Cytokines in Allergic Conjunctivitis: Unraveling Their Pathophysiological Roles
Abstract
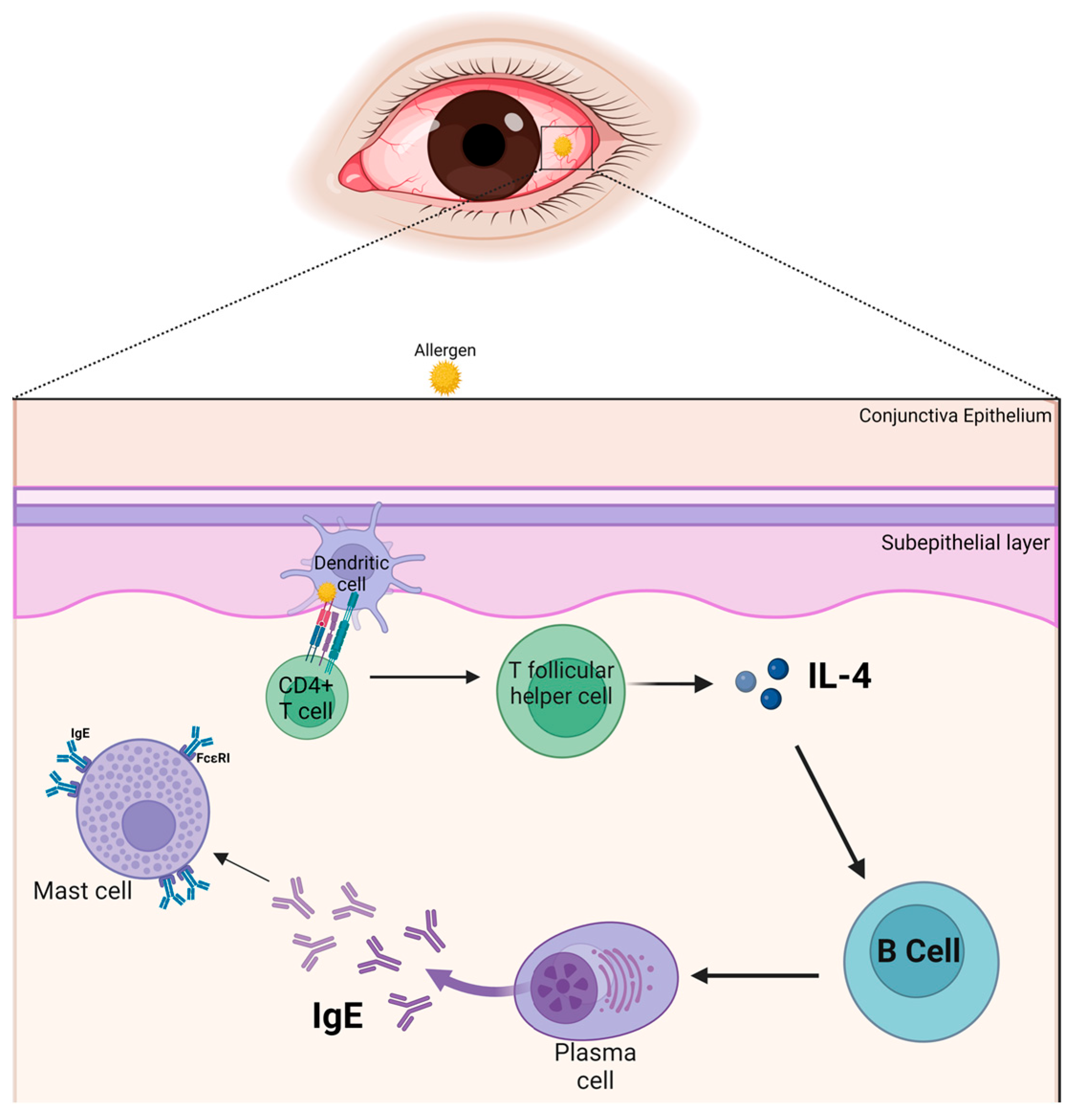
:1. Introduction
2. The Conjunctiva
3. The Allergic Immune Response in the Conjunctiva
4. Cytokines and Their Pathophysiological Roles
4.1. Interleukin-4
4.2. Intereukin-5
4.3. Interleukin-6
4.4. Interleukin-9
4.5. Interleukin-10
4.6. Interleukin-13
4.7. Interleukin-25
4.8. Interleukin-31
4.9. Interleukin-33
4.10. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin
5. Cytokines as Therapeutic Targets in the Management of Allergic Conjunctivitis
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Brien, T.P. Allergic conjunctivitis: An update on diagnosis and management. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 13, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butrus, S.; Portela, R. Ocular allergy: Diagnosis and treatment. Ophthalmol. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 18, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, M.; Lionetti, E.; Reibaldi, M.; Russo, A.; Longo, A.; Leonardi, S.; Tomarchio, S.; Avitabile, T.; Reibaldi, A. Allergic conjunctivitis: A comprehensive review of the literature. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2013, 39, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigbu, D.I.; Sandrasekaramudaly-Brown, S. Ocular surface disease: A case of vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2011, 34, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, A. Allergy and allergic mediators in tears. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 117, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawankar, R. Allergic diseases and asthma: A global public health concern and a call to action. World Allergy Organ. J. 2014, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, D.; Fukagawa, K.; Okamoto, S.; Fukushima, A.; Uchio, E.; Ebihara, N.; Shoji, J.; Namba, K.; Shimizu, Y. Epidemiological aspects of allergic conjunctivitis. Allergol. Int. 2020, 69, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abelson, M.B.; Smith, L.; Chapin, M. Ocular allergic disease: Mechanisms, disease sub-types, treatment. Ocul. Surf. 2003, 1, 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerman, S.; Smith, L.M.; Gomes, P.J. Ocular itch associated with allergic conjunctivitis: Latest evidence and clinical management. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2016, 7, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Caldez, M.J.; Akira, S. Innate immunity in allergy. Allergy 2019, 74, 1660–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoulis-Dimitriou, K.; Kotrba, J.; Voss, M.; Dudeck, J.; Dudeck, A. Mast Cell Functions Linking Innate Sensing to Adaptive Immunity. Cells 2020, 9, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, T.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Behrendt, H. Dendritic cells--the link between innate and adaptive immunity in allergy. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2002, 2, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Wandu, W.S.; St Leger, A.; Kielczewski, J.; Wawrousek, E.F.; Chan, C.C.; Gery, I. Unlike Th1/Th17 cells, Th2/Th9 cells selectively migrate to the limbus/conjunctiva and initiate an eosinophilic infiltration process. Exp. Eye Res. 2018, 166, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodfolk, J.A. Cytokines as a therapeutic target for allergic diseases: A complex picture. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 2349–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noelle, R.J.; Nowak, E.C. Cellular sources and immune functions of interleukin-9. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, K.; Nakajima, H.; Suzuki, K.; Kagami, S.; Hirose, K.; Suto, A.; Saito, Y.; Iwamoto, I. Mast cells produce interleukin-25 upon Fc epsilon RI-mediated activation. Blood 2003, 101, 3594–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Putheti, P.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, Q.; Gao, W. Structures and biological functions of IL-31 and IL-31 receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008, 19, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, H.; Takatsu, K. Role of cytokines in allergic airway inflammation. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2007, 142, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hom, M.M.; Bielory, L. The anatomical and functional relationship between allergic conjunctivitis and allergic rhinitis. Allergy Rhinol. (Provid.) 2013, 4, e110-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paiva, C.S.; Leger, A.J.S.; Caspi, R.R. Mucosal immunology of the ocular surface. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesta, M.F. Normal structure, function, and histology of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Toxicol. Pathol. 2006, 34, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassoun, D.; Malard, O.; Barbarot, S.; Magnan, A.; Colas, L. Type 2 immunity-driven diseases: Towards a multidisciplinary approach. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2021, 51, 1538–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, M.S. Anatomy of cornea and ocular surface. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 66, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shumway, C.L.; Motlagh, M.; Wade, M. Anatomy, Head and Neck, Eye Conjunctiva. In StatPearls; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gipson, I.K.; Spurr-Michaud, S.; Tisdale, A. Human conjunctival goblet cells express the membrane associated mucin MUC16: Localization to mucin granules. Exp. Eye Res. 2016, 145, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Posadas, L.; Contreras-Ruiz, L.; Soriano-Romani, L.; Dartt, D.A.; Diebold, Y. Conjunctival Goblet Cell Function: Effect of Contact Lens Wear and Cytokines. Eye Contact Lens 2016, 42, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. Ocular lymphatics: State-of-the-art review. Lymphology 2009, 42, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knoop, K.A.; Newberry, R.D. Goblet cells: Multifaceted players in immunity at mucosal surfaces. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.B.; Liu, L.; Anchouche, S.; Yung, A.; Mittal, S.K.; Blanco, T.; Dohlman, T.H.; Yin, J.; Dana, R. Ocular redness—I: Etiology, pathogenesis, and assessment of conjunctival hyperemia. Ocul. Surf. 2021, 21, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoukath, S.; Taylor, G.I.; Mendelson, B.C.; Corlett, R.J.; Shayan, R.; Tourani, S.S.; Ashton, M.W. The Lymphatic Anatomy of the Lower Eyelid and Conjunctiva and Correlation with Postoperative Chemosis and Edema. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 139, 628e–637e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Seong, Y.J.; Li, K.; Choi, D.; Park, E.; Daghlian, G.H.; Jung, E.; Bui, K.; Zhao, L.; Madhavan, S.; et al. Organogenesis and distribution of the ocular lymphatic vessels in the anterior eye. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e135121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarzuela, J.C.; Reinoso, R.; Armentia, A.; Enriquez-de-Salamanca, A.; Corell, A. Conjunctival Intraepithelial Lymphocytes, Lacrimal Cytokines and Ocular Commensal Microbiota: Analysis of the Three Main Players in Allergic Conjunctivitis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 911022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hingorani, M.; Metz, D.; Lightman, S.L. Characterisation of the normal conjunctival leukocyte population. Exp. Eye Res. 1997, 64, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Suarez, M.T.; Reinoso, R.; Martin, M.C.; Calonge, M.; Vallelado, A.I.; Fernandez, I.; Corell, A. Epithelial component and intraepithelial lymphocytes of conjunctiva-associated lymphoid tissue in healthy children. Histol. Histopathol. 2021, 36, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, N.; Al-Dossari, M.; Pritchard, N. In vivo confocal microscopy of the bulbar conjunctiva. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2009, 37, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Sano, Y.; Kinoshita, S. Conjunctival inflammation induces Langerhans cell migration into the cornea. Curr. Eye Res. 2000, 21, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrah, P.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Dana, M.R. Novel characterization of MHC class II-negative population of resident corneal Langerhans cell-type dendritic cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 639–646. [Google Scholar]
- Mudhar, H.S. Update on conjunctival pathology. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 65, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, N.; Knop, E. Conjunctiva-associated lymphoid tissue in the human eye. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Arnous, R.; Arshad, S.; Sandgren, K.; Cunningham, A.L.; Carnt, N.; White, A. Tissue resident memory T cells inhabit the deep human conjunctiva. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Gallegos, D.; Jiang, D.; Rinkevich, Y. Fibroblasts as confederates of the immune system. Immunol. Rev. 2021, 302, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Diebold, Y.; Sahu, S.K.; Leonardi, A. Epithelial barrier dysfunction in ocular allergy. Allergy 2022, 77, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enriquez-de-Salamanca, A.; Calder, V.; Gao, J.; Galatowicz, G.; Garcia-Vazquez, C.; Fernandez, I.; Stern, M.E.; Diebold, Y.; Calonge, M. Cytokine responses by conjunctival epithelial cells: An in vitro model of ocular inflammation. Cytokine 2008, 44, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calonge, M.; Enríquez-de-Salamanca, A. The role of the conjunctival epithelium in ocular allergy. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 5, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Nishida, T. Ocular allergic inflammation: Interaction between the cornea and conjunctiva. Cornea 2010, 29 (Suppl. 1), S62–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dartt, D.A.; Masli, S. Conjunctival epithelial and goblet cell function in chronic inflammation and ocular allergic inflammation. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 14, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujitsu, Y.; Fukuda, K.; Kimura, K.; Seki, K.; Kumagai, N.; Nishida, T. Protection of human conjunctival fibroblasts from NO-induced apoptosis by interleukin-4 or interleukin-13. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigbu, D.I.; Labib, B.A. Immunopharmacology in Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis: Current and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigbu, D.I.; Jain, P.; Khan, Z.K. Immune Mechanisms, Pathology, and Management of Allergic Ocular Diseases. In Advanced Concepts in Human Immunology: Prospects for Disease Control; Jain, P., Ndhlovu, L.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 229–277. [Google Scholar]
- Katelaris, C.H. Ocular allergy: Implications for the clinical immunologist. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2003, 90, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kohl, J. A complex role for complement in allergic asthma. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 6, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills-Karp, M.; Koehl, J. New insights into the role of the complement pathway in allergy and asthma. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2005, 5, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruo, K.; Akaike, T.; Ono, T.; Okamoto, T.; Maeda, H. Generation of anaphylatoxins through proteolytic processing of C3 and C5 by house dust mite protease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1997, 100, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.M.; Rahman, S.; Hubeau, C.; Ma, H.L. Cytokine pathways in allergic disease. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 40, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runswick, S.; Mitchell, T.; Davies, P.; Robinson, C.; Garrod, D. Pollen proteolytic enzymes degrade tight junctions. Respirology 2007, 12, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinhas, R.; Cortes, L.; Cardoso, I.; Mendes, V.M.; Manadas, B.; Todo-Bom, A.; Pires, E.; Verissimo, P. Pollen proteases compromise the airway epithelial barrier through degradation of transmembrane adhesion proteins and lung bioactive peptides. Allergy 2011, 66, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoki, K.; Boldogh, I.; Sur, S. Innate responses to pollen allergens. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 15, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamijo, S.; Takeda, H.; Tokura, T.; Suzuki, M.; Inui, K.; Hara, M.; Matsuda, H.; Matsuda, A.; Oboki, K.; Ohno, T.; et al. IL-33-mediated innate response and adaptive immune cells contribute to maximum responses of protease allergen-induced allergic airway inflammation. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 4489–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.; Winton, H.L.; Soeller, C.; Gruenert, D.C.; Thompson, P.J.; Cannell, M.B.; Stewart, G.A.; Garrod, D.R.; Robinson, C. Quantitative structural and biochemical analyses of tight junction dynamics following exposure of epithelial cells to house dust mite allergen Der p 1. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2000, 30, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Winton, H.L.; Soeller, C.; Taylor, G.W.; Gruenert, D.C.; Thompson, P.J.; Cannell, M.B.; Stewart, G.A.; Garrod, D.R.; Robinson, C. The transmembrane protein occludin of epithelial tight junctions is a functional target for serine peptidases from faecal pellets of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2001, 31, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montan, P.G.; Ekstrom, K.; Hedlin, G.; van Hage-Hamsten, M.; Hjern, A.; Herrmann, B. Vernal keratoconjunctivitis in a Stockholm ophthalmic centre--epidemiological, functional, and immunologic investigations. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 1999, 77, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konig, K.; Klemens, C.; Eder, K.; San Nicolo, M.; Becker, S.; Kramer, M.F.; Groger, M. Cytokine profiles in nasal fluid of patients with seasonal or persistent allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2015, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Winton, H.L.; Soeller, C.; Tovey, E.R.; Gruenert, D.C.; Thompson, P.J.; Stewart, G.A.; Taylor, G.W.; Garrod, D.R.; Cannell, M.B.; et al. Der p 1 facilitates transepithelial allergen delivery by disruption of tight junctions. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, B.A.; Chigbu, D.I. Therapeutic Targets in Allergic Conjunctivitis. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadani, S.P.; Cronk, J.C.; Norris, G.T.; Kipnis, J. IL-4 in the brain: A cytokine to remember. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 4213–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzina, I.G.; Keegan, A.D.; Heller, N.M.; Rook, G.A.; Shea-Donohue, T.; Atamas, S.P. Regulation of inflammation by interleukin-4: A review of “alternatives”. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, T.D.; Zhang, J.L.; Sebald, W.; Duschl, A. Structure, binding, and antagonists in the IL-4/IL-13 receptor system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1592, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goenka, S.; Kaplan, M.H. Transcriptional regulation by STAT6. Immunol. Res. 2011, 50, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.; Martinez, F.O. Alternative activation of macrophages: Mechanism and functions. Immunity 2010, 32, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueta, M.; Sotozono, C.; Kinoshita, S. Expression of interleukin-4 receptor alpha in human corneal epithelial cells. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 55, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueta, M.; Mizushima, K.; Yokoi, N.; Naito, Y.; Kinoshita, S. Expression of the interleukin-4 receptor alpha in human conjunctival epithelial cells. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 94, 1239–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaia, C.; Paoletti, G.; Puggioni, F.; Racca, F.; Pelaia, G.; Canonica, G.W.; Heffler, E. Interleukin-5 in the Pathophysiology of Severe Asthma. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chigbu, D.I. The pathophysiology of ocular allergy: A review. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2009, 32, 3–15, quiz 43-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esnault, S.; Kelly, E.A. Essential Mechanisms of Differential Activation of Eosinophils by IL-3 Compared to GM-CSF and IL-5. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 36, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doganci, A.; Sauer, K.; Karwot, R.; Finotto, S. Pathological role of IL-6 in the experimental allergic bronchial asthma in mice. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 28, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didion, S.P. Cellular and Oxidative Mechanisms Associated with Interleukin-6 Signaling in the Vasculature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, A.A.; Groom, J.R. Transcription tipping points for T follicular helper cell and T-helper 1 cell fate commitment. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevnikar, Z.; Östling, J.; Ax, E.; Calvén, J.; Thörn, K.; Israelsson, E.; Öberg, L.; Singhania, A.; Lau, L.C.; Wilson, S.J.; et al. Epithelial IL-6 trans-signaling defines a new asthma phenotype with increased airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. Targeting Interleukin-6 Signaling in Clinic. Immunity 2019, 50, 1007–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zheng, S.G. Hall of Fame among Pro-inflammatory Cytokines: Interleukin-6 Gene and Its Transcriptional Regulation Mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultner, L.; Kolsch, S.; Stassen, M.; Kaspers, U.; Kremer, J.P.; Mailhammer, R.; Moeller, J.; Broszeit, H.; Schmitt, E. In activated mast cells, IL-1 up-regulates the production of several Th2-related cytokines including IL-9. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 5556–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoine, F.; Lacy, P. Eosinophil cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors: Emerging roles in immunity. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajulas, A.; Zhang, J.; Kaplan, M.H. The World according to IL-9. J. Immunol. 2023, 211, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajulas, A.; Fu, Y.; Cheung, C.C.L.; Chu, M.; Cannon, A.; Alakhras, N.; Zhang, J.; Ulrich, B.J.; Nelson, A.S.; Zhou, B.; et al. Interleukin-9 promotes mast cell progenitor proliferation and CCR2-dependent mast cell migration in allergic airway inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2023, 16, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, R.; Kaplan, M.H. A brief history of IL-9. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 3283–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, M.; Vieira, P.; O’garra, A. Biology and therapeutic potential of interleukin-10. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabryšová, L.; Howes, A.; Saraiva, M.; O’Garra, A. The regulation of IL-10 expression. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 380, 157–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wong, K.; Ouyang, W.; Rutz, S. Targeting IL-10 Family Cytokines for the Treatment of Human Diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019, 11, a028548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulke, S. Induction of Interleukin-10 Producing Dendritic Cells As a Tool to Suppress Allergen-Specific T Helper 2 Responses. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouval, D.S.; Ouahed, J.; Biswas, A.; Goettel, J.A.; Horwitz, B.H.; Klein, C.; Muise, A.M.; Snapper, S.B. Interleukin 10 receptor signaling: Master regulator of intestinal mucosal homeostasis in mice and humans. Adv. Immunol. 2014, 122, 177–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walford, H.H.; Doherty, T.A. STAT6 and lung inflammation. JAKSTAT 2013, 2, e25301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeb, E. Interleukin-13 (IL-13)-A Pleiotropic Cytokine Involved in Wound Healing and Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Angkasekwinai, P.; Lu, N.; Voo, K.S.; Arima, K.; Hanabuchi, S.; Hippe, A.; Corrigan, C.J.; Dong, C.; Homey, B.; et al. IL-25 augments type 2 immune responses by enhancing the expansion and functions of TSLP-DC-activated Th2 memory cells. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angkasekwinai, P.; Park, H.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Chang, S.H.; Corry, D.B.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhu, Z.; Dong, C. Interleukin 25 promotes the initiation of proallergic type 2 responses. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonobe, Y.; Takeuchi, H.; Kataoka, K.; Li, H.; Jin, S.; Mimuro, M.; Hashizume, Y.; Sano, Y.; Kanda, T.; Mizuno, T.; et al. Interleukin-25 expressed by brain capillary endothelial cells maintains blood-brain barrier function in a protein kinase Cepsilon-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 31834–31842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.K.; Cheung, P.F.; Ip, W.K.; Lam, C.W. Interleukin-25-induced chemokines and interleukin-6 release from eosinophils is mediated by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and nuclear factor-kappaB. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2005, 33, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakura, Y.; Ishigame, H.; Saijo, S.; Nakae, S. Functional specialization of interleukin-17 family members. Immunity 2011, 34, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemmer, J.M.; Kuchner, M.; Datsi, A.; Olah, P.; Julia, V.; Raap, U.; Homey, B. Interleukin-31 Signaling Bridges the Gap Between Immune Cells, the Nervous System and Epithelial Tissues. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 639097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solimando, A.G.; Desantis, V.; Ribatti, D. Mast Cells and Interleukins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabashima, K.; Irie, H. Interleukin-31 as a Clinical Target for Pruritus Treatment. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 638325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Ochiai, S.; Jin, J.; Takahashi, N.; Toshima, S.; Ishigame, H.; Kabashima, K.; Kubo, M.; Nakayama, M.; Shiroguchi, K.; et al. Sensory neuronal STAT3 is critical for IL-31 receptor expression and inflammatory itch. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J.; Owyang, A.; Oldham, E.; Song, Y.; Murphy, E.; McClanahan, T.K.; Zurawski, G.; Moshrefi, M.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 2005, 23, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesenauer, B.; Paczesny, S. The ST2/IL-33 Axis in Immune Cells during Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, G.K.; D’Cruz, L.M.; Turnquist, H.R. Emerging Functions of IL-33 in Homeostasis and Immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 40, 15–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hammel, M.; He, Y.; Tainer, J.A.; Jeng, U.S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Structural insights into the interaction of IL-33 with its receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14918–14923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.M.; Lian, H.; Li, S. Signaling and functions of interleukin-33 in immune regulation and diseases. Cell Insight 2022, 1, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, K.; Takagi, T.; Tsukamoto, T.; Tetsuka, T.; Tominaga, S. Presence of a novel primary response gene ST2L, encoding a product highly similar to the interleukin 1 receptor type 1. FEBS Lett. 1993, 318, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, L.Y.; Kita, H. IL-33: Biological properties, functions, and roles in airway disease. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 278, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, S.F.; Artis, D. Sensing the outside world: TSLP regulates barrier immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.; Ozaki, K.; Baumann, H.; Levin, S.D.; Puel, A.; Farr, A.G.; Ziegler, S.F.; Leonard, W.J.; Lodish, H.F. Cloning of a receptor subunit required for signaling by thymic stromal lymphopoietin. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, L.S.; Martin, U.; Garka, K.; Gliniak, B.; Di Santo, J.P.; Muller, W.; Largaespada, D.A.; Copeland, N.G.; Jenkins, N.A.; Farr, A.G.; et al. Cloning of the murine thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) receptor: Formation of a functional heteromeric complex requires interleukin 7 receptor. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reche, P.A.; Soumelis, V.; Gorman, D.M.; Clifford, T.; Liu, M.; Travis, M.; Zurawski, S.M.; Johnston, J.; Liu, Y.J.; Spits, H.; et al. Human thymic stromal lymphopoietin preferentially stimulates myeloid cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebina-Shibuya, R.; Leonard, W.J. Role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in allergy and beyond. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelms, K.; Keegan, A.D.; Zamorano, J.; Ryan, J.J.; Paul, W.E. The IL-4 receptor: Signaling mechanisms and biologic functions. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999, 17, 701–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurdayal, R.; Brombacher, F. Interleukin-4 Receptor Alpha: From Innate to Adaptive Immunity in Murine Models of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.R.; Martin, L.D.; Stern, R.; Laxman, B.; Marroquin, B.A. Expression of IL-4/IL-13 receptors in differentiating human airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2010, 299, L681–L693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, M.H.; Schindler, U.; Smiley, S.T.; Grusby, M.J. Stat6 is required for mediating responses to IL-4 and for development of Th2 cells. Immunity 1996, 4, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, B.; Johnson, A.; Lewis, J.; Morgan, D.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Cell Signaling. In Molecular Biology of the Cell; Garland Sciences: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 813–888. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, K.P.; Weaver, C. The Induced Response of Innate Immunity. In Janeway’s Immunobiology, 9th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 77–138. [Google Scholar]
- Oetjen, L.K.; Mack, M.R.; Feng, J.; Whelan, T.M.; Niu, H.; Guo, C.J.; Chen, S.; Trier, A.M.; Xu, A.Z.; Tripathi, S.V.; et al. Sensory Neurons Co-opt Classical Immune Signaling Pathways to Mediate Chronic Itch. Cell 2017, 171, 217–228.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Fujitsu, Y.; Kumagai, N.; Nishida, T. Characterization of the interleukin-4 receptor complex in human corneal fibroblasts. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie, G.J.; Fallon, P.G.; Emson, C.L.; Grencis, R.K.; McKenzie, A.N. Simultaneous disruption of interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 defines individual roles in T helper cell type 2-mediated responses. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessner, A.; Mohrs, K.; Mohrs, M. Mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils acquire constitutive IL-4 and IL-13 transcripts during lineage differentiation that are sufficient for rapid cytokine production. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, B. Transcriptional regulation of mast cell and basophil lineage commitment. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 38, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Ohbayashi, M.; Morohoshi, K.; Zhang, L.; Liu, F.; Ono, S. Critical role of IgE-dependent mast cell activation in a murine model of allergic conjunctivitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotowicz, K.; Callard, R.E.; Friedrich, K.; Matthews, D.J.; Klein, N. Biological activity of IL-4 and IL-13 on human endothelial cells: Functional evidence that both cytokines act through the same receptor. Int. Immunol. 1996, 8, 1915–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaria, T.; Burgener, J.; Bachli, E.; Schoedon, G. IL-4 Causes Hyperpermeability of Vascular Endothelial Cells through Wnt5A Signaling. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujitsu, Y.; Fukuda, K.; Kumagai, N.; Nishida, T. IL-4-induced cell proliferation and production of extracellular matrix proteins in human conjunctival fibroblasts. Exp. Eye Res. 2003, 76, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, A.; Shmilowich, R.; Shasha, D.; Frucht-Pery, J.; Pe’er, J.; Bonini, S.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Conjunctival fibroblasts enhance the survival and functional activity of peripheral blood eosinophils in vitro. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Adachi, T.; Alam, R. The mechanism of IL-5 signal transduction. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, C623–C633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.E.; Maerz, M.D.; Buckner, J.H. IL-6: A cytokine at the crossroads of autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 55, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sismanopoulos, N.; Delivanis, D.A.; Alysandratos, K.D.; Angelidou, A.; Vasiadi, M.; Therianou, A.; Theoharides, T.C. IL-9 induces VEGF secretion from human mast cells and IL-9/IL-9 receptor genes are overexpressed in atopic dermatitis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounni, A.S.; Gregory, B.; Nutku, E.; Aris, F.; Latifa, K.; Minshall, E.; North, J.; Tavernier, J.; Levit, R.; Nicolaides, N.; et al. Interleukin-9 enhances interleukin-5 receptor expression, differentiation, and survival of human eosinophils. Blood 2000, 96, 2163–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demoulin, J.B.; Renauld, J.C. Interleukin 9 and its receptor: An overview of structure and function. Int. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temann, U.A.; Geba, G.P.; Rankin, J.A.; Flavell, R.A. Expression of interleukin 9 in the lungs of transgenic mice causes airway inflammation, mast cell hyperplasia, and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Gao, N.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Bian, F.; Chi, W.; Liu, Z.; de Paiva, C.S.; Pflugfelder, S.C.; et al. IL-33/ST2/IL-9/IL-9R signaling disrupts ocular surface barrier in allergic inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2020, 13, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paiva, C.S.; Raince, J.K.; McClellan, A.J.; Shanmugam, K.P.; Pangelinan, S.B.; Volpe, E.A.; Corrales, R.M.; Farley, W.J.; Corry, D.B.; Li, D.Q.; et al. Homeostatic control of conjunctival mucosal goblet cells by NKT-derived IL-13. Mucosal Immunol. 2011, 4, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tukler Henriksson, J.; Coursey, T.G.; Corry, D.B.; De Paiva, C.S.; Pflugfelder, S.C. IL-13 Stimulates Proliferation and Expression of Mucin and Immunomodulatory Genes in Cultured Conjunctival Goblet Cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 4186–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigbu, D.I.; Minhas, B.K. Immunopathology of allergic conjunctivitis. Eur. Med. J. 2018, 3, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Peng, N.; Xiao, F.; Shi, X.; Zhu, B.; Rui, K.; Tian, J.; Lu, L. New insights into the function of Interleukin-25 in disease pathogenesis. Biomark. Res. 2023, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, C.J.; Wang, W.; Meng, Q.; Fang, C.; Wu, H.; Reay, V.; Lv, Z.; Fan, Y.; An, Y.; Wang, Y.H.; et al. T-helper cell type 2 (Th2) memory T cell-potentiating cytokine IL-25 has the potential to promote angiogenesis in asthma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1579–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Smith, S.G.; Beaudin, S.; Dua, B.; Howie, K.; Gauvreau, G.; O’Byrne, P.M. IL-25 and IL-25 receptor expression on eosinophils from subjects with allergic asthma. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2014, 163, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, W.B.; Yoon, J.; Bartemes, K.R.; Iijima, K.; Kita, H. A novel IL-1 family cytokine, IL-33, potently activates human eosinophils. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, A.; Ebihara, N.; Yokoi, N.; Kawasaki, S.; Tanioka, H.; Inatomi, T.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; Hamuro, J.; Kinoshita, S.; Murakami, A. Functional role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in chronic allergic keratoconjunctivitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ma, P.; de Paiva, C.S.; Cunningham, M.A.; Hwang, C.S.; Pflugfelder, S.C.; Li, D.Q. TSLP and downstream molecules in experimental mouse allergic conjunctivitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 3076–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allakhverdi, Z.; Comeau, M.R.; Jessup, H.K.; Yoon, B.R.; Brewer, A.; Chartier, S.; Paquette, N.; Ziegler, S.F.; Sarfati, M.; Delespesse, G. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin is released by human epithelial cells in response to microbes, trauma, or inflammation and potently activates mast cells. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Redhu, N.S.; Saleh, A.; Halayko, A.J.; Chakir, J.; Gounni, A.S. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor-mediated IL-6 and CC/CXC chemokines expression in human airway smooth muscle cells: Role of MAPKs (ERK1/2, p38, and JNK) and STAT3 pathways. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 7134–7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.J.; Zhou, B. A new itch to scratch for TSLP. Trends Immunol. 2014, 35, 49–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwatra, S.G.; Misery, L.; Clibborn, C.; Steinhoff, M. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of itch and pain in atopic dermatitis and implications for novel therapeutics. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2022, 11, e1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsu, K. Interleukin-5 and IL-5 receptor in health and diseases. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2011, 87, 463–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irkec, M.T.; Bozkurt, B. Molecular immunology of allergic conjunctivitis. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 12, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubucquoi, S.; Desreumaux, P.; Janin, A.; Klein, O.; Goldman, M.; Tavernier, J.; Capron, A.; Capron, M. Interleukin 5 synthesis by eosinophils: Association with granules and immunoglobulin-dependent secretion. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 179, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, F.; Pan, Y.H.; Huang, X.; Zhu, H.Y.; Jiang, D.L. From bench to bedside: Therapeutic potential of interleukin-9 in the treatment of asthma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehra, S.; Yao, W.; Nguyen, E.T.; Glosson-Byers, N.L.; Akhtar, N.; Zhou, B.; Kaplan, M.H. TH9 cells are required for tissue mast cell accumulation during allergic inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 433–440.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ultsch, M.; Bevers, J.; Nakamura, G.; Vandlen, R.; Kelley, R.F.; Wu, L.C.; Eigenbrot, C. Structural basis of signaling blockade by anti-IL-13 antibody Lebrikizumab. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keegan, A.D.; Zamorano, J.; Keselman, A.; Heller, N.M. IL-4 and IL-13 Receptor Signaling From 4PS to Insulin Receptor Substrate 2: There and Back Again, a Historical View. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly-Welch, A.; Hanson, E.M.; Keegan, A.D. Interleukin-13 (IL-13) pathway. Sci. STKE 2005, 2005, cm8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershey, G.K. IL-13 receptors and signaling pathways: An evolving web. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 677–690, quiz 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeod, J.J.; Baker, B.; Ryan, J.J. Mast cell production and response to IL-4 and IL-13. Cytokine 2015, 75, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C. Regulation and pro-inflammatory function of interleukin-17 family cytokines. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 226, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, Z.; Shangguan, G.; Bie, Q.; Zhang, B. Biological Properties and the Role of IL-25 in Disease Pathogenesis. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 6519465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Peng, N.; Tang, Y.; Yu, N.; Wang, C.; Cai, X.; Zhang, L.; Hu, D.; Ciccia, F.; Lu, L. Roles of IL-25 in Type 2 Inflammation and Autoimmune Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 691559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, M. Interleukin 25 and its biological features and function in intestinal diseases. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2022, 47, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, A.; Shen, F.; Hanel, W.; Mossman, K.; Tocker, J.; Swart, D.; Gaffen, S.L. Distinct functional motifs within the IL-17 receptor regulate signal transduction and target gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7506–7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maezawa, Y.; Nakajima, H.; Suzuki, K.; Tamachi, T.; Ikeda, K.; Inoue, J.; Saito, Y.; Iwamoto, I. Involvement of TNF receptor-associated factor 6 in IL-25 receptor signaling. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zepp, J.A.; Wu, L.; Qian, W.; Ouyang, W.; Aronica, M.; Erzurum, S.; Li, X. TRAF4-SMURF2-mediated DAZAP2 degradation is critical for IL-25 signaling and allergic airway inflammation. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 2826–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowczyk, J.; Shutova, M.; Brembilla, N.C.; Boehncke, W.H. IL-25 (IL-17E) in epithelial immunology and pathophysiology. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zepp, J.A.; Qian, W.; Martin, B.N.; Ouyang, W.; Yin, W.; Bunting, K.D.; Aronica, M.; Erzurum, S.; Li, X. A novel IL-25 signaling pathway through STAT5. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 4528–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asada, Y.; Nakae, S.; Ishida, W.; Hori, K.; Sugita, J.; Sudo, K.; Fukuda, K.; Fukushima, A.; Suto, H.; Murakami, A.; et al. Roles of Epithelial Cell-Derived Type 2-Initiating Cytokines in Experimental Allergic Conjunctivitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 5194–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgia, F.; Custurone, P.; Li Pomi, F.; Cordiano, R.; Alessandrello, C.; Gangemi, S. IL-31: State of the Art for an Inflammation-Oriented Interleukin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zanvit, P.; Hu, L.; Tseng, P.Y.; Liu, N.; Wang, F.; Liu, O.; Zhang, D.; Jin, W.; Guo, N.; et al. The Cytokine TGF-beta Induces Interleukin-31 Expression from Dermal Dendritic Cells to Activate Sensory Neurons and Stimulate Wound Itching. Immunity 2020, 53, 371–383.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, K.; Uruno, T.; Shiraishi, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Ushijima, M.; Nakahara, T.; Watanabe, M.; Kido-Nakahara, M.; Tsuge, I.; Furue, M.; et al. The transcription factor EPAS1 links DOCK8 deficiency to atopic skin inflammation via IL-31 induction. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, E.M.; Shin, D.B.; Nattkemper, L.A.; Benoit, B.M.; Klein, R.S.; Didigu, C.A.; Loren, A.W.; Dentchev, T.; Wysocka, M.; Yosipovitch, G.; et al. IL-31 is produced by the malignant T-cell population in cutaneous T-Cell lymphoma and correlates with CTCL pruritus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 2783–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonkoly, E.; Muller, A.; Lauerma, A.I.; Pivarcsi, A.; Soto, H.; Kemeny, L.; Alenius, H.; Dieu-Nosjean, M.C.; Meller, S.; Rieker, J.; et al. IL-31: A new link between T cells and pruritus in atopic skin inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.C.; Yang, W.; Guo, C.; Jiang, H.; Li, F.; Xiao, M.; Davidson, S.; Yu, G.; Duan, B.; Huang, T.; et al. Anatomical and functional dichotomy of ocular itch and pain. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okano, M.; Hirahara, K.; Kiuchi, M.; Onoue, M.; Iwamura, C.; Kokubo, K.; Hishiya, T.; Morimoto, Y.; Ikehara, Y.; Murakami, A.; et al. Interleukin-33-activated neuropeptide CGRP-producing memory Th2 cells cooperate with somatosensory neurons to induce conjunctival itch. Immunity 2022, 55, 2352–2368.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevikbas, F.; Wang, X.; Akiyama, T.; Kempkes, C.; Savinko, T.; Antal, A.; Kukova, G.; Buhl, T.; Ikoma, A.; Buddenkotte, J.; et al. A sensory neuron-expressed IL-31 receptor mediates T helper cell-dependent itch: Involvement of TRPV1 and TRPA1. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carriere, V.; Roussel, L.; Ortega, N.; Lacorre, D.A.; Americh, L.; Aguilar, L.; Bouche, G.; Girard, J.P. IL-33, the IL-1-like cytokine ligand for ST2 receptor, is a chromatin-associated nuclear factor in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Hosotani, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Yasuda, K.; Nagai, M.; Jitsukawa, O.; Gomi, F.; Nakanishi, K.; Yoshimoto, T.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Expression of IL-33 in ocular surface epithelium induces atopic keratoconjunctivitis with activation of group 2 innate lymphoid cells in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkar, R.; Lee, R.T. The IL-33/ST2 pathway: Therapeutic target and novel biomarker. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funakoshi-Tago, M.; Tago, K.; Hayakawa, M.; Tominaga, S.; Ohshio, T.; Sonoda, Y.; Kasahara, T. TRAF6 is a critical signal transducer in IL-33 signaling pathway. Cell. Signal. 2008, 20, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, J.; Shin, J.W.; Ko, B.C.; Kim, H.Y. Targeting the Epithelium-Derived Innate Cytokines: From Bench to Bedside. Immune Netw. 2022, 22, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iikura, M.; Suto, H.; Kajiwara, N.; Oboki, K.; Ohno, T.; Okayama, Y.; Saito, H.; Galli, S.J.; Nakae, S. IL-33 can promote survival, adhesion and cytokine production in human mast cells. Lab. Investig. 2007, 87, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allakhverdi, Z.; Smith, D.E.; Comeau, M.R.; Delespesse, G. Cutting edge: The ST2 ligand IL-33 potently activates and drives maturation of human mast cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 2051–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuba-Kitamura, S.; Yoshimoto, T.; Yasuda, K.; Futatsugi-Yumikura, S.; Taki, Y.; Muto, T.; Ikeda, T.; Mimura, O.; Nakanishi, K. Contribution of IL-33 to induction and augmentation of experimental allergic conjunctivitis. Int. Immunol. 2010, 22, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraete, K.; Peelman, F.; Braun, H.; Lopez, J.; Van Rompaey, D.; Dansercoer, A.; Vandenberghe, I.; Pauwels, K.; Tavernier, J.; Lambrecht, B.N.; et al. Structure and antagonism of the receptor complex mediated by human TSLP in allergy and asthma. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Sharma, J.; Raju, R.; Palapetta, S.M.; Prasad, T.S.; Huang, T.C.; Yoda, A.; Tyner, J.W.; van Bodegom, D.; Weinstock, D.M.; et al. TSLP signaling pathway map: A platform for analysis of TSLP-mediated signaling. Database 2014, 2014, bau007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quentmeier, H.; Drexler, H.G.; Fleckenstein, D.; Zaborski, M.; Armstrong, A.; Sims, J.E.; Lyman, S.D. Cloning of human thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and signaling mechanisms leading to proliferation. Leukemia 2001, 15, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin: Master switch for allergic inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, Y.; Kashyap, M.; Robinson, G.W.; Sakamoto, K.; Gomez-Rodriguez, J.; Wagner, K.U.; Leonard, W.J. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin-mediated STAT5 phosphorylation via kinases JAK1 and JAK2 reveals a key difference from IL-7-induced signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19455–19460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Biehl, A.; Gadina, M.; Hasni, S.; Schwartz, D.M. JAK-STAT Signaling as a Target for Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases: Current and Future Prospects. Drugs 2017, 77, 521–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Yao, J.; Li, B. Expression of TSLP and Downstream Molecules IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 on the Eye Surface of Patients with Various Types of Allergic Conjunctivitis. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 2016, 5072781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Liu, Y.J. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin, OX40-ligand, and interleukin-25 in allergic responses. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederkorn, J. Immune regulatory mechanisms in allergic conjunctivitis: Insights from mouse models. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 8, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, M.; Siemasko, K.; Niederkorn, J. The Th1/Th2 paradigm in ocular allergy. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 5, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; Hu, S.; Cheung, P.F.; Lam, C.W. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin induces chemotactic and prosurvival effects in eosinophils: Implications in allergic inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 43, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.; Kershaw, N.J.; Babon, J.J. The molecular details of cytokine signaling via the JAK/STAT pathway. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 1984–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Su, W.; Liang, D. Tofacitinib suppresses mast cell degranulation and attenuates experimental allergic conjunctivitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 86, 106737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieber, T.; Simpson, E.L.; Silverberg, J.I.; Thaci, D.; Paul, C.; Pink, A.E.; Kataoka, Y.; Chu, C.Y.; DiBonaventura, M.; Rojo, R.; et al. Abrocitinib versus Placebo or Dupilumab for Atopic Dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stander, S.; Kwatra, S.G.; Silverberg, J.I.; Simpson, E.L.; Thyssen, J.P.; Yosipovitch, G.; Zhang, F.; Cameron, M.C.; Cella, R.R.; Valdez, H.; et al. Early Itch Response with Abrocitinib Is Associated with Later Efficacy Outcomes in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: Subgroup Analysis of the Randomized Phase III JADE COMPARE Trial. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2023, 24, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junttila, I.S. Tuning the Cytokine Responses: An Update on Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 Receptor Complexes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Bissonnette, R.; Ungar, B.; Suarez-Farinas, M.; Ardeleanu, M.; Esaki, H.; Suprun, M.; Estrada, Y.; Xu, H.; Peng, X.; et al. Dupilumab progressively improves systemic and cutaneous abnormalities in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, K.; Kishimoto, T.; Sumi, T.; Yamashiro, K.; Ebihara, N. Biologics for allergy: Therapeutic potential for ocular allergic diseases and adverse effects on the eye. Allergol. Int. 2023, 72, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, A.; Trikha, A.; Calhoun, W.J. Benralizumab—A humanized mAb to IL-5Ralpha with enhanced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity—A novel approach for the treatment of asthma. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2012, 12, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose-John, S.; Jenkins, B.J.; Garbers, C.; Moll, J.M.; Scheller, J. Targeting IL-6 trans-signalling: Past, present and future prospects. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Li, J.; Fu, M.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway: From bench to clinic. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose-John, S. Local and systemic effects of interleukin-6 (IL-6) in inflammation and cancer. FEBS Lett. 2022, 596, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose-John, S. IL-6 trans-signaling via the soluble IL-6 receptor: Importance for the pro-inflammatory activities of IL-6. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballantyne, S.J.; Barlow, J.L.; Jolin, H.E.; Nath, P.; Williams, A.S.; Chung, K.F.; Sturton, G.; Wong, S.H.; McKenzie, A.N. Blocking IL-25 prevents airway hyperresponsiveness in allergic asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stander, S.; Yosipovitch, G.; Lacour, J.P.; Legat, F.J.; Paul, C.; Reich, A.; Chaouche, K.; Ahmad, F.; Piketty, C. Nemolizumab efficacy in prurigo nodularis: Onset of action on itch and sleep disturbances. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1820–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabashima, K.; Matsumura, T.; Komazaki, H.; Kawashima, M.; Nemolizumab, J.P.S.G. Trial of Nemolizumab and Topical Agents for Atopic Dermatitis with Pruritus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, E.; Rees, D.G.; Scott, I.C.; Carmen, S.; Chan, D.T.Y.; Chaillan Huntington, C.E.; Houslay, K.F.; Erngren, T.; Penney, M.; Majithiya, J.B.; et al. Tozorakimab (MEDI3506): An anti-IL-33 antibody that inhibits IL-33 signalling via ST2 and RAGE/EGFR to reduce inflammation and epithelial dysfunction. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavord, I.D.; Hoyte, F.C.L.; Lindsley, A.W.; Ambrose, C.S.; Spahn, J.D.; Roseti, S.L.; Cook, B.; Griffiths, J.M.; Hellqvist, A.; Martin, N.; et al. Tezepelumab reduces exacerbations across all seasons in patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma (NAVIGATOR). Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023, 131, 587–597.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Cytokines | Cellular Sources | Cytokine Receptors | Cytokine Receptor Components | Cells Expressing Cytokine Receptors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-4 | Th2 cells, mast cells, eosinophils, and basophils [65,66]. | IL-4R | IL-4R alpha (CD124), IL-2R chain (CD132) [68,69]. | Monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, T cells, smooth muscle cells, and B cells [54]. |
| IL-5 | Th2 cells, group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2), mast cells, and eosinophils [18,49,72,73]. | IL-5R | IL-5R alpha (CD125), IL-2R chain (CD122) [18,72,74]. | Eosinophils and basophils [18,72,74]. |
| IL-6 | Dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, B cells, epithelial cells, and endothelial cells [75]. T cells, fibroblasts, vascular smooth muscle cells, glial cells, and keratinocytes [76,77]. | IL-6R | IL-6R alpha chain (CD126) and IL-6R beta chain/gp130 (CD130) [78,79,80]. | Lymphocytes, monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, and hepatocytes [79,80]. |
| IL-9 | Th9 cells [15], mast cells [81] and eosinophils [82]. Th2 cells, eosinophils, and basophils [83]. | IL-9R | IL-9R alpha chain, IL-2R chain (CD132) [84]. | Epithelial cells, fibroblasts, granulocytes, lymphocytes, macrophages, mast cells [84,85], T cells, smooth muscle cells [54], and B cells [83]. |
| IL-10 | Macrophages, monocytes, dendritic cells, neutrophils, mast cells, eosinophils, NK cells, CD4+T cells, CD8+T cells, and B cells, microglia, and epithelial cells [86,87,88]. | IL-10R | IL-10R alpha chain and IL-10R beta chain [89]. | Immune cells, fibroblasts, and epithelial cells [90]. |
| IL-13 | Th2 cells, mast cells, type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2), and basophils [91,92]. | IL-13R | IL-4R alpha chain, IL-13R alpha1 chain [49,91,92]. | Smooth muscle cells, epithelial cells, fibroblasts, B cells, macrophages, endothelial cells, and goblet cells [49,91,92]. |
| IL-25 | Th2 cells, mast cells [16], basophils, eosinophils [93], epithelial cells [94], and endothelial cells [95]. | IL-25R | IL-17RA, IL-17RB [96,97]. | Eosinophils [96] and T cells [97]. |
| IL-31 | Th2 cells, mast cells, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, and dendritic cells [17,98,99]. | 1L-31R | IL-31RA, oncostatin M receptor beta (OSMR) subunit [100]. | Dendritic cells, eosinophils, mast cells, basophils, sensory neurons, and monocytes [98,100,101]. |
| IL-33 | Endothelial cells, fibroblasts, epithelial cells, mast cells, and smooth muscle cells [18,102,103,104]. | 1L-33R | Suppression of tumorigenicity 2 (ST2), IL-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP) [103,105,106]. | Dendritic cells, mast cells, Th2 cells, Th9 cells, fibroblasts, macrophages, basophils, epithelial cells, endothelial cells, and eosinophils [103,106,107,108]. |
| TSLP | Epithelial cells, fibroblasts, mast cells, and smooth muscle cells [54,109]. | TSLPR | IL-7R alpha chain, TSLP receptor chain [54,110,111,112]. | Dendritic cells, mast cells, T cells, basophils, sensory neurons, and eosinophils [54,113]. |
| Cytokines | Pathophysiological Role of Cytokines |
|---|---|
| IL-4 | IL-4 and IL-13 can induce the chronic itch sensation via the IL-4R alpha-JAK1 pathway [120]. IL-4 can stimulate conjunctival fibroblast to proliferate and produce excess collagen leading to the development of papillae on the palpebral conjunctiva [128]. IL-4 induces the production of IgE-secreting plasma cells [122]. IL-4 induces induce vasodilation and vasopermeability by upregulating the expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) on endothelial cells of blood vessels [126,127]. |
| IL-5 | IL-5 induces the proliferation, maturation, differentiation, and chemotaxis of eosinophils to the site of allergen-induced inflammation in the conjunctiva [64,72,129,130]. |
| IL-6 | IL-6 is essential for the development of the germinal center, as it drives the differentiation of activated CD4+T cell into T follicular helper cells that are required for providing signals to B cells in the germinal center to produce high affinity antibodies [77,79,131]. IL-6 can activate vascular endothelial cells to induce endothelial dysfunction and vascular permeability as well as the recruitment of immune cells and molecules to the site of inflammation [76,79]. |
| IL-9 | IL-9 induces the proliferation, migration, and activation of mast cells during allergic immune responses [84]. IL-9 can induce mast cells to secrete vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) [132]. IL-9 induces the secretion of chemokine from epithelial cells [83]. IL-9 induces the hyperplasia of goblet cells [83]. IL-9 induces the upregulation of IL-5R alpha chain on eosinophils [133]. IL-9 facilitates the production of IgE-secreting plasma cells [134,135]. IL-9 can induce the breach of the epithelial barrier function of the conjunctiva [136]. |
| IL-13 | IL-13 induces hyperplasia of goblet cells in the epithelial layer of the conjunctiva [14,137]. IL-13 induces the hypersecretion of mucin from activated goblet cells [48,138,139]. IL-13 can activate sensory neurons to induce the chronic pruritus [120]. IL-13 can promote the development of papillae on the palpebral conjunctiva by inducing the proliferation of conjunctival fibroblasts [47]. |
| IL-25 | IL-25 initiates and exacerbates type 2 immune responses at the site of allergic inflammation [140]. IL-25 has the potential to stimulate angiogenesis at the site of allergic inflammation [141]. IL-25 can activate eosinophils during the allergic immune response [142]. |
| IL-31 | IL-31 mediates the acute and chronic itch sensation [100]. |
| IL-33 | IL-33 promotes type 2 immune responses in allergic conjunctivitis by mediating the release of Th2 cytokines by Th2 cells and mast cells [54]. IL-33 can induce the degranulation of eosinophils to release eosinophilic mediators that are toxic to the ocular surface [103]. IL-33 can activate mast cells and eosinophils during type 2 immune responses in allergic diseases [54,143]. |
| TSLP | TSLP-stimulated dendritic cells facilitate the generation of Th2 cells [144,145]. TSLP activates mast cells to secrete mediators that promote type 2 allergic immune responses in the conjunctiva [109,146]. TSLP-stimulated dendritic cell can release chemokines that recruit eosinophils and Th2 cells to the site of allergic inflammation in the conjunctiva [18,109,147]. TSLP activates sensory nerve fibers to induce pruritus [148,149] |
| Therapeutic drug | Targeted Cytokine | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Tofacitinib | IL-4, IL-6 and IL-13 | JAK1, JAK2 and JAK3 inhibitor [131,198]. |
| Abrocitinib | IL-4 and IL-13 | JAK1 inhibitor [199,200]. |
| Dupilumab | IL-4 and IL-13 | IL-4R alpha antagonist [202]. |
| Benralizumab | IL-5 | IL-5R alpha antagonist [203]. |
| Mepolizumab | IL-5 | Inhibits IL-5 release [203]. |
| Tocilizumab | IL-6 | Blocks IL-6R [205] |
| Olamkicept | IL-6 | Blocks IL-6 trans-signaling [208]. |
| Nemolizumab | IL-31 | IL-31RA chain antagonist [210,211]. |
| Tozorakimab | IL-33 | Inhibits IL-33 signaling [212]. |
| Tezepelumab | TSLP | Blocks TLSP [213]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chigbu, D.I.; Karbach, N.J.; Abu, S.L.; Hehar, N.K. Cytokines in Allergic Conjunctivitis: Unraveling Their Pathophysiological Roles. Life 2024, 14, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14030350
Chigbu DI, Karbach NJ, Abu SL, Hehar NK. Cytokines in Allergic Conjunctivitis: Unraveling Their Pathophysiological Roles. Life. 2024; 14(3):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14030350
Chicago/Turabian StyleChigbu, DeGaulle I., Nicholas J. Karbach, Sampson L. Abu, and Navpreet K. Hehar. 2024. "Cytokines in Allergic Conjunctivitis: Unraveling Their Pathophysiological Roles" Life 14, no. 3: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14030350
APA StyleChigbu, D. I., Karbach, N. J., Abu, S. L., & Hehar, N. K. (2024). Cytokines in Allergic Conjunctivitis: Unraveling Their Pathophysiological Roles. Life, 14(3), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14030350






