Can Grasslands in Photovoltaic Parks Play a Role in Conserving Soil Arthropod Biodiversity?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Soil Sampling
2.2. Chemical Analyses
2.3. Arthropods Extraction and Characterization
2.4. Statistical Analysis
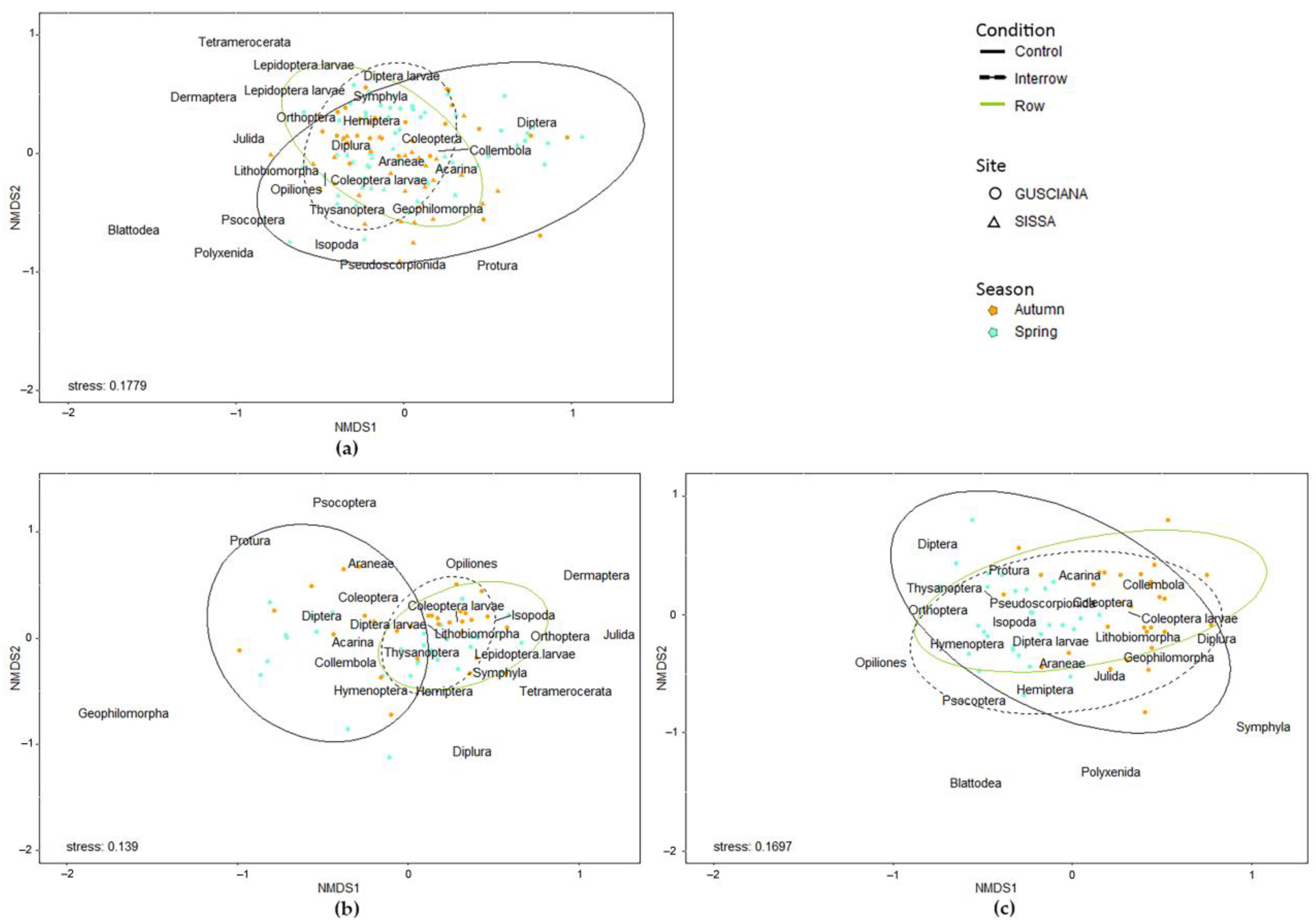
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Parameters
3.2. Arthropod Community
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission Committee; Committee of the Regions EU. Biodiversity Strategy for 2030 Bringing Nature Back into Our Lives; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, S.; Guo, M.; Zou, P.; Wu, W.; Zhou, X. Effects of photovoltaic panels on soil temperature and moisture in desert areas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 17506–17518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weselek, A.; Ehmann, A.; Zikeli, S.; Lewandowski, I.; Schindele, S.; Högy, P. Agrophotovoltaic systems: Applications, challenges, and opportunities. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 39, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, R.R.; Armstrong, A.; Burney, J.; Ryan, G.; Moore-O’leary, K.; Diédhiou, I.; Grodsky, S.M.; Saul-Gershenz, L.; Davis, R.; Macknick, J.; et al. Techno–ecological synergies of solar energy for global sustainability. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez, R.R.; Easter, S.B.; Murphy-Mariscal, M.L.; Maestre, F.T.; Tavassoli, M.; Allen, E.B.; Barrows, C.W.; Belnap, J.; Ochoa-Hueso, R.; Ravi, S.; et al. Environmental impacts of utility-scale solar energy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 766–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cook, P. Infrastructure, rural electrification and development. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2011, 15, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron-Gafford, G.A.; Minor, R.L.; Allen, N.A.; Cronin, A.D.; Brooks, A.E.; Pavao-Zuckerman, M.A. The Photovoltaic Heat Island Effect: Larger solar power plants increase local temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semeraro, T.; Pomes, A.; Del Giudice, C.; Negro, D.; Aretano, R. Planning ground based utility scale solar energy as green infrastructure to enhance ecosystem services. Energy Policy 2018, 117, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veen, G.F.; Jasper Wubs, E.R.; Bardgett, R.D.; Barrios, E.; Bradford, M.A.; Carvalho, S.; De Deyn, G.B.; de Vries, F.T.; Giller, K.E.; Kleijn, D.; et al. Applying the Aboveground-Belowground Interaction Concept in Agriculture: Spatio-Temporal Scales Matter. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menta, C.; Remelli, S. Soil Health and Arthropods: From Complex System to Worthwhile Investigation. Insects 2020, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armstrong, A.; Ostle, N.J.; Whitaker, J. Solar park microclimate and vegetation management effects on grassland carbon cycling. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 074016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moscatelli, M.C.; Marabottini, R.; Massaccesi, L.; Marinari, S. Soil properties changes after seven years of ground mounted photovoltaic panels in Central Italy coastal area. Geoderma Reg. 2022, 29, e00500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikoski, J.M.; Ferguson, S.H.; Meyer, L. Effects of water addition on soil arthropods and soil characteristics in a precipitation-limited environment. Acta Oecologica 2006, 30, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suuronen, A.; Muñoz-Escobar, C.; Lensu, A.; Kuitunen, M.; Celis, N.G.; Astudillo, P.E.; Ferrú, M.; Taucare-Ríos, A.; Miranda, M.; Kukkonen, J.V.K. The Influence of Solar Power Plants on Microclimatic Conditions and the Biotic Community in Chilean Desert Environments. Environ. Manag. 2017, 60, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, B.Y.; Blaustein, L.; Lotan, R.; Shalom, H.; Kadas, G.J.; Seifan, M. Green roof and photovoltaic panel integration: Effects on plant and arthropod diversity and electricity production. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 225, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Società Italiana della Scienza del Suolo. Metodi Normalizzati di Analisi del Suolo; Edagricole, Ed.; Edagricole: Bologna, Italy, 1985; ISBN 8820626748. [Google Scholar]
- Miano, T.; Mondelli, D. Sostanza Organica e Carbonio Organico. In Metodi di Analisi Chimica del Suolo; Associazione Italiana dei Laboratori Pubblici di Agrochimica, Claudio, C., Società Italiana della Scienza del Suolo, Miano, T., Eds.; Pubblicità & Stampa: Modugno, Italy, 2015; pp. 253–254. ISBN 9788894067903. [Google Scholar]
- Parisi, V.; Menta, C.; Gardi, C.; Jacomini, C.; Mozzanica, E. Microarthropod communities as a tool to assess soil quality and biodiversity: A new approach in Italy. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 105, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menta, C.; Conti, F.D.; Pinto, S.; Bodini, A. Soil Biological Quality index (QBS-ar): 15 years of application at global scale. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, W.; Chen, J.; Du, W.; Gao, X. Environmental impacts of photovoltaic power plants in northwest China. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assessments 2023, 56, 103120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, R.R.; Hoffacker, M.K.; Murphy-Mariscal, M.L.; Wu, G.C.; Allen, M.F. Solar energy development impacts on land cover change and protected areas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13579–13584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.; Waldron, S.; Whitaker, J.; Ostle, N.J. Wind farm and solar park effects on plant-soil carbon cycling: Uncertain impacts of changes in ground-level microclimate. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González-Ubierna, S.; Lai, R. Modelling the effects of climate factors on soil respiration across Mediterranean ecosystems. J. Arid. Environ. 2019, 165, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, J.H.; Boynton, R.M.; Flint, L.E.; Flint, A.L. The magnitude and spatial patterns of historical and future hydrologic change in California’s watersheds. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, K.E.; Moore-O’Leary, K.A.; Parker, I.M.; Pavlik, B.M.; Hernandez, R.R. Simulated solar panels create altered microhabitats in desert landforms. Ecosphere 2020, 11, e03089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holloway, L.; Portland State University; Starry, O.; McClung, R.; Rosenstiel, T. The influence of microclimates created by photovoltaic panels and irrigation on green roof ecosystem properties. J. Living Arch. 2020, 7, 62–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.B. Trend setting impacts of organic matter on soil physico-chemical properties in traditional vis -a- vis chemical-based amendment practices. PLoS Sustain. Transform. 2022, 1, e0000007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilimire, K.; Gliessman, S.R.; Muramoto, J. Soil fertility and crop growth under poultry/crop integration. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2012, 28, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Begum, F.; Bajracharya, R.M.; Sharma, S.; Sitaula, B.K. Influence of slope aspect on soil physico-chemical and biological properties in the mid hills of central Nepal. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2010, 17, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, D.J.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Travers, S.K.; Val, J.; Oliver, I. Do grazing intensity and herbivore type affect soil health? Insights from a semi-arid productivity gradient. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 54, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiberg, J.A.; Dambros, C.D.S.; Rodrigues, E.N.L.; Teixeira, R.A.; Vieira, Â.D.H.N.; de Almeida, H.S.; Carvalho, P.C.D.F.; Jacques, R.J.S. Increased grazing intensity in pastures reduces the abundance and richness of ground spiders in an integrated crop-livestock system. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 40, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiglieno, I.; Simonetto, A.; Orlando, F.; Donna, P.; Tonni, M.; Valenti, L.; Gilioli, G. Response of the Arthropod Community to Soil Characteristics and Management in the Franciacorta Viticultural Area (Lombardy, Italy). Agronomy 2020, 10, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, Q.; Bischoff, A.; Cueff, S.; Cluchier, A.; Gros, R. Effects of solar park construction and solar panels on soil quality, microclimate, CO 2 effluxes, and vegetation under a Mediterranean climate. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 5190–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColloch, J.W.; Hayes, W.P. The Reciprocal Relation of Soil and Insects. Ecology 1922, 3, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, W. To Freeze or Not to Freeze? Invertebrate Survival of Sub-Zero Temperatures. Funct. Ecol. 1991, 5, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, G.K.; Van Den Brink, P.J.; Gould, P.J.L. Effects of spring precipitation on a temperate arable collembolan community analysed using Principal Response Curves. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2000, 14, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santorufo, L.; Van Gestel, C.A.M.; Maisto, G. Sampling season affects conclusions on soil arthropod community structure responses to metal pollution in Mediterranean urban soils. Geoderma 2014, 226-227, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkin, S.P. Biology of the Springtails: (Insecta: Collembola); OUP Oxford: Oxford, UK, 1997; pp. 1–330. ISBN 978-0-19-158925-6. [Google Scholar]

| GUSCIANA (BS) | SISSA (PR) | |
|---|---|---|
| Region | Lombardy | Emilia-Romagna |
| Year of completion | 2010 | 2012 |
| Power (kWp) | 5525 | 2088 |
| Panel modules material | polycrystalline silicon | polycrystalline silicon |
| Size of the panels (m) | 0.99 × 1.64 | 0.99 × 1.61 |
| Surface covered by panels (m2) | 39,000 | 32,630 |
| Ground clearance (m) | 0.5–3 | 0.5–2.4 |
| Distance between panels (m) | 3.5 | 4 |
| Former destination use of the area | Poultry farming with a building made from Eternit | Agricultural |
| Vegetation management | By animals (donkeys or sheep), trimmer, or a forage harvester on a small excavator | Tractor or forage harvester |
| Panels’ washing | 3 times from March to September without using detergent | no |
| Gusciana | Sissa | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Inter-Row | Row | Control | Inter-Row | Row | |
| pH | 7.40 ± 0.14 b | 7.85 ± 0.05 a | 7.54 ± 0.09 b | 7.86 ± 0.03 | 7.84 ± 0.02 | 7.87 ± 0.01 |
| SOM (%) | 13.12 ± 0.92 a | 9.08 ± 0.59 b | 10.04 ± 0.41 b | 7.70 ± 0.36 | 8.32 ± 0.41 | 7.78 ± 0.23 |
| Parameter | Contrasts | Overall % | Most Influential Groups | Cum. % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Season | Autumn | - | Spring | 51 * | Acarina | 0.24 |
| Collembola | 0.44 | |||||
| Hymenoptera | 0.57 | |||||
| Hemiptera | 0.65 | |||||
| Diptera | 0.69 | |||||
| Isopoda | 0.73 | |||||
| Condition | Row Row | - | Control | 58 ** | Acarina | 0.29 |
| Collembola | 0.48 | |||||
| Hymenoptera | 0.61 | |||||
| Hemiptera | 0.68 | |||||
| Isopoda | 0.72 | |||||
| - | Inter-row | 56 ** | Acarina | 0.24 | ||
| Collembola | 0.45 | |||||
| Hymenoptera | 0.57 | |||||
| Hemiptera | 0.66 | |||||
| Coleoptera larvae | 0.71 | |||||
| Inter-row | - | Control | 40 | Acarina | 0.21 | |
| Collembola | 0.42 | |||||
| Hymenoptera | 0.56 | |||||
| Hemiptera | 0.65 | |||||
| Diptera larvae | 0.69 | |||||
| Isopoda | 0.72 | |||||
| Photovoltaic system | Sissa | - | Gusciana | 51 * | Acarina | 0.24 |
| Collembola | 0.45 | |||||
| Hymenoptera | 0.57 | |||||
| Hemiptera | 0.64 | |||||
| Isopoda | 0.69 | |||||
| Diptera | 0.73 | |||||
| Parameter | Order |
|---|---|
| Season | |
| Spring | Isopoda ** |
| Lepidoptera larvae * | |
| Orthoptera ** | |
| Psocoptera ** | |
| Autumn | Diplura ** |
| Hymenoptera larvae * | |
| Lithobiomorpha ** | |
| Condition | |
| Row | Pseudoscorpionida ** |
| Inter-row | Geophilomorpha * |
| Control + Inter-row | Coleoptera larvae *** |
| Diptera larvae *** | |
| Hemiptera *** | |
| Hymenoptera *** | |
| Hymenoptera larvae ** | |
| Lepidoptera larvae * | |
| Symphyla ** | |
| Photovoltaic system | |
| Sissa | Diplura * |
| Isopoda *** | |
| Pseudoscorpionida ** | |
| Psocoptera ** | |
| Thysanoptera *** | |
| Gusciana | Diptera larvae *** |
| Hymenoptera larvae *** | |
| Lepidoptera larvae *** | |
| Symphyla *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Menta, C.; Remelli, S.; Andreoni, M.; Gatti, F.; Sergi, V. Can Grasslands in Photovoltaic Parks Play a Role in Conserving Soil Arthropod Biodiversity? Life 2023, 13, 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13071536
Menta C, Remelli S, Andreoni M, Gatti F, Sergi V. Can Grasslands in Photovoltaic Parks Play a Role in Conserving Soil Arthropod Biodiversity? Life. 2023; 13(7):1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13071536
Chicago/Turabian StyleMenta, Cristina, Sara Remelli, Matteo Andreoni, Fabio Gatti, and Valeria Sergi. 2023. "Can Grasslands in Photovoltaic Parks Play a Role in Conserving Soil Arthropod Biodiversity?" Life 13, no. 7: 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13071536
APA StyleMenta, C., Remelli, S., Andreoni, M., Gatti, F., & Sergi, V. (2023). Can Grasslands in Photovoltaic Parks Play a Role in Conserving Soil Arthropod Biodiversity? Life, 13(7), 1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13071536










