Abstract
The clinical diagnosis of oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum (OAVS) is established when microtia is present in association with hemifacial hypoplasia (HH) and/or ocular, vertebral, and/or renal malformations. Genetic and non-genetic factors have been associated with microtia/OAVS. Although the etiology remains unknown in most patients, some cases may have an autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or multifactorial inheritance. Among the possible genetic factors, gene–gene interactions may play important roles in the etiology of complex diseases, but the literature lacks related reports in OAVS patients. Therefore, we performed a gene–variant interaction analysis within five microtia/OAVS candidate genes (HOXA2, TCOF1, SALL1, EYA1 and TBX1) in 49 unrelated OAVS Mexican patients (25 familial and 24 sporadic cases). A statistically significant intergenic interaction (p-value < 0.001) was identified between variants p.(Pro1099Arg) TCOF1 (rs1136103) and p.(Leu858=) SALL1 (rs1965024). This intergenic interaction may suggest that the products of these genes could participate in pathways related to craniofacial alterations, such as the retinoic acid (RA) pathway. The absence of clearly pathogenic variants in any of the analyzed genes does not support a monogenic etiology for microtia/OAVS involving these genes in our patients. Our findings could suggest that in addition to high-throughput genomic approaches, future gene–gene interaction analyses could contribute to improving our understanding of the etiology of microtia/OAVS.
1. Introduction
Microtia (HP:0008551) is a congenital anomaly of heterogeneous etiology that arises from alterations in structures derived from the first and second pharyngeal arches during the embryonic period [1,2,3]. When microtia is associated with hemifacial hypoplasia (HH, HP:0011332) and ocular, vertebral, cardiac, and/or renal malformations, the diagnosis of oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum (OAVS, MIM #164210) is suggested. However, there is no agreement on the minimum diagnostic criteria for OAVS [4,5,6,7,8].
Microtia is a minimal expression of the OAVS clinical spectrum, since both entities have variable phenotypic expression, asymmetric involvement of facial structures, right-side predominance, and male predilection. Moreover, familial occurrence with incomplete penetrance may be seen for microtia and/or related anomalies, such as preauricular tags and pits [9,10,11].
Genetic factors and non-genetic factors have been associated with the etiology of microtia/OAVS. Prenatal exposure to alcohol, retinoids, or maternal diabetes are considered environmental causal factors of this entity [5,12,13]. The genetic contribution to the development of microtia/OAVS is supported by diverse lines of evidence, such as: (a) the identification of families with variable expression and incomplete penetrance segregating as an autosomal dominant (AD), autosomal recessive (AR), or multifactorial trait [10]; (b) the greater concordance between monozygotic versus dizygotic twins (38.5% vs. 4.5%, respectively) [14]; (c) the differences in its prevalence across ethnicities [1], such as in Hispanic (1.12/10,000), U.S.-born Hispanic (0.83/10,000), Asian (0.54/10,000) [15], Pacific Island native (4.61/10,000), and Philippine (4.77/10,000) [16] populations; (d) the finding that murine models develop microtia due to pathogenic variants (PV) in genes orthologous to those identified as mutated in some microtia patients (i.e., Hoxa2, Tcof1, Eya1, and Tbx1) [4,17,18,19,20,21]; and (e) the observation of microtia within the clinical spectrum of more than 50 chromosomal and monogenic syndromes [4,5,22]. Despite these findings, however, the etiology underlying microtia/OAVS in most patients remains unknown.
Recently, several chromosomal abnormalities associated with microtia/OAVS have been described [23]. Genetic studies using next-generation sequencing (NGS) have been performed in patients with this entity [24,25,26,27], but only in a few cases candidate genes have been identified. These include MYT1 (MIM*600379) [23,24,25], AMIGO2 (MIM*615690) [26], ZYG11B (MIM*618673) [27], ZIC3 (MIM*300265) [28], VWA1 (MIM*611901) [29], SF3B2 (MIM*605591) [30], and EYA3 (MIM*601655) [31]. Variants in these genes were identified at a low frequency, supporting the notion that this clinical spectrum has high genetic heterogeneity [32]. Interestingly, the products encoded by MYT1 and ZYG11B are involved in the retinoic acid (RA) signaling pathway [23,27], and prenatal exposure to RA was reported to have a teratogenic effect with a clinical presentation similar to that of microtia/OAVS [13].
Gene–gene interactions have been shown to play important roles in the etiologies of complex diseases [33]. However, the literature lacks any report addressing potential gene interactions in patients with microtia/OAVS [34,35]. Given that Mexican and Hispanic populations show the highest prevalence of microtia worldwide [15], we performed an epistasis analysis [36] in a group of Mexican patients by the Multifactorial Dimensionality Reduction (MDR) method in five microtia/OAVS candidate genes. We assessed HOXA2 (MIM*604685, 7p15.2), TCOF1 (MIM*606847, 5q32), SALL1 (MIM*602218, 16q12.1), EYA1 (MIM*601653, 8q13.3), and TBX1 (MIM*602054, 22q11.21), whose selection was supported by various lines of evidence (see Table 1).

Table 1.
Evidence supporting the selection of the studied candidate microtia/OAVS genes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
Forty-nine unrelated Mexican patients (31 males, 18 females; ages 0 to 18 years old) who were evaluated between 2015 and 2019 at the National Institute of Pediatrics (Mexico) and given a clinical diagnosis of microtia/OAVS (microtia or anotia with or without HH, structural alterations in the spine and/or kidneys) were included. Patients who met the clinical criteria for microtia/OAVS but had congenital malformations distinct from those involving the spine and/or kidneys and/or an alteration in somatic growth (low or high height) or intellectual disability were excluded. Those with reported prenatal exposure to specific teratogens associated with microtia/OAVS (e.g., alcohol, retinoids, or maternal diabetes) were also excluded. Each patient underwent a systematic physical examination by clinical geneticists and a detailed family history was obtained (25 familial cases and 24 sporadic cases). Imaging studies (computed tomography of the inner ear, orthopantomography, complete spinal radiography, and renal ultrasound) were performed on the patients and their parents. Detailed clinical information related to all included patients was previously published [41]. This research protocol was approved and registered by the Ethics, Research and Biosafety Committees of the National Institute of Pediatrics (Mexico City, Mexico, registry number 004/2017).
2.2. NGS of the Five Microtia/OAVS Candidate Genes
Genomic DNA isolated from peripheral blood or buccal cell samples of all patients was analyzed with a targeted five-gene NGS panel consisting of HOXA2 (NM_006735.3), TCOF1 (NM_001135243.1), SALL1 (NM_002968.2), EYA1 (NM_000503.5), and TBX1 (NM_080647.1). The studied sequences covered the promoter region, all coding exons, and the intron–exon boundaries (200 bp). NGS libraries were prepared with an IDT xGen lockdown probe customized panel kit according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Libraries were sequenced on an Illumina MiSeq 2 × 150 platform (San Diego, CA, USA) through the Admera Health Company (South Plainfield, NJ, USA). Our in-house bioinformatics analysis pipeline included a quality evaluation and trimming of low-quality raw reads, alignment against the GRCh38 human reference sequence, and calling of single nucleotide variants (SNVs) and small insertion–deletion variants. The GATK Toolkit (version 4.2.6.1) [42] and the Alamut Batch (version 1.4), Focus (version 1.0), and Visual (version 2.7.2, Interactive Biosoftware, Rouen, France) software packages were used for variant annotation and filtering. All clinically relevant variants were confirmed by Sanger automated sequencing in the index cases and their available relatives. The identified gene variants were classified according to the criteria of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology (ACMG/AMP) [43].
2.3. Statistical and Gene Interaction Analyses
The allele frequencies of the variants identified in the five studied genes were obtained using the allelic counting method. We first determined if the variant was in Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium using the two-tailed Fisher’s exact test, which assessed whether the distribution of genotypes was as expected in our population. When information was available, an association analysis was performed to compare the genotype frequencies in our study population with those reported in Mexican individuals from Los Angeles (1000 Genomes Project, phase 3; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/gdv/, accessed on 17 May 2022) using Armitage’s trend test as applied by the deFinetti online software (https://ihg.helmholtz-muenchen.de/cgi-bin/hw/hwa1.pl, accessed on 17 May 2022).
To identify possible intergenic and/or intragenic interactions between the variants in the analyzed loci, we used the Multifactor Dimensionality Reduction (MDR) ver. 3.0.2 software (Vanderbilt University Medical School, Nashville, TN, USA) [36].
Additionally, the STRING software (http://string-db.org, accessed on 20 September 2022) was used to look for interacting partners of known craniofacial and RA-associated proteins, including those encoded by the five studied genes. The selected candidate interacting protein partners were: AMIGO2, BAPX1, CHD7, CYP26B1, EYA1, EYA3, FGF3, FGF10, FGFR2, FRAS1, FREM2, GDF3, GRIP1, GSC, HDAC1, HDAC2, HOXA2, HOXA13, HOXD13, MLL2, MYT1, PHF5A, PITX2, PLCB4, RARB, SALL1, SF3B2, SIN3B, SIX1, SIX2, TBX1, TCOF1, TFAP2A, VWA1, ZIC3, and ZYG11B.
3. Results
The median read depth for the five-gene panel was 639X (range 86X–1940X), and the coverage was 99.9%. Thirty-nine gene coding variants were identified in TCOF1, SALL1, EYA1, and TBX1; of them, 17 were predicted to alter the amino acid sequence (non-synonymous). These included 15 missense mutations, 1 in-frame microdeletion, and 1 in-frame microduplication that were classified as benign (B, n = 12) and likely benign (LB, n = 5) according to ACMG/AMP criteria (see Table 2). Furthermore, 22 synonymous or non-coding variants were identified in our patients (see Table 3). No variant was identified in the coding region of the HOXA2 gene.

Table 2.
Comparison of allelic frequencies (AFs) for the 17 non-synonymous gene variants of TCOF1, SALL1, TBX1, and EYA1 identified in our population versus those reported in the reference group (Mexicans from LA, 1000 Genomes Project Database).

Table 3.
Detailed information on the synonymous variants observed in our population.
3.1. Association Analysis
When we compared the allelic frequencies (AFs) of benign (B) or likely benign (LB) variants observed in our population with those reported in Mexican individuals from Los Angeles (1000 Genomes Project), a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) was observed only for the p.(Ser159del) SALL1 variant, which was found specifically in microtia/OAVS patients (n = 5, 3 familial and 2 sporadic cases). Since the missense p.(Val1275Ile) SALL1 variant was present in a homozygous state in all cases and all individuals of the reference group, we did not perform an association analysis for this variant (see Table 2). Comparing the AFs of synonymous variants among our patients with those of the reference group, a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) was observed only for the p.(Gly587=) TCOF1 variant (see Table 3).
3.2. MDR Interaction Analysis
We analyzed possible interactions among the 17 genotypes of the variants found in TCOF1, SALL1, EYA1, and TBX1 for our 49 microtia/OAVS cases and those present in the 63 individuals belonging to the reference group of a Mexican population from Los Angeles (1000 Genomes Project). Five synonymous variants (TCOF1: p.(Thr210=); SALL1: p.(Pro558=) and p.(Val190=); EYA1: p.(Ile195=); and TBX1: p.(Pro45=)) could not be subjected to MDR interaction analysis due to the lack of information in the reference group.
One significant gene–gene interaction related to the presentation of microtia/OAVS was identified: that between the non-synonymous p.(Pro1099Arg) TCOF1 variant and the synonymous p.(Leu858=) SALL1 variant (Figure 1). In this MDR interaction analysis, the balance accurate cross-validation testing result was 0.8175 and the cross-validation consistency value was 10/10. In a permutation analysis performed with 10,000 repetitions, the obtained p-value was statistically significant (p < 0.001).
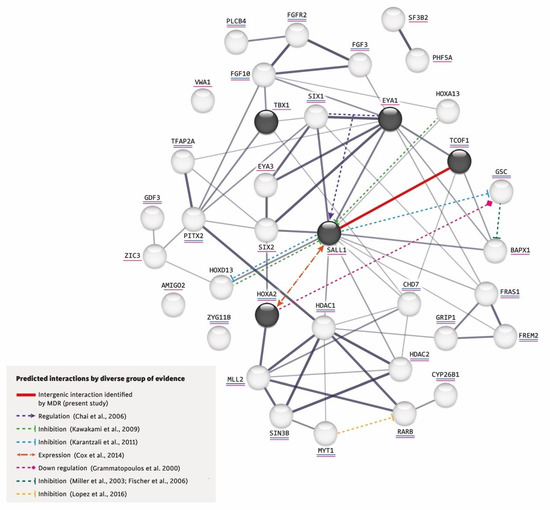
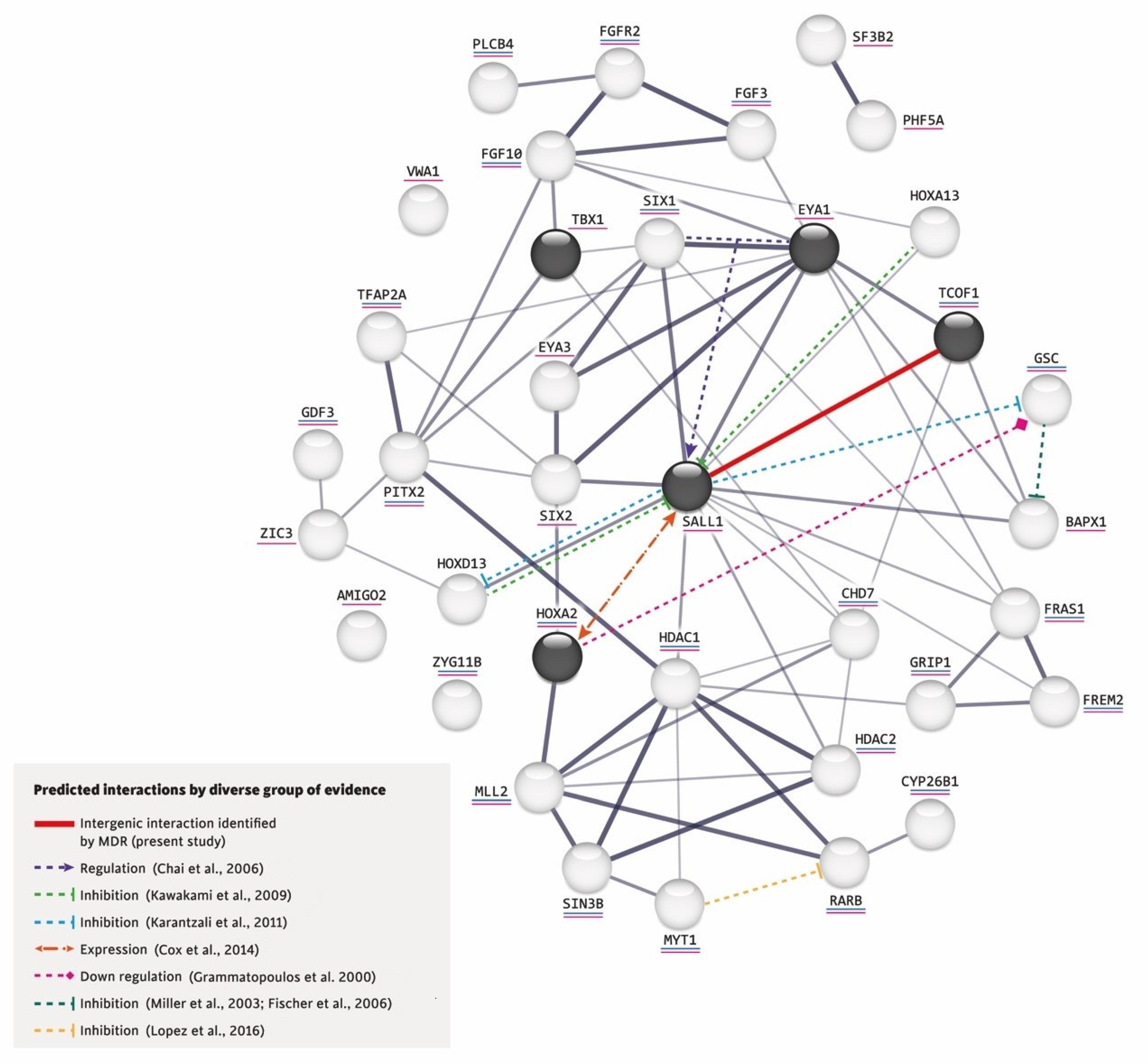
Figure 1.
Interactions predicted by diverse lines of evidence [23,40,44,47,48,49,50,51].
Furthermore, using the network created by STRING, we added the intergenic interaction that we identified in this study between the variants p.(Pro1099Arg) TCOF1 (rs1136103) and p.(Leu858=) SALL1 (rs1965024) and incorporated in this network the following based on reported evidence for other gene–gene interactions: (a) The co-expression of SIX1 and Eya1 synergistically regulates the expression of SALL1 during kidney development [44] and also play keys roles in ear determination [45,46]. (b) In the mouse limb bud, Hoxa13 and Hoxd13 inhibit the expression of Sall1 [47]. In mouse embryonic stem cells, Sall1 appears to inhibit various Hox genes, including Hoxd13 and Gsc [48]. (c) Although it is not known whether Sall1 has a regulatory relationship with Hoxa2 in the branchial arches, the former is expressed early in head mesenchyme and then becomes restricted around the first branchial cleft in close proximity of Hoxa2, which encodes an important transcription factor in the external ear morphogenesis of mice [40]. (d) Hoxa2 coordinates the downregulation of Gsc, which acts as a transcriptional repressor in wild-type cartilage during mouse embryogenesis [49]. (e) In zebrafish, gsc downregulates the expression of bapx1 in the second pharyngeal arch [50,51]. (f) Both increased and decreased RA signaling could induce craniofacial abnormalities, such as those found in OAVS [13]. (g) MYT1 overexpression reportedly induces the downregulation of RA receptor β (RARB), whereas mutated MYT1 does not [23] (see Figure 1).
This interaction network was built by the STRING V.11.0 software (https://string-db.org/, accessed on 20 September 2022) and includes the proteins encoded by the five genes studied herein (in dark circles) plus those related to RA (underlined in blue) and craniofacial disorders (underlined in pink). The thickness of a gray line indicates the strength of the data compatibility based on the STRING evidence. The solid red line indicates the intergenic interaction that we herein identified between p.(Pro1099Arg) TCOF1 (rs1136103) and p.(Leu858=) SALL1 (rs1965024) variants, and the colored dotted lines represent the interactions documented in the literature.
4. Discussion
Since microtia/OAVS shows a heterogeneous etiology, incomplete penetrance, and variable expressivity, its clinical and molecular diagnoses have proven challenging. In the literature, the inclusion criteria for patients with this spectrum are diverse and not always well described or defined, which could be considered a limitation when interpreting and discussing results. We consider that the clinical inclusion criteria utilized herein allowed us to study a more homogeneous population and thereby avoid biases.
Some groups have previously analyzed genetic factors related to microtia/OAVS [22,23,24,26,27,28,52,53,54,55,56], but no previous gene–gene interaction analysis has been performed in these patients. Given the genomic differences found across populations and the high prevalence of this disorder in Latin-American populations worldwide, it is important to obtain a more precise knowledge in patients with microtia/OAVS of this ethnic origin. Gaining a better understanding of the genetic etiology of this malformation could enable clinicians to provide more accurate genetic counseling to families [17,18,19,20,21,37].
4.1. Association Analysis
When we performed the association study between the variants identified in our patients and the reference group, we identified that the in-frame p.(Ser159del) microdeletion of SALL1 appears to be a risk factor for microtia, as evidenced by the statistically significant difference in the AF between our patients and the reference group and the presence of this variant in only our microtia/OAVS cases. Similar associations have been identified between variants of certain genes and the risk of developing malformations, such as congenital heart defects, biliary atresia, pyloric stenosis, hypospadias, and microtia [53,54,57].
The genome-wide association study (GWAS) approach has been successful in identifying new susceptibility loci for common structural congenital defects, such as oral clefts, congenital heart defects, biliary atresia, pyloric stenosis, hypospadias, craniosynostosis, and clubfoot [57]. However, congenital ear abnormalities, including anotia/microtia, have not previously been addressed by GWAS. The sole exception to this was a genome-wide linkage analysis performed on two families with OAVS [58]. In one family, the authors identified a highly suggestive linkage to a region harboring the GSC (Goosecoid homeobox) gene, which was considered to be a good candidate gene for this entity. However, coding-region changes and gross rearrangements were excluded in these two OAVS familial cases and in 120 additional sporadic cases [58].
Synonymous variants may influence the development of various human diseases, including birth defects [59,60]. A statistically significant difference was identified for the p.(Gly587=) TCOF1 variant. The AF for this variant was greater in the reference group, suggesting that it confers protection against or a decreased risk for microtia/OAVS in our Mexican population. There is no single mechanism by which a synonymous change could exert a biological effect. Accumulating evidence shows that biological systems take advantage of the degeneracy of the genetic code to control gene expression, protein folding efficiency, and coordinated expression across several gene families. The most obvious and well-characterized mechanism by which synonymous changes can exert a deleterious biological effect is by perturbing pre-mRNA splicing [59]. However, a synonymous variant could also be in linkage disequilibrium with deleterious functional variants located nearby. To our knowledge, the p.(Gly587=) of TCOF1 could be the first described synonymous variant associated with the microtia/OAVS trait.
4.2. MDR Interaction Analysis
In a very recent review of genetic and non-genetic factors involved in the development of microtia/OAVS, there was no mention of data related to gene–gene interactions [32]. As the interaction analysis for benign and/or synonymous variants could suggest a genetic protection or susceptibility factor for complex traits [34], such as ear malformations, we decided to apply an MDR analysis, which is a nonparametric model-free method for identifying epistasis using the identified variants [61]. This strategy identified a single statistically significant intergenic interaction between the non-synonymous p.(Pro1099Arg) TCOF1 variant and the synonymous p.(Leu858=) SALL1 variant (Figure 1). At the statistical level, combining the TCOF1 and SALL1 genotypes allowed us to discriminate between cases and controls, indicating that there is an interaction between these two genes. Although this interaction has not previously been reported, the TCOF1 and SALL1 proteins are related to craniofacial disorders [23] (Figure 1). The available evidence generally supports the involvement of the analyzed genes/proteins and various other genes/proteins in the development of microtia/OAVS. Notably, SALL1 interacts with most of these genes/proteins and thus appears to play a central role. In addition, it was the gene in which the most non-synonymous variants were identified in our group of patients (Figure 1), suggesting that SALL1 warrants future study in this regard.
Moving forward, the inclusion of a larger number of microtia/OAVS-related genes or the use of whole-exome sequencing should identify new variants that can be considered in future gene–gene interaction studies [62]. Epigenetic inheritance also has been suggested as a possible pathogenic mechanism [5]. For example, a histone acetylation-dependent imbalance in the allelic expression of the key craniofacial development gene, BAPX1 (also called NKX3-2, MIM*602183), was observed in five patients with OAVS [51]. Thus, the contribution of epigenetic mechanisms to the etiology of microtia/OAVS deserves attention in future genetic studies.
The published evidence and our present findings collectively support the complexity of ear embryogenesis and microtia/OAVS development, which involves the temporal and spatial expression of different proteins and signaling by multiple pathways. We did not identify any pathogenic variant in the five studied genes, but we found a gene–gene interaction between TCOF1 and SALL1. This highlights the need to identify other genes and genotype interactions that contribute to the etiology of craniofacial disorders, including microtia/OAVS [33]. Future research is also needed to assess the involvement of the RA pathway in the genetic etiology of microtia/OAVS.
5. Conclusions
Although gene–gene interactions are known to play an important role in the etiology of many complex diseases, no previous study has addressed gene interactions in patients with microtia/OAVS. Our finding of a gene interaction between TCOF1 and SALL1 in a group of Mexican patients with this entity supports the complex nature of ear embryogenesis and the development of microtia/OAVS. Further research is warranted, such as the inclusion of more candidate loci, which should lead to the identification of new gene–gene interactions underlying microtia/OAVS.
Author Contributions
B.E.-O.: Research (literature review), structuring and review of the research protocol, recruitment, and selection of candidate patients to be included in the study, interpretation of genotypes, analysis and discussion of results, writing of the original draft, review and editing of subsequent versions. M.E.R.-F.: Research (literature review), structuring and review of the research protocol, molecular methodology, NGS bioinformatic analyses, interpretation of genotypes, analysis and discussion of results, writing of the original draft, review and editing of subsequent versions. J.A.V.-A.: Interpretation of genotypes in cases and reference groups, statistical analysis, study of association and interaction between the identified variants, analysis and discussion of results, revision and editing of manuscript. A.G.-d.A.: Structuring and review of the research protocol, recruitment, and selection of candidate patients to be included in the study, clinical methodology, analysis and discussion of results, and revision and editing of manuscript. L.F.-H.: Research (literature review), structuring and review of the research protocol, recruitment and selection of candidate patients, molecular methodology, analysis and discussion of results, revision and editing of manuscript. M.A.A.-O.: Structuring and review of the research protocol, molecular methodology, interpretation of genotypes, analysis and discussion of results, funding administration, project management, supervision, revision and editing of manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Instituto Nacional de Pediatría, Secretaría de Salud (Recursos Fiscales 2015–2019, Programa E022 Investigación y Desarrollo Tecnológico en Salud, Ciudad de México, México).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved and registered by the Ethics, Research and Biosafety Committees of the National Institute of Pediatrics (Mexico, registry number 004/2017).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The genotypic datasets generated in this study have been uploaded to the Leiden Open Variation Database (LOVD) version 3.0 (https://www.lovd.nl/3.0/home, accessed on 20 September 2022).
Acknowledgments
We thank Juan Carlos Zenteno Ruíz, Samuel Canizales Quinteros, and Carlos Sabas Cruz Fuentes for their valuable comments and critical review of the manuscript. We also thank Katherine Fabián Aviléz for designing the figures that accompany the text.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationship that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Alasti, F.; Van Camp, G. Genetics of Microtia and Associated Syndromes. J. Med. Genet. 2009, 46, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barisic, I.; Odak, L.; Loane, M.; Garne, E.; Wellesley, D.; Calzolari, E.; Dolk, H.; Addor, M.C.; Arriola, L.; Bergman, J.; et al. Prevalence, Prenatal Diagnosis and Clinical Features of Oculo-Auriculo-Vertebral Spectrum: A Registry-Based Study in Europe. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 22, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beleza-Meireles, A.; Clayton-Smith, J.; Saraiva, J.M.; Tassabehji, M. Oculo-Auriculo-Vertebral Spectrum: A Review of the Literature and Genetic Update. J. Med. Genet. 2014, 51, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luquetti, D.V.; Heike, C.L.; Hing, A.V.; Cunningham, M.L.; Cox, T.C. Microtia: Epidemiology and Genetics. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2012, 158A, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendron, C.; Schwentker, A.; van Aalst, J. Genetic Advances in the Understanding of Microtia. J. Pediatr. Genet. 2016, 5, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragagnolo, S.; Colovati, M.E.S.; Souza, M.Z.; Dantas, A.G.; de Soares, M.F.F.; Melaragno, M.I.; Perez, A.B. Clinical and Cytogenomic Findings in OAV Spectrum. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2018, 176, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaeser, A.B.; Diniz, B.L.; Deconte, D.; Santos, A.S.; Rosa, R.F.M.; Zen, P.R.G. Microarray-Based Comparative Genomic Hybridization, Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification, and High-Resolution Karyotype for Differential Diagnosis Oculoauriculovertebral Spectrum: A Systematic Review. J. Pediatr. Genet. 2020, 09, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, V.; Calzari, L.; Fadda, M.T.; Piceci-Sparascio, F.; Digilio, M.C.; Bernardini, L.; Brancati, F.; Mattina, T.; Melis, D.; Forzano, F.; et al. Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Analysis of a Cohort of 41 Patients Affected by Oculo-Auriculo-Vertebral Spectrum (OAVS). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollnick, B.R.; Kaye, C.I. Hemifacial Microsomia and Variants: Pedigree Data. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1983, 15, 233–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llano-Rivas, I.; González-del Angel, A.; del Castillo, V.; Reyes, R.; Carnevale, A. Microtia: A Clinical and Genetic Study at the National Institute of Pediatrics in Mexico City. Arch. Med. Res. 1999, 30, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasse, C.; Majewski, F.; Böhringer, S.; Fischer, S.; Lüdecke, H.J.; Gillessen-Kaesbach, G.; Wieczorek, D. A Family with Autosomal Dominant Oculo-Auriculo-Vertebral Spectrum. Clin. Dysmorphol. 2007, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroud, T.; Wetherill, L.; Vinci-booher, S.; Elizabeth, S.; Ward, R.E.; Hoyme, H.E.; Robinson, L.K.; Rogers, J.; Meintjes, E.M.; Molteno, C.D.; et al. Relation Over Time Between Facial Measurements and Cognitive Outcomes in Fetal Alcohol Exposed. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 36, 1634–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenguer, M.; Darnaudery, M.; Claverol, S.; Bonneu, M.; Lacombe, D.; Rooryck, C. Prenatal Retinoic Acid Exposure Reveals Candidate Genes for Craniofacial Disorders. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artunduaga, M.A.; Quintanilla-Dieck, M.D.L.; Greenway, S.; Betensky, R.; Nicolau, Y.; Hamdan, U.; Jarrin, P.; Osorno, G.; Brent, B.; Eavey, R.; et al. A Classic Twin Study of External Ear Malformations, Including Microtia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1216–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, G.M.; Carmichael, S.L.; Kaidarova, Z.; Harris, J.A. Epidemiologic Characteristics of Anotia and Microtia in California, 1989–1997. Birth Defects Res. Part A-Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2004, 70, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrester, M.B.; Merz, R.D. Descriptive Epidemiology of Anotia and Microtia, Hawaii, 1986–2002. Congenit. Anom. 2005, 45, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasti, F.; Sadeghi, A.; Sanati, M.H.; Farhadi, M.; Stollar, E.; Somers, T.; Van Camp, G. A Mutation in HOXA2 Is Responsible for Autosomal-Recessive Microtia in an Iranian Family. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 82, 982–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.K.; Viana, L.M.; Helwig, C.C.; Artunduaga, M.A.; Quintanilla-Dieck, L.; Jarrin, P.; Osorno, G.; Mcdonough, B.; Depalma, S.R.; Eavey, R.D.; et al. HOXA2 Haploinsufficiency in Dominant Bilateral Microtia and Hearing Loss. Hum. Mutat. 2013, 34, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piceci, F.; Morlino, S.; Castori, M.; Buffone, E.; De Luca, A.; Grammatico, P.; Guida, V. Identification of a Second HOXA2 Nonsense Mutation in a Family with Autosomal Dominant Non-Syndromic Microtia and Distinctive Ear Morphology. Clin. Genet. 2017, 91, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meddaugh, H.R.; Zambrano, R.M. Novel HOXA2 Variant Presenting with Microtia and Variable Hearing Impairment in Four-Generation Pedigree. Clin. Dysmorphol. 2020, 29, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, N.; Meng, X.; Lu, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, C.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Guo, P.; Zhang, X.; et al. Identification of Loss-of-Function HOXA2 Mutations in Chinese Families with Dominant Bilateral Microtia. Gene 2020, 757, 144945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel-Friedrich, S. Congenital Auricular Malformations: Description of Anomalies and Syndromes. Fac. Plast. Surg. 2015, 31, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, E.; Berenguer, M.; Tingaud-Sequeira, A.; Marlin, S.; Toutain, A.; Denoyelle, F.; Picard, A.; Charron, S.; Mathieu, G.; de Belvalet, H.; et al. Mutations in MYT1, Encoding the Myelin Transcription Factor 1, Are a Rare Cause of OAVS. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 53, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenguer, M.; Tingaud-Sequeira, A.; Colovati, M.; Melaragno, M.I.; Bragagnolo, S.; Perez, A.B.A.; Arveiler, B.; Lacombe, D.; Rooryck, C. A Novel de Novo Mutation in MYT1, the Unique OAVS Gene Identified so Far. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 25, 1083–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luquetti, D.V.; Heike, C.L.; Zarante, I.; Timms, A.E.; Gustafson, J.; Pachajoa, H.; Porras-Hurtado, G.L.; Ayala-Ramirez, P.; Duenas-Roque, M.M.; Jimenez, N.; et al. MYT1 Role in the Microtia-Craniofacial Microsomia Spectrum. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rengasamy Venugopalan, S.; Farrow, E.; Sanchez–Lara, P.A.; Yen, S.; Lypka, M.; Jiang, S.; Allareddy, V. A Novel Nonsense Substitution Identified in the AMIGO2 Gene in an Occulo-Auriculo-Vertebral Spectrum Patient. Orthod. Craniofacial Res. 2019, 22, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingaud-Sequeira, A.; Trimouille, A.; Marlin, S.; Lopez, E.; Berenguer, M.; Gherbi, S.; Arveiler, B.; Lacombe, D.; Rooryck, C. Functional and Genetic Analyses of ZYG11B Provide Evidences for Its Involvement in OAVS. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, e1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimouille, A.; Tingaud-Sequeira, A.; Lacombe, D.; Duelund Hjortshøj, T.; Kreiborg, S.; Buciek Hove, H.; Rooryck, C. Description of a Family with X-Linked Oculo-Auriculo-Vertebral Spectrum Associated with Polyalanine Tract Expansion in ZIC3. Clin. Genet. 2020, 98, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ping, L.; Luan, X.; Chen, Y.; Fan, X.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, B.; et al. A Mutation in VWA1, Encoding von Willebrand Factor A Domain-Containing Protein 1, Is Associated With Hemifacial Microsomia. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 571004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timberlake, A.T.; Griffin, C.; Heike, C.L.; Hing, A.V.; Cunningham, M.L.; Chitayat, D.; Davis, M.R.; Doust, S.J.; Drake, A.F.; Duenas-Roque, M.M.; et al. Haploinsufficiency of SF3B2 Causes Craniofacial Microsomia. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingaud-Sequeira, A.; Trimouille, A.; Salaria, M.; Stapleton, R.; Claverol, S.; Plaisant, C.; Bonneu, M.; Lopez, E.; Arveiler, B.; Lacombe, D.; et al. A Recurrent Missense Variant in EYA3 Gene Is Associated with Oculo-Auriculo-Vertebral Spectrum. Hum. Genet. 2021, 140, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tingaud-Sequeira, A.; Trimouille, A.; Sagardoy, T.; Lacombe, D.; Rooryck, C. Oculo-Auriculo-Vertebral Spectrum: New Genes and Literature Review on a Complex Disease. J. Med. Genet. 2022, 59, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez-Aragón, J.A.; Alcántara-Ortigoza, M.A.; Estandia-Ortega, B.; Reyna-Fabián, M.E.; Méndez-Adame, C.D.; González-Del Angel, A. Gene Interactions Provide Evidence for Signaling Pathways Involved in Cleft Lip/Palate in Humans. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.H.; Williams, S.M. Epistasis and Its Implications for Personal Genetics. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 85, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, A.R.; Hsiao, C.L.; Chang, S.W.; Wang, H.M.; Fann, C.S.J. On the Use of Multifactor Dimensionality Reduction (MDR) and Classification and Regression Tree (CART) to Identify Haplotype-Haplotype Interactions in Genetic Studies. Genomics 2011, 97, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.H.; Gilbert, J.C.; Tsai, C.-T.; Chiang, F.-T.; Holden, T.; Barney, N.; White, B.C. A Flexible Computational Framework for Detecting, Characterizing, and Interpreting Statistical Patterns of Epistasis in Genetic Studies of Human Disease Susceptibility. J. Theor. Biol. 2006, 241, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaki, R.; Fujimaru, R.; Samejima, H.; Yamada, H.; Izumi, K.; Iijima, K.; Kosaki, K. Wide Phenotypic Variations within a Family WithSALL1 Mutations: Isolated External Ear Abnormalities to Goldenhar Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2007, 143, 1087–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitelli, F.; Viola, A.; Morishima, M.; Pramparo, T.; Baldini, A.; Lindsay, E. TBX1 Is Required for Inner Ear Morphogenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003, 12, 2041–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.; Jones, N.C.; Sandell, L.L.; Jayasinghe, S.M.; Crane, J.; Rey, J.P.; Dixon, M.J.; Trainor, P.A. Tcof1/Treacle Is Required for Neural Crest Cell Formation and Proliferation Deficiencies That Cause Craniofacial Abnormalities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13403–13408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, T.C.; Camci, E.D.; Vora, S.; Luquetti, D.V.; Turner, E.E. The Genetics of Auricular Development and Malformation: New Findings in Model Systems Driving Future Directions for Microtia Research. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2014, 57, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estandia-Ortega, B.; Fernández-Hernández, L.; Alcántara-Ortigoza, M.A.; González-del Angel, A. Proposed Clinical Approach and Imaging Studies in Families with Oculo-Auriculo-Vertebral Spectrum to Assess Variable Expressivity. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2022, 188, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce Framework for Analyzing next-Generation DNA Sequencing Data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology Sue. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Yang, J.; Di, C.; Cui, W.; Kawakami, K.; Lai, R.; Ma, Y. Transcriptional Activation of the SALL1 by the Human SIX1 Homeodomain during Kidney Development. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 18918–18926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzedine, H.; Tankere, F.; Launay-Vacher, V.; Deray, G. Ear and Kidney Syndromes: Molecular versus Clinical Approach. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torban, E.; Goodyer, P. The Kidney and Ear: Emerging Parallel Functions. Annu. Rev. Med. 2009, 60, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, Y.; Uchiyama, Y.; Esteban, C.R.; Inenaga, T.; Koyano-Nakagawa, N.; Kawakami, H.; Marti, M.; Kmita, M.; Monaghan-Nichols, P.; Nishinakamura, R.; et al. Sall Genes Regulate Region-Specific Morphogenesis in the Mouse Limb by Modulating Hox Activities. Development 2009, 136, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantzali, E.; Lekakis, V.; Ioannou, M.; Hadjimichael, C.; Papamatheakis, J.; Kretsovali, A. Sall1 Regulates Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation in Association with Nanog. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammatopoulos, G.A.; Bell, E.; Toole, L.; Lumsden, A.; Tucker, A.S. Homeotic Transformation of Branchial Arch Identity after Hoxa2 Overexpression. Development 2000, 127, 5355–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.T.; Yelon, D.; Stainier, D.Y.R.; Kimmel, C.B. Two Endothelin 1 Effectors, Hand2 and Bapx1, Pattern Ventral Pharyngeal Cartilage and the Jaw Joint. Development 2003, 130, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Lüdecke, H.J.; Wieczorek, D.; Böhringer, S.; Gillessen-Kaesbach, G.; Horsthemke, B. Histone Acetylation Dependent Allelic Expression Imbalance of BAPX1 in Patients with the Oculo-Auriculo-Vertebral Spectrum. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, F.; Mar Aung, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chai, G. Whole-Exome Sequencing Reveals Rare Germline Mutations in Patients With Hemifacial Microsomia. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 580761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Fan, X.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X. Target Sequencing of 307 Deafness Genes Identifies Candidate Genes Implicated in Microtia. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 63324–63332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Fan, X.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Liu, T.; Chen, C.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X. Identification of Sequence Variants Associated with Severe Microtia-Astresia by Targeted Sequencing. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamariolli, M.; Colovati, M.; Moysés-Oliveira, M.; Nunes, N.; Caires dos Santos, L.; Alvarez Perez, A.B.; Bragagnolo, S.; Melaragno, M.I. Rare Single-Nucleotide Variants in Oculo-Auriculo-Vertebral Spectrum (OAVS). Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e00959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Cai, Z.; Li, Z.; Pan, B.; Jiang, H. Whole-Exome Sequencing Analysis in 10 Families of Sporadic Microtia with Thoracic Deformities. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2021, 9, e1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupo, P.J.; Mitchell, L.E.; Jenkins, M.M. Genome-Wide Association Studies of Structural Birth Defects: A Review and Commentary. Birth Defects Res. 2019, 111, 1329–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelberman, D.; Tyson, J.; Chandler, D.; McInerney, A.; Slee, J.; Albert, D.; Aymat, A.; Botma, M.; Calvert, M.; Goldblatt, J.; et al. Hemifacial Microsomia: Progress in Understanding the Genetic Basis of a Complex Malformation Syndrome. Hum. Genet. 2001, 109, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, R.C.; Simhadri, V.L.; Iandoli, M.; Sauna, Z.E.; Kimchi-Sarfaty, C. Exposing Synonymous Mutations. Trends Genet. 2014, 30, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, R.; Kumar, A.; Mohapatra, B. Implication of GATA4 Synonymous Variants in Congenital Heart Disease: A Comprehensive in-Silico Approach. Mutat. Res. 2019, 813, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, J.; Moore, J.H.; Williams, S.M.; Andrews, P.; Hillege, H.L.; van der Harst, P.; Navis, G.; Van Gilst, W.H.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Gilbert-Diamond, D. A Simple and Computationally Efficient Approach to Multifactor Dimensionality Reduction Analysis of Gene-Gene Interactions for Quantitative Traits. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Ankala, A.; Wilcox, W.R.; Hegde, M.R. Solving the Molecular Diagnostic Testing Conundrum for Mendelian Disorders in the Era of Next-Generation Sequencing: Single-Gene, Gene Panel, or Exome/Genome Sequencing. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).