Myocardial Ischemia in Patients with COVID-19 Infection: Between Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Electrocardiographic Findings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
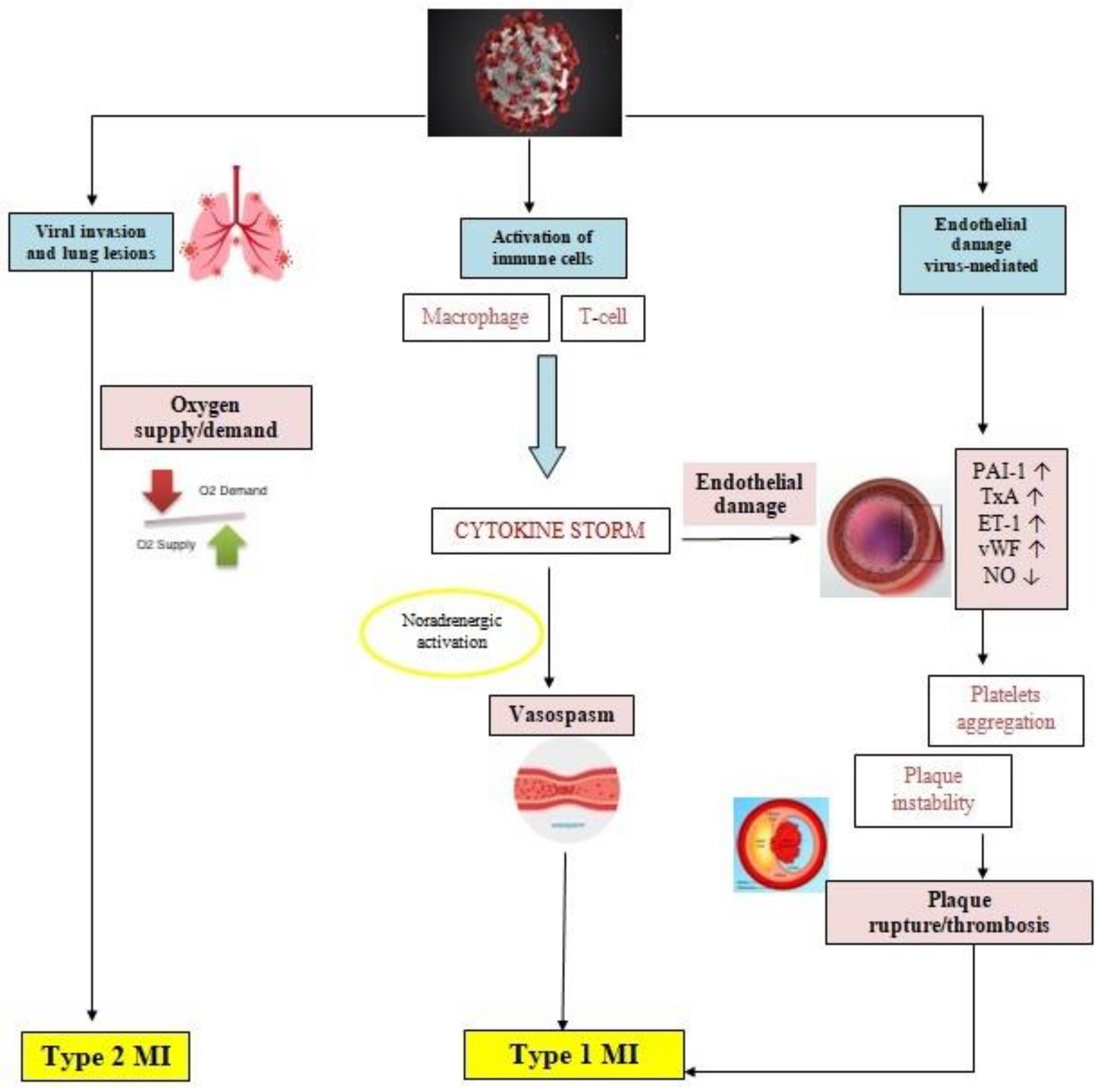
2. Pathophysiology of Myocardial Ischemia in COVID-19 Patients
3. Electrocardiographic Changes in Myocardial Ischemia in COVID-19 Patients
3.1. ST-T Abnormalities
3.1.1. STEMI Pattern
3.1.2. ST-Depression Pattern
3.1.3. T-Wave Inversion and Other Patterns of ST-Abnormalities
3.2. Q Waves
3.3. Specific Electrocardiographic Patterns
3.3.1. Takotsubo Pattern
3.3.2. Wellens Pattern
3.3.3. De Winter Pattern
3.3.4. Triangular Electrocardiographic Pattern
3.4. Other Electrocardiographic Aspects Associated with Myocardial Ischemia in COVID-19 Patients
4. Why Is It Important to Analyze Myocardial Ischemic-like Electrocardiographic Changes in COVID-19 Patients?
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuki, K.; Fujiogi, M.; Koutsogiannaki, S. COVID-19 pathophysiology: A review. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 215, 108427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauci, A.S.; Lane, H.C.; Redfield, R.R. COVID-19—Navigating the Uncharted. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1268–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, L.; Ruiz, D.; Tehrani, B.; Sinha, S. Acute coronary thrombosis as a complication of COVID-19. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e238218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, X.; Huang, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. COVID-19: Immunopathogenesis and Immunotherapeutics. Signal. Transduct. Target Ther. 2020, 5, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velavan, T.P.; Meyer, C.G. The COVID-19 epidemic. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2020, 25, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiavone, M.; Gobbi, C.; Biondi-Zoccai, G.; D’Ascenzo, F.; Palazzuoli, A.; Gasperetti, A.; Mitacchione, G.; Viecca, M.; Galli, M.; Fedele, F.; et al. Acute Coronary Syndromes and COVID-19: Exploring the Uncertainties. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anupama, B.K.; Chaudhuri, D. A Review of Acute Myocardial Injury in Coronavirus Disease 2019. Cureus 2020, 12, e8426. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, S.J. Long COVID or post-COVID-19 syndrome: Putative pathophysiology, risk factors, and treatments. Infect. Dis. 2021, 53, 737–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, D.L.; Holdsworth, L.; Jawad, N.; Gunasekera, P.; Morice, A.H.; Crooks, M.G. Post-COVID-19 Symptom Burden: What is Long-COVID and How Should We Manage It. Lung 2021, 199, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, S.R.; Arnold, A.C.; Barboi, A.; Claydon, V.E.; Limberg, J.K.; Lucci, V.M.; Numan, M.; Peltier, A.; Snapper, H.; Vernino, S. Long-COVID postural tachycardia syndrome: An American Autonomic Society statement. Clin. Auton. Res. 2021, 31, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehraeen, E.; Seyed Alinaghi, S.A.; Nowroozi, A.; Dadras, O.; Alilou, S.; Shobeiri, P.; Behnezhad, F.; Karimi, A. A systematic review of ECG findings in patients with COVID-19. Indian Heart J. 2020, 72, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, P.; Poterucha, T.J.; Jain, S.S.; Sayer, G.; Raikhelkar, J.; Fried, J.; Clerkin, K.; Griffin, J.; DeFilippis, E.M.; Gupta, A.; et al. The Prognostic Value of Electrocardiogram at Presentation to Emergency Department in Patients with COVID-19. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 2099–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barman, H.A.; Atici, A.; Alici, G.; Sit, O.; Tugrul, S.; Gungor, B.; Okuyan, E.; Sahin, I. The effect of the severity COVID-19 infection on electrocardiography. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 46, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosén, J.; Noreland, M.; Stattin, K.; Lipcsey, M.; Frithiof, R.; Malinovschi, A.; Hultström, M. Uppsala Intensive Care COVID-19 Research Group. ECG pathology and its association with death in critically ill COVID-19 patients, a cohort study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261315. [Google Scholar]
- McCullough, S.A.; Goyal, P.; Krishnan, U.; Choi, J.J.; Safford, M.M.; Okin, P.M. Electrocardiographic Findings in Coronavirus Disease-19: Insights on Mortality and Underlying Myocardial Processes. J. Card. Fail. 2020, 26, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseeb, S.; Gul, E.E.; Çinier, G.; Bazoukis, G.; Alvarez-Garcia, J.; Garcia-Zamora, S.; Lee, S.; Yeung, C.; Liu, T.; Tse, G.; et al. International Society of Electrocardiology Young Community (ISE-YC). Value of electrocardiography in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). J. Electrocardiol. 2020, 62, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemati, R.; Ganjoo, M.; Jadidi, F.; Tanha, A.; Baghbani, R. Electrocardiography in Early Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Complications of COVID-19; a Systematic Literature Review. Arch. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2020, 9, e10. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, J.; Gabr, M.; Diaz, J.C. Electrocardiographic Features of COVID-19 patients: An Updated Review. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2021, 14, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.; Brady, W.J.; Bridwell, R.E.; Ramzy, M.; Montrief, T.; Singh, M.; Gottlieb, M. Electrocardiographic manifestations of COVID-19. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 41, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, G.A.; De Vita, A.; Ravenna, S.E.; D’Aiello, A.; Covino, M.; Franceschi, F.; Crea, F. Electrocardiographic findings at presentation and clinical outcome in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Europace 2021, 23, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denegri, A.; Pezzuto, G.; D’Arienzo, M.; Morelli, M.; Savorani, F.; Cappello, C.G.; Luciani, A.; Boriani, G. Clinical and electrocardiographic characteristics at admission of COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia infection. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2021, 16, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galidevara, J.; Veeramani Kartheek, A.S. Electrocardiographic findings in COVID-19 patients. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2021, 9, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predabon, B.; Souza, A.Z.M.; Sumnienski Bertoldi, G.H.; Sales, R.L.; Luciano, K.S.; de March Ronsoni, R. The electrocardiogram in the differential diagnosis of cardiologic conditions related to the covid-19 pandemic. J. Cardiac. Arrhythmias 2020, 33, 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Boukhris, M.; Hillani, A.; Moroni, F.; Annabi, M.S.; Addad, F.; Ribeiro, M.H.; Mansour, S.; Zhao, X.; Ybarra, L.F.; Abbate, A.; et al. Cardiovascular Implications of the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Global Perspective. Can. J. Cardiol. 2020, 36, 1068–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolis, A.S.; Manolis, T.A. Cardiovascular complications of the coronavirus (COVID-19) infection. Rhythmos 2020, 15, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, S.; Stanberry, L.; Schmidt, C.; Sharkey, S.; Megaly, M.; Albaghdadi, M.S.; Meraj, P.M.; Garberich, R.; Jaffer, F.A.; Stefanescu Schmidt, A.C.; et al. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on STEMI care: An expanded analysis from the United States. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2021, 98, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, W.; Yi, S.; Zhang, J.; Gu, X.; Xu, Y.; Huang, K.; Su, X.; Yu, B.; et al. Management and Outcomes of Patients with STEMI during the COVID-19 Pandemic in China. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammalleri, V.; Muscoli, S.; Benedetto, D.; Stifano, G.; Macrini, M.; Di Landro, A.; Di Luozzo, M.; Marchei, M.; Mariano, E.G.; Cota, L.; et al. Who Has Seen Patients with ST-Segment-Elevation Myocardial Infarction? First Results from Italian Real-World Coronavirus Disease 2019. Am. Heart J. 2020, 9, e017126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struyf, T.; Deeks, J.J.; Dinnes, J.; Takwoingi, Y.; Davenport, C.; Leeflang, M.M.; Spijker, R.; Hooft, L.; Emperador, D.; Dittrich, S.; et al. Cochrane COVID-19 Diagnostic Test Accuracy Group. Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19 disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 7, CD013665. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval, Y.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Jaffe, A.S. Cardiac troponin for the diagnosis and risk-stratification of myocardial injury in COVID-19: JACC review topic of the week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1244–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustino, G.; Croft, L.B.; Stefanini, G.G.; Bragato, R.; Silbiger, J.J.; Vicenzi, M.; Danilov, T.; Kukar, N.; Shaban, N.; Kini, A.; et al. Characterization of Myocardial Injury in Patients with COVID-19. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2043–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, G.; Campia, U.; Hurwitz, S.; Snyder, J.E.; Rizzo, S.M.; Pfeferman, M.B.; Morrison, R.B.; Leiva, O.; Fanikos, J.; Nauffal, V.; et al. Registry of Arterial and Venous Thromboembolic Complications in Patients with COVID-19. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2060–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lala, A.; Johnson, K.W.; Januzzi, J.L.; Russak, A.J.; Paranjpe, I.; Richter, F.; Zhao, S.; Somani, S.; Van Vleck, T.; Vaid, A.; et al. Prevalence and Impact of Myocardial Injury in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 Infection. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolis, A.S.; Manolis, A.A.; Manolis, T.A.; Melita, H. COVID-19 and Acute Myocardial Injury and Infarction: Related Mechanisms and Emerging Challenges. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 26, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaze, D.C. Clinical utility of cardiac troponin measurement in COVID-19 infection. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2020, 57, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collet, J.P.; Thiele, H.; Barbato, E.; Barthélémy, O.; Bauersachs, J.; Bhatt, D.L.; Dendale, P.; Dorobantu, M.; Edvardsen, T.; Folliguet, T.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 1289–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudry, F.A.; Hamshere, S.M.; Rathod, K.S.; Akhtar, M.M.; Archbold, R.A.; Guttmann, O.P.; Woldman, S.; Jain, A.K.; Knight, C.J.; Baumbach, A.; et al. High Thrombus Burden in Patients with COVID-19 Presenting With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1168–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadeh, A.; Aldujeli, A.; Briedis, K.; Tecson, K.M.; Sanz-Sánchez, J.; Al Dujeili, M.; Al-Obeidi, A.; Diez, J.L.; Žaliūnas, R.; Stoler, R.C.; et al. Characteristics and Outcomes in Patients Presenting with COVID-19 and ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial and ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Am. J. Cariol. 2020, 131, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, L.; Cancro, F.P.; Silverio, A.; Di Maio, M.; Iannece, P.; Damato, A.; Alfano, C.; De Luca, G.; Vecchione, C.; Galasso, G. COVID-19 and Acute Coronary Syndromes: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Perspectives. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 4936571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; McAuley, D.F.; Brown, M.; Sanchez, E.; Tattersall, R.S.; Manson, J.J.; HLH Across Speciality Collaboration, UK. COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet 2020, 395, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Favaloro, E.J. D-dimer is associated with severity of coronavirus disease 2019: A pooled analysis. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 876–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lippi, G.; Plebani, M.; Henry, B.M. Thrombocytopenia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infections: A meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 506, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, N.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panigada, M.; Bottino, N.; Tagliabue, P.; Grasselli, G.; Novembrino, C.; Chantarangkul, V.; Pesenti, A.; Peyvandi, F.; Tripodi, A. Hypercoagulability of COVID-19 patients in intensive care unit: A report of thromboelastography findings and other parameters of hemostasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1738–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakopoulos, B.; Krilis, S.A. The pathogenesis of the antiphospholipid syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 268, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestas, J.; Ley, K. Monocyte-endothelial cell interactions in the development of atherosclerosis. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2008, 18, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noels, H.; Weber, C.; Koenen, R.R. Chemokines as Therapeutic Targets in Cardiovascular Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pober, J.S.; Sessa, W.C. Evolving functions of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampsas, S.; Tsaplaris, P.; Pantelidis, P.; Oikonomou, E.; Marinos, G.; Charalambous, G.; Souvaliotis, N.; Mystakidi, V.C.; Goliopoulou, A.; Katsianos, E.; et al. The Role of Endothelial Related Circulating Biomarkers in COVID-19. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 3790–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, D.M.; Kim-Schulze, S.; Huang, H.H.; Beckmann, N.D.; Nirenberg, S.; Wang, B.; Lavin, Y.; Swartz, T.H.; Madduri, D.; Stock, A.; et al. An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, E.; Flammer, A.J.; Lerman, L.O.; Elízaga, J.; Lerman, A.; Fernández-Avilés, F. Endothelial dysfunction over the course of coronary artery disease. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 3175–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varga, Z.; Flammer, A.J.; Steiger, P.; Haberecker, M.; Andermatt, R.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Mehra, M.R.; Schuepbach, R.A.; Ruschitzka, F.; Moch, H. Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19. Lancet 2020, 395, 1417–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, F.A.; Kruip, M.J.H.A.; van der Meer, N.J.M.; Arbous, M.S.; Gommers, D.A.M.P.J.; Kant, K.M.; Kaptein, F.H.J.; van Paassen, J.; Stals, M.A.M.; Huisman, M.V.; et al. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb. Res. 2020, 191, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, K.; Gronski, P.A.; Kiyan, Y.; Seeliger, B.; Bertram, A.; Pape, T.; Welte, T.; Hoeper, M.M.; Haller, H.; David, S. Injury to the Endothelial Glycocalyx in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Gayosso, I.; Platts, S.H.; Duling, B.R. Reactive oxygen species mediate modification of glycocalyx during ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 290, H2247–H2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alphonsus, C.S.; Rodseth, R.N. The endothelial glycocalyx: A review of the vascular barrier. Anaesthesia 2014, 69, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchimido, R.; Schmidt, E.P.; Shapiro, N.I. The glycocalyx: A novel diagnostic and therapeutic target in sepsis. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buijsers, B.; Yanginlar, C.; de Nooijer, A.; Grondman, I.; Maciej-Hulme, M.L.; Jonkman, I.; Janssen, N.A.F.; Rother, N.; de Graaf, M.; Pickkers, P.; et al. Increased Plasma Heparanase Activity in COVID-19 Patients. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 575047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, K.; Libby, P. Intertwining of thrombosis and inflammation in atherosclerosis. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2007, 14, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennathur, S.; Heinecke, J.W. Oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in vascular disease. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2007, 7, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafnsson, A.; Matic, L.P.; Lengquist, M.; Mahdi, A.; Shemyakin, A.; Paulsson-Berne, G.; Hansson, G.K.; Gabrielsen, A.; Hedin, U.; Yang, J.; et al. Endothelin-1 increases expression and activity of arginase 2 via ETB receptors and is co-expressed with arginase 2 in human atherosclerotic plaques. Atherosclerosis 2020, 292, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Hansson, G.K. Inflammation in atherosclerosis: From pathophysiology to practice. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1985, 54, 2129–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ardlie, N.G.; McGuiness, J.A.; Garrett, J.J. Effect on human platelets of catecholamines at levels achieved in the circulation. Atherosclerosis 1985, 58, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katritsis, D.G.; Pantos, J.; Efstathopoulos, E. Hemodynamic factors and atheromatic plaque rupture in the coronary arteries: From vulnerable plaque to vulnerable coronary segment. Coron Artery Dis. 2007, 18, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, S.J.; Auger, K.R.; Libby, P. Human interleukin 1 induces interleukin 1 gene expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Exp. Med. 1987, 165, 1316–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, S.; Arnaud, M.; Loiselle, M.; Arrii, E.; Azoulay, E.; Zafrani, L. Immune Consequences of Endothelial Cells’ Activation and Dysfunction During Sepsis. Crit. Care Clin. 2020, 36, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, J.; Tacquard, C.; Severac, F.; Leonard-Lorant, I.; Ohana, M.; Delabranche, X.; Merdji, H.; Clere-Jehl, R.; Schenck, M.; Fagot Gandet, F.; et al. High risk of thrombosis in patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: A multicenter prospective cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Leor, O.; Cid Alvarez, A.B.; Pérez de Prado, A.; Rossello, X.; Ojeda, S.; Serrador, A.; López-Palop, R.; Martin-Moreiras, J.; Rumoroso, J.R.; Cequier, A.; et al. In-hospital outcomes of COVID-19 ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients. EuroIntervention 2021, 16, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, B.; Varlot, J.; Metzdorf, P.A.; Jeulin, H.; Goehringer, F.; Camenzind, E. Changes in characteristics and management among patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction due to COVID-19 infection. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2021, 97, E319–E326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, C.; Leone, O.; Rizzo, S.; De Gaspari, M.; van der Wal, A.C.; Aubry, M.C.; Bois, M.C.; Lin, P.T.; Maleszewski, J.J.; Stone, J.R. Pathological features of COVID-19-associated myocardial injury: A multicentre cardiovascular pathology study. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 3827–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Qin, M.; Shen, B.; Cai, Y.; Liu, T.; Yang, F.; Gong, W.; Liu, X.; Liang, J.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Association of Cardiac Injury with Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chapman, A.R.; Shah, A.S.V.; Lee, K.K.; Anand, A.; Francis, O.; Adamson, P.; McAllister, D.A.; Strachan, F.E.; Newby, D.E.; Mills, N.L. Long-Term Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Myocardial Infarction and Myocardial Injury. Circulation 2018, 137, 1236–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanini, G.G.; Montorfano, M.; Trabattoni, D.; Andreini, D.; Ferrante, G.; Ancona, M.; Metra, M.; Curello, S.; Maffeo, D.; Pero, G.; et al. ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction in Patients with COVID-19: Clinical and Angiographic Outcomes. Circulation 2020, 141, 2113–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangalore, S.; Sharma, A.; Slotwiner, A.; Yatskar, L.; Harari, R.; Shah, B.; Ibrahim, H.; Friedman, G.H.; Thompson, C.; Alviar, C.L.; et al. ST-Segment Elevation in Patients with COVID-19—A Case Series. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2478–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, F.; Antuña, P.; Cuesta, J.; Alfonso, F. Severe coronary spasm in a COVID-19 patient. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2021, 97, E670–E672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, H.R.; Maehara, A.; Kwong, R.Y.; Sedlak, T.; Saw, J.; Smilowitz, N.R.; Mahmud, E.; Wei, J.; Marzo, K.; Matsumura, M.; et al. Coronary Optical Coherence Tomography and Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Determine Underlying Causes of Myocardial Infarction with Nonobstructive Coronary Arteries in Women. Circulation 2021, 143, 624–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastidar, A.G.; Baritussio, A.; De Garate, E.; Drobni, Z.; Biglino, G.; Singhal, P.; Milano, E.G.; Angelini, G.D.; Dorman, S.; Strange, J.; et al. Prognostic Role of CMR and Conventional Risk Factors in Myocardial Infarction with Nonobstructed Coronary Arteries. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 1973–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daubert, M.A.; Jeremias, A. The utility of troponin measurement to detect myocardial infarction: Review of the current findings. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2010, 6, 691–699. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, J.E.; Abendschein, D.R.; Jaffe, A.S. Biochemical markers of myocardial injury. Is MB creatine kinase the choice for the 1990s. Circulation 1993, 88, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rhinehardt, J.; Brady, W.J.; Perron, A.D.; Mattu, A. Electrocardiographic manifestations of Wellens’ syndrome. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2002, 20, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García de Guadiana-Romualdo, L.; Morell-García, D.; Rodríguez-Fraga, O.; Morales-Indiano, C.; María Lourdes Padilla Jiménez, A.; Gutiérrez Revilla, J.I.; Urrechaga, E.; Álamo, J.M.; Hernando Holgado, A.M.; Lorenzo-Lozano, M.D.C.; et al. Cardiac troponin and COVID-19 severity: Results from BIOCOVID study. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoso, A.; Pranata, R.; Wibowo, A.; Al-Farabi, M.J.; Huang, I.; Antariksa, B. Cardiac injury is associated with mortality and critically ill pneumonia in COVID-19: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 44, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, J.; Alviz, I.; Parides, M.; Diaz, J.C.; Briceno, D.; Gabr, M.; Gamero, M.; Patel, K.; Braunstein, E.D.; Purkayastha, S.; et al. T-wave inversion as a manifestation of COVID-19 infection: A case series. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2020, 59, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, M.A.; El Masry, H.; Khan, B.R.; Das, M.K. Electrocardiographic signs of remote myocardial infarction. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2007, 50, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landesberg, G. Monitoring for myocardial ischemia. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2005, 19, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Tse, G.; Wu, M.; Jiang, J.; Liu, M.; Tao, L. Electrocardiograhic characteristics in patients with coronavirus infection: A single-center observational study. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2020, 25, e12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Huang, F.; Chen, J.; Yang, X. Electrocardiogram analysis of patients with different types of COVID-19. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2020, 25, e12806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, F.; Reboldi, G.; Spanevello, A.; De Ponti, R.; Visca, D.; Marazzato, J.; Zappa, M.; Trapasso, M.; Masnaghetti, S.; Fabbri, L.M.; et al. Electrocardiographic features of patients with COVID-19: One year of unexpected manifestations. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 95, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poterucha, T.J.; Elias, P.; Jain, S.S.; Sayer, G.; Redfors, B.; Burkhoff, D.; Rosenblum, H.; DeFilippis, E.M.; Gupta, A.; Lawlor, M.; et al. Admission Cardiac Diagnostic Testing with Electrocardiography and Troponin Measurement Prognosticates Increased 30-Day Mortality in COVID-19. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e018476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonsoz, M.R.; Oncul, A.; Cevik, E.; Orta, H.; Yilmaz, M.; Ayduk Govdeli, E.; Nalbant, A.; Demirtakan, Z.G.; Tonyali, M.; Durmus, D.; et al. Wide QRS Complex and Lateral ST-T Segment Abnormality Are Associated with Worse Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 361, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, S.; He, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Q. Risk factors and electrocardiogram characteristics for mortality in critical inpatients with COVID-19. Clin. Cardiol. 2020, 43, 1624–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzieh, M.; Rezvanjeh, S.; Maryam, C. A novel electrocardiogram characteristic in patients with myocardial injury due to COVID-19. Res. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 10, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamaschi, L.; D’Angelo, E.C.; Paolisso, P.; Toniolo, S.; Fabrizio, M.; Angeli, F.; Donati, F.; Magnani, I.; Rinaldi, A.; Bartoli, L.; et al. The value of ECG changes in risk stratification of COVID-19 patients. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2021, 26, e12815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogungbe, O.; Kumbe, B.; Fadodun, O.; Latha, T.; Meyer, D.; Asala, A.; Davidson, P.M.; Dennison Himmelfarb, C.R.; Post, W.S.; Commodore-Mensah, Y. Subclinical myocardial injury, coagulopathy, and inflammation in COVID-19: A meta-analysis of 41,013 hospitalized patients. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2022, 40, 100950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorin, E.; Dai, M.; Kogan, E.; Wadhwani, L.; Shulman, E.; Nadeau-Routhier, C.; Knotts, R.; Bar-Cohen, R.; Barbhaiya, C.; Aizer, A.; et al. Electrocardiographic Risk Stratification in COVID-19 Patients. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021, 8, 636073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.Y.; Hussein, K.I.; Howes, C.J.; Setaro, F.S. The Challenges of ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction in COVID-19 Patients. Case Rep. Cardiol. 2021, 2021, 9915650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thygesen, K.; Alpert, J.S.; Jaffe, A.S.; White, H.D. Diagnostic application of the universal definition of myocardial infarction in the intensive care unit. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2008, 14, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, A.; D’Amico, G.; Brunetti, G.; Vescovo, G.M.; Donato, F.; Gambato, M.; Dall’Aglio, P.B.; Cardaioli, F.; Previato, M.; Martini, N.; et al. Electrocardiographic Predictors of Primary Ventricular Fibrillation and 30-Day Mortality in Patients Presenting with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centurión, O.A. Wide QRS Complex and Left Ventricular Lateral Repolarization Abnormality: The Importance of ECG Markers on Outcome Prediction in Patients with COVID-19. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 362, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haji Aghajani, M.; Toloui, A.; Aghamohammadi, M.; Pourhoseingholi, A.; Taherpour, N.; Sistanizad, M.; Madani Neishaboori, A.; Asadpoordezaki, Z.; Miri, R. Electrocardiographic Findings and In-Hospital Mortality of COVID-19 Patients; a Retrospective Cohort Study. Arch. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2021, 9, e45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siddamreddy, S.; Thotakura, R.; Dandu, V.; Kanuru, S.; Meegada, S. Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Presenting as Acute ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Cureus 2020, 12, e7782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Z.; Xu, C.; Wang, D.; Zeng, H. The experience of treating patients with acute myocardial infarction under the COVID-19 epidemic. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2021, 97, E244–E248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, F.; Gramegna, M.; Ajello, S.; Beneduce, A.; Baldetti, L.; Vilca, L.M.; Cappelletti, A.; Scandroglio, A.M.; Azzalini, L. Collateral Damage: Medical Care Avoidance Behavior among Patients with Myocardial Infarction during the COVID-19 Pandemic. JACC Case Rep. 2020, 2, 1620–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, M.M.; Zubaidi, A.A. ST-elevation myocardial infarction in a patient with COVID-19. Vis. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 25, 101151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrman, R.R.; Brennan, E.E.; Creighton, T.; Ottenhoff, J.; Favot, M.J. ST Elevation in the COVID-19 Era: A Diagnostic Challenge. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 60, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolcu, M.; Gunesdogdu, F.; Bektas, M.; Bayirli, D.T.; Serefhanoglu, K. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and simultaneous acute anteroseptal and inferior ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2020, 31, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulkoti, V.; Acharya, S.; Talwar, D.; Khanna, S. Medical Science l Case Report Myocardial infarction in a young female: A rare case report. Med. Sci. 2021, 25, 1281–1285. [Google Scholar]
- Harari, R.; Bangalore, S.; Chang, E.; Shah, B. COVID-19 complicated by acute myocardial infarction with extensive thrombus burden and cardiogenic shock. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2021, 97, E661–E666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertini, M.; Ferrari, R.; Guardigli, G.; Malagù, M.; Vitali, F.; Zucchetti, O.; D’Aniello, E.; Volta, C.A.; Cimaglia, P.; Piovaccari, G.; et al. Electrocardiographic features of 431 consecutive, critically ill COVID-19 patients: An insight into the mechanisms of cardiac involvement. Europace 2020, 22, 1848–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, T.; Ali, Z. Transient ST Segment Elevation in Two Patients with COVID-19 and a Normal Transthoracic Echocardiogram. Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2020, 7, 001672. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meizinger, C.; Klugherz, B. Focal ST-segment elevation without coronary occlusion: Myocardial infarction with no obstructive coronary atherosclerosis associated with COVID-19—A case report. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2021, 5, ytaa532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, F.; Spanevello, A.; De Ponti, R.; Visca, D.; Marazzato, J.; Palmiotto, G.; Feci, D.; Reboldi, G.; Fabbri, L.M.; Verdecchia, P. Electrocardiographic features of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 78, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channer, K.; Morris, F. ABC of clinical electrocardiography: Myocardial ischaemia. BMJ 2002, 324, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antwi-Amoabeng, D.; Beutler, B.D.; Singh, S.; Taha, M.; Ghuman, J.; Hanfy, A.; Manasewitsch, N.T.; Ulanja, M.B.; Ghuman, J.; Awad, M.; et al. Association between electrocardiographic features and mortality in COVID-19 patients. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2021, 26, e12833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberto, A.B.; Carlos, P.C.J.; Antonio, C.R.J.; Patricia, P.P.; Enrique, T.R.; Danira, M.P.J.; Benito, G.Á.E.; Alfredo, M.R.J. Implications of myocardial injury in Mexican hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2020, 30, 100638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, M.P.; Wan, E.Y.; Waase, M.P.; Morrow, J.P.; Dizon, J.M.; Yarmohammadi, H.; Berman, J.P.; Rubin, G.A.; Kushnir, A.; Poterucha, T.J.; et al. Clinical and cardiac characteristics of COVID-19 mortalities in a diverse New York City Cohort. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2020, 31, 3086–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Feng, Y.; Tang, J.; Hu, W.; Zhao, P.; Guo, X.; Huang, N.; Gu, Y.; Hu, L.; Duru, F.; et al. Surface electrocardiographic characteristics in coronavirus disease 2019: Repolarization abnormalities associated with cardiac involvement. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 4408–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Obata, R.; Rizk, D.; Kuno, T. Cardiac Injury and Outcomes of Patients with COVID-19 in New York City. Heart Lung Circ. 2021, 30, 848–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaccione, K.M.; Leb, J.S.; D’souza, B.; Utukuri, P.; Salvatore, M.M. Acute myocardial infarction secondary to COVID-19 infection: A case report and review of the literature. Clin. Imaging 2021, 72, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho, H.; Leonard-Pons, L.; Segard, J.; Goffinet, N.; Javaudin, F.; Martinage, A.; Cattin, G.; Tiberghien, S.; Therasse, D.; Trotignon, M.; et al. Electrocardiographic abnormalities in COVID-19 patients visiting the emergency department: A multicenter retrospective study. BMC Emerg. Med. 2021, 21, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryawan, I.G.R.; Bakhriansyah, J.; Puspitasari, M.; Gandi, P.; Intan, R.E.; Alkaff, F.F. To reperfuse or not to reperfuse: A case report of Wellens’ syndrome with suspected COVID-19 infection. Egypt. Heart J. 2020, 72, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoor, A.; Chang, D.; Mitra, R. Rhythm, conduction, and ST elevation with COVID-19: Myocarditis or myocardial infarction? HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2020, 6, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelliccia, F.; Kaski, J.C.; Crea, F.; Camici, P.G. Pathophysiology of Takotsubo Syndrome. Circulation 2017, 135, 2426–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangieh, A.H.; Obeid, S.; Ghadri, J.R.; Imori, Y.; D’Ascenzo, F.; Kovac, M.; Ruschitzka, F.; Lüscher, T.F.; Duru, F.; Templin, C.; et al. ECG Criteria to Differentiate between Takotsubo (Stress) Cardiomyopathy and Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e003418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dichtl, W.; Tuovinen, N.; Barbieri, F.; Adukauskaite, A.; Senoner, T.; Rubatscher, A.; Hintringer, F.; Siedentopf, C.; Bauer, A.; Gizewski, E.R.; et al. Functional neuroimaging in the acute phase of Takotsubo syndrome: Volumetric and functional changes of the right insular cortex. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2020, 109, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minhas, A.S.; Scheel, P.; Garibaldi, B.; Liu, G.; Horton, M.; Jennings, M.; Jones, S.R.; Michos, E.D.; Hays, A.G. Takotsubo Syndrome in the Setting of COVID-19. JACC Case Rep. 2020, 2, 1321–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moady, G.; Atar, S. Takotsubo Syndrome during the COVID-19 Pandemic: State-of-the-Art Review. CJC Open 2021, 3, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okura, H. Update of takotsubo syndrome in the era of COVID-19. J. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, E.L.; Torres-Acosta, N.; O’Keefe, J.H.; Sturgess, J.E.; Lavie, C.J.; Bybee, K.A. Takotsubo Syndrome: Cardiotoxic Stress in the COVID Era. Mayo Clin. Proc. Innov. Qual. Outcomes 2020, 4, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, H.D.; Sharma, K.; Jadeja, D.M.; Desai, H.M.; Moliya, P. COVID-19 pandemic induced stress cardiomyopathy: A literature review. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2020, 31, 100628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, L.; Galli, F.; Conconi, B.; Gregorini, T.; Lucreziotti, S.; Mafrici, A.; Pravettoni, G.; Sommaruga, M.; Carugo, S. Takotsubo syndrome in COVID-19 era: Is psychological distress the key. J. Psychosom. Res. 2021, 140, 110297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miner, B.; Grigg, W.S.; Hart, E.H. Wellens Syndrome; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tandy, T.K.; Bottomy, D.P.; Lewis, J.G. Wellens’ syndrome. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1999, 33, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prousi, G.S.; Giordano, J.; McCann, P.J. A 75-Year-Old Woman with COVID-19 Pneumonia and Wellens Syndrome Diagnosed by Electrocardiography. Am. J. Case. Rep. 2021, 22, e930125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkholy, K.O.; Mirashi, E.; Malyshev, Y.; Charles, G.; Sahni, S. Wellens’ Syndrome in the Setting of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19). Cureus 2021, 13, e13290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Spigno, F.; Spezzano, T.; Halasz, G.; Piepoli, M. Un caso di sindrome di Wellens durante la pandemia COVID-19 [A case of Wellens syndrome during the COVID-19 pandemic]. G Ital. Cardiol. 2021, 22, 888–890. [Google Scholar]
- Caiati, C.; Desario, P.; Tricarico, G.; Iacovelli, F.; Pollice, P.; Favale, S.; Lepera, M.E. Wellens’ Syndrome from COVID-19 Infection Assessed by Enhanced Transthoracic Coronary Echo Doppler: A Case Report. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Mai, L.; Lu, J.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y. Evolutionary de Winter pattern: From STEMI to de Winter ECG—A case report. ESC Heart Fail. 2022, 9, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, H.; Hemaya, S.; Squires, J.; Adam, Z. Recognising the de Winter ECG pattern—A time critical electrocardiographic diagnosis in the Emergency Department. J. Electrocardiol. 2018, 51, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, A.; Liu, L.; Chen, Z. The de winter electrocardiogram pattern is a transient electrocardiographic phenomenon that presents at the early stage of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Clin. Cardiol. 2018, 41, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almendro-Delia, M.; Ruíz-Salmerón, R.; García-Del Río, M.; Seoane-García, T.; Trujillo-Berraquero, F.; Hidalgo-Urbano, R. The de Winter electrocardiographic pattern as an ST-elevation myocardial infarction equivalent in a young patient with COVID-19. Emergencias 2021, 33, 484–485. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, J.M.; de Oliveira, W.S.; de Sá, V.P.; de Sá, I.F.; Neto, N.O. Transient triangular QRS-ST-T waveform with good outcome in a patient with left main coronary artery stenosis: A case report. J. Electrocardiol. 2019, 54, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celli, D.; Byer, M.; Sancassani, R.; Colombo, R. Triangular ECG Pattern in a Young Female with COVID-19. Am. J. Med. 2021, 134, 751–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, E.; Dauerman, H.L.; Welt, F.G.P.; Messenger, J.C.; Rao, S.V.; Grines, C.; Mattu, A.; Kirtane, A.J.; Jauhar, R.; Meraj, P.; et al. Management of acute myocardial infarction during the COVID-19 pandemic: A Consensus Statement from the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI), the American College of Cardiology (ACC), and the American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP). Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 96, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]


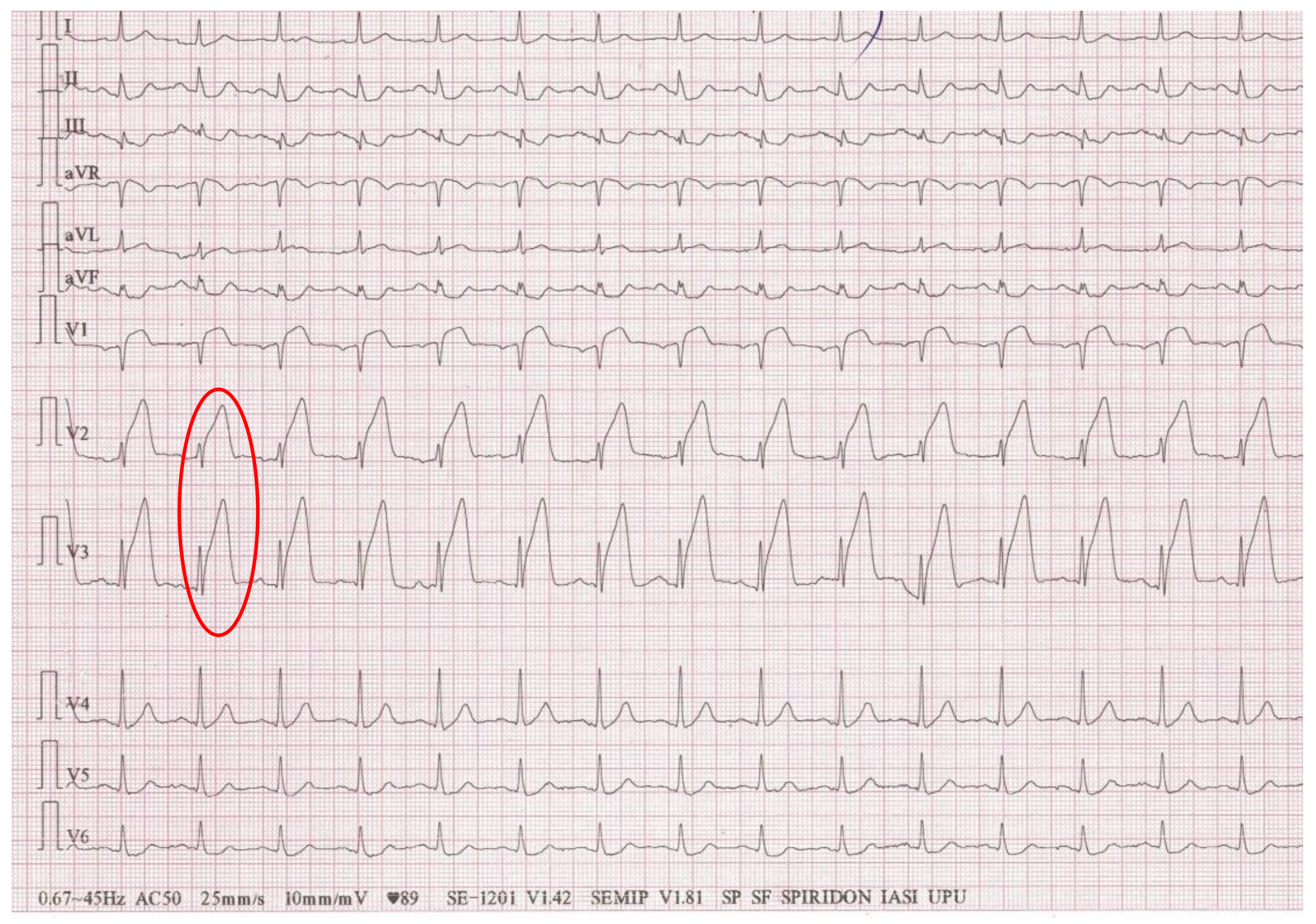
| Age | Sex | Symptoms | Time to in-Hospital Presentation | Treatment at Home | ECG Aspect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64 | M 1 | Chest pressure Shortness of breath | 10 days | Homemade natural remedies | Q waves and ST-segment elevation on the anterior leads |
| 65 | F 1 | Epigastric tightness Dyspnea Orthopnea | 5 days | Antiacids | Q waves and ST-segment elevation on the anterior leads |
| 60 | M 1 | Hypotension Diaphoresis Respiratory distress | 4 days | None | Q waves and ST-segment elevation on the anterior leads |
| Article | Age | Sex | Symptoms | ECG Findings | Treatment | Angiography |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prousi et al. | 75 | F 1 | Fatigue Dyspnea | Diffuse T-wave inversions in precordial leads Biphasic T waves in V1–V2 | Statin Aspirin P2Y12 inhibitors Heparin | Not performed |
| Elkholy et al. | 86 | M 1 | Dyspnea | Biphasic T wave in V2–V3 T-wave inversion in V4–V6 | Statin Aspirin P2Y12 inhibitors Enoxaparin | Chronic total occlusion of the right coronary artery. Severe disease of the first diagonal. Severe stenosis of the distal obtuse marginal 1 |
| Di Spigno et al. | 62 | M 1 | Atypical chest pain Dyspnea | Biphasic T waves in V2 | - | Subocclusion of the proximal left anterior descending artery |
| Caiati et al. | 69 | M 1 | Typical chest pain Dyspnea | T-waves inversion in V2–V3 T-wave flattening in V4–V6 | Statin Aspirin P2Y12 inhibitors Heparin | Subocclusive stenosis of the proximal LAD |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duca, Ș.T.; Chetran, A.; Miftode, R.Ș.; Mitu, O.; Costache, A.D.; Nicolae, A.; Iliescu-Halițchi, D.; Halițchi-Iliescu, C.-O.; Mitu, F.; Costache, I.I. Myocardial Ischemia in Patients with COVID-19 Infection: Between Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Electrocardiographic Findings. Life 2022, 12, 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12071015
Duca ȘT, Chetran A, Miftode RȘ, Mitu O, Costache AD, Nicolae A, Iliescu-Halițchi D, Halițchi-Iliescu C-O, Mitu F, Costache II. Myocardial Ischemia in Patients with COVID-19 Infection: Between Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Electrocardiographic Findings. Life. 2022; 12(7):1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12071015
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuca, Ștefania Teodora, Adriana Chetran, Radu Ștefan Miftode, Ovidiu Mitu, Alexandru Dan Costache, Ana Nicolae, Dan Iliescu-Halițchi, Codruța-Olimpiada Halițchi-Iliescu, Florin Mitu, and Irina Iuliana Costache. 2022. "Myocardial Ischemia in Patients with COVID-19 Infection: Between Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Electrocardiographic Findings" Life 12, no. 7: 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12071015
APA StyleDuca, Ș. T., Chetran, A., Miftode, R. Ș., Mitu, O., Costache, A. D., Nicolae, A., Iliescu-Halițchi, D., Halițchi-Iliescu, C.-O., Mitu, F., & Costache, I. I. (2022). Myocardial Ischemia in Patients with COVID-19 Infection: Between Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Electrocardiographic Findings. Life, 12(7), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12071015









