Streptomyces Diversity Maps Reveal Distinct High-Specificity Biogeographical and Environmental Patterns Compared to the Overall Bacterial Diversity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Retrieval
2.2. Bioinformatics and Data Processing
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
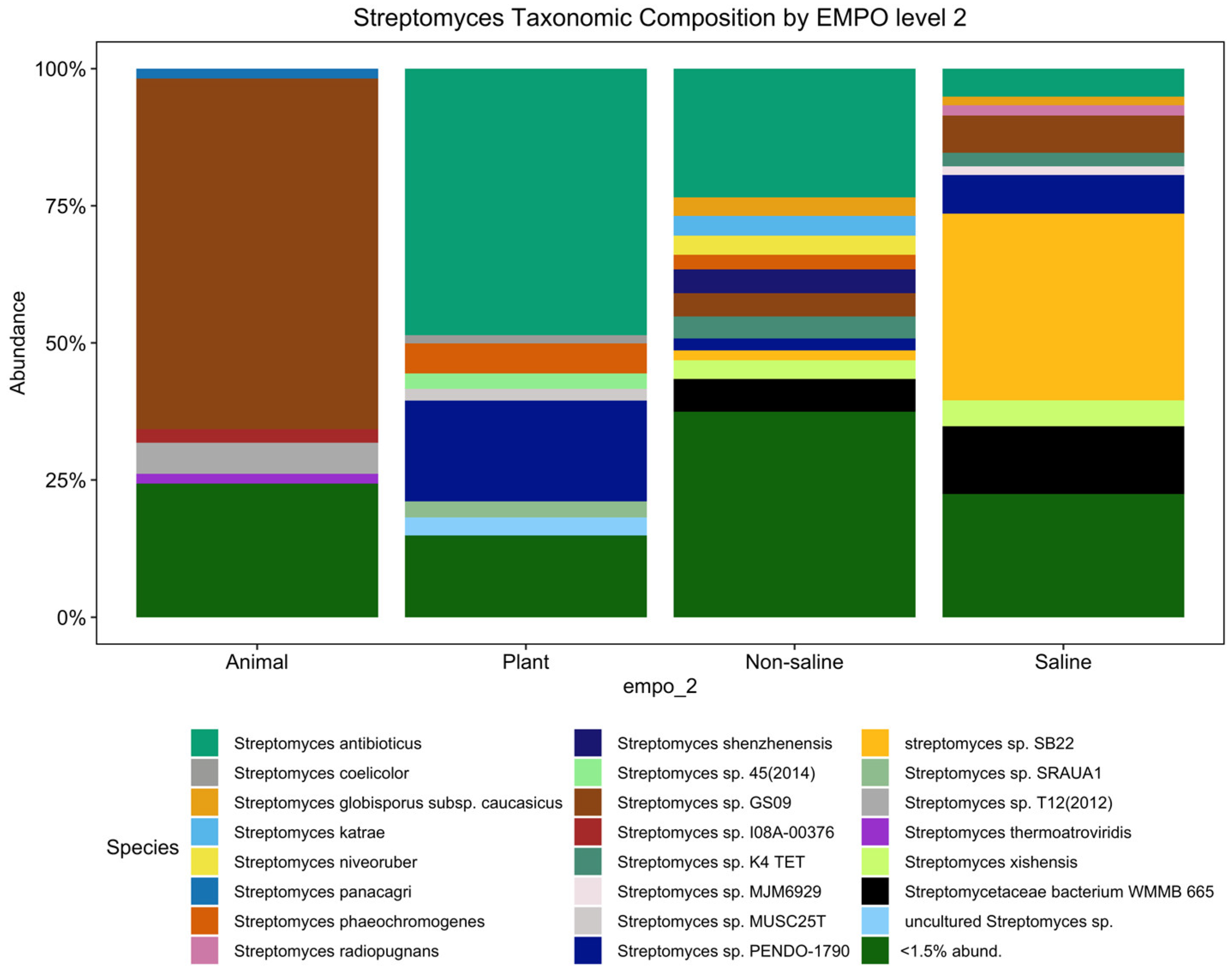
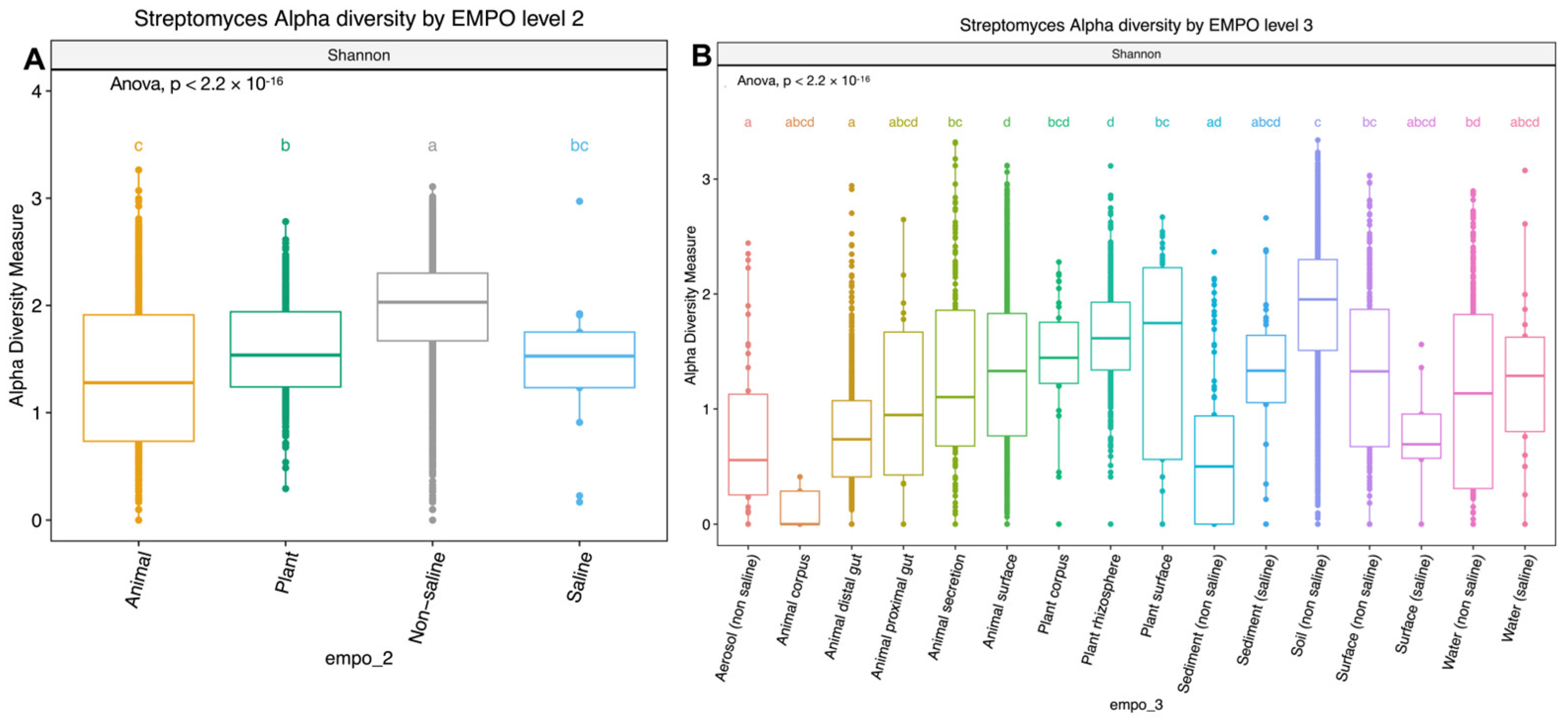
3.1. Does the Environment Shape Streptomyces Composition and Richness Differently Compared to the Overall Bacterial Community Pattern Found in the EMP?
3.2. A Comprehensive Streptomyces Diversity Map: Do Geographical Locations Structure Streptomyces Community Diversity?
4. Discussion
- Comprehensive Streptomyces diversity maps: Current sampling and future survey
- EMP dataset at a finer resolution: Streptomyces vs. overall bacterial global diversity environmental pattern
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Lima Procópio, R.E.; da Silva, I.R.; Martins, M.K.; de Azevedo, J.L.; de Araújo, J.M. Antibiotics Produced by Streptomyces. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labeda, D.P.; Goodfellow, M.; Brown, R.; Ward, A.C.; Lanoot, B.; Vanncanneyt, M.; Swings, J.; Kim, S.-B.; Liu, Z.; Chun, J.; et al. Phylogenetic Study of the Species within the Family Streptomycetaceae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2012, 101, 73–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barka, E.A.; Vatsa, P.; Sanchez, L.; Gaveau-Vaillant, N.; Jacquard, C.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Klenk, H.-P.; Clément, C.; Ouhdouch, Y.; van Wezel, G.P. Taxonomy, Physiology, and Natural Products of Actinobacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, M.; Sánchez, J. Nuclease Activities and Cell Death Processes Associated with the Development of Surface Cultures of Streptomyces antibioticus ETH 7451. Microbiology 2002, 148, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Meij, A.; Worsley, S.F. Chemical Ecology of Antibiotic Production by Actinomycetes. FEMS Microbiol. 2017, 41, 392–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, C.; Braña, A.F.; Manzanal, M.B.; Hardisson, C. Role of Substrate Mycelium in Colony Development in Streptomyces. Can. J. Microbiol. 1985, 31, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildermuth, H. Development and Organization of the Aerial Mycelium in Streptomyces Coelicolor. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1970, 60, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinkel, L.L.; Schlatter, D.C.; Bakker, M.G.; Arenz, B.E. Streptomyces Competition and Co-Evolution in Relation to Plant Disease Suppression. Res. Microbiol. 2012, 163, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, H.; Ishikawa, J.; Hanamoto, A.; Shinose, M.; Takahashi, C.; Horikawa, H.; Nakazawa, H.; Osonoe, T.; Kikuchi, H.; Shiba, T.; et al. Genome Sequence of an Industrial Microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis. In Proceedings of the Microbiological Society of Korea Conference; The Microbiological Society of Korea: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2001; pp. 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Bentley, S.D.; Chater, K.F.; Cerdeño-Tárraga, A.-M.; Challis, G.L.; Thomson, N.R.; James, K.D.; Harris, D.E.; Quail, M.A.; Kieser, H.; Harper, D.; et al. Complete Genome Sequence of the Model Actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 2002, 417, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaidis, M.; Hesketh, A.; Frangou, N.; Mossialos, D.; Van de Peer, Y.; Oliver, S.G.; Amoutzias, G.D. A Panoramic View of the Genomic Landscape of the Genus Streptomyces. Microb. Genom. 2023, 9, 001028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.M.; Crawford, D.L. Characterization of Streptomyces lydicus WYEC108 as a Potential Biocontrol Agent against Fungal Root and Seed Rots. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 3119–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordovez, V.; Carrion, V.J.; Etalo, D.W.; Mumm, R.; Zhu, H.; van Wezel, G.P.; Raaijmakers, J.M. Diversity and Functions of Volatile Organic Compounds Produced by Streptomyces from a Disease-Suppressive Soil. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chater, K.F. Recent Advances in Understanding Streptomyces. F1000Research 2016, 5, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viaene, T.; Langendries, S.; Beirinckx, S.; Maes, M.; Goormachtig, S. Streptomyces as a Plant’s Best Friend? FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, P.A.; Jebakumar, S.R.D. Unexplored Hypersaline Habitats Are Sources of Novel Actinomycetes. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalisay, D.S.; Williams, D.E.; Wang, X.L.; Centko, R.; Chen, J.; Andersen, R.J. Marine Sediment-Derived Streptomyces Bacteria from British Columbia, Canada Are a Promising Microbiota Resource for the Discovery of Antimicrobial Natural Products. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, S.; Choi, T.J.; Kim, H.; Kim, B.Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, S.K.; Oh, K.-B.; Shin, J.; Oh, D.-C. Ohmyungsamycins A and B: Cytotoxic and Antimicrobial Cyclic Peptides Produced by Streptomyces Sp. from a Volcanic Island. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 12321–12329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, M.S.A.; Philippon, T.; Asenjo, J.A.; Bull, A.T.; Goodfellow, M.; Ebel, R.; Jaspars, M.; Rateb, M.E. Asenjonamides A–C, Antibacterial Metabolites Isolated from Streptomyces asenjonii Strain KNN 42.f from an Extreme-Hyper Arid Atacama Desert Soil. J. Antibiot. 2018, 71, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tian, X.-P.; Zhu, T.-J.; Yang, L.-L.; Li, W.-J. Streptomyces fildesensis Sp. Nov., a Novel Streptomycete Isolated from Antarctic Soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2011, 100, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andam, C.P.; Doroghazi, J.R.; Campbell, A.N.; Kelly, P.J.; Choudoir, M.J.; Buckley, D.H. A Latitudinal Diversity Gradient in Terrestrial Bacteria of the Genus Streptomyces. mBio 2016, 7, e02200-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudoir, M.J.; Doroghazi, J.R.; Buckley, D.H. Latitude Delineates Patterns of Biogeography in Terrestrial Streptomyces. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 4931–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, N. Advanced Sequencing Technologies and Their Wider Impact in Microbiology. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R. Global Patterns in Bacterial Diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11436–11440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, S.T.; Clemente, J.C.; Flores, G.E.; Walters, W.A.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Global Biogeography of Highly Diverse Protistan Communities in Soil. ISME J. 2013, 7, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livermore, J.A.; Jones, S.E. Local–global Overlap in Diversity Informs Mechanisms of Bacterial Biogeography. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2413–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, J.A.; Meyer, F.; Antonopoulos, D.; Balaji, P.; Brown, C.T.; Brown, C.T.; Desai, N.; Eisen, J.A.; Evers, D.; Field, D.; et al. Meeting Report: The Terabase Metagenomics Workshop and the Vision of an Earth Microbiome Project. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2010, 3, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, J.A. The Earth Microbiome Project and Modeling the Planets Microbial Potential (Invited). Volume 2013, p. B54B-01. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2013AGUFM.B54B..01G/abstract (accessed on 1 December 2013).
- Gilbert, J.A.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. The Earth Microbiome Project: Successes and Aspirations. BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, J.A.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Earth Microbiome Project and Global Systems Biology. mSystems 2018, 3, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.R.; Sanders, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Amir, A.; Ladau, J.; Locey, K.J.; Prill, R.J.; Tripathi, A.; Gibbons, S.M.; Ackermann, G.; et al. A Communal Catalogue Reveals Earth’s Multiscale Microbial Diversity. Nature 2017, 551, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighe, S.; Afshinnekoo, E.; Rock, T.M.; McGrath, K.; Alexander, N.; McIntyre, A.; Ahsanuddin, S.; Bezdan, D.; Green, S.J.; Joye, S.; et al. Genomic Methods and Microbiological Technologies for Profiling Novel and Extreme Environments for the Extreme Microbiome Project (XMP). J. Biomol. Tech. 2017, 28, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danko, D.; Bezdan, D.; Afshin, E.E.; Ahsanuddin, S.; Bhattacharya, C.; Butler, D.J.; Chng, K.R.; Donnellan, D.; Hecht, J.; Jackson, K.; et al. A Global Metagenomic Map of Urban Microbiomes and Antimicrobial Resistance. Cell 2021, 184, 3376–3393.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contador, C.A.; Veas-Castillo, L.; Tapia, E.; Antipán, M.; Miranda, N.; Ruiz-Tagle, B.; García-Araya, J.; Andrews, B.A.; Marin, M.; Dorador, C.; et al. Atacama Database: A Platform of the Microbiome of the Atacama Desert. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissett, A.; Fitzgerald, A.; Court, L.; Meintjes, T.; Mele, P.M.; Reith, F.; Dennis, P.G.; Breed, M.F.; Brown, B.; Brown, M.V.; et al. Erratum to: Introducing BASE: The Biomes of Australian Soil Environments Soil Microbial Diversity Database. Gigascience 2017, 6, gix021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME Allows Analysis of High-Throughput Community Sequencing Data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, D.; Clemente, J.C.; Kuczynski, J.; Rideout, J.R.; Stombaugh, J.; Wendel, D.; Wilke, A.; Huse, S.; Hufnagle, J.; Meyer, F.; et al. The Biological Observation Matrix (BIOM) Format or: How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Love the Ome-Ome. Gigascience 2012, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Rodríguez de Gil, P.; Chen, Y.-H.; Kromrey, J.D.; Kim, E.S.; Pham, T.; Nguyen, D.; Romano, J.L. Comparing the Performance of Approaches for Testing the Homogeneity of Variance Assumption in One-Factor ANOVA Models. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2017, 77, 305–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Henry, M.; Stevens, M.H.H.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. Ordination Methods, Diversity Analysis and Other Functions for Community and Vegetation Ecologists, R Package Verion 2.3-1. 2015.
- Higgins, S.A.; Panke-Buisse, K.; Buckley, D.H. The Biogeography of Streptomyces in New Zealand Enabled by High-Throughput Sequencing of Genus-Specific rpoB Amplicons. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 1452–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harir, M.; Bendif, H.; Bellahcene, M.; Fortas, Z.; Pogni, R. Streptomyces Secondary Metabolites. Basic Biol. Appl. Actinobacteria 2018, 6, 99–122. [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishnan, S.; Srinivas, V.; Prasanna, S.L. Streptomyces. In Beneficial Microbes in Agro-Ecology; Amaresan, N., Senthil Kumar, M., Annapurna, K., Kumar, K., Sankaranarayanan, A., Eds.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020; pp. 55–71. ISBN 9780128234143. [Google Scholar]
- Adegboye, M.F.; Babalola, O.O.; Ngoma, L.; Okoh, A.I. Analysis of Streptomyces spp. Native to Mahikeng Soils in South Africa. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 6, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Donald, L.; Pipite, A.; Subramani, R.; Owen, J.; Keyzers, R.A.; Taufa, T. Streptomyces: Still the Biggest Producer of New Natural Secondary Metabolites, a Current Perspective. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 13, 418–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmaraj, S. Marine Streptomyces as a Novel Source of Bioactive Substances. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 2123–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathi, S.; Sathya, S.; Bupesh, G.; Samy, R.D.; Mohan, M.R.; Kumar, G.S.; Manikandan, M.; Kim, C.J.; Balakrishna, K. Isolation and Characterization of Antimicrobial Compound from Marine Streptomyces hygroscopicus BDUS 49. World J. Fish Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 268–277. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; He, J.; Wei, X.; Ju, J.; Ma, J. Exploration and Genome Mining of Natural Products from Marine Streptomyces. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Wei, D.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Goodfellow, M. Streptomyces radiopugnans sp. nov., a Radiation-Resistant Actinomycete Isolated from Radiation-Polluted Soil in China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2578–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhamodharan, D. Novel Fibrinolytic Protease Producing Streptomyces radiopugnans VITSD8 from Marine Sponges. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinkel, L.L.; Bakker, M.G.; Schlatter, D.C. A Coevolutionary Framework for Managing Disease-Suppressive Soils. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.C. Bacterial Diversity in Agroecosystems. In Invertebrate Biodiversity as Bioindicators of Sustainable Landscapes; Paoletti, M.G., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 65–76. ISBN 9780444500199. [Google Scholar]
- Seipke, R.F.; Kaltenpoth, M.; Hutchings, M.I. Streptomyces as Symbionts: An Emerging and Widespread Theme? FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Huang, Y. Taxonomic Evaluation of the Streptomyces griseus Clade Using Multilocus Sequence Analysis and DNA-DNA Hybridization, with Proposal to Combine 29 Species and Three Subspecies as 11 Genomic Species. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Huang, Y. Taxonomic Evaluation of the Streptomyces hygroscopicus Clade Using Multilocus Sequence Analysis and DNA--DNA Hybridization, Validating the MLSA Scheme for Systematics of the Whole Genus. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 35, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komaki, H. Recent Progress of Reclassification of the Genus Streptomyces. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balvočiūtė, M.; Huson, D.H. SILVA, RDP, Greengenes, NCBI and OTT—How Do These Taxonomies Compare? BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Chuvochina, M.; Rinke, C.; Mussig, A.J.; Chaumeil, P.-A.; Hugenholtz, P. GTDB: An Ongoing Census of Bacterial and Archaeal Diversity through a Phylogenetically Consistent, Rank Normalized and Complete Genome-Based Taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D785–D794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.; Romero, J.; Espejo, R.T. Polymorphism in Repeated 16S rRNA Genes Is a Common Property of Type Strains and Environmental Isolates of the Genus Vibrio. Microbiology 2002, 148, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pombubpa, N.; Lakmuang, C.; Tiwong, P.; Kanchanabanca, C. Streptomyces Diversity Maps Reveal Distinct High-Specificity Biogeographical and Environmental Patterns Compared to the Overall Bacterial Diversity. Life 2024, 14, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14010011
Pombubpa N, Lakmuang C, Tiwong P, Kanchanabanca C. Streptomyces Diversity Maps Reveal Distinct High-Specificity Biogeographical and Environmental Patterns Compared to the Overall Bacterial Diversity. Life. 2024; 14(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14010011
Chicago/Turabian StylePombubpa, Nuttapon, Chayaporn Lakmuang, Pornnapat Tiwong, and Chompoonik Kanchanabanca. 2024. "Streptomyces Diversity Maps Reveal Distinct High-Specificity Biogeographical and Environmental Patterns Compared to the Overall Bacterial Diversity" Life 14, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14010011
APA StylePombubpa, N., Lakmuang, C., Tiwong, P., & Kanchanabanca, C. (2024). Streptomyces Diversity Maps Reveal Distinct High-Specificity Biogeographical and Environmental Patterns Compared to the Overall Bacterial Diversity. Life, 14(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14010011





