Dextromethorphan Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects in a Murine Model: Therapeutic Implication in Psoriasis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Imiquimod (IMQ)-Induced Psoriasis Murine Model
2.3. Histological Analysis
2.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.5. Psoriasis Area and Severity and IndexScore (PASI)
2.6. RT-PCR
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
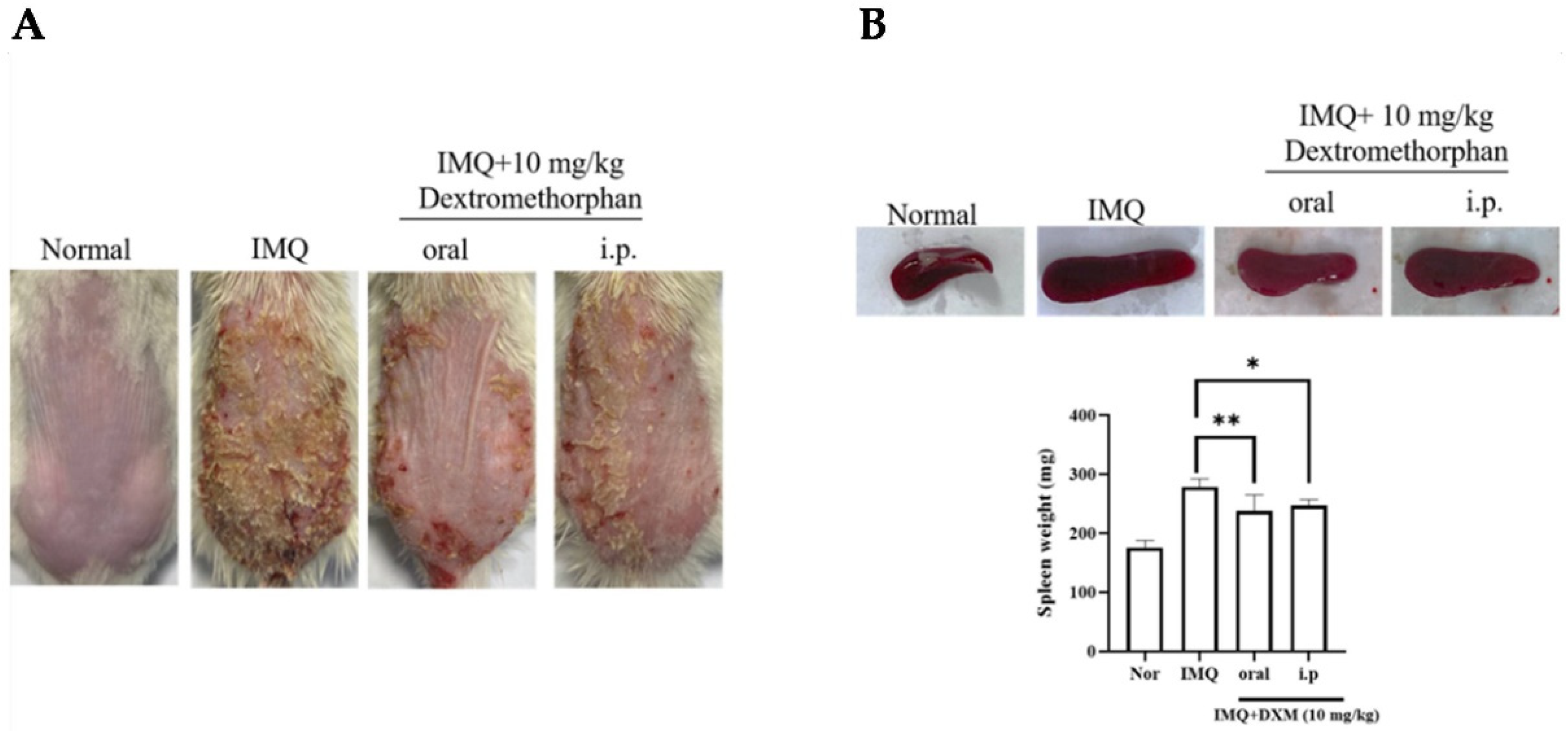
3.1. Oral Dextromethorphan Alleviates Skin Lesions in IMQ-Induced Psoriasis-like Mice Erythema and Scaling
3.2. DXM Decreased the Severity of IMQ-Induced Psoriasis form Dermatitis
3.3. DXM Reduced Inflammatory Cytokines in IMQ-Treated Mice’s Skin Lesions
3.4. DXM Decreased the Frequency of IL-17/IL-22-Producing TCRγδT Cells in the Spleens of IMQ-Treated Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christophers, E. Psoriasis-Epidemiology and clinical spectrum. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2001, 26, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebwohl, M. Psoriasis. Lancet 2003, 361, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorachoo, J.; Saeloh, D.; Srichana, T.; Amnuaikit, T.; Musthafa, K.S.; Sretrirutchai, S.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. Rhodomyrtone as a potential anti-proliferative and apoptosis inducing agent in HaCaT keratinocyte cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 772, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.A.N.; Armstrong, A.W. Clinical and Histologic Diagnostic Guidelines for Psoriasis: A Critical Review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 44, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurd, S.K.; Troxel, A.B.; Crits-Christoph, P.; Gelfand, J.M. The risk of depression, anxiety, and suicidality in patients with psoriasis: A population-based cohort study. Arch. Dermatol. 2010, 146, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coates, L.C.; Helliwell, P.S. Psoriatic arthritis: State of the art review. Clin. Med. 2017, 17, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bs, S.E.L.; Cohen, J.M.; Ho, R.S. Psoriasis and suicidality: A review of the literature. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huerta, C.; Rivero, E.; Rodríguez, L.A.G. Incidence and Risk Factors for Psoriasis in the General Population. Arch. Dermatol. 2007, 143, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, S.; Krueger, J.G.; Li, K.; Jabbari, A.; Brodmerkel, C.; Lowes, M.A.; Suárez-Fariñas, M. Meta-Analysis Derived (MAD) Transcriptome of Psoriasis Defines the “Core” Pathogenesis of Disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nestle, F.O.; Kaplan, D.H.; Barker, J. Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Meglio, P.; Villanova, F.; Nestle, F.O. Psoriasis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a015354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harden, J.L.; Krueger, J.G.; Bowcock, A.M. The immunogenetics of Psoriasis: A comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 64, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Y.; Chang, C.; Lu, Q. The Inflammatory Response in Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 50, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowes, M.A.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Krueger, J.G. Immunology of Psoriasis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 227–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nair, R.P.; for the Collaborative Association Study of Psoriasis; Duffin, K.C.; Helms, C.; Ding, J.; Stuart, P.E.; Goldgar, D.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Li, Y.; Tejasvi, T.; et al. Genome-wide scan reveals association of psoriasis with IL-23 and NF-κB pathways. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goldminz, A.; Au, S.; Kim, N.; Gottlieb, A.; Lizzul, P. NF-κB: An essential transcription factor in psoriasis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 69, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.E.; Barker, J.N.W.N. Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet 2007, 370, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.M.; Rubin, C.J.; Khandpur, R.; Wang, J.Y.; Riblett, M.; Yalavarthi, S.; Villanueva, E.C.; Shah, P.; Kaplan, M.J.; Bruce, A.T. Mast Cells and Neutrophils Release IL-17 through Extracellular Trap Formation in Psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keijsers, R.R.M.C.; Joosten, I.; van Erp, P.; Koenen, H.J.P.M.; Van De Kerkhof, P.C.M. Cellular sources of IL-17 in psoriasis: A paradigm shift? Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 23, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowes, M.A.; Bowcock, A.M.; Krueger, J.G. Pathogenesis and therapy of psoriasis. Nature 2007, 445, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoruso, G.; Nisticò, S.; Iannone, L.; Russo, E.; Rago, G.; Patruno, C.; Bennardo, L. Ixekizumab May Improve Renal Function in Psoriasis. Healthcare 2021, 9, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passante, M.; Dastoli, S.; Nisticò, S.P.; Bennardo, L.; Patruno, C. Effectiveness of brodalumab in acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau: A case report. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.; Thomas, K.; Lucke-Wold, B.P.; Cavendish, J.Z.; Crowe, M.S.; Matsumoto, R.R. Dextromethorphan: An update on its utility for neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 159, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortella, F.C.; Pellicano, M.; Bowery, N.G. Dextromethorphan and neuromodulation: Old drug coughs up new activities. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1989, 10, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-L.; Li, Y.-H.; Shi, G.-Y.; Tang, S.-H.; Jiang, S.-J.; Huang, C.-W.; Liu, P.-Y.; Hong, J.-S.; Wu, H.-L. Dextromethorphan reduces oxidative stress and inhibits atherosclerosis and neointima formation in mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 82, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.-Y.; Lin, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-M.; Chao, Y.-H.; Yang, D.-H. Dextromethorphan Exhibits Anti-inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects in a Murine Model of Collagen-Induced Arthritis and in Human Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.; Koppu, S.; Perche, P.O.; Feldman, S.R. The Cytokine Mediated Molecular Pathophysiology of Psoriasis and Its Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reagan-Shaw, S.; Nihal, M.; Ahmad, N. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrum, A.G.; Palmer, E.; Turka, L.A. Distinct temporal programming of naive CD4+ T?cells for cell division versus TCR-dependent death susceptibility by antigen-presenting macrophages. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huppa, J.B.; Gleimer, M.; Sumen, C.; Davis, M.M. Continuous T cell receptor signaling required for synapse maintenance and full effector potential. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iezzi, G.; Karjalainen, K.; Lanzavecchia, A. The Duration of Antigenic Stimulation Determines the Fate of Naive and Effector T Cells. Immunity 1998, 8, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- PASI Score. Available online: http://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/pasi-score/ (accessed on 21 March 2022).
- Van Belle, A.B.; De Heusch, M.; Lemaire, M.M.; Hendrickx, E.; Warnier, G.; Dunussi-Joannopoulos, K.; Fouser, L.A.; Renauld, J.-C.; Dumoutier, L. IL-22 Is Required for Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasiform Skin Inflammation in Mice. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.; Shen, X.; Ding, C.; Qi, C.; Li, K.; Li, X.; Jala, V.R.; Zhang, H.-G.; Wang, T.; Zheng, J.; et al. Pivotal Role of Dermal IL-17-Producing γδ T Cells in Skin Inflammation. Immunity 2011, 35, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cozzi, E.; Bosio, E.; Seveso, M.; Rubello, D.; Ancona, E. Xenotransplantation as a model of integrated, multidisciplinary research. Organogenesis 2009, 5, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Der Fits, L.; Mourits, S.; Voerman, J.S.A.; Kant, M.; Boon, L.; Laman, J.D.; Cornelissen, F.; Mus, A.-M.; Florencia, E.; Prens, E.; et al. Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin Inflammation in Mice Is Mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 Axis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5836–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qin, L.; Li, G.; Zhang, W.; An, L.; Liu, B.; Hong, J.-S. Dextromethorphan Protects Dopaminergic Neurons against Inflammation-Mediated Degeneration through Inhibition of Microglial Activation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 305, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Tzeng, N.-S.; Cui, G.; Block, M.L.; Wilson, B.; Qin, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; et al. Protective effect of dextromethorphan against endotoxic shock in mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 69, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N.J.; Boniface, K.; Chan, J.R.; McKenzie, B.S.; Blumenschein, W.M.; Mattson, J.D.; Basham, B.; Smith, K.J.; Chen, T.; Morel, F.; et al. Development, cytokine profile and function of human interleukin 17–producing helper T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowes, M.A.; Kikuchi, T.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Cardinale, I.; Zaba, L.C.; Haider, A.S.; Bowman, E.P.; Krueger, J.G. Psoriasis Vulgaris Lesions Contain Discrete Populations of Th1 and Th17 T Cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1207–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagami, S.; Rizzo, H.L.; Lee, J.J.; Koguchi, Y.; Blauvelt, A. Circulating Th17, Th22, and Th1 Cells Are Increased in Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-M.; Chen, I.-C.; Chao, Y.-H.; Chen, H.-H.; Chen, P.-K.; Chang, S.-H.; Yeo, K.-J.; Wey, S.-J.; Lin, C.-C.; Chen, D.-Y. Dextromethorphan Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects in a Murine Model: Therapeutic Implication in Psoriasis. Life 2022, 12, 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12050696
Chen Y-M, Chen I-C, Chao Y-H, Chen H-H, Chen P-K, Chang S-H, Yeo K-J, Wey S-J, Lin C-C, Chen D-Y. Dextromethorphan Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects in a Murine Model: Therapeutic Implication in Psoriasis. Life. 2022; 12(5):696. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12050696
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yi-Ming, I-Chieh Chen, Ya-Hsuan Chao, Hsin-Hua Chen, Po-Ku Chen, Shih-Hsin Chang, Kai-Jieh Yeo, Shiow-Jiuan Wey, Chi-Chien Lin, and Der-Yuan Chen. 2022. "Dextromethorphan Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects in a Murine Model: Therapeutic Implication in Psoriasis" Life 12, no. 5: 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12050696
APA StyleChen, Y.-M., Chen, I.-C., Chao, Y.-H., Chen, H.-H., Chen, P.-K., Chang, S.-H., Yeo, K.-J., Wey, S.-J., Lin, C.-C., & Chen, D.-Y. (2022). Dextromethorphan Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects in a Murine Model: Therapeutic Implication in Psoriasis. Life, 12(5), 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12050696






