Effectiveness of Different Training Modalities on Static Balance in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Systematic Literature Search
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Screening, Selection and Data Extraction Process
2.4. Methodological Quality and Risk of Bias
2.5. Data Synthesis and Analysis
3. Results
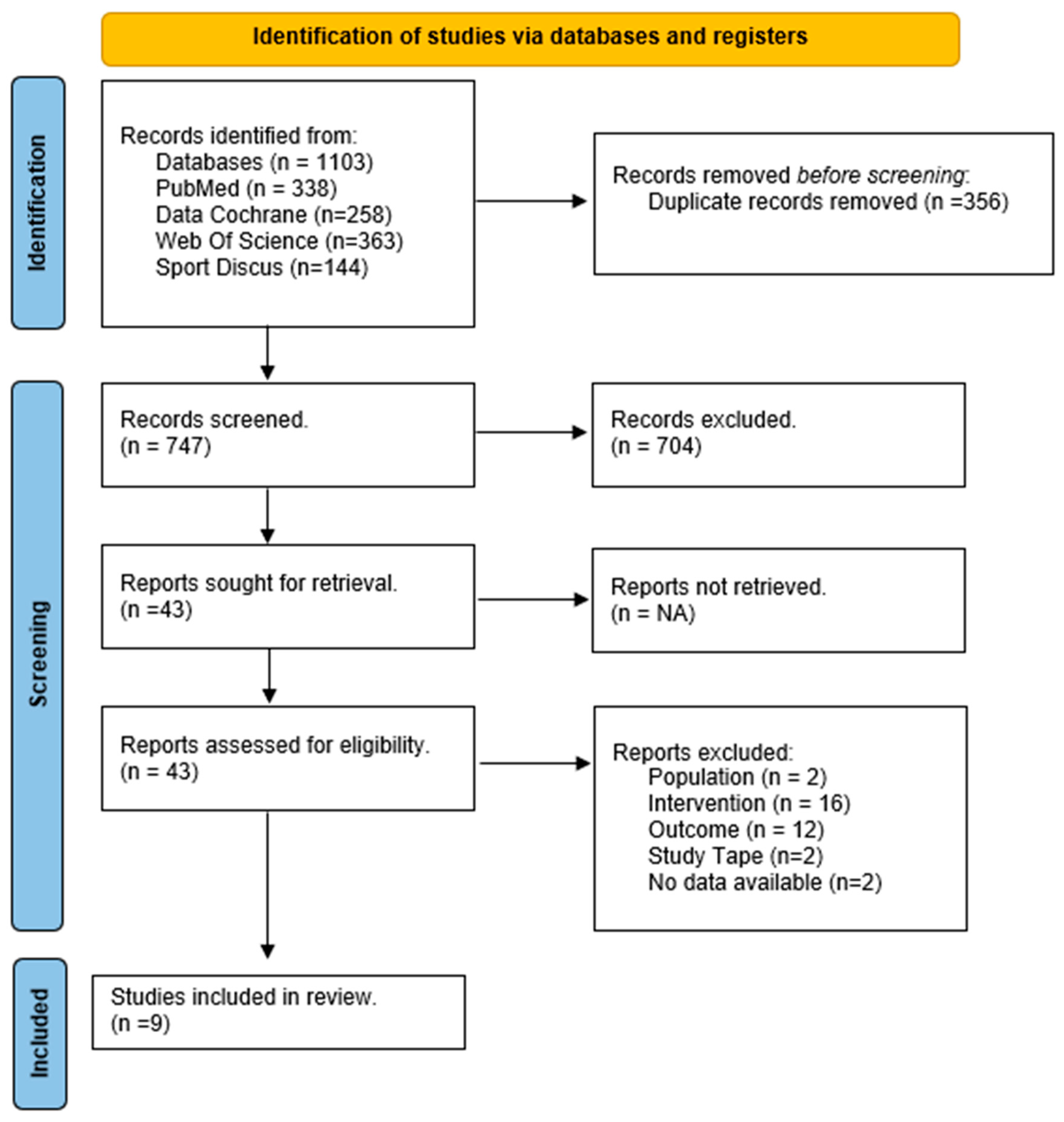
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Methodological Quality
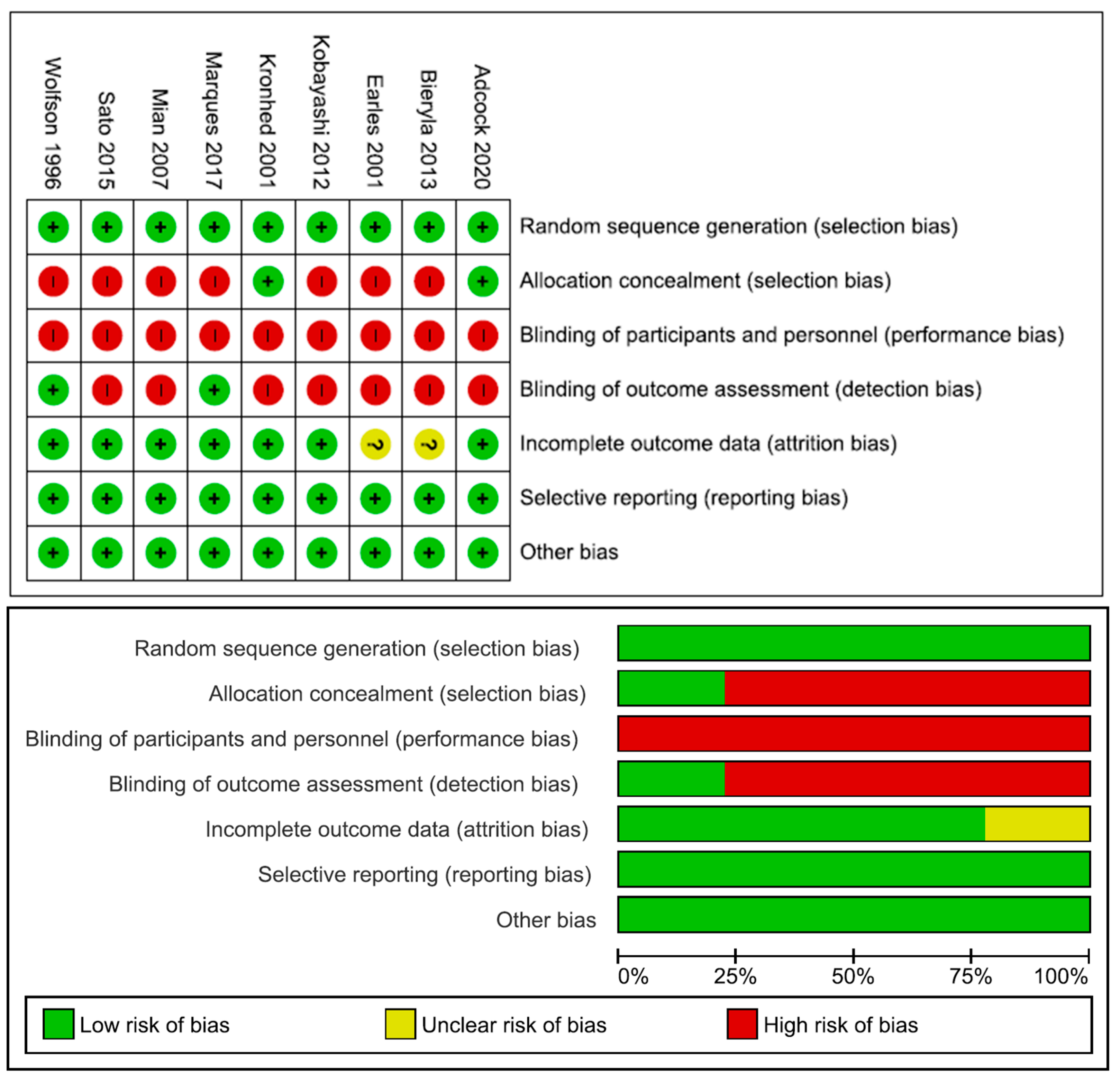
3.4. Risk of Bias
3.5. Effectiveness of Interventions
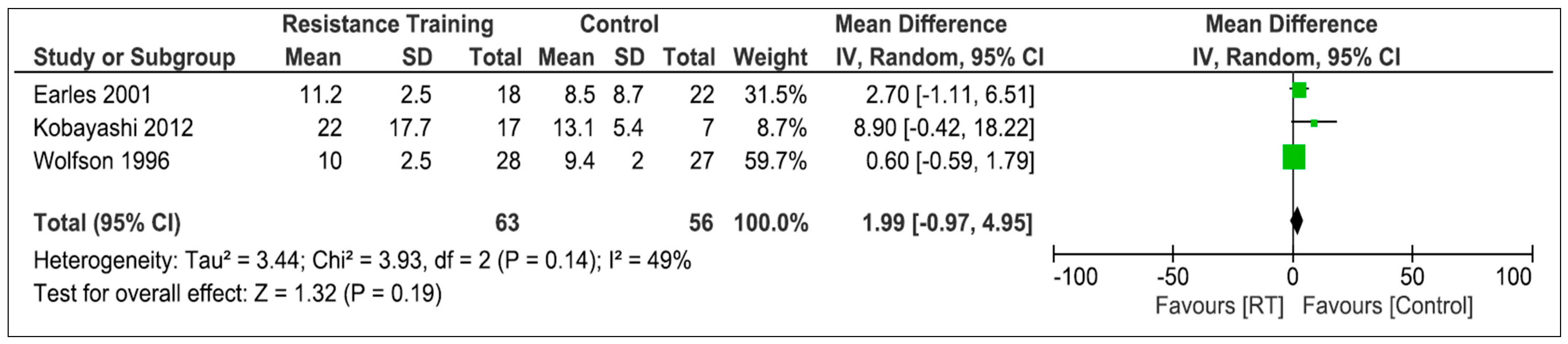
3.5.1. Resistance Training
3.5.2. Aerobic Training
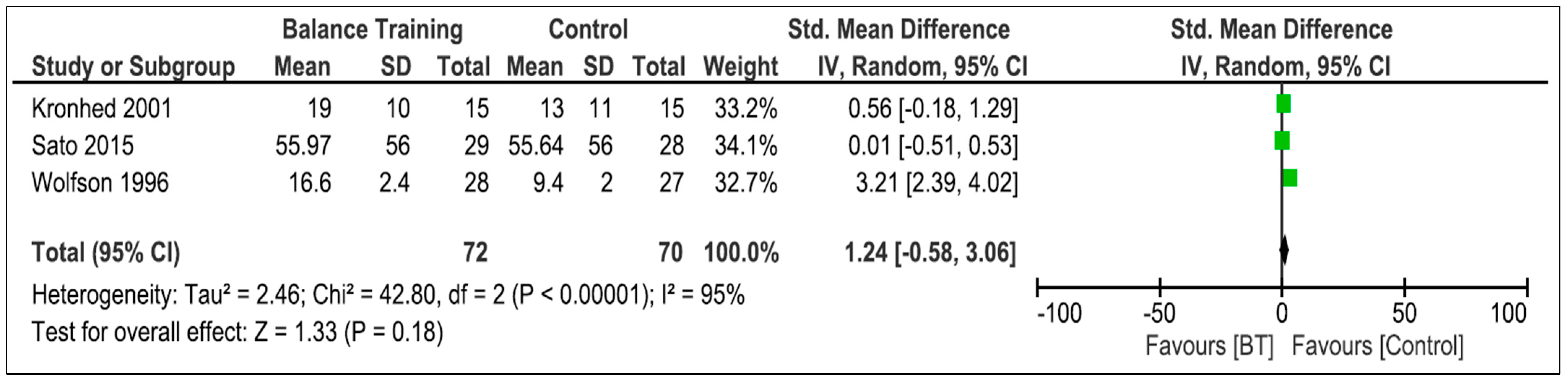
3.5.3. Balance Training
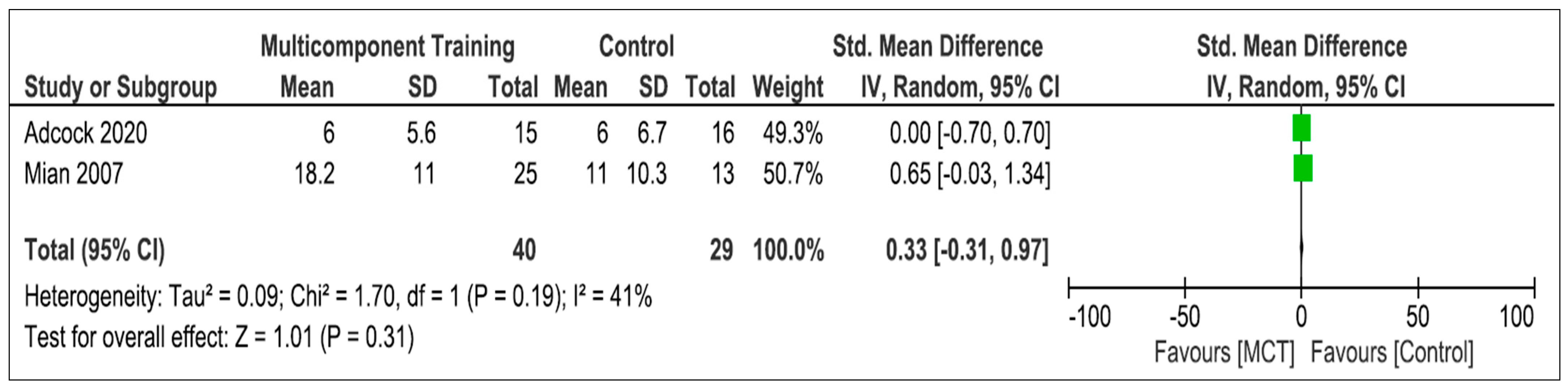
3.5.4. Multicomponent Training
4. Discussion
4.1. Resistance Training
4.2. Multi-Component Training
4.3. Balance Training
4.4. Aerobic Training
4.5. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lesinski, M.; Hortobágyi, T.; Muehlbauer, T.; Gollhofer, A.; Granacher, U. Effects of Balance Training on Balance Performance in Healthy Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sport Med. 2015, 45, 1721–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labata-Lezaun, N.; González-Rueda, V.; Llurda-Almuzara, L.; López-de-Celis, C.; Rodríguez-Sanz, J.; Bosch, J.; Vicente-Rodríguez, G.; Gorczakowska, D.; Araluze-Arizti, P.; Pérez-Bellmunt, A. Effectiveness of multicomponent training on physical performance in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2023, 104, 104838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, E.; Alud, A. La actividad física y sus beneficios físicos como estrategia de inclusión social del adulto mayor. Incl. Desarro. 2018, 5, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adcock, M.; Fankhauser, M.; Post, J.; Lutz, K.; Zizlsperger, L.; Luft, A.R.; Guimarães, V.; Schättin, A.; De Bruin, E.D. Effects of an In-home Multicomponent Exergame Training on Physical Functions, Cognition, and Brain Volume of Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Med. 2020, 6, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, L.D.; Robertson, M.C.; Gillespie, W.J.; Sherrington, C.; Gates, S.; Clemson, L.; E Lamb, S. Interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 2012, CD007146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, J.R.; Cotton, K.; Verghese, J. Multisensory integration predicts balance and falls in older adults. J. Gerontol. 2019, 74, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-de-Celis, C.; Zegarra-Chávez, D.; Cadellans-Arróniz, A.; Carrasco-Uribarren, A.; Izquierdo-Nebreda, P.; Canet-Vintró, M.; Rodríguez-Sanz, J.; Pérez-Bellmunt, A. Study on Balance and Postural Control According to the Stabilometry in Indoor Skydivers: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 20, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Era, P. Posture control in the elderly. Int. J. Technol. Aging 1988, 1, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreland, J.D.; Richardson, J.A.; Goldsmith, C.H.; Clase, C.M. Muscle weakness and falls in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2004, 52, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijlsma, A.Y.; Pasma, J.; Lambers, D.; Stijntjes, M.; Blauw, G.J.; Meskers, C.G.; Maier, A. Muscle strength rather than muscle mass is associated with standing balance in elderly outpatients. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garatachea, N.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Santos-Lozano, A.; Fiuza-Luces, C.; Morán, M.; Emanuele, E.; Joyner, M.J.; Lucia, A. Exercise attenuates the major hallmarks of aging. Rejuven. Res. 2015, 18, 57–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragao, F.A.; Karamanidis, K.; Vaz, M.A.; Arampatzis, A. Mini-trampoline exercise related to mechanisms of dynamic stability improves the ability to regain balance in elderly. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2011, 21, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littbrand, H.; Lundin-Olsson, L.; Gustafson, Y.; Rosendahl, E. The Effect of a High-Intensity Functional Exercise Program on Activities of Daily Living: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Residential Care Facilities. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2009, 57, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitre, J.; Jully, J.L.; Gasnier, Y.; Paillard, T. Chronic physical activity preserves efficiency of proprioception in postural control in older women. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2013, 50, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, A.; Bianco, A.; Paoli, A.; Messina, G.; Montalto, M.A.; Bellafiore, M.; Battaglia, G.; Iovane, A.; Palma, A. Effects of pilates exercise programs in people with chronic low back pain: A systematic review. Medicine 2015, 94, e383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas-Herrero, Á.; de Asteasu, M.L.S.; Antón-Rodrigo, I.; Sánchez-Sánchez, J.L.; Montero-Odasso, M.; Marín-Epelde, I.; Ramón-Espinoza, F.; Zambom-Ferraresi, F.; Petidier-Torregrosa, R.; Elexpuru-Estomba, J.; et al. Effects of Vivifrail multicomponent intervention on functional capacity: A multicentre, randomized controlled trial. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 33, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, M.; Merchant, R.A.; Morley, J.E.; Anker, S.D.; Aprahamian, I.; Arai, H.; Aubertin-Leheudre, M.; Bernabei, R.; Cadore, E.L.; Cesari, M.; et al. International Exercise Recommendations in Older Adults (ICFSR): Expert Consensus Guidelines. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2021, 25, 824–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrington, C.; Michaleff, Z.A.; Fairhall, N.; Paul, S.S.; Tiedemann, A.; Whitney, J.; Cumming, R.G.; Herbert, R.D.; Close, J.C.T.; Lord, S.R. Exercise to prevent falls in older adults: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sport. Med. 2017, 51, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brox, E.; Luque, L.F.; Evertsen, G.J.; Hernández, J.E.G. Exergames for elderly: Social exergames to persuade seniors to increase physical activity. In Proceedings of the 2011 5th International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare (PervasiveHealth) and Workshops, Dublin, Ireland, 23–26 May 2011; pp. 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramaki, A.L.; Sampaio, R.F.; Reis, A.C.; Cavalcanti, A.; Dutra, F.C. Virtual reality in the rehabilitation of patients with stroke: An integrative review. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2019, 77, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laufer, Y.; Dar, G.; Kodesh, E. Does a Wii-based exercise program enhance balance control of independently functioning older adults? A systematic review. Clin. Interv. Aging 2014, 9, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Methley, A.M.; Campbell, S.; Chew-Graham, C.; McNally, R.; Cheraghi-Sohi, S. PICO, PICOS and SPIDER: A comparison study of specificity and sensitivity in three search tools for qualitative systematic reviews. BMC. Health Serv. Res. 2014, 14, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.; Chandler, J.; Welch, V.; Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cashin, A.G.; McAuley, J.H. Clinimetrics: Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro) Scale. J. Physiother. 2020, 66, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomized trials. BMJ 2019, 366, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.; Deeks, J.; Altman, D. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Koyama, Y.; Enoka, R.M.; Suzuki, S. A unique form of light-load training improves steadiness and performance on some functional tasks in older adults. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport 2014, 24, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfson, L.; Whipple, R.; Derby, C.; Judge, J.; King, M.; Amerman, P.; Schmidt, J.; Smyers, D. Gains and Tai Chi Maintenance. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1996, 44, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earles, D.R.; Judge, J.O.; Gunnarsson, O.T. Velocity training induces power-specific adaptations in highly functioning older adults. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2001, 82, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Kuroki, K.; Saiki, S.; Nagatomi, R. Improving Walking, Muscle Strength, and Balance in the Elderly with an Exergame Using Kinect: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Games Health J. 2015, 4, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronhed, A.-C.G.; Möller, C.; Olsson, B.; Möller, M. The Effect of Short-Term Balance Training on Community-Dwelling Older Adults. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2001, 9, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, O.; Thom, J.; Ardigò, L.; Morse, C.; Narici, M.; Minetti, A. Effect of a 12-month physical conditioning programme on the metabolic cost of walking in healthy older adults. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 100, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieryla, K.A. Dold NM. Feasibility of Wii Fit training to improve clinical measures of balance in older adults. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadore, E.L.; Casas-Herrero, A.; Zambom-Ferraresi, F.; Idoate, F.; Millor, N.; Gómez, M.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L.; Izquierdo, M. Multicomponent exercises including muscle power training enhance muscle mass, power output, and functional outcomes in institutionalized frail nonagenarians. Age 2014, 36, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, R.; Boreham, C.A.G.; Leite, J.C.; De Vito, G.; Brennan, L.; Gibney, E.R.; Pesce, C. Enhancing cognitive functioning in the elderly: Multicomponent vs resistance training. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, E.A.; Figueiredo, P.; Harris, T.B.; Wanderley, F.A.; Carvalho, J. Are resistance and aerobic exercise training equally effective at improving knee muscle strength and balance in older women? Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2017, 68, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knerl, C.; Schuler, P.; Taylor, L.; Cosio-Lima, L.; Caillouet, K. The effects of six weeks of balance and strength training on measures of dynamic balance of older adults. Calif. J. Health Promot. 2009, 7, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motalebi, S.A.; Cheong, L.S.; Iranagh, J.A.; Mohammadi, F. Effect of low-cost resistance training on lower-limb strength and balance in institutionalized seniors. Exp. Aging Res. 2018, 44, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrinho, A.C.d.S.; Almeida, M.L.d.; Rodrigues, G.d.S.; Finzeto, L.C.; Silva, V.R.R.; Bernatti, R.F.; Bueno Junior, C.R. Effect of Flexibility Training Associated with Multicomponent Training on Posture and Quality of Movement in Physically Inactive Older Women: A Randomized Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlicht, J.; Camaione, D.N.; Owen, S.V. Effect of intense strength training on standing balance, walking speed, and sit-to-stand performance in older adults. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, M281–M286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fragala, M.S.; Cadore, E.L.; Dorgo, S.; Izquierdo, M.; Kraemer, W.J.; Peterson, M.D.; Ryan, E.D. Resistance Training for Older Adults: Position Statement From the National Strength and Conditioning Association. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 2019–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadjapong, U.; Yodkeeree, S.; Sungkarat, S.; Siviroj, P. Multicomponent Exercise Program Reduces Frailty and Inflammatory Biomarkers and Improves Physical Performance in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahor, M.; Guralnik, J.M.; Ambrosius, W.T.; Blair, S.; Bonds, D.E.; Church, T.S.; Espeland, M.A.; Fielding, R.A.; Gill, T.M.; Groessl, E.J.; et al. Effect of structured physical activity on prevention of major mobility disability in older adults: The LIFE study randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2014, 311, 2387–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, J.C.; Arango, E.F. Efectos del entrenamiento en superficies inestables sobre el equilibrio y funcionalidad en adultos mayores. Rev. Fac. Nac. Salud. Pública. 2015, 33, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Javadpour, S.; Sinaei, E.; Salehi, R.; Zahednejad, S.; Motealleh, A. Comparing the Effects of Single-Task versus Dual-Task Balance Training on Gait Smoothness and Functional Balance in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2022, 30, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinaei, E.; Kamali, F.; Nematollahi, A.; Etminan, Z. Comparing the effects of balance training with and without cognitive tasks on the quality of life and balance performance in community-dwelling older adults: A single-blind randomized clinical trial. J. Rehabil. Sci. Res. 2016, 3, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, B. ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription 9th Ed. 2014. J. Can. Chiropr. Assoc. 2014, 58, 328. [Google Scholar]
- Spagnuolo, D.L.; Jurgensen, S.P.; Iwama, A.M.; Dourado, V.Z. Walking for the assessment of balance in healthy subjects older than 40 years. Gerontology 2010, 56, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigematsu, R.; Chang, M.; Yabushita, N.; Sakai, T.; Nakagaichi, M.; Nho, H. Dance-based aerobic exercise may improve indices of falling risk in older women. Age Ageing 2002, 31, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidarte-Claros, J.A.; Quintero-Cruz, M.V.; Herazo-Beltrán, Y. Efectos del ejercicio físico en la condición física funcional y la estabilidad en adultos mayores. Hacia Promoc. Salud 2012, 17, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, D.; Gonçalves, C.G.; Parreira, R.B.; Fernandes, K.B.; Teixeira, D.C.; Silva, R.A.; Probst, V.S. Postural balance and physical activity in daily life (PADL) in physically independent older adults with different levels of aerobic exercise capacity. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2012, 55, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | N (IG/CG) | Age (±SD) | Gender (F/M) | Modality | Variable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wolfson, 1996 [31] | 55 (28/27) | 80 | 32/23 | BT | OLS-CE |
| Wolfson, 1996 [31] | 55 (28/27) | 80 | 34/21 | RT | OLS-CE |
| Earles, 2001 [32] | 40 (18/22) | 78 ± 5 | 26/14 | RT | OLS |
| Kronhed, 2001 [34] | 30 (15/15) | 73 ± 2 | 16/14 | BT | Romberg |
| Mian, 2007 [35] | 38 (25/13) | 73 ± 3.4 | 19/19 | MCT | OLS |
| Kobayashi, 2012 [30] | 24 (17/7) | 67.5 ± 5.23 | 14/10 | RT | OLS-CE |
| Bieryla, 2013 [36] | 12 (6/6) | 81.5 ± 5.5 | 10/2 | BT | BBS |
| Sato, 2015 [33] | 58 (29/28) | 69.25 ± 5.41 | 43/14 | BT | BBS |
| Marques, 2017 [39] | 47 (24/23) | 69 | 47/0 | RT | OLS |
| Marques, 2017 [39] | 48 (24/24) | 69 | 48/0 | AT | OLS |
| Adcock, 2020 [4] | 31 (15/16) | 73.9 ± 6.4 | 16/15 | MCT | SPPB Balance |
| Study | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wolfson, 1996 [31] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Earles, 2001 [32] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Kronhed, 2001 [34] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Mian, 2007 [35] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Kobayashi, 2012 [30] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Bieryla, 2013 [36] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Sato, 2015 [33] | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Marques, 2017 [39] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Adcock, 2020 [4] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Average | 5 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Labata-Lezaun, N.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, S.; López-de-Celis, C.; Rodríguez-Sanz, J.; Canet-Vintró, M.; R.-Oviedo, G.; González-Rueda, V.; Pérez-Bellmunt, A. Effectiveness of Different Training Modalities on Static Balance in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life 2023, 13, 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051193
Labata-Lezaun N, Rodríguez-Rodríguez S, López-de-Celis C, Rodríguez-Sanz J, Canet-Vintró M, R.-Oviedo G, González-Rueda V, Pérez-Bellmunt A. Effectiveness of Different Training Modalities on Static Balance in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life. 2023; 13(5):1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051193
Chicago/Turabian StyleLabata-Lezaun, Noé, Sergi Rodríguez-Rodríguez, Carlos López-de-Celis, Jacobo Rodríguez-Sanz, Max Canet-Vintró, Guillermo R.-Oviedo, Vanessa González-Rueda, and Albert Pérez-Bellmunt. 2023. "Effectiveness of Different Training Modalities on Static Balance in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Life 13, no. 5: 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051193
APA StyleLabata-Lezaun, N., Rodríguez-Rodríguez, S., López-de-Celis, C., Rodríguez-Sanz, J., Canet-Vintró, M., R.-Oviedo, G., González-Rueda, V., & Pérez-Bellmunt, A. (2023). Effectiveness of Different Training Modalities on Static Balance in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life, 13(5), 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051193