Generation of Asynaptic Mutants in Potato by Disrupting StDMC1 Gene Using RNA Interference Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Identification of StDMC1 CDS, Sense and Anti-Sense Region
2.3. Sense and Anti-Sense Amplification
2.4. Development of siRNA Construct
2.5. Transformation of RNAi Construct in Agrobacterium Strain GV3101
2.6. Agrobacterium-Mediated Plant Transformation
2.7. Screening of Putative Transformants
2.8. Pollen Viability Analysis
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the DMC1 Gene in the Kufri Jyoti Potato Cultivar
3.2. Confirmation of pRI101 RNAi Construct
3.3. Agrobacterium-Mediated Plant Transformation
3.4. Pollen Viability
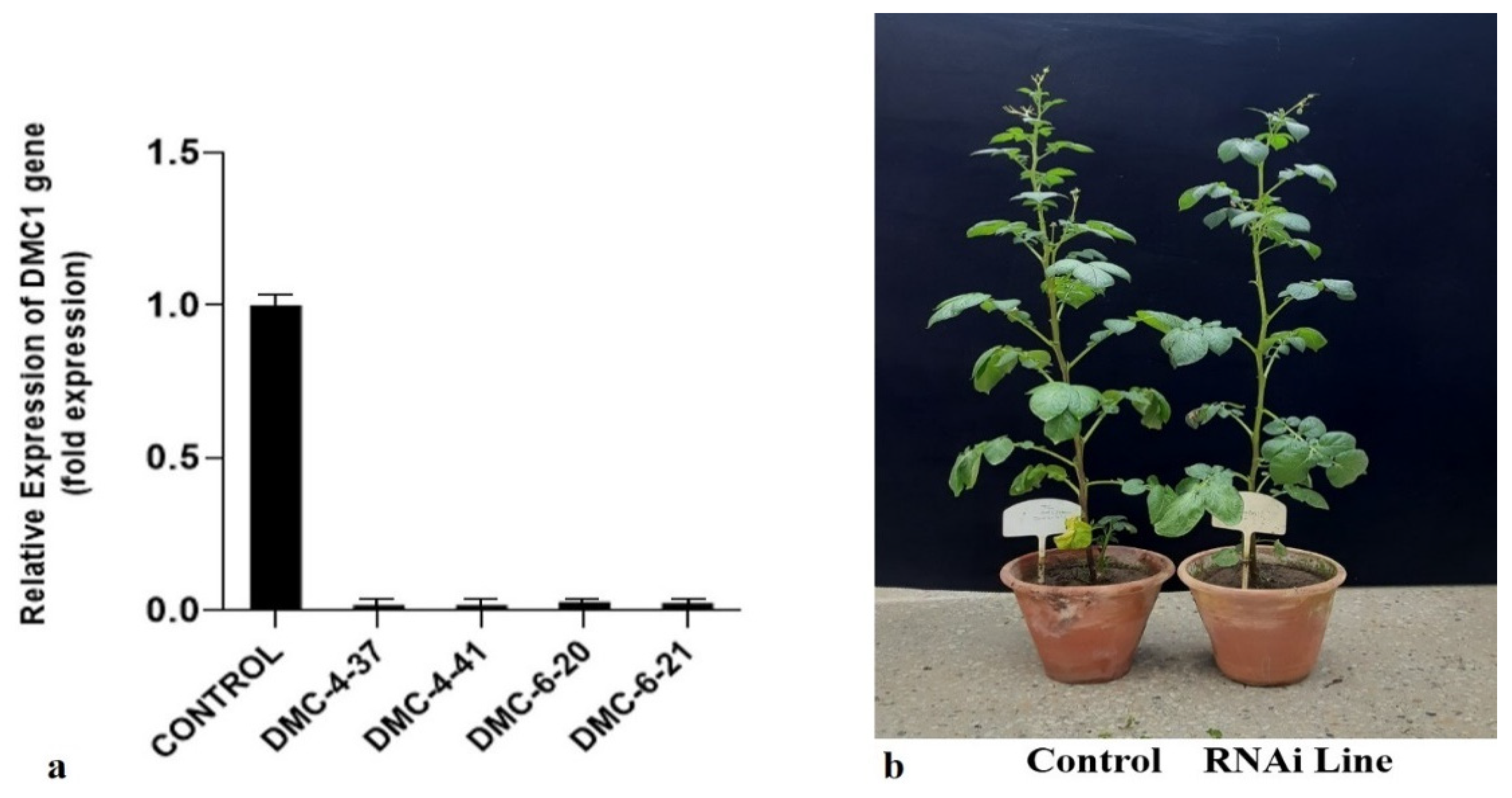
3.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guchi, E. Disease Management Practice on Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) in Ethiopia. World J. Agric. Res. 2015, 3, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Goutam, U.; Kukreja, S.; Siddappa, S.; Sood, S.; Sharma, J.; Bhardwaj, V. Biofortification Strategies to Improve Iron Concentrations in Potato Tubers: Lessons and Future Opportunities. Potato Res. 2021, 65, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, P.B.; Venkateshwaran, M.; Wu, L.; Ané, J.M.; Jiang, J. Agrobacterium-Mediated Transient Gene Expression and Silencing: A Rapid Tool for Functional Gene Assay in Potato. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreugdenhil, D.; Bradshaw, J.; Gebhardt, C.; Govers, F.; Mackerron, D.; Taylor, M.A.; Ross, H.A. Potato Biology and Biotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 157–177. ISBN 9780444510181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonierbale, M.W.; Amoros, W.R.; Salas, E.; de Jong, W. Potato Breeding. In The Potato Crop Its Agricultural, Nutritional and Social Contribution to Humankind; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 163–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, P.G.; Uitdewilligen, J.G.A.M.L.; Voorrips, R.E.; Visser, R.G.F.; van Eck, H.J. Development and Analysis of a 20K SNP Array for Potato (Solanum tuberosum): An Insight into the Breeding History. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 2387–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrino, E.V.; Perrino, P. Crop wild relatives: Know how past and present to improve future research, conservation and utilization strategies, especially in Italy: A review. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2020, 67, 1067–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, S.; Mangal, V.; Bhardwaj, V.; Kardile, H.; Sharma, A.K. Diploid F1 Hybrid TPS Potato Breeding Pipeline and Prospects. Potato J. 2021, 48, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw, J.E. Improving the Nutritional Value of Potatoes by Conventional Breeding and Genetic Modification. In Quality Breeding in Field Crops; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 41–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Kumar, M.; Solankey, S.S. Breeding Potato for Quality Improvement. In Potato—From Incas to All Over World; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandemir, N.; Saygili, İ. Apomixis: New Horizons in Plant Breeding. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2015, 39, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, S.; Kumar, A.; Sundaresha, S.; Bhardwaj, V. Genome Editing Prospects to Develop Disease/Pest-Resistant Potato Varieties. In Sustainable Management of Potato Pests Diseases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 413–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.S.; Bishop, D.K. DNA Strand Exchange and RecA Homologs in Meiosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a016659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symington, L.S.; Rothstein, R.; Lisby, M. Mechanisms and Regulation of Mitotic Recombination in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Genetics 2014, 198, 795–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crickard, J.B.; Greene, E.C. The Biochemistry of Early Meiotic Recombination Intermediates. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 2520–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoharaa, A.; Shinohara, M. Roles of RecA Homologues Rad51 and Dmc1 during Meiotic Recombination. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2004, 107, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Kong, H.; Nei, M.; Ma, H. Origins and Evolution of the RecA/RAD51 Gene Family: Evidence for Ancient Gene Duplication and Endosymbiotic Gene Transfer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10328–10333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurzbauer, M.T.; Uanschou, C.; Chen, D.; Schlögelhofer, P. The Recombinases DMC1 and RAD51 Are Functionally and Spatially Separated during Meiosis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 2058–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, D.; Grubb, J.; Bishop, D.K. A Mutant Form of Dmc1 That Bypasses the Requirement for Accessory Protein Mei5-Sae3 Reveals Independent Activities of Mei5-Sae3 and Rad51 in Dmc1 Filament Stability. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kobayashi, E.; Sato, S.; Hotta, Y.; Miyajima, N.; Tanaka, A.; Tabata, S. Characterization of CDNAs Induced in Meiotic Prophase in Lily Microsporocytes. DNA Res. 1994, 1, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Hotta, Y.; Research, S.T.-D. Structural Analysis of a RecA-like Gene in the Genome of Arabidopsis thaliana. DNA Res. 1995, 2, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doutriaux, M.P.; Couteau, F.; Bergounioux, C.; White, C. Isolation and Characterisation of the RAD51 and DMC1 Homologs from Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Gen. Genet. MGG 1998, 257, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.J.; Wang, T.; Chong, K.; Bai, S. Isolation and Characterization of OsDMC1, the Rice Homologue of the Yeast DMC1 Gene Essential for Meiosis. Sex. Plant Reprod. 2001, 13, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metkar, S.S.; Sainis, J.K.; Mahajan, S.K. Cloning and Characterization of the DMC1 Genes in Oryza sativa. Curr. Sci. 2004, 87, 353–357. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.Y.; Wang, T. OsDMC1 Is Required for Homologous Pairing in Oryza sativa. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 65, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakane, I.; Kamataki, C.; Takizawa, Y.; Nakashima, M.; Toki, S.; Ichikawa, H.; Ikawa, S.; Shibata, T.; Kurumizaka, H. Filament Formation and Robust Strand Exchange Activities of the Rice DMC1A and DMC1B Proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 4266–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etedali, F.; Kohnehrouz, B.B.; Valizadeh, M.; Gholizadeh, A. Genome Wide Cloning of Maize Meiotic Recombinase Dmc1 and Its Functional Structure through Molecular Phylogeny. Genet. Mol. Res. 2011, 10, 1636–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalendar, R.; Lee, D.; Schulman, A.H. FastPCR Software for PCR, in Silico PCR, and Oligonucleotide Assembly and Analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1116, 271–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakate, A.; Higgins, J.D.; Vivera, S.; Stephens, J.; Perry, R.M.; Ramsay, L.; Colas, I.; Oakey, H.; Waugh, R.; Franklin, F.C.H.; et al. The Synaptonemal Complex Protein ZYP1 Is Required for Imposition of Meiotic Crossovers in Barley. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devisetty, U.K.; Mayes, K.; Mayes, S. The RAD51 and DMC1 Homoeologous Genes of Bread Wheat: Cloning, Molecular Characterization and Expression Analysis. BMC Res. Notes 2010, 3, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaresha, S.; Jeevalatha, A.; Kumar, R.; Sood, S.; Sharma, S.; Bhardwaj, V.; Singh, B.; Chakrabarti, S.K. RNA Interference: A Versatile Tool to Augment Plant Protection Strategies in Potato. In Sustainable Management of Potato Pests and Diseases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 369–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Wolters, A.M.A.; Vossen, J.H.; Rouwet, M.E.; Loonen, A.E.H.M.; Jacobsen, E.; Visser, R.G.F.; Bai, Y. Silencing of Six Susceptibility Genes Results in Potato Late Blight Resistance. Transgen. Res. 2016, 25, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, A.; Tahir, M.N.; Asad, S.; Bilal, R.; van Eck, J.; Jander, G.; Mansoor, S. RNAi-Mediated Simultaneous Resistance Against Three RNA Viruses in Potato. Mol. Biotechnol. 2017, 59, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Ines, O.; Degroote, F.; Goubely, C.; Amiard, S.; Gallego, M.E.; White, C.I. Meiotic Recombination in Arabidopsis Is Catalysed by DMC1, with RAD51 Playing a Supporting Role. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draeger, T.; Martin, A.C.; Alabdullah, A.K.; Pendle, A.; Rey, M.D.; Shaw, P.; Moore, G. Dmc1 Is a Candidate for Temperature Tolerance during Wheat Meiosis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 809–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szurman-Zubrzycka, M.; Baran, B.; Stolarek-Januszkiewicz, M.; Kwaśniewska, J.; Szarejko, I.; Gruszka, D. The Dmc1 Mutant Allows an Insight into the DNA Double-Strand Break Repair during Meiosis in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanju, S.; Siddappa, S.; Thakur, A.; Shukla, P.K.; Srivastava, N.; Pattanayak, D.; Sharma, S.; Singh, B.P. Host-Mediated Gene Silencing of a Single Effector Gene from the Potato Pathogen Phytophthora Infestans Imparts Partial Resistance to Late Blight Disease. Funct. Integr. Genomics 2015, 15, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomar, G.; Chakrabarti, S.K.; Sharma, N.N.; Jeevalatha, A.; Sundaresha, S.; Vyas, K.; Azmi, W. RNAi-Based Transgene Conferred Extreme Resistance to the Geminivirus Causing Apical Leaf Curl Disease in Potato. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 12, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Guleria, S.; Reddy, M.S.; Kumar, A. A Robust Genetic Transformation Protocol to Obtain Transgenic Shoots of Solanum tuberosum L. Cultivar ‘Kufri Chipsona 1’. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2020, 26, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijnker, E.; Deurhof, L.; van de Belt, J.; de Snoo, C.B.; Blankestijn, H.; Becker, F.; Ravi, M.; Chan, S.W.L.; van Dun, K.; Lelivelt, C.L.C.; et al. Hybrid Recreation by Reverse Breeding in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colas, I.; Barakate, A.; MacAulay, M.; Schreiber, M.; Stephens, J.; Vivera, S.; Halpin, C.; Waugh, R.; Ramsay, L. Desynaptic5 Carries a Spontaneous Semi-Dominant Mutation Affecting Disrupted Meiotic CDNA 1 in Barley. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 2683–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.M.; Yan, B.; Gao, J.Y.; Si, Y.H.; Zang, X. Dissecting 2 Meiotic Mutations (Dmc1 and Asy1) in Artificial Allopolyploid Arabidopsis thaliana. Cytologia 2011, 76, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
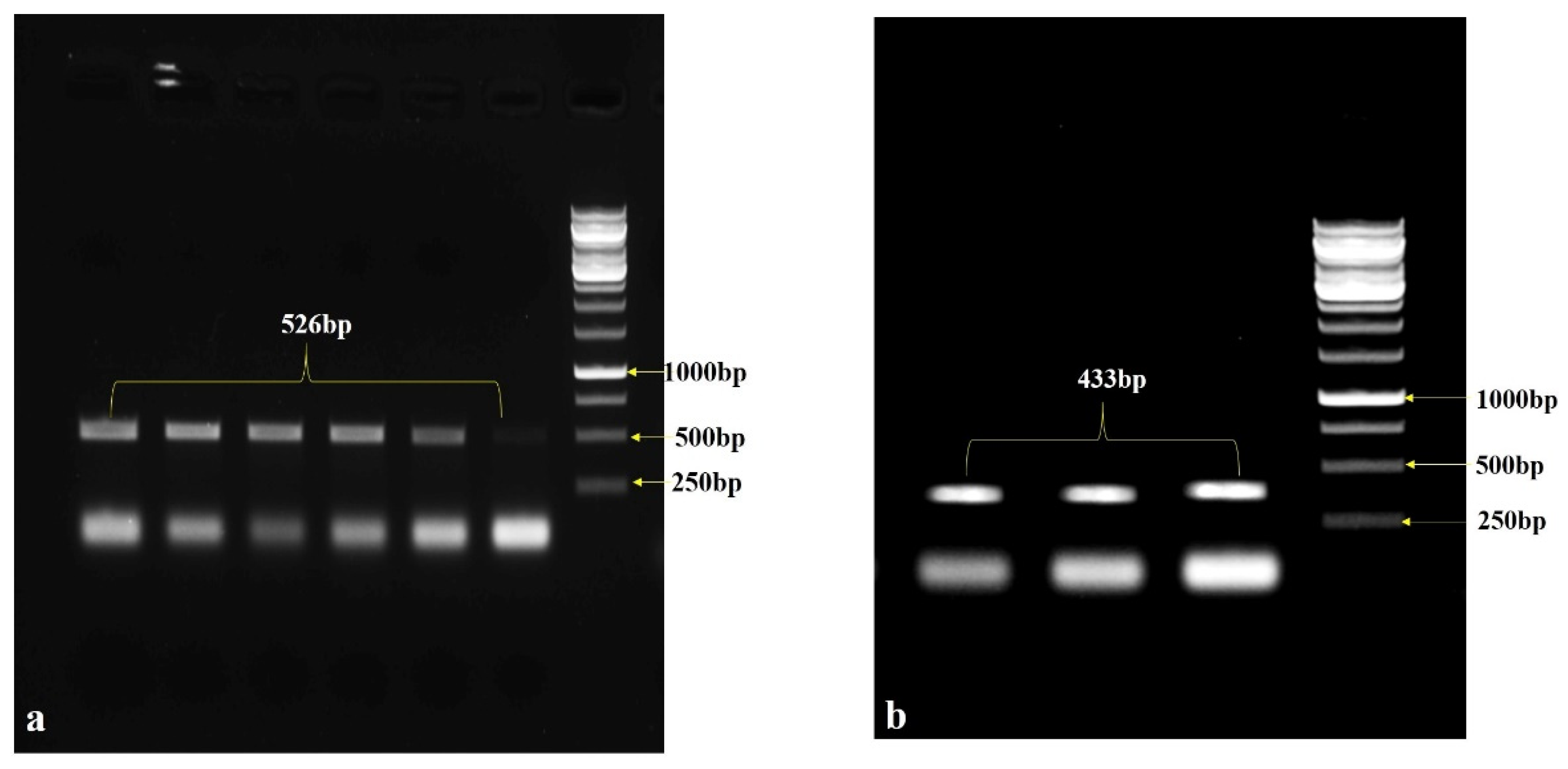







| Primer | Sequence with Restriction Enzyme | Size (bp) | Enzymes |
|---|---|---|---|
| StDMC1 Sense-F | CGCGTCGACGAAGATAGTGAACTTCGGC | 526 | Sal 1 |
| StDMC1 Sense-R | CCCGGGTACCCTTTATCAATCGGGACAGC | Kpn 1 | |
| StDMC1 Antisense-F | CGCGGATCCGAAGATAGTGAACTTCGGC | 433 | Bam H1 |
| StDMC1 Antisense-R | CCCGGGTACCAGAATCCACAATCAGAAGTC | Kpn 1 | |
| NPT II-F | TTTGTCAAGACCGACCTGTC | 530 | |
| NPT II-R | CCAACGCTATGTCCTGATAG |
| Real-Time Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| StDMC RT-F | TACATTACTGGGGAGTGAGGC |
| StDMC RT-R | CCCCAAAAGCTTCAGTTATTGC |
| elf-F | CGTTGTATCATGAATTTGTTTCTCTGT |
| elf-R | CCCCCTGAGGTTTCAACG |
| Explant (Internode) | No. of Cuttings | Callus | No. of Regeneration of Shoots | NPTII Positive | Percentage of Transformation Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kufri Jyoti | 140 | 100 | 310 | 137 | 44 |
| Mutant Lines | Viable Pollens | Non-Viable Pollens | Total | % Viability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMC4-37 | 18 | 107 | 125 | 14.4 |
| DMC4-41 | 12 | 53 | 65 | 18.46 |
| DMC6-20 | 26 | 97 | 123 | 21.14 |
| DMC6-21 | 18 | 88 | 106 | 16.98 |
| Kufri Jyoti- Control | 112 | 31 | 143 | 78.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, A.; Siddappa, S.; Bhardwaj, V.; Dalamu; Singh, B.; Sharma, N.; Dipta, B.; Kumar, V.; Goutam, U.; Sood, S. Generation of Asynaptic Mutants in Potato by Disrupting StDMC1 Gene Using RNA Interference Approach. Life 2023, 13, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010174
Kumar A, Siddappa S, Bhardwaj V, Dalamu, Singh B, Sharma N, Dipta B, Kumar V, Goutam U, Sood S. Generation of Asynaptic Mutants in Potato by Disrupting StDMC1 Gene Using RNA Interference Approach. Life. 2023; 13(1):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010174
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Ashwani, Sundaresha Siddappa, Vinay Bhardwaj, Dalamu, Baljeet Singh, Neha Sharma, Bhawna Dipta, Vinod Kumar, Umesh Goutam, and Salej Sood. 2023. "Generation of Asynaptic Mutants in Potato by Disrupting StDMC1 Gene Using RNA Interference Approach" Life 13, no. 1: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010174
APA StyleKumar, A., Siddappa, S., Bhardwaj, V., Dalamu, Singh, B., Sharma, N., Dipta, B., Kumar, V., Goutam, U., & Sood, S. (2023). Generation of Asynaptic Mutants in Potato by Disrupting StDMC1 Gene Using RNA Interference Approach. Life, 13(1), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010174






