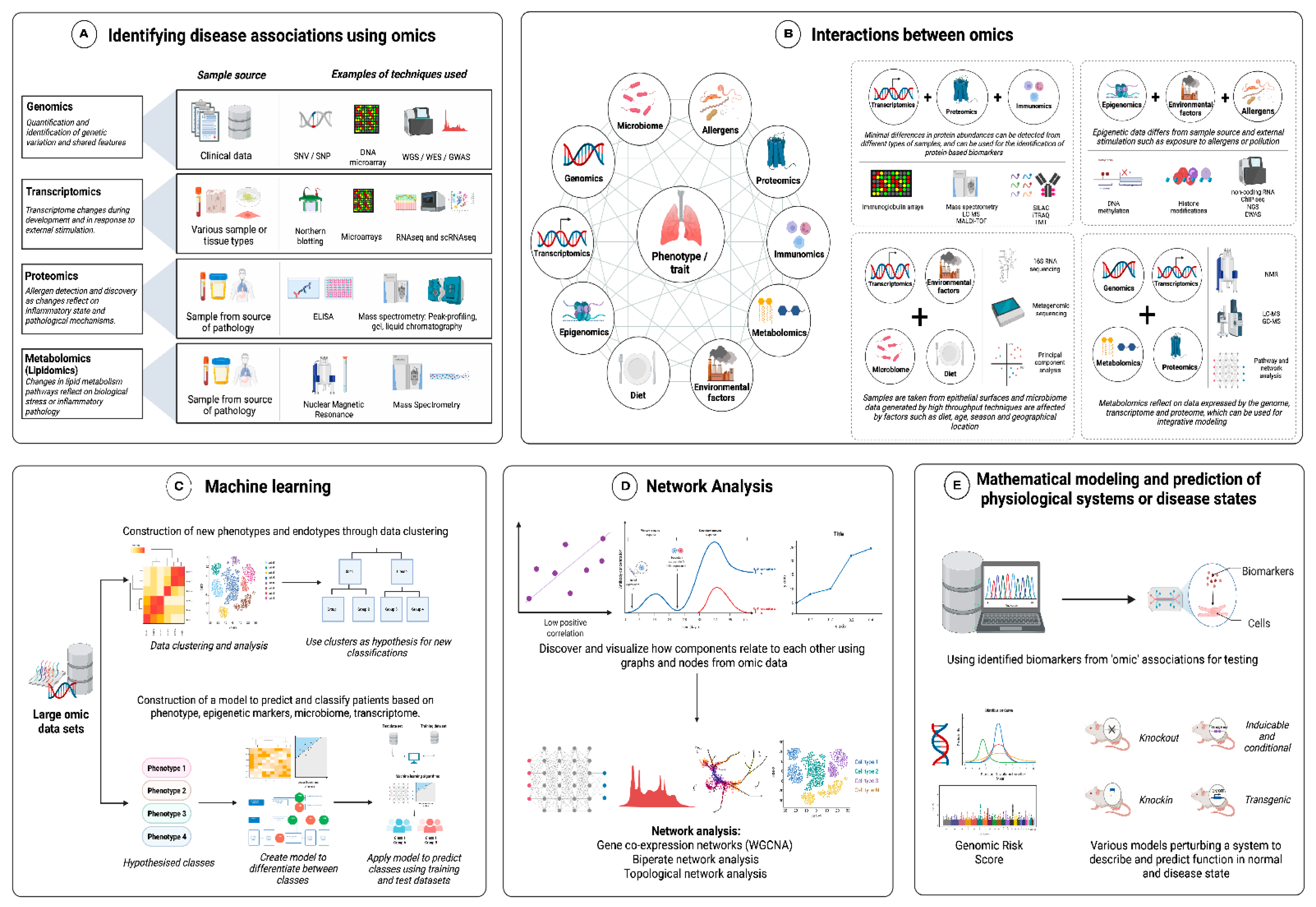
4.2. Multi-Omics
5. Systems Biology Findings and Applications in Asthma
5.1. Asthma Classification, including Phenotyping and Genotyping
5.2. Systems Biology Enables the Identification of Biomarkers
5.3. Genomics and Their Role and Applications in Asthma
5.4. Transcriptomics and Its Applications in Asthma
5.5. Microbiome and Asthma
5.6. Metabolomics and Breathomics in Asthma Research
5.7. Epigenome, Environment, and Asthma
6. Limitations of Systems Biology in Asthma
6.1. Limitations
6.2. Confounding Factors Are a Limitation of Systems Biology
6.3. Data Integration Strategies, Such as Machine Learning, Dimension Reduction, Clustering, and Network Analysis in Asthma
7. Summary of The Issues of Asthma
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braman, S.S. The Global Burden of Asthma. Chest 2006, 130 (Suppl. S1), 4S–12S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, J.J.; Stocks, J.; Kirkham, F.; Rosen, C.L.; Dietzen, D.J.; Semon, T.; Kirkby, J.; Bates, P.; Seicean, S.; DeBaun, M.R.; et al. Airway Hyperresponsiveness in Children with Sickle Cell Anemia. Chest 2011, 139, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, T.; Lim, S.S.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi, M.; Abbasifard, M.; Bhutta, Z.A. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, G.; Vatrella, A.; Maselli, R. Introduction. In Asthma: Targeted Biological Therapies; Pelaia, G., Vatrella, A., Maselli, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Papi, A.; Brightling, C.; Pedersen, E.S.; Reddel, K.H. Seminar Asthma. Lancet 2018, 391, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.J.; Holtzman, M.J. A Centennial History of Research on Asthma Pathogenesis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2005, 32, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.R.; Saglani, S.; Schwarze, J.; Skevaki, C.; Smith, J.A.; Ainsworth, B.; Johnston, S.L. Addressing unmet needs in understanding asthma mechanisms: From the European Asthma Research and Innovation Partnership (EARIP) Work Package (WP) 2 collaborators. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1602448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittka, A.; Vera, J.; Lai, X.; Schmeck, B.T. Asthma phenotyping, therapy, and prevention: What can we learn from systems biology? Pediatr. Res. 2013, 73 Pt 2, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bunyavanich, S.; Schadt, E.E. Systems biology of asthma and allergic diseases: A multiscale approach. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbarao, P.; Mandhane, P.J.; Sears, M.R. Asthma: Epidemiology, etiology and risk factors. CMAJ 2009, 181, E181–E190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ober, C. Asthma Genetics in the Post-GWAS Era. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13 (Suppl. S1), S85–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demenais, F.; Margaritte-Jeannin, P.; Barnes, K.C.; Cookson, W.O.C.; Altmüller, J.; Ang, W.; Barr, R.G.; Beaty, T.H.; Becker, A.B.; Beilby, J.; et al. Multiancestry association study identifies new asthma risk loci that colocalize with immune-cell enhancer marks. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Hizawa, N. Genetics in Asthma. In Advances in Asthma; Yokoyama, A., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Jia, Q.; Jahani, P.S.; Hurrell, B.P.; Pan, C.; Huang, P.; Gukasyan, J.; Woodward, N.C.; Eskin, E.; Gilliland, F.D.; et al. Genome-wide analysis highlights contribution of immune system pathways to the genetic architecture of asthma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, L.E.; Kirkpatrick, B.; Backer, L.C.; Bean, J.A.; Wanner, A.; Reich, A.; Zaias, J.; Cheng, Y.S.; Pierce, R.; Naar, J.; et al. Aerosolized Red-Tide Toxins (Brevetoxins) and Asthma. Chest 2007, 131, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toskala, E.; Kennedy, D.W. Asthma risk factors. Int. Forum. Allergy Rhinol. 2015, 5 (Suppl. S1), S11–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, M.R. Trends in the Prevalence of Asthma. Chest 2014, 145, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, C.; Sheikh, A. Epidemiology of Asthma: A Worldwide Perspective. In Clinical Asthma; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ierodiakonou, D.; Zanobetti, A.; Coull, B.A.; Melly, S.; Postma, D.S.; Boezen, H.M.; Vonk, J.M.; Williams, P.; Shapiro, G.G.; McKone, E.F.; et al. Ambient air pollution, lung function, and airway responsiveness in asthmatic children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, T.; Zhu, Y.; Mu, L.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Liu, S. Pulmonary diseases induced by ambient ultrafine and engineered nanoparticles in twenty-first century. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2016, 3, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foong, R.X.; du Toit, G.; Fox, A.T. Asthma, Food Allergy, and How They Relate to Each Other. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.A.; Solensky, R. Drug allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125 (Suppl. S2), S126–S137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, M.; Lockey, R.F. Aspirin-exacerbated asthma. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2008, 4, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- The, L. Asthma diagnosis and control. Lancet 2015, 385, 482. [Google Scholar]
- Brasier, A.R. Identification of Innate Immune Response Endotypes in Asthma: Implications for Personalized Medicine. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2013, 13, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dharmage, S.C.; Perret, J.L.; Custovic, A. Epidemiology of Asthma in Children and Adults. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogliani, P.; Calzetta, L.; Matera, M.G.; Laitano, R.; Ritondo, B.L.; Hanania, N.A.; Cazzola, M. Severe Asthma and Biological Therapy: When, Which, and for Whom. Pulm. Ther. 2020, 6, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, J.M.; McDonald, V.M.; Guo, M.; Reddel, H. “I have lost in every facet of my life”: The hidden burden of severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papi, A.; Blasi, F.; Canonica, G.W.; Morandi, L.; Richeldi, L.; Rossi, A. Treatment strategies for asthma: Reshaping the concept of asthma management. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2020, 16, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Expert Panel Working Group of the National Heart, Lung; Blood Institute (NHLBI) administered; coordinated National Asthma Education; Prevention Program Coordinating Committee (NAEPPCC); Cloutier, M.M.; Baptist, A.P.; Blake, K.V.; Brooks, E.G.; Bryant-Stephens, T.; DiMango, E.; et al. 2020 Focused Updates to the Asthma Management Guidelines: A Report from the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Coordinating Committee Expert Panel Working Group. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 1217–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzakouk, M.; Ghorab, O.K.H.A.; Mahboub, B.; Alzaabi, A.; Uzbeck, M.H.; Nasir, M.; Zoumot, Z.; Grandon, D.; Abu El Sameed, Y.; Namas, R.; et al. Demographic and clinical patterns of severe asthma in the Middle East. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2021, 16, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragonieri, S.; Carpagnano, G.E. Biological therapy for severe asthma. Asthma Res. Pract. 2021, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.H.; Sly, P.D.; Holt, P.G.; Holt, K.E.; Inouye, M. Systems biology and big data in asthma and allergy: Recent discoveries and emerging challenges. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1900844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhondalay, G.K.; Rael, E.; Acharya, S.; Zhang, W.; Sampath, V.; Galli, S.J.; Tibshirani, R.; Boyd, S.D.; Maecker, H.; Nadeau, K.C.; et al. Food allergy and omics. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee on the Review of Omics-Based Tests for Predicting Patient Outcomes in Clinical Trials. Evolution of Translational Omics: Lessons Learned and the Path Forward; Micheel, C.M., Nass, S.J., Omenn, G.S., Eds.; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 23 March 2012; National Academies Press (US) Copyright 2012 by the National Academy of Sciences. All Rights Reserved. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK202160/ (accessed on 20 August 2022).
- He, Y.; Shi, J.; Nguyen, Q.T.; You, E.; Liu, H.; Ren, X.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Qiu, W.; Khoo, S.K.; et al. Development of highly potent glucocorticoids for steroid-resistant severe asthma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 6932–6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, A.; Adcock, I.M.; Tliba, O. Steroid Resistance in Severe Asthma: Current Mechanisms and Future Treatment. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajt, M.L.; Wenzel, S.E. Asthma phenotypes and the use of biologic medications in asthma and allergic disease: The next steps toward personalized care. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 299–310, quiz 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffat, I.; Chepelev, N.L.; Labib, S.; Bourdon-Lacombe, J.; Kuo, B.; Buick, J.K.; Lemieux, F.; Williams, A.; Halappanavar, S.; Malik, A.I.; et al. Comparison of toxicogenomics and traditional approaches to inform mode of action and points of departure in human health risk assessment of benzo[a]pyrene in drinking water. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2015, 45, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachim, M.Y.; Hachim, I.Y.; Elemam, N.M.; Hamoudi, R.A. Toxicogenomic analysis of publicly available transcriptomic data can predict food, drugs, and chemical-induced asthma. Pharm. Pers. Med. 2019, 12, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matucci, A.; Vivarelli, E.; Nencini, F.; Maggi, E.; Vultaggio, A. IL-13 Augments Histone Demethylase JMJD2B/KDM4B Expression Levels, Activity, and Nuclear Translocation in Airway Fibroblasts in Asthma. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 6629844. [Google Scholar]
- Soliai, M.M.; Kato, A.; Helling, B.A.; Stanhope, C.T.; Norton, J.E.; Naughton, K.A.; Klinger, A.I.; Thompson, E.E.; Clay, S.M.; Kim, S.; et al. Multi-omics colocalization with genome-wide association studies reveals a context-specific genetic mechanism at a childhood onset asthma risk locus. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, S.R.; Chun, Y.; Ribeiro, V.M.; Grishina, G.; Grishin, A.; Hoffman, G.E.; Do, A.N.; Bunyavanich, S. Merged Affinity Network Association Clustering: Joint multi-omic/clinical clustering to identify disease endotypes. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 108975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douwes, J.; Pearce, N. Epidemiology of Allergic Diseases. In Allergy and Asthma; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 31–51. [Google Scholar]
- Nishio, T.; Wakahara, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Nishio, N.; Majima, S.; Nakamura, S.; Teranishi, M.; Nakatochi, M.; Sone, M.; Hasegawa, Y. Mixed cell type in airway inflammation is the dominant phenotype in asthma patients with severe chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergol. Int. 2019, 68, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, T.F.; Zeki, A.A.; Kraft, M. Eosinophilic and Noneosinophilic Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, R.A.; Calhoun, W.J. Introduction to Asthma and Phenotyping. In Heterogeneity in Asthma; Brasier, A.R., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, H.; Kwon, A.; Ramilowski, J.A.; Silberberg, G.; Söderhäll, C.; Orsmark-Pietras, C.; Nordlund, B.; Konradsen, J.R.; de Hoon, M.J.; Melén, E.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of controlled and therapy-resistant childhood asthma reveals distinct gene expression profiles. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.H.S.; Pavlidis, S.; Loza, M.; Baribaud, F.; Rowe, A.; Pandis, I.; Chung, K.F. A Transcriptome-driven Analysis of Epithelial Brushings and Bronchial Biopsies to Define Asthma Phenotypes in U-BIOPRED. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, C.E.; Torr, E.E.; Jamili, N.H.M.; Bosquillon, C.; Sayers, I. Evaluation of Differentiated Human Bronchial Epithelial Cell Culture Systems for Asthma Research. J. Allergy 2012, 2012, 943982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.C.; Bleecker, E.R. Asthma heterogeneity and severity-why is comprehensive phenotyping important? Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, J.C.; Bastarache, L.; Roden, D.M. Phenome-Wide Association Studies as a Tool to Advance Precision Medicine. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2016, 17, 353–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diogo, D.; Tian, C.; Franklin, C.S.; Kinnunen, M.; March, M.; Spencer, C.C.A.; Vangjeli, C.; Weale, M.; Mattsson, H.; Kilpeläinen, E.; et al. Phenome-wide association studies across large population cohorts support drug target validation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappori, A.; De Ferrari, L.; Folli, C.; Mauri, P.; Riccio, A.M.; Canonica, G.W. Biomarkers and severe asthma: A critical appraisal. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2015, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, S.-J.; Tsui, D.W.; Murtaza, M.; Biggs, H.; Rueda, O.M.; Chin, S.-F.; Dunning, M.J.; Gale, D.; Forshew, T.; Mahler-Araujo, B.; et al. Analysis of Circulating Tumor DNA to Monitor Metastatic Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.C.; Woodruff, P.G. Biomarkers in Severe Asthma. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2016, 36, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Ellis, A.K.; Fischer, D.; Noseworthy, M.; Olivenstein, R.; Chapman, K.R.; Lee, J. Asthma biomarkers in the age of biologics. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, A.; Busse, W.W. Biomarkers in asthmatic patients: Has their time come to direct treatment? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiotiu, A. Biomarkers in asthma: State of the art. Asthma Res. Pract. 2018, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.W.; Oh, T.J.; Park, S.-M.; Park, J.S.; Jang, A.S.; Park, S.W.; Uh, S.T.; An, S.; Park, C.-S. Asthma-Predictive Genetic Markers in Gene Expression Profiling of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2011, 3, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachim, M.Y.; Aljaibeji, H.; Hamoudi, R.A.; Hachim, I.Y.; Elemam, N.M.; Mohammed, A.K.; Salehi, A.; Taneera, J.; Sulaiman, N. An Integrative Phenotype–Genotype Approach Using Phenotypic Characteristics from the UAE National Diabetes Study Identifies HSD17B12 as a Candidate Gene for Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Genes 2020, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachim, M.Y.; Elemam, N.M.; Ramakrishnan, R.K.; Salameh, L.; Olivenstein, R.; Hachim, I.Y.; Venkatachalam, T.; Mahboub, B.; Al Heialy, S.; Hamid, Q.; et al. Derangement of cell cycle markers in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of asthmatic patients as a reliable biomarker for asthma control. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ober, C.; Yao, T.-C. The genetics of asthma and allergic disease: A 21st century perspective. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 242, 10–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis-Owen, S.A.; Cookson, W.O.; Moffatt, M.F. The Genetics and Genomics of Asthma. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2018, 19, 223–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portelli, M.; Hodge, E.; Sayers, I. Genetic risk factors for the development of allergic disease identified by genome-wide association. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 45, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Lv, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, K.; Ying, S. Elevated Expression of IL-33 and TSLP in the Airways of Human Asthmatics In Vivo: A Potential Biomarker of Severe Refractory Disease. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, W.; Nie, X. Association of β2-adrenergic receptor gene polymorphisms (rs1042713, rs1042714, rs1042711) with asthma risk: A systematic review and updated meta-analysis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffatt, M.F.; Gut, I.G.; Demenais, F.; Strachan, D.P.; Bouzigon, E.; Heath, S.; von Mutius, E.; Farrall, M.; Lathrop, M.; Cookson, W.O. A Large-Scale, Consortium-Based Genomewide Association Study of Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgerson, D.G.; Ampleford, E.J.; Chiu, G.Y.; Gauderman, W.J.; Gignoux, C.R.; Graves, P.E.; Hancock, D.B. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of asthma in ethnically diverse North American populations. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 887–892. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.-W.; Weiss, S.T. Understanding the Molecular Mechanisms of Asthma through Transcriptomics. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2020, 12, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, Y.; Johansson, E.; Mersha, T.B. Multi-Omics Profiling Approach to Asthma: An Evolving Paradigm. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsmark-Pietras, C.; James, A.; Konradsen, J.R.; Nordlund, B.; Söderhäll, C.; Pulkkinen, V.; Pedroletti, C.; Daham, K.; Kupczyk, M.; Dahlén, B.; et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals upregulation of bitter taste receptors in severe asthmatics. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.-L.; Su, M.-W.; Chiang, B.-L.; Yang, Y.-H.; Tsai, C.-H.; Lee, Y.L. Genetic profiles of transcriptomic clusters of childhood asthma determine specific severe subtype. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachim, M.Y.; Elemam, N.M.; Ramakrishnan, R.K.; Bajbouj, K.; Olivenstein, R.; Hachim, I.Y.; Al Heialy, S.; Hamid, Q.; Busch, H.; Hamoudi, R. Wnt Signaling Is Deranged in Asthmatic Bronchial Epithelium and Fibroblasts. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 645005744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baines, K.J.; Simpson, J.L.; Wood, L.G.; Scott, R.J.; Fibbens, N.L.; Powell, H.; Cowan, D.C.; Taylor, D.R.; Cowan, J.O.; Gibson, P.G. Sputum gene expression signature of 6 biomarkers discriminates asthma inflammatory phenotypes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, B.M.; Bastarache, L.; Turi, K.N.; Zutter, M.M.; Hartert, T.V. The current state of omics technologies in the clinical management of asthma and allergic diseases. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 123, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sbihi, H.; Boutin, R.; Cutler, C.; Suen, M.; Finlay, B.B.; Turvey, S.E. Thinking bigger: How early-life environmental exposures shape the gut microbiome and influence the development of asthma and allergic disease. Allergy 2019, 74, 2103–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.I.; Vijverberg, S.J.H.; Neerincx, A.H.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Der Zee, A.H.M. The crosstalk between microbiome and asthma: Exploring associations and challenges. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 1067–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logotheti, M.; Agioutantis, P.; Katsaounou, P.; Loutrari, H. Microbiome Research and Multi-Omics Integration for Personalized Medicine in Asthma. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, J.F.; Bosco, A. Decoding Susceptibility to Respiratory Viral Infections and Asthma Inception in Children. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.I.; Vijverberg, S.J.H.; Neerincx, A.H.; Brinkman, P.; Wagener, A.H.; Riley, J.H.; Sousa, A.R.; Bates, S.; Wagers, S.S.; De Meulder, B.; et al. A multi-omics approach to delineate sputum microbiome-associated asthma inflammatory phenotypes. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 59, 2102603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A. Persistent Bacterial Bronchitis: Time to Venture beyond the Umbrella. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Atherton, H.J.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L. Systems level studies of mammalian metabolomes: The roles of mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 387–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinke, S.N.; Gallart-Ayala, H.; Gómez, C.; Checa, A.; Fauland, A.; Naz, S.; Kamleh, M.A.; Djukanović, R.; Hinks, T.S.; Wheelock, C.E. Metabolomics analysis identifies different metabotypes of asthma severity. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comhair, S.A.A.; McDunn, J.; Bennett, C.; Fettig, J.; Erzurum, S.C.; Kalhan, S.C. Metabolomic Endotype of Asthma. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntontsi, P.; Ntzoumanika, V.; Loukides, S.; Benaki, D.; Gkikas, E.; Mikros, E.; Bakakos, P. EBC metabolomics for asthma severity. J. Breath Res. 2020, 14, 036007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loureiro, C.C.; Oliveira, A.S.; Santos, M.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Todo-Bom, A.; Bousquet, J.; Rocha, S.M. Urinary metabolomic profiling of asthmatics can be related to clinical characteristics. Allergy 2016, 71, 1362–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pite, H.; Morais-Almeida, M.; Rocha, S.M. Metabolomics in asthma: Where do we stand? Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2018, 24, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, L.; Gheware, A.; Rehman, R.; Yadav, M.K.; Jayaraj, B.S.; Madhunapantula, S.V.; Mabalirajan, U. Linoleic acid metabolite leads to steroid resistant asthma features partially through NF-kappaB. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, B.; Basanta, M.; Cadden, P.; Singh, D.; Douce, D.; Woodcock, A.; Fowler, S.J. Non-invasive phenotyping using exhaled volatile organic compounds in asthma. Thorax 2011, 66, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkman, P.; Ahmed, W.M.; Gómez, C.; Knobel, H.H.; Weda, H.; Vink, T.J.; Nijsen, T.M.; Wheelock, C.E.; Dahlen, S.-E.; Montuschi, P.; et al. Exhaled volatile organic compounds as markers for medication use in asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1900544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neerincx, A.H.; Vijverberg, S.J.H.; Bos, L.D.J.; Brinkman, P.; Van Der Schee, M.P.; De Vries, R.; Sterk, P.J.; Maitland-van Der Zee, A.-H. Breathomics from exhaled volatile organic compounds in pediatric asthma. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2017, 52, 1616–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Schee, M.P.; Palmay, R.; Cowan, J.O.; Taylor, D.R. Predicting steroid responsiveness in patients with asthma using exhaled breath profiling. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2013, 43, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.L. Epigenetics in Asthma. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2019, 19, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, I.V.; Lozupone, C.A.; Schwartz, D.A. The environment, epigenome, and asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanowicz, D.; Hackett, T.-L.; Garmaroudi, F.S.; Günther, O.; Neumann, S.; Sutanto, E.N.; Ling, K.-M.; Kobor, M.; Kicic, A.; Stick, S.; et al. DNA Methylation Profiles of Airway Epithelial Cells and PBMCs from Healthy, Atopic and Asthmatic Children. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, P.E.; Kim, S.T.; Flavell, R.A. Cutting edge: Changes in histone acetylation at the IL-4 and IFN-gamma loci accompany Th1/Th2 differentiation. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, S.; Kesper, D.A.; Teich, R.; Kilic-Niebergall, E.; Pinkenburg, O.; Bothur, E.; Renz, H. DNA methylation of TH1/TH2 cytokine genes affects sensitization and progress of experimental asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1602–1610.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seumois, G.; Chavez, L.; Gerasimova, A.; Lienhard, M.; Omran, N.; Kalinke, L.; Vedanayagam, M.; Ganesan, A.P.V.; Chawla, A.; Djukanovic, R.; et al. Epigenomic analysis of primary human T cells reveals enhancers associated with TH2 memory cell differentiation and asthma susceptibility. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taka, S.; Tzani-Tzanopoulou, P.; Wanstall, H.; Papadopoulos, N.G. MicroRNAs in Asthma and Respiratory Infections: Identifying Common Pathways. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2020, 12, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, I.S.; Czieso, S.; Ktistaki, E.; Roderick, K.; Coomes, S.M.; Pelly, V.S.; Kannan, Y.; Perez-Lloret, J.; Zhao, J.L.; Baltimore, D.; et al. Transcriptomics identified a critical role for Th2 cell-intrinsic miR-155 in mediating allergy and antihelminth immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E3081–E3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinius, L.E.; Gref, A.; Sääf, A.; Acevedo, N.; Joerink, M.; Kupczyk, M.; D’Amato, M.; Bergström, A.; Melén, E.; Scheynius, A.; et al. DNA Methylation in the Neuropeptide S Receptor 1 (NPSR1) Promoter in Relation to Asthma and Environmental Factors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chogtu, B.; Bhattacharjee, D.; Magazine, R. Epigenetics: The New Frontier in the Landscape of Asthma. Scientifica 2016, 2016, 4638949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, A.; Petersen, H.; Blanchette, C.M.; Meek, P.; Picchi, M.A.; Belinsky, S.A.; Tesfaigzi, Y. Methylated Genes in Sputum among Older Smokers with Asthma. Chest 2012, 142, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Soto-Ramírez, N.; Arshad, S.H.; Holloway, J.W.; Zhang, H.; Schauberger, E.; Ewart, S.; Patil, V.; Karmaus, W. The interaction of genetic variants and DNA methylation of the interleukin-4 receptor gene increase the risk of asthma at age 18 years. Clin. Epigenet. 2013, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, R.P.; Kenny, L.C. ‘Omic’ technologies: Genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics and metabolomics. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2011, 13, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, K.C. Genetic Studies of the Etiology of Asthma. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2011, 8, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forno, E.; Celedon, J.C. Epigenomics and Transcriptomics in the Prediction and Diagnosis of Childhood Asthma: Are We There Yet? Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, M.C.; Busse, W.W. A Deep Dive into Asthma Transcriptomics. Lessons from U-BIOPRED. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 1279–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, S.T.; Raby, B.A.; Celedón, J.C. Asthma Genomics. In Essentials of Genomic and Personalized Medicine; Ginsburg, G.S., Willard, H.F., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 590–602. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente, C.T.; Revez, J.A.; Ferreira, M.A.R. Lessons from ten years of genome-wide association studies of asthma. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2017, 6, e165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, R.; Shirley, N.; Bleackley, M.; Dolan, S.; Shafee, T. Transcriptomics technologies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calza, S.; Pawitan, Y. Normalization of Gene-Expression Microarray Data. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 673, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Hong, Q.; Liu, J.; Tong, W.; Shi, L. Estimating relative noise to signal in DNA microarray data. Int. J. Bioinform. Res. Appl. 2013, 9, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansel, N.N.; Diette, G.B. Gene Expression Profiling in Human Asthma. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2007, 4, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, P.A.; Smyth, G.K.; Robins-Browne, R.; Curtis, N. Technical Variability Is Greater than Biological Variability in a Microarray Experiment but Both Are Outweighed by Changes Induced by Stimulation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novianti, P.W.; Van Der Tweel, I.; Jong, V.L.; Roes, K.C.B.; Eijkemans, M.J.C. An Application of Sequential Meta-Analysis to Gene Expression Studies. Cancer Inform. 2015, 14 (Suppl. S5), CIN.S27718-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.D.; Park, P.J. Improving identification of differentially expressed genes in microarray studies using information from public databases. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modena, B.D.; Tedrow, J.R.; Milosevic, J.; Bleecker, E.R.; Meyers, D.A.; Wu, W.; Bar-Joseph, Z.; Erzurum, S.C.; Gaston, B.M.; Busse, W.W.; et al. Gene Expression in Relation to Exhaled Nitric Oxide Identifies Novel Asthma Phenotypes with Unique Biomolecular Pathways. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 1363–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.I.; Neerincx, A.H.; Vijverberg, S.J.; Hashimoto, S.; Brinkman, P.; Gorenjak, M. A System Pharmacology Multi-Omics Approach toward Uncontrolled Pediatric Asthma. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, S.F. Genetics of asthma: An introduction for the clinician. Eur. Clin. Respir. J. 2015, 2, 24643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglino, N.; Roth, M.; Baty, F.; Brutsche, M.; Tamm, M.; Borger, P. Asthma and the regulated retrotransposon transcriptome. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 788–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leek, J.T.; Scharpf, R.B.; Bravo, H.C.; Simcha, D.; Langmead, B.; Johnson, W.; Geman, D.; Baggerly, K.; Irizarry, R.A. Tackling the widespread and critical impact of batch effects in high-throughput data. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toubia, J.; Conn, V.M.; Conn, S.J. Don’t go in circles: Confounding factors in gene expression profiling. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e97945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhou, X. Controlling for Confounding Effects in Single Cell RNA Sequencing Studies Using both Control and Target Genes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruning, O.; Rodenburg, W.; Wackers, P.; Van Oostrom, C.; Jonker, M.J.; Dekker, R.J.; Rauwerda, H.; Ensink, W.A.; De Vries, A.; Breit, T.M. Confounding Factors in the Transcriptome Analysis of an In-Vivo Exposure Experiment. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0145252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachim, M.Y.; Elemam, N.M.; Maghazachi, A.A. The Beneficial and Debilitating Effects of Environmental and Microbial Toxins, Drugs, Organic Solvents and Heavy Metals on the Onset and Progression of Multiple Sclerosis. Toxins 2019, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinke, S.N.; Galindo-Prieto, B.; Skotare, T.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Singhania, A.; Horowitz, D.; Wheelock, C.E. OnPLS-Based Multi-Block Data Integration: A Multivariate Approach to Interrogating Biological Interactions in Asthma. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13400–13408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustine, T.; Al-Aghbar, M.A.; Al-Kowari, M.; Espino-Guarch, M.; van Panhuys, N. Asthma and the Missing Heritability Problem: Necessity for Multiomics Approaches in Determining Accurate Risk Profiles. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 822324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radzikowska, U.; Baerenfaller, K.; Cornejo-Garcia, J.A.; Karaaslan, C.; Barletta, E.; Sarac, B.E.; Zhakparov, D.; Villaseñor, A.; Eguiluz-Gracia, I.; Mayorga, C.; et al. Omics technologies in allergy and asthma research: An EAACI position paper. Allergy 2022, 77, 2888–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillien, A.; Lepeule, J.; Seyve, E.; Le Moual, N.; Pin, I.; Degano, B.; Garcia-Aymerich, J.; Pépin, J.-L.; Pison, C.; Dumas, O.; et al. Profile of exposures and lung function in adults with asthma: An exposome approach in the EGEA study. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anto, J.M.; Bousquet, J.; Akdis, M.; Auffray, C.; Keil, T.; Momas, I.; Postma, D.S.; Valenta, R.; Wickman, M.; Cambon-Thomsen, A.; et al. Mechanisms of the Development of Allergy (MeDALL): Introducing novel concepts in allergy phenotypes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Subtypes | Definition |
|---|---|
| PBB—micro | History of chronic cough; positive BAL cultures; 2-week amoxicillin–clavulanic acid course |
| PBB—clinical | History of chronic cough; 2-week amoxicillin–clavulanic acid course |
| PBB—extended | PBB-micro or PBB extended; 4-week antibiotic course |
| PBB—recuring | More than 3 attacks of PBB-micro or PBB-clinical annually |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hachim, M.Y.; Alqutami, F.; Hachim, I.Y.; Heialy, S.A.; Busch, H.; Hamoudi, R.; Hamid, Q. The Role of Systems Biology in Deciphering Asthma Heterogeneity. Life 2022, 12, 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101562
Hachim MY, Alqutami F, Hachim IY, Heialy SA, Busch H, Hamoudi R, Hamid Q. The Role of Systems Biology in Deciphering Asthma Heterogeneity. Life. 2022; 12(10):1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101562
Chicago/Turabian StyleHachim, Mahmood Yaseen, Fatma Alqutami, Ibrahim Yaseen Hachim, Saba Al Heialy, Hauke Busch, Rifat Hamoudi, and Qutayba Hamid. 2022. "The Role of Systems Biology in Deciphering Asthma Heterogeneity" Life 12, no. 10: 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101562
APA StyleHachim, M. Y., Alqutami, F., Hachim, I. Y., Heialy, S. A., Busch, H., Hamoudi, R., & Hamid, Q. (2022). The Role of Systems Biology in Deciphering Asthma Heterogeneity. Life, 12(10), 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101562








