Heavy Metals Levels in Soil, Water and Feed and Relation to Slaughtered Camels’ Tissues (Camelus dromedarius) from Five Districts in Saudi Arabia during Spring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Districts and Temperatures
2.2. Samples Collection and Preparation
2.3. Heavy Metals Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ogbomida, E.T.; Nakayama, S.M.M.; Bortey-Sam, N.; Oroszlany, B.; Tongo, I.; Enuneku, A.A.; Ozekeke, O.; Ainerua, M.O.; Fasipe, I.P.; Ezemonye, L.I.; et al. Accumulation patterns and risk assessment of metals and metalloid in muscle and offal of free-range chickens, cattle and goat in Benin City, Nigeria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 151, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Londoño Franco, L.F.; Londoño Muñoz, P.T.; Muñoz Garcia, F.G. Los riesgos de los metales pesados en la salud humana y animal. Biotecnoloía Sect. Agropecu. Y Agroind. 2016, 14, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.A.; Shamat, A.M.; Hussien, M.O.; El Hussein, A.R. Profile of some trace elements in the liver of camels, sheep, and goats in the sudan. J. Vet. Med. 2013, 2013, 736497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; Mishra, A.; Kumar, G.; Shukla, D. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and contaminants of River Palar. Renew. Energy 2017, 102, 44182–44186. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, M.S.; Ahmed, D.E. Investigation on the effect of polluted underground water with minerals metals and trace elements on different meat types in Tambol area- Sudan. Sudan J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Almayahi, B.A.; Saheb, L.; Abbood, A.H. Determination of alpha particles and heavy metals contamination in meat samples in Najaf, Iraq. Iran. J. Med. Phys. 2019, 16, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baramaki Yazdi, R.; Ebrahimpour, M.; Mansouri, B.; Rezaei, M.R.; Babaei, H. Contamination of metals in tissues of Ctenopharyngodon idella and Perca fluviatilis, from Anzali Wetland, Iran. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 89, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oymak, T.; Tokalıoğlu, Ş.; Yılmaz, V.; Kartal, Ş.; Aydın, D. Determination of lead and cadmium in food samples by the coprecipitation method. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 1314–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovic, S.; Kalaba, P.; Stankovic, A.R. Biota as toxic metal indicators. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2013, 12, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyaee, M.; Mansouri, B.; Rezaei, Z. Comparison of the metal concentrations in the muscles of slaughtered cows, calves, and sheep in Sanandaj city, Iran. Iran. J. Toxicol. 2015, 9, 1235–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Badis, B. Levels of selected heavy metals in fresh meat from cattle, sheep, chicken and camel produced in Algeria. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2014, 4, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, A.; Junaidu, A.U.; Salihu, M.D.; Agaie, B.M.; Saulawa, M.A.; Musawa, A.I.; Ahmad, K.H. Determination of heavy metal residues in slaughtered camels at Sokoto and Gusau modern abattoirs, Nigeria. J. Health Pollut. 2018, 8, 181204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazargani-Gilani, B.; Pajohi-Alamoti, M.; Bahari, A.; Sari, A.A. Heavy metals and trace elements in the livers and kidneys of slaughtered cattle, sheep and goats. Iran. J. Toxicol. 2016, 10, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, S.M.; Khan, S.W.; Hayat, I. Effect of environmental pollution on quality of meat in district Bagh, Azad Kashmir. Pak. J. Nutr. 2003, 2, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M. Heavy metal concentrations in bovine tissues (muscle, liver and kidney) and their relationship with heavy metal contents in consumed feed. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 154, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, R. Camel; Reaktion Books Ltd.: London, UK, 2010; pp. 1–88. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, P.A.; Ciani, E.; Faye, B. Old world camels in a modern world—A balancing act between conservation and genetic improvement. Anim. Genet. 2019, 50, 598–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouajd, S.; Kamel, B. Physiological particularities of dromedary (Camelus dromedarius) and experimental implications. Scand. J. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2009, 36, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.M.; Alhidary, I.A.; Alobre, M.M.; Matar, A.M.; Alharthi, A.S.; Faye, B.; Aljumaah, R.S. Regional and seasonal variability of mineral patterns in some organs of slaughtered one-humped camels (Camelus dromedarius) from Saudi Arabia. Animals 2022, 12, 3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.; Xanthos, S.J.; Galiotos, J.K.; Douvris, C. Investigation of the metal content of sediments around the historically polluted Potomac River basin in Washington, D.C., United States by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES). Microchem. J. 2018, 142, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadim, I.T.; Mahgoub, O.; Al-Marzooqi, W. Meat quality and composition of Longissimus thoracis from Arabian camel (Camelus dromedaries) and Omani beef: A comparative study. J. Camelid Sci. 2008, 1, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelbasset, C.; Rabia, E.; Abdallah, B.; Boubker, N.; Abdelkhalid, E. Distribution of trace elements and heavy metals in liver, lung, meat, heart and kidney of cattle, sheep, camel and equine slaughtered in Casablanca city. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2014, 5, 294–303. [Google Scholar]
- Al-perkhdri, A.S.A. Study of the Some Heavy Metals Residues in the Camel Meat in different regions of Kirkuk governorate during the spring and Summer Seasons. In Proceedings of the 2nd Virtual International Scintific Agrticultural Conference; IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP: London, UK, 2021; p. 012080. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, Y.A.; Meligy, A.M.A.; El-Ghareeb, W.R.; Al-Shokair, S.S.; Abdel-Raheem, S.M. Selected heavy metals and their risk assessment in camels (Camelus dromedarius). J. Camel Pract. Res. 2022, 29, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, A.; Mohamed, F. Estimation of some heavy metals residues in blood serum and tissues of camels. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 2015, 61, 221–229. [Google Scholar]
- Alturiqi, A.S.; Albedair, L.A. Evaluation of some heavy metals in certain fish, meat and meat products in Saudi Arabian markets. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2012, 38, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Scientific opinion of the panel on contaminants in the food Chainona request from the European Commission on cadmium in food. EFSA J. 2009, 980, 1–139. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhiet, A.; Mohammed, A.; Siham, E.; El Badwi, M.S. Some trace-elements profile in the liver of camels, cattle, sheep and goats. Int. J. Trop. Med. 2007, 2, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Khalafalla, F.A.; Abdel-Atty, N.S.; Abd-El-Wahab, M.A.; Ali, O.I.; Abo-Elsoud, R.B. Assessment of heavy metal residues in retail meat and offals. Am. Sci. 2015, 11, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Commission, C.A. Procedural Manual, 21st ed.; Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme: Rome, Italy, 2013; Volume 21. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, C.W.N.; Smith, S.L.; Jeyakumar, P.; Thompson-Morrison, H.; Cavanagh, J.E. Forage crops and cadmium: How changing farming systems might impact cadmium accumulation in animals. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALI, S.; Rehman, R.; Abbas, A.; Mahmud, T.; Anwar, J.; Salman, M. Minerals and nutritional composition of camel (Camelus dromedarius) meat in Pakistan. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2011, 33, 835–838. [Google Scholar]
- Asli, M.; Azizzadeh, M.; Moghaddamjafari, A.; Mohsenzadeh, M. Copper, iron, manganese, zinc, cobalt, arsenic, cadmium, chrome, and lead concentrations in liver and muscle in Iranian camel (Camelus dromedarius). Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 194, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabir, A.; Altaf, F.; Batool, R.; Shafiq, M.; Khan, R.U.; Jacob, K.I. Agricultural waste absorbents for heavy metal removal. In Green Adsorbents to Remove Metals, Dyes and Boron from Polluted Water; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 49, pp. 195–228. [Google Scholar]
- Baydan, E.; Kanbur, M.; Arslanbaş, E.; Gönül Aydin, F.; Gürbüz, S.; Yasin Tekeli, M. Contaminants in animal products. In Livestock Science; Books on Demand GmbH: Norderstedt, Germany, 2017; Volume 129, Chapter 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoto, O.; Bismark, E.F.; Darko, G.; Adei, E. Concentrations and health risk assessments of heavy metals in fish from the Fosu Lagoon. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2014, 8, 403–410. [Google Scholar]
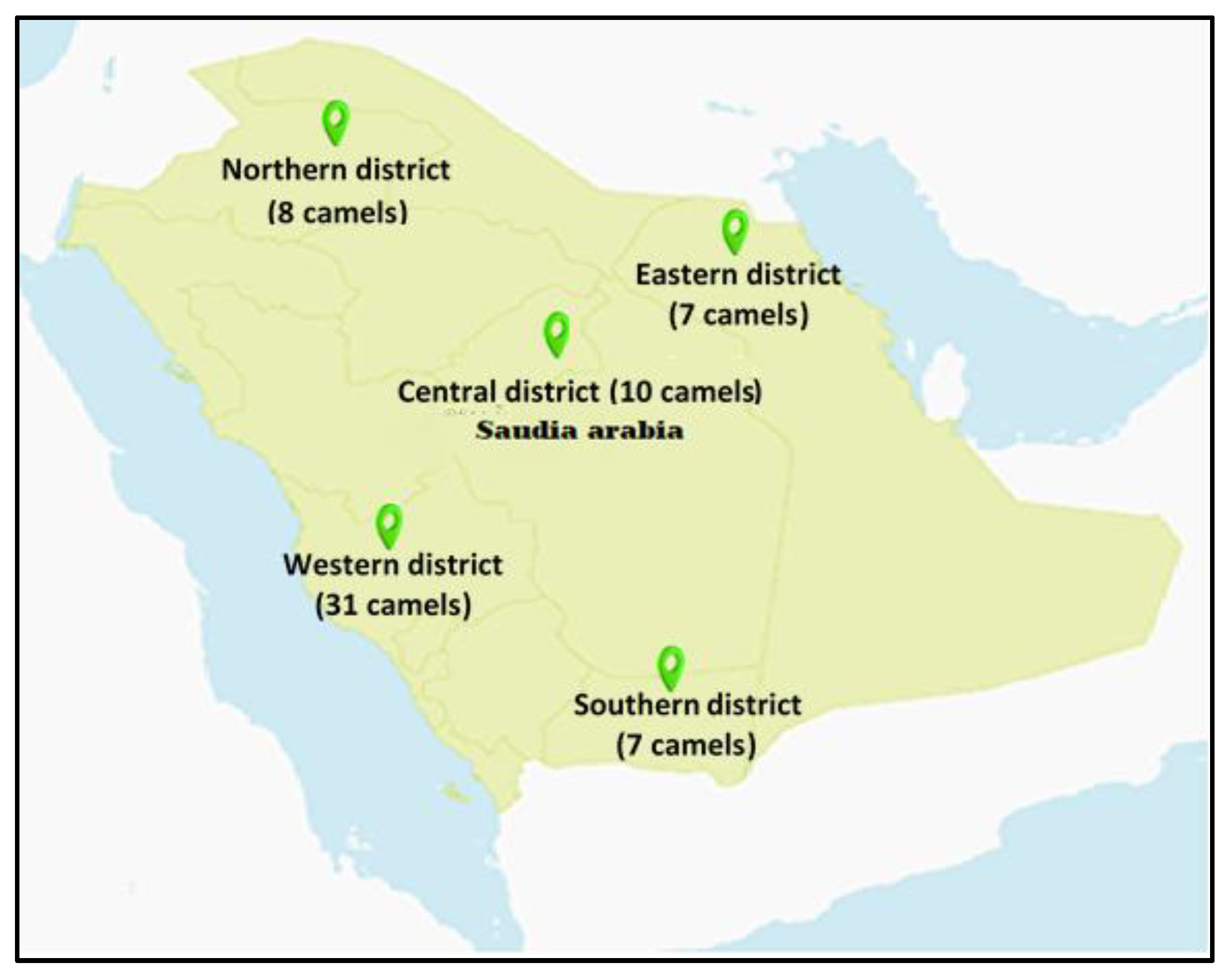


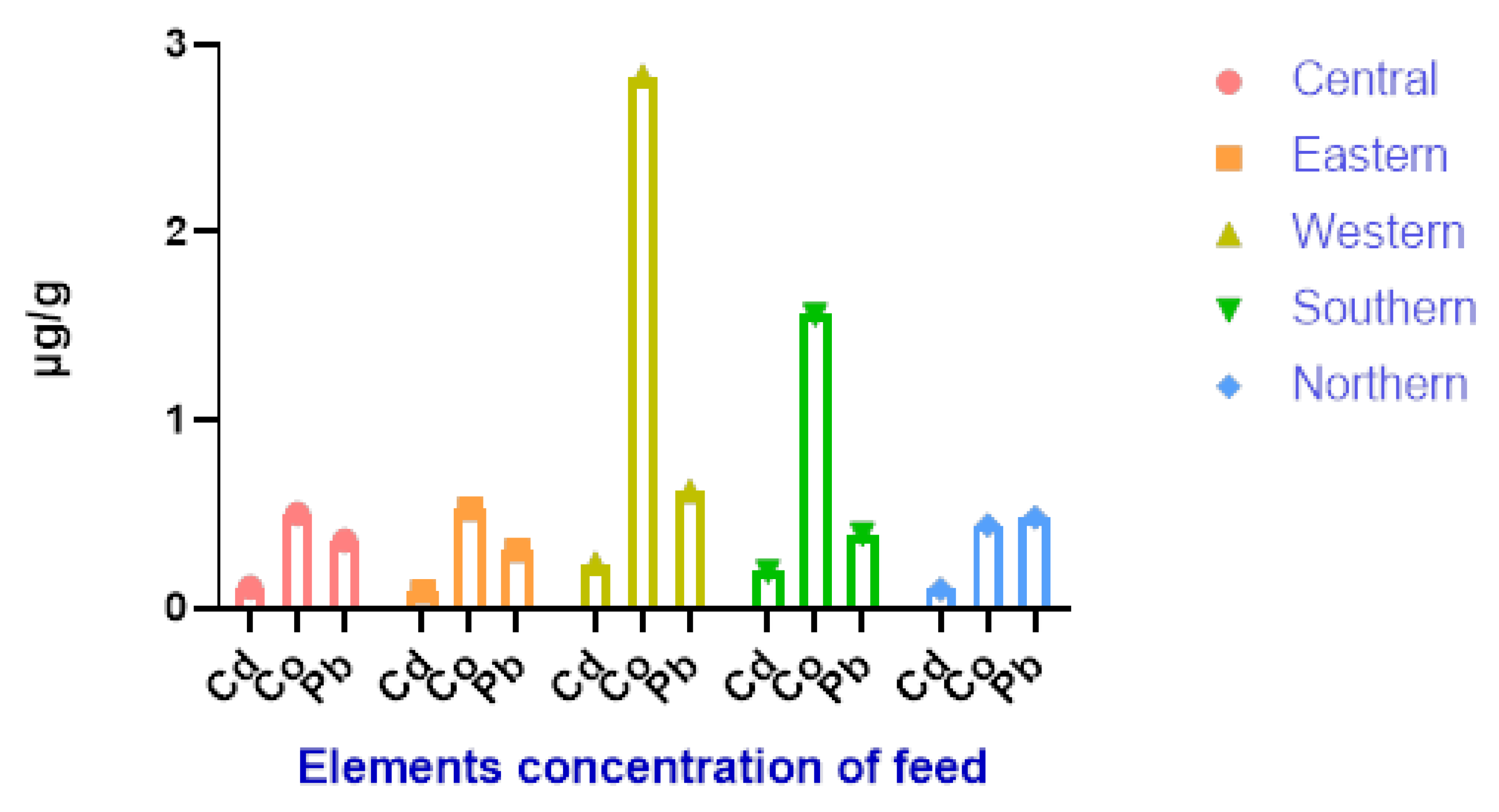
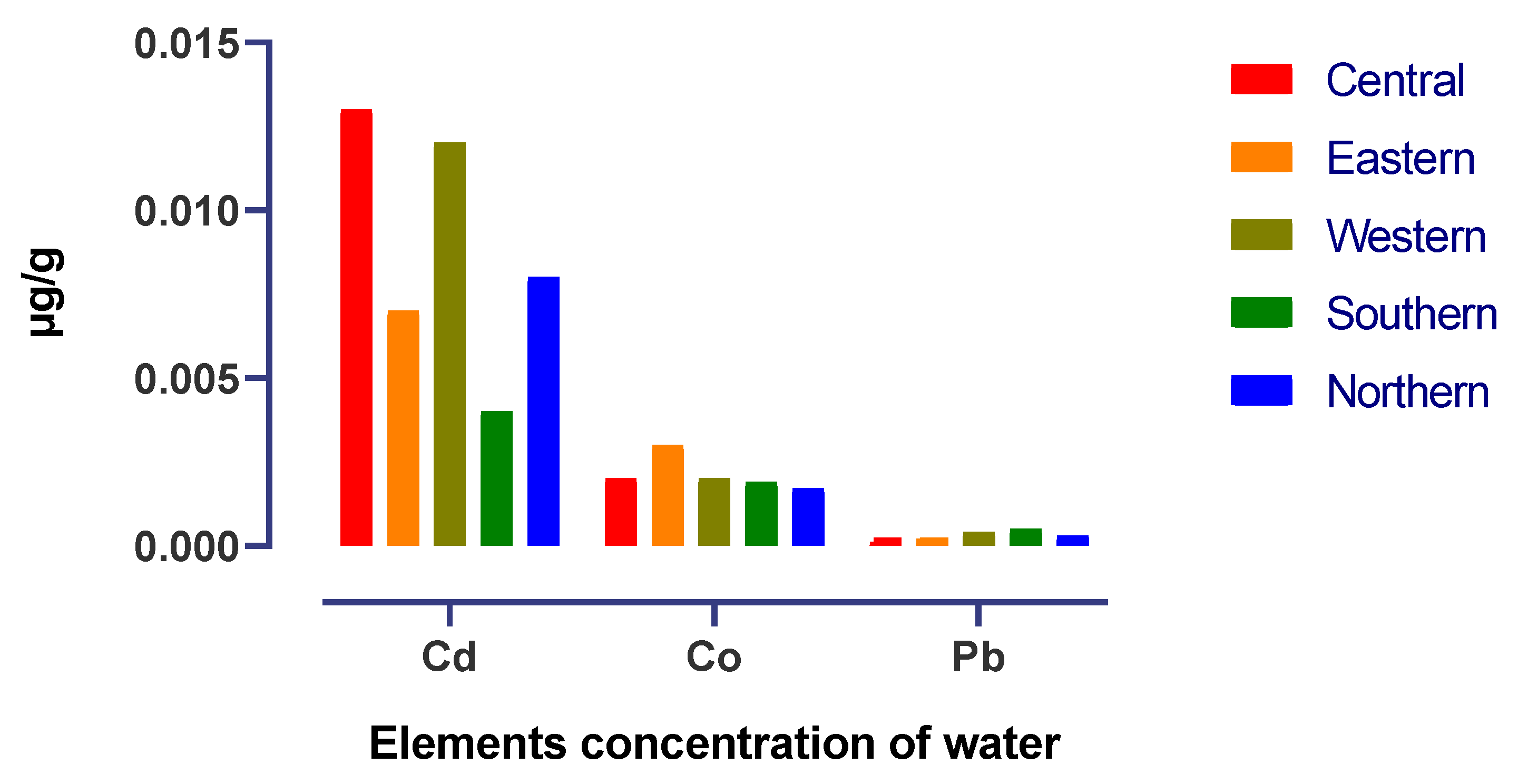
| District | Pb | Cd | Co |
|---|---|---|---|
| Central | 2.981 a | 0.339 b | 4.621 a |
| Eastern | 1.670 b | 0.351 b | 1.262 c |
| Western | 0.906 c | 0.774 a | 2.461 b |
| Southern | 1.144 c | 0.314 b | 4.052 a |
| Northern | 1.621 b | 0.626 a | 1.118 c |
| SEM | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.60 |
| Significance | ** | *** | ** |
| District | Pb | Cd | Co |
|---|---|---|---|
| Central | 1.386 b | 0.358 a | 1.705 b |
| Eastern | 1.001 d | 0.134 c | 1.396 c |
| Western | 1.229 b | 0.282 b | 3.255 a |
| Southern | 1.127 c | 0.193 c | 1.853 b |
| Northern | 2.058 a | 0.334 a | 2.664 a |
| SEM | 0.103 | 0.022 | 0.380 |
| Significance | ** | ** | * |
| District | Pb | Cd | Co |
|---|---|---|---|
| Whole blood (µg/mL) | |||
| Central | 0.058 | 0.027 | 0.504 |
| Eastern | 0.061 | 0.027 | 0.038 |
| SEM | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.099 |
| Significance | NS | NS | ** |
| Rumen fluids (µg/mL WW) | |||
| Central | 0.221 | 0.017 | 0.063 |
| Eastern | 0.202 | 0.022 | 0.110 |
| SEM | 0.018 | 0.001 | 0.016 |
| Significance | NS | * | * |
| Rumen tissues (µg/g WW) | |||
| Central | 0.359 | 0.111 | 0.362 |
| Eastern | 0.407 | 0.129 | 0.518 |
| SEM | 0.016 | 0.004 | 0.120 |
| Significance | NS | NS | * |
| Organ | Meat | Liver | Whole Blood | Rumen Tissue | Rumen Fluid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meat | 1 | ||||
| Liver | 0.398 0.601 | 1 | |||
| Whole blood | 0.555 0.445 | −0.540 0.460 | 1 | ||
| Rumen tissue | −0.078 0.921 | −0.656 0.343 | 0.478 0.521 | 1 | |
| Rumen Fluid | −0.129 0.871 | 0.411 0.588 | −0.439 0.560 | −0.954 0.045 * | 1 |
| Organ | Meat | Liver | Whole Blood | Rumen Tissue | Rumen Fluid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meat | 1 | ||||
| Liver | 0.254 0.745 | 1 | |||
| Whole blood | −0.914 0.086 | −0.329 0.671 | 1 | ||
| Rumen tissue | 0.029 0.970 | 0.375 0.625 | 0.298 0.701 | 1 | |
| Rumen Fluid | −0.211 0.789 | −0.353 0.646 | −0.141 0.858 | −0.981 0.018 ** | 1 |
| Organ | Meat | Liver | Whole Blood | Rumen Tissue | Rumen FLUID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meat | 1 | ||||
| Liver | −0.191 0.808 | 1 | |||
| Whole blood | 0.328 0.671 | 0.496 0.503 | 1 | ||
| Rumen tissue | −0.307 0.692 | −0.015 0.984 | 0.571 0.429 | 1 | |
| Rumen Fluid | −0.640 0.359 | 0.653 0.347 | −0.313 0.686 | −0.362 0.638 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelrahman, M.M.; Alhidary, I.A.; Matar, A.M.; Alobre, M.M.; Ayadi, M.; Aljumaah, R.S. Heavy Metals Levels in Soil, Water and Feed and Relation to Slaughtered Camels’ Tissues (Camelus dromedarius) from Five Districts in Saudi Arabia during Spring. Life 2023, 13, 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030732
Abdelrahman MM, Alhidary IA, Matar AM, Alobre MM, Ayadi M, Aljumaah RS. Heavy Metals Levels in Soil, Water and Feed and Relation to Slaughtered Camels’ Tissues (Camelus dromedarius) from Five Districts in Saudi Arabia during Spring. Life. 2023; 13(3):732. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030732
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelrahman, Mutassim M., Ibrahim A. Alhidary, Abdulkareem M. Matar, Mohsen M. Alobre, Moez Ayadi, and Riyadh S. Aljumaah. 2023. "Heavy Metals Levels in Soil, Water and Feed and Relation to Slaughtered Camels’ Tissues (Camelus dromedarius) from Five Districts in Saudi Arabia during Spring" Life 13, no. 3: 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030732
APA StyleAbdelrahman, M. M., Alhidary, I. A., Matar, A. M., Alobre, M. M., Ayadi, M., & Aljumaah, R. S. (2023). Heavy Metals Levels in Soil, Water and Feed and Relation to Slaughtered Camels’ Tissues (Camelus dromedarius) from Five Districts in Saudi Arabia during Spring. Life, 13(3), 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030732









