Co-Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Straw-Decomposing Microbial Inoculant on Decomposition and Transformation of Field Composted Wheat Straw
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site Description
2.2. Material Preparation, Experimental Design, and Treatment Application
2.3. Measurements of Straw Decomposition and Nutrient Release
2.4. Straw Chemical Analyses
2.5. Determination of Enzyme Activities
2.6. Statistical Examination
3. Results
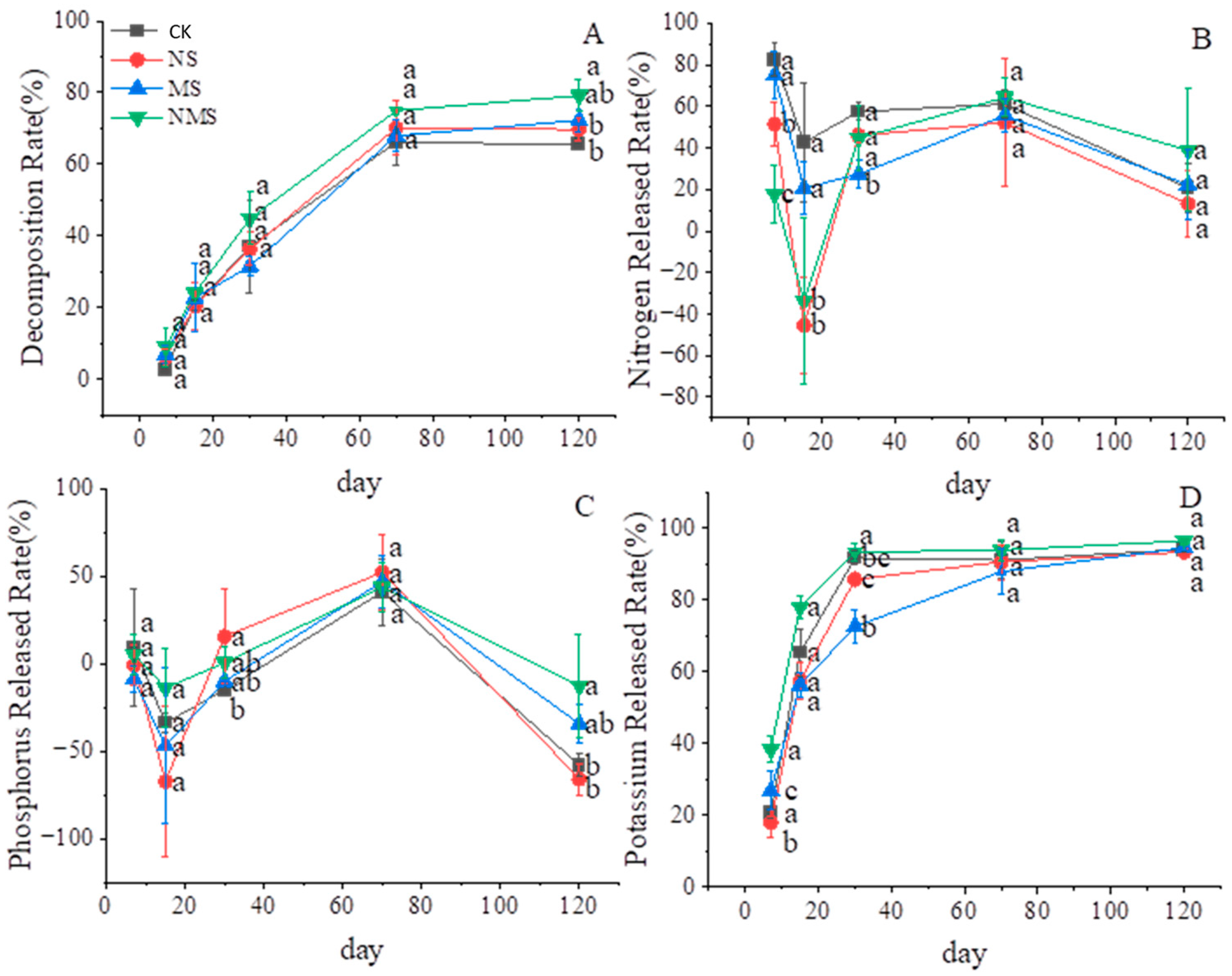
3.1. The Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Microorganisms on the Straw Mass and Nutrient Release
3.2. The Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Microorganisms on the Straw Chemical Composition
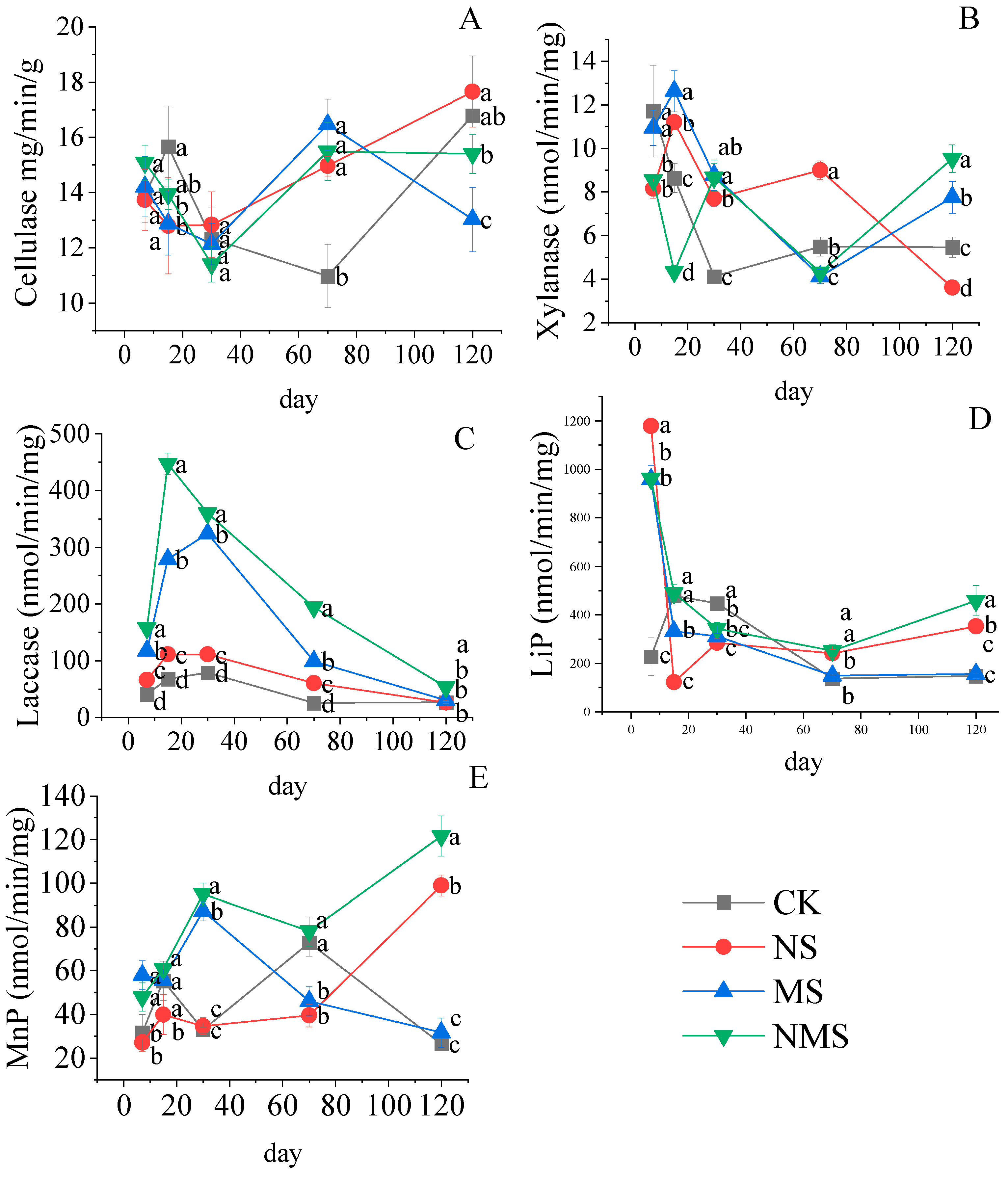
3.3. The Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Microorganisms on the Straw Enzyme Activity
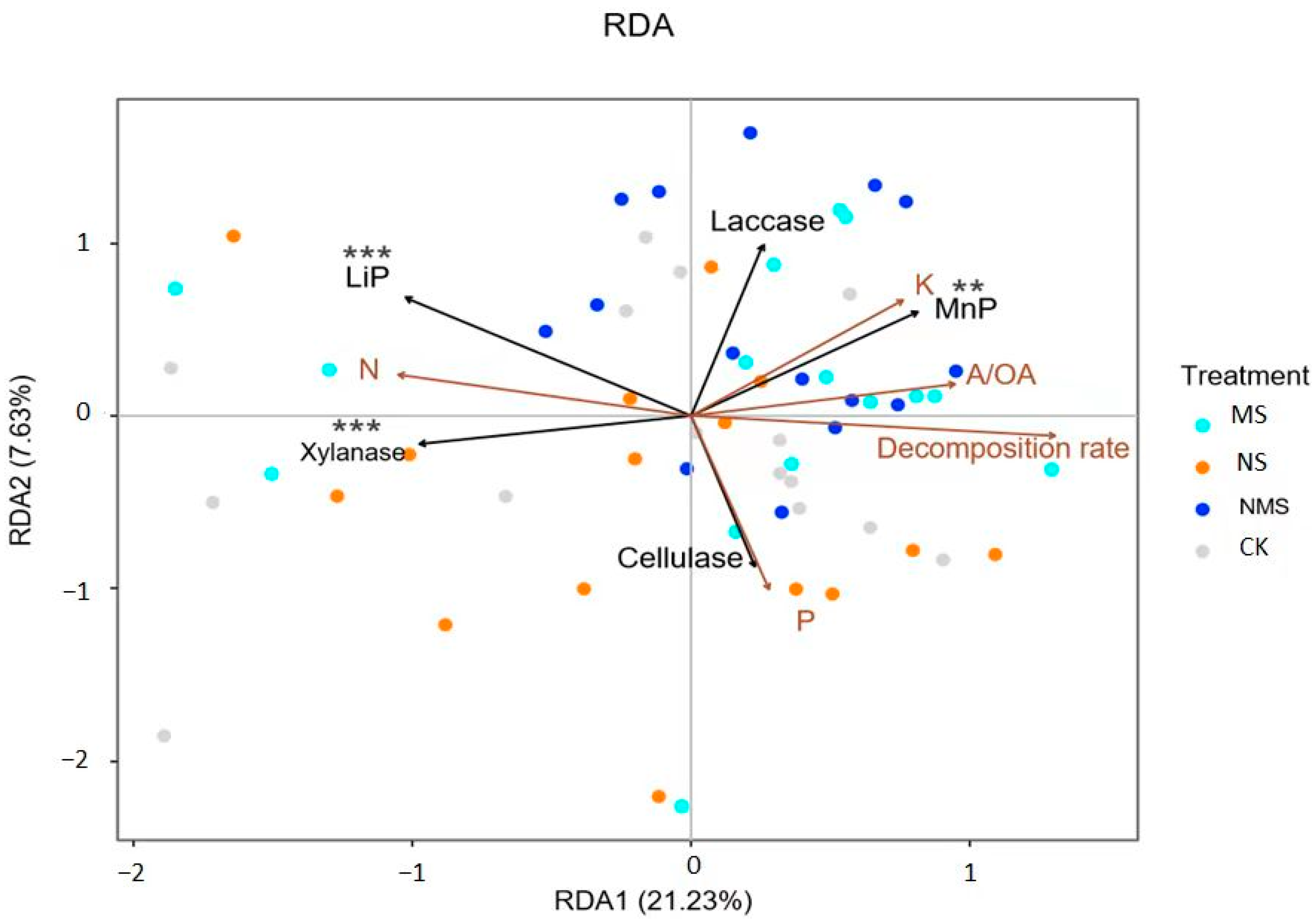
3.4. Relationship between Straw Decomposition and Straw Lignocellulase Activities
4. Discussion
4.1. Nitrogen Fertilizer and Microorganisms Improved the Rate of straw Decomposition
4.2. N Fertilizer and Microorganisms Enhance the Nutrient Release of Straw Decomposition
4.3. Nitrogen Fertilizer and Microorganisms Improved the Activity of the Stalk Rot Enzyme
4.4. The Positive Relationships of Straw Decomposition and Enzyme Activities with Nutrient Addition
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carrosio, G. Energy production from biogas in the Italian countryside: Modernization vs. repeasantization. Biomass-Bioenergy 2014, 70, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Menna, F.; Malagnino, R.A.; Vittuari, M.; Molari, G.; Seddaiu, G.; Deligios, P.A.; Solinas, S.; Ledda, L. Potential biogas production from artichoke byproducts in sardinia, italy. Energies 2016, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, C.; Montero, G.; Coronado, M.; Torres, R.; Vázquez, A.M.; Ayala, J.R.; León, J.A.; Sagaste, C.A. Power generation estimation from wheat straw in Mexico. Energy Sustain. VI WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 195, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamoud, Y.A.; Shaghaleh, H.; Wang, R.; Gouertoumbo, W.F.; Hamad, A.A.A.; Sheteiwy, M.S.; Wang, Z.; Xiangping, G. Wheat Straw Burial Improves Physiological Traits, Yield and Grain Quality of Rice by Regulating Antioxidant System and Nitrogen Assimilation Enzymes under Alternate Wetting and Drying Irrigation. Rice Sci. 2022, 29, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deligios, P.A.; Farina, R.; Tiloca, M.T.; Francaviglia, R.; Ledda, L. C-sequestration and resilience to climate change of globe artichoke cropping systems depend on crop residues management. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 41, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Guo, X.; Liu, M.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Zheng, J.; Qiu, R. Effects of uneven vertical distribution of soil salinity under a buried straw layer on the growth, fruit yield, and fruit quality of tomato plants. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 203, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Bons, H.K. Mulching: A viable option to increase productivity of field and fruit crops. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2017, 9, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francaviglia, R.; Renzi, G.; Doro, L.; Parras-Alcántara, L.; Lozano-García, B.; Ledda, L. Soil sampling approaches in Mediterranean agro-ecosystems. Influence on soil organic carbon stocks. CATENA 2017, 158, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yao, S.-H.; Jiang, H.; Ge, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, J.; Dou, S.; Zhang, B. Effects of mixing maize straw with soil and placement depths on decomposition rates and products at two cold sites in the mollisol region of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerda, A.; Artola, A.; Font, X.; Barrena, R.; Gea, T.; Sánchez, A. Composting of food wastes: Status and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaghaleh, H.; Xu, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Dong, F.; Luo, J. The effect of atmospheric pressure plasma pretreatment with various gases on the structural characteristics and chemical composition of wheat straw and applications to enzymatic hydrolysis. Energy 2019, 176, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, G.; Xu, W.; Boutton, T.W.; Zhuge, Y.; Bai, E. Effects of nitrogen addition on soil organic carbon mineralization after maize stalk addition. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2018, 89, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Li, J.H.; Wei, C.Z.; Zhang, Y.T. Decomposition characteristics and nutrient release rules of maize straw under different returning amounts. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 3695–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiti, T.; Gardin, L.; Perugini, L.; Valentini, R. Soil organic carbon stock assessment for the different cropland land uses in Italy. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2012, 48, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, R.; Klose, M.; Yuan, Q.; Lu, Y.; Chidthaisong, A. Stable carbon isotope fractionation, carbon flux partitioning and priming effects in anoxic soils during methanogenic degradation of straw and soil organic matter. Soil Biol. Bio. 2012, 49, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Wang, X.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Lu, M.; Shaghaleh, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Ma, C. Dynamic variation of bacterial community assemblage and functional profiles during rice straw degradation. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1173442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacenetti, J.; Sala, C.; Fusi, A.; Fiala, M. Agricultural anaerobic digestion plants: What LCA studies pointed out and what can be done to make them more environmentally sustainable. Appl. Energy 2016, 179, 669–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Kang, K.; Chen, D.; Liu, N. Impacts of delayed addition of N-rich and acidic substrates on nitrogen loss and compost quality during pig manure composting. Waste Manag. 2018, 72, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkhajeh, Y.K.; He, Z.; Yang, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Gao, H.; Ma, C. Co-application of nitrogen and straw-decomposing microbial inoculant enhanced wheat straw decomposition and rice yield in a paddy soil. J. Agric. Food Res. 2021, 4, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; O’Sullivan, J.B.; Wang, X.; Tang, C. Elevated CO2 alters the rhizosphere effect on crop residue decomposition. Plant Soil 2019, 436, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhao, B.; Olk, D.C.; Zhang, J. Soil texture and straw type modulate the chemical structure of residues during four-year decomposition by regulating bacterial and fungal communities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 155, 103664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbi, D.K.; Brar, K.; Toor, A.S.; Sharma, S. Sensitivity of Labile Soil Organic Carbon Pools to Long-Term Fertilizer, Straw and Manure Management in Rice-Wheat System. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.G.; Jia, B.; Lv, J.; Ma, Q.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Li, F.-M. Nitrogen fertilization decreases the decomposition of soil organic matter and plant residues in planted soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 112, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, E.; Chi, F.; Jeng, A.S.; Su, Q.; Zhang, J. A comparison of different methods of decomposing maize straw in China. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B-Soil Plant Sci. 2014, 63, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Pangga, G.; Blair, G.; Lefroy, R. Measurement of decomposition and associated nutrient release from straw (Oryza sativa L.) of different rice varieties using a perfusion system. Plant Soil 2000, 223, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddi, G.A.; Hafidi, M.; Cegarra, J.; Alburquerque, J.A.; Gonzálvez, J.; Gilard, V.; Revel, J.-C. Characterization of fulvic acids by elemental and spectroscopic (FTIR and 13C-NMR) analyses during composting of olive mill wastes plus straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 93, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.-J.; Almendros, G. Chemical transformation, phytotoxicity and nutrient availability in progressive composting stages of wheat straw. Plant Soil 1997, 196, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, J.; Mao, J.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L.; Xin, X.; Zhao, B. Mass loss and chemical structures of wheat and maize straws in response to ultraviolet-B radiation and soil contact. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Marschner, P. Soil amendment with high and low C/N residue -influence of low soil water content between first and second residue addition on soil respiration, microbial biomass and nutrient availability. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, A.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D. Preparation of samples for compositional analysis. Lab. Anal. Proced. (LAP) 2008, 1617, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M.; Norman, A.G. Inorganic Forms of Nitrogen. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 9.2; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1965; pp. 1179–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, D.; Peterson, G.A.; Pratt, P.F. Lithium, sodium, and potassium. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 9.2.2; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, J.M.; Smeck, N. Comparisons of Humic Substances Extracted from Contiguous Alfisols and Mollisols of Southwestern Ohio. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Mohamed, T.A.; Zhu, L.; Wu, J.; Meng, Q.; Yao, C.; Zhao, R. Improved lignocellulose degradation efficiency based on Fenton pretreatment during rice straw composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 294, 122132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Liu, E.K.; Tian, Q.; Yan, C.; Zhang, Y. Soil nitrogen dynamics and crop residues. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasielski, J.; Deen, B. Nitrogen applications made close to silking: Implications for yield formation in maize. Field Crop. Res. 2019, 243, 107621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, S. Linkages between straw decomposition rate and the change in microbial fractions and extracellular enzyme activities in soils under different long-term fertilization treatments. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jin, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Gao, H.; Chu, W.; Mao, J.; Thompson, M.L. Nitrogen application increases abundance of recalcitrant compounds of soil organic matter: A 6-year case study. Soil Sci. 2018, 183, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Chacon, S.S.; German, D.P. Substrate concentration constraints on microbial decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 79, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-X.; Wang, Y.-F.; Lü, H.-H.; Chen, Y.; Tang, X.; Wu, C.-Y.; Zhong, Z.-K.; Yang, S.-M. Effects of biochar application on greenhouse gas emission from paddy soil and its physical and chemical properties. Ying yong sheng tai xue bao = J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 24, 2166–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Di Lonardo, D.P.; Manrubia, M.; De Boer, W.; Zweers, H.; Veen, G.F.; Van der Wal, A. Relationship between home-field advantage of litter decomposition and priming of soil organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 126, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanin, N.; Alavoine, G.; Bertrand, I. Temporal dynamics of litter quality, soil properties and microbial strategies as main drivers of the priming effect. Geoderma Int. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 377, 114576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunan, N.; Schmidt, H.; Raynaud, X. The ecology of heterogeneity: Soil bacterial communities and c dynamics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 375, 20190249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Marschner, P. Soil Respiration, Microbial Biomass and Nutrient Availability in Soil After Addition of Residues with Adjusted N and P Concentrations. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Sun, Y.; Hui, X.; Jiang, M.; Xiang, K.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Sun, Y. The effect of straw mulch on nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium uptake and use in hybrid rice. Paddy Water Environ. 2019, 17, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Peñuelas, J.; Xu, X.; Sardans, J.; Fang, Y.; Wiesmeier, M.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, W. Effects of addition of nitrogen-enriched biochar on bacteria and fungi community structure and C, N, P, and Fe stoichiometry in subtropical paddy soils. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2021, 106, 103351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Qu, Z.; You, P.; Qu, D. Effect of biochar on photosynthetic microorganism growth and iron cycling in paddy soil under different phosphate levels. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 612, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T. Does ecoenzymatic stoichiometry really determine microbial nutrient limitations? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 146, 107816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Leppert, K.N.; Eichenberg, D.; Bruelheide, H.; Niklaus, P.A.; Buscot, F.; Gutknecht, J.L.M. Leaf litter diversity alters microbial activity, microbial abundances, and nutrient cycling in a subtropical forest ecosystem. Biogeochemistry 2017, 134, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Razavi, B.S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Blagodatskaya, E. Microbial growth and enzyme kinetics in rhizosphere hotspots are modulated by soil organics and nutrient availability. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 141, 107662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Christie, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. Response of the soil microbial community to different fertilizer inputs in a wheat-maize rotation on a calcareous soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 260, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, D.J.; Weintraub, M.N.; Hewins, C.R.; Kalisz, S. Relationship between soil enzyme activities, nutrient cycling and soil fungal communities in a northern hardwood forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.-K.; Wei, L.; Turner, N.C.; Ma, S.-C.; Yang, M.-D.; Wang, T.-C. Improved straw management practices promote in situ straw decomposition and nutrient release, and increase crop production. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 250, 119514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rineau, F.; Shah, F.; Smits, M.M.; Persson, P.; Johansson, T.; Carleer, R.; Troein, C.; Tunlid, A. Carbon availability triggers the decomposition of plant litter and assimilation of nitrogen by an ectomycorrhizal fungus. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2010–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Bei, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Hu, S.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Jin, H.; Hu, T.; et al. Microbial metabolic efficiency and community stability in high and low fertility soils following wheat residue addition. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 159, 103848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Tang, S.; Gong, J.; Zeng, G.; Tang, W.; Song, B.; Zhang, P.; Yang, Z.; Luo, Y. Responses of enzymatic activity and microbial communities to biochar/compost amendment in sulfamethoxazole polluted wetland soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Su, Y.; He, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; He, H.; Kariman, K.; Wu, J.; Chen, X. Effects of long-term straw incorporation on lignin accumulation and its association with bacterial laccase-like genes in arable soils. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1961–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, U.; Johnson, C.E. Characterization of organic matter in a northern hardwood forest soil by c-13 nmr spectroscopy and chemical methods. Geoderma Int. J. Soil Sci. 2003, 111, 123–149. [Google Scholar]
- Tambone, F.; Adani, F. Nitrogen mineralization from digestate in comparison to sewage sludge, compost and urea in a laboratory incubated soil experiment. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2017, 180, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Time | Treatment | 220–188 ppm | 188–162 ppm | 162–142 ppm | 142–113 ppm | 113–93 ppm | 93–64 ppm | 64–44 ppm | 44–0 ppm | Other | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days | Applied | C=O | COO/N-C=O | Aromatic C-O | Aromatic C-C | Anomeric C | O-Alkyl C | OCH3 | Alkyl C | A/OA | Aromaticity | Hydrophobic |
| 7 | CK | NA | 1.10 ± 0.26 c | 2.42 ± 0.13 c | 4.04 ± 0.31 c | 16.2 ± 0.14 a | 55.6 ± 0.35 a | 15.2 ± 0.46 a | 6.10 ± 0.24 a | 0.11 ± 0.00 a | 0.06 ± 0.00 c | 0.23 ± 0.01 c |
| NS | 0.14 ± 0.24 ab | 2.48 ± 0.36 b | 3.53 ± 0.07 b | 6.19 ± 0.35 b | 16.7 ± 0.27 a | 53.3 ± 0.62 b | 12.7 ± 0.68 b | 4.96 ± 0.68 a | 0.09 ± 0.01 a | 0.10 ± 0.01 b | 0.27 ± 0.02 bc | |
| MS | 0.09 ± 0.16 ab | 2.41 ± 0.24 b | 3.39 ± 0.07 b | 6.01 ± 0.32 b | 16.6 ± 0.7 a | 53.3 ± 1.77 b | 13.2 ± 0.75 b | 5.07 ± 1.54 a | 0.10 ± 0.03 a | 0.01 ± 0.01 b | 0.27 ± 0.04 b | |
| NMS | 0.34 ± 0.08 a | 3.53 ± 0.43 a | 4.23 ± 0.15 a | 7.00 ± 0.39 a | 16.2 ± 0.13 a | 50.7 ± 1.10 c | 12.5 ± 0.09 b | 5.63 ± 0.29 a | 0.11 ± 0.01 a | 0.11 ± 0.01 a | 0.30 ± 0.02 a | |
| 15 | CK | 1.94 ± 0.30 a | 4.69 ± 0.61 a | 4.27 ± 0.16 a | 8.16 ± 0.27 a | 14.7 ± 0.26 a | 42.3 ± 1.45 a | 14.5 ± 0.69 a | 9.52 ± 1.14 a | 0.23 ± 0.03 a | 0.14 ± 0.00 a | 0.50 ± 0.05 a |
| NS | 2.03 ± 0.36 a | 5.02 ± 0.22 a | 4.34 ± 0.14 a | 7.90 ± 0.89 a | 14.5 ± 0.30 a | 41.7 ± 2.06 a | 14.8 ± 0.70 a | 9.69 ± 1.36 a | 0.23 ± 0.04 a | 0.13 ± 0.02 a | 0.50 ± 0.07 a | |
| MS | 1.64 ± 0.51 a | 4.81 ± 0.57 a | 4.17 ± 0.44 a | 7.62 ± 0.50 a | 14.3 ± 0.21 a | 41.0 ± 1.51 a | 15.5 ± 1.39 a | 11.1 ± 1.65 a | 0.24 ± 0.05 a | 0.13 ± 0.01 a | 0.41 ± 0.05 a | |
| NMS | 1.84 ± 0.17 a | 4.96 ± 0.39 a | 4.53 ± 0.02 a | 7.68 ± 0.07 a | 14.3 ± 0.31 a | 41.5 ± 0.91 a | 15.3 ± 0.35 a | 9.84 ± 0.69 a | 0.27 ± 0.02 a | 0.13 ± 0.00 a | 0.51 ± 0.02 a | |
| 30 | CK | 1.85 ± 0.24 a | 4.53 ± 0.28 a | 4.36 ± 0.03 a | 8.16 ± 0.50 a | 14.6 ± 0.12 a | 41.3 ± 1.50 a | 14.9 ± 0.36 a | 10.3 ± 1.47 a | 0.25 ± 0.04 a | 0.14 ± 0.01 a | 0.53 ± 0.07 a |
| NS | 2.02 ± 0.67 a | 4.97 ± 1.29 a | 4.58 ± 0.54 a | 8.01 ± 0.81 a | 14.4 ± 0.64 a | 40.7 ± 2.88 a | 15.2 ± 0.75 a | 10.1 ± 2.01 a | 0.25 ± 0.06 a | 0.14 ± 0.02 a | 0.54 ± 0.08 a | |
| MS | 2.09 ± 0.73 a | 5.38 ± 0.83 a | 4.89 ± 0.28 a | 8.49 ± 0.29 a | 14.3 ± 0.11 a | 39.9 ± 0.31 a | 14.4 ± 0.74 a | 10.6 ± 1.24 a | 0.26 ± 0.03 a | 0.14 ± 0.01 a | 0.57 ± 0.02 a | |
| NMS | 1.98 ± 0.19 a | 5.29 ± 0.60 a | 4.62 ± 0.15 a | 8.08 ± 0.22 a | 13.8 ± 0.78 a | 39.6 ± 2.28 a | 15.0 ± 0.21 a | 11.7 ± 2.12 a | 0.30 ± 0.07 a | 0.14 ± 0.00 a | 0.59 ± 0.09 a | |
| 70 | CK | 2.35 ± 1.03 a | 6.20 ± 1.06 ab | 4.85 ± 0.45 ab | 9.66 ± 0.91 a | 12.2 ± 0.42 b | 31.1 ± 1.81 b | 16.1 ± 1.44 a | 17.5 ± 1.05 a | 0.57 ± 0.05 a | 0.17 ± 0.02 a | 0.96 ± 0.08 a |
| NS | 1.94 ± 0.42 a | 5.13 ± 1.22 b | 4.57 ± 0.22 b | 8.26 ± 0.92 a | 13.9 ± 1.03 a | 39.6 ± 4.74 a | 15.3 ± 0.10 a | 11.4 ± 3.07 b | 0.30 ± 0.12 b | 0.14 ± 0.02 a | 0.59 ± 0.17 b | |
| MS | 2.36 ± 0.15 a | 7.00 ± 0.29 a | 5.27 ± 0.06 a | 9.16 ± 0.39 a | 12.0 ± 0.43 b | 31.9 ± 1.27 b | 16.3 ± 0.24 a | 16.0 ± 1.06 a | 0.50 ± 0.05 a | 0.16 ± 0.01 a | 0.89 ± 0.07 a | |
| NMS | 2.24 ± 0.24 a | 6.12 ± 0.44 ab | 4.78 ± 0.13 ab | 9.33 ± 1.63 a | 12.7 ± 0.55 ab | 33.6 ± 3.79 ab | 15.8 ± 0.60 a | 15.5 ± 2.52 a | 0.47 ± 0.13 ab | 0.16 ± 0.03 a | 0.84 ± 0.20 ab | |
| 120 | CK | 2.84 ± 0.71 a | 6.58 ± 0.47 a | 5.59 ± 0.51 a | 10.3 ± 0.95 a | 13.5 ± 0.58 a | 33.4 ± 0.87 b | 14.2 ± 1.19 a | 13.5 ± 1.45 a | 0.40 ± 0.04 a | 0.18 ± 0.02 a | 0.81 ± 0.01 ab |
| NS | 3.27 ± 0.21 a | 6.63 ± 0.06 a | 5.47 ± 0.10 a | 10.9 ± 0.25 a | 13.1 ± 0.13 a | 32.2 ± 0.41 b | 14.2 ± 0.16 a | 14.3 ± 0.43 a | 0.44 ± 0.02 a | 0.19 ± 0.00 a | 0.87 ± 0.02 ab | |
| MS | 2.90 ± 0.37 a | 5.78 ± 1.08 ab | 5.58 ± 0.98 a | 10.0 ± 1.31 a | 13.2 ± 0.77 a | 31.9 ± 1.70 b | 15.8 ± 1.60 a | 14.9 ± 2.29 a | 0.47 ± 0.09 a | 0.18 ± 0.03 a | 0.88 ± 0.10 a | |
| NMS | 1.71 ± 0.54 b | 5.00 ± 0.38 b | 4.76 ± 0.09 a | 8.03 ± 0.03 b | 13.0 ± 0.48 a | 36.1 ± 1.80 a | 16.5 ± 1.14 a | 15.0 ± 1.45 a | 0.42 ± 0.06 a | 0.14 ± 0.00 b | 0.74 ± 0.08 b | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shaghaleh, H.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, X.; Alhaj Hamoud, Y.; Ma, C. Co-Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Straw-Decomposing Microbial Inoculant on Decomposition and Transformation of Field Composted Wheat Straw. Life 2023, 13, 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13101993
Shaghaleh H, Zhu Y, Shi X, Alhaj Hamoud Y, Ma C. Co-Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Straw-Decomposing Microbial Inoculant on Decomposition and Transformation of Field Composted Wheat Straw. Life. 2023; 13(10):1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13101993
Chicago/Turabian StyleShaghaleh, Hiba, Yuanpeng Zhu, Xinyi Shi, Yousef Alhaj Hamoud, and Chao Ma. 2023. "Co-Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Straw-Decomposing Microbial Inoculant on Decomposition and Transformation of Field Composted Wheat Straw" Life 13, no. 10: 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13101993
APA StyleShaghaleh, H., Zhu, Y., Shi, X., Alhaj Hamoud, Y., & Ma, C. (2023). Co-Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Straw-Decomposing Microbial Inoculant on Decomposition and Transformation of Field Composted Wheat Straw. Life, 13(10), 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13101993









